Risperidone Controlled Release Microspheres Based on Poly(Lactic Acid)-Poly(Propylene Adipate) Novel Polymer Blends Appropriate for Long Acting Injectable Formulations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Poly(Propylene Adipate) (PPAd) Aliphatic Polyesters
2.3. Poly(Lactic Acid)-Poly(Propylene Adipate) (PLA/PPAd) Blend Preparation
2.4. Characterization of Synthesized Polymers
2.4.1. Intrinsic Viscosity
2.4.2. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR)
2.4.3. Gel permeation Chromatography
2.4.4. Wide Angle X-ray Scattering
2.4.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.4.6. Enzymatic Hydrolysis
2.4.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.5. Preparation of Risperidone Microspheres
2.6. Characterization Techniques
2.6.1. Fourier-Transformed Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
2.6.2. Drug Loading, Yield, and Entrapment Efficiency (EE)
2.6.3. In-Vitro Drug Release
2.6.4. Statistical Moments
2.6.5. HPLC Method
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Prepared Polyesters
3.1.1. Synthesis and Characterization of PPAd
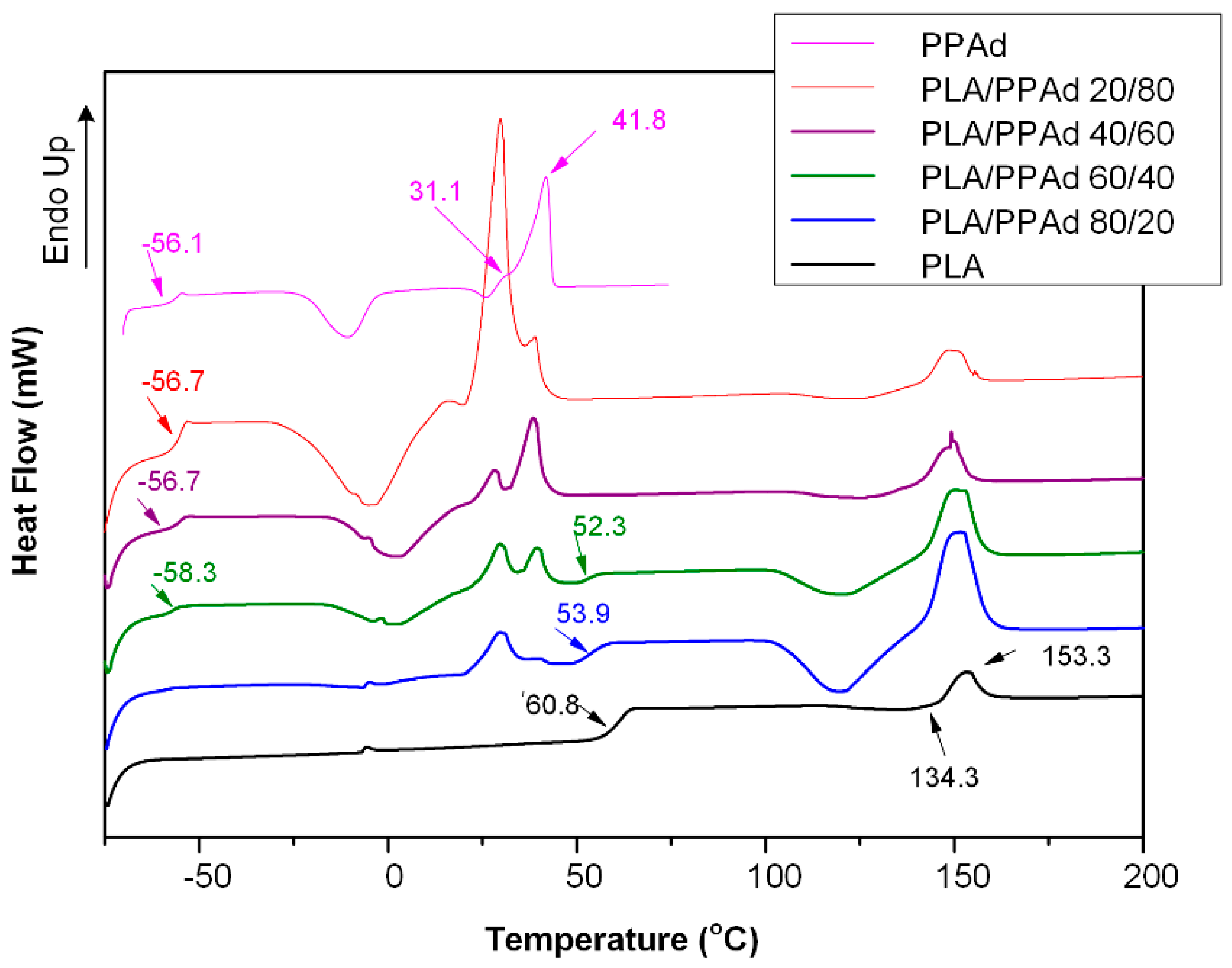
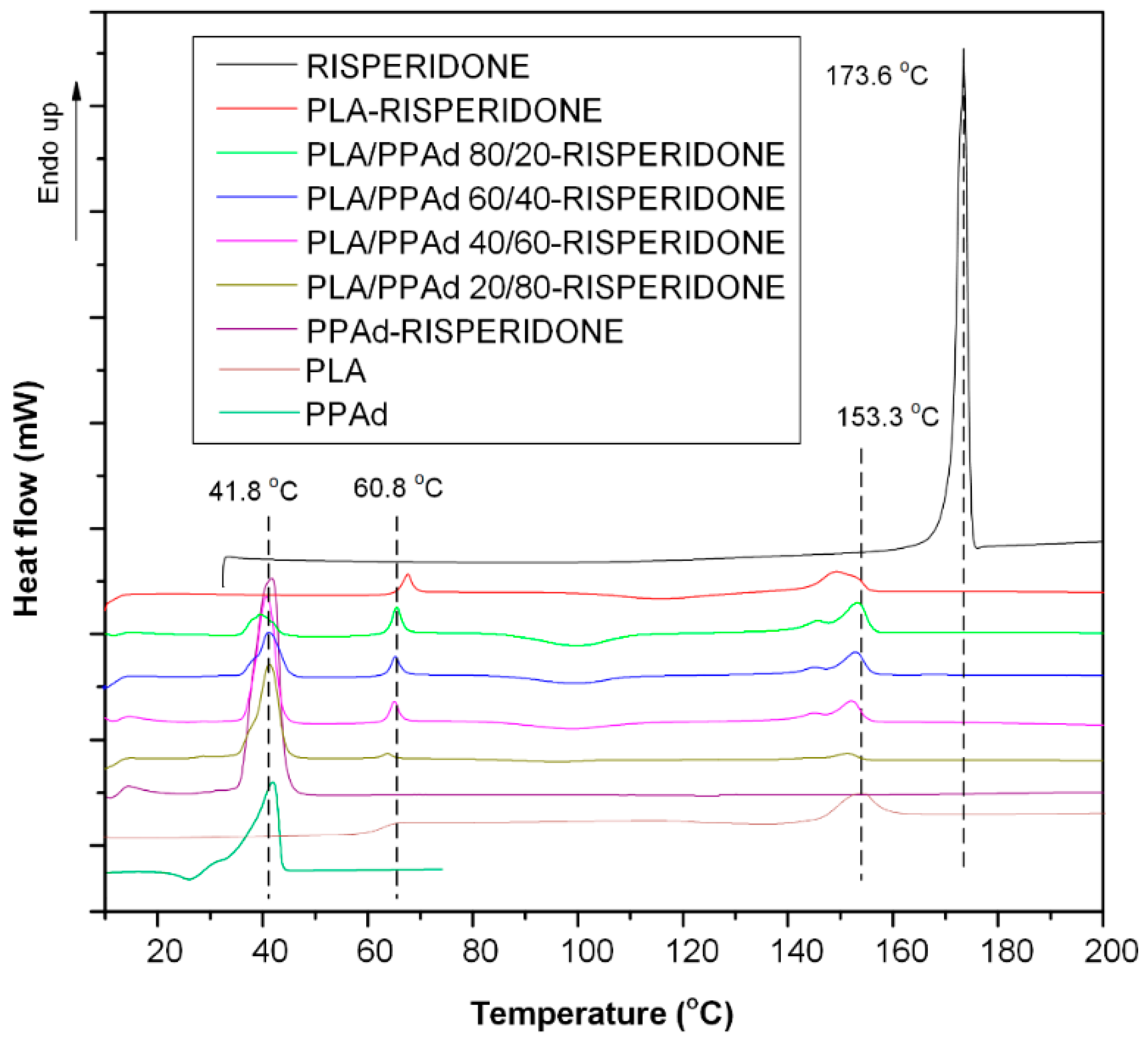
3.1.2. Thermal Analysis
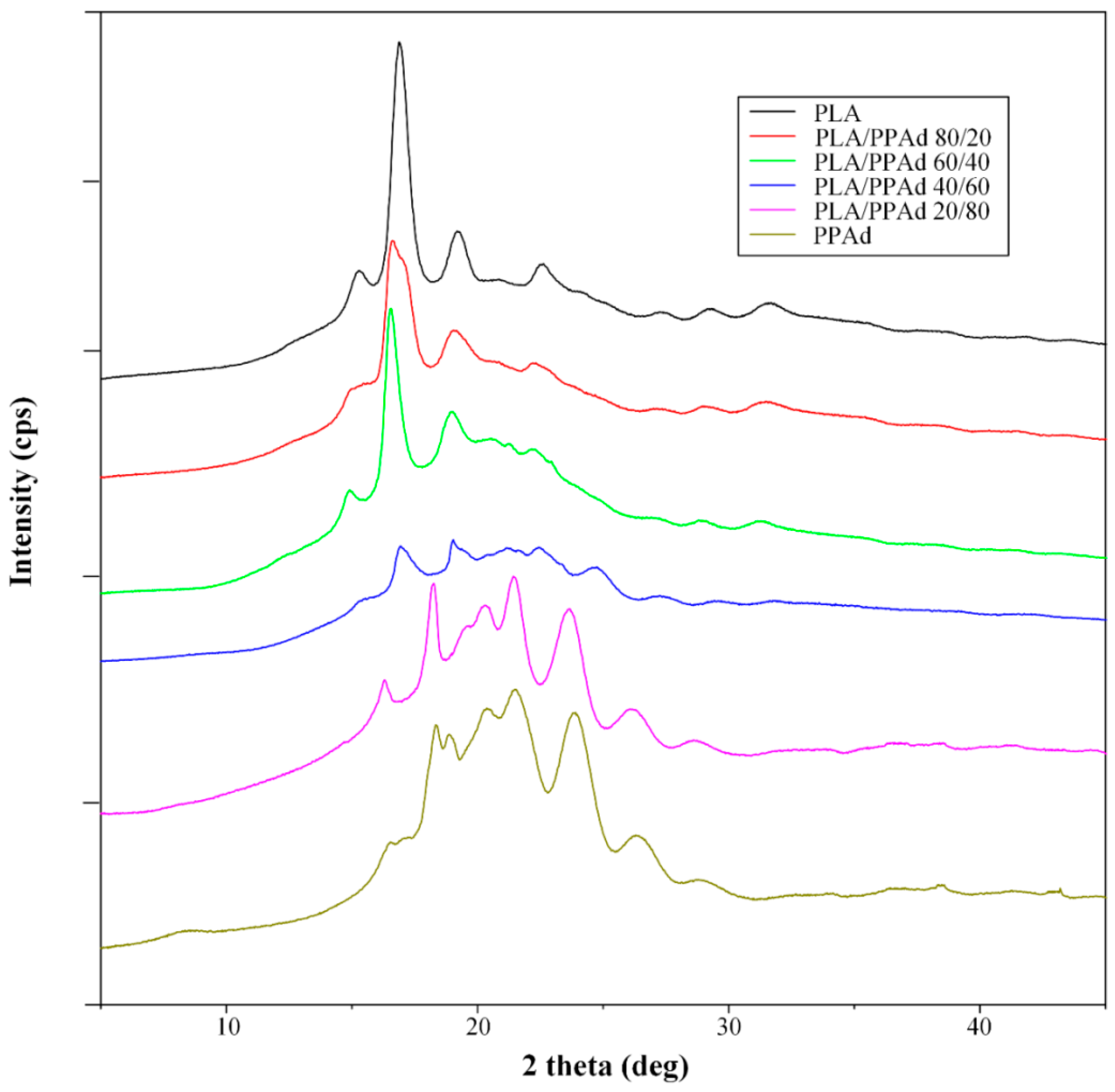
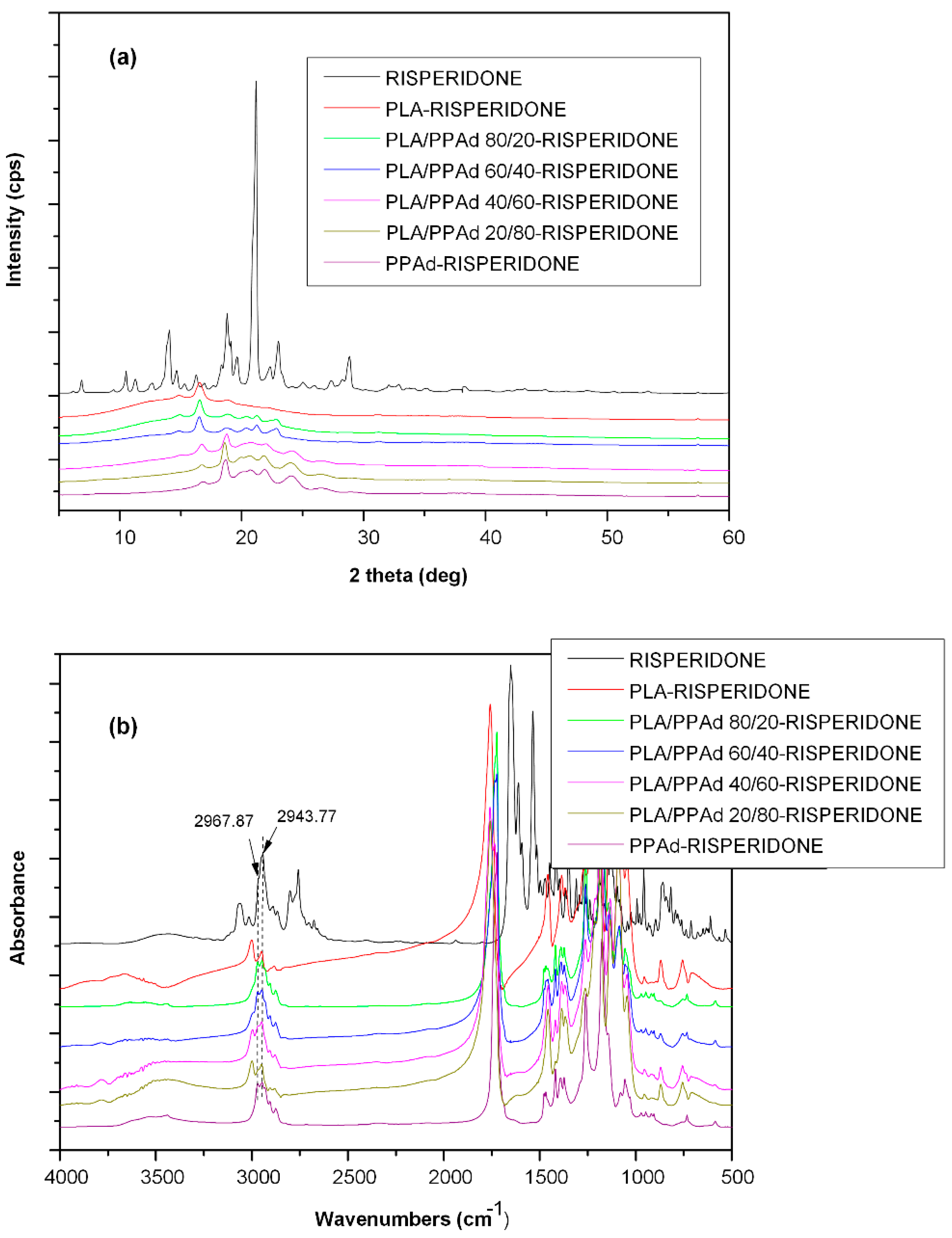
3.1.3. X-ray Diffraction Studies
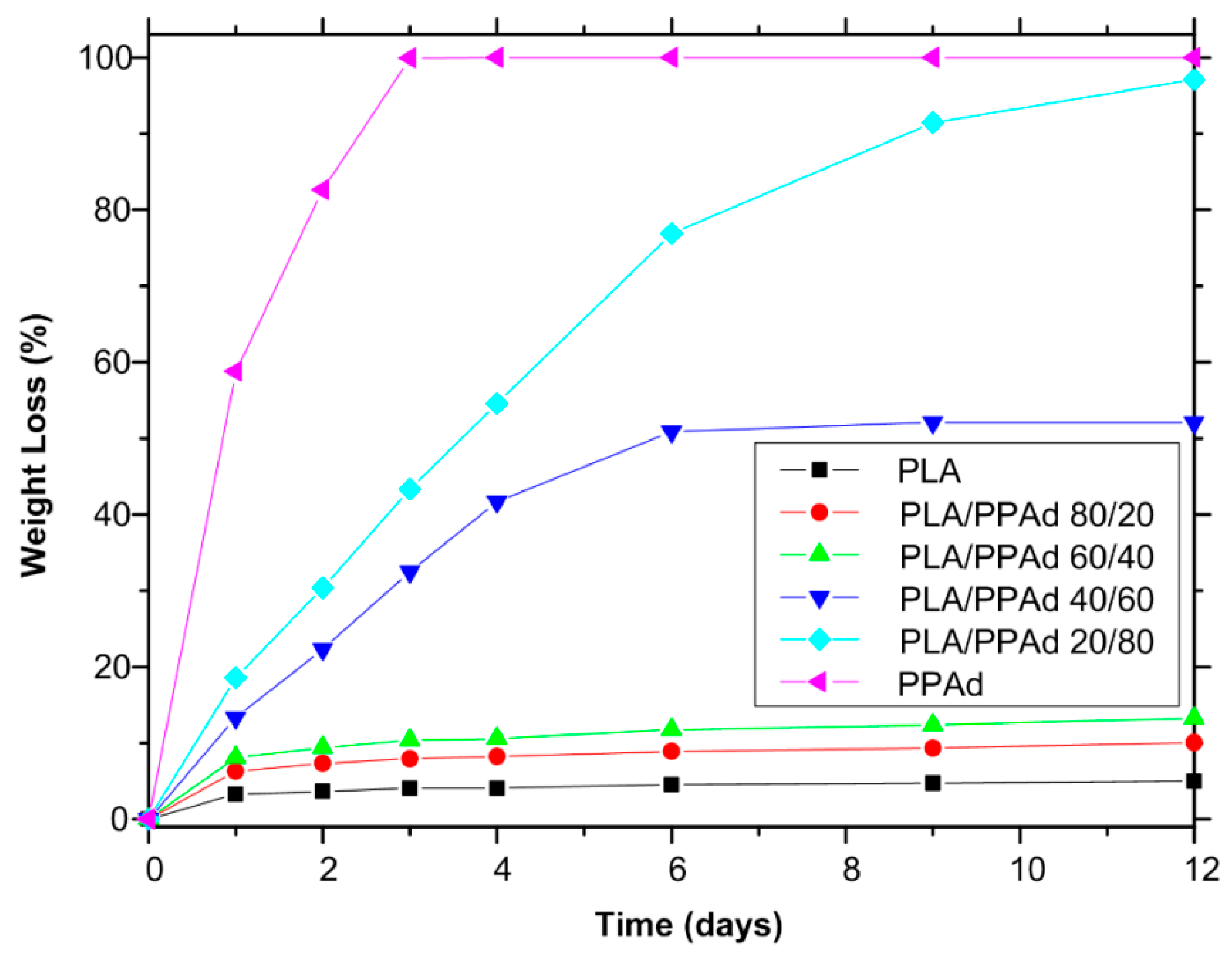
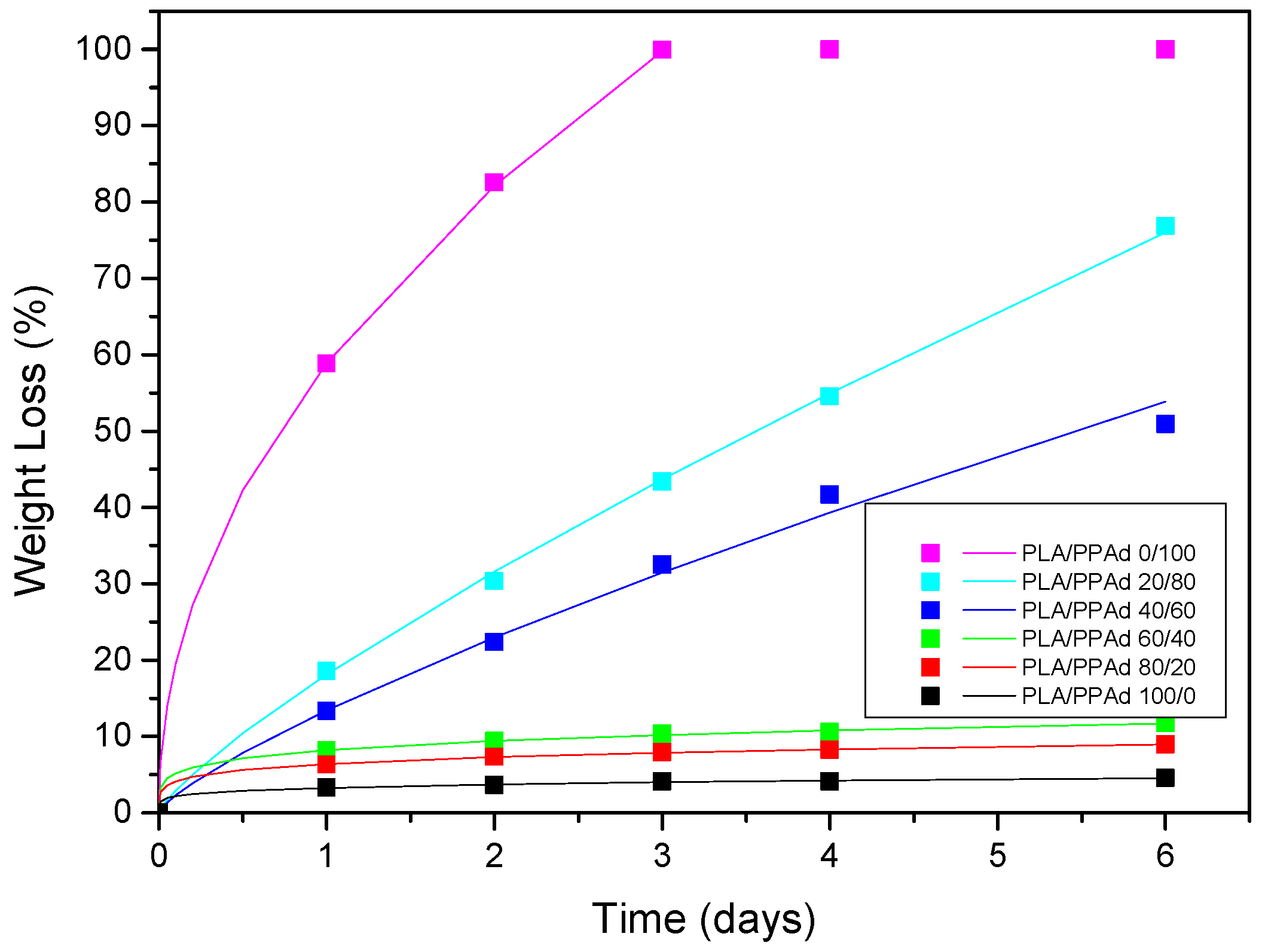
3.1.4. Hydrolysis Rate
3.2. Characterization of Risperidone Drug Formulations
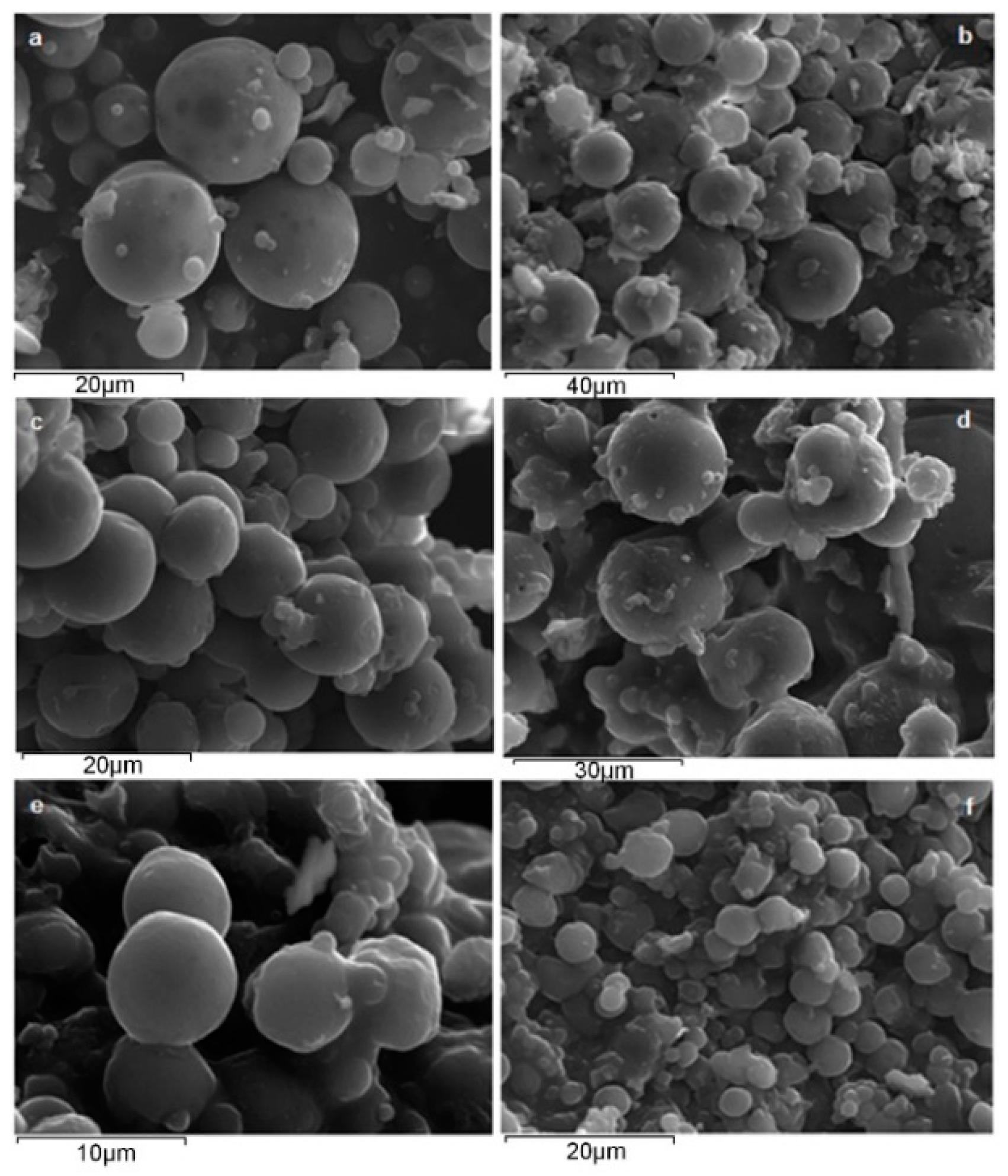
3.2.1. Microsphere Morphology
3.2.2. API Physical State Characterization
3.2.3. Drug Loading, Yield and % EE
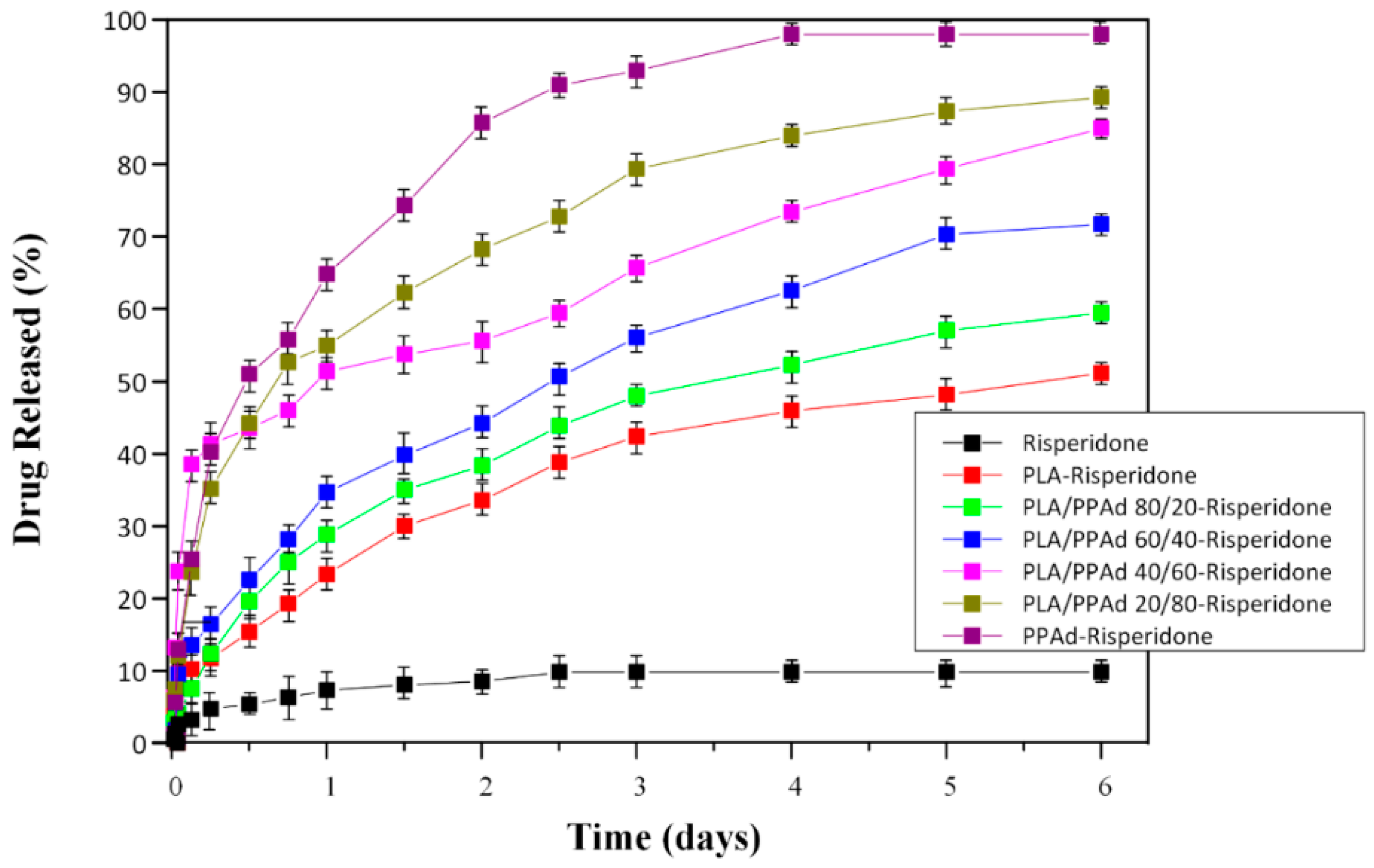
3.2.4. Dissolution Studies Results
3.2.5. Statistical Moment Analysis
3.2.6. Release Data Modeling
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baweja, R.; Sedky, K.; Lippmann, S. Long-acting antipsychotic medications. Curr. Drug Targets 2012, 13, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwendeman, S.P.; Shah, R.B.; Bailey, B.A.; Schwendeman, A.S. Injectable controlled release depots for large molecules. J. Control. Release 2014, 190, 240–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, F.; Yang, M. Design of PLGA-based depot delivery systems for biopharmaceuticals prepared by spray drying. Int. Pharm. 2016, 498, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischhacker, W.W. Second-generation antipsychotic long-acting injections: Systematic review. Br. J. Psychiatry 2009, 52, S29–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chaurasia, S.; Mounika, K.; Bakshi, V.; Prasad, V. 3-month parenteral PLGA microsphere formulations of risperidone: Fabrication, characterization and neuropharmacological assessments. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 75, 1496–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remenar, J.F. Making the Leap from Daily Oral Dosing to Long-Acting Injectables: Lessons from the Antipsychotics. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 1739–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, W.; Schulze, S.; Brandl, M.; Winter, G. Vesicular phospholipid gel-based depot formulations for pharmaceutical proteins: Development and in vitro evaluation. J. Control. Release 2010, 142, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, C.; Wang, B.; Zhao, H. Microencapsulation peptide and protein drugs delivery system. Colloids Surfaces B 2005, 41, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, V.R.; Trehan, A. Biodegradable microspheres for protein delivery. J. Control. Release 2003, 90, 261–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Gaudio, C.; Crognale, V.; Serino, G.; Galloni, P.; Audenino, A.; Ribatti, D.; Morbiducci, U. Natural polymeric microspheres for modulated drug delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 75, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Gaete, C.; Retamal, M.; Chavez, C.; Bustos, P.; Godoy, R.; Torres-Vergara, P. Development, characterization and in vitro evaluation of biodegradable rhein-loaded microparticles for treatment of osteoarthritis. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 96, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Gong, C.; Gou, M.; Fu, S.; Guo, Q.; Shi, S.; Luo, F.; Guo, G.; Qiu, L.; Qian, Z. Biodegradable poly(epsilon-caprolactone)-poly(ethylene glycol) copolymers as drug delivery system. Int. Pharm. 2009, 381, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paciello, A.; Amalfitano, G.; Garziano, A.; Urciuolo, F.; Netti, P.A. Hemoglobin-Conjugated Gelatin Microsphere as a Smart Oxygen Releasing Biomaterial. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 2655–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Chen, X.; Fu, H.; Wen, X.; Ma, C.; Zhang, J.; Wu, C.; Huang, Y.; Pan, X.; Wu, C. Formation Mechanism and In Vitro Evaluation of Risperidone-Containing PLGA Microspheres Fabricated by Ultrafine Particle Processing System. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 3363–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siafaka, P.I.; Barmpalexis, P.; Lazaridou, M.; Papageorgiou, G.Z.; Koutris, E.; Karavas, E.; Kostoglou, M.; Bikiaris, D.N. Controlled release formulations of risperidone antipsychotic drug in novel aliphatic polyester carriers: Data analysis and modelling. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 94, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, A.S. The origins and evolution of “controlled” drug delivery systems. J. Control. Release 2008, 132, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Jin, T. Polymer-Based Sustained-Release Dosage Forms for Protein Drugs, Challenges, and Recent Advances. AAPS PharmSciTech 2008, 9, 1218–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitragotri, S.; Burke, P.A.; Langer, R. Overcoming the challenges in administering biopharmaceuticals: Formulation and delivery strategies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 655–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, S.; Guo, C.; Shi, Y.; Li, L.C. Recent advances in polymeric microspheres for parenteral drug delivery—Part 1. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2012, 9, 1161–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasmi, H.; Siepmann, F.; Hamoudi, M.C.; Danede, F.; Verin, J.; Willart, J.F.; Siepmann, J. Towards a better understanding of the different release phases from PLGA microparticles: Dexamethasone-loaded systems. Int. Pharm. 2016, 514, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casalini, T.; Rossi, F.; Lazzari, S.; Perale, G.; Masi, M. Mathematical modeling of PLGA microparticles: From polymer degradation to drug release. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 4036–4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.J.; Amatya, S.; Kim, M.S.; Park, J.H.; Seol, E.; Lee, H.; Shin, Y.H.; Na, D.H. Long-acting injectable formulations of antipsychotic drugs for the treatment of schizophrenia. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2013, 36, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, P.A.; Niemegeers, C.J.; Awouters, F.; Schellekens, K.H.; Megens, A.A.; Meert, T.F. Pharmacology of risperidone (R 64 766), a new antipsychotic with serotonin-S2 and dopamine-D2 antagonistic properties. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1988, 244, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cheng, F.; Jones, P.B. Drug treatments for schizophrenia: Pragmatism in trial design shows lack of progress in drug design. Epidemiol. Psychiatr. Sci. 2013, 22, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ereshefsky, L.; Mascarenas, C.A. Comparison of the effects of different routes of antipsychotic administration on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2003, 64 (Suppl. 16), 18–23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yerragunta, B.; Jogala, S.; Chinnala, K.M.; Aukunuru, J. Development of a novel 3-month drug releasing risperidone microspheres. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2015, 7, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Su, Z.; Sun, F.; Shi, Y.; Jiang, C.; Meng, Q.; Teng, L.; Li, Y. Effects of formulation parameters on encapsulation efficiency and release behavior of risperidone poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) microsphere. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 57, 1251–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Z.X.; Shi, Y.N.; Teng, L.S.; Li, X.; Wang, L.X.; Meng, Q.F.; Teng, L.R.; Li, Y.X. Biodegradable poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) microspheres for sustained release of risperidone: Zero-order release formulation. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2011, 16, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, W.; Wu, F.; Su, J.; Jin, T. Effect of bases with different solubility on the release behavior of risperidone loaded PLGA microspheres. Colloids Surfaces B 2011, 86, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karavelidis, V.; Giliopoulos, D.; Karavas, E.; Bikiaris, D. Nanoencapsulation of a water soluble drug in biocompatible polyesters. Effect of polyesters melting point and glass transition temperature on drug release behavior. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 41, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karavelidis, V.; Bikiaris, D.; Avgoustakis, K. New thermosensitive nanoparticles prepared by biocompatible pegylated aliphatic polyester block copolymers for local cancer treatment. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2015, 67, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, O.F.; Ciutǎ, I.Z. Détermination de la viscosité intrinsèque de solutions de polymères par une simple détermination de la viscosité. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1962, 6, 683–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barmpalexis, P.; Kachrimanis, K.; Malamataris, S. Statistical moments in modelling of swelling, erosion and drug release of hydrophilic matrix-tablets. Int. Pharm. 2018, 540, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanaki, S.G.; Pantopoulos, K.; Bikiaris, D.N. Synthesis of biocompatible poly(varepsilon-caprolactone)-block-poly(propylene adipate) copolymers appropriate for drug nanoencapsulation in the form of core-shell nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 2981–2995. [Google Scholar]
- Beslikas, T.; Gigis, I.; Goulios, V.; Christoforides, J.; Papageorgiou, G.Z.; Bikiaris, D.N. Crystallization study and comparative in vitro-in vivo hydrolysis of PLA reinforcement ligament. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 6597–6618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papageorgiou, G.; Beslikas, T.; Gigis, J.; Christoforides, J.; Bikiaris, D.N. Crystallization and enzymatic hydrolysis of PLA grade for orthopedics. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2010, 29, 280–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikiaris, D.N.; Nianias, N.P.; Karagiannidou, E.G.; Docoslis, A. Effect of different nanoparticles on the properties and enzymatic hydrolysis mechanism of aliphatic polyesters. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 2077–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Ikehara, T.; Nishi, T. Poly(hydroxybutyrate)/poly(butylene succinate) blends: Miscibility and nonisothermal crystallization. Polymer 2003, 44, 2503–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Z.; Abe, H.; Kurokawa, H.; Doi, Y. Solid-State Microstructures, Thermal Properties, and Crystallization of Biodegradable Poly(butylene succinate) (PBS) and Its Copolyesters. Biomacromolecules 2001, 2, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniel, J.S.P.; Veronez, I.P.; Rodrigues, L.L.; Trevisan, M.G.; Garcia, J.S. Risperidone—Solid-state characterization and pharmaceutical compatibility using thermal and non-thermal techniques. Thermochim. Acta 2013, 568, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappa, C.; Nanaki, S.; Giliopoulos, D.; Triantafyllidis, K.; Kostoglou, M.; Avgeropoulos, A.; Bikiaris, D. Nanostructured Composites of Sodium Montmorillonite Clay and PEO Used in Dissolution Improvement of Aprepitant Drug by Melt Mixing. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanaki, S.; Tseklima, M.; Terzopoulou, Z.; Nerantzaki, M.; Giliopoulos, D.J.; Triantafyllidis, K.; Kostoglou, M.; Bikiaris, D.N. Use of mesoporous cellular foam (MCF) in preparation of polymeric microspheres for long acting injectable release formulations of paliperidone antipsychotic drug. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 117, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanaki, S.; Siafaka, P.I.; Zachariadou, D.; Nerantzaki, M.; Giliopoulos, D.J.; Triantafyllidis, K.S.; Kostoglou, M.; Nikolakaki, E.; Bikiaris, D.N. PLGA/SBA-15 mesoporous silica composite microparticles loaded with paclitaxel for local chemotherapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 99, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iordanskii, A.L.; Zaikov, G.E.; Berlin, A.A. Diffusion kinetics of hydrolysis of biodegradable polymers. Weight loss and control of the release of low molecular weight substances. Polym. Sci. Ser. D 2015, 8, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tien, C. Adsorption Calculations and Modeling; Butterworth-Heinemann: Woburn, MA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Korsmeyer, R.W.; Gurny, R.; Doelker, E.; Buri, P.; Peppas, N.A. Mechanisms of solute release from porous hydrophilic polymers. Int. Pharm. 1983, 15, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crank, J. The Mathematics of Diffusion; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Georgiadis, M.C.; Kostoglou, M. On the optimization of drug release from multi-laminated polymer matrix devices. J. Control. Release 2001, 77, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sample | Particle Size Range (μm) | Microparticles Yield (%) | Drug Loading (%) | Entrapment Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLA–risperidone | 3–17 | 78.34 ± 2.1 | 9.84 ± 1.7 | 36.51 ± 2.2 |
| PLA/PPAd 80/20-risperidone | 3–15 | 79.56 ± 2.1 | 11.24 ± 3.1 | 38.46 ± 3.1 |
| PLA/PPAd 60/40-risperidone | 3–14 | 82.37 ± 1.9 | 12.87 ± 3.0 | 41.87 ± 3.2 |
| PLA/PPAd 40/60-risperidone | 3–15 | 81.48 ± 2.9 | 14.21 ± 2.5 | 40.42 ± 2.6 |
| PLA/PPAd 20/80-risperidone | 2–10 | 80.54 ± 3.0 | 10.07 ± 3.1 | 39.17 ± 4.1 |
| PPAd-risperidone | 2–8 | 82.17 ± 2.0 | 12.49 ± 1.9 | 42.82 ± 3.0 |
| Polyester Type | First Statistical Moment about Zero for: | |
|---|---|---|
| Dissolution (h) | Hydrolysis (h) | |
| PLA | 90.25 | 300.72 |
| PLA/PPAd 80/20 | 81.85 | 300.24 |
| PLA/PPAd 60/40 | 69.90 | 256.80 |
| PLA/PPAd 40/60 | 51.89 | 169.92 |
| PLA/PPAd 20/80 | 40.39 | 99.36 |
| PPAd | 23.50 | 26.16 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nanaki, S.; Barmpalexis, P.; Iatrou, A.; Christodoulou, E.; Kostoglou, M.; Bikiaris, D.N. Risperidone Controlled Release Microspheres Based on Poly(Lactic Acid)-Poly(Propylene Adipate) Novel Polymer Blends Appropriate for Long Acting Injectable Formulations. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030130
Nanaki S, Barmpalexis P, Iatrou A, Christodoulou E, Kostoglou M, Bikiaris DN. Risperidone Controlled Release Microspheres Based on Poly(Lactic Acid)-Poly(Propylene Adipate) Novel Polymer Blends Appropriate for Long Acting Injectable Formulations. Pharmaceutics. 2018; 10(3):130. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030130
Chicago/Turabian StyleNanaki, Stavroula, Panagiotis Barmpalexis, Alexandros Iatrou, Evi Christodoulou, Margaritis Kostoglou, and Dimitrios N. Bikiaris. 2018. "Risperidone Controlled Release Microspheres Based on Poly(Lactic Acid)-Poly(Propylene Adipate) Novel Polymer Blends Appropriate for Long Acting Injectable Formulations" Pharmaceutics 10, no. 3: 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030130
APA StyleNanaki, S., Barmpalexis, P., Iatrou, A., Christodoulou, E., Kostoglou, M., & Bikiaris, D. N. (2018). Risperidone Controlled Release Microspheres Based on Poly(Lactic Acid)-Poly(Propylene Adipate) Novel Polymer Blends Appropriate for Long Acting Injectable Formulations. Pharmaceutics, 10(3), 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030130