Epidemiological, Clinical, and Molecular Insights into Canine Distemper Virus in the Mekong Delta Region of Vietnam
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Hematology and Blood Biochemistry
2.3. RNA Extraction, Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR), and Sequencing of the Partial H and F Gene of CDV
2.4. Phylogenetic, Recombination, and Potential N-Linked Glycosylation Sites Analysis
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Epidemiological Features
3.2. Clinical Signs
3.3. Hematology and Blood Biochemistry
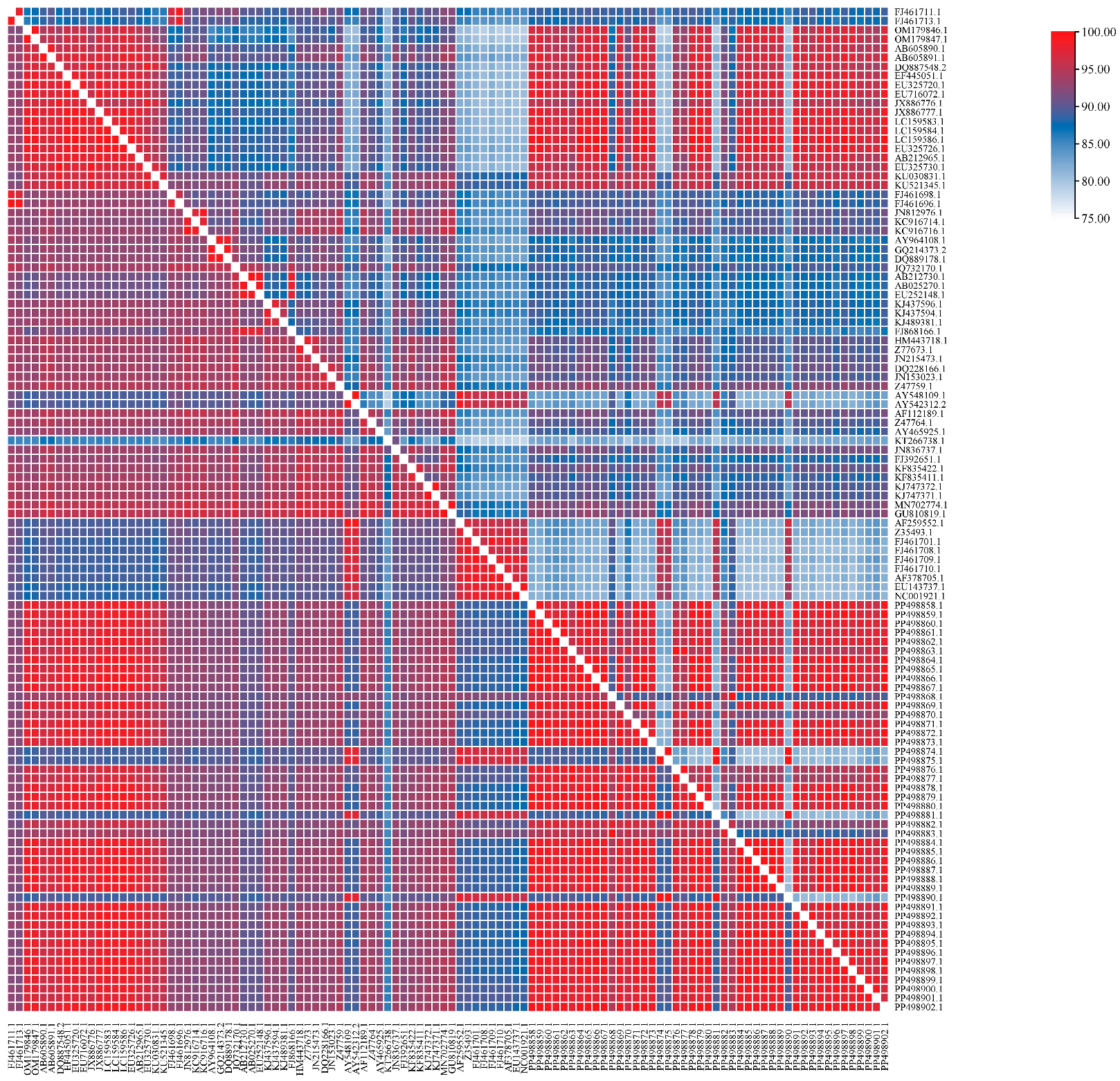
3.4. Nucleotide and Amino Acid Homology
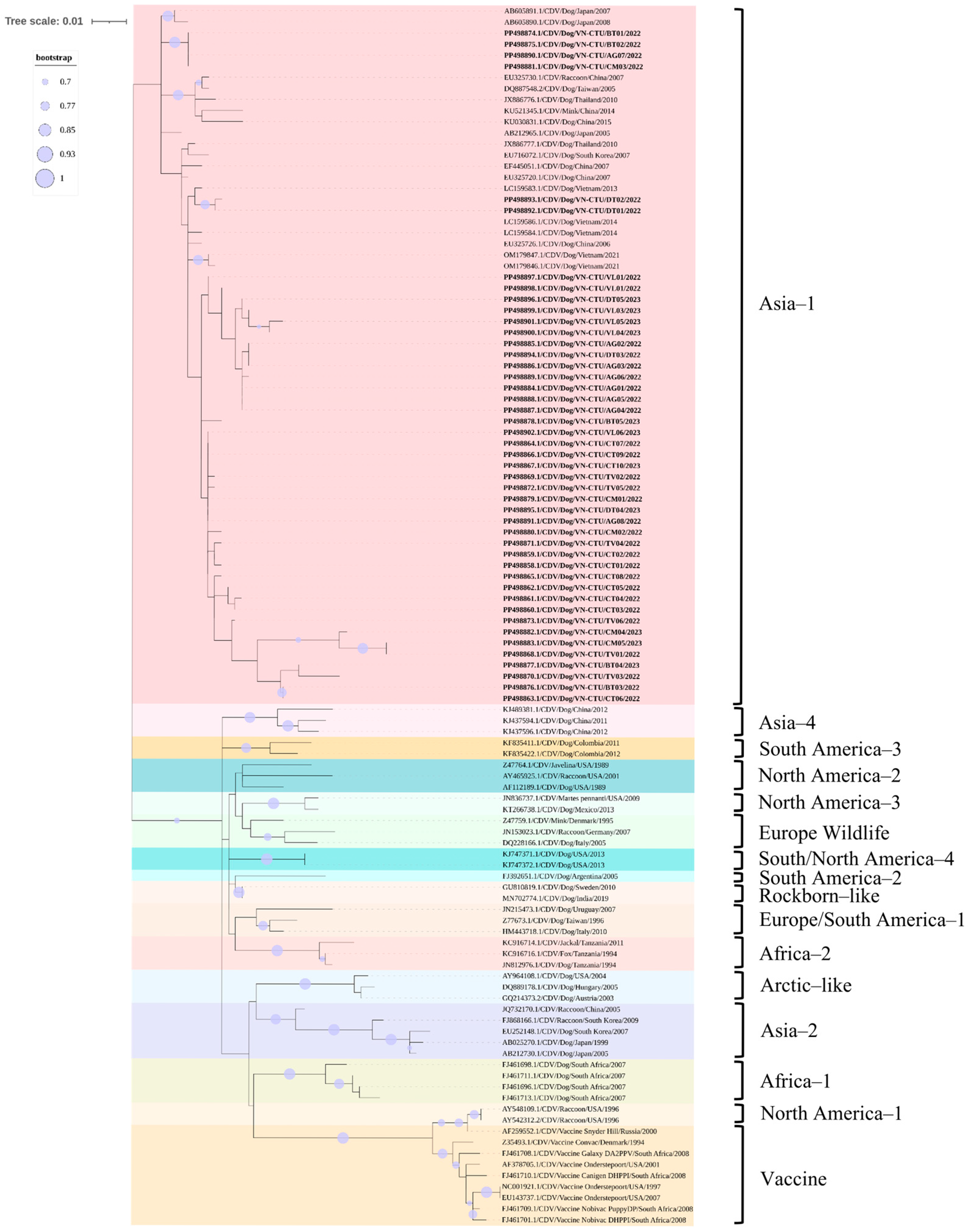
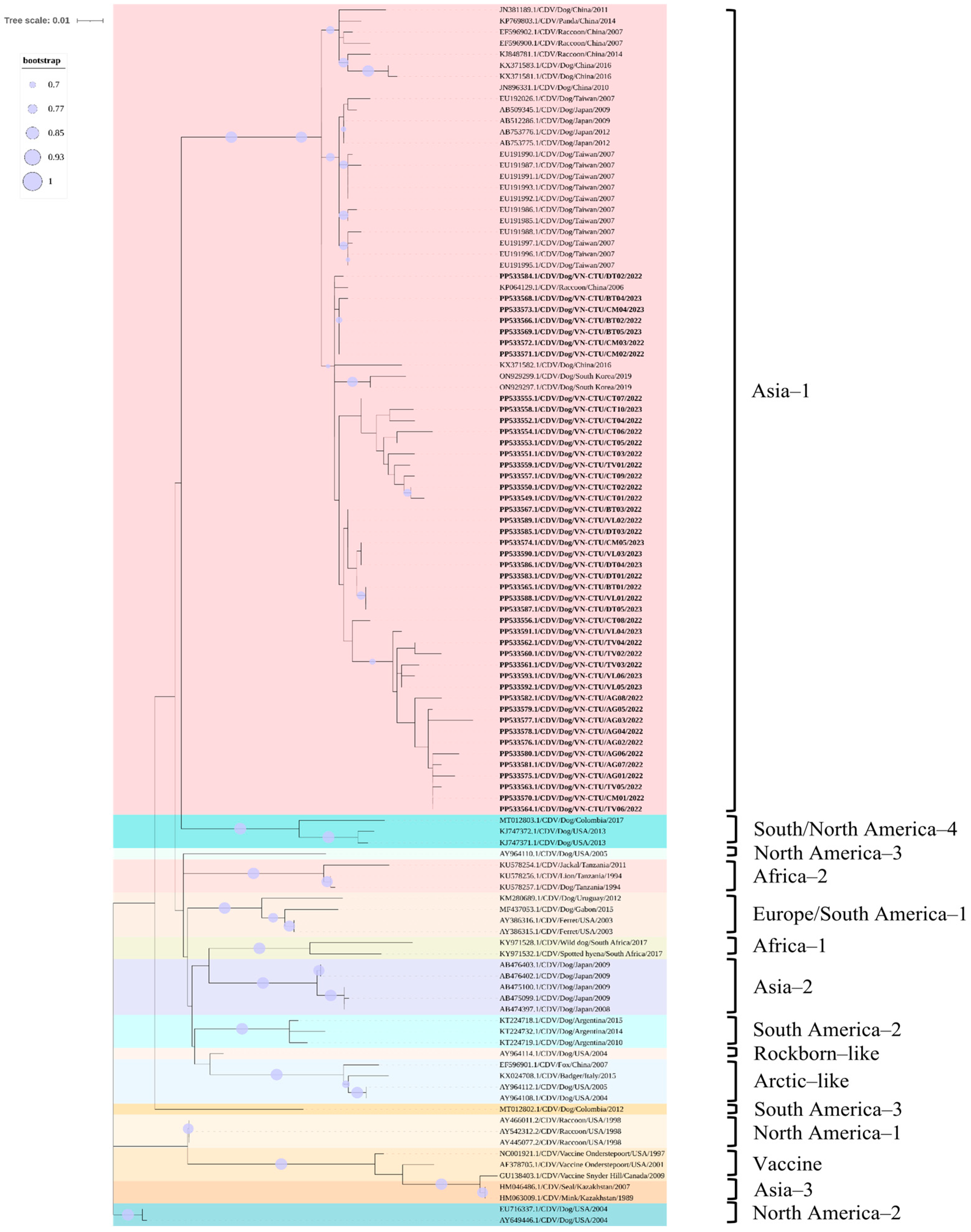
3.5. Phylogenetic and Recombination Analysis
3.6. Potential N-Linked Glycosylation Sites
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sidhu, M.S.; Husar, W.; Cook, S.D.; Dowling, P.C.; Udem, S.A. Canine distemper terminal and intergenic non-protein coding nucleotide sequences: Completion of the entire CDV genome sequence. Virology 1993, 193, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rendon-Marin, S.; da Fontoura Budaszewski, R.; Canal, C.W.; Ruiz-Saenz, J. Tropism and molecular pathogenesis of canine distemper virus. Virol. J. 2019, 16, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, R.A. Paramyxovirus fusion: A hypothesis for changes. Virology 1993, 197, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.-J.; Yan, X.-J.; Chai, X.-L.; Martella, V.; Luo, G.-L.; Zhang, H.-L.; Gao, H.; Liu, Y.-X.; Bai, X.; Zhang, L. Phylogenetic analysis of the haemagglutinin gene of canine distemper virus strains detected from breeding foxes, raccoon dogs and minks in China. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 140, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Wen, Y.-J.; Wang, F.-X.; Zhang, S.-Q.; Wang, X.-D.; Hu, J.-X.; Shi, X.-C.; Yang, B.-C.; Chen, L.-Z.; Cheng, S.-P. Pathogenesis and phylogenetic analyses of canine distemper virus strain ZJ7 isolate from domestic dogs in China. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, W.; Wu, H.; Ding, H.; Cao, Y.; Spibey, N.; Wang, L.; He, W.; Hao, L. Isolation and sequence analysis of the complete H gene of canine distemper virus from domestic dogs in Henan Province, China. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 2153–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, T.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Yang, S.; Feng, N.; Sun, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Bu, Z. Genetic characterization of an isolate of canine distemper virus from a Tibetan Mastiff in China. Virus Genes 2014, 49, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanutti, C.; Calderón, M.G.; Keller, L.; Mattion, N.; La Torre, J. RT-PCR and sequence analysis of the full-length fusion protein of canine distemper virus from domestic dogs. J. Virol. Methods 2016, 228, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, L.A.; Leme, R.A.; Saporiti, V.; Alfieri, A.A.; Alfieri, A.F. Molecular analysis of the full-length F gene of Brazilian strains of canine distemper virus shows lineage co-circulation and variability between field and vaccine strains. Virus Res. 2019, 264, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wipf, A.; Perez-Cutillas, P.; Ortega, N.; Huertas-López, A.; Martínez-Carrasco, C.; Candela, M. Geographical Distribution of Carnivore Hosts and Genotypes of Canine Distemper Virus (CDV) Worldwide: A Scoping Review and Spatial Meta-Analysis. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2025, 2025, 6632068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martella, V.; Blixenkrone-Møller, M.; Elia, G.; Lucente, M.S.; Cirone, F.; Decaro, N.; Nielsen, L.; Banyai, K.; Carmichael, L.; Buonavoglia, C. Lights and shades on an historical vaccine canine distemper virus, the Rockborn strain. Vaccine 2011, 29, 1222–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radtanakatikanon, A.; Keawcharoen, J.; taya Charoenvisal, N.; Poovorawan, Y.; Prompetchara, E.; Yamaguchi, R.; Techangamsuwan, S. Genotypic lineages and restriction fragment length polymorphism of canine distemper virus isolates in Thailand. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 166, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa, V.G.; Saivish, M.V.; de Oliveira, P.G.; Silva-Júnior, A.; Moreli, M.L.; Krüger, R.H. First complete genome sequence and molecular characterization of Canine morbillivirus isolated in Central Brazil. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saltık, H.S.; Atlı, K. Approaches to identify canine distemper virus with neurological symptoms on the basis of molecular characterization of hemagglutinin and fusion genes. Virus Genes 2023, 59, 591–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-S.; Tsai, K.-J.; Chen, L.-H.; Chen, C.-Y.; Liu, Y.-P.; Chang, C.-C.; Lee, S.-H.; Hsu, W.-L. The identification of frequent variations in the fusion protein of canine distemper virus. Vet. J. 2010, 183, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piewbang, C.; Radtanakatikanon, A.; Puenpa, J.; Poovorawan, Y.; Techangamsuwan, S. Genetic and evolutionary analysis of a new Asia-4 lineage and naturally recombinant canine distemper virus strains from Thailand. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzera, Y.; Sarute, N.; Iraola, G.; Hernández, M.; Pérez, R. Molecular phylogeography of canine distemper virus: Geographic origin and global spreading. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2015, 92, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Martínez, A.; Rodríguez-Alarcón, C.A.; Adame-Gallegos, J.R.; Laredo-Tiscareño, S.V.; de Luna-Santillana, E.d.J.; Hernández-Triana, L.M.; Garza-Hernández, J.A. Canine Distemper Virus: Origins, Mutations, Diagnosis, and Epidemiology in Mexico. Life 2024, 14, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, N.T.; Yamaguchi, R.; Kien, T.T.; Hirai, T.; Hidaka, Y.; Nam, N.H. First isolation and characterization of canine distemper virus in Vietnam with the immunohistochemical examination of the dog. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2009, 71, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nguyen, D.; Suzuki, J.; Minami, S.; Yonemitsu, K.; Nagata, N.; Kuwata, R.; Shimoda, H.; Vu, C.K.; Truong, T.Q.; Maeda, K. Isolation and phylogenetic analysis of canine distemper virus among domestic dogs in Vietnam. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2017, 79, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, Q.L.; Duc, H.M.; Anh, T.N.; Thi, Y.N.; Van, T.N.; Thi, P.H.; Thu, H.N.T.; Thi, L.N. Isolation and genetic characterization of canine distemper virus in domestic dogs from central and northern provinces in Vietnam. Res. Vet. Sci. 2022, 153, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van, T.M.; Le, T.Q.; Tran, B.N. Phylogenetic characterization of the canine distemper virus isolated from veterinary clinics in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Vet. World 2023, 16, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gámiz, C.; Martella, V.; Ulloa, R.; Fajardo, R.; Quijano-Hernandéz, I.; Martínez, S. Identification of a new genotype of canine distemper virus circulating in America. Vet. Res. Commun. 2011, 35, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucl. Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL) v6: Recent updates to the phylogenetic tree display and annotation tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, gkae268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.P.; Murrell, B.; Golden, M.; Khoosal, A.; Muhire, B. RDP4: Detection and analysis of recombination patterns in virus genomes. Virus Evol. 2015, 1, vev003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lole, K.S.; Bollinger, R.C.; Paranjape, R.S.; Gadkari, D.; Kulkarni, S.S.; Novak, N.G.; Ingersoll, R.; Sheppard, H.W.; Ray, S.C. Full-length human immunodeficiency virus type 1 genomes from subtype C-infected seroconverters in India, with evidence of intersubtype recombination. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Brunak, S. Prediction of glycosylation across the human proteome and the correlation to protein function. Pac. Symp. Biocomput. 2002, 7, 310–322. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; Chen, H.; He, Y. TBtools-II: A “one for all, all for one” bioinformatics platform for biological big-data mining. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loots, A.K.; Mokgokong, P.S.; Mitchell, E.; Venter, E.H.; Kotze, A.; Dalton, D.L. Phylogenetic analysis of canine distemper virus in South African wildlife. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deem, S.L.; Spelman, L.H.; Yates, R.A.; Montali, R.J. Canine distemper in terrestrial carnivores: A review. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2000, 31, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Buragohain, M.; Goswani, S.; Kalita, D. Clinicopathological findings of canine distemper virus infection in dogs. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2017, 5, 1817–1819. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, M.d.L.e.; Silva, G.E.B.; Borin-Crivellenti, S.; Alvarenga, A.W.O.; Aldrovani, M.; Braz, L.A.d.N.; Aoki, C.; Santana, A.E.; Pennacchi, C.S.; Crivellenti, L.Z. Renal abnormalities caused by canine distemper virus infection in terminal patients. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 822525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, M.C.; Wilkes, R.P. Sequencing of emerging canine distemper virus strain reveals new distinct genetic lineage in the United States associated with disease in wildlife and domestic canine populations. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Guo, H.; Hein, V.G.; Xu, Y.; Yu, S.; Wang, X. The evolutionary dynamics history of canine distemper virus through analysis of the hemagglutinin gene during 1930–2020. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2023, 69, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, M.; Rajak, K.; Chakravarti, S.; Yadav, A.; Kumar, A.; Gupta, V.; Chander, V.; Mathesh, K.; Chandramohan, S.; Sharma, A. Phylogenetic analysis of haemagglutinin gene deciphering a new genetically distinct lineage of canine distemper virus circulating among domestic dogs in India. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 1252–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkes, R.P. Canine distemper virus in endangered species: Species jump, clinical variations, and vaccination. Pathogens 2022, 12, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo-Duc, T. Climate change in the coastal regions of Vietnam. In Coastal Disasters and Climate Change in Vietnam; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 175–198. [Google Scholar]
- Lechner, E.S.; Crawford, P.C.; Levy, J.K.; Edinboro, C.H.; Dubovi, E.J.; Caligiuri, R. Prevalence of protective antibody titers for canine distemper virus and canine parvovirus in dogs entering a Florida animal shelter. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2010, 236, 1317–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, I.; Gilbert, M.; Shah, M.K.; Sadaula, A.; Anderson, N.E. Seroprevalence of canine distemper virus (CDV) in the free-roaming dog (Canis familiaris) population surrounding Chitwan National Park, Nepal. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0281542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greeley, E.H.; Spitznagel, E.; Lawler, D.F.; Kealy, R.D.; Segre, M. Modulation of canine immunosenescence by life-long caloric restriction. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2006, 111, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, R.; Thiel, B.; Mukhtar, E.; Sharp, P.; Larson, L. Age and long-term protective immunity in dogs and cats. J. Comp. Pathol. 2010, 142, S102–S108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, M. Immune system development in the dog and cat. J. Comp. Pathol. 2007, 137, S10–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Jamett, G.; Chalmers, W.; Cunningham, A.; Cleaveland, S.; Handel, I.; Bronsvoort, B.d. Urban domestic dog populations as a source of canine distemper virus for wild carnivores in the Coquimbo region of Chile. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 152, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jóźwik, A.; Frymus, T.; Mizak, B.; Rzeżutka, A. Antibody titres against canine distemper virus in vaccinated and unvaccinated dogs. J. Vet. Med. Ser. B 2004, 51, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghafona, N.; Jacob, J.; Yah, S. Evaluation of post-vaccination immunity to canine distemper and parvoviruses in Benin City, Nigeria. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2007, 6, 1898–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapil, S.; Yeary, T.J. Canine distemper spillover in domestic dogs from urban wildlife. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2011, 41, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.; Siedek, E.; Thomas, A.; King, V.; Stirling, C.; Plevová, E.; Salt, J.; Sture, G. Influence of maternally-derived antibodies in 6-week old dogs for the efficacy of a new vaccine to protect dogs against virulent challenge with canine distemper virus, adenovirus or parvovirus. Trials Vaccinol. 2014, 3, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorji, T.; Tenzin, T.; Tenzin, K.; Tshering, D.; Rinzin, K.; Phimpraphai, W.; de Garine-Wichatitsky, M. Seroprevalence and risk factors of canine distemper virus in the pet and stray dogs in Haa, western Bhutan. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, V.G.d.; Saivish, M.V.; Rodrigues, R.L.; Lima Silva, R.F.d.; Moreli, M.L.; Krüger, R.H. Molecular and serological surveys of canine distemper virus: A meta-analysis of cross-sectional studies. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, G.; Li, C.; Wei, L.; Lin, W. A meta-analysis of cross-sectional studies on the frequency and risk factors associated with canine morbillivirus infection in China. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 161, 105258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, C.E. Infectious Diseases of the Dog and Cat; WB Saunders\Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Amude, A.; Alfieri, A.; Alfieri, A. Clinicopathological findings in dogs with distemper encephalomyelitis presented without characteristic signs of the disease. Res. Vet. Sci. 2007, 82, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beineke, A.; Baumgärtner, W.; Wohlsein, P. Cross-species transmission of canine distemper virus—An update. One Health 2015, 1, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebara, C.; Wosiacki, S.; Negrao, F.; De Oliveira, D.; Beloni, S.; Alfieri, A.; Alfieri, A. Detection of canine distemper virus nucleoprotein gene by RT-PCR in urine of dogs with distemper clinical signs. Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. E Zootec. 2004, 56, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, O.V.; Botelho, C.V.; Ferreira, C.G.T.; Scherer, P.O.; Soares-Martins, J.A.P.; Almeida, M.R.; Silva Júnior, A. Immunopathogenic and neurological mechanisms of canine distemper virus. Adv. Virol. 2012, 2012, 163860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, N. Canine viral diarrhea: Clinical, hematologic and biochemical alterations with particular reference to in-clinic rapid diagnosis. Glob. Vet. 2014, 13, 302–307. [Google Scholar]
- Saaed, M.M.; Al-Obaidi, Q.T. Clinical, Hematological and Some Biochemical Changes In Dogs Infected With Canine Distemper. J. Agric. Vet. Sci. 2021, 14, 26–33. [Google Scholar]
- Willi, B.; Spiri, A.M.; Meli, M.L.; Grimm, F.; Beatrice, L.; Riond, B.; Bley, T.; Jordi, R.; Dennler, M.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R. Clinical and molecular investigation of a canine distemper outbreak and vector-borne infections in a group of rescue dogs imported from Hungary to Switzerland. BMC Vet. Res. 2015, 11, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noyce, R.S.; Delpeut, S.; Richardson, C.D. Dog nectin-4 is an epithelial cell receptor for canine distemper virus that facilitates virus entry and syncytia formation. Virology 2013, 436, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, G.-M.; Ho, C.-H.; Chiang, M.-J.; Sanno-Duanda, B.; Chung, C.-S.; Lin, M.-Y.; Shi, Y.-Y.; Yang, M.-H.; Tyan, Y.-C.; Liao, P.-C. Phylodynamic analysis of the canine distemper virus hemagglutinin gene. BMC Vet. Res. 2015, 11, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harder, T.; Osterhaus, A. Canine distemper virus—a morbillivirus in search of new hosts? Trends Microbiol. 1997, 5, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mochizuki, M.; Hashimoto, M.; Hagiwara, S.; Yoshida, Y.; Ishiguro, S. Genotypes of canine distemper virus determined by analysis of the hemagglutinin genes of recent isolates from dogs in Japan. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 2936–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, S.A.; Belsham, G.J.; Barrett, T. The role of the 5′ nontranslated regions of the fusion protein mRNAs of canine distemper virus and rinderpest virus. Virology 1990, 177, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque-Valencia, J.; Diaz, F.J.; Ruiz-Saenz, J. Phylogenomic analysis of two co-circulating canine distemper virus lineages in Colombia. Pathogens 2019, 9, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuques, E.; Tomás, G.; Grecco, S.; Condon, E.; Techera, C.; Marandino, A.; Sarute, N.; Aldaz, J.; Enciso, J.; Benech, A. Origin and spreading of canine morbillivirus in South America. Virus Res. 2022, 319, 198858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawatsky, B.; von Messling, V. Canine distemper viruses expressing a hemagglutinin without N-glycans lose virulence but retain immunosuppression. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 2753–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwatsuki, K.; Miyashita, N.; Yoshida, E.; Gemma, T.; Shin, Y.-S.; Mori, T.; Hirayama, N.; Kai, C.; Mikami, T. Molecular and phylogenetic analyses of the haemagglutinin (H) proteins of field isolates of canine distemper virus from naturally infected dogs. J. Gen. Virol. 1997, 78, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
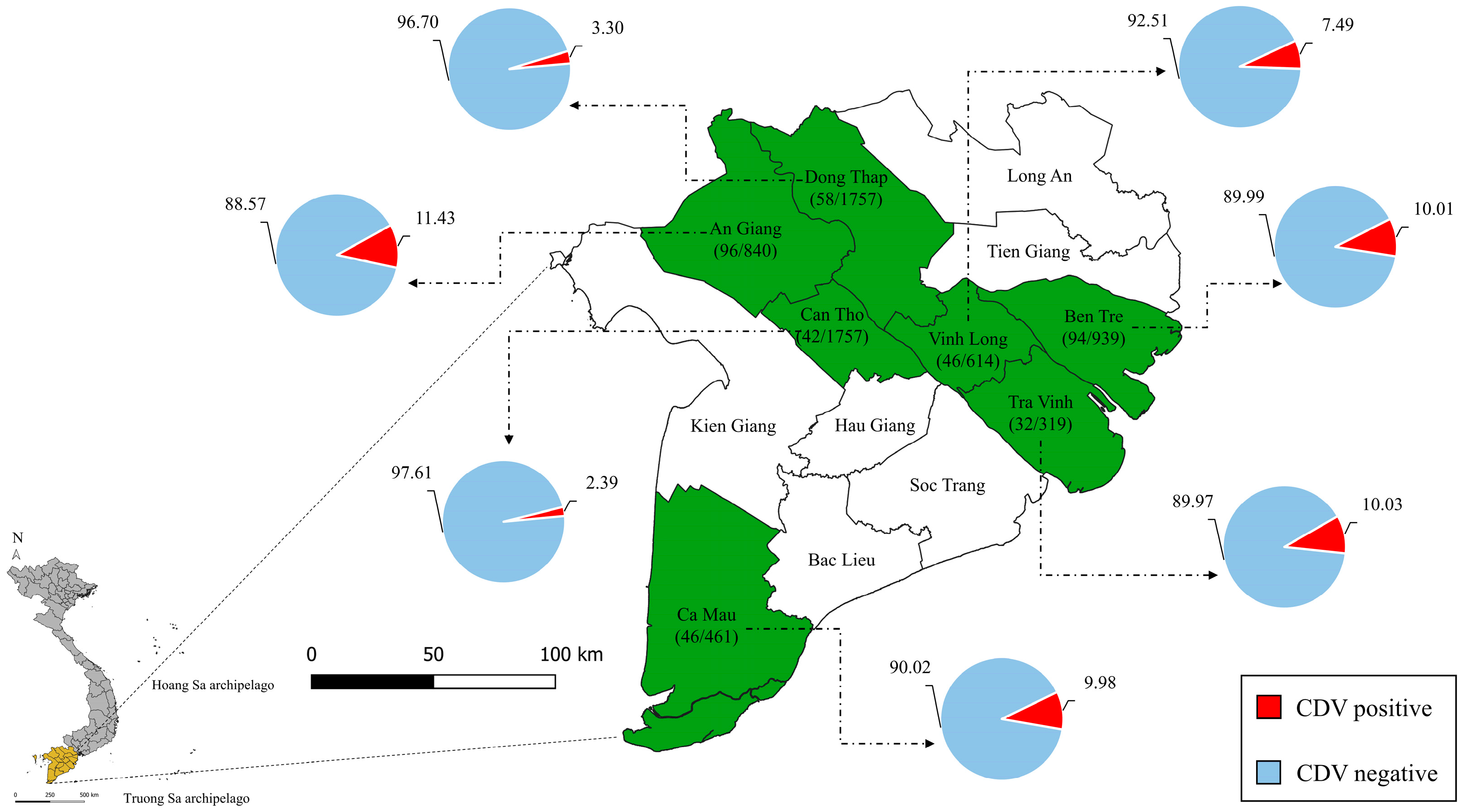

| Category | No. of Positive Dogs/Total | Percentage (%) | OR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | ||||
| <6 months | 202/1729 | 11.68 a | Ref. | 0.001 |
| 6 months–2 years | 38/1662 | 2.29 c | 5.65 (3.97–8.05) | |
| 2–5 years | 49/1694 | 2.89 c | 4.44 (3.22–6.11) | |
| >5 years | 125/1602 | 7.80 b | 1.56 (1.24–1.98) | |
| Breed | ||||
| Pure/cross | 189/2836 | 6.66 | 0.88 (0.72–1.07) | 0.20 |
| Local | 225/3851 | 5.84 | ||
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 225/3431 | 6.56 | 1.14 (0.93–1.39) | 0.20 |
| Female | 189/3256 | 5.80 | ||
| Roaming status | ||||
| Free-roaming | 272/3735 | 7.28 a | 1.51 (1.23–1.87) | 0.001 |
| Confined | 142/2952 | 4.81 b | ||
| Vaccination status | ||||
| No | 298/2180 | 13.67 a | Ref. | 0.001 |
| One dose | 95/2087 | 4.55 b | 3.32 (2.61–4.22) | |
| Two doses | 21/2420 | 0.87 c | 18.09 (11.57–28.27) | |
| Category | Reference | CDV-Infected Dogs (Mean ± SE) | Min–Max |
|---|---|---|---|
| RBC (106/mm3) | 5–10 | 4.02 ± 0.06 | 1.10–5.99 |
| HCT (%) | 30–45 | 31.38 ± 0.28 | 20.00–39.80 |
| MCV (fL) | 60–77 | 52.48 ± 0.80 | 21.10–74.90 |
| HGB (g/dL) | 8–15 | 8.38 ± 0.06 | 6.10–10.90 |
| MCH (Pg) | 19.50–24.50 | 14.94 ± 0.19 | 10.00–22.50 |
| MCHC (%) | 32–36 | 28.20 ± 0.09 | 22.60–35.00 |
| WBC (103/mm3) | 5.50–19.50 | 4.45 ± 0.08 | 1.05–7.60 |
| Neutrophil (%) | 35–75 | 78.33 ± 0.18 | 75.00–97.39 |
| Lymphocyte (%) | 20–55 | 27.21 ± 0.08 | 25.00–40.80 |
| Monocyte (%) | 1–4 | 2.72 ± 0.10 | 1.01–13.06 |
| Eosinophil (%) | 2–12 | 6.54 ± 0.04 | 3.46–7.98 |
| Basophil (%) | 0–1 | 0.43 ± 0.003 | 0.30–0.66 |
| PLT (103/mm3) | 300–700 | 283.58 ± 5.06 | 101.00–499.40 |
| AST (U/L) | 8.90–48.50 | 54.69 ± 1.15 | 28.00–159.00 |
| ALT (U/L) | 8.20–57.30 | 56.44 ± 0.94 | 22.00–114.00 |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 3.10–9.20 | 27.46 ± 0.25 | 20.10–39.90 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.50–1.60 | 1.50 ± 0.01 | 1.00–1.90 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Van, T.M.; Tran, D.T.A.; Nguyen, C.T.P.; Huynh, G.T.; Luu, M.T.N.; Le, T.Q.; Tran, B.N. Epidemiological, Clinical, and Molecular Insights into Canine Distemper Virus in the Mekong Delta Region of Vietnam. Viruses 2025, 17, 781. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17060781
Van TM, Tran DTA, Nguyen CTP, Huynh GT, Luu MTN, Le TQ, Tran BN. Epidemiological, Clinical, and Molecular Insights into Canine Distemper Virus in the Mekong Delta Region of Vietnam. Viruses. 2025; 17(6):781. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17060781
Chicago/Turabian StyleVan, Tien My, Dao Thi Anh Tran, Chien Tran Phuoc Nguyen, Giang Truong Huynh, Mong Thi Nhu Luu, Trung Quang Le, and Bich Ngoc Tran. 2025. "Epidemiological, Clinical, and Molecular Insights into Canine Distemper Virus in the Mekong Delta Region of Vietnam" Viruses 17, no. 6: 781. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17060781
APA StyleVan, T. M., Tran, D. T. A., Nguyen, C. T. P., Huynh, G. T., Luu, M. T. N., Le, T. Q., & Tran, B. N. (2025). Epidemiological, Clinical, and Molecular Insights into Canine Distemper Virus in the Mekong Delta Region of Vietnam. Viruses, 17(6), 781. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17060781







