Customized Novel Design of 3D Printed Pregabalin Tablets for Intra-Gastric Floating and Controlled Release Using Fused Deposition Modeling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Pregabalin-Loaded Filaments
2.3. Design and Printing of Tablets
2.4. Characterization of Filaments and Tablets
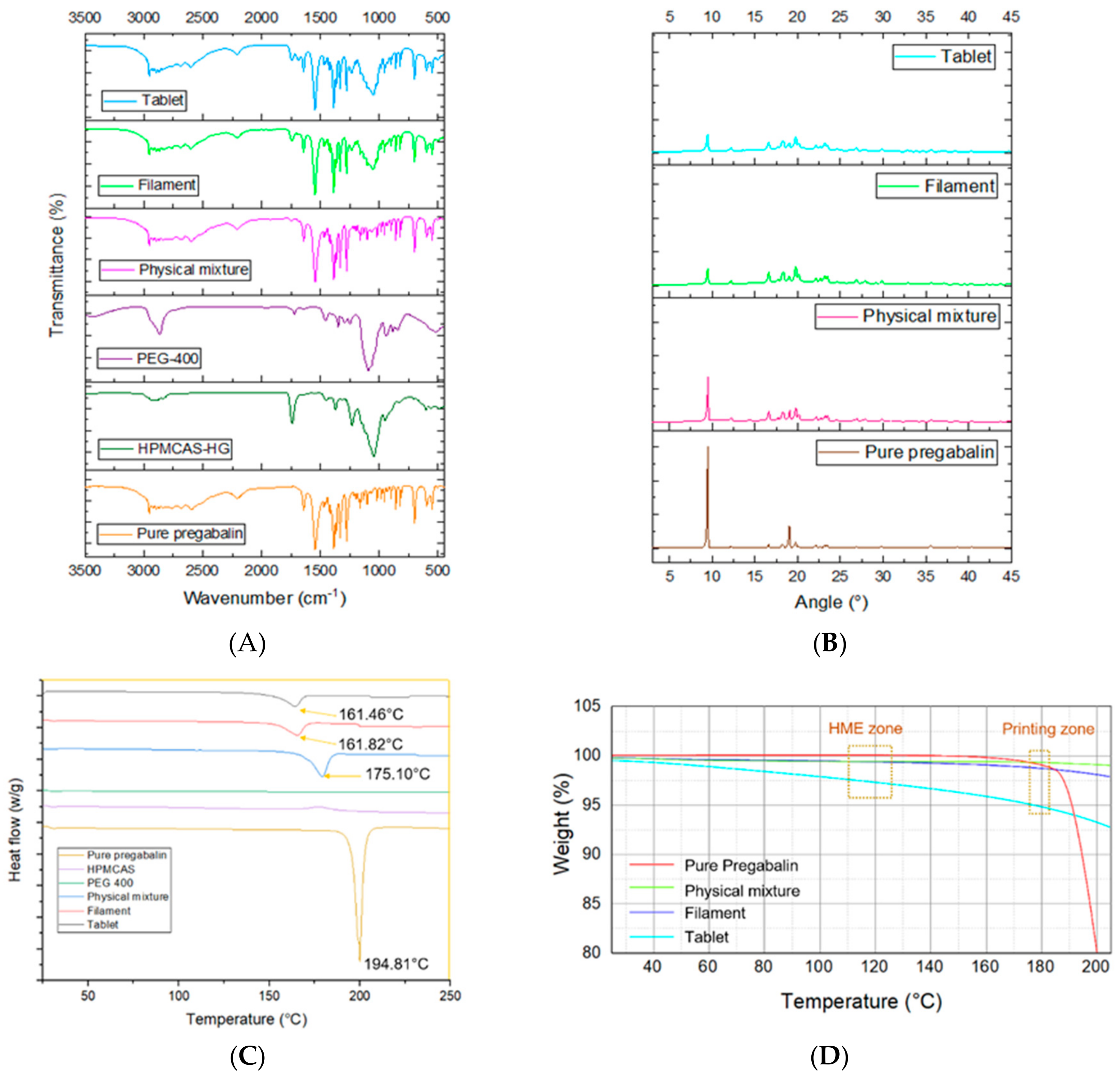
2.4.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.4.2. X-ray Powder Diffractometry (XRPD)
2.4.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.4.4. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
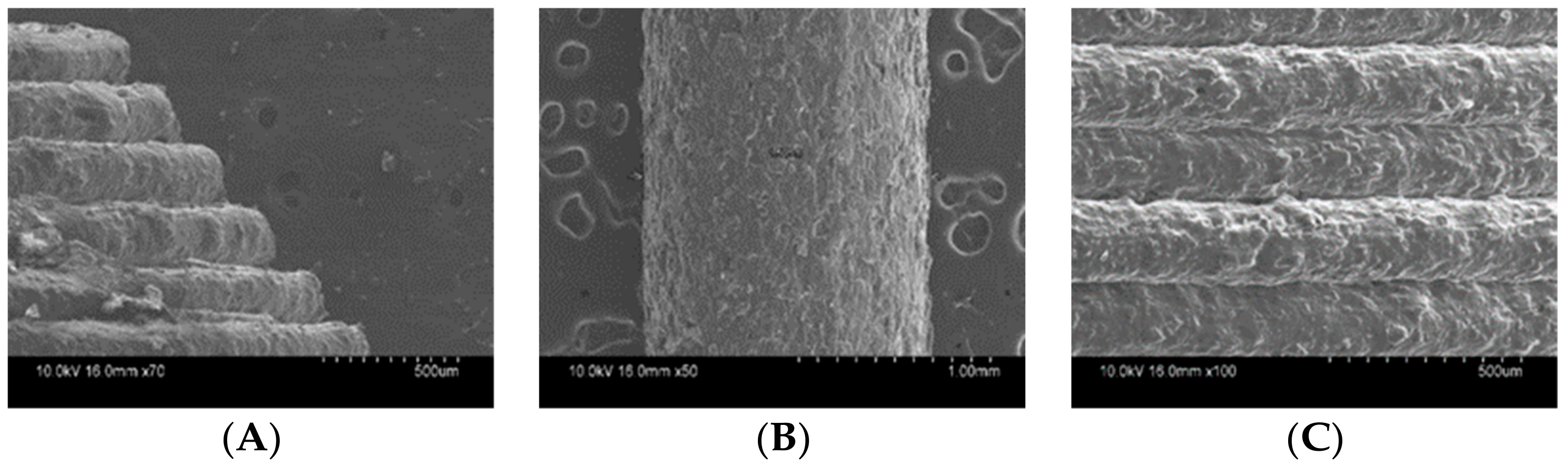
2.4.5. Scanning Electronic Microscopy (SEM)
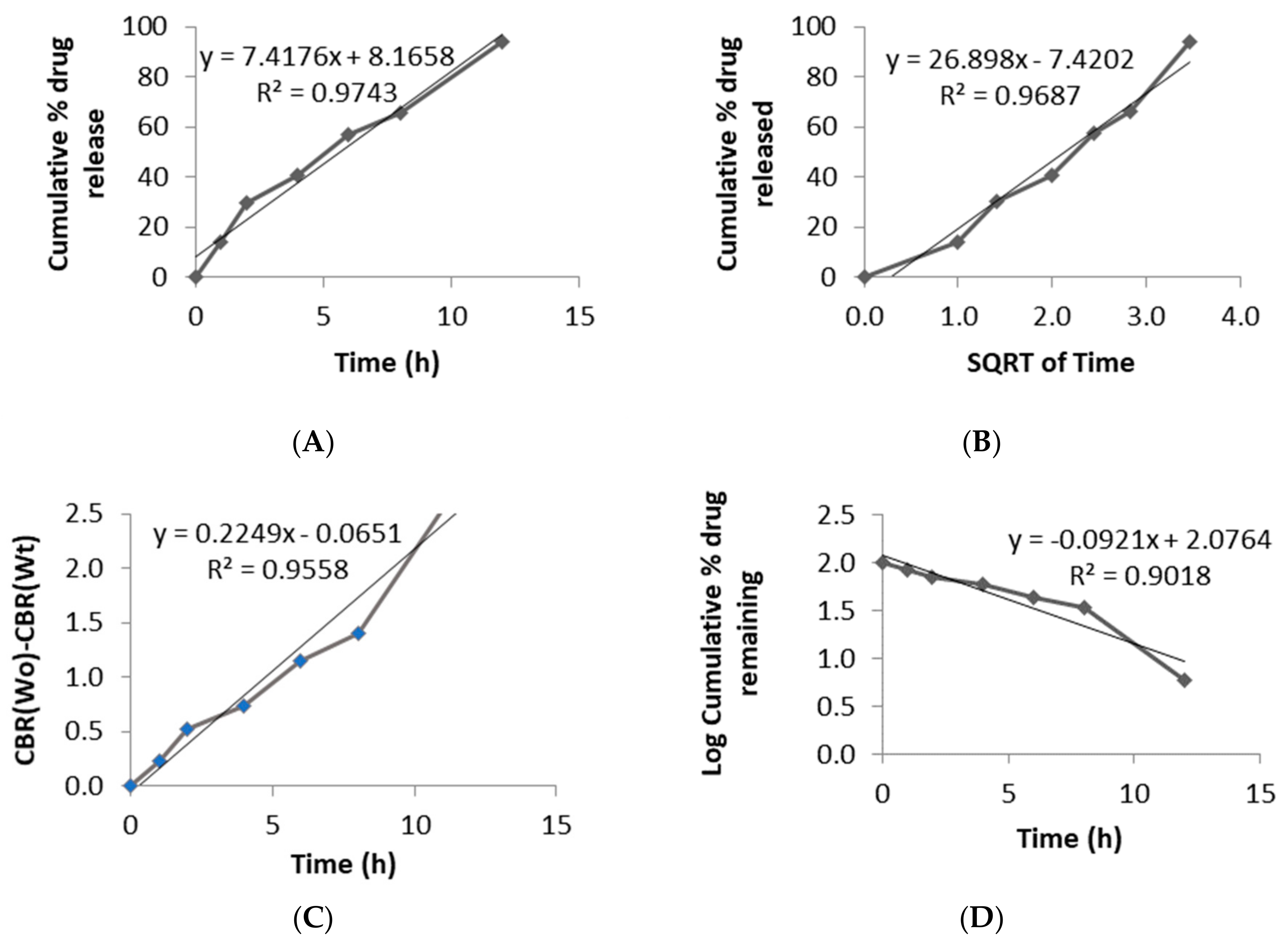
2.4.6. In Vitro Floating and Release Study
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kodama, H. Automatic method for fabricating a three-dimensional plastic model with photo-hardening polymer. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1981, 52, 1770–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.; Laviv, A.; Berman, P.; Nashef, R.; Abu-Tair, J. Mandibular reconstruction using stereolithographic 3-dimensional printing modeling technology. Oral. Surg. Oral. Med. Oral. Pathol. Oral. Radiol. Endodontology 2009, 108, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trenfield, S.J.; Awad, A.; Goyanes, A.; Gaisford, S.; Basit, A.W. 3D Printing Pharmaceuticals: Drug Development to Frontline Care. Trends Pharm. Sci. 2018, 39, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamichhane, S.; Bashyal, S.; Keum, T.; Noh, G.; Seo, J.E.; Bastola, R.; Choi, J.; Sohn, D.H.; Lee, S. Complex formulations, simple techniques: Can 3D printing technology be the Midas touch in pharmaceutical industry? Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 14, 465–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attaran, M. The rise of 3-D printing: The advantages of additive manufacturing over traditional manufacturing. Bus. Horiz. 2017, 60, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.J.; Choi, H.J.; Moon, S.J.; Kim, S.J.; Bajracharya, R.; Min, J.Y.; Han, H.-K. Pharmaceutical applications of 3D printing technology: current understanding and future perspectives. J. Pharm. Investig. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.; Xu, G.; Mao, S.-S.; Yang, H.-Y.; Sang, X.-T.; Sun, W.; Mao, Y.-L. Three-dimensional printing: review of application in medicine and hepatic surgery. Cancer Biol. Med. 2016, 13, 443. [Google Scholar]
- Fina, F.; Goyanes, A.; Madla, C.M.; Awad, A.; Trenfield, S.J.; Kuek, J.M.; Patel, P.; Gaisford, S.; Basit, A.W. 3D printing of drug-loaded gyroid lattices using selective laser sintering. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 547, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fina, F.; Goyanes, A.; Gaisford, S.; Basit, A.W. Selective laser sintering (SLS) 3D printing of medicines. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 529, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fina, F.; Madla, C.M.; Goyanes, A.; Zhang, J.; Gaisford, S.; Basit, A.W. Fabricating 3D printed orally disintegrating printlets using selective laser sintering. Int. Pharm. 2018, 541, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakh Ali, S.F.; Mohamed, E.M.; Ozkan, T.; Kuttolamadom, M.A.; Khan, M.A.; Asadi, A.; Rahman, Z. Understanding the effects of formulation and process variables on the printlets quality manufactured by selective laser sintering 3D printing. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 570, 118651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.M.; Borland, S.W.; Giordano, R.A.; Cima, L.G.; Sachs, E.M.; Cima, M.J. Solid free-form fabrication of drug delivery devices. J. Control. Release 1996, 40, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, Y.; Shin, I.; Ham, G.; Abuzar, S.M.; Hyun, S.-M.; Hwang, S.-J. The advent of a novel manufacturing technology in pharmaceutics: Superiority of fused deposition modeling 3D printer. J. Pharm. Investig 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, J.; Madurawe, R.D.; Moore, C.M.; Khan, M.A.; Khairuzzaman, A. A new chapter in pharmaceutical manufacturing: 3D-printed drug products. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 108, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyanes, A.; Det-Amornrat, U.; Wang, J.; Basit, A.W.; Gaisford, S. 3D scanning and 3D printing as innovative technologies for fabricating personalized topical drug delivery systems. J. Control. Release 2016, 234, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrzak, K.; Isreb, A.; Alhnan, M.A. A flexible-dose dispenser for immediate and extended release 3D printed tablets. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 96, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melocchi, A.; Parietti, F.; Maroni, A.; Foppoli, A.; Gazzaniga, A.; Zema, L. Hot-melt extruded filaments based on pharmaceutical grade polymers for 3D printing by fused deposition modeling. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 509, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyanes, A.; Buanz, A.B.M.; Basit, A.W.; Gaisford, S. Fused-filament 3D printing (3DP) for fabrication of tablets. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 476, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyanes, A.; Chang, H.; Sedough, D.; Hatton, G.B.; Wang, J.; Buanz, A.; Gaisford, S.; Basit, A.W. Fabrication of controlled-release budesonide tablets via desktop (FDM) 3D printing. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 496, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skowyra, J.; Pietrzak, K.; Alhnan, M.A. Fabrication of extended-release patient-tailored prednisolone tablets via fused deposition modelling (FDM) 3D printing. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 68, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamróz, W.; Kurek, M.; Łyszczarz, E.; Szafraniec, J.; Knapik-Kowalczuk, J.; Syrek, K.; Paluch, M.; Jachowicz, R. 3D printed orodispersible films with Aripiprazole. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 533, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyanes, A.; Allahham, N.; Trenfield, S.J.; Stoyanov, E.; Gaisford, S.; Basit, A.W. Direct powder extrusion 3D printing: Fabrication of drug products using a novel single-step process. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 567, 118471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlier, E.; Marquette, S.; Peerboom, C.; Denis, L.; Benali, S.; Raquez, J.M.; Amighi, K.; Goole, J. Investigation of the parameters used in fused deposition modeling of poly(lactic acid) to optimize 3D printing sessions. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 565, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nober, C.; Manini, G.; Carlier, E.; Raquez, J.-M.; Benali, S.; Dubois, P.; Amighi, K.; Goole, J. Feasibility study into the potential use of fused-deposition modeling to manufacture 3D-printed enteric capsules in compounding pharmacies. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 569, 118581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenstock, J.; Tuchman, M.; LaMoreaux, L.; Sharma, U. Pregabalin for the treatment of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Pain 2004, 110, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crofford, L.J.; Rowbotham, M.C.; Mease, P.J.; Russell, I.J.; Dworkin, R.H.; Corbin, A.E.; Young Jr, J.P.; LaMoreaux, L.K.; Martin, S.A.; Sharma, U. Pregabalin for the treatment of fibromyalgia syndrome: results of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum 2005, 52, 1264–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Hwang, K.-M.; Park, Y.S.; Nguyen, T.-T.; Park, E.-S. Preparation and evaluation of non-effervescent gastroretentive tablets containing pregabalin for once-daily administration and dose proportional pharmacokinetics. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 550, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bockbrader, H.N.; Radulovic, L.L.; Posvar, E.L.; Strand, J.C.; Alvey, C.W.; Busch, J.A.; Randinitis, E.J.; Corrigan, B.W.; Haig, G.M.; Boyd, R.A. Clinical pharmacokinetics of pregabalin in healthy volunteers. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2010, 50, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, C.L.; Goldenberg, J.N.; Weintraub, J.; Sanin, L.; Driscoll, J.; Yang, R.; Chew, M.L.; Scavone, J.M. Efficacy and Safety of Once-Daily Controlled-Release Pregabalin for the Treatment of Patients With Postherpetic Neuralgia. Clin. J. Pain 2017, 33, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Wu, M.; Xu, S.; Wang, X.; Shi, W.; Dong, Y.; Yang, L.; He, W.; Han, X.; Yin, L. Design and optimization of gastro-floating sustained-release tablet of pregabalin: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 545, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, X.; Chai, H.; Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Cai, W.; Tao, T.; Xiang, X. Fused deposition modeling (FDM) 3D printed tablets for intragastric floating delivery of domperidone. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Peng, H.; Tian, B.; Gou, J.; Yao, Q.; Tao, X.; He, H.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, X.; Cai, C. Preparation and characterization of azithromycin–Aerosil 200 solid dispersions with enhanced physical stability. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 486, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dash, S.; Murthy, P.N.; Nath, L.; Chowdhury, P. Kinetic modeling on drug release from controlled drug delivery systems. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2010, 67, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gibaldi, M.; Feldman, S. Establishment of sink conditions in dissolution rate determinations. Theoretical considerations and application to nondisintegrating dosage forms. J. Pharm. Sci. 1967, 56, 1238–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloomquist, C.J.; Mecham, M.B.; Paradzinsky, M.D.; Janusziewicz, R.; Warner, S.B.; Luft, J.C.; Mecham, S.J.; Wang, A.Z.; DeSimone, J.M. Controlling release from 3D printed medical devices using CLIP and drug-loaded liquid resins. J. Control. Release 2018, 278, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higuchi, T. Mechanism of sustained-action medication. Theoretical analysis of rate of release of solid drugs dispersed in solid matrices. J. Pharm. Sci. 1963, 52, 1145–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hixson, A.; Crowell, J. Dependence of reaction velocity upon surface and agitation. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1931, 23, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, N.; Bauer, M.; Boussac, N.; Khan-Malek, R.; Munden, P.; Sardaro, M. An evaluation of fit factors and dissolution efficiency for the comparison of in vitro dissolution profiles. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1998, 17, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.; Lobo, J.M.S. Modeling and comparison of dissolution profiles. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 13, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repka, M.A.; Battu, S.K.; Upadhye, S.B.; Thumma, S.; Crowley, M.M.; Zhang, F.; Martin, C.; McGinity, J.W. Pharmaceutical applications of hot-melt extrusion: Part II. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2007, 33, 1043–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Feng, X.; Patil, H.; Tiwari, R.V.; Repka, M.A. Coupling 3D printing with hot-melt extrusion to produce controlled-release tablets. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 519, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melocchi, A.; Parietti, F.; Loreti, G.; Maroni, A.; Gazzaniga, A.; Zema, L. 3D printing by fused deposition modeling (FDM) of a swellable/erodible capsular device for oral pulsatile release of drugs. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2015, 30, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaman, C.R.P.; Tesson, N.; Castano, M.T.; Romana, L.C. Crystalline forms of pregabalin and co-formers in the treatment of pain. European Patent EP 2 527 319 A1, 24 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Goyanes, A.; Buanz, A.B.M.; Hatton, G.B.; Gaisford, S.; Basit, A.W. 3D printing of modified-release aminosalicylate (4-ASA and 5-ASA) tablets. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 89, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyanes, A.; Fina, F.; Martorana, A.; Sedough, D.; Gaisford, S.; Basit, A.W. Development of modified release 3D printed tablets (printlets) with pharmaceutical excipients using additive manufacturing. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 527, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moscato, S.; Bahr, R.; Le, T.; Pasian, M.; Bozzi, M.; Perregrini, L.; Tentzeris, M.M. Infill-dependent 3-D-printed material based on NinjaFlex filament for antenna applications. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2016, 15, 1506–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyanes, A.; Martinez, P.R.; Buanz, A.; Basit, A.W.; Gaisford, S. Effect of geometry on drug release from 3D printed tablets. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 494, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, T.D.; Mitchell, S.A.; Balwinski, K.M. Investigation of the effect of tablet surface area/volume on drug release from hydroxypropylmethylcellulose controlled-release matrix tablets. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2002, 28, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
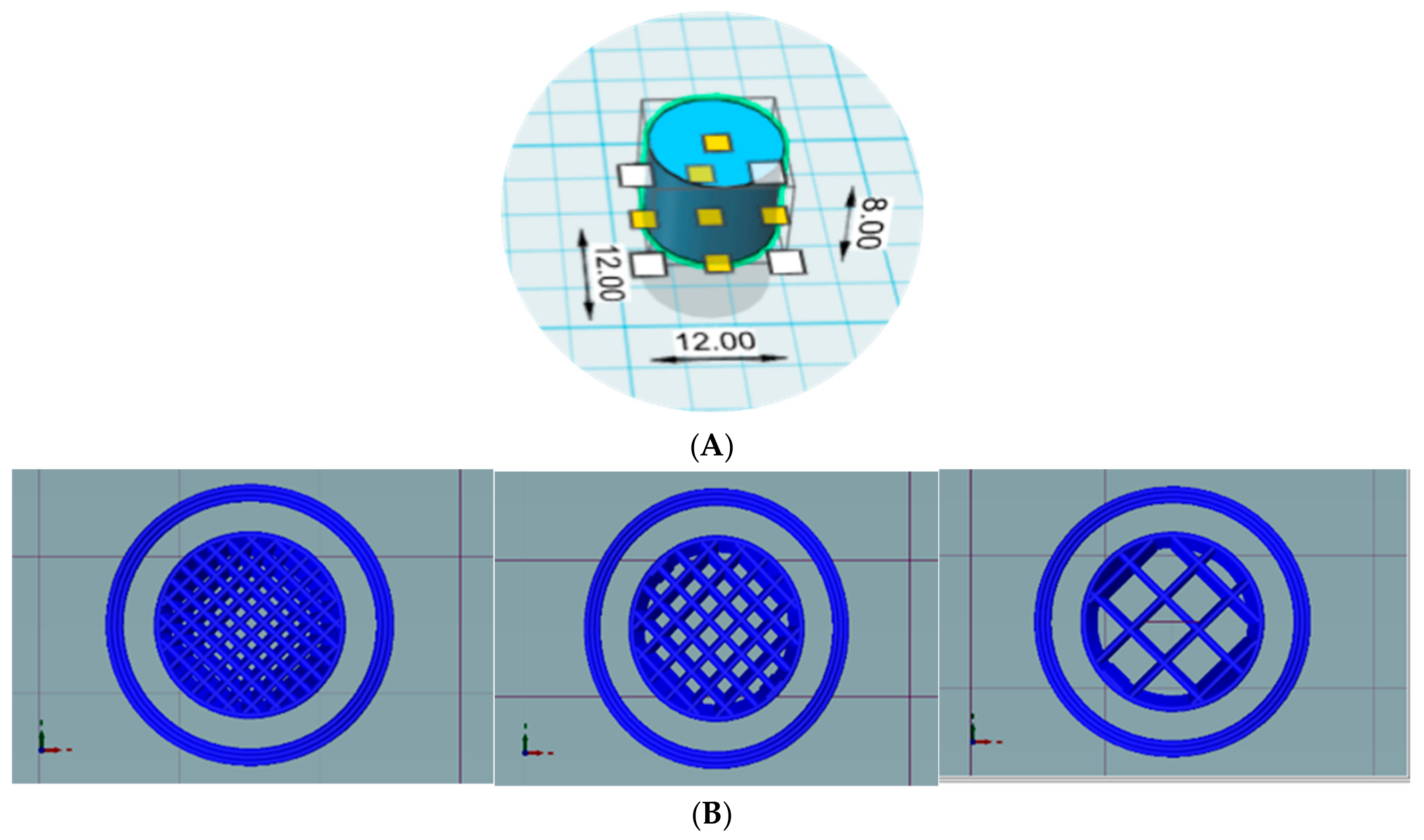
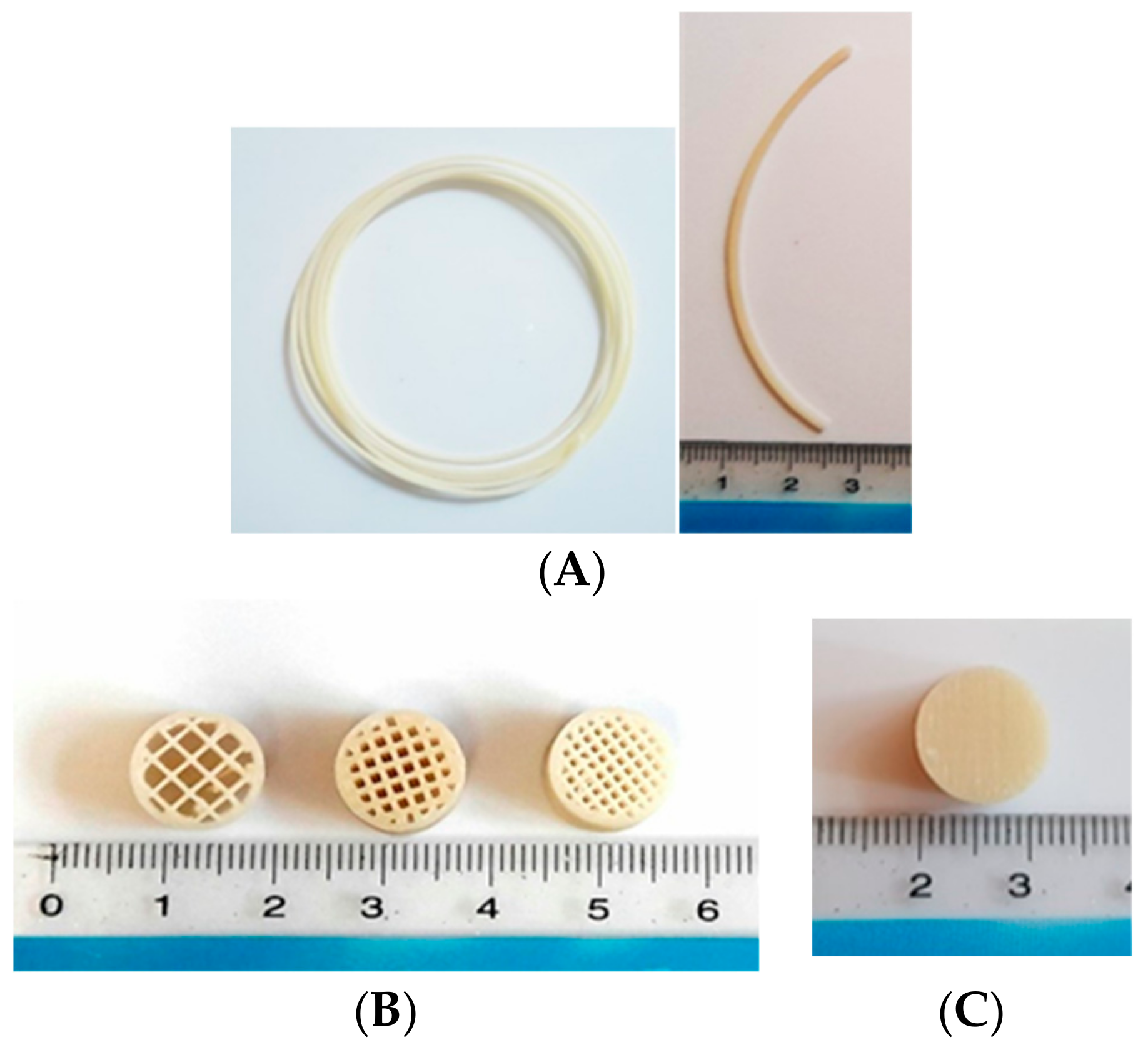
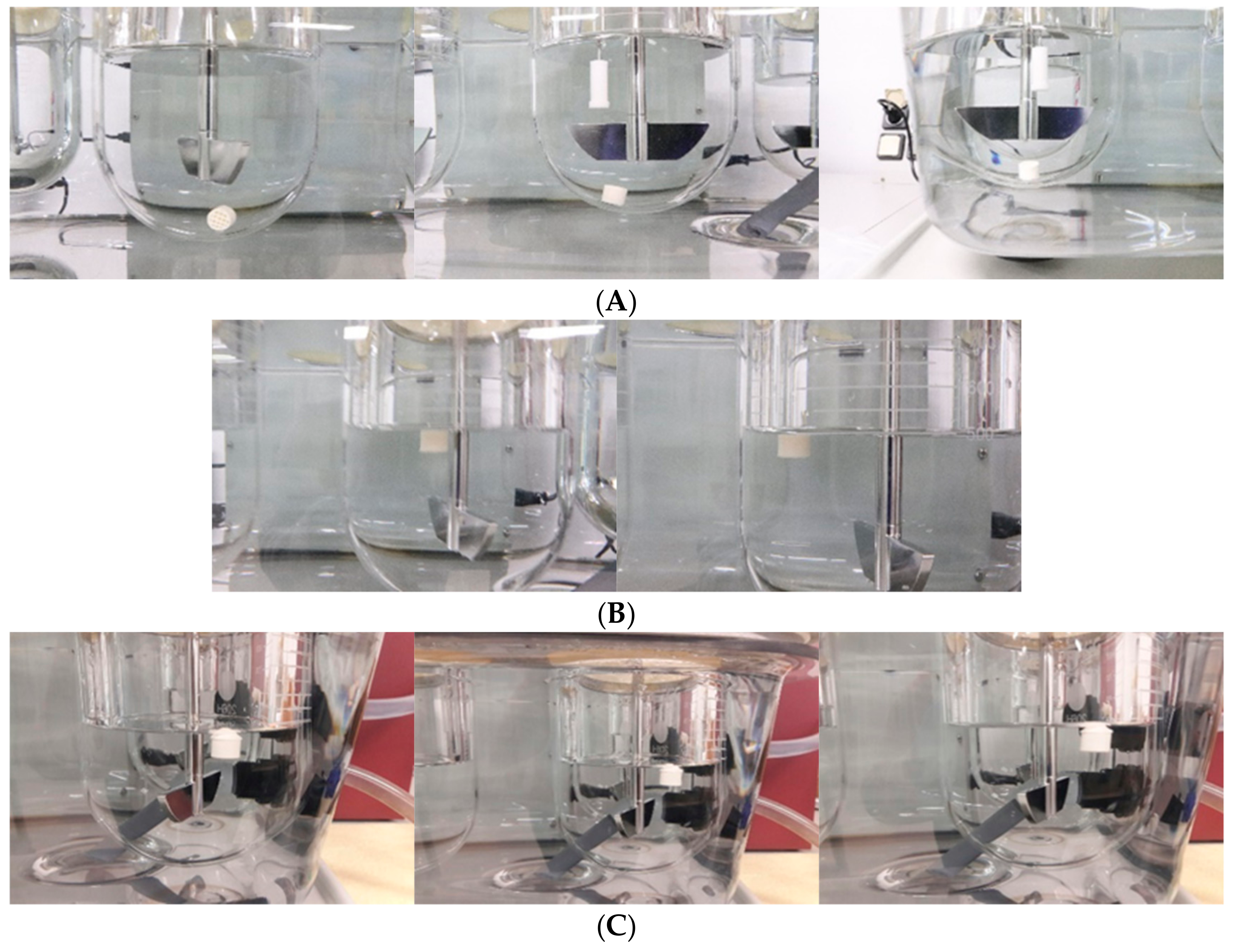
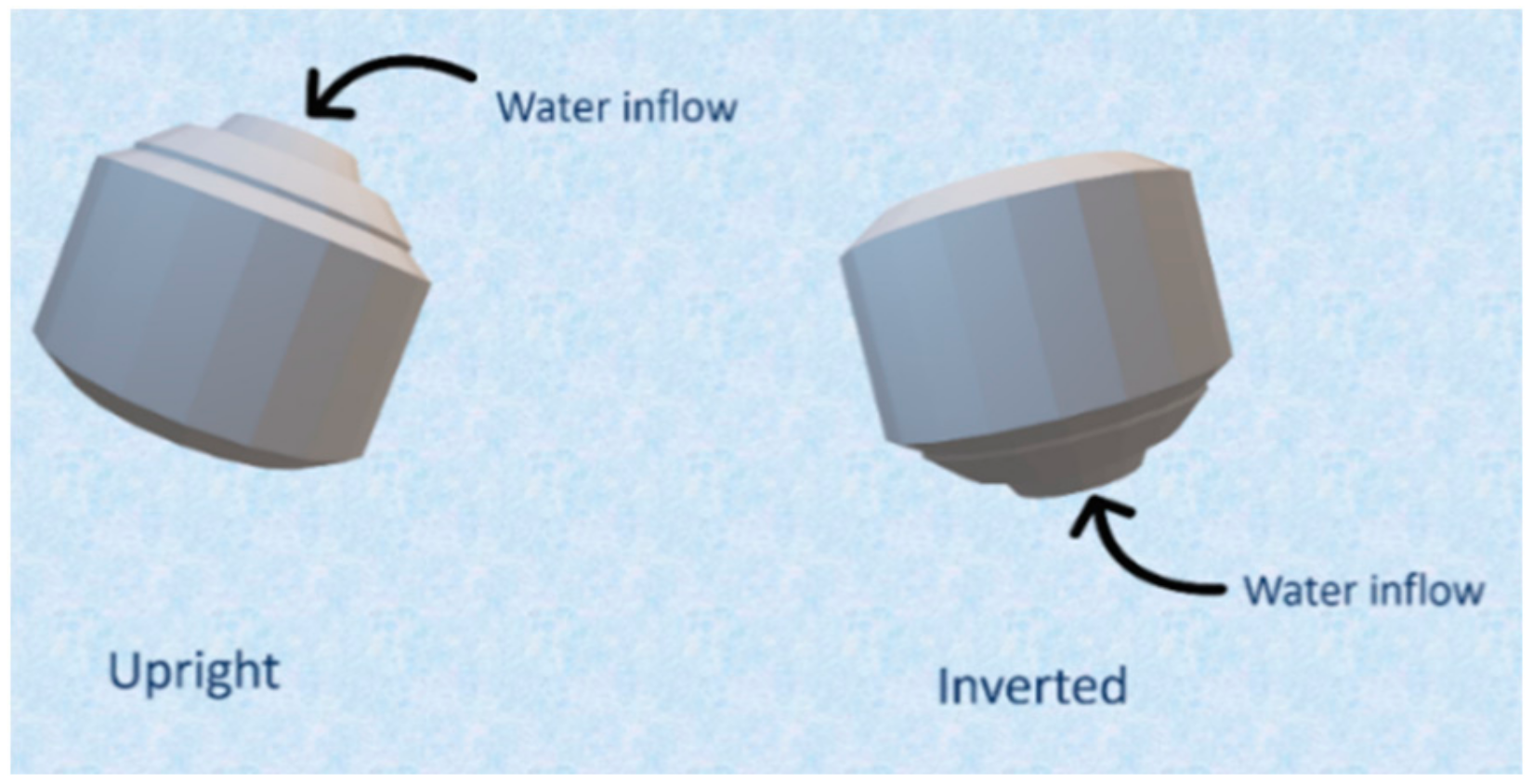
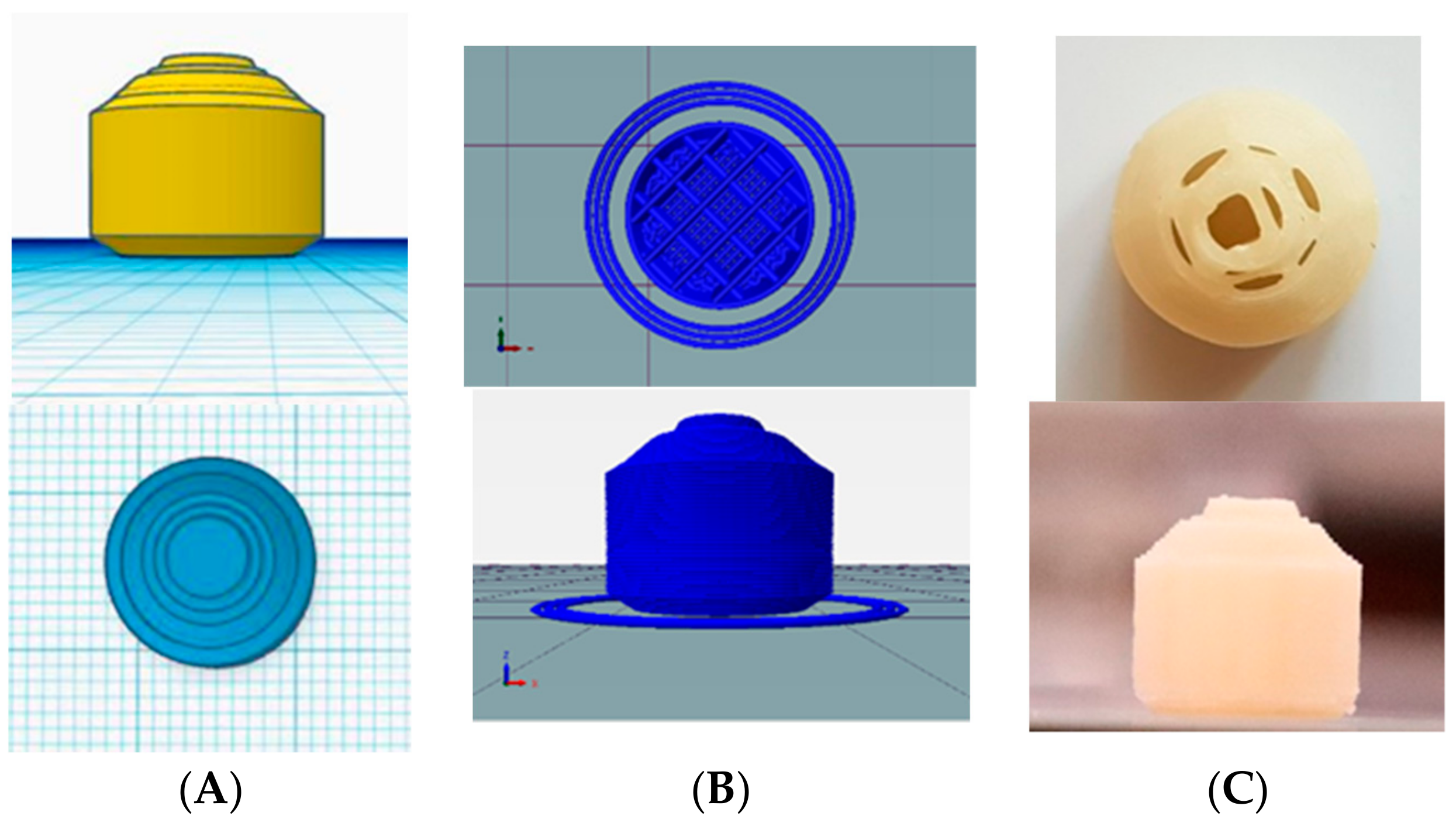
| Filaments | Pregabalin (%) | HPMCAS HG (%) | PEG 400 (%) | PVA (%) | HPMC E4 (%) | HPMC HME 15 LV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FIL-1 | - | - | - | - | 100 | - |
| FIL-2 | - | - | - | 10 | 90 | - |
| FIL-3 | - | - | 10 | - | 90 | - |
| FIL-4 | 25 | - | 10 | - | - | 65 |
| FIL-5 | 25 | 5 | - | - | 70 | |
| FIL-6 | 50 | 20 | 10 | - | - | 20 |
| FIL-7 | 25 | 65 | 10 | - | - | - |
| FIL-8 | 50 | 40 | 10 | - | - | - |
| Filaments | Result | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| FIL-1 | Difficulty in extrusion | High viscosity of polymer clogged extruder nozzle |
| FIL-2 | Difficulty in printing | Filaments clogged print head due to gluey consistency after melting |
| FIL-3 | Difficulty in printing | Filaments hardened with elevated temperature while printing |
| FIL-4 | Difficulty in printing | Very flexible filaments |
| FIL-5 | Difficulty in extrusion | Low concentration of plasticizer |
| FIL-6 | Difficulty in printing | Very flexible filaments |
| FIL-7 | Suitable for extrusion and printing | Filaments of enough strength and flow |
| FIL-8 | Suitable for extrusion and printing | Filaments of enough strength and flow |
| Formulation | Dimension (mm) | Infill (%) | Shell Thickness (mm) | Weight (mg) | Density (g/cm3) | Drug Content (mg) | Drug Loading (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 12 × 8 | 25 | 0.6 | 361.45 ± 0.35 | 0.40 ± 0.0003 | 168.22 ± 3.71 | 93.08 ± 1.54 |
| F2 | 12 × 8 | 50 | 0.6 | 470.50 ± 8.48 | 0.52 ± 0.0091 | 227.75 ± 3.53 | 96.80 ± 1.26 |
| F3 | 12 × 8 | 75 | 0.6 | 668.50 ± 27.57 | 0.74 ± 0.0304 | 322.75 ± 10.25 | 96.54 ± 3.22 |
| F4 | 12 × 8 | 25 | 0.4 | 498.60 ± 4.52 | 0.55 ± 0.0050 | 235.95 ± 7.70 | 94.64 ± 3.03 |
| F5 | 12 × 8 | 50 | 0.4 | 691.00 ± 14.14 | 0.76 ± 0.0156 | 335.47 ± 7.10 | 97.08 ± 2.06 |
| F6 | 12 × 8 | 25 | 0.4 | 475.00 ± 2.57 | - | 234.90 ± 12.97 | 98.52 ± 5.40 |
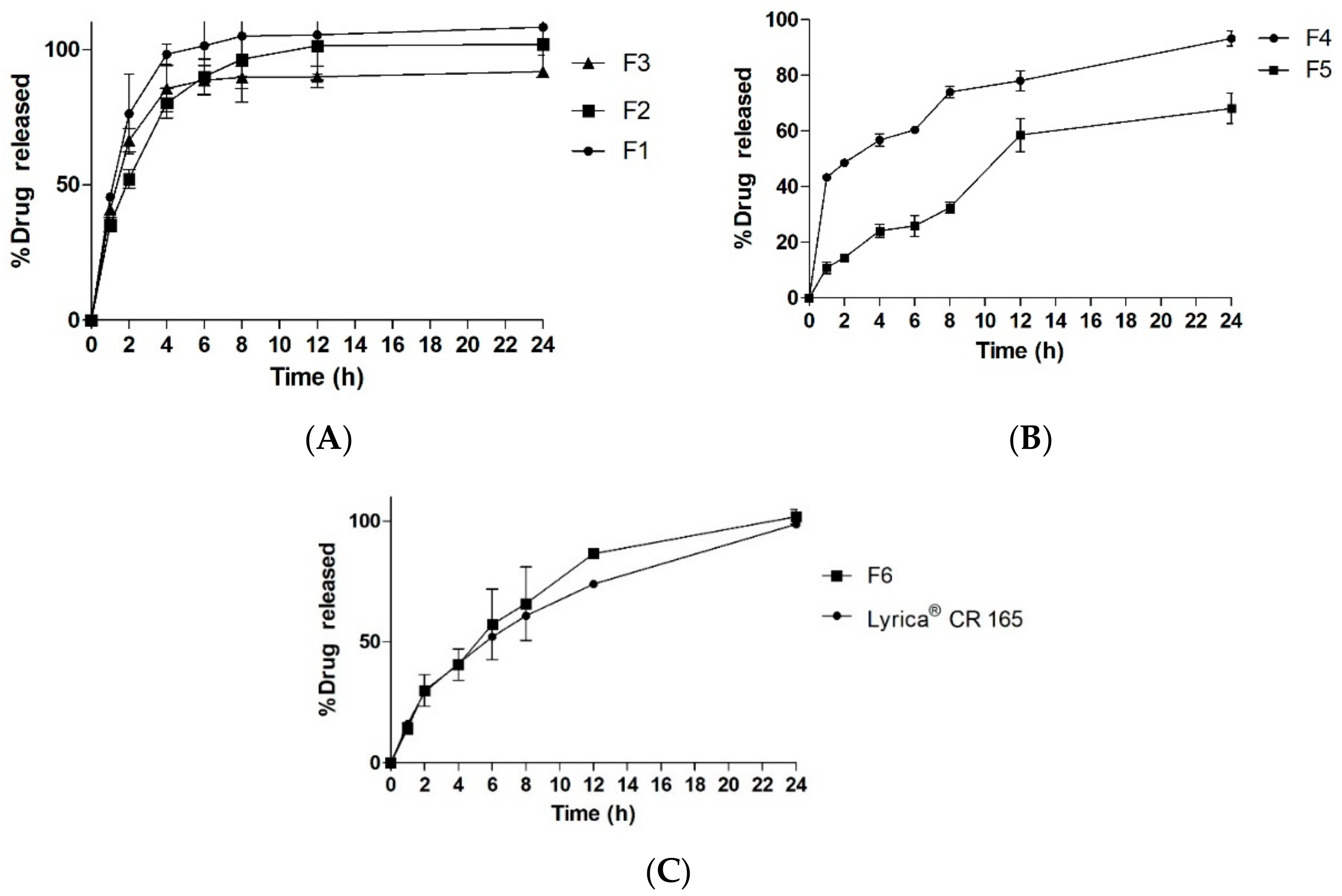
| Formulations | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | F6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lyrica® CR 165 | 19.53 | 26.9 | 25.7 | 40.88 | 37.2 | 65.32 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lamichhane, S.; Park, J.-B.; Sohn, D.H.; Lee, S. Customized Novel Design of 3D Printed Pregabalin Tablets for Intra-Gastric Floating and Controlled Release Using Fused Deposition Modeling. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 564. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11110564
Lamichhane S, Park J-B, Sohn DH, Lee S. Customized Novel Design of 3D Printed Pregabalin Tablets for Intra-Gastric Floating and Controlled Release Using Fused Deposition Modeling. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(11):564. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11110564
Chicago/Turabian StyleLamichhane, Shrawani, Jun-Bom Park, Dong Hwan Sohn, and Sangkil Lee. 2019. "Customized Novel Design of 3D Printed Pregabalin Tablets for Intra-Gastric Floating and Controlled Release Using Fused Deposition Modeling" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 11: 564. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11110564
APA StyleLamichhane, S., Park, J.-B., Sohn, D. H., & Lee, S. (2019). Customized Novel Design of 3D Printed Pregabalin Tablets for Intra-Gastric Floating and Controlled Release Using Fused Deposition Modeling. Pharmaceutics, 11(11), 564. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11110564




