Implementing Symptom-Based Predictive Models for Early Diagnosis of Pediatric Respiratory Viral Infections
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Sample Collection
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
2.3. Ethical Considerations
2.4. Data Collection and Processing
2.5. Modeling Approach
2.6. SHAP Value Analysis
2.7. Software and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Dataset of the Symptoms and Respiratory Viral Infections Present in the Population
3.2. Symptom-Based Model Performance Accuracy in the Detection of Respiratory Viruses
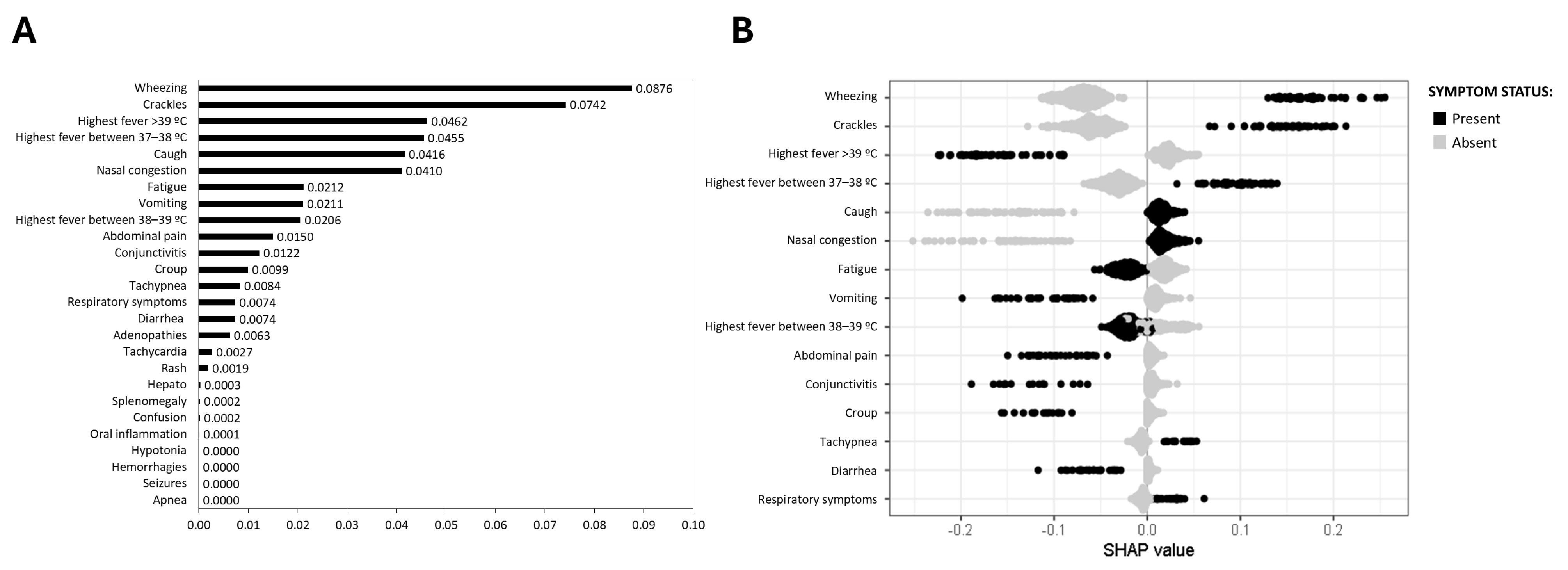
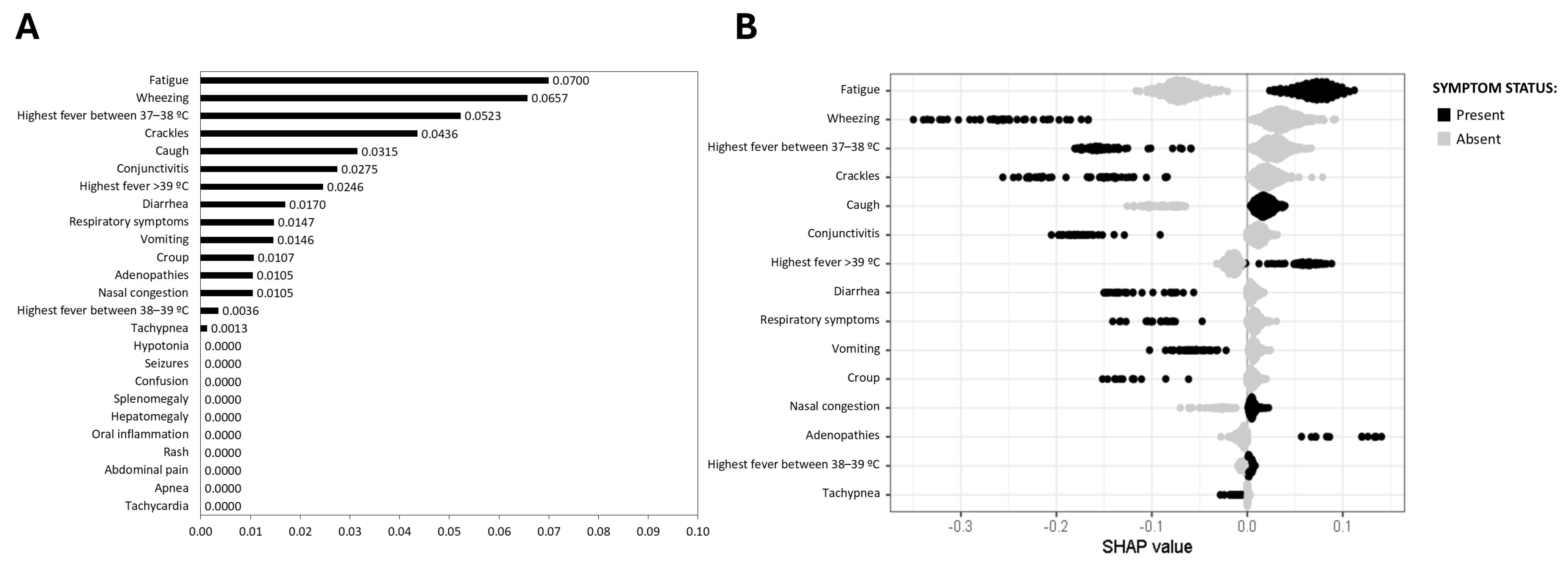
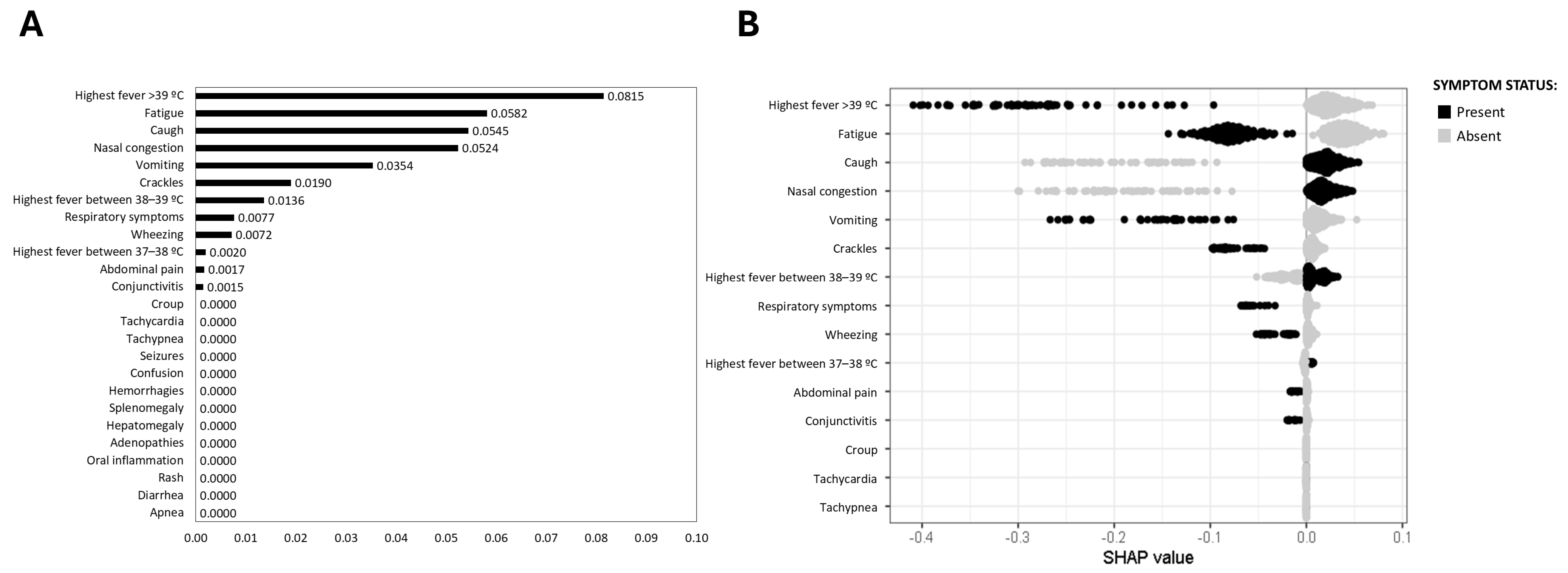
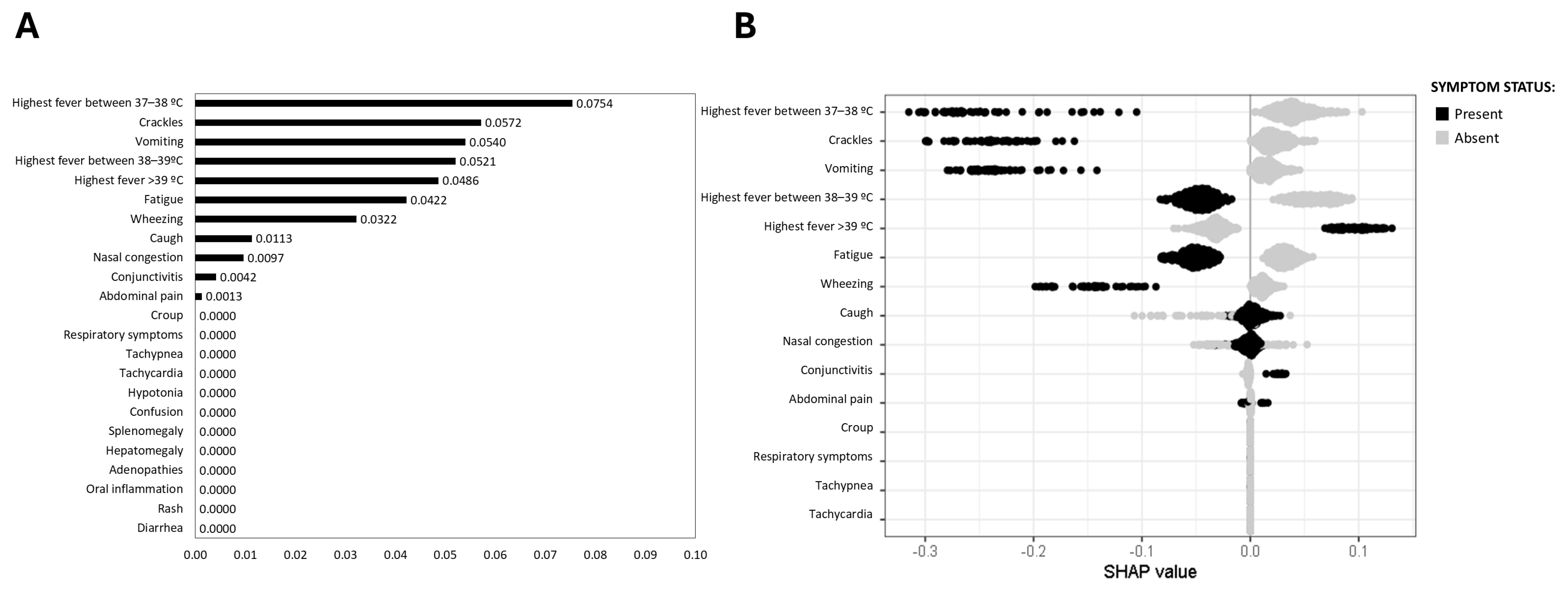
3.3. Virus-Specific Predictive Symptoms for Respiratory Infections
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| ARI | Acute Respiratory Infection |
| CAP | Centre d’Atenció Primària (Primary Care Center) |
| COPEDICAT | Coronavirus Pediatria Catalunya |
| EAP | Equip d’Atenció Primària (Primary Care Team) |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| RSV | Respiratory Syncytial Virus |
| SHAP | Shapley Additive Explanations |
| SMOTE-NC | Synthetic Minority Over-Sampling Technique for Nominal and Continuous Features |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 |
References
- Litwin, C.M.; Bosley, J.G. Seasonality and prevalence of respiratory pathogens detected by multiplex PCR at a tertiary care medical center. Arch. Virol. 2014, 159, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieren, D.K.J.; Boer, M.C.; de Wit, J. The adaptive immune system in early life: The shift makes it count. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1031924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Xu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhang, L.; Gu, W.; Shen, M. Epidemiological characteristics of four common respiratory viral infections in children. Virol. J. 2021, 18, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koonin, E.V.; Krupovic, M.; Agol, V.I. The Baltimore Classification of Viruses 50 Years Later: How Does It Stand in the Light of Virus Evolution? Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2021, 85, e0005321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahy, B.W. The Evolution and Emergence of RNA Viruses. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debiaggi, M.; Canducci, F.; Ceresola, E.R.; Clementi, M. The role of infections and coinfections with newly identified and emerging respiratory viruses in children. Virol. J. 2012, 9, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filip, R.; Gheorghita Puscaselu, R.; Anchidin-Norocel, L.; Dimian, M.; Savage, W.K. Global challenges to public health care systems during the COVID-19 pandemic: A review of pandemic measures and problems. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, R.; Sharma, R. Pediatric COVID: How is it different from adults? Indian J. Respir. Care, 2022; Unpublished Work. [Google Scholar]
- Shearah, Z.; Ullah, Z.; Fakieh, B. Intelligent framework for early detection of severe pediatric diseases from mild symptoms. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, A.R.; López, S.M.; Contreras-Arrieta, S.; Tamayo-Cabeza, G.; Restrepo-Restrepo, S.; Sarmiento-Barbieri, I.; Caballero-Díaz, Y.; Hernandez-Florez, L.J.; González, J.M.; Salas-Zapata, L.; et al. Prediction of SARS-CoV-2 infection with a symptoms-based model to aid public health decision making in Latin America and other low and middle income settings. Prev. Med. Rep. 2022, 27, 101798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tso, C.F.; Lam, C.; Calvert, J.; Mao, Q. Machine learning early prediction of respiratory syncytial virus in pediatric hospitalized patients. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 886212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, T.; Camargo, C.A., Jr.; Faridi, M.K.; Freishtat, R.J.; Hasegawa, K. Machine learning-based prediction of clinical outcomes for children during emergency department triage. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e186937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barenfanger, J.; Drake, C.; Leon, N.; Mueller, T.; Troutt, T. Clinical and financial benefits of rapid detection of respiratory viruses: An outcomes study. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 2824–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoñanzas, J.M.; Perramon, A.; López, C.; Boneta, M.; Aguilera, C.; Capdevila, R.; Gatell, A.; Serrano, P.; Poblet, M.; Canadell, D.; et al. Symptom-based predictive model of COVID-19 disease in children. Viruses 2021, 14, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petric, M.; Comanor, L.; Petti, C.A. Role of the laboratory in diagnosis of influenza during seasonal epidemics and potential pandemics. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 194, S98–S110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramgopal, S.; Sanchez-Pinto, L.N.; Horvat, C.M.; Carroll, M.S.; Luo, Y.; Florin, T.A. Artificial intelligence-based clinical decision support in pediatrics. Pediatr. Res. 2023, 93, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagne, H.; Andualem, Z.; Dagnew, B.; Taddese, A.A. Acute respiratory infection and its associated factors among children under-five years attending pediatrics ward at University of Gondar Comprehensive Specialized Hospital, Northwest Ethiopia: Institution-based cross-sectional study. BMC Pediatr. 2020, 20, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gabory, L.; Alharbi, A.; Kérimian, M.; Lafon, M.E. The influenza virus, SARS-CoV-2, and the airways: Clarification for the otorhinolaryngologist. Eur. Ann. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Dis. 2020, 137, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Y.F.; Khan, S.J.; Vishal, F.; Alam, S.; Murtaza, S.F. Respiratory syncytial virus prevention: A new era of vaccines. Cureus 2023, 15, e45012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gea-Izquierdo, E.; Gil-Prieto, R.; Hernández-Barrera, V.; Gil-de-Miguel, Á. Respiratory syncytial virus-associated hospitalization in children aged <2 years in Spain from 2018 to 2021. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2023, 19, 2231818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera-Hueso, F.J.; Álvarez-Arroyo, L.; Poquet-Jornet, J.E.; Vázquez-Ferreiro, P.; Martínez-Gonzalbez, R.; El-Qutob, D.; Ramón-Barrios, M.A.; Martínez-Martínez, F.; Poveda-Andrés, J.L.; Crespo-Palomo, C. Hospitalization budget impact during the COVID-19 pandemic in Spain. Health Econ. Rev. 2021, 11, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brañas, P.; Muñoz-Gallego, I.; Espartosa, E.; Moral, N.; Abellán, G.; Folgueira, L. Dynamics of respiratory viruses other than SARS-CoV-2 during the COVID-19 pandemic in Madrid, Spain. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2023, 17, e13199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esneau, C.; Bartlett, N.; Bochkov, Y. Rhinovirus structure, replication, and classification. In Rhinovirus Infections; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, J.P., III; Kajon, A.E. Adenovirus: Epidemiology, global spread of novel serotypes, and advances in treatment and prevention. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 37, 586–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandini, S.; Biagi, C.; Fischer, M.; Lanari, M. Impact of rhinovirus infections in children. Viruses 2019, 11, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challener, D.W.; Dowdy, S.C.; O’Horo, J.C. Analytics and prediction modeling during the COVID-19 pandemic. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2020, 95, S8–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Noren, D.P.; Kulkarni, C.; Mariani, S.; Zhao, C.; Ghosh, E.; Swearingen, D.; Frassica, J.; McFarlane, D.; Conroy, B. Machine learning-based clinical decision support for infection risk prediction. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1213411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Metric | SARS-CoV-2 | RSV | Influenza | Rhinovirus | Adenovirus |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Samples | 95 | 154 | 382 | 103 | 126 |
| AUC | 0.71 | 0.81 | 0.70 | 0.62 | 0.69 |
| Accuracy | 0.64 | 0.76 | 0.63 | 0.61 | 0.68 |
| Kappa | 0.09 | 0.27 | 0.27 | 0.04 | 0.13 |
| Sensitivity | 0.64 | 0.64 | 0.70 | 0.50 | 0.57 |
| Specificity | 0.64 | 0.77 | 0.59 | 0.62 | 0.69 |
| Positive Predicted Value | 0.12 | 0.29 | 0.50 | 0.09 | 0.17 |
| Negative Predicted Value | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.77 | 0.94 | 0.94 |
| Prevalence | 0.08 | 0.13 | 0.37 | 0.07 | 0.10 |
| Detection Rate | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.26 | 0.03 | 0.06 |
| Detection Prevalence | 0.38 | 0.28 | 0.52 | 0.39 | 0.33 |
| Balanced Accuracy | 0.64 | 0.71 | 0.65 | 0.56 | 0.63 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soriano-Arandes, A.; Andrés, C.; Perramon-Malavez, A.; Creus-Costa, A.; Gatell, A.; Martín-Martín, R.; Solà-Segura, E.; Riera-Bosch, M.T.; Fernández, E.; Biosca, M.; et al. Implementing Symptom-Based Predictive Models for Early Diagnosis of Pediatric Respiratory Viral Infections. Viruses 2025, 17, 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17040546
Soriano-Arandes A, Andrés C, Perramon-Malavez A, Creus-Costa A, Gatell A, Martín-Martín R, Solà-Segura E, Riera-Bosch MT, Fernández E, Biosca M, et al. Implementing Symptom-Based Predictive Models for Early Diagnosis of Pediatric Respiratory Viral Infections. Viruses. 2025; 17(4):546. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17040546
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoriano-Arandes, Antoni, Cristina Andrés, Aida Perramon-Malavez, Anna Creus-Costa, Anna Gatell, Ramona Martín-Martín, Elisabet Solà-Segura, Maria Teresa Riera-Bosch, Eduard Fernández, Mireia Biosca, and et al. 2025. "Implementing Symptom-Based Predictive Models for Early Diagnosis of Pediatric Respiratory Viral Infections" Viruses 17, no. 4: 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17040546
APA StyleSoriano-Arandes, A., Andrés, C., Perramon-Malavez, A., Creus-Costa, A., Gatell, A., Martín-Martín, R., Solà-Segura, E., Riera-Bosch, M. T., Fernández, E., Biosca, M., Capdevila, R., Sánchez, A., Soler, I., Chiné, M., Sanz, L., Quezada, G., Pérez, S., Canadell, D., Salvadó, O., ... Prats, C. (2025). Implementing Symptom-Based Predictive Models for Early Diagnosis of Pediatric Respiratory Viral Infections. Viruses, 17(4), 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17040546






