Sub-Nucleolar Trafficking of Hendra Virus Matrix Protein Is Regulated by Ubiquitination
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture, Transfection, and Treatment
2.2. Virus Infections
2.3. Constructs
2.4. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM) and Image Analysis
2.5. Immunofluorescence (IF)
2.6. 5-Ethnyl Uridine (EU) Incorporation Assays
3. Results
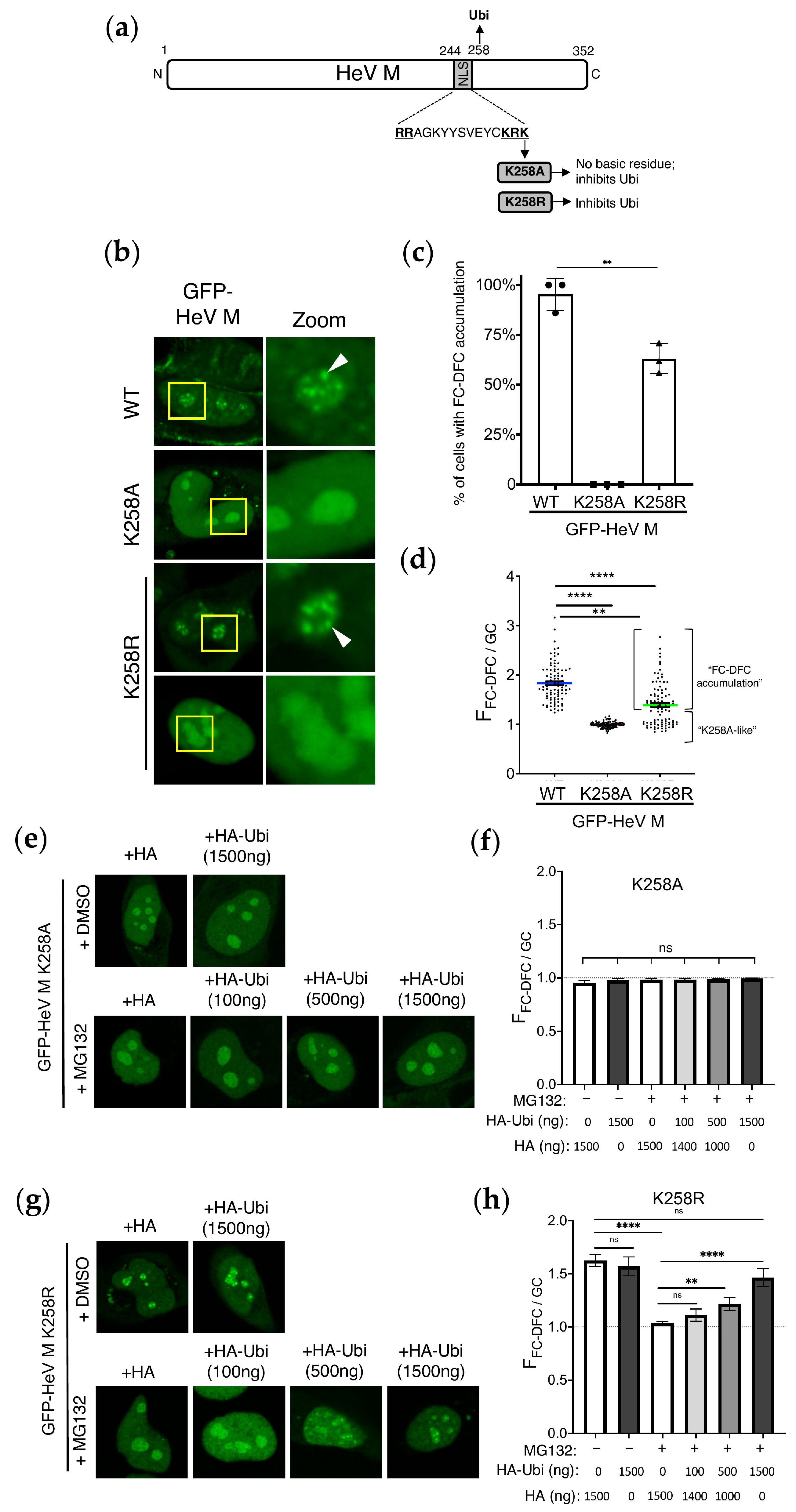
3.1. Ubiquitination Affects Sub-Nucleolar Trafficking of HeV M Protein
3.2. Conservative Substitution of K258 to R Reduces FC-DFC Targeting by HeV M
3.3. Dynamic Localisation of HeV M in Sub-Nucleolar Compartments Is Regulated by K258
3.4. Loss of HeV M FC-DFC Accumulation Does Not Relate to Disruption or Loss of FC-DFC
3.5. Ubiquitination Regulates Sub-Nucleolar Trafficking of M Proteins of Multiple Henipaviruses
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BSA | Bovine Serum Albumin |
| BSL | Biosafety Level |
| CedV | Cedar Virus |
| CLSM | Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy |
| DFC | Dense Fibrillar Component |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium |
| DMSO | Dimethyl Sulfoxide |
| DDR | DNA Damage Response |
| FC | Fibrillar Center |
| FC-DFC | Fibrillar Center–Dense Fibrillar Component |
| FCS | Fetal Calf Serum |
| Fn | Nuclear Fluorescence |
| Fc | Cytoplasmic Fluorescence |
| FFC-DFC | Fluorescence intensity in FC–DFC |
| FGC | Fluorescence intensity in Granular Component |
| GC | Granular Component |
| GFP | Green Fluorescent Protein |
| HA | Hemagglutinin |
| HeV | Hendra Virus |
| IF | Immunofluorescence |
| LLPS | Liquid–Liquid Phase Separation |
| MLO | Membrane-Less Organelle |
| MOI | Multiplicity of Infection |
| NLS | Nuclear Localisation Signal |
| NES | Nuclear Export Signal |
| NiV | Nipah Virus |
| p.i. | Post-Infection |
| p.t. | Post-Transfection |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| SEM | Standard Error of the Mean |
| TCID50 | Tissue Culture Infective Dose 50% |
| UBF1 | Upstream Binding Factor 1 |
| VLP | Virus-Like Particle |
| WT | Wild Type |
References
- Boisvert, F.M.; van Koningsbruggen, S.; Navascues, J.; Lamond, A.I. The multifunctional nucleolus. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 574–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iarovaia, O.V.; Minina, E.P.; Sheval, E.V.; Onichtchouk, D.; Dokudovskaya, S.; Razin, S.V.; Vassetzky, Y.S. Nucleolus: A Central Hub for Nuclear Functions. Trends Cell Biol. 2019, 29, 647–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feric, M.; Vaidya, N.; Harmon, T.S.; Mitrea, D.M.; Zhu, L.; Richardson, T.M.; Kriwacki, R.W.; Pappu, R.V.; Brangwynne, C.P. Coexisting Liquid Phases Underlie Nucleolar Subcompartments. Cell 2016, 165, 1686–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafontaine, D.L.J.; Riback, J.A.; Bascetin, R.; Brangwynne, C.P. The nucleolus as a multiphase liquid condensate. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiscox, J.A. RNA viruses: Hijacking the dynamic nucleolus. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iarovaia, O.V.; Ioudinkova, E.S.; Velichko, A.K.; Razin, S.V. Manipulation of Cellular Processes via Nucleolus Hijaking in the Course of Viral Infection in Mammals. Cells 2021, 10, 1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlinson, S.M.; Moseley, G.W. The nucleolar interface of RNA viruses. Cell Microbiol. 2015, 17, 1108–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deffrasnes, C.; Marsh, G.A.; Foo, C.H.; Rootes, C.L.; Gould, C.M.; Grusovin, J.; Monaghan, P.; Lo, M.K.; Tompkins, S.M.; Adams, T.E.; et al. Genome-wide siRNA Screening at Biosafety Level 4 Reveals a Crucial Role for Fibrillarin in Henipavirus Infection. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaghan, P.; Green, D.; Pallister, J.; Klein, R.; White, J.; Williams, C.; McMillan, P.; Tilley, L.; Lampe, M.; Hawes, P.; et al. Detailed morphological characterisation of Hendra virus infection of different cell types using super-resolution and conventional imaging. Virol. J. 2014, 11, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pentecost, M.; Vashisht, A.A.; Lester, T.; Voros, T.; Beaty, S.M.; Park, A.; Wang, Y.E.; Yun, T.E.; Freiberg, A.N.; Wohlschlegel, J.A.; et al. Evidence for ubiquitin-regulated nuclear and subnuclear trafficking among Paramyxovirinae matrix proteins. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.E.; Park, A.; Lake, M.; Pentecost, M.; Torres, B.; Yun, T.E.; Wolf, M.C.; Holbrook, M.R.; Freiberg, A.N.; Lee, B. Ubiquitin-regulated nuclear-cytoplasmic trafficking of the Nipah virus matrix protein is important for viral budding. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battisti, A.J.; Meng, G.; Winkler, D.C.; McGinnes, L.W.; Plevka, P.; Steven, A.C.; Morrison, T.G.; Rossmann, M.G. Structure and assembly of a paramyxovirus matrix protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 13996–14000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.C.; Grusovin, J.; Adams, T.E. Electrostatic Interactions between Hendra Virus Matrix Proteins Are Required for Efficient Virus-Like-Particle Assembly. J. Virol. 2018, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawlinson, S.M.; Zhao, T.; Rozario, A.M.; Rootes, C.L.; McMillan, P.J.; Purcell, A.W.; Woon, A.; Marsh, G.A.; Lieu, K.G.; Wang, L.F.; et al. Viral regulation of host cell biology by hijacking of the nucleolar DNA-damage response. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; McCrory, T.S.; Khaw, W.Y.; Petzing, S.; Myers, T.; Schmitt, A.P. Matrix proteins of Nipah and Hendra viruses interact with beta subunits of AP-3 complexes. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 13099–13110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, C.M.; Vogel, O.A.; Edwards, M.R.; Taylor, P.E.; Roby, J.A.; Forwood, J.K.; Basler, C.F. Henipavirus Matrix Protein Employs a Non-Classical Nuclear Localization Signal Binding Mechanism. Viruses 2023, 15, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLinton, E.C.; Wagstaff, K.M.; Lee, A.; Moseley, G.W.; Marsh, G.A.; Wang, L.F.; Jans, D.A.; Lieu, K.G.; Netter, H. Nuclear localization and secretion competence is conserved among henipavirus matrix proteins. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, D.; Zhang, L.; Peng, C.; He, M.; Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Liu, C.; Du, J.; Zhou, J.; Yin, L.; et al. The E3 ligase RAD18-mediated ubiquitination of henipavirus matrix protein promotes its nuclear-cytoplasmic trafficking and viral egress. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2025, 14, 2432344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkinson, R.E.; Lee, B. Nipah virus matrix protein: Expert hacker of cellular machines. FEBS Lett. 2016, 590, 2494–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, C.R.; Marsh, G.A.; Jenkins, K.A.; Gantier, M.P.; Tizard, M.L.; Middleton, D.; Lowenthal, J.W.; Haining, J.; Izzard, L.; Gough, T.J.; et al. Promotion of Hendra virus replication by microRNA 146a. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 3782–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, D.; Garnish, S.E.; Sandow, J.J.; Weir, A.; Liu, L.; Clayer, E.; Meza, L.; Rashidi, M.; Cobbold, S.A.; Scutts, S.R.; et al. Ubiquitylation of RIPK3 beyond-the-RHIM can limit RIPK3 activity and cell death. iScience 2022, 25, 104632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svistunova, D.M.; Musinova, Y.R.; Polyakov, V.Y.; Sheval, E.V. A simple method for the immunocytochemical detection of proteins inside nuclear structures that are inaccessible to specific antibodies. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2012, 60, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, D.H.; Hari, F.; Clapperton, J.A.; Gwerder, M.; Gutsche, K.; Altmeyer, M.; Jungmichel, S.; Toledo, L.I.; Fink, D.; Rask, M.B.; et al. The NBS1-Treacle complex controls ribosomal RNA transcription in response to DNA damage. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014, 16, 792–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mooser, C.; Symeonidou, I.E.; Leimbacher, P.A.; Ribeiro, A.; Shorrocks, A.K.; Jungmichel, S.; Larsen, S.C.; Knechtle, K.; Jasrotia, A.; Zurbriggen, D.; et al. Treacle controls the nucleolar response to rDNA breaks via TOPBP1 recruitment and ATR activation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlinson, S.M.; Zhao, T.; Ardipradja, K.; Zhang, Y.; Veugelers, P.F.; Harper, J.A.; David, C.T.; Sundaramoorthy, V.; Moseley, G.W. Henipaviruses and lyssaviruses target nucleolar treacle protein and regulate ribosomal RNA synthesis. Traffic 2023, 24, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ditlev, J.A.; Case, L.B.; Rosen, M.K. Who’s In and Who’s Out-Compositional Control of Biomolecular Condensates. J. Mol. Biol. 2018, 430, 4666–4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmott, E.; Hiscox, J.A. Nucleolar targeting: The hub of the matter. EMBO Rep. 2009, 10, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.Y.; Wu, J.J.; Li, Y.M. Regulation of liquid-liquid phase separation with focus on post-translational modifications. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 13275–13287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, P.; Kapoor, U.; Sundaravadivelu Devarajan, D.; Phan, T.M.; Rizuan, A.; Mittal, J. Principles Governing the Phase Separation of Multidomain Proteins. Biochemistry 2022, 61, 2443–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, B.A.; Oppikofer, M. Biomolecular condensates: New opportunities for drug discovery and RNA therapeutics. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 43, 820–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrea, D.M.; Mittasch, M.; Gomes, B.F.; Klein, I.A.; Murcko, M.A. Modulating biomolecular condensates: A novel approach to drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 841–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risso-Ballester, J.; Galloux, M.; Cao, J.; Le Goffic, R.; Hontonnou, F.; Jobart-Malfait, A.; Desquesnes, A.; Sake, S.M.; Haid, S.; Du, M.; et al. A condensate-hardening drug blocks RSV replication in vivo. Nature 2021, 595, 596–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Dai, T.; Qin, Z.; Pan, T.; Chu, F.; Lou, L.; Zhang, L.; Yang, B.; Huang, H.; Lu, H.; et al. Targeting liquid-liquid phase separation of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein promotes innate antiviral immunity by elevating MAVS activity. Nat. Cell Biol. 2021, 23, 718–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maehama, T.; Nishio, M.; Otani, J.; Mak, T.W.; Suzuki, A. Nucleolar stress: Molecular mechanisms and related human diseases. Cancer Sci. 2023, 114, 2078–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stochaj, U.; Weber, S.C. Nucleolar Organization and Functions in Health and Disease. Cells 2020, 9, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, T.; Gomez, F.A.; David, C.T.; Rootes, C.L.; Stewart, C.R.; Moseley, G.W.; Rawlinson, S.M. Sub-Nucleolar Trafficking of Hendra Virus Matrix Protein Is Regulated by Ubiquitination. Viruses 2025, 17, 797. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17060797
Zhao T, Gomez FA, David CT, Rootes CL, Stewart CR, Moseley GW, Rawlinson SM. Sub-Nucleolar Trafficking of Hendra Virus Matrix Protein Is Regulated by Ubiquitination. Viruses. 2025; 17(6):797. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17060797
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Tianyue, Florian A. Gomez, Cassandra T. David, Christina L. Rootes, Cameron R. Stewart, Gregory W. Moseley, and Stephen M. Rawlinson. 2025. "Sub-Nucleolar Trafficking of Hendra Virus Matrix Protein Is Regulated by Ubiquitination" Viruses 17, no. 6: 797. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17060797
APA StyleZhao, T., Gomez, F. A., David, C. T., Rootes, C. L., Stewart, C. R., Moseley, G. W., & Rawlinson, S. M. (2025). Sub-Nucleolar Trafficking of Hendra Virus Matrix Protein Is Regulated by Ubiquitination. Viruses, 17(6), 797. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17060797





