Alphaviruses in Gene Therapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
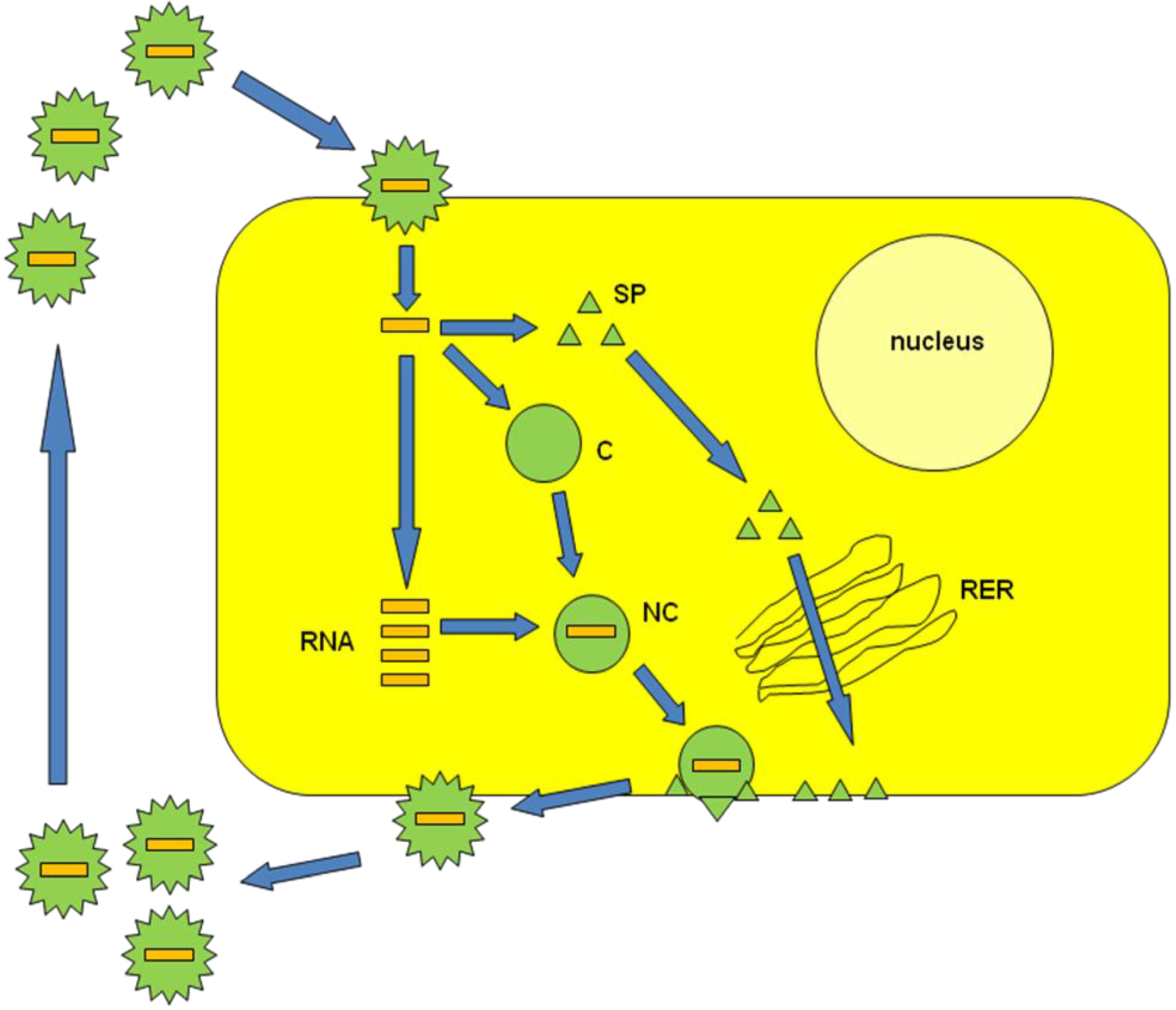
2. Alphavirus Vector Systems
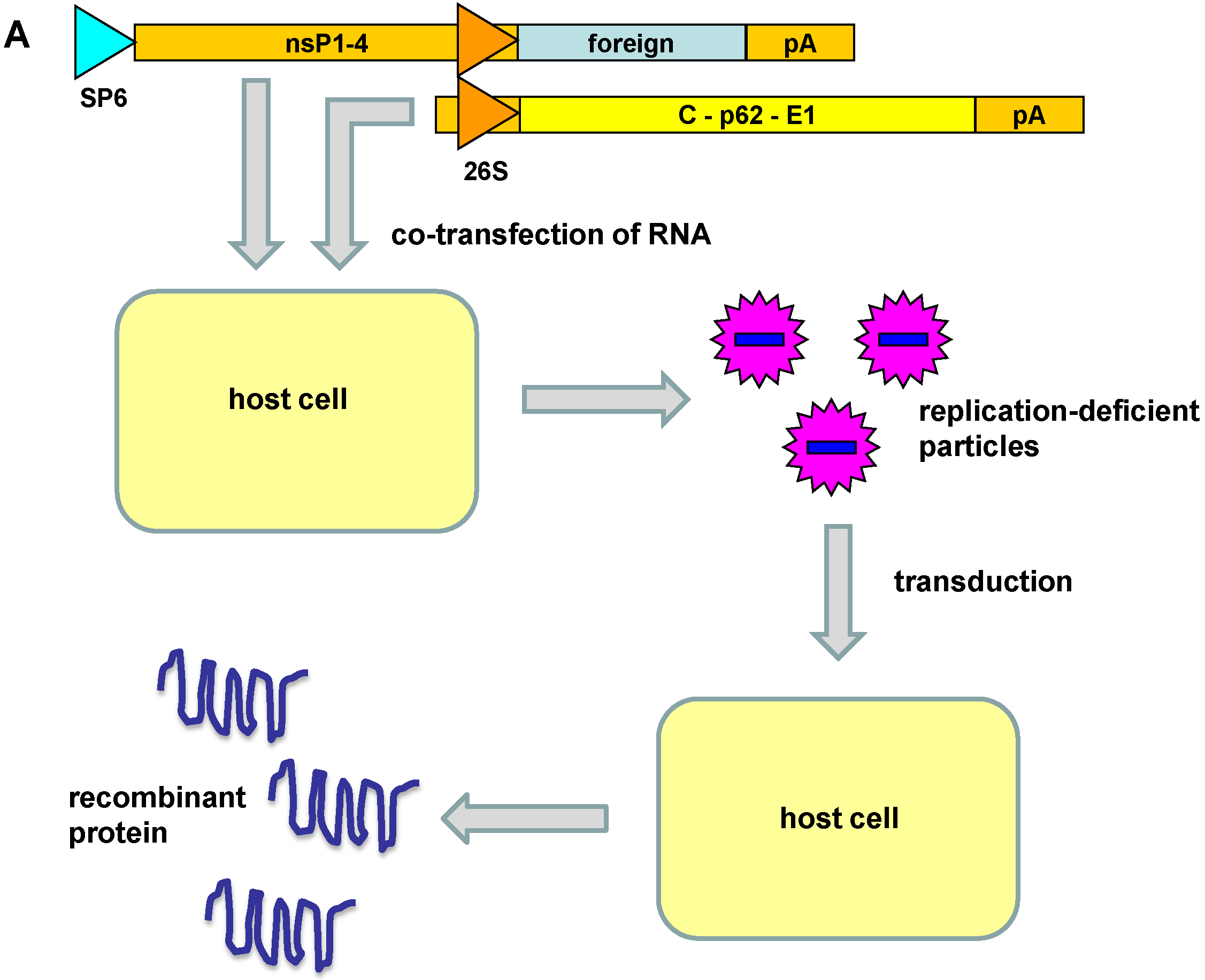
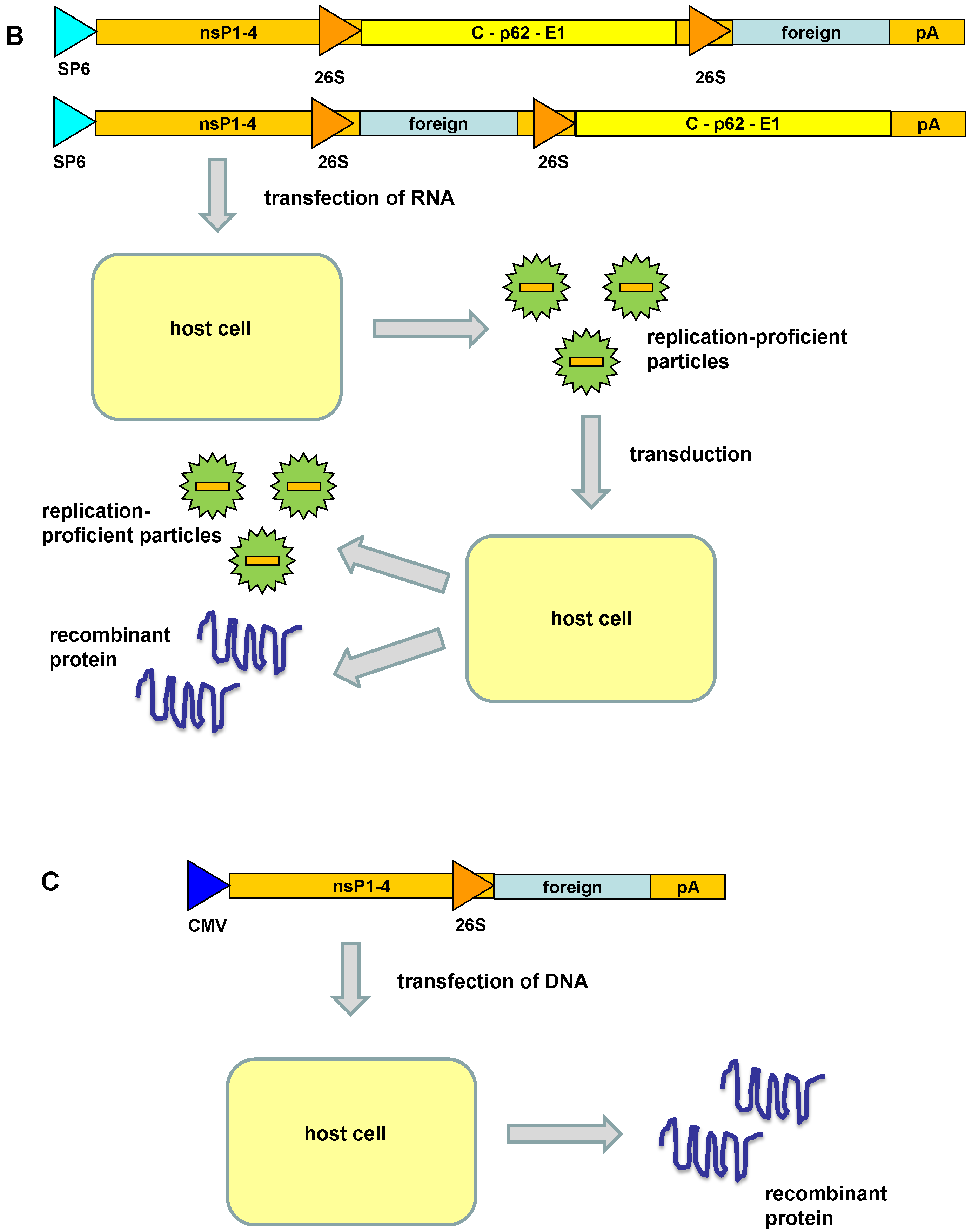
3. Engineered Alphavirus Vectors
4. Alphavirus Vectors in Gene Therapy
4.1. Tumor Targeting and Cancer Therapy
4.2. Cancer Vaccines
4.3. RNA Interference Approaches
5. Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Strauss, J.H.; Strauss, E.G. The Alphaviruses: Gene Expression, Replication and Evolution. Micobiol. Rev. 1994, 58, 491–562. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.S.; Kuhn, R.J.; Strauss, E.G.; Ou, S.; Strauss, J.H. High-affinity laminin receptor is a receptor of Sindbis virus in mammalian cells. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 4992–5001. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mathiot, C.C.; Grimaud, G.; Garry, P.; Bouquety, J.C.; Mada, A.; Daguisy, A.M.; Georges, A.J. An outbreak of human Semliki Forest virus infection in Central African Republic. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1990, 42, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Niklasson, B. Sindbis and Sindbis-like viruses. In The Arboviruses: Epidemiology and Ecology; Monath, T.P., Ed.; CRC Press, Inc.: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1988; pp. 167–176. [Google Scholar]
- Liljestrom, P.; Garoff, H. A new generation of animal cell expression vectors based on the Semliki Forest virus replicon. Biotechnology 1991, 9, 1356–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrengruber, M.U.; Lundstrom, K.; Schweitzer, C.; Heuss, C.; Schlesinger, S.; Gahwiler, B.H. Recombinant Semliki Forest virus and Sindbis virus efficiently infect neurons in hippocampal slice cultures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 7041–7046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundstrom, K.; Richards, J.G.; Pink, J.R.; Jenck, F. Efficient in vivo expression of a reporter gene in rat brain after injection of recombinant replication-deficient Semliki Forest virus. Gene Ther. Mol. Biol. 1999, 3, 15–23. [Google Scholar]
- Lundstrom, K. Biology and application of alphaviruses in gene therapy. Gene Ther. 2005, 12 (Suppl. 1), S92–S97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundstrom, K. Alphavirus vectors for vaccine production and gene therapy. Exp. Rev. Vaccines 2003, 2, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.P.; Hutchinson, L.E.; Kakar, S.S. Emerging role of microRNAs in diagnosis and treatment of various diseases including ovarian cancer. J. Ovarian Res. 2009, 2, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, C.; Levis, R.; Shen, P.; Schlesinger, S.; Rice, C.M.; Huang, H.V. Sindbis virus: An efficient, broad host range vector for gene expression in animal cells. Science 1989, 243, 1188–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, N.L.; Brown, K.W.; Johnston, R.E. In vitro synthesis of infectious Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus RNA from a cDNA clone: Analysis of a viable deletion mutant. Virology 1989, 171, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiCiommo, D.P.; Bremner, R. Rapid, high level protein production using DNA-based Semliki Forest virus vectors. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 18060–18066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundstrom, K. Alphavirus vectors in gene therapy and neuroscinece. In Cell and Gene Therapy: Therapeutic Mechanisms and Strategies; Templeton, N.S., Ed.; CRC Press, Inc.: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 175–184. [Google Scholar]
- Leitner, W.W.; Hwang, L.N.; deVeer, M.J.; Zhou, A.; Silverman, R.H.; Williams, B.R.; Dubensky, T.W.; Ying, H.; Restifo, N.P. Alphavirus-based DNA vaccine breaks immunological tolerance by activating innate antiviral pathways. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, H.; Zaks, T.Z.; Wang, R.F.; Irvine, K.R.; Kammula, U.S.; Marincola, F.M.; Leitner, W.W.; Restifo, N.P. Cancer therapy using a self-replicating RNA vaccine. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 823–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berglund, P.; Sjöberg, M.; Garoff, H.; Atkins, G.J.; Sheahan, B.J.; Liljeström, P. Semliki Forest virus expression system: Production of conditionally infectious recombinant particles. Biotechnology 1993, 11, 916–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smerdou, C.; Liljestrom, P. Two-helper RNA system for production of recombinant Semliki Forest virus particles. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 1092–1098. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schlesinger, S. Alphavirus vectors: Development and potential therapeutic applications. Exp. Opin. Biol. Ther. 2001, 1, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Madoz, J.R.; Prieto, J.; Smerdou, C. Semliki forest virus vectors engineered to express higher IL-12 levels induce efficient elimination of murine colon adenocarcinomas. Mol. Ther. 2005, 12, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundstrom, K.; Rotmann, D.; Hermann, D. Novel mutant Semliki Forest virus vectors: Gene expression and localization studies in neuronal cells. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2000, 115, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundstrom, K.; Abenavoli, A.; Margaroli, A.; Ehrengruber, M.U. Novel Semliki Forest virus vectors with reduced cytotoxicity and temperature sensitivity for long-term enhancement of transgene expression. Mol. Ther. 2003, 7, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agapov, E.V.; Frolov, I.; Lindenbach, B.D.; Prágai, B.M.; Schlesinger, S.; Rice, C.M. Noncythopathic Sindbis virus RNA vectors for heterologous gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 12989–12994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perri, S.; Driver, D.A.; Gardner, J.P.; Sherrill, S.; Belli, B.A.; Dubensky TW, Jr.; Polo, J.M. Replicon vectors derived from Sindbis virus and Semliki Forest virus that establish persistent replication in host cells. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 9402–9407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dryga, S.A.; Dryga, O.A.; Schlesinger, S. Identification of mutations in a Sindbis virus variant able to establish a persistent infection in BHK cells: The importance of a mutation in the nsP2 gene. Virology 1997, 228, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrengruber, M.U.; Renggli, M.; Raineteau, O.; Hennou, S.; Vähä-Koskela, M.J.; Hinkkanen, A.E.; Lundstrom, K. Semliki Forest virus A7(74) transduces hippocampal neurons and glial cells in a temperature-dependent dual manner. J. Neurovirol. 2003, 9, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vähä-Koskela, M.J.; Tuittila, M.T.; Nygardas, P.T.; Nyman, J.K.E.; Ehrengruber, M.U.; Renggli, M.; Hinkkanen, A.E. A novel neurotrophic expression vector based on the avirulent A7(74) strain of Semliki Forest virus. J. Neurovirol. 2003, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.Y.; Atasheva, S.; McAuley, A.J.; Plante, J.A.; Frolova, E.I.; Beasley, D.W.; Frolov, I. Enhancement of protein expression by alphavirus replicons by designing self-replicating subgenomic RNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 10708–10713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tellinghuisen, T.L.; Hamburger, A.E.; Fischer, B.R.; Ostendorp, R.; Kuhn, R.J. In vitro assembly of alphavirus cores by using nucleocapsid cores in mature virus. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 5300–5019. [Google Scholar]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Chipman, P.R.; Hong, E.M.; Kuhn, R.J.; Rossmann, M.G. In vitro assembled alphavirus core-like particles maintain a structure similar to that of nucleocapsid cores in mature virus. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 11128–11132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, F.; Tsvetkova, I.B.; Khuong, Y.-L.; Moore, A.W.; Arnold, R.J.; Goicochea, N.L.; Dragnea, B.; Mukhopadhyay, S. The packaging of different cargo into enveloped viral nanoparticles. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 10, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.; Boulikas, T.; Lundstrom, K.; Söling, A.; Warnke, P.C.; Rainov, N.G. Immunogene therapy of recurrent glioblastoma multiforme with a liposomally encapsulated replication-incompetent Semliki forest virus vector carrying the human interleukin-12 gene—A phase I/II clinical protocol. J. Neurooncol. 2003, 64, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ohno, K.; Sawai, K.; Iijima, Y.; Levin, B.; Meruelo, D. Cell-specific targeting of Sindbis virus vectors displaying IgG-binding domains of protein A. Nat. Biotechnol. 1997, 15, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, J.C.; Levin, B.; Hurtado, A.; Yee, H.; de Castro, I.P.; Jimenez, M.; Shamamian, P.; Jin, R.; Novick, R.P.; Pellicer, A.; et al. Systemic tumor targeting and killing by Sindbis viral vectors. Nat. Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Madoz, J.R.; Prieto, J.; Smerdou, C. Biodistribution and tumor infectivity of Semliki Forest virus vectors in mice: Effect of re-administration. Mol. Ther. 2007, 15, 2164–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.Y.; Guo, J.H.; Hwang, L.H. Oncolytic Sindbis virus targets tumors defective in interferon response and induces significant bystander antitumor immunity in vivo. Mol. Ther. 2012, 20, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geall, A.J.; Verma, A.; Otten, G.R.; Shaw, C.A.; Hekele, A.; Banerjee, K.; Cu, Y.; Beard, C.W.; Brito, L.A.; Krucker, T.; et al. Nonviral delivery of self-amplifying RNA vaccines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 14604–14609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asselin-Paturel, C.; Lassau, N.; Guinebretière, J.M.; Zhang, J.; Gay, F.; Bex, F.; Hallez, S.; Leclere, J.; Peronneau, P.; Mami-Chouaib, F.; et al. Transfer of the murine interleukin-12 gene in vivo by a Semliki Forest virus vector induces B16 tumor regression through inhibition of tumor blood vessel formation monitored by Doppler ultrasonography. Gene Ther. 1999, 6, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, A.M.; Morris-Downes, M.M.; Sheahan, B.J.; Atkins, G.J. Inhibition of human lung carcinoma cell growth by apoptosis induction using Semliki Forest virus recombinant particles. Gene Ther. 2000, 7, 1477–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chikkanna-Gowda, C.P.; Sheahan, B.J.; Fleeton, M.N.; Atkins, G.J. Regression of mouse tumours and inhibition of metastases following administration of a Semliki Forest virus vector with enhanced expression of IL-12. Gene Ther. 2005, 12, 1253–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chikkanna-Gowda, C.P.; McNally, S.; Sheahan, B.J.; Fleeton, M.N.; Atkins, G.J. Inhibition of murine K-BALB and CT26 tumour growth using a Semliki Forest virus vector with enhanced expression of IL-18. Oncol. Rep. 2006, 16, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lyons, J.A.; Sheahan, B.J.; Galbraith, S.E.; Mehra, R.; Atkins, G.J.; Fleeton, M.N. Inhibition of angiogenesis by a Semliki Forest virus vector expressing VEGFR-2 reduces tumour growth and metastasis in mice. Gene Ther. 2007, 14, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vähä-Koskela, M.J.; Kuusinen, T.I.; Holmlund-Hampf, J.C.; Furu, P.T.; Heikkilä, J.E.; Hinkkanen, A.E. Semliki Forest virus vectors expressing transforming growth factor beta inhibit experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in Balb/c mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 355, 776–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketola, A.; Hinkkanen, A.; Yongabi, F.; Furu, P.; Määttä, A.M.; Liimatainen, T.; Pirinen, R.; Björn, M.; Hakkarainen, T.; Mäkinen, K.; et al. Oncolytic Semliki forest virus vector as a novel candidate against unresectable osteosarcoma. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 8342–8350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Määttä, A.M.; Mäkinen, K.; Ketola, A.; Liimatainen, T.; Yongabi, F.N.; Vähä-Koskela, M.; Pirinen, R.; Rautsi, O.; Pellinen, R.; Hinkkanen, A.; et al. Replication competent Semliki Forest virus prolongs survival in experimental lung cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 123, 1704–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundstrom, K. Alphavirus-based vaccines. Viruses 2014, 6, 2392–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colmenero, P.; Liljestrom, P.; Jondal, M. Induction of P815 tumor immunity by recombinant Semliki Forest virus expressing the P1A gene. Gene Ther. 1999, 6, 1728–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velders, M.P.; McElhiney, S.; Cassetti, M.C.; Eiben, G.L.; Higgins, T.; Kovacs, G.R.; Elmishad, A.G.; Kast, W.M.; Smith, L.R. Eradication of established tumors by vaccination with Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus replicon particles delivering human papillomavirus 16 E7 RNA. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 7861–7867. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yamanaka, R.; Zullo, S.A.; Tanaka, R.; Blaese, M.; Xanthopoulos, K.G. Enhancement of antitumor response in glioma models in mice by genetically modified dendritic cells pulsed with Semliki Forest virus-mediated complementary DNA. J. Neurosurg. 2001, 94, 478–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, T.P.; Burgents, J.E.; Long, B.; Ferrer, I.; Jaffee, E.M.; Tisch, R.M.; Johnston, R.E.; Serody, J.S. Alphaviral vector-transduced dendritic cells are successful therapeutic vaccines against neu-overexpressing tumors in wild-type mice. Vaccine 2007, 25, 6604–6612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, M.C.; Zhao, Y.J.; Lachman, L.B.; Hwu, P.; Wu, G.J.; Bar-Eli, M. Immunization against MUC18/MCAM, a novel antigen that drives melanoma invasion and metastasis. Gene Ther. 2007, 14, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachman, L.B.; Rao, X.M.; Kremer, R.H.; Ozpolat, B.; Kiriakova, G.; Price, J.E. DNA vaccination against neu reduces breast cancer incidence and metastasis in mice. Cancer Gene Ther. 2001, 8, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, J.P.; Rao, X.M.; Price, J.E.; Zhou, H.S.; Lachman, L.B. Prime-boost vaccination with plasmid and adenovirus gene vaccines control HER2/neu+ metastatic breast cancer in mice. Breast Cancer Res. 2005, 7, R580–R588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanaka, R.; Xanthopoulos, K.G. Induction of antigen-specific immune responses against malignant brain tumors by intramuscular injection of sindbis DNA encoding gp100 and IL-18. DNA Cell Biol. 2005, 24, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leitner, W.W.; Ying, H.; Driver, D.A.; Dubensky, T.W.; Restifo, N.P. Enhancement of tumor-specific immune response with plasmid DNA replicon vectors. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Seyhan, A.A.; Alizadeh, B.N.; Lundstrom, K.; Johnston, B.H. RNA interference-mediated inhibition of Semliki Forest virus replication in mammalian cells. Oligonucleotides 2007, 17, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyhan, A.A.; Vitiello, D.; Shields, M.T.; Burke, J.M. Ribozyme inhibition of alphavirus replication. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 25957–25962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhlirova, M.; Foy, B.D.; Beaty, B.J.; Olson, K.E.; Riddiford, L.M.; Jindra, M. Use of Sindbis virus-mediated RNA interference to demonstrate a conserved role of Broad-Complex in insect metamorphosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 15607–15612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attardo, G.M.; Higgs, S.; Klingler, K.A.; Vanlandingham, D.L.; Raikhel, A.S. RNA interference-mediated knockdown of a GATA factor reveals a link to anautogeny in the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 13373–13379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ylösmäki, E.; Martikainen, M.; Hinkkanen, A.; Saksela, K. Attenuation of Semliki Forest virus neurovirulence by micro-RNA detargeting. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polo, J.M.; Belli, B.A.; Driver, D.A.; Frolov, I.; Sherrill, S.; Hariharan, M.J.; Townsend, K.; Perri, S.; Mento, S.J.; Jolly, D.J.; et al. Stable alphavirus packaging cell lines for Sindbis virus and Semliki Forest virus-derived vectors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 4598–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.Y.; Liang, G.D. Selection and characterization of packaging cell lines for XJ-160 virus. Intervirology 2009, 52, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lundstrom, K. Alphaviruses in Gene Therapy. Viruses 2015, 7, 2321-2333. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7052321
Lundstrom K. Alphaviruses in Gene Therapy. Viruses. 2015; 7(5):2321-2333. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7052321
Chicago/Turabian StyleLundstrom, Kenneth. 2015. "Alphaviruses in Gene Therapy" Viruses 7, no. 5: 2321-2333. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7052321
APA StyleLundstrom, K. (2015). Alphaviruses in Gene Therapy. Viruses, 7(5), 2321-2333. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7052321




