Engineered RNase P Ribozymes Effectively Inhibit Human Cytomegalovirus Gene Expression and Replication
Abstract
:1. Introduction
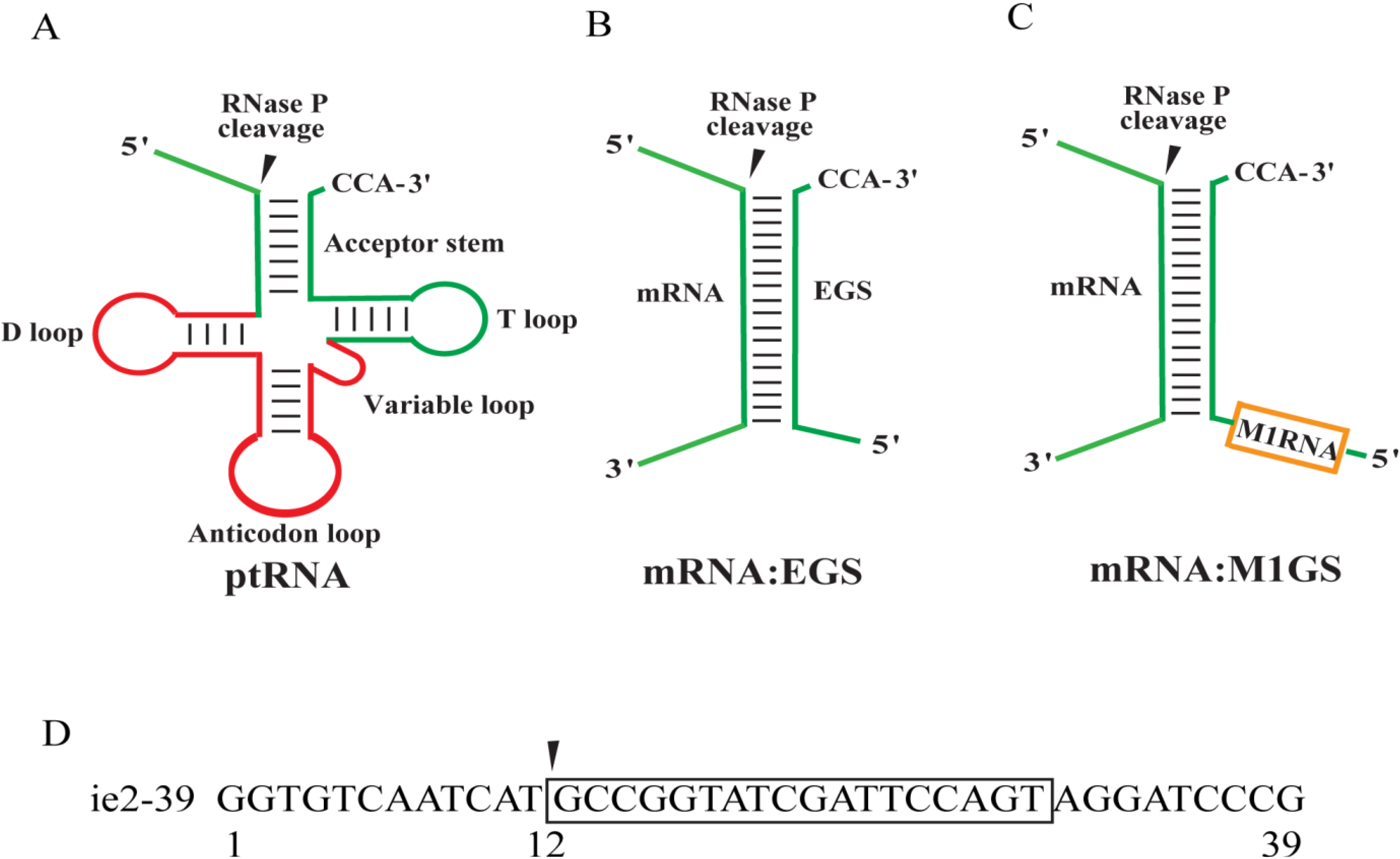
2. Results
2.1. Targeting and Cleavage Activities of the M1GS RNAs in Vitro
| Enzyme | (kcat/Km)s (µM−1·min−1) | Kd (nM) |
|---|---|---|
| M1-IE2 | 0.20 ± 0.05 | 0.34 ± 0.06 |
| V661-IE2 | 10.5 ± 0.5 | 0.30 ± 0.05 |
| M1-IE2-C | <5 × 10−6 | 0.33 ± 0.07 |
| V661-IE2-C | <5 × 10−6 | 0.32 ± 0.07 |
| M1-TK | <5 × 10−6 | ND |
2.2. Expression of Ribozymes in Human Cell Culture
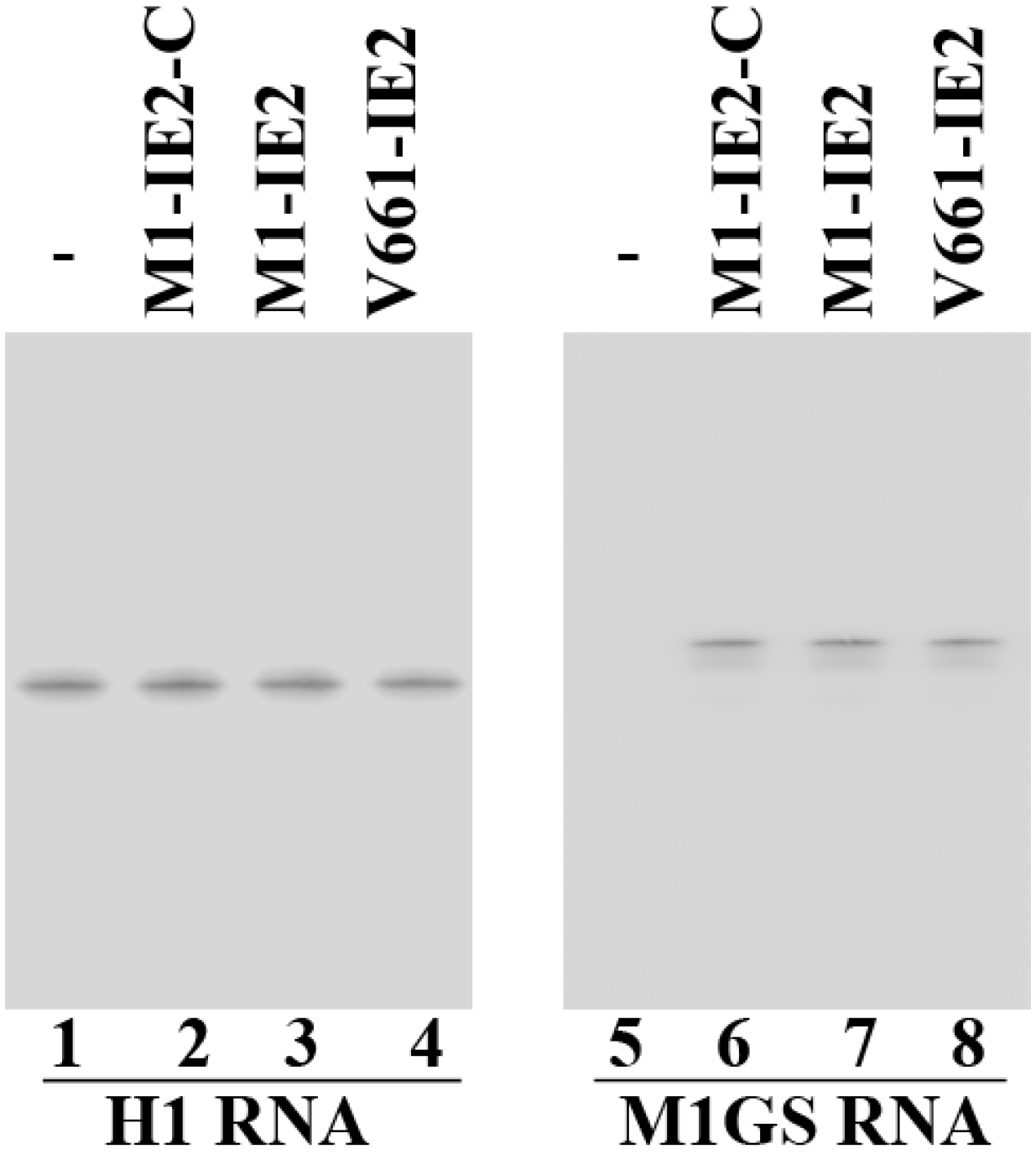
2.3. Enhanced Reduction of HCMV IE2 Expression in Cells Expressing the Engineered Ribozymes
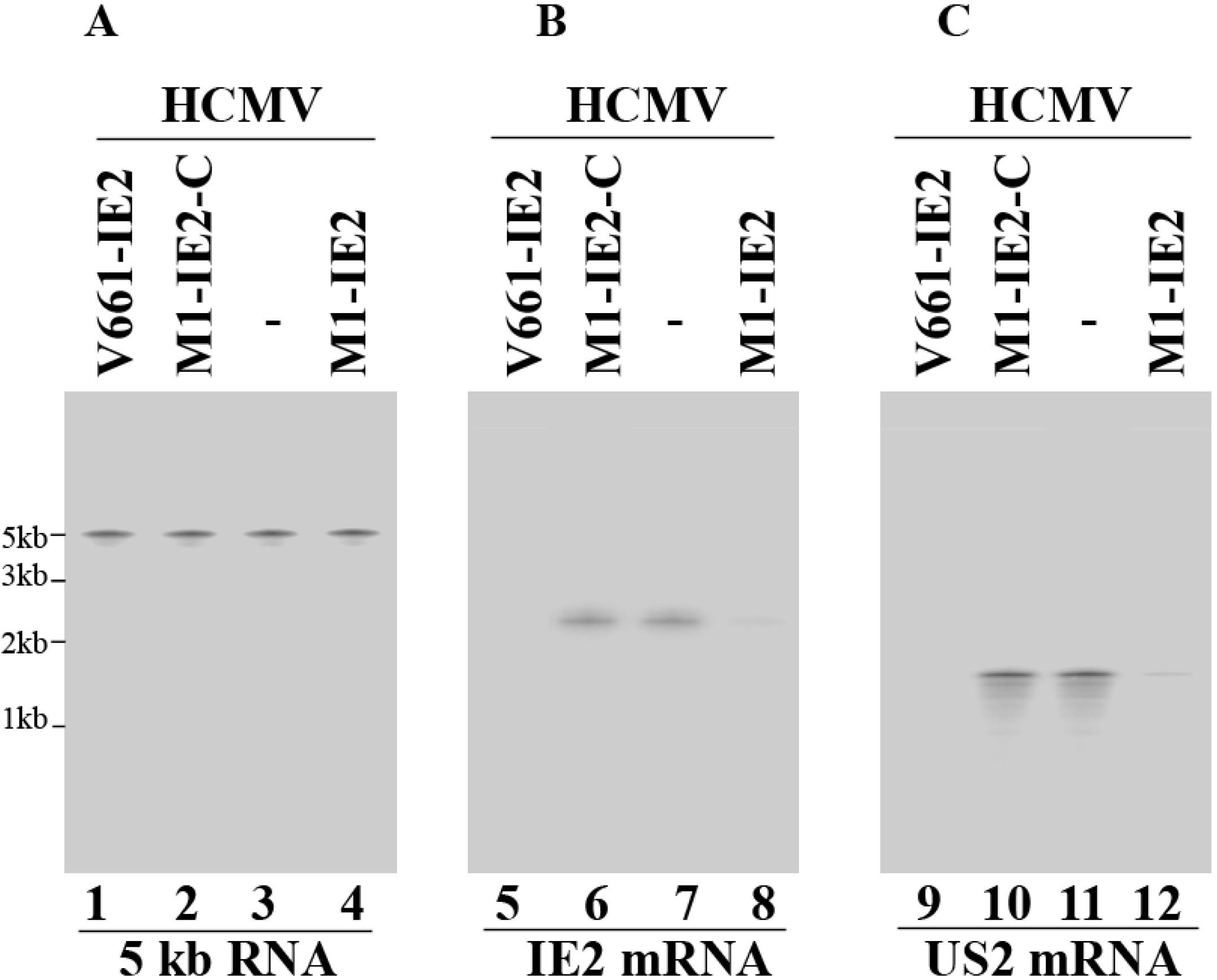
| Viral Gene Class | Ribozymes | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U373MG | M1-IE2-C | V661-IE2-C | M1-IE2 | V661-IE2 | M1-TK | ||
| IE2 mRNA | α | 0% | 6% | 5% | 75% ± 7% | 98% ± 7% | 1% |
| US2 mRNA | β | 0% | 1% | 1% | 70% ± 6% | 96% ± 8% | 0% |
| IE2 protein | α | 0% | 4% | 5% | 75% ± 8% | 98% ± 8% | 0% |
| UL44 protein | β,γ | 0% | 1% | 0% | 71% ± 8% | 95% ± 7% | 1% |
| UL99 protein | γ | 0% | 0% | 1% | 72% ± 7% | 94% ± 6% | 0% |
| gH protein | γ | 0% | 0% | 0% | 71% ± 8% | 98% ± 7% | 1% |
2.4. Increased Reduction of HCMV Infection by the Ribozymes

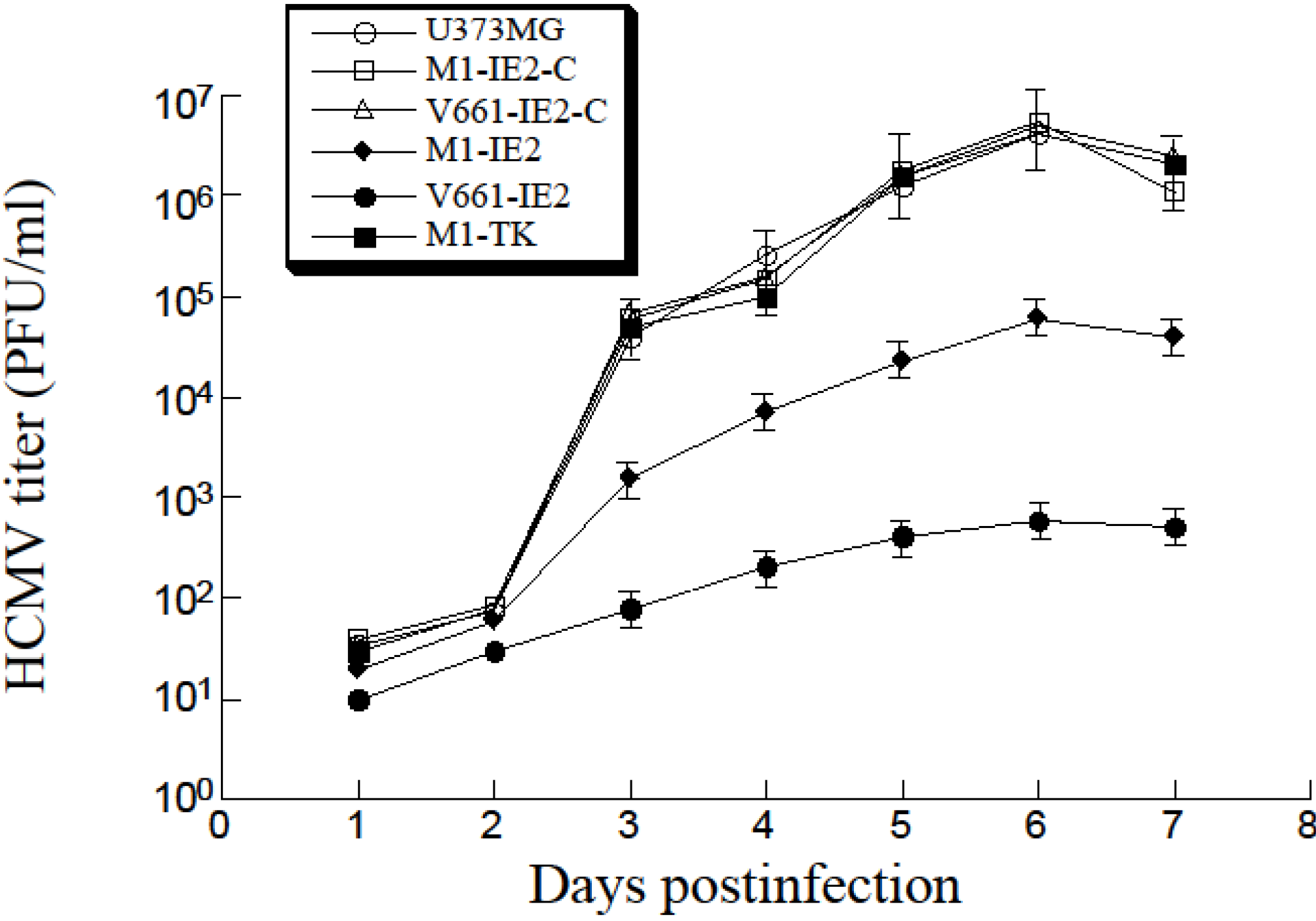
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Viruses, Cells and Antibodies
4.2. Mapping of the Accessible Regions of HCMV IE2 mRNA in Cells
4.3. Ribozyme Studies in Vitro
4.4. Construction of the M1GS-Expressing Cell Lines
4.5. Assaying of Gene Expression and Viral Infection
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References and Notes
- Mocarski, E.S.; Shenk, T.; Pass, R.F. Cytomegalovirus. In Fields Virology; Knipe, D.M., Howley, P.M., Griffin, D.E., Martin, M.A., Lamb, R.A., Roizman, B., Straus, S.E., Eds.; Lippincott-William & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2007; pp. 2701–2772. [Google Scholar]
- Boppana, S.B.; Ross, S.A.; Fowler, K.B. Congenital cytomegalovirus infection: Clinical outcome. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 57, S178–S181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palella, F.J., Jr.; Delaney, K.M.; Moorman, A.C.; Loveless, M.O.; Fuhrer, J.; Satten, G.A.; Aschman, D.J.; Holmberg, S.D. Declining morbidity and mortality among patients with advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection. HIV Outpatient Study Investigators. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 338, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallant, J.E.; Moore, R.D.; Richman, D.D.; Keruly, J.; Chaisson, R.E. Incidence and natural history of cytomegalovirus disease in patients with advanced human immunodeficiency virus disease treated with zidovudine. The Zidovudine Epidemiology Study Group. J. Infect. Dis. 1992, 166, 1223–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, L.J.; Rossi, J.J. Approaches for the sequence-specific knockdown of mRNA. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 1457–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, C.A.; Cheng, Y.C. Antisense oligonucleotides as therapeutic agents—Is the bullet really magical? Science 1993, 261, 1004–1012. [Google Scholar]
- Wiebusch, L.; Truss, M.; Hagemeier, C. Inhibition of human cytomegalovirus replication by small interfering RNAs. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacque, J.M.; Triques, K.; Stevenson, M. Modulation of HIV-1 replication by RNA interference. Nature 2002, 418, 435–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu Putlitz, J.; Yu, Q.; Burke, J.M.; Wands, J.R. Combinatorial screening and intracellular antiviral activity of hairpin ribozymes directed against hepatitis B virus. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 5381–5387. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, M.; Ojwang, J.; Yamada, O.; Hampel, A.; Rapapport, J.; Looney, D.; Wong-Staal, F. A hairpin ribozyme inhibits expression of diverse strains of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 6340–6344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarver, N.; Cantin, E.M.; Chang, P.S.; Zaia, J.A.; Ladne, P.A.; Stephens, D.A.; Rossi, J.J. Ribozymes as potential anti-HIV-1 therapeutic agents. Science 1990, 247, 1222–1225. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.H.; Li, H.; Zhou, T.; Kim, K.; Liu, F. Engineered external guide sequences are highly effective in inducing RNase P for inhibition of gene expression and replication of human cytomegalovirus. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, S.; Kirsebom, L.A. Ribonuclease P. In The RNA World; Gesteland, R.F., Cech, T.R., Atkins, J.F., Eds.; Cold Spring Harbor Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 351–380. [Google Scholar]
- Gopalan, V.; Altman, S. RNase P:structure and catalysis. The RNA World; Gesteland, R., Cech, T., Atkins, J., Eds.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2006; Volume 277. Chapter 6.1. Available online: http://rna.cshl.edu/ (accessed on 18 May 2014).
- Kazantsev, A.V.; Pace, N.R. Bacterial RNase P: A new view of an ancient enzyme. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrier-Takada, C.; Gardiner, K.; Marsh, T.; Pace, N.; Altman, S. The RNA moiety of ribonuclease P is the catalytic subunit of the enzyme. Cell 1983, 35, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marvin, M.C.; Engelke, D.R. Broadening the mission of an RNA enzyme. J. Cell Biochem. 2009, 108, 1244–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, A.C.; Altman, S. External guide sequences for an RNA enzyme. Science 1990, 249, 783–786. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Hwang, E.S.; Altman, S. Targeted cleavage of mRNA by human RNase P. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 8006–8010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, D.N.; Harris, M.; Pace, N.R. Rational design of self-cleaving pre-tRNA-ribonuclease P RNA conjugates. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 10800–10808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Altman, S. Inhibition of viral gene expression by the catalytic RNA subunit of RNase P from Escherichia coli. Genes Dev. 1995, 9, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trang, P.; Lee, M.; Nepomuceno, E.; Kim, J.; Zhu, H.; Liu, F. Effective inhibition of human cytomegalovirus gene expression and replication by a ribozyme derived from the catalytic RNA subunit of RNase P from Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 5812–5817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trang, P.; Kilani, A.F.; Kim, J.; Liu, F. A ribozyme derived from the catalytic subunit of RNase P from Escherichia coli is highly effective in inhibiting replication of herpes simplex virus 1. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 301, 817–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobaleda, C.; Sanchez-Garcia, I. In vitro inhibition by a site-specific catalytic RNA subunit of RNase P designed against the BCR-ABL oncogenic products: A novel approach for cancer treatment. Blood 2000, 95, 731–737. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Rossi, J.J. Current progress in the development of RNAi-based therapeutics for HIV-1. Gene Ther. 2011, 18, 1134–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ditzler, M.A.; Bose, D.; Shkriabai, N.; Marchand, B.; Sarafianos, S.G.; Kvaratskhelia, M.; Burke, D.H. Broad-spectrum aptamer inhibitors of HIV reverse transcriptase closely mimic natural substrates. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 8237–8247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Held, D.M.; Kissel, J.D.; Patterson, J.T.; Nickens, D.G.; Burke, D.H. HIV-1 inactivation by nucleic acid aptamers. Front. Biosci. 2006, 11, 89–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Chen, Y.C.; Bai, Y.; Trang, P.; Vu, G.P.; Lu, S.; Wu, J.; Liu, F. Effective inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus 1 replication by engineered RNase P ribozyme. PLoS One 2012, 7, e51855. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, H.; Ben-Asouli, Y.; Schein, A.; Moussa, S.; Jarrous, N. Eukaryotic RNase P: Role of RNA and protein subunits of a primordial catalytic ribonucleoprotein in RNA-based catalysis. Mol. Cell 2003, 12, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F. Ribonuclease P as a Tool; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 257–276. [Google Scholar]
- Kilani, A.F.; Trang, P.; Jo, S.; Hsu, A.; Kim, J.; Nepomuceno, E.; Liou, K.; Liu, F. RNase P ribozymes selected in vitro to cleave a viral mRNA effectively inhibit its expressionin cell culture. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 10611–10622. [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, W.; Chou, C.; Li, H.; Hai, R.; Patterson, D.; Stolc, V.; Zhu, H.; Liu, F. Functional profiling of human cytomegalovirus genome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 14223–14228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchini, A.; Liu, H.; Zhu, H. Human cytomegalovirus with IE-2 (UL122) deleted fails to express early lytic genes. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 1870–1878. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, D.; Silva, M.C.; Shenk, T. Functional map of human cytomegalovirus AD169 defined by global mutational analysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 12396–12401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaug, A.J.; Cech, T.R. Analysis of the structure of Tetrahymena nuclear RNAs in vivo: Telomerase RNA, the self-splicing rRNA intron, and U2 snRNA. RNA 1995, 1, 363–374. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Chen, Y.C.; Gong, H.; Trang, P.; Lu, S.; Liu, F. Ribonuclease P-mediated inhibition of human cytomegalovirus gene expression and replication induced by engineered external guide sequences. RNA Biol. 2012, 9, 1186–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.J.; Kilani, A.F.; Zhan, X.; Altman, S.; Liu, F. The protein cofactor allows the sequence of an RNase P ribozyme to diversify by maintaining the catalytically active structure of the enzyme. RNA 1997, 3, 613–623. [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand, E.; Castanotto, D.; Zhou, C.; Carbonnelle, C.; Lee, N.S.; Good, P.; Chatterjee, S.; Grange, T.; Pictet, R.; Kohn, D.; et al. The expression cassette determines the functional activity of ribozymes in mammalian cells by controlling their intracellular localization. RNA 1997, 3, 75–88. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Cong, J.P.; Mamtora, G.; Gingeras, T.; Shenk, T. Cellular gene expression altered by human cytomegalovirus: Global monitoring with oligonucleotide arrays. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 14470–14475. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.; Kim, J.; Kilani, A.F.; Kim, K.; Dunn, W.; Jo, S.; Nepomuceno, E.; Liu, F. In vitro selection of external guide sequences for directing RNase P-mediated inhibition of viral gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 30112–30120. [Google Scholar]
- Kieff, E.D.; Rickinson, A.B. Epstein-Barr virus and its replication. In Fields Virology; Knipe, D.M., Howley, P.M., Griffin, D.E., Martin, M.A., Lamb, R.A., Roizman, B., Straus, S.E., Eds.; Lippincott-William & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2007; pp. 2604–2654. [Google Scholar]
- Roizman, B.; Knipe, D.M.; Whitley, R.J. Herpes simplex viruses. In Fields Virology; Knipe, D.M., Howley, P.M., Griffin, D.E., Martin, M.A., Lamb, R.A., Roizman, B., Straus, S.E., Eds.; Lippincott-William & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2007; pp. 2503–2601. [Google Scholar]
- Fedor, M.J.; Uhlenbeck, O.C. Kinetics of intermolecular cleavage by hammerhead ribozymes. Biochemistry 1992, 31, 12042–12054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trang, P.; Lee, J.; Kilani, A.F.; Kim, J.; Liu, F. Effective inhibition of herpes simplex virus 1 gene expression and growth by engineered RNase P ribozyme. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 5071–5078. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, A.D.; Rosman, G.J. Improved retroviral vectors for gene transfer and expression. Biotechniques 1989, 7, 980–990. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Shen, A.; Rider, P.J.; Yu, Y.; Wu, K.; Mu, Y.; Hao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Gong, H.; Zhu, Y.; et al. A liver-specific microRNA binds to a highly conserved RNA sequence of hepatitis B virus and negatively regulates viral gene expression and replication. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 4511–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Z.; Vu, G.-P.; Qian, H.; Chen, Y.-C.; Wang, Y.; Reeves, M.; Zen, K.; Liu, F. Engineered RNase P Ribozymes Effectively Inhibit Human Cytomegalovirus Gene Expression and Replication. Viruses 2014, 6, 2376-2391. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6062376
Yang Z, Vu G-P, Qian H, Chen Y-C, Wang Y, Reeves M, Zen K, Liu F. Engineered RNase P Ribozymes Effectively Inhibit Human Cytomegalovirus Gene Expression and Replication. Viruses. 2014; 6(6):2376-2391. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6062376
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Zhu, Gia-Phong Vu, Hua Qian, Yuan-Chuan Chen, Yu Wang, Michael Reeves, Ke Zen, and Fenyong Liu. 2014. "Engineered RNase P Ribozymes Effectively Inhibit Human Cytomegalovirus Gene Expression and Replication" Viruses 6, no. 6: 2376-2391. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6062376
APA StyleYang, Z., Vu, G.-P., Qian, H., Chen, Y.-C., Wang, Y., Reeves, M., Zen, K., & Liu, F. (2014). Engineered RNase P Ribozymes Effectively Inhibit Human Cytomegalovirus Gene Expression and Replication. Viruses, 6(6), 2376-2391. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6062376




