Multilayer-Coated Tablet of Clopidogrel and Rosuvastatin: Preparation and In Vitro/In vivo Characterization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
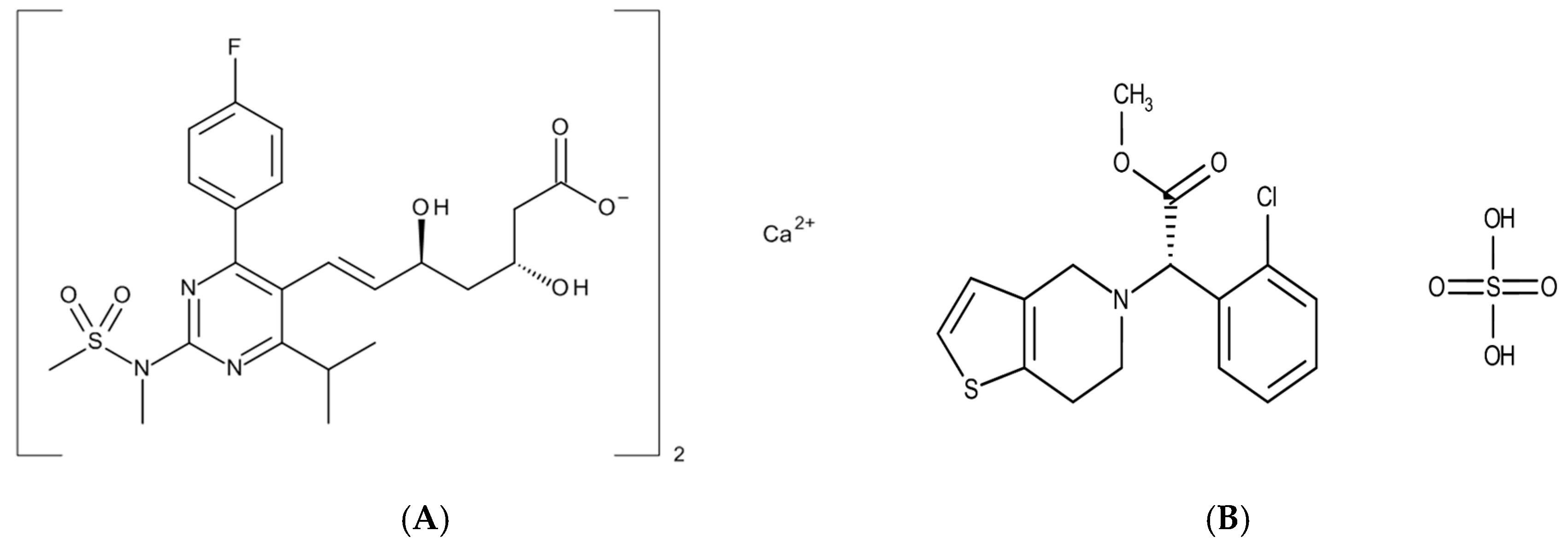
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of Clopidogrel Core Tablets
2.2.2. Screening Coating Materials for Separating Clopidogrel and Rosuvastatin
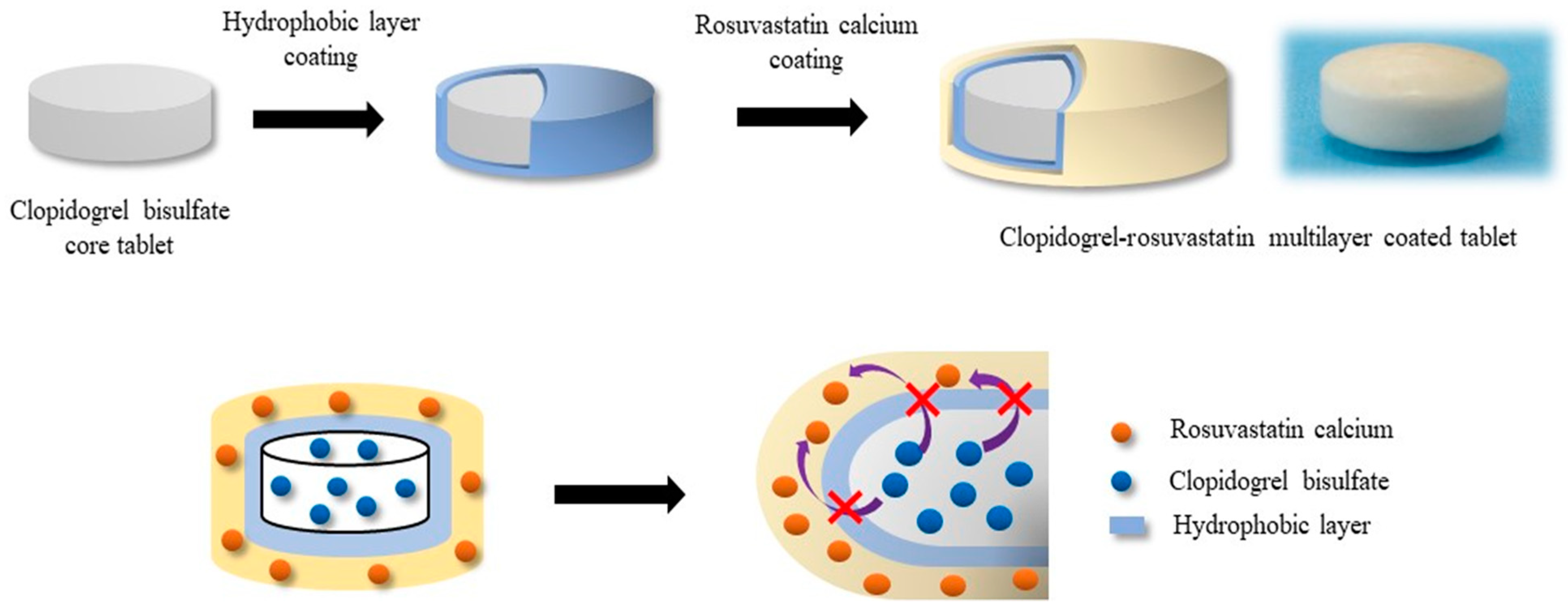
2.2.3. Preparation of the Multilayer-Coated Tablet
2.2.4. Disintegration Study
2.2.5. Dissolution study
2.2.6. Stability study
2.2.7. Pharmacokinetic Study in Dogs
2.2.8. HPLC Analysis
2.2.9. LC-MS/MS Analysis
2.2.10. Pharmacokinetic Analysis and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Screening of Optimal Excipients
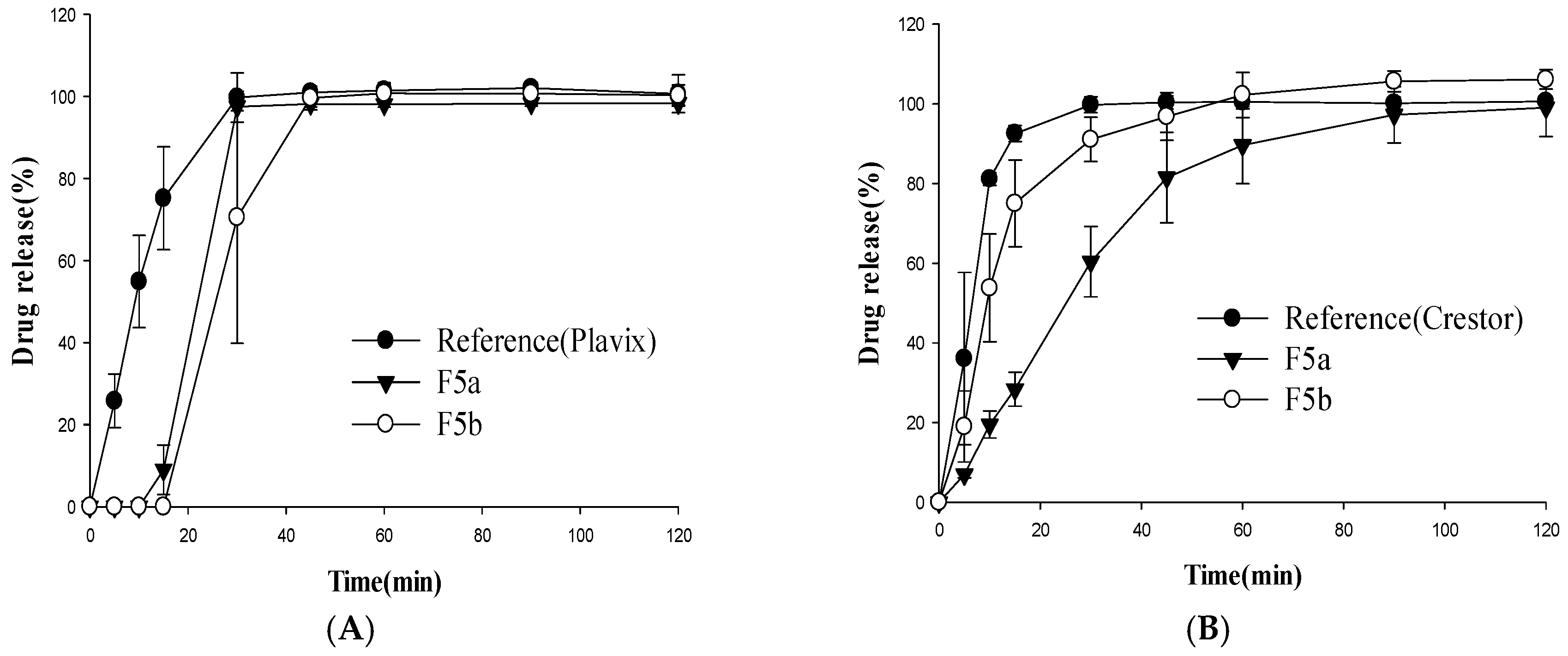
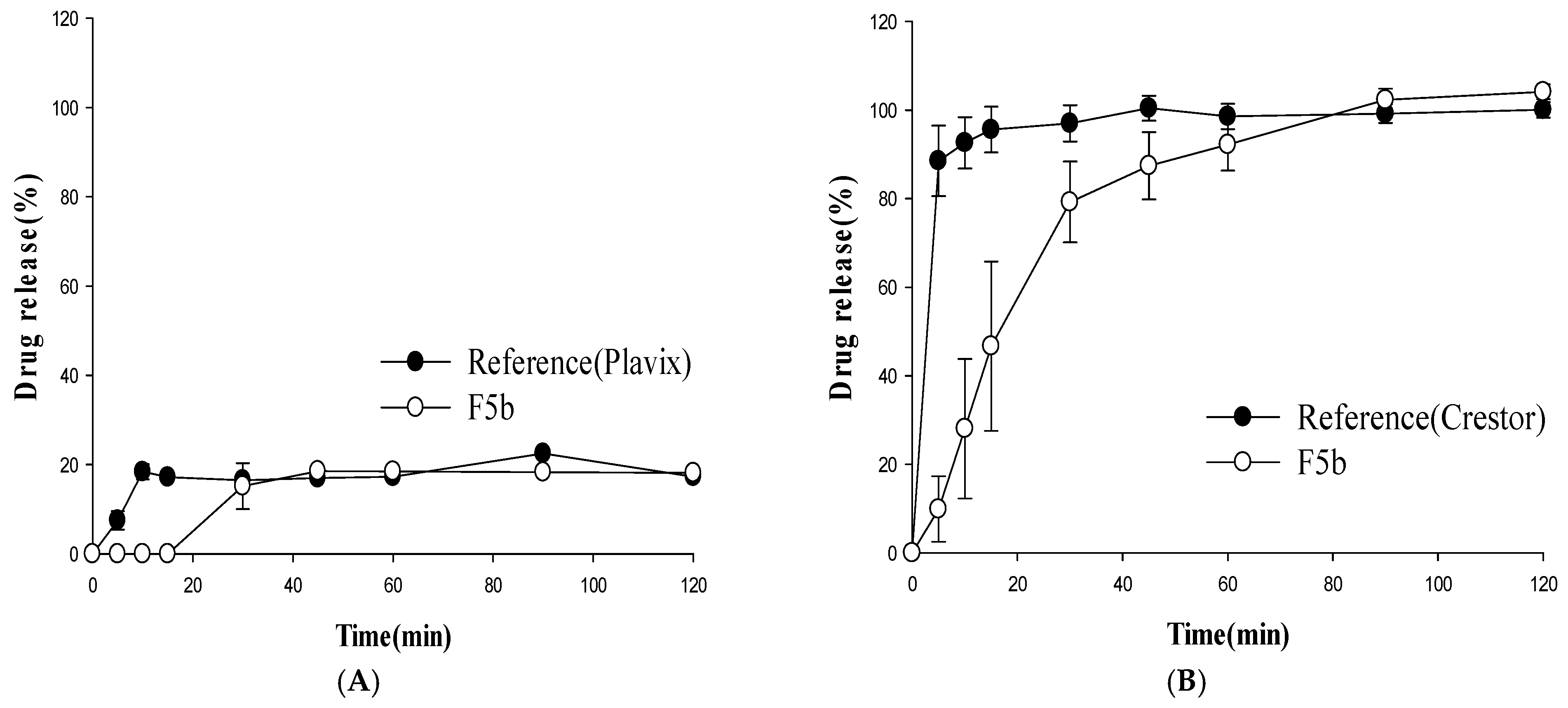
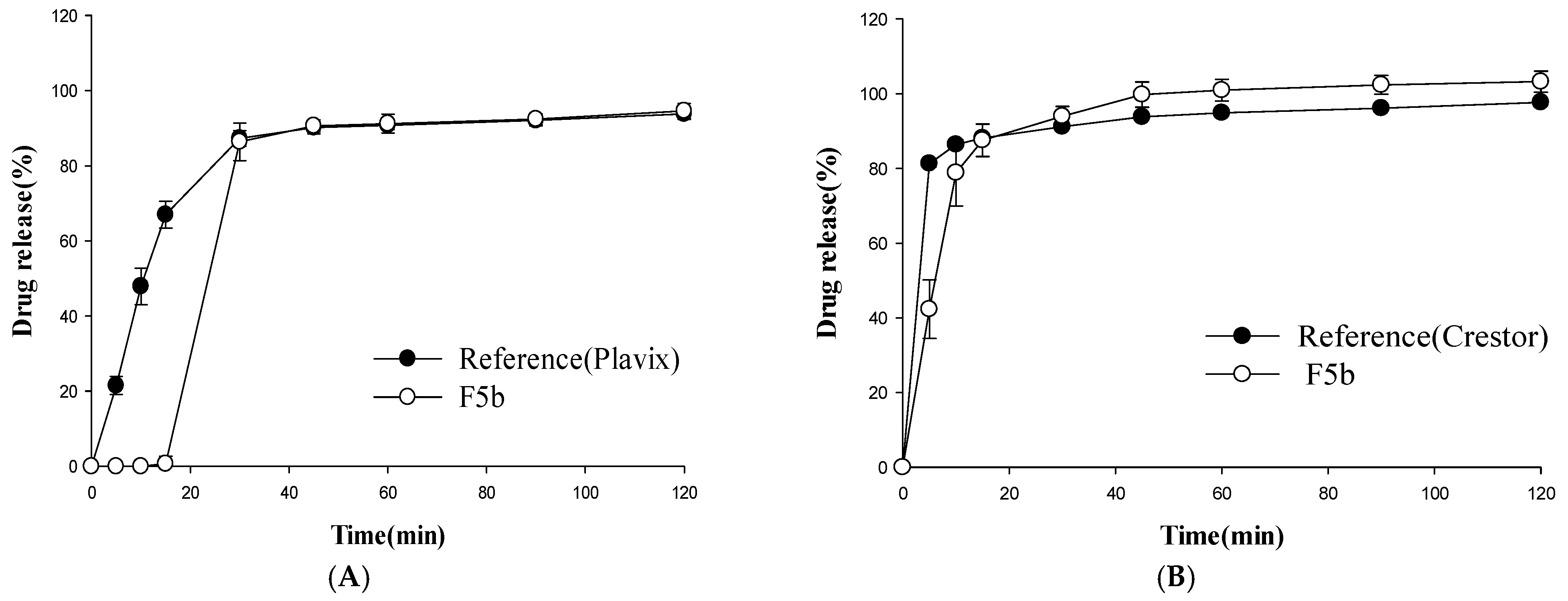
3.2. Dissolution Studies
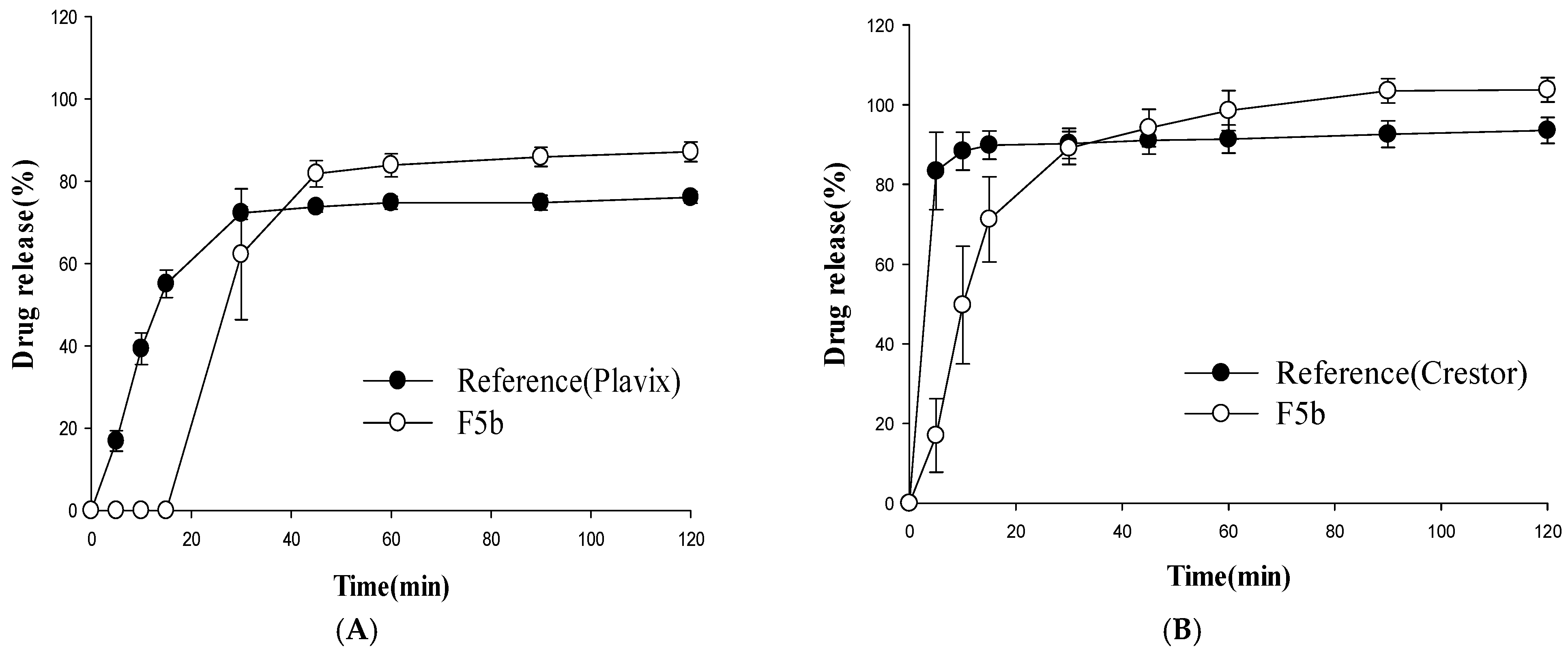
3.3. In Vitro Stability Study
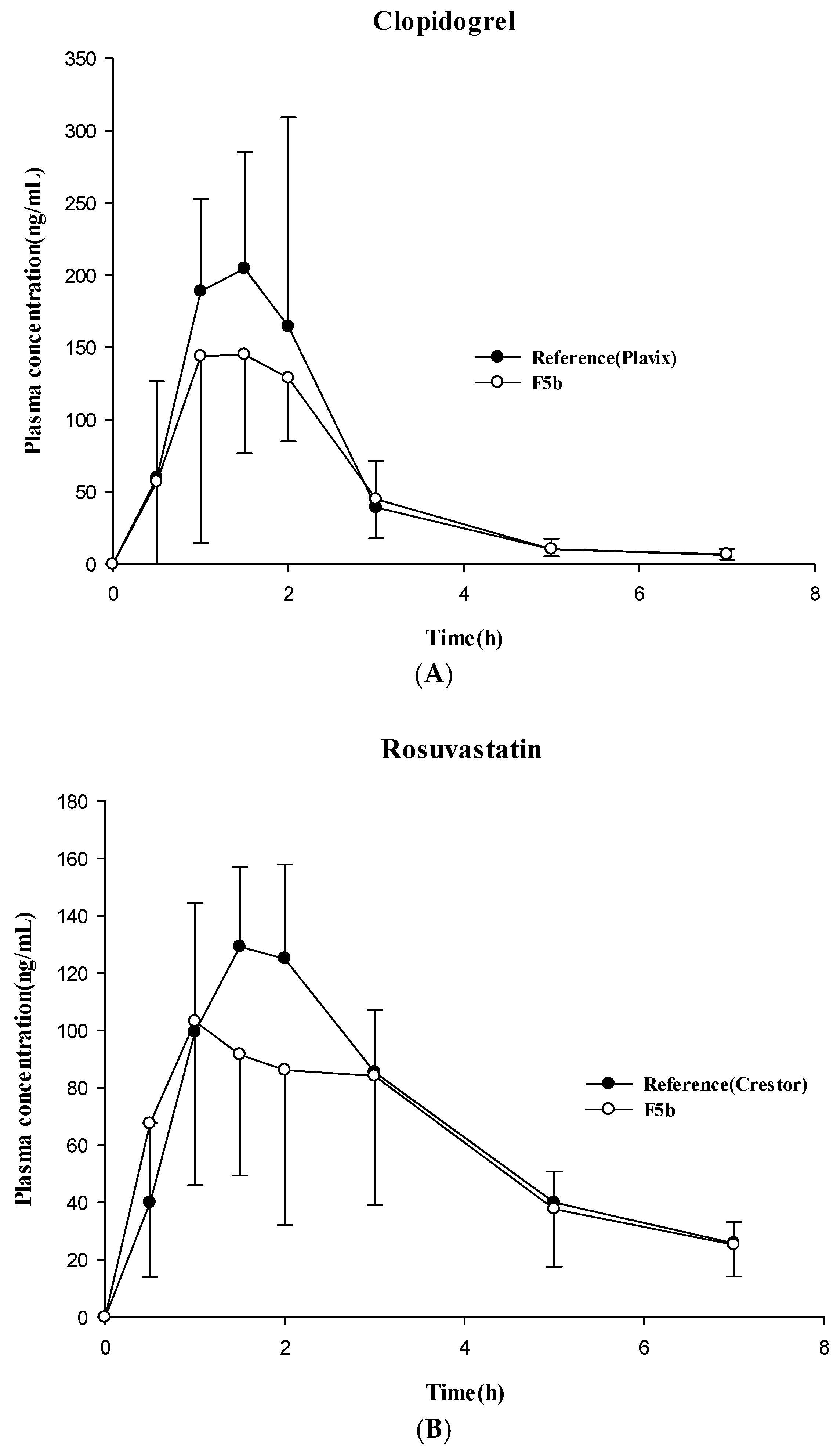
3.4. Pharmacokinetic Studies in Dogs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Penzak, S.R.; Chuck, S.K.; Stajich, G.V. Safety and efficacy of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors for treatment of hyperlipidemia in patients with HIV. Pharmacotherapy 2000, 20, 1066–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Moon, Y.A. Current drugs, targets, and drug delivery systems for the treatment of dyslipidemia. J. Pharm. Investig. 2018, 48, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Saxena, R.; Srinivas, G.; Pande, G.; Chattopadhyay, A. Cholesterol Biosynthesis and Homeostasis in Regulation of the Cell Cycle. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostner, G.M.; Gavish, D.; Leopold, B.; Bolzano, K.; Weintraub, M.S.; Breslow, J.L. HMG CoA reductase inhibitors lower LDL cholesterol without reducing Lp(a) levels. Circulation 1989, 80, 1313–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenson, R.S. Rosuvastatin: A new inhibitor of HMG-coA reductase for the treatment of dyslipidemia. Expert Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2003, 1, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokharkar, V.; Patil-Gadhe, A.; Kaur, G. Physicochemical and pharmacokinetic evaluation of rosuvastatin loaded nanostructured lipid carriers: Influence of long- and medium-chain fatty acid mixture. J. Pharm. Investig. 2018, 48, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishore, C.R.P.; Mohan, G.V.K. Structural identification and estimation of Rosuvastatin calcium related impurities in Rosuvastatin calcium tablet dosage form. Anal. Chem. Res. 2017, 12, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, G.V.R.; Reddy, B.V.; Haque, S.W.; Gautam, H.D.; Kumar, P.; Kumar, A.P.; Park, J.H. Development and validation of a stability-indicating uplc method for rosuvastatin and its related impurities in pharmaceutical dosage forms. Quim. Nova 2011, 34, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, H.C.; Ringleb, P.A.; Savi, P. Clopidogrel for the secondary prevention of stroke. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2005, 6, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrör, K. Clinical pharmacology of the adenosine diphosphate (ADP) receptor antagonist, clopidogrel. Vasc. Med. 1998, 3, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izar, M.C.; Pinheiro, L.; Franca, C.N.; Barbosa, S.P.; Kasmas, S.H.; Bianco, H.T.; Povoa, R.M.; Fonseca, F. Pharmacokinetic Interactions Between Clopidogrel and Rosuvastatin: Effects on Vascular Protection in Subjects with Coronary Heart Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 59, E1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.J.; Spencer, F.A.; Gore, J.M.; Dabbous, O.H.; Agnelli, G.; Kline-Rogers, E.M.; DiBenedetto, D.; Eagle, K.A.; Mehta, R.H. Impact of combined pharmacologic treatment with clopidogrel and a statin on outcomes of patients with non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndromes: Perspectives from a large multinational registry. Eur. Heart J. 2005, 26, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riondino, S.; Petrini, N.; Donato, L.; Torromeo, C.; Tanzilli, G.; Pulcinelli, F.M.; Barillà, F. Effects of rosuvastatin on platelet inhibition by clopidogrel in cardiovascular patients. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2009, 28, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, Y.; Adams, E.; Hoogmartens, J. Analysis of purity in 19 drug product tablets containing clopidogrel: 18 copies versus the original brand. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2004, 34, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ki, M.H.; Choi, M.H.; Ahn, K.B.; Kim, B.S.; Im, D.S.; Ahn, S.K.; Shin, H.J. The efficacy and safety of clopidogrel resinate as a novel polymeric salt form of clopidogrel. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2008, 31, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, H.P.; Prajapati, S.T. Quality by design based development and optimization of novel gastroretentive floating osmotic capsules of clopidogrel bisulfate. J. Pharm. Investig. 2019, 49, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metil, D.S.; Sampath, A.; Reddy, C.V.R.; Bandichhor, R. Synthesis and characterization of potential related substances of the antiplatelet agent clopidogrel bisulfate. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthelemy, P.; Lafore, J.P.; Farah, N.; Joachim, J. Compritol 888 ATO: An innovative hot-melt coating agent for prolonged-release drug formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 1999, 47, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, K.H.; Woo, H.S.; Kim, C.J.; Lee, K.H.; Jeon, J.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Kang, J.H.; Lee, S.; Choi, Y.W. Formulation of a modified-release pregabalin tablet using hot-melt coating with glyceryl behenate. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 495, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, I.; Kang, C.Y.; Park, J.B. Advances in hot-melt extrusion technology toward pharmaceutical objectives. J. Pharm. Investig. 2017, 47, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaidat, A.A.; Obaidat, R.M. Controlled release of tramadol hydrochloride from matrices prepared using glyceryl behenate. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2001, 52, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, P.M.; Liew, C.V.; Heng, P.W.S. Review of Disintegrants and the Disintegration Phenomena. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2545–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, T.; Suzuki, H.; Hironaka, K.; Ito, K. Studies of Rapidly Disintegrating Tablets in the Oral Cavity Using Co-ground Mixtures of Mannitol with Crospovidone. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 2002, 50, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellanos Gil, E.; Iraizoz Colarte, A.; Lara Sampedro, J.L.; Bataille, B. Subcoating with Kollidon VA 64 as water barrier in a new combined native dextran/HPMC-cetyl alcohol controlled release tablet. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 69, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, L.; Müller, R.; Römer, M.; Gordon, K.C.; Heinämäki, J.; Kleinebudde, P.; Pepper, M.; Rades, T.; Shen, Y.C.; Strachan, C.J.; et al. Analysis of sustained-release tablet film coats using terahertz pulsed imaging. J. Control. Release 2007, 119, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.W.; Lee, B.S.; Park, S.J.; Jeon, H.R.; Moon, K.Y.; Kang, M.H.; Park, S.H.; Choi, S.U.; Song, W.H.; Lee, J.; et al. Solid dispersion formulations of megestrol acetate with copovidone for enhanced dissolution and oral bioavailability. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2011, 34, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maniruzzaman, M.; Rana, M.M.; Boateng, J.S.; Mitchell, J.C.; Douroumis, D. Dissolution enhancement of poorly water-soluble APIs processed by hot-melt extrusion using hydrophilic polymers. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2013, 39, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Materials (mg) | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium starch glycolate | 5.0 | ||||
| Croscarmellose sodium | 5.0 | ||||
| Crospovidone | 5.0 | 12 | |||
| Clopidogrel bisulfate | 97.9 | 97.9 | 97.9 | 97.9 | 97.9 |
| L-HPC | 25.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 |
| Lactose | 110.1 | 105.1 | 105.1 | 105.1 | 105.1 |
| Copovidone | 12.0 | 12.0 | 12.0 | 12.0 | 12.0 |
| Colloidal silicon dioxide | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| Talc | 4.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 |
| Magnesium stearate | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 |
| Total weight | 255.0 | 255.0 | 255.0 | 255.0 | 262.0 |
| Coating Layer | Materials (mg) | F5a | F5b |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrophobic separation coating layer | Glyceryl behenate | 15 | 15 |
| Copovidone | 10 | 10 | |
| Titanium dioxide | 0.5 | 0.5 | |
| Talc | 0.5 | 0.5 | |
| Water | 75 | 75 | |
| Ethanol | 300 | 300 | |
| Rosuvastatin coating layer | Rosuvastatin calcium | 10.4 | 10.4 |
| Copovidone | 39.6 | 59.6 | |
| Talc | 2.0 | 2.0 | |
| Water | 70.0 | 70.0 | |
| Ethanol | 200.0 | 200.0 |
| Disintegrants | Disintegration Time (min) |
|---|---|
| Sodium starch glycolate | 9.1 |
| Croscarmellose sodium | 8.48 |
| Crospovidone | 7.93 |
| Crospovidone (12 mg/tablet) | 3.38 |
| Impurity | Formulation | Rosuvastatin Impurity Amount (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40 °C /RH 75% | 25 °C/RH 60% | |||
| 0 Month | 3 Months | 3 Months | ||
| Lactone | Crestor® | 0.11±0.07 | 0.76±0.14 * | 0.14±0.02 |
| F5b | 0.15±0.01 | 0.28±0.03 * | 0.19±0.01 | |
| Total impurity | Crestor® | 0.43±0.06 | 1.21±0.14 * | 0.66±0.04 * |
| F5b | 0.73±0.02 | 0.78±0.04 | 0.72±0.01 | |
| Drug | Parameters | Formulations | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reference | Test (F5b) | ||
| Clopidogrel | Cmax (ng/mL) | 249 ± 90.0 | 224 ± 107 |
| Tmax (h) | 1.38 ± 0.52 | 1.44 ± 0.56 | |
| AUC (ng·h/mL) | 436 ± 197 | 364 ± 138 | |
| Rosuvastatin | Cmax (ng/mL) | 139 ± 24.7 | 122 ± 47.6 |
| Tmax (h) | 1.56 ± 0.32 | 1.38 ± 0.83 | |
| AUC (ng·h/mL) | 462 ± 107 | 423 ± 214 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seo, K.-S.; Han, H.-K. Multilayer-Coated Tablet of Clopidogrel and Rosuvastatin: Preparation and In Vitro/In vivo Characterization. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11070313
Seo K-S, Han H-K. Multilayer-Coated Tablet of Clopidogrel and Rosuvastatin: Preparation and In Vitro/In vivo Characterization. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(7):313. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11070313
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeo, Ki-Soo, and Hyo-Kyung Han. 2019. "Multilayer-Coated Tablet of Clopidogrel and Rosuvastatin: Preparation and In Vitro/In vivo Characterization" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 7: 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11070313
APA StyleSeo, K.-S., & Han, H.-K. (2019). Multilayer-Coated Tablet of Clopidogrel and Rosuvastatin: Preparation and In Vitro/In vivo Characterization. Pharmaceutics, 11(7), 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11070313






