Cannabis Use Moderates Methamphetamine- and HIV-Related Inflammation: Evidence from Human Plasma Markers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Measures
2.1.1. Neuromedical and Laboratory Assessments
2.1.2. HIV Disease and Treatment Characteristics
2.1.3. Psychiatric and Substance Use History
2.2. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
3.1.1. HIV Treatment History and Indices of Severity
3.1.2. Cannabis Use
3.1.3. Methamphetamine Use
3.2. Modeled Associations with Plasma Biomarkers
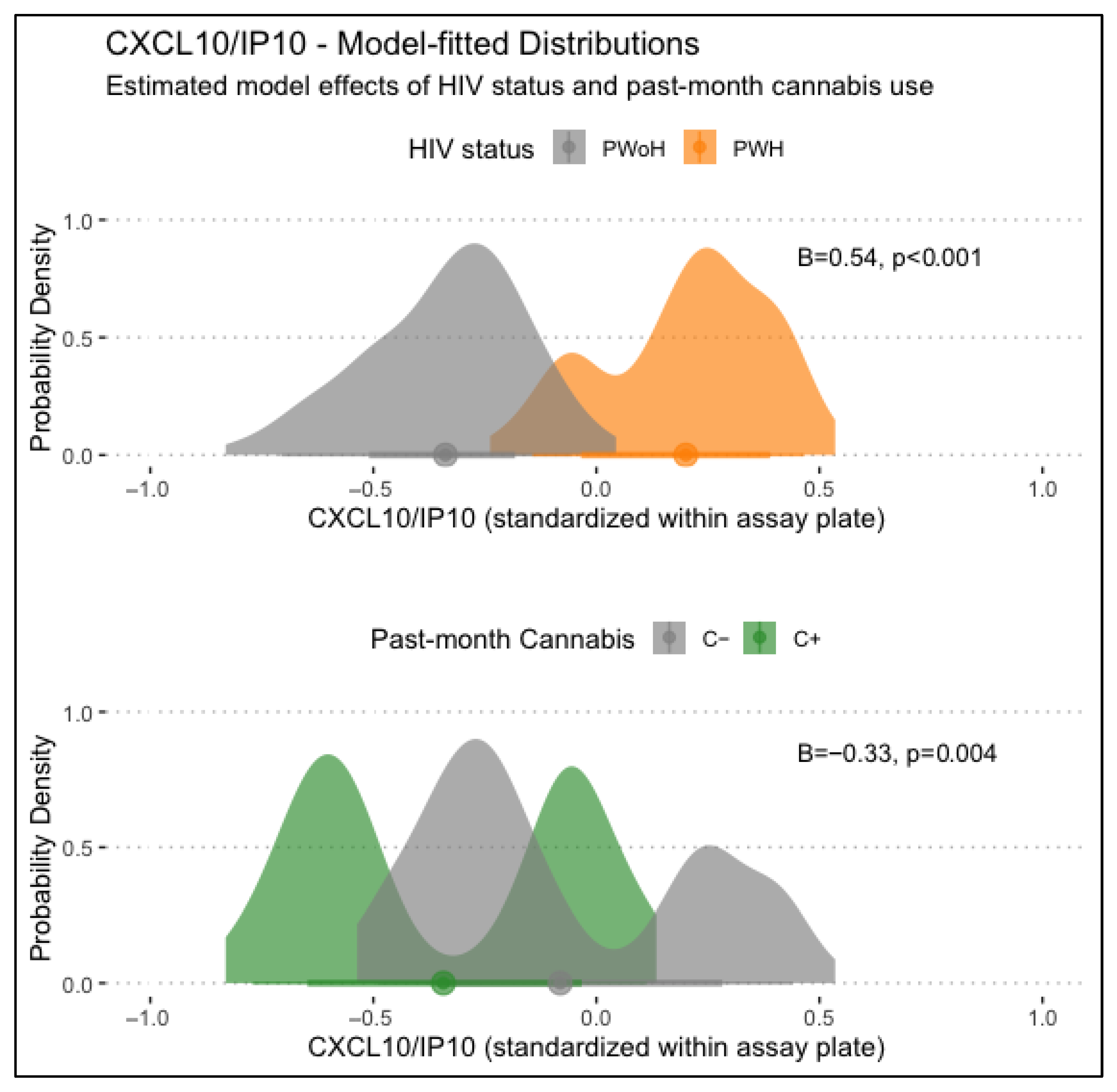
3.2.1. CXCL10/IP-10
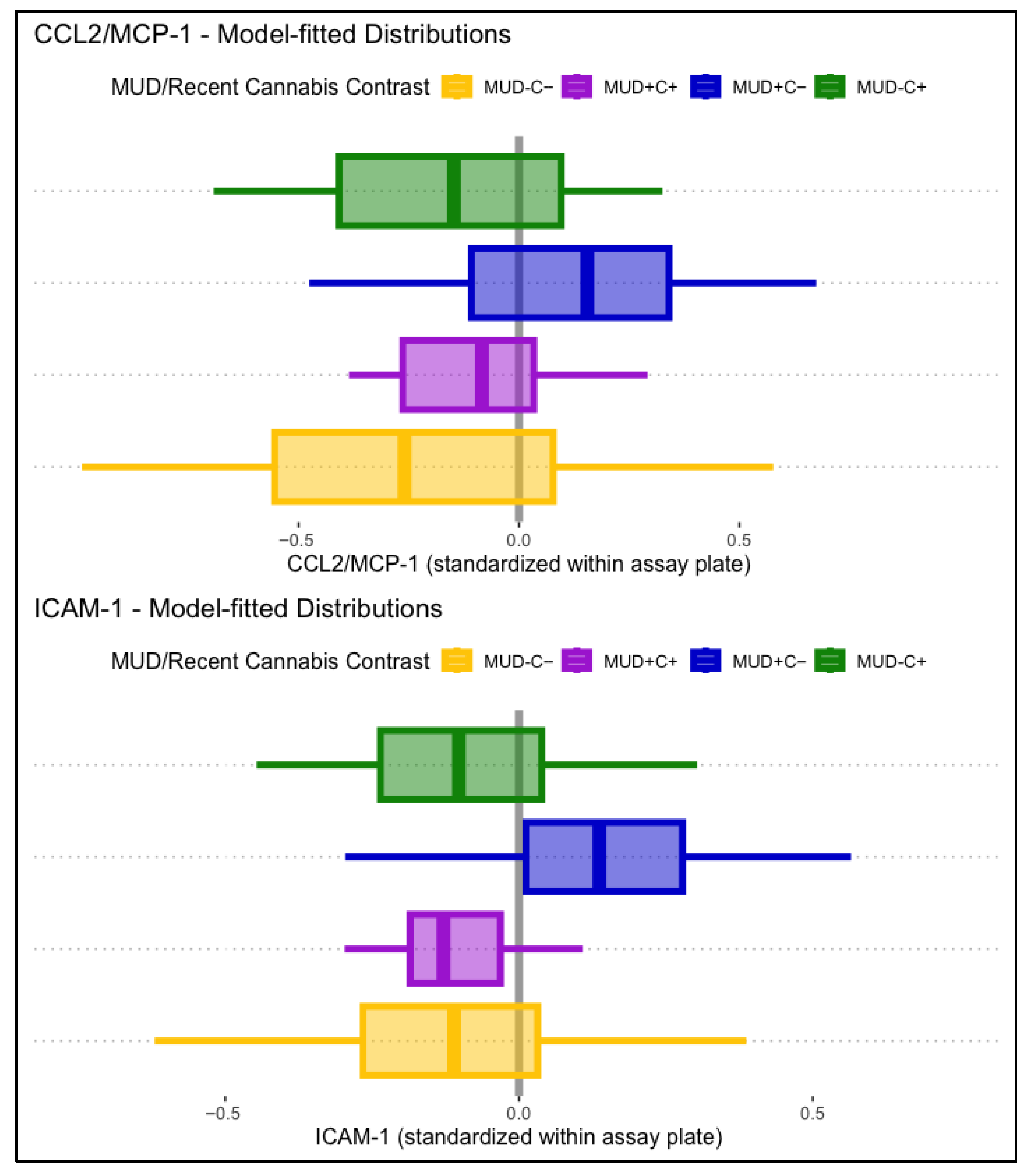
3.2.2. CCL2/MCP-1
3.2.3. ICAM-1
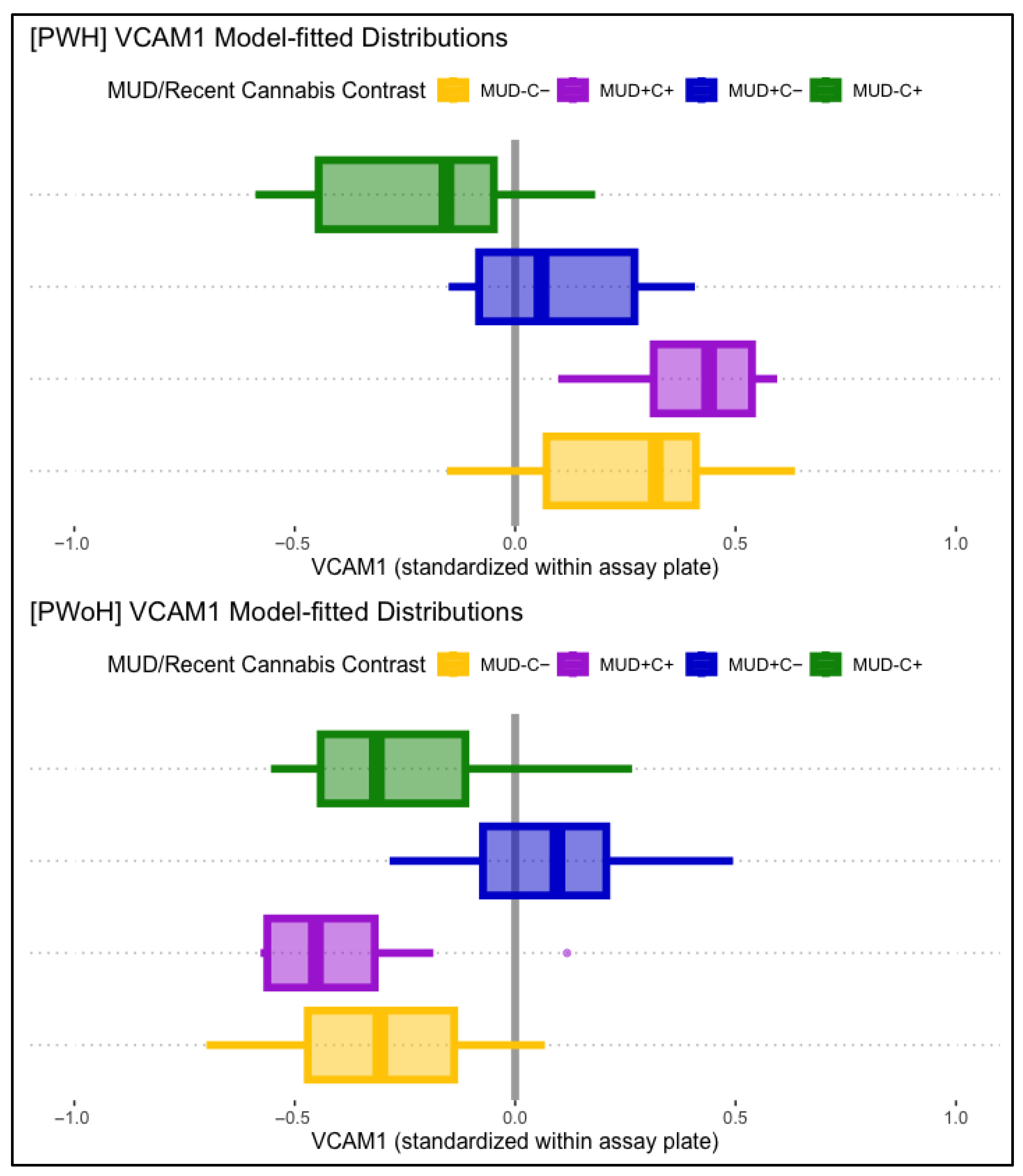
3.2.4. VCAM-1
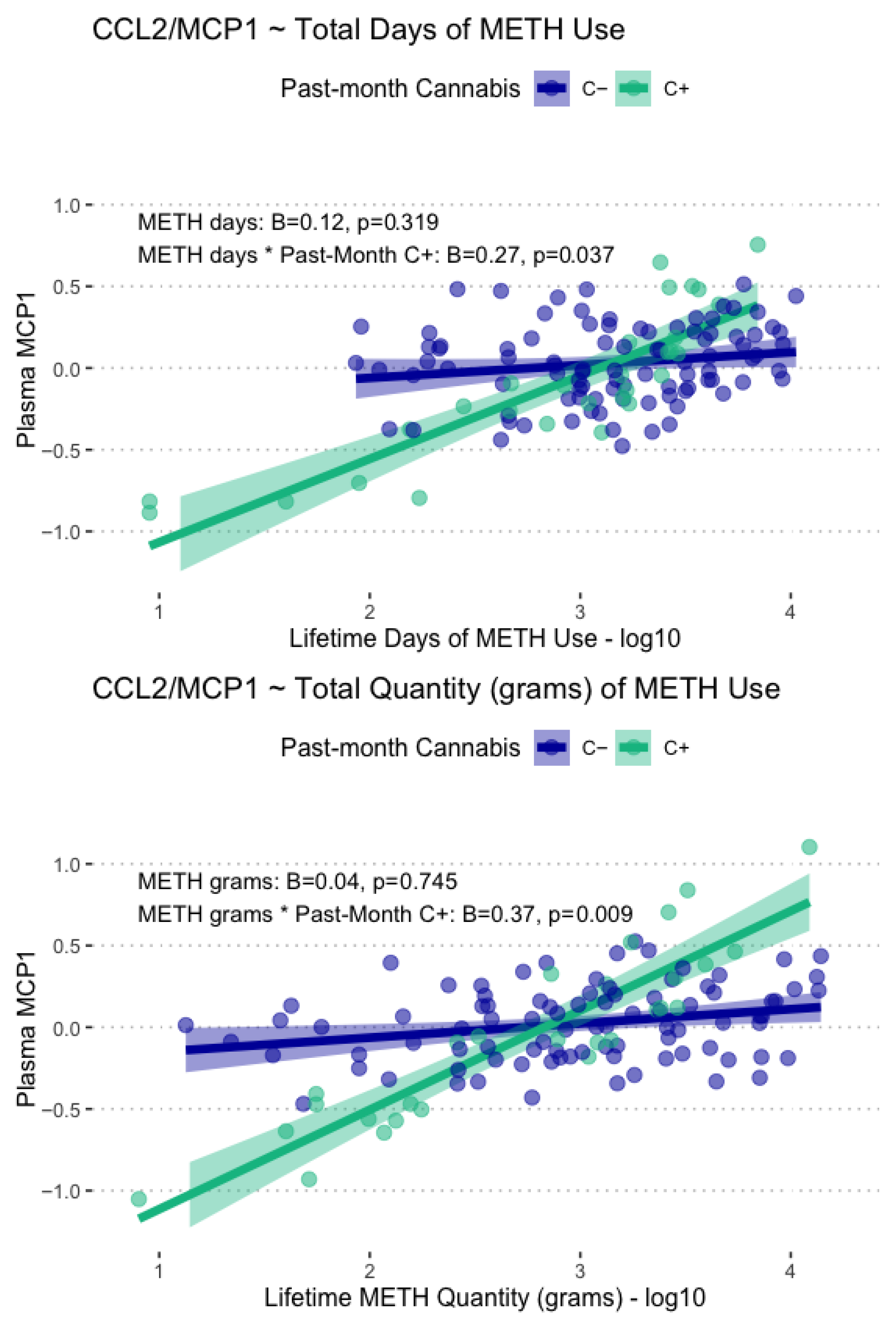
3.3. Associations Between Lifetime Cannabis and METH Use Characteristics and Plasma Biomarkers
4. Discussion
4.1. CXCL10/IP-10
4.2. CCL2/MCP-1
4.3. VCAM-1
4.4. ICAM-1
4.5. Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AIDS | Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome |
| ART | Antiretroviral (drug) therapy |
| ARV | Antiretroviral (drug) |
| CBD | Cannabidiol |
| CCL2/MCP-1 | Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2/Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein 1 |
| CXCL10/IP-10 | C-X-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 10/ Interferon Gamma-Induced Protein 10 |
| DSM-IV | American Psychiatric Association Diagnostic Statistical Manual IV |
| ICAM-1 | Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 1 |
| METH | Methamphetamine |
| MUD | DSM-IV methamphetamine abuse/dependence |
| NSDUH | National Survey on Drug Use and Health |
| PWoH | People without HIV |
| US | United States |
| VCAM-1 | Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule 1 |
| Δ9-THC | Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol |
References
- Tobolski, J.; Sawyer, D.B.; Song, S.J.; Afari, M.E. Cardiovascular Disease Associated with Methamphetamine Use: A Review. Heart Fail. Rev. 2022, 27, 2059–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadet, J.L.; Krasnova, I.N. Molecular Bases of Methamphetamine-Induced Neurodegeneration. In International Review of Neurobiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; Volume 88, pp. 101–119. ISBN 978-0-12-374504-0. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, H.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, T.; Tan, H.; Zhong, N.; Du, J.; Zhao, M. A Research of Methamphetamine Induced Psychosis in 1,430 Individuals with Methamphetamine Use Disorder: Clinical Features and Possible Risk Factors. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerin, A.A.; Bridson, T.; Plapp, H.M.; Bedi, G. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Health, Functional, and Cognitive Outcomes in Young People Who Use Methamphetamine. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2023, 153, 105380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordahl, T.E.; Salo, R.; Leamon, M. Neuropsychological Effects of Chronic Methamphetamine Use on Neurotransmitters and Cognition: A Review. J. Neuropsychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Wan, J.; Meng, J.; Banerjee, S.; Ramakrishnan, S.; Roy, S. Methamphetamine Induces Autophagy as a Pro-Survival Response against Apoptotic Endothelial Cell Death through the Kappa Opioid Receptor. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazari, A.; Zahmatkesh, M.; Mortaz, E.; Hosseinzadeh, S. Effect of Methamphetamine Exposure on the Plasma Levels of Endothelial-Derived Microparticles. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2018, 186, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, S.H.; Potula, R.; Fan, S.; Eidem, T.; Papugani, A.; Reichenbach, N.; Dykstra, H.; Weksler, B.B.; Romero, I.A.; Couraud, P.O.; et al. Methamphetamine Disrupts Blood–Brain Barrier Function by Induction of Oxidative Stress in Brain Endothelial Cells. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2009, 29, 1933–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macur, K.; Ciborowski, P. Immune System and Methamphetamine: Molecular Basis of a Relationship. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2021, 19, 2067–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peerzada, H.; Gandhi, J.A.; Guimaraes, A.J.; Nosanchuk, J.D.; Martinez, L.R. Methamphetamine Administration Modifies Leukocyte Proliferation and Cytokine Production in Murine Tissues. Immunobiology 2013, 218, 1063–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAMSHA Data Tools: Data Analysis System. Crosstab Results: Past-Year METH Use by Past-Year Cannabis Use. National Survey on Drug Use and Health 2002–2019; SAMSHA: Rockville, MD, USA, 2019. Available online: https://datatools.samhsa.gov/das/nsduh/2019/nsduh-2002-2019-ds0001/crosstab?row=MRJYR&column=MTHYR&weight=ANALWC18 (accessed on 17 August 2025).
- Costiniuk, C.T.; Jenabian, M.-A. Cannabinoids and Inflammation: Implications for People Living with HIV. AIDS 2019, 33, 2273–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, J.M.; Iudicello, J.E.; Marcondes, M.C.G.; Morgan, E.E.; Cherner, M.; Ellis, R.J.; Letendre, S.L.; Heaton, R.K.; Grant, I. The Combined Effects of Cannabis, Methamphetamine, and HIV on Neurocognition. Viruses 2023, 15, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, J.M.; Grant, I.; Marcondes, M.C.G.; Morgan, E.E.; Cherner, M.; Ellis, R.J.; Letendre, S.L.; Heaton, R.K.; Iudicello, J.E. Cannabis Use May Attenuate Neurocognitive Performance Deficits Resulting from Methamphetamine Use Disorder. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2024, 30, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, C.L.; Woods, S.P.; Rippeth, J.D.; Gonzalez, R.; Heaton, R.K.; Grant, I.; The HIV Neurobehavioral Research Center (HNRC) Group. Additive Deleterious Effects of Methamphetamine Dependence and Immunosuppression on Neuropsychological Functioning in HIV Infection. AIDS Behav. 2006, 10, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Ernst, T.; Speck, O.; Grob, C.S. Additive Effects of HIV and Chronic Methamphetamine Use on Brain Metabolite Abnormalities. Am. J. Psychiatry 2005, 162, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAMSHA Data Tools: Data Analysis System. Crosstab Results: Past-Year METH Use by Lifetime HIV Diagnosis. National Survey on Drug Use and Health 2023; SAMSHA: Rockville, MD, USA, 2023. Available online: https://datatools.samhsa.gov/das/nsduh/2023/nsduh-2023-ds0001/crosstab?row=METHAMYR&column=HIVAIDSEV&weight=ANALWT2_C (accessed on 17 August 2025).
- Papageorgiou, M.; Raza, A.; Fraser, S.; Nurgali, K.; Apostolopoulos, V. Methamphetamine and Its Immune-Modulating Effects. Maturitas 2019, 121, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAMSHA Data Tools: Data Analysis System. Crosstab Results: Past-Year Cannabis Use by Lifetime HIV Diagnosis. National Survey on Drug Use and Health 2023; SAMSHA: Rockville, MD, USA, 2023. Available online: https://datatools.samhsa.gov/das/nsduh/2023/nsduh-2023-ds0001/crosstab?row=MRJYR&column=HIVAIDSEV&weight=ANALWT2_C (accessed on 17 August 2025).
- Furler, M.D.; Einarson, T.R.; Millson, M.; Walmsley, S.; Bendayan, R. Medicinal and Recreational Marijuana Use by Patients Infected with HIV. AIDS Patient Care STDs 2004, 18, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paterson, D.L.; Swindells, S.; Mohr, J.; Brester, M.; Vergis, E.N.; Squier, C.; Wagener, M.M.; Singh, N. Adherence to Protease Inhibitor Therapy and Outcomes in Patients with HIV Infection. Ann. Intern. Med. 2000, 133, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannheimer, S.B.; Matts, J.; Telzak, E.; Chesney, M.; Child, C.; Wu, A.W.; Friedland, G.; Terry Beirn Community Programs for Clinical Research on AIDS. Quality of Life in HIV-Infected Individuals Receiving Antiretroviral Therapy Is Related to Adherence. AIDS Care 2005, 17, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samji, H.; Cescon, A.; Hogg, R.S.; Modur, S.P.; Althoff, K.N.; Buchacz, K.; Burchell, A.N.; Cohen, M.; Gebo, K.A.; Gill, M.J.; et al. Closing the Gap: Increases in Life Expectancy among Treated HIV-Positive Individuals in the United States and Canada. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeks, S.G.; Lewin, S.R.; Havlir, D.V. The End of AIDS: HIV Infection as a Chronic Disease. Lancet 2013, 382, 1525–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaton, R.K.; Franklin, D.R.; Deutsch, R.; Letendre, S.; Ellis, R.J.; Casaletto, K.; Marquine, M.J.; Woods, S.P.; Vaida, F.; Atkinson, J.H.; et al. Neurocognitive Change in the Era of HIV Combination Antiretroviral Therapy: The Longitudinal CHARTER Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 60, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saloner, R.; Cysique, L.A. HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorders: A Global Perspective. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2017, 23, 860–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeks, S.G. HIV Infection, Inflammation, Immunosenescence, and Aging. Annu. Rev. Med. 2011, 62, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezoh, G.; Crowther, N.J. Deciphering Endothelial Dysfunction in the HIV-Infected Population. In Reviews on Biomarker Studies of Metabolic and Metabolism-Related Disorders; Guest, P.C., Ed.; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 1134, pp. 193–215. ISBN 978-3-030-12667-4. [Google Scholar]
- Neuhaus, J.; Angus, B.; Kowalska, J.D.; Rosa, A.L.; Sampson, J.; Wentworth, D.; Mocroft, A. Risk of All-Cause Mortality Associated with Nonfatal AIDS and Serious Non-AIDS Events among Adults Infected with HIV. AIDS 2010, 24, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinsch, N.; Neuhaus, K.; Esser, S.; Potthoff, A.; Hower, M.; Mostardt, S.; Neumann, A.; Brockmeyer, N.H.; Gelbrich, G.; Erbel, R.; et al. Are HIV Patients Undertreated? Cardiovascular Risk Factors in HIV: Results of the HIV-HEART Study. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2012, 19, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castley, A.; Williams, L.; James, I.; Guelfi, G.; Berry, C.; Nolan, D. Plasma CXCL10, sCD163 and sCD14 Levels Have Distinct Associations with Antiretroviral Treatment and Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chistiakov, D.A.; Orekhov, A.N.; Bobryshev, Y.V. Endothelial Barrier and Its Abnormalities in Cardiovascular Disease. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luciano-Mateo, F.; Cabré, N.; Fernández-Arroyo, S.; Baiges-Gaya, G.; Hernández-Aguilera, A.; Rodríguez-Tomàs, E.; Muñoz-Pinedo, C.; Menéndez, J.A.; Camps, J.; Joven, J. Chemokine C–C Motif Ligand 2 Overexpression Drives Tissue-Specific Metabolic Responses in the Liver and Muscle of Mice. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saika, F.; Kiguchi, N.; Wakida, N.; Kobayashi, D.; Fukazawa, Y.; Matsuzaki, S.; Kishioka, S. Upregulation of CCL7 and CCL2 in Reward System Mediated through Dopamine D1 Receptor Signaling Underlies Methamphetamine-Induced Place Preference in Mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2018, 665, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenbark, A.A.; Meza-Romero, R.; Benedek, G.; Offner, H. A Novel Neurotherapeutic for Multiple Sclerosis, Ischemic Injury, Methamphetamine Addiction, and Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Li, L.; Zhu, P.; Zhang, M.; Hou, L.; Sun, Y.; Liu, X.; Peng, X.; Gu, Y. Chronic Administration of Methamphetamine Promotes Atherosclerosis Formation in ApoE−/− Knockout Mice Fed Normal Diet. Atherosclerosis 2015, 243, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolluru, G.K.; Glawe, J.D.; Pardue, S.; Kasabali, A.; Alam, S.; Rajendran, S.; Cannon, A.L.; Abdullah, C.S.; Traylor, J.G.; Shackelford, R.E.; et al. Methamphetamine Causes Cardiovascular Dysfunction via Cystathionine Gamma Lyase and Hydrogen Sulfide Depletion. Redox Biol. 2022, 57, 102480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftis, J.M.; Choi, D.; Hoffman, W.; Huckans, M.S. Methamphetamine Causes Persistent Immune Dysregulation: A Cross-Species, Translational Report. Neurotox. Res. 2011, 20, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalayasiri, R.; Dadwat, K.; Thika, S.; Sirivichayakul, S.; Maes, M. Methamphetamine (MA) Use and MA-Induced Psychosis Are Associated with Increasing Aberrations in the Compensatory Immunoregulatory System, Interleukin-1α, and CCL5 Levels. Transl. Psychiatry 2023, 13, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.J.; Briones, M.S.; Heinzerling, K.G.; Kalmin, M.M.; Shoptaw, S.J. Ibudilast Attenuates Peripheral Inflammatory Effects of Methamphetamine in Patients with Methamphetamine Use Disorder. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2020, 206, 107776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, R.J.; Wilson, N.; Peterson, S. Cannabis and Inflammation in HIV: A Review of Human and Animal Studies. Viruses 2021, 13, 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manuzak, J.A.; Gott, T.M.; Kirkwood, J.S.; Coronado, E.; Hensley-McBain, T.; Miller, C.; Cheu, R.K.; Collier, A.C.; Funderburg, N.T.; Martin, J.N.; et al. Heavy Cannabis Use Associated with Reduction in Activated and Inflammatory Immune Cell Frequencies in Antiretroviral Therapy–Treated Human Immunodeficiency Virus–Infected Individuals. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 66, 1872–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teichmann, E.; Blessing, E.; Hinz, B. Non-Psychoactive Phytocannabinoids Inhibit Inflammation-Related Changes of Human Coronary Artery Smooth Muscle and Endothelial Cells. Cells 2023, 12, 2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, C.W.-M.; Campbell, L.M.; Sun-Suslow, N.; Hong, S.; Umlauf, A.; Ellis, R.J.; Iudicello, J.E.; Letendre, S.; Marcotte, T.D.; Heaton, R.K.; et al. Daily Cannabis Use Is Associated with Lower CNS Inflammation in People with HIV. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2021, 27, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robins, L.N. The Composite International Diagnostic Interview: An Epidemiologic Instrument Suitable for Use in Conjunction with Different Diagnostic Systems and in Different Cultures. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1988, 45, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, S.M.; Sobell, L.C.; Sobell, M.B.; Leo, G.I. Reliability of the Timeline Followback for Cocaine, Cannabis, and Cigarette Use. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2014, 28, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Hayes, A.F.; Cai, L. Using Heteroskedasticity-Consistent Standard Error Estimators in OLS Regression: An Introduction and Software Implementation. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Sloan, L.; Saxena, D.; Scott, D.A. The Antimicrobial Properties of Cannabis and Cannabis-Derived Compounds and Relevance to CB2-Targeted Neurodegenerative Therapeutics. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Kong, W.; Chambers, C.R.; Yu, D.; Ganea, D.; Tuma, R.F.; Ward, S.J. The Non-Psychoactive Phytocannabinoid Cannabidiol (CBD) Attenuates pro-Inflammatory Mediators, T Cell Infiltration, and Thermal Sensitivity Following Spinal Cord Injury in Mice. Cell. Immunol. 2018, 329, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruhanya, V.; Jacobs, G.B.; Naidoo, S.; Paul, R.H.; Joska, J.A.; Seedat, S.; Nyandoro, G.; Engelbrecht, S.; Glashoff, R.H. Impact of Plasma IP-10/CXCL10 and RANTES/CCL5 Levels on Neurocognitive Function in HIV Treatment-Naive Patients. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2021, 37, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.E.; Ipser, J.C.; Stein, D.J.; Joska, J.A.; Naudé, P.J.W. Peripheral Immune Dysregulation in the ART Era of HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Impairments: A Systematic Review. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2020, 118, 104689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, R.J.; Peterson, S.N.; Li, Y.; Schrier, R.; Iudicello, J.; Letendre, S.; Morgan, E.; Tang, B.; Grant, I.; Cherner, M. Recent Cannabis Use in HIV Is Associated with Reduced Inflammatory Markers in CSF and Blood. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 7, e809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, M.D.; Crawford, R.B.; Henriquez, J.E.; Aldhamen, Y.A.; Gulick, P.; Amalfitano, A.; Kaminski, N.E. HIV-Infected Cannabis Users Have Lower Circulating CD16+ Monocytes and IFN-γ-Inducible Protein 10 Levels Compared with Nonusing HIV Patients. AIDS 2018, 32, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, A.W.; Ahmad, F.; Alam, M.A.; Raheed, T.; Zaqout, A.; Al-Maslamani, M.; Ahmad, A.; Buddenkotte, J.; Al-Khal, A.; Steinhoff, M. Virus-Induced Host Chemokine CCL2 in COVID-19 Pathogenesis: Potential Prognostic Marker and Target of Anti-Inflammatory Strategy. Rev. Med. Virol. 2024, 34, e2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhillon, N.K. Roles of MCP-1 in Development of HIV-Dementia. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 3913–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hage, N.; Wu, G.; Wang, J.; Ambati, J.; Knapp, P.E.; Reed, J.L.; Bruce-Keller, A.J.; Hauser, K.F. HIV-1 Tat and Opiate-induced Changes in Astrocytes Promote Chemotaxis of Microglia through the Expression of MCP-1 and Alternative Chemokines. Glia 2006, 53, 132–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro De Almeida, S.; Letendre, S.; Zimmerman, J.; Lazzaretto, D.; McCutchan, A.; Ellis, R. Dynamics of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein Type One (MCP-1) and HIV Viral Load in Human Cerebrospinal Fluid and Plasma. J. Neuroimmunol. 2005, 169, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeregui, E.; Viladés, C.; Domingo, P.; Ceausu, A.; Pacheco, Y.M.; Veloso, S.; Inciarte, A.; Vidal-González, J.; Peraire, M.; Perpiñán, C.; et al. High Circulating SDF-1and MCP-1 Levels and Genetic Variations in CXCL12, CCL2 and CCR5: Prognostic Signature of Immune Recovery Status in Treated HIV-Positive Patients. eBioMedicine 2020, 62, 103077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchese, M.E.; Berdnikovs, S.; Cook-Mills, J.M. Distinct Sites within the Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 (VCAM-1) Cytoplasmic Domain Regulate VCAM-1 Activation of Calcium Fluxes versus Rac1 during Leukocyte Transendothelial Migration. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 8235–8246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saloner, R.; Sun-Suslow, N.; Morgan, E.E.; Lobo, J.; Cherner, M.; Ellis, R.J.; Heaton, R.K.; Grant, I.; Letendre, S.L.; Iudicello, J.E. Plasma Biomarkers of Vascular Dysfunction Uniquely Relate to a Vascular-Risk Profile of Neurocognitive Deficits in Virally-Suppressed Adults with HIV. Brain Behav. Immun.-Health 2022, 26, 100560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Q.; Zhang, L.; Qi, Z.; Huang, B. The Mechanism of Inflammatory Factors and Soluble Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 Regulated by Nuclear Transcription Factor NF-κB in Unstable Angina Pectoris. J. Immunol. Res. 2022, 2022, 6137219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Tian, J.; Jin, Y. VCAM1 Expression in the Myocardium Is Associated with the Risk of Heart Failure and Immune Cell Infiltration in Myocardium. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, L.A.; Kim, C.; Gupta, S.K.; Rajashekhar, G.; Rehman, J.; Clauss, M. Pentoxifylline Reduces Tumor Necrosis Factor-α and HIV-Induced Vascular Endothelial Activation. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2012, 28, 1207–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louboutin, J.-P.; Strayer, D.S. Blood-Brain Barrier Abnormalities Caused by HIV-1 Gp120: Mechanistic and Therapeutic Implications. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 482575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverstein, P.; Shah, A.; Weemhoff, J.; Kumar, S.; Singh, D.; Kumar, A. HIV-1 Gp120 and Drugs of Abuse: Interactions in the Central Nervous System. Curr. HIV Res. 2012, 10, 369–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitarelli Da Silva, T.; Bernardes, D.; Oliveira-Lima, O.C.; Fernandes Pinto, B.; Limborço Filho, M.; Fraga Faraco, C.C.; Juliano, M.A.; Esteves Arantes, R.M.; Moreira, F.A.; Carvalho-Tavares, J. Cannabidiol Attenuates In Vivo Leukocyte Recruitment to the Spinal Cord Microvasculature at Peak Disease of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2024, 9, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hind, W.H.; England, T.J.; O’Sullivan, S.E. Cannabidiol Protects an in Vitro Model of the Blood–Brain Barrier from Oxygen-glucose Deprivation via PPARγ and 5-HT1A Receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wei, R.; Deng, J.; Guo, W. Research Progress in the Management of Vascular Disease with Cannabidiol: A Review. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2024, 19, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElSohly, M.A.; Chandra, S.; Radwan, M.; Majumdar, C.G.; Church, J.C. A Comprehensive Review of Cannabis Potency in the United States in the Last Decade. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2021, 6, 603–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Bakain, R.Z.; Al-Degs, Y.S.; Cizdziel, J.V.; Elsohly, M.A. Comprehensive Classification of USA Cannabis Samples Based on Chemical Profiles of Major Cannabinoids and Terpenoids. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2020, 43, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Halloran, J.; Dunne, E.; Gurwith, M.; Lambert, J.; Sheehan, G.; Feeney, E.; Pozniak, A.; Reiss, P.; Kenny, D.; Mallon, P. The Effect of Initiation of Antiretroviral Therapy on Monocyte, Endothelial and Platelet Function in HIV -1 Infection. HIV Med. 2015, 16, 608–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, R.M.; Stapleton, J.A.; Sutherland, G.; Coward, P.Y.; Wilson, R.F.; Scott, D.A. Effect of Nicotine Replacement and Quitting Smoking on Circulating Adhesion Molecule Profiles (sICAM-1, sCD44v5, sCD44v6). Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 32, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| PWoH (n = 148) | PWH (n = 86) | Total (n = 234) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | .023 | |||
| Mean | 40.53 | 44.70 | 42.06 | |
| SD | 14.15 | 12.20 | 13.59 | |
| Sex | <.001 | |||
| Female | 56 (37.8%) | 6 (7.0%) | 62 (26.5%) | |
| Male | 92 (62.2%) | 80 (93.0%) | 172 (73.5%) | |
| Ethnicity | .829 | |||
| White | 76 (51.4%) | 47 (54.7%) | 123 (52.6%) | |
| Hispanic | 35 (23.6%) | 22 (25.6%) | 57 (24.4%) | |
| Black | 25 (16.9%) | 12 (14.0%) | 37 (15.8%) | |
| Other | 12 (8.1%) | 5 (5.8%) | 17 (7.3%) | |
| Education Years | .03 | |||
| Mean | 13.57 | 14.30 | 13.84 | |
| SD | 2.48 | 2.42 | 2.48 | |
| Hypertension | 21 (14.2%) | 20 (23.3%) | 41 (17.5%) | .079 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 16 (10.8%) | 21 (24.4%) | 37 (15.8%) | .006 |
| Diabetes | 6 (4.1%) | 3 (3.5%) | 9 (3.8%) | .828 |
| Lifetime Major Depressive Disorder | 40 (27.0%) | 36 (41.9%) | 76 (32.5%) | .019 |
| Past-month Tobacco Use | 66 (44.6%) | 34 (39.5%) | 100 (42.7%) | .451 |
| Past-month Cannabis Use | 30 (20.3%) | 25 (29.1%) | 55 (23.5%) | .126 |
| Past-month METH Use | 27 (18.2%) | 16 (18.6%) | 43 (18.4%) | .945 |
| Lifetime DSM-IV Cannabis | 47 (31.8%) | 25 (29.1%) | 72 (30.8%) | .668 |
| Lifetime DSM-IV METH | 65 (43.9%) | 42 (48.8%) | 107 (45.7%) | .467 |
| Lifetime DSM-IV Alcohol | 76 (51.4%) | 34 (39.5%) | 110 (47.0%) | .081 |
| Lifetime DSM-IV Cocaine | 20 (13.5%) | 14 (16.3%) | 34 (14.5%) | .563 |
| Lifetime DSM-IV Hallucinogen | 11 (7.4%) | 7 (8.1%) | 18 (7.7%) | .845 |
| Lifetime DSM-IV Opioid | 14 (9.5%) | 5 (5.8%) | 19 (8.1%) | .325 |
| Lifetime DSM-IV Sedative | 8 (5.4%) | 6 (7.0%) | 14 (6.0%) | .625 |
| PWH (n = 86) Sample Characteristics | |
|---|---|
| Months on Current ARV Regimen | |
| Mean (SD) | 29.3 (38.7) |
| Median (IQR) | 13.5 (32.6) |
| HIV Plasma RNA (copies/mL) | |
| Mean (SD) | 11.8 (17.4) |
| Median (IQR) | 0.0 (33.0) |
| Current CD4+ T cell count | |
| Mean (SD) | 668.6 (257.9) |
| Median (IQR) | 642.0 (342.0) |
| Nadir CD4+ T cell count | |
| Mean (SD) | 282 (195.1) |
| Median (IQR) | 275 (271.8) |
| AIDS Diagnosis | |
| n (%) | 38 (44.2%) |
| Cannabis Use Characteristics (n = 168) | PWoH (n = 104) | PWH (n = 64) | Total (n = 168) | p |
| Past-month Cannabis Use | 30 (28.8%) | 25 (39.1%) | 55 (32.7%) | 0.171 |
| Lifetime DSM-IV Cannabis Use Disorder | 47 (45.2%) | 25 (39.1%) | 72 (42.9%) | 0.436 |
| Lifetime Days of Cannabis Use | 0.295 | |||
| Mean (SD) | 2115.7 (3206.6) | 2672.3 (3535.0) | 2327.7 (3336.1) | |
| Median (IQR) | 750.5 (2534.5) | 1188.0 (4007.0) | 961.5 (2750.5) | |
| Lifetime Cannabis Quantity (grams) | 0.473 | |||
| Mean (SD) | 3238 (6767.7) | 2552.1 (4457.7) | 2976.7 (5988.1) | |
| Median (IQR) | 230.7 (2657.2) | 412.6 (3456.6) | 340.3 (3131) | |
| Days Since Last Cannabis Use | 0.38 | |||
| Mean (SD) | 2045 (3505.4) | 1588 (2831.4) | 1870.9 (3263.9) | |
| Median (IQR) | 365.2 (2617.6) | 182.6 (1964.2) | 334.8 (2476.6) | |
| Age at First Cannabis Use | 0.388 | |||
| Mean (SD) | 16.3 (5) | 17 (6) | 16.6 (5.4) | |
| Median (IQR) | 15.5 (4.3) | 16 (4.3) | 16 (4) | |
| METH Use Characteristics (n = 123) | PWoH (n = 73) | PWH (n = 50) | Total (n = 123) | p |
| Past-month METH Use | 27 (37.0%) | 16 (32.0%) | 43 (35.0%) | 0.569 |
| Lifetime DSM-IV METH Use Disorder | 65 (89.0%) | 42 (84.0%) | 107 (87.0%) | 0.414 |
| Lifetime Days of METH Use | 0.564 | |||
| Mean (SD) | 2457.3 (2447.9) | 2206.3 (2234.9) | 2355.3 (2357.5) | |
| Median (IQR) | 1583 (2348) | 1347 (3081.8) | 1563 (2611.5) | |
| Lifetime METH Quantity (grams) | 0.049 | |||
| Mean (SD) | 4092.5 (7649.4) | 1859.6 (2605.8) | 3184.8 (6202.6) | |
| Median (IQR) | 1330.5 (4056.5) | 1065.9 (1957.9) | 1192.8 (2689) | |
| Days Since Last METH Use | 0.678 | |||
| Mean (SD) | 199.6 (598.5) | 248.2 (688.1) | 219.4 (634.2) | |
| Median (IQR) | 60.9 (168.6) | 60.9 (214.3) | 60.9 (168.6) | |
| Age at First METH Use | 0.11 | |||
| Mean (SD) | 24.2 (11.2) | 27.3 (8.9) | 25.4 (10.4) | |
| Median (IQR) | 21 (14) | 25 (13) | 23 (14.5) |
| CXCL10/IP-10 | CCL2/MCP-1 | ICAM-1 | VCAM-1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | 95% CI | B | 95% CI | B | 95% CI | B | 95% CI | |
| Base Model (Covariates-only) | ||||||||
| Age | 0.11 * | [0.02, 0.19] | 0.31 *** | [0.19, 0.42] | 0.11 * | [0.02, 0.19] | 0.07 | [−0.01, 0.15] |
| Sex: Female -> Male | 0.40 * | [0.08, 0.72] | −0.17 | [−0.36, 0.02] | −0.15 | [−0.32, 0.03] | ||
| Ethnicity: White -> US Minority | 0.17 | [−0.00, 0.35] | 0.19 | [−0.09, 0.47] | −0.35 *** | [−0.51, −0.20] | ||
| Education Years | −0.12 ** | [−0.20, −0.04] | −0.06 | [−0.13, 0.01] | ||||
| Past-month Tobacco Use | 0.26 * | [0.05, 0.47] | −0.11 | [−0.28, 0.06] | ||||
| R2 | 0.08 | 0.16 | 0.13 | 0.19 | ||||
| Main Effects: Lifetime DSM-IV METH Use Disorder, Past-month Cannabis Use, and HIV Status | ||||||||
| Lifetime DSM-IV METH Use Disorder | 0.01 | [−0.17, 0.18] | 0.32 * | [0.05, 0.59] | 0.10 | [−0.12, 0.32] | 0.25 ** | [0.09, 0.41] |
| Past-month Cannabis Use | −0.33 ** | [−0.54, −0.11] | −0.04 | [−0.31, 0.22] | −0.09 | [−0.31, 0.12] | −0.10 | [−0.29, 0.08] |
| HIV Status: PWoH -> PWH | 0.54 *** | [0.35, 0.73] | 0.13 | [−0.14, 0.40] | 0.17 | [−0.02, 0.37] | 0.31 *** | [0.15, 0.47] |
| R2 | 0.19 | 0.17 | 0.13 | 0.22 | ||||
| Conditional Effects: Lifetime DSM-IV METH Use Disorder, Past-month Cannabis Use, and HIV Status | ||||||||
| MUD−C− > MUD+C+ | 0.21 | [−0.23, 0.65] | 0.00 | [−0.30, 0.30] | 0.10 | [−0.30, 0.50] | ||
| MUD−C− > MUD+C− | 0.36 * | [0.08, 0.64] | 0.26 ** | [0.07, 0.45] | 0.42 *** | [0.19, 0.66] | ||
| MUD−C− > MUD−C+ | 0.04 | [−0.36, 0.44] | 0.01 | [−0.25, 0.28] | 0.19 | [−0.14, 0.51] | ||
| MUD−C− > MUD+C+: PWoH -> PWH | 0.15 | [−0.39, 0.69] | ||||||
| MUD−C−> MUD+C−: PWoH -> PWH | −0.44 ** | [−0.78, −0.11] | ||||||
| MUD−C− > MUD−C+: PWoH -> PWH | −0.61 ** | [−1.08, −0.14] | ||||||
| R2 | - | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.26 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rogers, J.M.; Chentsova, V.O.; Wang, C.X.; Marcondes, M.C.G.; Cherner, M.; Ellis, R.J.; Letendre, S.L.; Heaton, R.K.; Grant, I.; Iudicello, J.E. Cannabis Use Moderates Methamphetamine- and HIV-Related Inflammation: Evidence from Human Plasma Markers. Viruses 2025, 17, 1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17081143
Rogers JM, Chentsova VO, Wang CX, Marcondes MCG, Cherner M, Ellis RJ, Letendre SL, Heaton RK, Grant I, Iudicello JE. Cannabis Use Moderates Methamphetamine- and HIV-Related Inflammation: Evidence from Human Plasma Markers. Viruses. 2025; 17(8):1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17081143
Chicago/Turabian StyleRogers, Jeffrey M., Victoria O. Chentsova, Crystal X. Wang, Maria Cecilia Garibaldi Marcondes, Mariana Cherner, Ronald J. Ellis, Scott L. Letendre, Robert K. Heaton, Igor Grant, and Jennifer E. Iudicello. 2025. "Cannabis Use Moderates Methamphetamine- and HIV-Related Inflammation: Evidence from Human Plasma Markers" Viruses 17, no. 8: 1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17081143
APA StyleRogers, J. M., Chentsova, V. O., Wang, C. X., Marcondes, M. C. G., Cherner, M., Ellis, R. J., Letendre, S. L., Heaton, R. K., Grant, I., & Iudicello, J. E. (2025). Cannabis Use Moderates Methamphetamine- and HIV-Related Inflammation: Evidence from Human Plasma Markers. Viruses, 17(8), 1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17081143






