Molecular Signatures of Hepatitis C Virus (HCV)-Induced Type II Mixed Cryoglobulinemia (MCII)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. HCV in Induction of MCII
2.1. HCV
2.2. HCV Infection and MCII
3. Molecular Mechanisms Involved in the Establishment of HCV-Related MCII
3.1. Molecular Mimicry
3.2. HCV Lymphotropism and Interaction with CD81
3.3. HCV-Restricted Induction of Determined Ig VH and Vκ Subfamily Genes
3.4. Complement Factors and Proteins
4. B-cell Subsets Involved in MCII
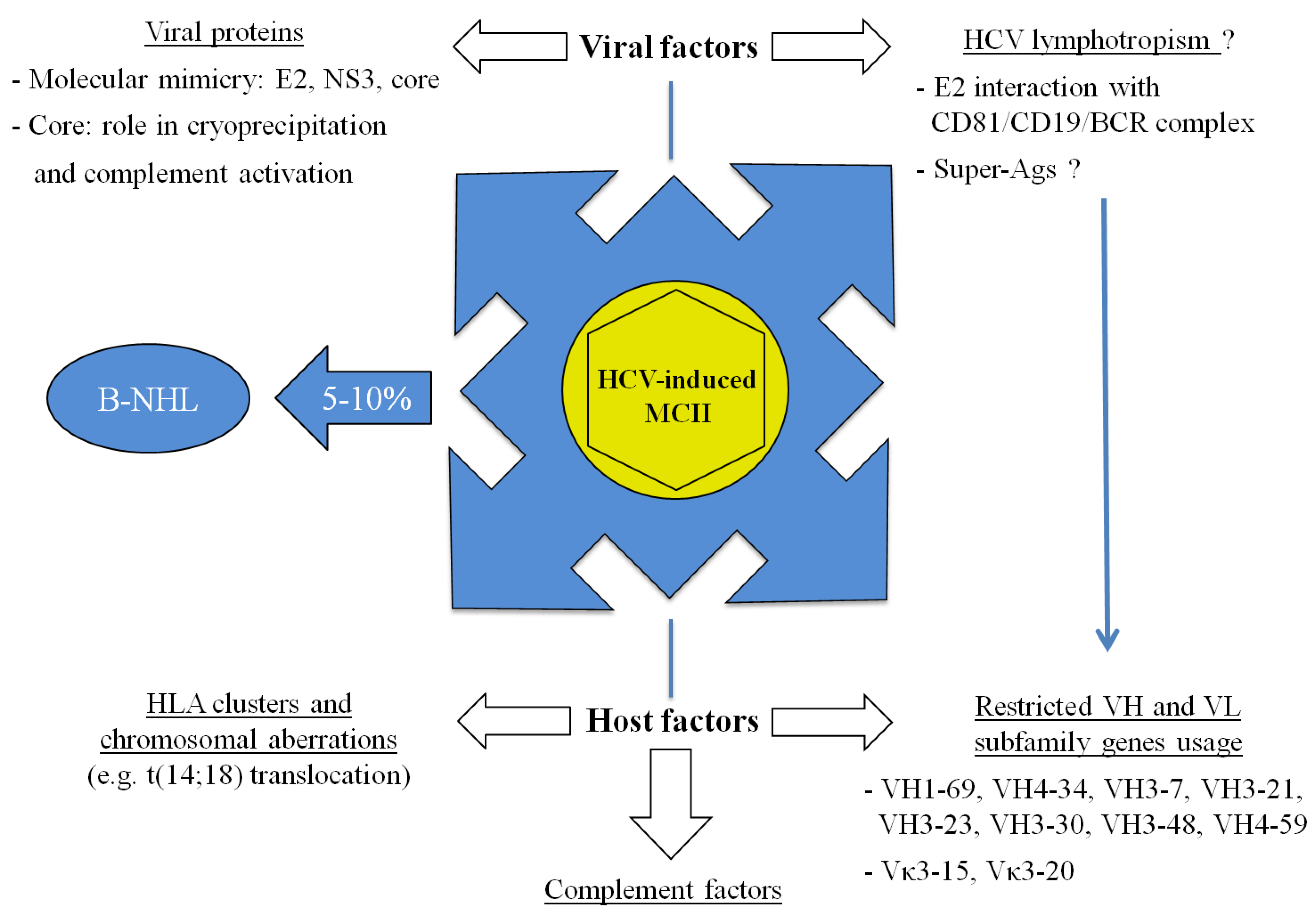
5. Conclusions
Conflict of Interest
References
- Shepard, C.W.; Finelli, L.; Alter, M.J. Global epidemiology of hepatitis c virus infection. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2005, 5, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galossi, A.; Guarisco, R.; Bellis, L.; Puoti, C. Extrahepatic manifestations of chronic hcv infection. J. Gastrointestin. Liver Dis. 2007, 16, 65–73. [Google Scholar]
- Agnello, V. The aetiology of mixed cryoglobulinaemia associated with hepatitis c virus infection. Scand. J. Immunol. 1995, 42, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadoun, D.; Resche-Rigon, M.; Thibault, V.; Piette, J.C.; Cacoub, P. Antiviral therapy for hepatitis c virus-associated mixed cryoglobulinemia vasculitis: A long-term followup study. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 3696–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassilopoulos, D.; Calabrese, L.H. Hepatitis c virus infection and vasculitis: Implications of antiviral and immunosuppressive therapies. Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 46, 585–597. [Google Scholar]
- Donada, C.; Crucitti, A.; Donadon, V.; Tommasi, L.; Zanette, G.; Crovatto, M.; Santini, G.F.; Chemello, L.; Alberti, A. Systemic manifestations and liver disease in patients with chronic hepatitis c and type ii or iii mixed cryoglobulinaemia. J. Viral Hepat. 1998, 5, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcucci, F.; Mele, A. Hepatitis viruses and non-hodgkin lymphoma: Epidemiology, mechanisms of tumorigenesis, and therapeutic opportunities. Blood 2011, 117, 1792–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shihabi, Z.K. Cryoglobulins: An important but neglected clinical test. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2006, 36, 395–408. [Google Scholar]
- Cacoub, P.; Costedoat-Chalumeau, N.; Lidove, O.; Alric, L. Cryoglobulinemia vasculitis. Curr Opin. Rheumatol. 2002, 14, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viganò, M.; Lampertico, P.; Rumi, M.G.; Folli, C.; Maggioni, L.; Morabito, A.; Del Ninno, E.; Cicardi, M.; Colombo, M. Natural history and clinical impact of cryoglobulins in chronic hepatitis c: 10-year prospective study of 343 patients. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 835–842. [Google Scholar]
- Kayali, Z.; Buckwold, V.E.; Zimmerman, B.; Schmidt, W.N. Hepatitis c, cryoglobulinemia, and cirrhosis: A meta-analysis. Hepatology 2002, 36, 978–985. [Google Scholar]
- Monti, G.; Galli, M.; Invernizzi, F.; Pioltelli, P.; Saccardo, F.; Monteverde, A.; Pietrogrande, M.; Renoldi, P.; Bombardieri, S.; Bordin, G.; et al. Cryoglobulinaemias: A multi-centre study of the early clinical and laboratory manifestations of primary and secondary disease. Gisc – italian group for the study of cryoglobulinaemias. QJM 1995, 88, 115–126. [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura, Y.; Ikeda, K.; Arase, Y.; Yatsuji, H.; Sezaki, H.; Hosaka, T.; Akuta, N.; Kobayashi, M.; Suzuki, F.; Suzuki, Y.; et al. Viral elimination reduces incidence of malignant lymphoma in patients with hepatitis c. Am. J. Med. 2007, 120, 1034–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Invernizzi, F.; Galli, M.; Serino, G.; Monti, G.; Meroni, P.L.; Granatieri, C.; Zanussi, C. Secondary and essential cryoglobulinemias. Frequency, nosological classification, and long-term follow-up. Acta Haematol. 1983, 70, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohsawa, M.; Shingu, N.; Miwa, H.; Yoshihara, H.; Kubo, M.; Tsukuma, H.; Teshima, H.; Hashimoto, M.; Aozasa, K. Risk of non-hodgkin's lymphoma in patients with hepatitis c virus infection. Int. J. Cancer 1999, 80, 237–239. [Google Scholar]
- Giordano, T.P.; Henderson, L.; Landgren, O.; Chiao, E.Y.; Kramer, J.R.; El-Serag, H.; Engels, E.A. Risk of non-hodgkin lymphoma and lymphoproliferative precursor diseases in us veterans with hepatitis c virus. JAMA 2007, 297, 2010–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sautto, G.; Mancini, N.; Solforosi, L.; Diotti, R.A.; Clementi, M.; Burioni, R. Hcv proteins and immunoglobulin variable gene (igv) subfamilies in hcv-induced type ii mixed cryoglobulinemia: A concurrent pathogenetic role. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 2012, 705013. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, B.; Myers, G.; Howard, C.; Brettin, T.; Bukh, J.; Gaschen, B.; Gojobori, T.; Maertens, G.; Mizokami, M.; Nainan, O.; et al. Classification, nomenclature, and database development for hepatitis c virus (hcv) and related viruses: Proposals for standardization. International committee on virus taxonomy. Arch. Virol. 143, 1998; 2493–2503. [Google Scholar]
- Choo, Q.L.; Richman, K.H.; Han, J.H.; Berger, K.; Lee, C.; Dong, C.; Gallegos, C.; Coit, D.; Medina-Selby, R.; Barr, P.J.; et al. Genetic organization and diversity of the hepatitis c virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 1991, 88, 2451–2455. [Google Scholar]
- Ashfaq, U.A.; Javed, T.; Rehman, S.; Nawaz, Z.; Riazuddin, S. An overview of hcv molecular biology, replication and immune responses. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 161. [Google Scholar]
- Koutsoudakis, G.; Kaul, A.; Steinmann, E.; Kallis, S.; Lohmann, V.; Pietschmann, T.; Bartenschlager, R. Characterization of the early steps of hepatitis c virus infection by using luciferase reporter viruses. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 5308–5320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, H.; Schafer, C.; Adah, M.I.; Zhang, F.; Linhardt, R.J.; Toyoda, H.; Kinoshita-Toyoda, A.; Toida, T.; Van Kuppevelt, T.H.; Depla, E.; et al. Cellular binding of hepatitis c virus envelope glycoprotein e2 requires cell surface heparan sulfate. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 41003–41012. [Google Scholar]
- Dubuisson, J.; Hsu, H.H.; Cheung, R.C.; Greenberg, H.B.; Russell, D.G.; Rice, C.M. Formation and intracellular localization of hepatitis c virus envelope glycoprotein complexes expressed by recombinant vaccinia and sindbis viruses. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 6147–6160. [Google Scholar]
- Agnello, V.; Abel, G.; Elfahal, M.; Knight, G.B.; Zhang, Q.X. Hepatitis c virus and other flaviviridae viruses enter cells via low density lipoprotein receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 1999, 96, 12766–12771. [Google Scholar]
- Molina, S.; Castet, V.; Fournier-Wirth, C.; Pichard-Garcia, L.; Avner, R.; Harats, D.; Roitelman, J.; Barbaras, R.; Graber, P.; Ghersa, P. The low-density lipoprotein receptor plays a role in the infection of primary human hepatocytes by hepatitis c virus. J. Hepatol. 2007, 46, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarselli, E.; Ansuini, H.; Cerino, R.; Roccasecca, R.M.; Acali, S.; Filocamo, G.; Traboni, C.; Nicosia, A.; Cortese, R.; Vitelli, A. The human scavenger receptor class b type i is a novel candidate receptor for the hepatitis c virus. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 5017–5025. [Google Scholar]
- Pileri, P.; Uematsu, Y.; Campagnoli, S.; Galli, G.; Falugi, F.; Petracca, R.; Weiner, A.J.; Houghton, M.; Rosa, D.; Grandi, G.; et al. Binding of hepatitis c virus to cd81. Science 1998, 282, 938–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.J.; von Hahn, T.; Tscherne, D.M.; Syder, A.J.; Panis, M.; Wolk, B.; Hatziioannou, T.; McKeating, J.A.; Bieniasz, P.D.; Rice, C.M. Claudin-1 is a hepatitis c virus co-receptor required for a late step in entry. Nature 2007, 446, 801–805. [Google Scholar]
- Ploss, A.; Evans, M.J.; Gaysinskaya, V.A.; Panis, M.; You, H.; de Jong, Y.P.; Rice, C.M. Human occludin is a hepatitis c virus entry factor required for infection of mouse cells. Nature 2009, 457, 882–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedicto, I.; Molina-Jimenez, F.; Bartosch, B.; Cosset, F.L.; Lavillette, D.; Prieto, J.; Moreno-Otero, R.; Valenzuela-Fernandez, A.; Aldabe, R.; Lopez-Cabrera, M.; et al. The tight junction-associated protein occludin is required for a postbinding step in hepatitis c virus entry and infection. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 8012–8020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Yang, W.; Shen, L.; Turner, J.R.; Coyne, C.B.; Wang, T. Tight junction proteins claudin-1 and occludin control hepatitis c virus entry and are downregulated during infection to prevent superinfection. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 2011–2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sainz, B., Jr.; Barretto, N.; Martin, D.N.; Hiraga, N.; Imamura, M.; Hussain, S.; Marsh, K.A.; Yu, X.; Chayama, K.; Alrefai, W.A.; et al. Identification of the niemann-pick c1-like 1 cholesterol absorption receptor as a new hepatitis c virus entry factor. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 281–285. [Google Scholar]
- Burioni, R.; Plaisant, P.; Manzin, A.; Rosa, D.; Delli Carri, V.; Bugli, F.; Solforosi, L.; Abrignani, S.; Varaldo, P.E.; Fadda, G.; et al. Dissection of human humoral immune response against hepatitis c virus e2 glycoprotein by repertoire cloning and generation of recombinant fab fragments. Hepatology 1998, 28, 810–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burioni, R.; Perotti, M.; Mancini, N.; Clementi, M. Perspectives for the utilization of neutralizing human monoclonal antibodies as anti-hcv drugs. J. Hepatol. 2008, 49, 299–300. [Google Scholar]
- Mancini, N.; Diotti, R.A.; Perotti, M.; Sautto, G.; Clementi, N.; Nitti, G.; Patel, A.H.; Ball, J.K.; Clementi, M.; Burioni, R. Hepatitis c virus (hcv) infection may elicit neutralizing antibodies targeting epitopes conserved in all viral genotypes. PLoS One 2009, 4, e8254. [Google Scholar]
- Mancini, N.; Sautto, G.; Clementi, N.; Diotti, R.A.; Criscuolo, E.; Castelli, M.; Solforosi, L.; Clementi, M.; Burioni, R. Neutralization interfering antibodies: A “novel” example of humoral immune dysfunction facilitating viral escape? Viruses 2012, 4, 1731–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sautto, G.; Mancini, N.; Diotti, R.A.; Solforosi, L.; Clementi, M.; Burioni, R. Anti-hepatitis c virus e2 (hcv/e2) glycoprotein monoclonal antibodies and neutralization interference. Antiviral Res. 2012, 96, 82–89. [Google Scholar]
- Burioni, R.; Williamson, R.A.; Sanna, P.P.; Bloom, F.E.; Burton, D.R. Recombinant human fab to glycoprotein d neutralizes infectivity and prevents cell-to-cell transmission of herpes simplex viruses 1 and 2 in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 1994, 91, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burioni, R.; Bugli, F.; Mancini, N.; Rosa, D.; Di Campli, C.; Moroncini, G.; Manzin, A.; Abrignani, S.; Varaldo, P.E.; Clementi, M.; et al. Nonneutralizing human antibody fragments against hepatitis c virus e2 glycoprotein modulate neutralization of binding activity of human recombinant fabs. Virology 2001, 288, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zignego, A.L.; Ferri, C.; Giannini, C.; Monti, M.; La Civita, L.; Careccia, G.; Longombardo, G.; Lombardini, F.; Bombardieri, S.; Gentilini, P. Hepatitis c virus genotype analysis in patients with type ii mixed cryoglobulinemia. Ann. Intern. Med. 1996, 124, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos-Casals, M.; Forns, X.; Brito-Zeron, P.; Vargas, A.; Ruiz, M.; Laguno, M.; Yague, J.; Sanchez-Tapias, J.M.; Gatell, J.M.; Font, J. Cryoglobulinaemia associated with hepatitis c virus: Influence of hcv genotypes, hcv-rna viraemia and hiv coinfection. J. Viral. Hepat. 2007, 14, 736–742. [Google Scholar]
- Crovatto, M.; Ceselli, S.; Mazzaro, C.; Modolo, M.L.; Martelli, P.; Mazzi, G.; Pozzato, G.; Giannini, F.; Barbisin, M.; Chiarotto, B.; et al. Hcv genotypes and cryoglobulinemia. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 1995, 13 Suppl 13, S79–S82. [Google Scholar]
- Sinico, R.A.; Ribero, M.L.; Fornasieri, A.; Renoldi, P.; Zhou, J.; Fasola, M.; Portera, G.; Arrigo, G.; Gibelli, A.; D'Amico, G.; et al. Hepatitis c virus genotype in patients with essential mixed cryoglobulinaemia. QJM 1995, 88, 805–810. [Google Scholar]
- Zehender, G.; de Maddalena, C.; Monti, G.; Ballare, M.; Saccardo, F.; Piconi, S.; Invernizzi, F.; Monteverde, A.; Galli, M. Hcv genotypes in bone marrow and peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with mixed cryoglobulinemia. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 1995, 13 Suppl 13, S87–S90. [Google Scholar]
- Monteverde, A.; Ballare, M.; Pileri, S. Hepatic lymphoid aggregates in chronic hepatitis c and mixed cryoglobulinemia. Springer Semin. Immunopathol. 1997, 19, 99–110. [Google Scholar]
- Sansonno, D.; De Vita, S.; Iacobelli, A.R.; Cornacchiulo, V.; Boiocchi, M.; Dammacco, F. Clonal analysis of intrahepatic b cells from hcv-infected patients with and without mixed cryoglobulinemia. J. Immunol. 1998, 160, 3594–3601. [Google Scholar]
- Knight, G.B.; Gao, L.; Gragnani, L.; Elfahal, M.M.; De Rosa, F.G.; Gordon, F.D.; Agnello, V. Detection of wa b cells in hepatitis c virus infection: A potential prognostic marker for cryoglobulinemic vasculitis and b cell malignancies. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 2152–2159. [Google Scholar]
- Racanelli, V.; Sansonno, D.; Piccoli, C.; D'Amore, F.P.; Tucci, F.A.; Dammacco, F. Molecular characterization of b cell clonal expansions in the liver of chronically hepatitis c virus-infected patients. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Sansonno, D.; Lauletta, G.; Nisi, L.; Gatti, P.; Pesola, F.; Pansini, N.; Dammacco, F. Non-enveloped hcv core protein as constitutive antigen of cold-precipitable immune complexes in type ii mixed cryoglobulinaemia. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2003, 133, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrielli, A.; Zhang, Z.X.; Cherubini, G.; Candela, M.; Savoldi, S.; Manzin, A.; Clementi, M.; Amoroso, A.; Sallberg, M. Differential humoral immune response against hepatitis c virus antigenic synthetic peptides in infected patients with and without mixed cryoglobulinaemia. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1996, 105, 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- Gorevic, P.D. Rheumatoid factor, complement, and mixed cryoglobulinemia. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 2012, 439018. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, T.; Lau, J.Y.; Mizokami, M.; Orito, E.; Tanaka, E.; Kiyosawa, K.; Yasui, K.; Ohta, Y.; Hasegawa, A.; Tanaka, S.; et al. Simple fluorescent enzyme immunoassay for detection and quantification of hepatitis c viremia. J. Hepatol. 1995, 23, 742–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzin, A.; Solforosi, L.; Candela, M.; Cherubini, G.; Piccinini, G.; Brugia, M.; Gabrielli, A.; Clementi, M. Hepatitis c virus infection and mixed cryoglobulinaemia: Assessment of hcv rna copy numbers in supernatant, cryoprecipitate and non-liver cells. J. Viral Hepat. 1996, 3, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansonno, D.; Dammacco, F. Hepatitis c virus, cryoglobulinaemia, and vasculitis: Immune complex relations. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2005, 5, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghebrehiwet, B.; Peerschke, E.I. Structure and function of gc1q-r: A multiligand binding cellular protein. Immunobiology 1998, 199, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansonno, D.; Tucci, F.A.; Ghebrehiwet, B.; Lauletta, G.; Peerschke, E.I.; Conteduca, V.; Russi, S.; Gatti, P.; Sansonno, L.; Dammacco, F. Role of the receptor for the globular domain of c1q protein in the pathogenesis of hepatitis c virus-related cryoglobulin vascular damage. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 6013–6020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, R.B.; Meyer, K.; Ray, R. Suppression of apoptotic cell death by hepatitis c virus core protein. Virology 1996, 226, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, T.; Shibuya, K.; Yasui, K.; Mitamura, K.; Ueda, S. Expression of hepatitis c virus core protein associated with malignant lymphoma in transgenic mice. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2003, 26, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canducci, F.; Saita, D.; Foglieni, C.; Piscopiello, M.R.; Chiesa, R.; Colombo, A.; Cianflone, D.; Maseri, A.; Clementi, M.; Burioni, R. Cross-reacting antibacterial auto-antibodies are produced within coronary atherosclerotic plaques of acute coronary syndrome patients. PLoS One 2012, 7, e42283. [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone, M.B. Molecular mimicry and immune-mediated diseases. FASEB J. 1998, 12, 1255–1265. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.W.; Rocheleau, L.; Larke, B.; Chui, L.; Lee, B.; Ma, M.; Liu, S.; Omlin, T.; Pelchat, M.; Brown, E.G. Immunoglobulin mimicry by hepatitis c virus envelope protein e2. Virology 2005, 332, 538–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondelli, M.U.; Cerino, A.; Segagni, L.; Meola, A.; Cividini, A.; Silini, E.; Nicosia, A. Hypervariable region 1 of hepatitis c virus: Immunological decoy or biologically relevant domain? Antiviral Res. 2001, 52, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martell, M.; Esteban, J.I.; Quer, J.; Vargas, V.; Esteban, R.; Guardia, J.; Gomez, J. Dynamic behavior of hepatitis c virus quasispecies in patients undergoing orthotopic liver transplantation. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 3425–3436. [Google Scholar]
- Lawal, Z.; Petrik, J.; Wong, V.S.; Alexander, G.J.; Allain, J.P. Hepatitis c virus genomic variability in untreated and immunosuppressed patients. Virology 1997, 228, 107–111. [Google Scholar]
- Ndifon, W.; Wingreen, N.S.; Levin, S.A. Differential neutralization efficiency of hemagglutinin epitopes, antibody interference, and the design of influenza vaccines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 2009, 106, 8701–8706. [Google Scholar]
- Clementi, N.; Mancini, N.; Solforosi, L.; Castelli, M.; Clementi, M.; Burioni, R. Phage display-based strategies for cloning and optimization of monoclonal antibodies directed against human pathogens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 8273–8292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, P.K.; Hazari, S.; Poat, B.; Gunduz, F.; Prabhu, R.; Liu, G.; Burioni, R.; Clementi, M.; Garry, R.F.; Dash, S. Intracytoplasmic stable expression of igg1 antibody targeting ns3 helicase inhibits replication of highly efficient hepatitis c virus 2a clone. Virol. J. 2010, 7, 118. [Google Scholar]
- Corper, A.L.; Sohi, M.K.; Bonagura, V.R.; Steinitz, M.; Jefferis, R.; Feinstein, A.; Beale, D.; Taussig, M.J.; Sutton, B.J. Structure of human igm rheumatoid factor fab bound to its autoantigen igg fc reveals a novel topology of antibody-antigen interaction. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1997, 4, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, K.N. Molecular characterization of cold agglutinins. Transfus. Sci. 2000, 22, 113–119. [Google Scholar]
- Potter, K.N.; Hobby, P.; Klijn, S.; Stevenson, F.K.; Sutton, B.J. Evidence for involvement of a hydrophobic patch in framework region 1 of human v4-34-encoded igs in recognition of the red blood cell i antigen. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 3777–3782. [Google Scholar]
- Ferri, S.; Dal Pero, F.; Bortoletto, G.; Bianchi, F.B.; Lenzi, M.; Alberti, A.; Gerotto, M. Detailed analysis of the e2-igm complex in hepatitis c-related type ii mixed cryoglobulinaemia. J. Viral Hepat. 2006, 13, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, E.R.; Chan, C.H.; Hadlock, K.G.; Foung, S.K.; Flint, M.; Levy, S. The b-cell receptor of a hepatitis c virus (hcv)-associated non-hodgkin lymphoma binds the viral e2 envelope protein, implicating hcv in lymphomagenesis. Blood 2001, 98, 3745–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domiati-Saad, R.; Attrep, J.F.; Brezinschek, H.P.; Cherrie, A.H.; Karp, D.R.; Lipsky, P.E. Staphylococcal enterotoxin d functions as a human b cell superantigen by rescuing vh4-expressing b cells from apoptosis. J. Immunol. 1996, 156, 3608–3620. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Z.Q.; Nguyen, D.T.; Hiotellis, A.I.; Hahn, Y.S. Hepatitis c virus core protein inhibits human t lymphocyte responses by a complement-dependent regulatory pathway. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 5264–5272. [Google Scholar]
- Zignego, A.L.; Macchia, D.; Monti, M.; Thiers, V.; Mazzetti, M.; Foschi, M.; Maggi, E.; Romagnani, S.; Gentilini, P.; Brechot, C. Infection of peripheral mononuclear blood cells by hepatitis c virus. J. Hepatol. 1992, 15, 382–386. [Google Scholar]
- Valli, M.B.; Crema, A.; Lanzilli, G.; Serafino, A.; Bertolini, L.; Ravagnan, G.; Ponzetto, A.; Menzo, S.; Clementi, M.; Carloni, G. Molecular and cellular determinants of cell-to-cell transmission of hcv in vitro. J. Med. Virol. 2007, 79, 1491–1499. [Google Scholar]
- Sung, V.M.; Shimodaira, S.; Doughty, A.L.; Picchio, G.R.; Can, H.; Yen, T.S.; Lindsay, K.L.; Levine, A.M.; Lai, M.M. Establishment of b-cell lymphoma cell lines persistently infected with hepatitis c virus in vivo and in vitro: The apoptotic effects of virus infection. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 2134–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navas, M.C.; Fuchs, A.; Schvoerer, E.; Bohbot, A.; Aubertin, A.M.; Stoll-Keller, F. Dendritic cell susceptibility to hepatitis c virus genotype 1 infection. J. Med. Virol. 2002, 67, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardin, F.; Tobler, L.; Walsh, I.; Williams, J.D.; Busch, M.; Delwart, E. Clearance of hepatitis c virus rna from the peripheral blood mononuclear cells of blood donors who spontaneously or therapeutically control their plasma viremia. Hepatology 2008, 47, 1446–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, M.; Kusunoki, H.; Mochida, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Mizuochi, T. Hcv infection and b-cell lymphomagenesis. Adv. Hematol. 2011, 2011, 835314. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, T.N.; Michalak, T.I. Occult persistence and lymphotropism of hepatitis c virus infection. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 2789–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machida, K.; Kondo, Y.; Huang, J.Y.; Chen, Y.C.; Cheng, K.T.; Keck, Z.; Foung, S.; Dubuisson, J.; Sung, V.M.; Lai, M.M. Hepatitis c virus (hcv)-induced immunoglobulin hypermutation reduces the affinity and neutralizing activities of antibodies against hcv envelope protein. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 6711–6720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau, D.A.; Saadoun, D.; Calabrese, L.H.; Cacoub, P. The pathophysiology of hcv induced b-cell clonal disorders. Autoimmun. Rev. 2007, 6, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machida, K.; Cheng, K.T.; Pavio, N.; Sung, V.M.; Lai, M.M. Hepatitis c virus e2-cd81 interaction induces hypermutation of the immunoglobulin gene in b cells. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 8079–8089. [Google Scholar]
- De Re, V.; De Vita, S.; Marzotto, A.; Rupolo, M.; Gloghini, A.; Pivetta, B.; Gasparotto, D.; Carbone, A.; Boiocchi, M. Sequence analysis of the immunoglobulin antigen receptor of hepatitis c virus-associated non-hodgkin lymphomas suggests that the malignant cells are derived from the rheumatoid factor-producing cells that occur mainly in type ii cryoglobulinemia. Blood 2000, 96, 3578–3584. [Google Scholar]
- Thomssen, R.; Bonk, S.; Thiele, A. Density heterogeneities of hepatitis c virus in human sera due to the binding of beta-lipoproteins and immunoglobulins. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 1993, 182, 329–334. [Google Scholar]
- Silverman, G.J. B cell superantigens: Possible roles in immunodeficiency and autoimmunity. Semin. Immunol. 1998, 10, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karray, S.; Juompan, L.; Maroun, R.C.; Isenberg, D.; Silverman, G.J.; Zouali, M. Structural basis of the gp120 superantigen-binding site on human immunoglobulins. J. Immunol. 1998, 161, 6681–6688. [Google Scholar]
- Graille, M.; Stura, E.A.; Corper, A.L.; Sutton, B.J.; Taussig, M.J.; Charbonnier, J.B.; Silverman, G.J. Crystal structure of a staphylococcus aureus protein a domain complexed with the fab fragment of a human igm antibody: Structural basis for recognition of b-cell receptors and superantigen activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 2000, 97, 5399–5404. [Google Scholar]
- Silverman, G.J.; Goodyear, C.S. Confounding b-cell defences: Lessons from a staphylococcal superantigen. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, G.J. Adoptive transfer of a superantigen-induced hole in the repertoire of natural igm-secreting cells. Cell Immunol. 2001, 209, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Re, V.; Simula, M.P.; Pavan, A.; Garziera, M.; Marin, D.; Dolcetti, R.; de Vita, S.; Sansonno, D.; Geremia, S.; Toffoli, G. Characterization of antibodies directed against the immunoglobulin light kappa chain variable chain region (vk) of hepatitis c virus-related type-ii mixed cryoglobulinemia and b-cell proliferations. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1173, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, E.D.; Orloff, M.I.; Dustin, L.B. A flow cytometry-based strategy to identify and express igm from vh1-69+ clonal peripheral b cells. J. Immunol. Methods 2011, 363, 210–220. [Google Scholar]
- Perotti, M.; Ghidoli, N.; Altara, R.; Diotti, R.A.; Clementi, N.; De Marco, D.; Sassi, M.; Clementi, M.; Burioni, R.; Mancini, N. Hepatitis c virus (hcv)-driven stimulation of subfamily-restricted natural igm antibodies in mixed cryoglobulinemia. Autoimmun. Rev. 2008, 7, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazi, C.; Dagklis, A.; Cottini, F.; Scarfo, L.; Bertilaccio, M.T.; Finazzi, R.; Memoli, M.; Ghia, P. Monoclonal b cell lymphocytosis in hepatitis c virus infected individuals. Cytometry B Clin. Cytom. 2010, 78 Suppl 1, S61–S68. [Google Scholar]
- Perotti, M.; Mancini, N.; Diotti, R.A.; Tarr, A.W.; Ball, J.K.; Owsianka, A.; Adair, R.; Patel, A.H.; Clementi, M.; Burioni, R. Identification of a broadly cross-reacting and neutralizing human monoclonal antibody directed against the hepatitis c virus e2 protein. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 1047–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugli, F.; Mancini, N.; Kang, C.Y.; Di Campli, C.; Grieco, A.; Manzin, A.; Gabrielli, A.; Gasbarrini, A.; Fadda, G.; Varaldo, P.E.; et al. Mapping b-cell epitopes of hepatitis c virus e2 glycoprotein using human monoclonal antibodies from phage display libraries. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 9986–9990. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, C.H.; Hadlock, K.G.; Foung, S.K.; Levy, S. V(h)1-69 gene is preferentially used by hepatitis c virus-associated b cell lymphomas and by normal b cells responding to the e2 viral antigen. Blood 2001, 97, 1023–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keck, Z.Y.; Xia, J.; Cai, Z.; Li, T.K.; Owsianka, A.M.; Patel, A.H.; Luo, G.; Foung, S.K. Immunogenic and functional organization of hepatitis c virus (hcv) glycoprotein e2 on infectious hcv virions. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 1043–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marco, D.; Clementi, N.; Mancini, N.; Solforosi, L.; Moreno, G.J.; Sun, X.; Tumpey, T.M.; Gubareva, L.V.; Mishin, V.; Clementi, M.; et al. A non-vh1-69 heterosubtypic neutralizing human monoclonal antibody protects mice against h1n1 and h5n1 viruses. PLoS One 2012, 7, e34415. [Google Scholar]
- Clementi, N.; De Marco, D.; Mancini, N.; Solforosi, L.; Moreno, G.J.; Gubareva, L.V.; Mishin, V.; Di Pietro, A.; Vicenzi, E.; Siccardi, A.G.; et al. A human monoclonal antibody with neutralizing activity against highly divergent influenza subtypes. PLoS One 2011, 6, e28001. [Google Scholar]
- Solforosi, L.; Mancini, N.; Canducci, F.; Clementi, N.; Sautto, G.A.; Diotti, R.A.; Clementi, M.; Burioni, R. A phage display vector optimized for the generation of human antibody combinatorial libraries and the molecular cloning of monoclonal antibody fragments. New Microbiol. 2012, 35, 289–294. [Google Scholar]
- Mancini, N.; Solforosi, L.; Clementi, N.; De Marco, D.; Clementi, M.; Burioni, R. A potential role for monoclonal antibodies in prophylactic and therapeutic treatment of influenza. Antiviral Res. 2011, 92, 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- Burioni, R.; Canducci, F.; Mancini, N.; Clementi, N.; Sassi, M.; De Marco, D.; Diotti, R.A.; Saita, D.; Sampaolo, M.; Sautto, G.; et al. Monoclonal antibodies isolated from human b cells neutralize a broad range of h1 subtype influenza a viruses including swine-origin influenza virus (s-oiv). Virology 2010, 399, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burioni, R.; Canducci, F.; Mancini, N.; Clementi, N.; Sassi, M.; De Marco, D.; Saita, D.; Diotti, R.A.; Sautto, G.; Sampaolo, M.; et al. Molecular cloning of the first human monoclonal antibodies neutralizing with high potency swine-origin influenza a pandemic virus (s-oiv). New Microbiol. 2009, 32, 319–324. [Google Scholar]
- Sui, J.; Hwang, W.C.; Perez, S.; Wei, G.; Aird, D.; Chen, L.M.; Santelli, E.; Stec, B.; Cadwell, G.; Ali, M.; et al. Structural and functional bases for broad-spectrum neutralization of avian and human influenza a viruses. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2009, 16, 265–273. [Google Scholar]
- Burioni, R.; Mancini, N.; De Marco, D.; Clementi, N.; Perotti, M.; Nitti, G.; Sassi, M.; Canducci, F.; Shvela, K.; Bagnarelli, P.; et al. Anti-hiv-1 response elicited in rabbits by anti-idiotype monoclonal antibodies mimicking the cd4-binding site. PLoS One 2008, 3, e3423. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.C.; Venturi, M.; Majeed, S.; Moore, M.J.; Phogat, S.; Zhang, M.Y.; Dimitrov, D.S.; Hendrickson, W.A.; Robinson, J.; Sodroski, J.; et al. Structural basis of tyrosine sulfation and vh-gene usage in antibodies that recognize the hiv type 1 coreceptor-binding site on gp120. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 2004, 101, 2706–2711. [Google Scholar]
- Burioni, R.; Matsuura, Y.; Mancini, N.; Tani, H.; Miyamura, T.; Varaldo, P.E.; Clementi, M. Diverging effects of human recombinant anti-hepatitis c virus (hcv) antibody fragments derived from a single patient on the infectivity of a vesicular stomatitis virus/hcv pseudotype. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 11775–11779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messmer, B.T.; Albesiano, E.; Efremov, D.G.; Ghiotto, F.; Allen, S.L.; Kolitz, J.; Foa, R.; Damle, R.N.; Fais, F.; Messmer, D.; et al. Multiple distinct sets of stereotyped antigen receptors indicate a role for antigen in promoting chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 200, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonari, M.; Caprini, E.; Tedesco, T.; Mazzetta, F.; Tocco, V.; Casato, M.; Russo, G.; Fiorilli, M. Hepatitis c virus drives the unconstrained monoclonal expansion of vh1-69-expressing memory b cells in type ii cryoglobulinemia: A model of infection-driven lymphomagenesis. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 6532–6539. [Google Scholar]
- Messmer, B.T.; Albesiano, E.; Messmer, D.; Chiorazzi, N. The pattern and distribution of immunoglobulin vh gene mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia b cells are consistent with the canonical somatic hypermutation process. Blood 2004, 103, 3490–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, E.D.; Green, R.M.; Marukian, S.; Talal, A.H.; Lake-Bakaar, G.V.; Jacobson, I.M.; Rice, C.M.; Dustin, L.B. Clonal expansion of immunoglobulin m+cd27+ b cells in hcv-associated mixed cryoglobulinemia. Blood 2008, 111, 1344–1356. [Google Scholar]
- Bende, R.J.; Aarts, W.M.; Riedl, R.G.; de Jong, D.; Pals, S.T.; van Noesel, C.J. Among b cell non-hodgkin's lymphomas, malt lymphomas express a unique antibody repertoire with frequent rheumatoid factor reactivity. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 1229–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasca, R.; Vaccari, P.; Luppi, M.; Zucchini, P.; Castelli, I.; Barozzi, P.; Cuoghi, A.; Torelli, G. Immunoglobulin gene mutations and frequent use of vh1-69 and vh4-34 segments in hepatitis c virus-positive and hepatitis c virus-negative nodal marginal zone b-cell lymphoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 159, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackworth-Young, C.G.; Harmer, I.J.; Mageed, R.A. The role of antigen in the selection of the human v3-23 immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region gene. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2003, 134, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanovski, M.; Silvestri, F.; Pozzato, G.; Anand, S.; Mazzaro, C.; Burrone, O.R.; Efremov, D.G. Somatic hypermutation, clonal diversity, and preferential expression of the vh 51p1/vl kv325 immunoglobulin gene combination in hepatitis c virus-associated immunocytomas. Blood 1998, 91, 2433–2442. [Google Scholar]
- Herve, M.; Xu, K.; Ng, Y.S.; Wardemann, H.; Albesiano, E.; Messmer, B.T.; Chiorazzi, N.; Meffre, E. Unmutated and mutated chronic lymphocytic leukemias derive from self-reactive b cell precursors despite expressing different antibody reactivity. J. Clin. Invest. 2005, 115, 1636–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.C.; Catera, R.; Zhang, L.; Didier, S.; Agagnina, B.M.; Damle, R.N.; Kaufman, M.S.; Kolitz, J.E.; Allen, S.L.; Rai, K.R.; et al. Many chronic lymphocytic leukemia antibodies recognize apoptotic cells with exposed nonmuscle myosin heavy chain iia: Implications for patient outcome and cell of origin. Blood 2010, 115, 3907–3915. [Google Scholar]
- Burioni, R.; Mancini, N.; Carletti, S.; Perotti, M.; Grieco, A.; Canducci, F.; Varaldo, P.E.; Clementi, M. Cross-reactive pseudovirus-neutralizing anti-envelope antibodies coexist with antibodies devoid of such activity in persistent hepatitis c virus infection. Virology 2004, 327, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, N.; Clementi, M.; Burioni, R. Natalizumab-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 871–872, author reply 872.. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racanelli, V.; Brunetti, C.; De Re, V.; Caggiari, L.; De Zorzi, M.; Leone, P.; Perosa, F.; Vacca, A.; Dammacco, F. Antibody v(h) repertoire differences between resolving and chronically evolving hepatitis c virus infections. PLoS One 2011, 6, e25606. [Google Scholar]
- Matteucci, C.; Bracci, M.; Barba, G.; Carbonari, M.; Casato, M.; Visentini, M.; Pulsoni, A.; Varasano, E.; Roti, G.; La Starza, R.; et al. Different genomic imbalances in low- and high-grade hcv-related lymphomas. Leukemia 2008, 22, 219–222. [Google Scholar]
- Solé, F.; Salido, M.; Espinet, B.; Garcia, J.L.; Martinez Climent, J.A.; Granada, I.; Hernandez, J.M.; Benet, I.; Piris, M.A.; Mollejo, M.; et al. Splenic marginal zone b-cell lymphomas: Two cytogenetic subtypes, one with gain of 3q and the other with loss of 7q. Haematologica 2001, 86, 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- Gruszka-Westwood, A.M.; Matutes, E.; Coignet, L.J.; Wotherspoon, A.; Catovsky, D. The incidence of trisomy 3 in splenic lymphoma with villous lymphocytes: A study by fish. Br J. Haematol. 1999, 104, 600–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riethmuller, G.; Meltzer, M.; Franklin, E.; Miescher, P.A. Serum complement levels in patients with mixed (igm-igg) cryoglobulinaemia. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1966, 1, 337–339. [Google Scholar]
- Ohsawa, I.; Ohi, H.; Tamano, M.; Endo, M.; Fujita, T.; Satomura, A.; Hidaka, M.; Fuke, Y.; Matsushita, M. Cryoprecipitate of patients with cryoglobulinemic glomerulonephritis contains molecules of the lectin complement pathway. Clin. Immunol. 2001, 101, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roughan, J.E.; Reardon, K.M.; Cogburn, K.E.; Quendler, H.; Pockros, P.J.; Law, M. Chronic hepatitis c virus infection breaks tolerance and drives polyclonal expansion of autoreactive b cells. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2012, 19, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racanelli, V.; Frassanito, M.A.; Leone, P.; Galiano, M.; De Re, V.; Silvestris, F.; Dammacco, F. Antibody production and in vitro behavior of cd27-defined b-cell subsets: Persistent hepatitis c virus infection changes the rules. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 3923–3934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournillier, A.; Freida, D.; Defrance, T.; Merle, P.; Trepo, C.; Inchauspe, G. Analysis of b-lymphocyte differentiation in patients infected with hepatitis c virus. J. Med. Virol. 2004, 72, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsubo, K.; Sata, M.; Kawaguchi, T.; Morishige, S.; Takata, Y.; Oku, E.; Imamura, R.; Seki, R.; Hashiguchi, M.; Osaki, K.; et al. Characterization of the light chain-restricted clonal b cells in peripheral blood of hcv-positive patients. Int. J. Hematol. 2009, 89, 452–459. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis, M.; Rathaus, M.; Amiel, A.; Manor, Y.; Klein, A.; Lishner, M. Monoclonal lymphocyte proliferation and bcl-2 rearrangement in essential mixed cryoglobulinaemia. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 1995, 25, 833–837. [Google Scholar]
- Burioni, R.; Canducci, F.; Saita, D.; Perotti, M.; Mancini, N.; De Marco, D.; Clementi, N.; Chieffo, A.; Denaro, M.; Cianflone, D.; et al. Antigen-driven evolution of b lymphocytes in coronary atherosclerotic plaques. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 2537–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeremski, M.; Petrovic, L.M.; Talal, A.H. The role of chemokines as inflammatory mediators in chronic hepatitis c virus infection. J. Viral Hepat. 2007, 14, 675–687. [Google Scholar]
- De Re, V.; Caggiari, L.; Monti, G.; Libra, M.; Spina, M.; Dolcetti, R.; De Zorzi, M.; Racanelli, V.; Crovatto, M.; Toffoli, G. Hla dr-dq combination associated with the increased risk of developing human hcv positive non-hodgkin's lymphoma is related to the type ii mixed cryoglobulinemia. Tissue Antigens 2010, 75, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacoub, P.; Renou, C.; Kerr, G.; Hue, S.; Rosenthal, E.; Cohen, P.; Kaplanski, G.; Charlotte, F.; Thibault, V.; Ghillani, P.; et al. Influence of hla-dr phenotype on the risk of hepatitis c virus-associated mixed cryoglobulinemia. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44, 2118–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luppi, M.; Grazia Ferrari, M.; Bonaccorsi, G.; Longo, G.; Narni, F.; Barozzi, P.; Marasca, R.; Mussini, C.; Torelli, G. Hepatitis c virus infection in subsets of neoplastic lymphoproliferations not associated with cryoglobulinemia. Leukemia 1996, 10, 351–355. [Google Scholar]
- Ferri, C.; Caracciolo, F.; Zignego, A.L.; La Civita, L.; Monti, M.; Longombardo, G.; Lombardini, F.; Greco, F.; Capochiani, E.; Mazzoni, A.; et al. Hepatitis c virus infection in patients with non-hodgkin's lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 1994, 88, 392–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Sautto, G.; Mancini, N.; Clementi, M.; Burioni, R. Molecular Signatures of Hepatitis C Virus (HCV)-Induced Type II Mixed Cryoglobulinemia (MCII). Viruses 2012, 4, 2924-2944. https://doi.org/10.3390/v4112924
Sautto G, Mancini N, Clementi M, Burioni R. Molecular Signatures of Hepatitis C Virus (HCV)-Induced Type II Mixed Cryoglobulinemia (MCII). Viruses. 2012; 4(11):2924-2944. https://doi.org/10.3390/v4112924
Chicago/Turabian StyleSautto, Giuseppe, Nicasio Mancini, Massimo Clementi, and Roberto Burioni. 2012. "Molecular Signatures of Hepatitis C Virus (HCV)-Induced Type II Mixed Cryoglobulinemia (MCII)" Viruses 4, no. 11: 2924-2944. https://doi.org/10.3390/v4112924
APA StyleSautto, G., Mancini, N., Clementi, M., & Burioni, R. (2012). Molecular Signatures of Hepatitis C Virus (HCV)-Induced Type II Mixed Cryoglobulinemia (MCII). Viruses, 4(11), 2924-2944. https://doi.org/10.3390/v4112924





