Multimodal Decorations of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Improved Cancer Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. MSNs as Delivery Vehicles in Cancer Therapy
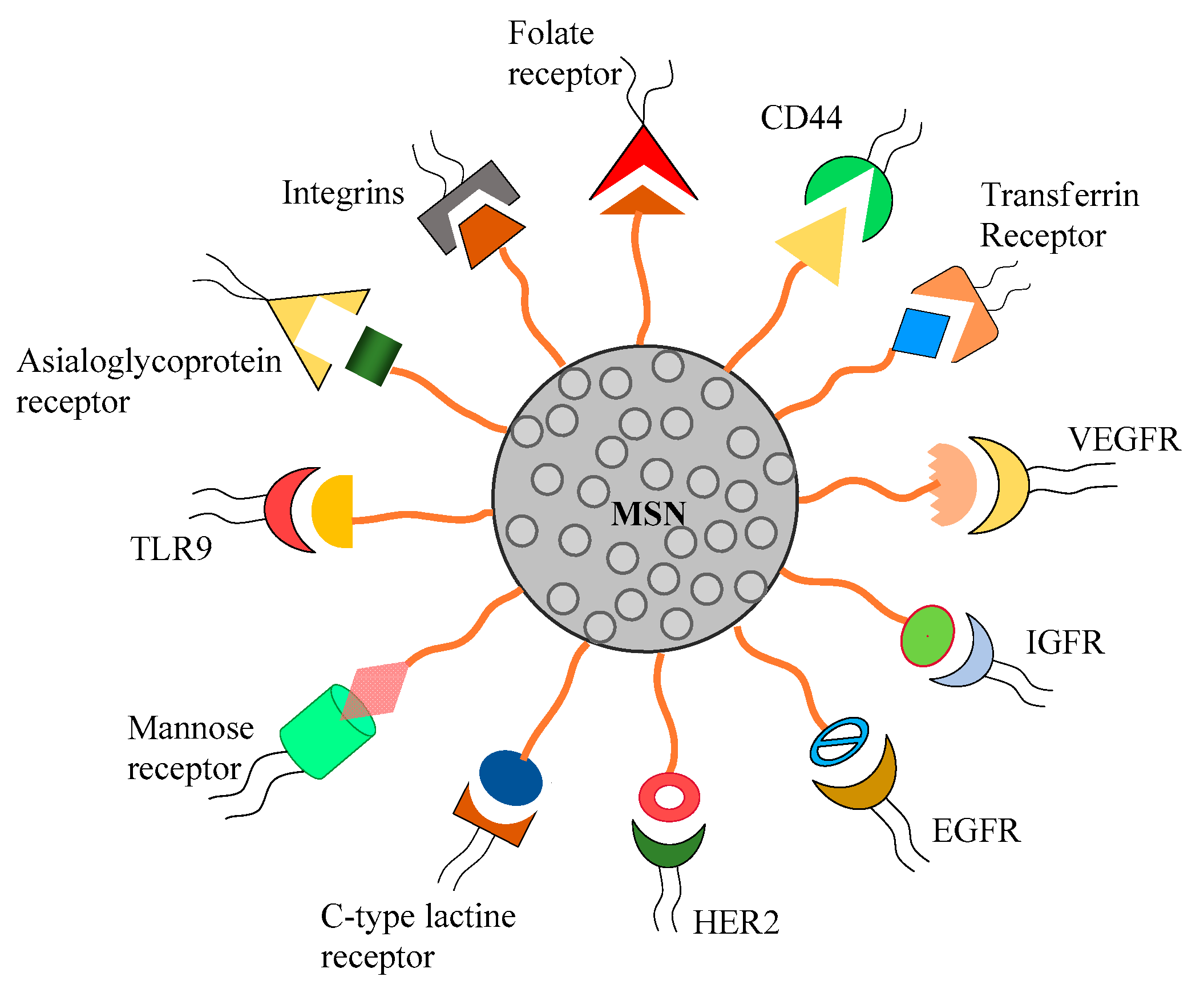
3. Surface Modification of MSN for Passive and Active Targeting Cancer Therapy
3.1. Passive Targeting
3.2. Active Targeting
3.2.1. Targeting Folate Receptor
3.2.2. Targeting Transferrin Receptor
3.2.3. Targeting Integrin Receptor and Nuclear Targeting
3.2.4. Targeting EGF Receptor and HER2 Receptor
3.2.5. Targeting VEGF Receptor
3.2.6. Targeting Mannose Receptor and C-Type Lectin Receptor
3.2.7. Other Active Targeted Delivery
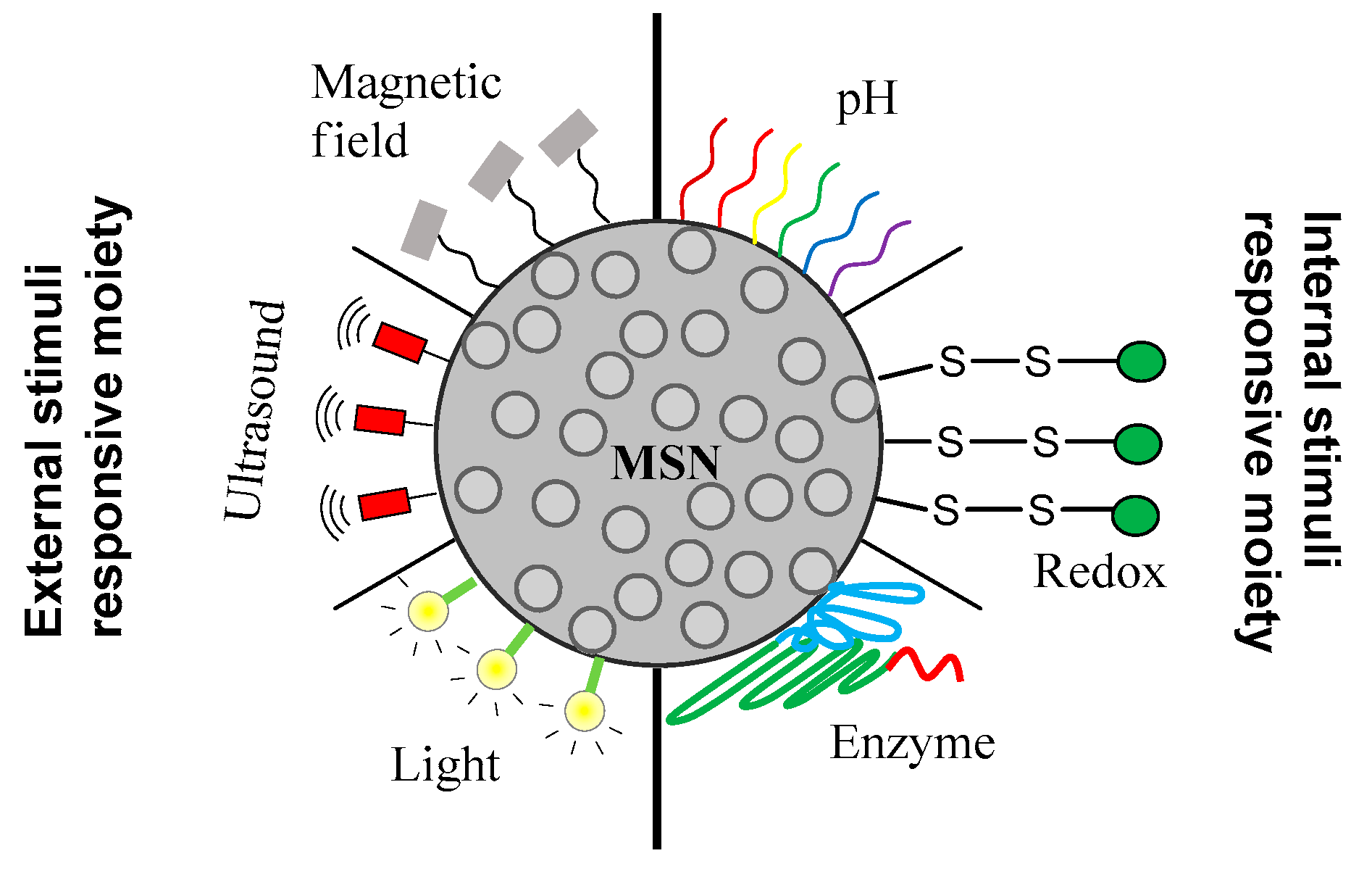
4. Stimuli-Responsive Drug Delivery Using MSN
4.1. PH-Responsive Gatekeepers
4.2. Redox-Responsive Gatekeepers
4.3. Enzyme-Responsive Gatekeepers
4.4. Magnetic Responsive Delivery System
4.5. Light-Responsive Delivery System
4.6. Ultrasound Based Delivery
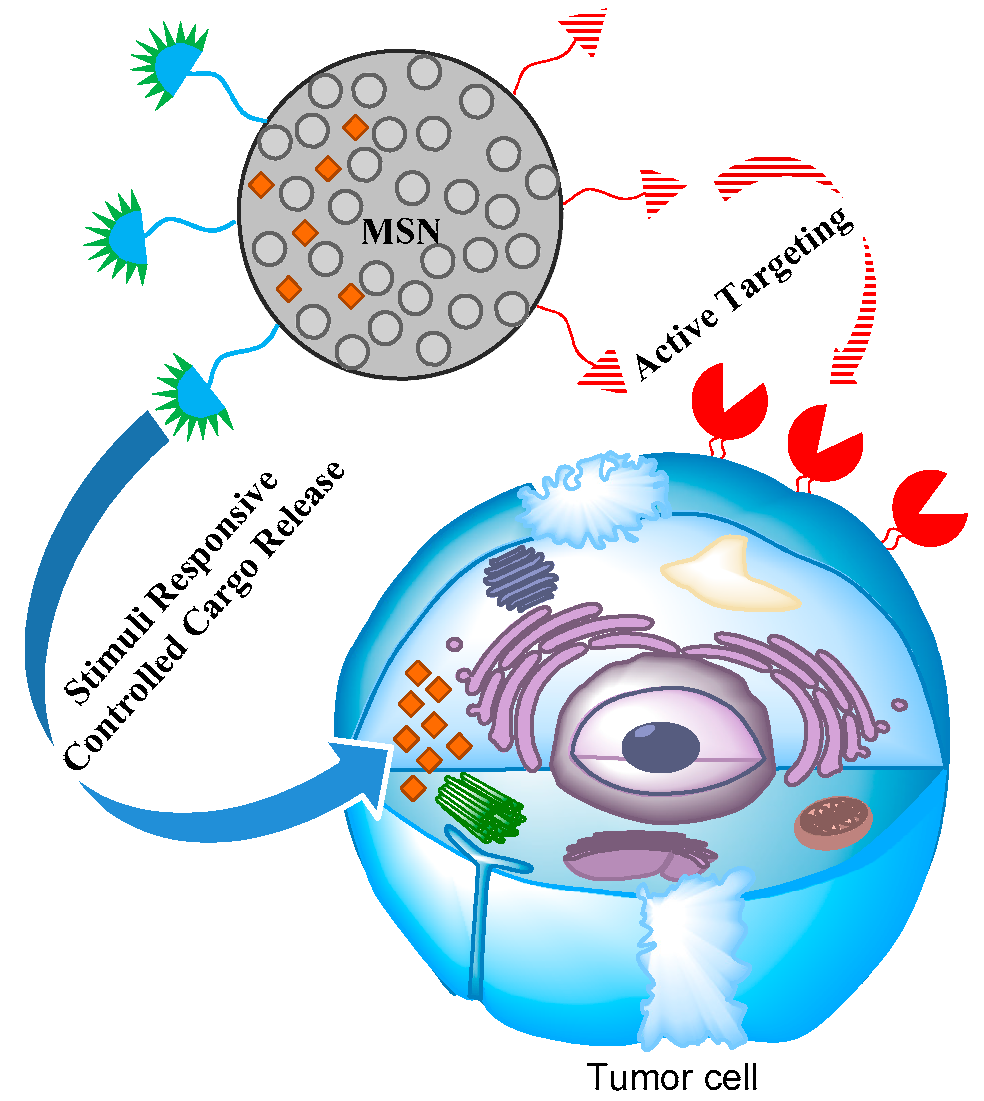
5. Effective Combination of Active Targeting Therapy and Stimuli-Responsive Therapy Using MSN in Cancer Therapy
6. MSN as Cancer Theranostics
7. Challenges Regarding MSN Application in Cancer Therapy
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anand, P.; Kunnumakara, A.B.; Sundaram, C.; Harikumar, K.B.; Tharakan, S.T.; Lai, O.S.; Sung, B.; Aggarwal, B.B. Cancer is a preventable disease that requires major lifestyle changes. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 2097–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biankin, A.V.; Piantadosi, S.; Hollingsworth, S.J. Patient-centric trials for therapeutic development in precision oncology. Nature 2015, 526, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baskar, R.; Itahana, K. Radiation therapy and cancer control in developing countries: Can we save more lives? Int. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 14, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillet, J.P.; Gottesman, M.M. Mechanisms of multidrug resistance in cancer. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 596, 47–76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vasan, N.; Baselga, J.; Hyman, D.M. A view on drug resistance in cancer. Nature 2019, 575, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greish, K. Enhanced permeability and retention of macromolecular drugs in solid tumors: A royal gate for targeted anticancer nanomedicines. J. Drug Target. 2007, 15, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, M.E.; Chen, Z.G.; Shin, D.M. Nanoparticle therapeutics: An emerging treatment modality for cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farokhzad, O.C.; Langer, R. Impact of nanotechnology on drug delivery. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Wu, J.; Sawa, T.; Matsumura, Y.; Hori, K. Tumor vascular permeability and the EPR effect in macromolecular therapeutics: A review. J. Control. Release 2000, 65, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Herrero, E.; Fernández-Medarde, A. Advanced targeted therapies in cancer: Drug nanocarriers, the future of chemotherapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 93, 52–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stylianopoulos, T.; Jain, R.K. Design considerations for nanotherapeutics in oncology. Nanomedicine 2015, 11, 1893–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kydd, J.; Jadia, R.; Velpurisiva, P.; Gad, A.; Paliwal, S.; Rai, P. Targeting Strategies for the Combination Treatment of Cancer Using Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egusquiaguirre, S.P.; Igartua, M.; Hernández, R.M.; Pedraz, J.L. Nanoparticle delivery systems for cancer therapy: Advances in clinical and preclinical research. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2012, 14, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhise, K.; Sau, S.; Alsaab, H.; Kashaw, S.K.; Tekade, R.K.; Iyer, A.K. Nanomedicine for cancer diagnosis and therapy: Advancement, success and structure-activity relationship. Ther. Deliv. 2017, 8, 1003–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayda, S.; Hadla, M.; Palazzolo, S.; Riello, P.; Corona, G.; Toffoli, G.; Rizzolio, F. Inorganic Nanoparticles for Cancer Therapy: A transition from lab to clinic. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 4269–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torchilin, V.P. Recent advances with liposomes as pharmaceutical carriers. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, G.; Barui, S.; Saha, S.; Chaudhuri, A. Tumor growth inhibition through targeting liposomally bound curcumin to tumor vasculature. J. Control. Release 2013, 172, 832–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barui, S.; Saha, S.; Mondal, G.; Haseena, S.; Chaudhuri, A. simultaneous delivery of doxorubicin and curcumin encapsulated in liposomes of pegylated RGDK-lipopeptide to tumor vasculature. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 1643–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobo, D.; Robinson, K.J.; Islam, J.; Thurecht, K.J.; Corrie, S.R. Nanoparticle-based medicines: A review of FDA-approved materials and clinical trials to date. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 2373–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Pinel, B.; Porras-Alcalá, C.; Ortega-Rodríguez, A.; Sarabia, F.; Prados, J.; Melguizo, C.; López-Romero, J.M. Lipid-based nanoparticles: Application and recent advances in cancer treatment. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2019, 9, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, C.O.; Guo, Z.; Hayes, M.F.; Marks, J.D.; Park, J.W.; Benz, C.C.; Kirpotin, D.B.; Drummond, D.C. Characterization of highly stable liposomal and immunoliposomal formulations of vincristine and vinblastine. Cancer Chemo. Pharm. 2009, 64, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Cao, Z.; Liu, R.; Liu, L.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Lu, C.; Liu, Y. AuNPs as an important inorganic nanoparticle applied in drug carrier systems. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 4222–4233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinel, S.; Thomas, N.; Boura, C.; Barberi-Heyob, M. Approaches to physical stimulation of metallic nanoparticles for glioblastoma treatment. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 138, 344–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negri, V.; Pacheco-Torres, J.; Calle, D.; López-Larrubia, P. Carbon nanotubes in biomedicine. Top. Curr. Chem (Cham). 2020, 378, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Shi, S.; Goel, S.; Shen, X.; Xie, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Qin, X.; Yang, H.; et al. Recent advancements in mesoporous silica nanoparticles towards therapeutic applications for cancer. Acta Biomater. 2019, 89, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Kilchrist, K.V.; Li, J.; Duvall, C.L.; Oupický, D. Endosomolytic and Tumor-Penetrating Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for siRNA/miRNA Combination Cancer Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 4308–4322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradbury, M.S.; Pauliah, M.; Zanzonico, P.; Wiesner, U.; Patel, S. Intraoperative mapping of SLN metastases using a clinically-translated ultrasmall silica nanoparticle. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 8, 535–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Tambe, P.; Paknikar, K.M.; Gajbhiye, V. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as cutting-edge theranostics: Advancement from merely a carrier to tailor-made smart delivery platform. J. Control. Release 2018, 287, 35–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iturrioz-Rodríguez, N.; Correa-Duarte, M.A.; Fanarraga, M.L. Controlled drug delivery systems for cancer based on mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 3389–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watermann, A.; Brieger, J. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery Vehicles in Cancer. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Food and Drug Administration GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Database-Select Committee on GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Opinion: Silicates. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/fdcc/?set=SCOGS (accessed on 10 April 2020).
- Chen, F.; Hableel, G.; Zhao, E.R.; Jokerst, J.V. Multifunctional Nanomedicine with silica: Role of silica in nanoparticles for theranostic, imaging, and drug monitoring. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 521, 261–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauss, D.J. Oral lipid-based formulations. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawabata, Y.; Wada, K.; Nakatani, M.; Yamada, S.; Onoue, S. Formulation design for poorly water-soluble drugs based on biopharmaceutics classification system: Basic approaches and practical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 420, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Liong, M.; Zink, J.I.; Tamanoi, F. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a delivery system for hydrophobic anticancer drugs. Small 2007, 3, 1341–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Liang, S.; Long, M.; Xu, H. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as potential carriers for enhanced drug solubility of paclitaxel. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 78, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badruddoza, A.Z.M.; Gupta, A.; Myerson, A.S.; Trout, B.L.; Doyle, P.S. Low energy nanoemulsions as templates for the formulation of hydrophobic drugs. Adv. Ther. 2018, 1, 1700020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wais, U.; Jackson, A.W.; He, T.; Zhang, H. Formation of hydrophobic drug nanoparticles via ambient solvent evaporation facilitated by branched diblock copolymers. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 533, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, A.; Kettiger, H.; Schoubben, A.; Rosenholm, J.M.; Ambrogi, V.; Hamidi, M. Mesoporous silica materials: From physico-chemical properties to enhanced dissolution of poorly water-soluble drugs. J. Control. Release 2017, 262, 329–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wu, B.; Quan, G.; Huang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Pan, X.; Zhang, X.; Wu, C. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug and gene delivery. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2018, 8, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Liong, M.; Li, Z.; Zink, J.I.; Tamanoi, F. Biocompatibility, biodistribution, and drug-delivery efficiency of mesoporous silica nanoparticles for cancer therapy in animals. Small 2010, 6, 1794–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafari, S.; Derakhshankhah, H.; Alaei, L.; Varnamkhasti, B.S.; Saboury, A.A.; Fattahi, A. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for therapeutic/diagnostic applications. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 1100–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barkat, A.; Beg, S.; Panda, S.K.; Alharbi, S.K.; Rahman, M.; Ahmed, F.J. Functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles in anticancer therapeutics. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019, S1044-579X, 30104–X. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayan, R.; Nayak, U.Y.; Raichur, A.M.; Garg, S. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: A Comprehensive Review on Synthesis and Recent Advances. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Toms, B.; Goodisman, J.; Asefa, T. Mesoporous silica microparticles enhance the cytotoxicity of anticancer platinum drugs. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, R.R.; Lozano, D.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as carriers for therapeutic biomolecules. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Lei, C.; Yu, C. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for protein protection and delivery. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knezevic, N.Z.; Durand, J.O. Large pore mesoporous silica nanomaterials for application in delivery of biomolecules. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 2199–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.J.; Xu, P. Smart mesoporous silica nanoparticles for protein delivery. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.I.; Pham, T.T.; Lee, J.W.; Roh, S.H. Releasing properties of proteins on SBA-15 spherical nanoparticles functionalized with aminosilanes. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2010, 10, 3467–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slowing, I.I.; Trewyn, B.G.; Lin, V.S.Y. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for intracellular delivery of membrane-impermeable proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 8845–8849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez, J.; Morales Cruz, M.; Delgado, Y.; Figueroa, C.M.; Orellano, E.A.; Morales, M.; Monteagudo, A.; Griebenow, K. Delivery of chemically glycosylated cytochrome c immobilized in mesoporous silica nanoparticles induces apoptosis in HeLa cancer cells. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.; Lim, D.-K.; Kim, S. Hydrolytic surface erosion of mesoporous silica nanoparticles for efficient intracellular delivery of cytochrome c. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 560, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Karmakar, S.; Yu, M.H.; Mitter, N.; Zou, J.; Yu, C.Z. Synthesis of silica vesicles with controlled entrance size for high loading, sustained release, and cellular delivery of therapeutical proteins. Small 2014, 10, 5068–5076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Yu, M.; Meka, A.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Yu, C. Understanding the contribution of surface roughness and hydrophobic modification of silica nanoparticles to enhanced therapeutic protein delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Meka, A.K.; Zhang, H.; Xu, C.; Xiang, C.; Lin, C.; Yu, M.; Yu, C. Biphasic synthesis of large-pore and well-dispersed benzene bridged mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles for intracellular protein delivery. Small 2015, 11, 2743–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Abbaraju, P.L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Xiang, G.; Yu, C. Multi-shelled dendritic mesoporous organosilica hollow spheres: Roles of composition and architecture in cancer immunotherapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 8446–8450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.F.; Chen, W.H.; Liu, Y.; Lei, Q.; Zhuo, R.X.; Zhanga, X.Z. Multifunctional enveloped mesoporous silica nanoparticles for subcellular co-delivery of drug and therapeutic peptide. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, D.; Li, M.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, X.; Lao, Y.H.; Chang, Z.; Zhang, F.; Lu, M.; Yue, J.; Hu, H.; et al. Bioinspired diselenide-bridged mesoporous silica nanoparticles for dual-responsive protein delivery. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1801198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Yang, K.; Liu, F.; Li, H.; Xu, Y.; Sun, S. Diverse gatekeepers for mesoporous silica nanoparticle based drug delivery systems. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 6024–6045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deodhar, G.V.; Adams, M.L.; Trewyn, B.G. Controlled release and intracellular protein delivery from mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Biotechnol. J. 2017, 12, 1600408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argyo, C.; Weiss, V.; Bräuchle, C.; Bein, T. Multifunctional mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a universal platform for drug delivery. Chem. Mater. 2013, 26, 435–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Colilla, M.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Manzano, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug delivery: Current insights. Molecules 2018, 23, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Yu, C. Advances in silica based nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2016, 12, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folkman, J. Role of angiogenesis in tumor growth and metastasis. Semin. Oncol. 2002, 29, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmeliet, P.; Jain, R.K. Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature 2000, 407, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, S.; Tavares, A.J.; Dai, Q.; Ohta, S.; Audet, J.; Dvorak, H.F.; Chan, W.C.W. Analysis of nanoparticle delivery to tumours. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Nakamura, H.; Maeda, H. The EPR effect: Unique features of tumor blood vessels for drug delivery, factors involved, and limitations and augmentation of the effect. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Fang, J.; Maeda, H. Development of next-generation macromolecular drugs based on the EPR effect: Challenges and pitfalls. Expert Opin. Drug Del. 2015, 12, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.E.; Lee, N.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, T.; Song, I.C.; Park, S.P.; Moon, W.K.; et al. Uniform mesoporous dye-doped silica nanoparticles decorated with multiple magnetite nanocrystals for simultaneous enhanced magnetic resonance imaging, fluorescence imaging, and drug delivery. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, F.; Li, Y.; Shi, J. In vivo biodistribution and urinary excretion of mesoporous silica nanoparticles: Effects of particle size and PEGylation. Small 2011, 7, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Fang, Y.; Borchardt, L.; Kaskel, S. PEGylated hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles as potential drug delivery vehicles. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2011, 141, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Mai, W.X.; Zhang, H.; Xue, M.; Xia, T.; Lin, S.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Ji, Z.; Zink, J.I.; et al. Codelivery of an optimal Drug/siRNA combination using mesoporous silica nanoparticles to overcome drug resistance in breast cancer in vitro and in vivo. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 994–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heldin, C.-H.; Rubin, K.; Pietras, K.; Östman, A. High interstitial fluid pressure-An obstacle in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, S.P.; Singh, A.; Sihorkar, V. Ligand-receptor-mediated drug delivery: An emerging paradigm in cellular drug targeting. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carrier Syst. 2001, 18, 1–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruoslahti, E.; Bhatia, S.N.; Sailor, M.J. Targeting of drugs and nanoparticles to tumors. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 188, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, N.; Turk, M.J.; Westrick, E.; Lewis, J.D.; Low, P.S.; Leamon, C.P. Folate receptor expression in carcinomas and normal tissues determined by a quantitative radioligand binding assay. Anal. Biochem. 2005, 338, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porta, F.; Lamers, G.E.M.; Morrhayim, J.; Chatzopoulou, A.; Schaaf, M.; den Dulk, H.; Backendorf, C.; Zink, J.I.; Kros, A. Folic acid-modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles for cellular and nuclear targeted drug delivery. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2013, 2, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwicke, G.H.; Mansoori, G.A.; Jeffery, C.J. Utilizing the folate receptor for active targeting of cancer nanotherapeutics. Nano Reviews 2012, 3, 18496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, A.; Bax, H.J.; Josephs, D.H.; Ilieva, K.M.; Pellizzari, G.; Opzoomer, J.; Bloomfield, J.; Fittall, M.; Grigoriadis, A.; Figini, M.; et al. Targeting folate receptor alpha for cancer treatment. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 52553–52574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slowing, I.; Trewyn, B.G.; Lin, V.S.Y. Effect of surface functionalization of MCM-41-type mesoporous silica nanoparticles on the endocytosis by human cancer cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 14792–14793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravian, P.; Ardestani, M.S.; Mehdi Khoobi, M.; Ostad, S.N.; Dorkoosh, F.A.; Javar, H.A.; Amanlou, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles functionalized with folic acid/methionine for active targeted delivery of docetaxel. Onco.Targets Ther. 2016, 9, 7315–7330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yinxuea, S.; Binb, Z.; Xiangyang, D.; Yong, W.; Jie, Z.; Yanqiu, A.; Zongjiang, X.; Gaofenge, Z. Folic acid (FA)-conjugated mesoporous silica nanoparticles combined with MRP-1 siRNA improves the suppressive effects of myricetin on non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 125, 109561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Shen, Y.; Zhao, R.; Chen, F.; Zhang, F.; Xu, A.; Shao, A. Dual-Targeting Multifuntional Mesoporous Silica Nanocarrier for Codelivery of siRNA and Ursolic Acid to Folate Receptor Overexpressing Cancer Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 6904–6911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Sun, S.; Jiang, K.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, S.; Li, Z.; Shu, Q.; Lin, H. In Situ Synthesis of Fluorescent Mesoporous Silica–Carbon Dot Nanohybrids Featuring Folate Receptor Overexpressing Cancer Cell Targeting and Drug Delivery. Nano-Micro Lett. 2019, 11, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Li, Z.; Zink, J.I.; Tamanoi, F. In vivo tumor suppression efficacy of mesoporous silica nanoparticles-based drug-delivery system: Enhanced efficacy by folate modification. Nanomedicine 2012, 8, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, V.; Villegas, M.R.; Rodríguez, V.; Villaverde, G.; Lozano, D.; Baeza, A.; Vallet-Regí, M. Janus mesoporous silica nanoparticles for dual targeting of tumor cells and mitochondria. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2017, 9, 26697–26706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenholm, J.M.; Peuhu, E.; Bate-Eya, L.T.; Eriksson, J.E.; Sahlgren, C.; Linden, M. Cancer-cell-specific induction of apoptosis using mesoporous silica nanoparticles as drug-delivery vectors. Small 2010, 6, 1234–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, T.R.; Bernabeu, E.; Rodríguez, J.A.; Patel, S.; Kozman, M.; Chiappetta, D.A.; Holler, E.; Ljubimova, J.Y.; Helguera, G.; Penicheta, M.L. Transferrin receptors and the targeted delivery of therapeutic agents against cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2012, 1820, 291–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Li, X.; Dong, D.; Zhang, B.; Xue, Y.; Shang, P. The review of TFR1 in cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2018, 8, 916–931. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, M.; Oh, I. Targeted drug delivery of Transferrin-Conjugated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Yakhak Hoeji 2017, 61, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferris, D.P.; Lu, J.; Gothard, C.; Yanes, R.; Thomas, C.R.; Olsen, J.C.; Stoddart, J.F.; Tamanoi, F.; Zink, J.I. Synthesis of Biomolecule-Modified Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Targeted Hydrophobic Drug Delivery to Cancer Cells. Small 2011, 7, 1816–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalvo-Quiros, S.; Aragoneses-Cazorla, G.; Garcia-Alcalde, L.; Vallet-Regí, M.; González, B.; Luque-Garcia, J.L. Cancer cell targeting and therapeutic delivery of silver nanoparticles by mesoporous silica nanocarrirs: Insights into the action mechanisms using quantitative proteomics. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 4531–4545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Xiang, C. Transferrin receptor-targeted hMsN for sorafenib delivery in refractory differentiated thyroid cancer therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 8339–8354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Wu, H.; Li, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yao, L.; Chen, X.; Han, X.; Zhou, Y.; Du, Z. Targeting transferrin receptor delivery of temozolomide for a potential glioma stem cell-mediated therapy. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 74451–74465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Lewik, G.; Ratcliffe, J.C.; Choi, C.H.J.; Mäkilä, E.; Tong, W.Y.; Voelcker, N.H. Systematic evaluation of transferrin-modified porous silicon nanoparticles for targeted delivery of doxorubicin to glioblastoma. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 33637–33649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheykhzadeh, S.; Luo, M.; Peng, B.; White, J.; Abdalla, Y.; Tang, T.; Mäkilä, E.; Voelcker, N.H.; Tong, W.Y. Transferrin-targeted porous silicon nanoparticles reduce glioblastoma cell migration across tight extracellular space. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barui, S.; Saha, S.; Yakati, V.; Chaudhuri, A. Systemic co-delivery of a homo-serine derived ceramide analog and curcumin to tumor vasculature inhibits mouse tumor growth. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 404–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Corso, A.; Pignataro, L.; Belvisi, L.; Gennari, C. αvβ3 Integrin-Targeted Peptide/Peptidomimetic-Drug Conjugates: In-Depth Analysis of the Linker Technology. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 314–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, I.J.; Slowing, I.I.; Wu, K.C.; Lin, V.S.; Trewyn, B.G. Ligand conformation dictates membrane and endosomal trafficking of arginine-glycine-aspartate (RGD)-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Chemistry 2012, 18, 7787–7792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; You, Y.; He, L.; Chen, T. The rational design of NAMI-A-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles as antiangiogenic nanosystems. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 6338–6346. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.; Arena, F.; Gianolio, E.; Boffa, C.; di Gregorio, E.; Stefania, R.; Orio, L.; Baroni, S.; Aime, S. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles functionalized with fluorescent and MRI reporters for the visualization of murine tumors overexpressing αvβ3 receptors. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 7094–7104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Kim, D.H.; Guo, Y.; Teng, Z.; Li, Y.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, Z.; Larson, A.C.; Lu, G. A c(RGDfE) conjugated multi-functional nanomedicine delivery system for targeted pancreatic cancer therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 1049–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarty, R.; Goel, S.; Hong, H.; Chen, F.; Valdovinos, H.F.; Hernandez, R.; Barnhart, T.E.; Cai, W. Hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles for tumor vasculature targeting and PET image-guided drug delivery. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2015, 10, 1233–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.; He, L.; Ma, B.; Chen, T. Tailoring Particle Size of Mesoporous Silica Nanosystem To Antagonize Glioblastoma and Overcome Blood-Brain Barrier. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 6811–6825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Liu, J.; He, Q.; Shi, J. MSN-mediated sequential vascular-to-cell nuclear-targeted drug delivery for efficient tumor regression. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6742–6748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kari, C.; Chan, T.O.; Rocha de Quadros, M.; Rodeck, U. Targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor in cancer: Apoptosis takes center stage. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.V.; Bell, D.W.; Settleman, J.; Haber, D.A. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2007, 7, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, X.; Chen, L.; Velleman, L.; Li, C.; He, C.; Denman, J.; Wang, T.; Shigdar, S.; Duanc, W.; Kong, L. The control of epidermal growth factor grafted on mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 6094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundarraj, S. Targeting efficiency and biodistribution of EGFR-conjugated mesoporous silica nanoparticles for cisplatin delivery in nude mice with lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23, ix70–ix71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, H.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Ji, H. Cetuximab-modified mesoporous silica nano-medicine specifically targets EGFR-mutant lung cancer and overcomes drug resistance. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, N.; Iqbal, N. Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) in cancers: Overexpression and therapeutic implications. Mol. Biol. Int. 2014, 2014, 852748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orphanos, G.; Kountourakis, P. Targeting the HER2 receptor in metastatic breast cancer. Hematol. Oncol. Stem Cell Ther. 2012, 5, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, C.; Chen, C.; Hung, Y.; Changb, F.; Mou, C. Monoclonal antibody-functionalized mesoporous silicananoparticles (MSN) for selective targeting breast cancer cells. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 5737–5743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, L.M.; Hicklin, D.J. VEGF-targeted therapy: Mechanisms of anti-tumour activity. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costache, M.I.; Ioana, M.; Iordache, S.; Ene, D.; Costache, C.A.; Săftoiu, A. VEGF Expression in Pancreatic Cancer and Other Malignancies: A Review of the Literature. Rom. J. Intern. Med. 2015, 53, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, S.; Chen, F.; Hong, H.; Valdovinos, H.F.; Barnhart, T.E.; Cai, W. VEGFR-targeted drug delivery in vivo with mesoporous silica nanoparticles. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55 (Suppl. 1), 222. [Google Scholar]
- Goel, S.; Chen, F.; Hong, H.; Valdovinos, H.F.; Hernandez, R.; Shi, S.; Barnhart, T.E.; Cai, W. VEGF121-Conjugated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle: A Tumor Targeted Drug Delivery System. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 21677–21685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, G.; Li, N.; Meng, Z.; Zhang, F.; Chang, J.; Wang, R. Antitumor effect of 131i-labeled anti-Vegfr2 targeted mesoporous silica nanoparticles in anaplastic thyroid cancer. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scodeller, P.; Simón-Gracia, L.; Kopanchuk, S.; Tobi, A.; Kilk, K.; Säälik, P.; Kaarel Kurm, K.; Squadrito, M.L.; Kotamraju, V.R.; Rinken, A.; et al. Precision targeting of tumor macrophages with a CD206 binding peptide. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, I.Y.; Kim, I.Y.; Yoo, M.K.; Choi, Y.J.; Cho, M.H.; Cho, C.S. Mannosylated polyethylenimine coupled mesoporous silica nanoparticles for receptor-mediated gene delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 359, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.-T.; Souris, J.S.; Cheng, S.-H.; Chu, C.-H.; Wang, Y.-C.; Konda, V.; Dougherty, U.; Bissonnette, M.; Mou, C.-Y.; Chen, C.-T.; et al. Lectin-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles for endoscopic detection of premalignant colonic lesions. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2017, 13, 1941–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Guo, N.; Zhao, J.; Cai, Y. Active targeting co-delivery system based on hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles for antitumor therapy in ovarian cancer stem-like cells. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 1442–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, G.; Pan, X.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Q.; Li, G.; Dian, L.; Chen, B.; Wu, C. Lactosaminated mesoporous silica nanoparticles for asialoglycoprotein receptor targeted anticancer drug delivery. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paramonov, V.M.; Desai, D.; Kettiger, H.; Mamaeva, V.; Rosenholm, J.M.; Sahlgren, C.; Rivero-Müller, A. Targeting somatostatin receptors by functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles—are we striking home? Nanotheranostics 2018, 2, 320–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Xu, C.; Wen, L.; Han, M.; Xiao, B.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Viennois, E.; Merlin, D. A hyaluronidase-responsive nanoparticle-based drug delivery system for targeting colon cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 7208–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Hong, H.; Shi, S.; Goel, S.; Valdovinos, H.F.; Hernandez, R.; Theuer, C.P.; Barnhart, T.E.; Cai, W. Engineering of hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles for remarkably enhanced tumor active targeting efficacy. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Nayak, T.R.; Goel, S.; Valdovinos, H.F.; Hong, H.; Theuer, C.P.; Barnhart, T.E.; Cai, W. In vivo tumor vasculature targeted PET/NIRF imaging with TRC105(Fab)-conjugated, dual-labeled mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 4007–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, S.K.; Luo, Y.; O’Donnell, M.A.; Assouline, J.G. Peptide-Mediated Targeting Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: A Novel Tool for Fighting Bladder Cancer. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2017, 13, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicke, B.J.; Stephens, A.W.; Gould, T.; Chang, Y.-F.; Lynott, C.K.; Heil, J.; Borkowski, S.; Hilger, C.-S.; Cook, G.; Warren, S.; et al. Tumor targeting by an aptamer. J. Nucl. Med. 2006, 47, 668–678. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Tan, W.; Lai, Z.; Fang, D.; Jiang, L.; Zuo, C.; Yang, N.; Lai, Y. An efficient cell-targeting drug delivery system based on aptamer-modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.L.; Cha, B.G.; Choi, Y.; Im, J.; Kim, J. Injectable dual-scale mesoporous silica cancer vaccine enabling efficient delivery of antigen/adjuvant-loaded nanoparticles to dendritic cells recruited in local macroporous scaffold. Biomaterials 2020, 239, 119859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mekaru, H.; Lu, J.; Tamanoi, F. Development of mesoporous silica-based nanoparticles with controlled release capability for cancer therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 95, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivero-Escoto, J.L.; Slowing, I.I.; Trewyn, B.G.; Lin, V.S.Y. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for intracellular controlled drug delivery. Small 2010, 6, 1952–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatenby, R.A.; Gillies, R.J. Why do cancers have high aerobic glycolysis? Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Agarwal, A.; Mueller, L.J.; Feng, P. pH-responsive nanogated ensemble based on gold-capped mesoporous silica through an acid-labile acetal linker. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 1500–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Q.; Lu, X.; Yuan, Y.; Qian, J.; Zhou, H.; Lu, X.; Shi, J.; Liu, C. A magnetic, reversible pH-responsive nanogated ensemble based on Fe3O4 nanoparticles-capped mesoporous silica. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 1932–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Lin, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, L.; Wei, W.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Nanoceria-triggered synergetic drug release based on CeO2-capped mesoporous silica host-guest interactions and switchable enzymatic activity and cellular effects of CeO2. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2013, 2, 1591–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Xue, M.; Xia, T.; Zhao, Y.L.; Tamanoi, F.; Stoddart, J.F.; Zink, J.I.; Nel, A.E. Autonomous in vitro anti cancer drug release from mesoporous silica nanoparticles by pH-sensitive nanovalves. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 12690–12697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Yang, C.; Liu, X.; Ma, R.; Kong, D.; Shi, L. A multifunctional nanocarrier based on nanogated mesoporous silica for enhanced tumor-specific uptake and intracellular delivery. Macromol. Biosci. 2012, 12, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Cheng, S.H.; Huang, I.P.; Souris, J.S.; Yang, C.S.; Mou, C.Y.; Lo, L.W. Intracellular pH-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles for the controlled release of anticancer chemotherapeutics. Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 8390–8395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Fan, L.; Lin, L.; Xu, Y.; Chen, S.; Shao, J. pH-Sensitive mesoporous silica nanoparticles anticancer prodrugs for sustained release of ursolic acid and the enhanced anti-cancer efficacy for hepatocellular carcinoma cancer. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 96, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, W.; Zhou, X.; He, C.; Qiu, K.; Nie, W.; Chen, L.; Wang, H.; Mo, X.; Zhang, Y. Polyelectrolyte multilayer functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles for pH-responsive drug delivery: Layer thickness dependent release profiles and biocompatibility. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 5886–5898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cauda, V.; Argyo, C.; Schlossbauera, A.; Bein, T. Controlling the delivery kinetics from colloidal mesoporous silicananoparticles with pH-sensitive gates. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 4305–4311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Guo, J.; Sun, Y.; Chang, B.; Ren, Q.; Yang, W. Facile synthesis of pH sensitive polymer-coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles and their application in drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 421, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popat, A.; Liu, J.; Lu, G.Q.M.; Qiao, S.Z. A pH-responsive drug delivery system based on chitosan coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 11173–11178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Bi, J.; Tang, Y.; Qiao, S.Z. Magnetic Core-Shell Silica Nanoparticles with Large Radial Mesopores for siRNA Delivery. Small 2016, 12, 4735–4742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisbert-Garzarán, M.; Lozano, D.; Vallet-Regí, M.; Manzano, M. Self-immolative polymers as novel pH-responsive gatekeepers for drug delivery. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Tang, Q.; Yang, D.; Zhang, J.Z.; Zhang, F.; Hu, J. Preparation of pH-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles and their application in controlled drug delivery. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 9926–9932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, F.; Guo, M.; Qi, W.; Sun, F.; Wang, A.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, G. pH-triggered controlled drug release from mesoporous silica nanoparticles via intracelluar dissolution of ZnO nanolids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 8778–8781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; He, D.; He, X.; Wang, K.; Yang, X.; Qing, Z.; Zhou, Q. Natural Gelatin Capped Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Intracellular Acid-Triggered Drug Delivery. Langmuir 2013, 29, 12804–12810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rim, H.P.; Min, K.H.; Lee, H.J.; Jeong, S.Y.; Lee, S.C. pH-tunable calcium phosphate covered mesoporous silica nanocontainers for intracellular controlled release of guest drugs. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 8853–8857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibowo, F.R.; Saputra, O.A.; Lestari, W.W.; Koketsu, M.; Mukti, R.R.; Martien, R. pH-triggered drug release controlled by poly(styrene sulfonate) growth hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 4261–4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrela, J.M.; Ortega, A.; Obrador, E. Glutathione in cancer biology and therapy. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2006, 43, 143–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croissant, J.; Cattoën, X.; Man, M.W.; Gallud, A.; Raehm, L.; Trens, P.; Maynadier, M.; Durand, J.O. Biodegradable ethylene-bis (Propyl) disulfide-based periodic mesoporous organosilica nanorods and nanospheres for efficient in-vitro drug delivery. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6174–6180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Xu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Liu, X.; Hou, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H. Fabrication of single-hole glutathione-responsive degradable hollow silica nanoparticles for drug delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 12600–12608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, S.; Park, C.; Lee, H.; Park, H.J.; Kim, C. Glutathione-induced intracellular release of guests from mesoporous silica nanocontainers with cyclodextrin gatekeepers. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 4280–4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, A.M.; Schlossbauer, A.; Ruthardt, N.; Cauda, V.; Bein, T.; Bräuchle, C. Role of endosomal escape for disulfide-based drug delivery from colloidal mesoporous silica evaluated by live-cell imaging. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 3684–3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Meng, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, M.; Cai, X.; Li, Y.; Yu, P.; Zhang, L.; Shi, J. Large pore-sized hollow mesoporous organosilica for redox-responsive gene delivery and synergistic cancer chemotherapy. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 1963–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadrah, P.; Maver, U.; Jemec, A.; Tišler, T.; Bele, M.; Dražić, G.; Benčina, M.; Pintar, A.; Planinšek, O.; Gaberšček, M. Hindered disulfide bonds to regulate release rate of model drug from mesoporous silica. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 3908–3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasetyanto, E.A.; Bertucci, A.; Septiadi, D.; Corradini, R.; Castro-Hartmann, P.; de Cola, L. Breakable hybrid organosilica nanocapsules for protein delivery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 3323–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Kleitz, F.; Li, X.; Huang, H.; Zhang, X.; Qiao, S.Z. Disulfide-bridged organosilica frameworks: Designed, synthesis, redox-triggered biodegradation, and nanobiomedical applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 1707325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhao, X.; Wu, T.; Feng, P. Tunable Redox-Responsive Hybrid Nanogated Ensembles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 14418–14419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Liu, Y.J.; Yang, Z.Z.; Qi, X.R. Tumor specific delivery with redox-triggered mesoporous silica nanoparticles inducing neovascularization suppression and vascular normalization. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 55566–55578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Z.; Li, W.; Tang, Y.; Elzatahry, A.; Lu, G.; Zhao, D. Mesoporous organosilica hollow nanoparticles: Synthesis and applications. Adv. Mater. 2018, 1707612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Angelos, S.; Dichtel, W.R.; Coskun, A.; Yang, Y.-W.; Zink, J.I.; Stoddart, J.F. Enzyme responsive snap-top covered silica nanocontainers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 2382–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondragón, L.; Mas, N.; Ferragud, V.; de la Torre, C.; Agostini, A.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Sancenón, F.; Amorós, P.; Pérez-Payá, E.; Orzáez, M. Enzyme-responsive intracellular-controlled release using silica mesoporous nanoparticles capped with ε-poly-L-lysine. Chemistry 2014, 20, 5271–5281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardos, A.; Mondragón, L.; Aznar, E.; Marcos, M.D.; Martínez-Mánez, R.; Sancenón, F.; Soto, J.; Barat, J.M.; Pérez-Payá, E.; Guillem, C.; et al. Enzyme-responsive intracellular controlled release using nanometric silica mesoporous supports capped with “saccharides”. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 6353–6368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlossbauer, A.; Kecht, J.; Bein, T. Biotin-Avidin as a protease-responsive cap system for controlled guest release from colloidal mesoporous silica. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 3092–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, K.; Gupta, S.; Gnanadhas, D.P.; Ramamurthy, P.C.; Chakravortty, D.; Raichur, A.M. Protamine-capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles for biologically triggered drug release. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2013, 31, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xua, J.-H.; Gao, F.-P.; Li, L.-L.; Ma, H.L.; Fan, Y.-S.; Liu, W.; Guo, S.-S.; Zhao, X.-Z.; Wang, H. Gelatin-mesoporous silica nanoparticles as matrix metalloproteinases-degradable drug delivery systems in vivo. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2015, 204, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rijt, S.H.; Bölükbas, D.A.; Argyo, C.; Datz, S.; Lindner, M.; Eickelberg, O.; Königshoff, M.; Bein, T.; Meiners, S. Protease-mediated release of chemotherapeutics from mesoporous silica nanoparticles to ex vivo human and mouse lung tumors. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 2377–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Karambelkar, A.; Gu, L.; Lin, K.; Miller, J.S.; Chen, C.S.; Sailor, M.J.; Bhatia, S.N. Bioresponsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles for triggered drug release. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 19582–19585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Kim, H.; Kim, S.; Kim, C. Enzyme responsive nanocontainers with cyclodextrin gatekeepers and synergistic effects in release of guests. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 16614–16615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeza, A.; Guisasola, E.; Torres-Pardo, A.; González-Calbet, J.M.; Melen, G.J.; Ramirez, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Hybrid enzyme-polymeric capsules/mesoporous silica nanodevice for in situ cytotoxic agent generation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 4625–4633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mura, S.; Nicolas, J.; Couvreur, P. Stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for drug delivery. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 991–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcos, D.; Fal -Miyar, V.; Ruiz-Hernández, E.; García-Hernández, M.; Ruiz-González, M.L.; González-Calbet, J.; Vallet-Regí, M. Supramolecular mechanisms in the synthesis of mesoporous magnetic nanospheres for hyperthermia. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-J.; Hu, S.-H.; Hsiao, C.-S.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Liu, D.-M.; Chen, S.-Y. Multifunctional magnetically removable nanogated lids of Fe3O4–capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles for intracellular controlled release and MR imaging. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.R.; Ferris, D.P.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, E.; Cho, M.H.; Kim, E.S.; Stoddart, J.F.; Shin, J.S.; Cheon, J.; Zink, J.I. Noninvasive remote-controlled release of drug molecules in vitro using magnetic actuation of mechanized nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 10623–10625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guisasola, E.; Baeza, A.; Talelli, M.; Arcos, D.; Vallet-Regí, M. Design of thermoresponsive polymeric gates with opposite controlled release behaviors. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 42510–42516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisasola, E.; Baeza, A.; Talelli, M.; Arcos, D.; Moros, M.; de la Fuente, J.M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Magnetic Responsive Release Controlled by Hot Spot Effect. Langmuir. 2015, 31, 12777–12782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baeza, A.; Guisasola, E.; Ruiz-Hernández, E.; Vallet-Regí, M. Magnetically triggered multidrug release by hybrid mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.; Liu, L.; Han, C.; Ma, X.; Qian, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhu, W. Cancer cell membrane-coated mesoporous silica loaded with superparamagnetic ferroferric oxide and paclitaxel for the combination of chemo/Magnetocaloric therapy on MDA-MB-231 cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, T.; Zhang, D.S.; Wang, Y.; Gu, H.; Di, W. Highly effective antiangiogenesis via magnetic mesoporous silica-based siRNA vehicle targeting the VEGF gene for orthotopic ovarian cancer therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 2579–2594. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Hernández, E.; Baeza, A.; Vallet-Regí, M. Smart drug delivery through DNA/magnetic nanoparticle gates. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mal, N.K.; Fujiwara, M.; Tanaka, Y. Photocontrolled reversible release of guest molecules from coumarin-modified mesoporous silica. Nature 2003, 421, 350–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferris, D.P.; Zhao, Y.-L.; Khashab, N.M.; Khatib, H.A.; Stoddart, J.F.; Zink, J.I. Light-operated mechanized nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 1686–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, T.; Lu, D.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Yan, C.-H.; Tan, W. Photon-manipulated drug release from a mesoporous nanocontainer controlled by azobenzene-modified nucleic acid. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 6337–6344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Boudjelal, M.; Kang, S. Ultraviolet irradiation of human skin causes functional vitamin A deficiency, preventable by all-trans retinoic acid pre-treatment. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindo, Y.; Witt, E.; Packer, L. Antioxidant defense mechanisms in murine epidermis and dermis and their responses to ultraviolet light. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1993, 100, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olejniczak, J.; Carling, C.J.; Almutairi, A. Photocontrolled release using one-photon absorption of visible or NIR light. J. Control. Release 2015, 219, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Carmona, M.; Lozano, D.; Baeza, A.; Colilla, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. A novel visible light responsive nanosystem for cancer treatment. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 15967–15973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guardado-Alvarez, T.M.; Sudha Devi, L.; Russell, M.M.; Schwartz, B.J.; Zink, J.I. Activation of snap-top capped mesoporous silica nanocontainers using two near-infrared photons. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 14000–14003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croissant, J.; Maynadier, M.; Gallud, A.; Peindy N’Dongo, H.; Nyalosaso, J.L.; Derrien, G.; Charnay, C.; Durand, J.O.; Raehm, L.; Serein-Spirau, F.; et al. Two-photon-triggered drug delivery in cancer cells using nanoimpellers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 13813–13817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirsi, S.R.; Borden, M.A. State-of-the-art materials for ultrasound-triggered drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 72, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Pelletier, M.; Zhang, H.J.; Xia, H.S.; Zhao, Y. High-frequency ultrasound-responsive block copolymer micelle. Langmuir 2009, 25, 13201–13205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, J.; Boissière, O.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, B.; Tremblay, L.; Lacelle, S.; Xia, H.; Zhao, Y. Ultrasound-responsive block copolymer micelles based on a new amplification mechanism. Langmuir 2012, 28, 16463–16468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Chen, Y.; Ma, M.; Zhang, K.; Li, F.; Zheng, Y.; Zeng, D.; Wang, Q.; Shi, J. Perfluorohexane-encapsulated mesoporous silica nanocapsules as enhancement agents for highly efficient High Intensity focused Ultrasound (HIFU). Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Zheng, Y.; Ma, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zeng, D.; Shi, J. Au-nanoparticle coated mesoporous silica nanocapsule-based multifunctional platform for ultrasound mediated imaging, cytoclasis and tumor ablation. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 2057–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, J.L.; Cabañas, M.V.; Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Polymer-grafted mesoporous silica nanoparticles as ultrasound-responsive drug carriers. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 11023–11033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauda, V.; Schlossbauer, A.; Kecht, J.; Zürner, A.; Bein, T. Multiple core-shell functionalized colloidal mesoporous silica nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 11361–11370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauda, V.; Argyo, C.; Piercey, D.G.; Bein, T. “Liquid-phase calcination” of colloidal mesoporous silica nanoparticles in high-boiling solvents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 6484–6486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Li, L.; Chen, D. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles: Synthesis, biocompatibility and drug delivery. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1504–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Carmona, M.; Colilla, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Smart mesoporous nanomaterials for antitumor therapy. Nanomaterials 2015, 5, 1906–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, R.R.; Colilla, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Advances in mesoporous silica-based nanocarriers for co-delivery and combination therapy against cancer. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2017, 14, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquib, M.; Farooq, M.A.; Banerjee, P.; Akhtar, F.; Filli, M.S.; Boakye-Yiadom, K.O.; Kesse, S.; Raza, F.; Maviah, M.B.J.; Mavlyanova, R.; et al. Targeted and stimuli-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug delivery and theranostic use. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2019, 107A, 2643–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenholm, J.M.; Meinander, A.; Peuhu, E.; Niemi, R.; Eriksson, J.E.; Sahlgren, C.; Lindén, M. Targeting of Porous Hybrid Silica Nanoparticles to Cancer Cells. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wang, N.; Yang, L.Y.; Ouyang, X.K.; Huang, F. Folic acid and pei modified mesoporous silica for targeted delivery of curcumin. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Nie, J.; Xu, L.; Liang, C.; Peng, Y.; Liu, G.; Wang, T.; Mei, L.; Huang, L.; Zeng, X. A pH-sensitive delivery vehicle based on folic acid-conjugated polydopamine-modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 18462–18473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yu, D.; Jin, C.; Song, X.; Cheng, J.; Zhao, X.; Qi, X.; Zhang, G. A dual responsive targeted drug delivery system based on smart polymer coated mesoporous silica for laryngeal carcinoma treatment. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 4830–4836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Yu, D.; Jia, B.; Jin, C.; Liu, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, G. Targeting CD133+ laryngeal carcinoma cells with chemotherapeutic drugs and siRNA against ABCG2 mediated by thermo/pH-sensitive mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 2209–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Xie, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Feng, N. Curcumin-loaded redox-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted breast cancer therapy. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 921–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbouAitah, K.; Hassan, H.A.; Swiderska-Sroda, A.; Gohar, L.; Shaker, O.G.; Wojnarowicz, J.; Opalinska, A.; Smalc-Koziorowska, J.; Gierlotka, S.; Lojkowski, W. Targeted nano-drug delivery of colchicine against colon cancer cells by means of mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Cancers 2020, 12, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Li, S. Dual functional mesoporous silicon nanoparticles enhance the radiosensitivity of VPA in glioblastoma. Transl. Oncol. 2017, 10, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Xie, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Guo, Z.; Gao, F.; Zhao, L.; Cai, Q. A theranostic nanocomposite system based on radial mesoporous silica hybridized with Fe3O4 nanoparticles for targeted magnetic field responsive chemotherapy of breast cancer. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 4321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wu, C.; Liu, Y.; Hu, L.; Shang, W.; Gao, Z.; Xia, N. Folate functionalized pH-sensitive photothermal therapy traceable hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a targeted drug carrier to improve the antitumor effect of doxorubicin in the hepatoma cell line SMMC-7721. Drug Delivery 2020, 27, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paredes, K.O.; Díaz-García, D.; García-Almodóvar, V.; Chamizo, L.L.; Marciello, M.; Díaz-Sánchez, M.; Prashar, S.; Gómez-Ruiz, S.; Filice, M. Multifunctional silica-based nanoparticles with controlled release of organotin metallodrug for targeted theranosis of breast cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Berríos, M.P.; Vivero-Escoto, J.L. In vitro evaluation of folic acid-conjugated redox-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles for the delivery of cisplatin. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 6251–6265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, K.; Bandyopadhyaya, R. Transferrin-Conjugated Polymer-Coated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Loaded with Gemcitabine for Killing Pancreatic Cancer Cells. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Wang, Z.; Zong, S.; Chen, H.; Zhu, D.; Zhong, Y.; Cui, Y. pH-controllable drug carrier with SERS activity for targeting cancer cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 57, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Sun, H.; Hu, J.; Han, X.; Liu, H.; Hu, Y. Transferrin gated mesoporous silica nanoparticles for redox-responsive and targeted drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 152, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Carmona, M.; Baeza, A.; Rodriguez-Milla, M.A.; García-Castro, J.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles grafted with a light-responsive protein shell for highly cytotoxic antitumoral therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 5746–5752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Er, Ö.; Colak, S.G.; Ocakoglu, K.; Ince, M.; Bresolí-Obach, R.; Mora, M.; Sagristá, M.L.; Yurt, F.; Nonell, S. Selective photokilling of human pancreatic cancer cells using cetuximab-targeted mesoporous silica nanoparticles for delivery of zinc phthalocyanine. Molecules 2018, 23, 2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngamcherdtrakul, W.; Morry, J.; Gu, S.; Castro, D.J.; Goodyear, S.M.; Sangvanich, T.; Reda, M.M.; Lee, R.; Mihelic, S.A.; Beckman, B.L.; et al. Cationic polymer modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted siRNA delivery to HER2 breast cancer. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 2646–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Li, M.; Liu, T.; Liu, J.; Youhua Xie, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xu, S.; Liu, H. A dual-functional HER2 aptamer-conjugated, pH-activated mesoporous silica nanocarrier-based drug delivery system provides in vitro synergistic cytotoxicity in HER2-positive breast cancer cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 4029–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, F.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Pang, J.; Pan, W. Galactosylated chitosan-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles for efficient colon cancer cell-targeted drug delivery. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 181027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Carmona, M.; Lozano, D.; Colilla, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Lectin-Conjugated pH-Responsive Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Targeted Bone Cancer Treatment. Acta Biomater. 2018, 65, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Yang, Z.; Li, B.; Meng, J.; Shi, Z.; Li, P.; Fu, S. RGD-conjugated mesoporous silica-encapsulated gold nanorods enhance the sensitization of triple-negative breast cancer to megavoltage radiation therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 5595–5610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Han, Z.; Schur, R.M.; Lu, Z.R. Targeted mesoporous silica nanoparticles delivering arsenic trioxide with environment sensitive drug release for effective treatment of triple negative breast cancer. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yuan, Z.F.; Wang, Y.; Chen, W.H.; Luo, G.F.; Cheng, S.X.; Zhuo, R.X.; Zhang, X.Z. Multifunctional envelope-type mesoporous silica nanoparticles for tumor-triggered targeting drug delivery. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 5068–5073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.J.; Zhang, A.Q.; Hu, J.J.; He, F.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, X.Z. Multifunctional peptide-amphiphile end-capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles for tumor targeting drug delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 2093–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Xie, Y.; Peltier, R.; Lei, H.; Wang, P.; Chen, J.; Hu, Y.; Wang, F.; Yao, X.; Sun, H. Peptide-decorated gold nanoparticles as functional nano-capping agent of mesoporous silica container for targeting drug delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 11204–11209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, D.; Hu, J.J.; Zhu, J.Y.; Wang, S.B.; Zhuo, R.X.; Zhang, X.Z. A redox-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticle with a therapeutic peptide shell for tumor targeting synergistic therapy. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 16702–16709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, G.F.; Chen, W.H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, S.X.; Zhuo, R.X.; Zhang, X.Z. Charge-reversal plug gate nanovalves on peptide-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 5723–5732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, C.; Gao, W.; Fan, X.; Wu, G. A facile strategy to fabricate a pH-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticle end-capped with amphiphilic peptides by self-assembly. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 179, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xing, L.; Hu, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Wang, R.; Xu, X.; Du, L.; Shen, M.; Shi, X. An RGD-modified hollow silica@Au core/shell nanoplatform for tumor combination therap. Acta Biomater. 2017, 62, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, O.; Bielecki, P.; Tong, K.; Covarrubias, G.; Moon, T.; Rahmy, A.; Cooley, S.; Park, Y.; Peiris, P.M.; Ghaghada, K.B.; et al. Effect of dose and selection of two different ligands on the deposition and antitumor efficacy of targeted nanoparticles in brain tumors. Mol. Pharmaceutics 2019, 16, 4352–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, X.; Wen, Z.; Tan, Y.; Huang, N.; Cheng, S.; Zheng, H.; Cheng, Y. Asn-Gly-Arg-modified polydopamine-coated nanoparticles for dual-targeting therapy of brain glioma in rats. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 73681–73696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, M.; Abnous, K.; Taghdisi, S.M.; Amel Farzad, S.; Peivandi, M.T.; Ramezani, M.; Alibolandi, M. Synthesis of theranostic epithelial cell adhesion molecule targeted mesoporous silica nanoparticle with gold gatekeeper for hepatocellular carcinoma. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2017, 12, 1261–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Hu, H.; Zhang, M.G.; Song, J.; Nie, L.; Wang, S.; Niu, G.; Huang, P.; Lu, G.; Chen, X. An aptamer-targeting photoresponsive drug delivery system using “off-on” graphene oxide wrapped mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 6304–6310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Tang, C.; Yin, C. Dual-targeting and pH/redox-responsive multi-layered nanocomplexes for smart co-delivery of doxorubicin and siRNA. Biomaterials 2015, 60, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, B.; Luo, Z.; Ding, X.; Li, J.; Dai, L.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, X.; Ye, J.; Cai, K. Enzyme responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted tumor therapy in vitro and in vivo. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 3614–3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Zhao, F.; Wang, X.; Fan, X.; Wu, G. Secondary nuclear targeting of mesoporous silica nano-particles for cancer-specific drug delivery based on charge inversion. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 70100–70112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Gao, L.; Wang, L.; Shi, L.; Wei, E.; Zhou, B.; Zhou, L.; Ge, B. Polydopamine and peptide decorated doxorubicinloaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a targeted drug delivery system for bladder cancer therapy. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Tang, C.; Yin, C. pH-Responsive Core−Shell Structured Nanoparticles for Triple-Stage Targeted Delivery of Doxorubicin to Tumors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 23498–23508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Geng, H.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S. Hyaluronic acid oligosaccharide modified redox-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 20290–20299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Li, X.; Xu, Z.; Du, F.; Wang, W.; Shi, R.; Gao, D. Hyaluronic acid-modified mesoporous silica-coated superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 5785–5797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Geng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Feng, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xie, X.; Qin, X.; Li, S.; Wu, C.; et al. Versatile nanoplatform for synergistic chemo-photothermal therapy and multimodal imaging against breast cancer. Expert Opin. Drug Del. 2020, 17, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, J. Mesoporous silica nanoparticle-based intelligent drug delivery system for bienzyme-responsive tumour targeting and controlled release. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 170986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Dai, R.; Wei, Q.; Li, W.; Zhu, G.; Chi, H.; Guo, Z.; Wang, L.; Cui, C.; Xu, J.; et al. Dual-functionalized janus mesoporous silica nanoparticles with active targeting and charge reversal for synergistic tumor-targeting therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 44582–44592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, X.; Mao, Y.; Chen, C.; Gao, Y.; Sun, C. Siling Wang. Multi-stimuli responsive mesoporous silica-coated carbon nanoparticles for chemo-photothermal therapy of tumor. Colloids Surf. B 2020, 190, 110941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Ding, C.; Wang, C.; Fu, J. UV-light cross-linked and pH de-cross-linked coumarin-decorated cationic copolymer grafted mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug and gene co-delivery in vitro. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xiao, L.; Chang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Chen, C.; Wang, D. pH and redox dual-responsive MSN-S-S-CS as a drug delivery system in cancer therapy. Materials 2020, 13, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hei, M.; Xu, Y.; Qian, X.; Zhu, W. Ammonium salt modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles for dual intracellular-responsive gene delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 511, 689–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Xu, X.; Zhou, J.; Liu, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, D.; Yang, F.; Zhang, H. Fabrication of a pH/redox-triggered mesoporous silica-based nanoparticle with microfluidics for anticancer drugs doxorubicin and paclitaxel codelivery. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 1216–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anirudhan, T.S.; Nair, A.S. Temperature and ultrasound sensitive gatekeepers for the controlled release of chemotherapeutic drugs from mesoporous silica nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.E.; Lee, N.; Kim, T.; Kim, J.; Hyeon, T. Multifunctional mesoporous silica nanocomposite nanoparticles for theranostic applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Sugihara, F.; Matsushita, H.; Yoshioka, Y.; Mizukami, S.; Kikuchi, K. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for (19)F magnetic resonance imaging, fluorescence imaging, and drug delivery. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 1986–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.-T.; Cheng, S.-H.; Souris, J.S.; Chen, C.-T.; Mou, C.-Y.; Lo, L.-W. Theranostic applications of mesoporous silica nanoparticles and their organic/inorganic hybrids. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wu, M.; Zhao, J.X. Recent development of silica nanoparticles as delivery vectors for cancer imaging and therapy. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2014, 10, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy, M.C.; Chan, H.R.; Ross, B.D.; Bhattacharya, P.K.; Marcus, C.M. In vivo magnetic resonance imaging of hyperpolarized silicon particles. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2013, 8, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Panwar, N.; Tng, D.J.H.; Tjin, S.C.; Wang, K.; Yong, K.-T. The application of mesoporous silica nanoparticle family in cancer theranostics. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 319, 86–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, H.; Mizukami, S.; Sugihara, F.; Nakanishi, Y.; Yoshioka, Y.; Kikuchi, K. Multifunctional core-shell silica nanoparticles for highly sensitive (19)F magnetic resonance imaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2014, 53, 1008–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milgroom, A.; Intrator, M.; Madhavan, K.; Mazzaro, L.; Shandas, R.; Liu, B.L.; Park, D. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as a Breast-Cancer Targeting Ultrasound Contrast Agent. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 116, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, B.G.; Kim, J. Functional mesoporous silica nanoparticles for bio-imaging applications. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 11, e1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouamrani, A.; Hu, Y.; Tasciotti, E.; Li, L.; Chiappini, C.; Liu, X.; Ferrari, M. Mesoporous silica chips for selective enrichment and stabilization of low molecular weight proteome. Proteomics 2010, 10, 496–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäger, T.; Szarvas, T.; Börgermann, C.; Schenck, M.; Schmid, K.; Rübben, H. Use of silicon chip technology to detect protein-based tumor markers in bladder cancer. Der Urologe. Ausg. A 2007, 46, 1152–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, K.; Wu, H.; Hu, T.Y.; Li, Y. Mesoporous silica chip: Enabled peptide profiling as an effective platform for controlling bio-sample quality and optimizing handling procedure. Clin. Proteom 2016, 13, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Bouamrani, A.; Tasciotti, E.; Li, L.; Liu, X.W.; Ferrari, M. Tailoring of the nanotexture of mesoporous silica films and their functionalized derivatives for selectively harvesting low molecular weight protein. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Peng, Y.; Lin, K.; Shen, H.; Brousseau, L.C., 3rd; Sakamoto, J.; Sun, T.; Ferrari, M. Surface engineering on mesoporous silica chips for enriching low molecular weight phosphorylated proteins. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; He, X.; Yang, X.; Shi, H. Functionalized silica nanoparticles: A platform for fluorescence imaging at the cell and small animal levels. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 1367–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Chen, F.; Cai, W. Biomedical applications of functionalized hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles: Focusing on molecular imaging. Nanomedicine 2013, 8, 2027–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alford, R.; Simpson, H.M.; Duberman, J.; Hill, G.C.; Ogawa, M.; Regino, C.; Kobayashi, H.; Choyke, P.L. Toxicity of organic fluorophores used in molecular imaging: Literature review. Mol. Imaging 2009, 8, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesse, S.; Boakye-Yiadom, K.O.; Ochete, B.O.; Opoku-Damoah, Y.; Akhtar, F.; Filli, M.S.; Farooq, M.A.; Aquib, M.; Mily, B.J.M.; Murtaza, G.; et al. Mesoporous silica nanomaterials: Versatile nanocarriers for cancer theranostics and drug and gene delivery. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, F.; Zhang, B.; Zeng, S.; Lin, G.; Tian, J.; Yang, C.; Wang, K.; Xu, G.; Yong, K.-T. Folic acid-conjugated organically modified silica nanoparticles for enhanced targeted delivery in cancer cells and tumor in vivo. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 6081–6093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resch-Genger, U.; Grabolle, M.; Cavaliere-Jaricot, S.; Nitschke, R.; Nann, T. Quantum dots versus organic dyes as fluorescent labels. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 763–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, B.H.; Hwang, D.W.; Jung, H.S.; Jang, J.; Kim, H.; Kang, H.; Kang, T.; Kyeong, S.; Lee, H.; Jeong, D.H.; et al. Ultrasensitive, biocompatible, quantum-dot-embedded silica nanoparticles for bioimaging. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 1843–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Huo, D.; Hou, C.; Yang, M.; Fa, H.; Xia, C.; Chen, M. Mesoporous silica-coated quantum dots functionalized with folic acid for lung cancer cell imaging. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 9649–9654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.-H.; Lee, C.-H.; Chen, M.-C.; Souris, J.S.; Tseng, F.-G.; Yang, C.-S.; Mou, C.-Y.; Chen, C.-T.; Lo, L.-W. Tri-functionalization of mesoporous silica nanoparticles for comprehensive cancer theranostics—The trio of imaging, targeting and therapy. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 6149–6157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, T.; Rodrigues, A.S.; Calderon, S.; Fidalgo, A.; Gonçalves, J.L.M.; André, V.; Teresa Duarte, M.; Ferreira, P.J.; Farinha, J.P.S.; Baleizão, C. Silica nanocarriers with user-defined precise diameters by controlled template self-assembly. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 561, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Zhang, J.; Shi, J.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Bu, W.; Guo, L.; Chen, Y. The effect of PEGylation of mesoporous silica nanoparticles on nonspecific binding of serum proteins and cellular responses. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 1902634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farjadian, F.; Roointan, A.; Mohammadi-Samani, S.; Hosseini, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles: Synthesis, pharmaceutical applications, biodistribution, and biosafety assessment. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 684–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, N. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles: Synthesis, classification, drug loading, pharmacokinetics, biocompatibility, and application in drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 219–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenholm, J.M.; Mamaeva, V.; Sahlgren, C.; Linden, M. Nanoparticles in targeted cancer therapy: Mesoporous silica nanoparticles entering preclinical development Stage. Nanomedicine 2012, 7, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Li, L.; Liu, T.; Hao, N.; Liu, H.; Chen, D.; Tang, F. The shape effect of mesoporous silica nanoparticles on biodistribution, clearance, and biocompatibility in vivo. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 5390–5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Hubbard, D.; Ray, A.; Ghandehari, H. In vivo biodistribution and pharmacokinetics of silica nanoparticles as a function of geometry, porosity and surface characteristics. J. Control. Release 2012, 163, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, T.; Fu, C.; Tan, L.; Meng, X.; Liu, H. Biodistribution, excretion, and toxicity of mesoporous silica nanoparticles after oral administration depend on their shape. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2015, 11, 1915–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogra, P.; Adolphi, N.L.; Wang, Z.; Lin, Y.-S.; Butler, K.S.; Durfee, P.N.; Croissant, J.G.; Noureddine, A.; Coker, E.N.; Bearer, E.L.; et al. Establishing the effects of mesoporous silica nanoparticle properties on in vivo disposition using imaging-based pharmacokinetics. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.-G.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, X.-P.; Shan, K.; Liu, B.-H.; Zhao, C.; Yan, B. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a delivery system for improving antiangiogenic therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 1489–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.; Tang, J.; Qiao, Q.; Wu, T.; Qi, Y.; Tan, S.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Z. Biodegradable hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles for regulating tumor microenvironment and enhancing antitumor efficiency. Theranostics 2017, 7, 3276–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paula, A.J.; Araujo Júnior, R.T.; Martinez, D.S.T.; Paredes-Gamero, E.J.; Nader, H.B.; Durán, N.; Justo, G.Z.; Alves, O.L. Influence of protein corona on the transport of molecules into cells by mesoporous silica nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 8387–8393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visalakshan, R.M.; García, L.E.G.; Benzigar, M.R.; Ghazaryan, A.; Simon, J.; Mierczynska-Vasilev, A.; Michl, T.D.; Vinu, A.; Mailänder, V.; Morsbach, S.; et al. The influence of nanoparticle shape on protein corona formation. Small Nano Micro. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauda, V.; Engelke, H.; Sauer, A.; Arcizet, D.; Bräuchle, C.; Rädler, J.; Bein, T. Colchicine-loaded lipid bilayer-coated 50 nm mesoporous nanoparticles efficiently induce microtubule depolymerization upon cell uptake. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 2484–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, W.; Zhang, Y.; Han, S.; Tao, J.; Zheng, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhu, J.; Li, F.; Wang, X. RGD conjugated liposome-hollow silica hybrid nanovehicles for targeted and controlled delivery of arsenic trioxide against hepatic carcinoma. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 519, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackowiak, S.A.; Schmidt, A.; Weiss, V.; Argyo, C.; Constantin von Schirnding, C.; Bein, T.; Bräuchle, C. Targeted drug delivery in cancer cells with red-light photoactivated mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 2576–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Miao, Y.; Chen, M.; Chen, X.; Li, F.; Zhang, X.; Gan, Y. Stepwise targeting and responsive lipid-coated nanoparticles for enhanced tumor cell sensitivity and hepatocellular carcinoma therapy. Theranostics 2020, 10, 3722–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durfee, P.N.; Lin, Y.S.; Darren, R.; Dunphy, D.R.; Muñiz, A.J.; Butler, K.S.; Humphrey, K.R.; Lokke, A.J.; Agola, J.O.; Chou, S.S.; et al. Mesoporous silica nanoparticle-supported lipid bilayers (protocells) for active targeting and delivery to individual leukemia cells. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 8325–8345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, K.S.; Durfee, P.N.; Theron, C.; Ashley, C.E.; Carnes, E.C.; Brinker, C.J. Protocells: Modular mesoporous silica nanoparticlesupported lipid bilayers for drug delivery. Small 2016, 12, 2173–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samanta, S.; Pradhan, L.; Bahadur, D. Mesoporous lipid-silica nanohybrids for folate-targeted drug-resistant ovarian cancer. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 2804–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; Jia, T.T.; Huang, Q.X.; Qiu, Y.Y.; Xu, J.; Yin, P.H.; Liu, T. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs)-based organic/inorganic hybrid nanocarriers loading 5-Fluorouracil for the treatment of colon cancer with improved anticancer efficacy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 159, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Li, H. Superiority of L-tartaric acid modified chiral mesoporous silica nanoparticle as a drug carrier: Structure, wettability, degradation, bio-adhesion and biocompatibility. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 601–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, K.; Wang, J.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, Q.; Kong, X. Poly(amidoamine)-modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a mucoadhesive drug delivery system for potential bladder cancer therapy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimarães, R.S.; Rodrigues, C.F.; Moreira, A.F.; Correia, I.J. Overview of stimuli-responsive mesoporous organosilica nanocarriers for drug delivery. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 155, 104742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.M.; Chen, G.B.; Chen, H.H.; Zhang, J.B.; Li, H.Z.; Sheng, M.X.; Weng, W.B.; Guo, S.M. Cancer cell membrane-cloaked mesoporous silica nanoparticles with a pH-sensitive gatekeeper for cancer treatment. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 175, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, J.; Wang, Z.; Shao, D.; Chang, Z.; Hu, R.; Li, L.; Luo, S.; Dong, W. Cancer cell membrane-modified biodegradable mesoporous silica nanocarriers for berberine therapy of liver cancer. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 40288–40297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauda, V.; Limongi, T.; Racca, L.; Canta, M.; Susa, F.; Piva, R.; Bergaggio, E.; Vitale, N.; Mereu, E. A biomimetic nanoporous carrier comprising an inhibitor directed towards the native form of IDH2 protein. Patent IB 2020/050401, 23 January 2019. [Google Scholar]
| Active Targeting | Stimuli Responsive Delivery | Cancer Therapeutics | Cancer Type | Outcome | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Stimulus | Linker/Moiety | ||||
| Folic acid | Folate | pH | poly(ethylene imine) (PEI) | - | cervical cancer | significantly higher number of particle internalization in cancer cells than normal cells | [208] |
| Folic acid | Folate | pH | poly(ethylene imine) (PEI) | Curcumin | colon cancer | suitable loading of fat-soluble antineoplastic drugs for sustained release | [209] |
| Folic acid | Folate | pH | polydopamine | Doxorubicin | cervical cancer | higher antitumor efficacy of MSNs@PDA-PEG-FA in vivo | [210] |
| Folic acid | Folate | Thermo/pH-coupling | poly[(N-isopropylacrylamide)-co-(methacrylic acid)] | Cisplatin | laryngeal carcinoma | higher cellular uptake, excellent drug release, greater cytotoxicity | [211], |
| Folic acid | Folate | Thermo/pH-coupling | poly[(N-isopropylacrylamide)-co-(methacrylic acid)] | siRNA against ABCG2 + cisplatin/5-fluorouracil (5-Fu)/paclitaxel | laryngeal carcinoma | down-regulation of ABCG2 significantly enhanced efficacy of chemotherapeutic drug-induced apoptosis of cancer cells | [212] |
| Folic acid | Folate | Redox | disulfide bonds | Curcumin | breast cancer | good biocompatibility, low toxicity, precise targeting and tumor growth inhibition | [213] |
| Folic acid | Folate | pH | chitosan-glycine | Colchicine (COL) | colon cancer | enhanced anticancer effects and reduced toxicity of free COL | [214] |
| Folic acid | Folate | pH | benzimidazole and β-cyclodextrin | valproic acid (VPA) | glioblastoma | enhanced effectiveness of radiotherapy | [215] |
| Folic acid | Folate | Magnetic field | iron oxide nanoparticles (IONPs) | Doxorubicin | breast cancer | effective active targeting and MRI-guided stimuli-responsive chemotherapy | [216] |
| Folic acid | Folate | pH and NIR light | polydopamine (PDA) | Doxorubicin | liver cancer | improved antitumor effect combining Dox-loaded MSN and NIR light | [217] |
| Folic acid | Folate | Enzyme (cathepsin B) | GFLG tetrapeptide linker | organotin-based cytotoxic compound | breast cancer | enhanced tumor growth inhibition with reduced hepatic and renal toxicity | [218] |
| Folic acid | Folate | Redox (Ascorbic acid) | cisplatin(IV) prodrug | cisplatin(IV) prodrug | cervical cancer | delivering cisplatin into cytosol, inducing DNA adducts and cell death | [219] |
| Transferrin | Transferrin | pH | chitosan or poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) | Gemcitabine | pancreatic cancer | improved uptake of NPs by cancer cells, inhibition of cancer cell growth | [220] |
| Transferrin | Transferrin | pH and surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) | chitosan/poly(methacrylic acid) (CS-PMAA) and SERS reporter tagged Ag-NPs | Doxorubicin | cervical cancer | pH-responsive drug release, SERS-traceable characteristics and cancer cells targeting | [221] |
| Transferrin | Transferrin | Redox | disulfide bonds | Doxorubicin | liver cancer | biocompatible system, potential in site-specific and controlled drug release | [222] |
| Transferrin | Transferrin | UV radiation (366 nm) | avidin, streptavidin and biotinylated photocleavable cross-linker | Doxorubicin | exposed tumors (skin, stomach and oesophagus) | efficient phototriggered drug delivery in accessible tumors and very high tumor cytotoxicity effect | [223] |
| Cetuximab | EGFR | photo | zinc phthalocyanine | ZnPcOBP | pancreatic Cancer | cell-line dependent photo-killing correlates well with EGFR expression levels | [224] |
| Trastuzumab | HER2 | pH | poly(ethylene imine) (PEI) | siRNA against human HER2 oncogene | breast cancer | high batch-to-batch reproducibility, excellent safety profile, ready for clinical evaluation | [225] |
| HApt aptamer | HER2 | pH | benzimidazole and β-cyclodextrin | Doxorubicin and biotherapeutic agent HApt | breast cancer | synergistic cytotoxic effects of chemotherapeutics in HER2-positive cancer cells | [226] |
| D-galactose | galactose receptor | pH | chitosan | 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) | colon cancer | high drug loading capacity, possessed higher cytotoxicity on cancer cells | [227] |
| lectin concana- valin A (ConA) | glycans, sialic acids (SA) | pH | polyacrylic acid capping, acetal linker | Doxorubicin | bone cancer | increased antitumor effectiveness and decreased toxicity towards normal cell | [228] |
| cyclic RGDfC | αvβ3 integrin | photons | gold nanorods | - | breast cancer | enhanced radiosensitization of triple-negative breast cancer | [229] |
| cyclic RGDfC | αvβ3 integrin | Glutathione | thiol-functionalization | arsenic trioxide (ATO) | breast cancer | superior therapeutic ability of ATO-MSNs-RGD | [230] |
| RGD | αvβ3 integrin | Glutathione | β-Cyclodextrin, disulfide linker | Doxorubicin | MMP-rich tumor (colorectal and head and neck cancer) | tumor-triggered targeting drug delivery to cancerous cells | [231] |
| matrix metallop- roteinase (MMP) | PLGVR peptide | ||||||
| RGD and Tat48–60 peptide | Integrin and nuclear targeting | Glutathione | disulfide linker | Doxorubicin | cervical cancer | facilitated active targeting delivery and enhanced intracellular drug release | [232] |
| RGD | αvβ3 integrin | pH | α-amide-β-carboxyl group | Doxorubicin | glioblastoma | diversified multifunctional nanocomposites | [233] |
| (RGDWWW)2KC | αvβ3 integrin | Glutathione | disulfide linker | Doxorubicin and therapeutic peptide | glioblastoma | tumor targeting and synergism of anticancer drug and therapeutic peptide | [234] |
| K8(RGD)2 | αvβ3 integrin | pH | acid-labile amides | Doxorubicin | glioblastoma | electrostatic repulsion induced nanovalve opening and drug release | [235] |
| RGD | αvβ3 integrin | pH | peptide-based amphiphile (P45) | Doxorubicin | Lung and breast cancer | targeted drug delivery and controlled drug release by the nanovalves | [236] |
| RGD | αvβ3 integrin | pH/NIR laser | gold nanostars (Au NSs) | Doxorubicin | glioblastoma | improved therapeutic efficacy combining chemotherapy and photothermal therapy (PTT) | [237] |
| cRGD and CREKA | αvβ3 integrin and fibronectin | radiofrequency (RF) | iron oxide core | Doxorubicin | brain tumor | remarkable increase in intratumoral drug levels | [238] |
| Asn-Gly-Arg (NGR) | cluster of differen- tiation 13 (CD13) | pH | polydopamine (PDA) | Doxorubicin | neovascular endothelial and glioma | greater BBB permeability, higher accumulation in intracranial tumor region | [239] |
| EpCAM aptamer | Epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) | pH | citrate-capped gold nanoparticles | 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) | hepatocellular carcinoma | preferential accumulation in tumor cells in vitro and in vivo | [240] |
| aptamer (Cy5.5-AS1411) | nucleolin (NCL) | laser irradiation (NIR light) | graphene oxide | Doxorubicin | breast cancer | synergism of chemotherapy and PTT | [241] |
| galactose (Gal) and TAT peptide | Asialoglycoprotein receptors and nuclear targeting | pH and Redox | poly(allylamine hydrochloride)-citraconic anhydride (PAH-Cit) and cysteine groups | Doxorubicinand VEGF-siRNA | hepato-carcinoma | effective and safe vector, sustained release, synergistic effect of chemodrugs and therapeutic genes | [242] |
| Phenylboronic acid (PBA) | sialic acid (SA) | MMP-2 | PVGLIG peptide | Doxorubicin | liver cancer | tumor growth inhibition, minimal toxic side effects | [243] |
| YSA-BHQ1 and TAT- FITC | EphA2 receptor and nuclear targeting | pH | citraconic anhydride (Cit) | Doxorubicin | breast cancer | successfully developed anticancer drug delivery and imaging nanosystem | [244] |
| peptide CSNRDARRC | Targeting bladder cancer | pH | polydopamine (PDA) | Doxorubicin | bladder cancer | significantly superior antitumor effects of loaded nanocarriers than free drug | [245] |
| galactose (Gal) ligands and TAT peptide | Gal receptors and nuclear targeting | pH | poly(allylamine hydrochloride)-citraconic anhydride | Doxorubicin | hepato-carcinoma | improved tumorous distribution and potent therapeutic efficacy | [246] |
| oligosaccharide of hyaluronic acid (oHA) | CD44 | Glutathione | disulfide linker | 6-mercaptopurine (6-MP) | colon cancer | increased stability and biocompatibility, efficient drug release in tumor cell | [247] |
| hyaluronic acid | CD44 | Magnetic field | superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles | Doxorubicin | breast cancer | active targeting to tumor cells and reduced off-target side effects | [248] |
| hyaluronic acid | CD44 | NIR light | indocyanine green (ICG) | Doxorubicin | breast cancer | synergetic effect of chemotherapy and PTT | [249] |
| hyaluronic acid | CD44 | Enzyme (MMP-2) | gelatin layer | Doxorubicin | breast cancer | successful bienzyme-responsive targeted and optimal drug delivery | [250] |
| hyaluronic acid | CD44 | pH | DMMA (2,3-dimethylmaleic anhydride) | Doxorubicin | lung cancer | synergistic effect of active targeting and charge reversal in drug delivery | [251] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barui, S.; Cauda, V. Multimodal Decorations of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Improved Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12060527
Barui S, Cauda V. Multimodal Decorations of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Improved Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(6):527. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12060527
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarui, Sugata, and Valentina Cauda. 2020. "Multimodal Decorations of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Improved Cancer Therapy" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 6: 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12060527
APA StyleBarui, S., & Cauda, V. (2020). Multimodal Decorations of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Improved Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics, 12(6), 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12060527





