Immunological and Neurological Signatures of the Co-Infection of HIV and HTLV: Current Insights and Future Perspectives
Abstract
1. Introduction
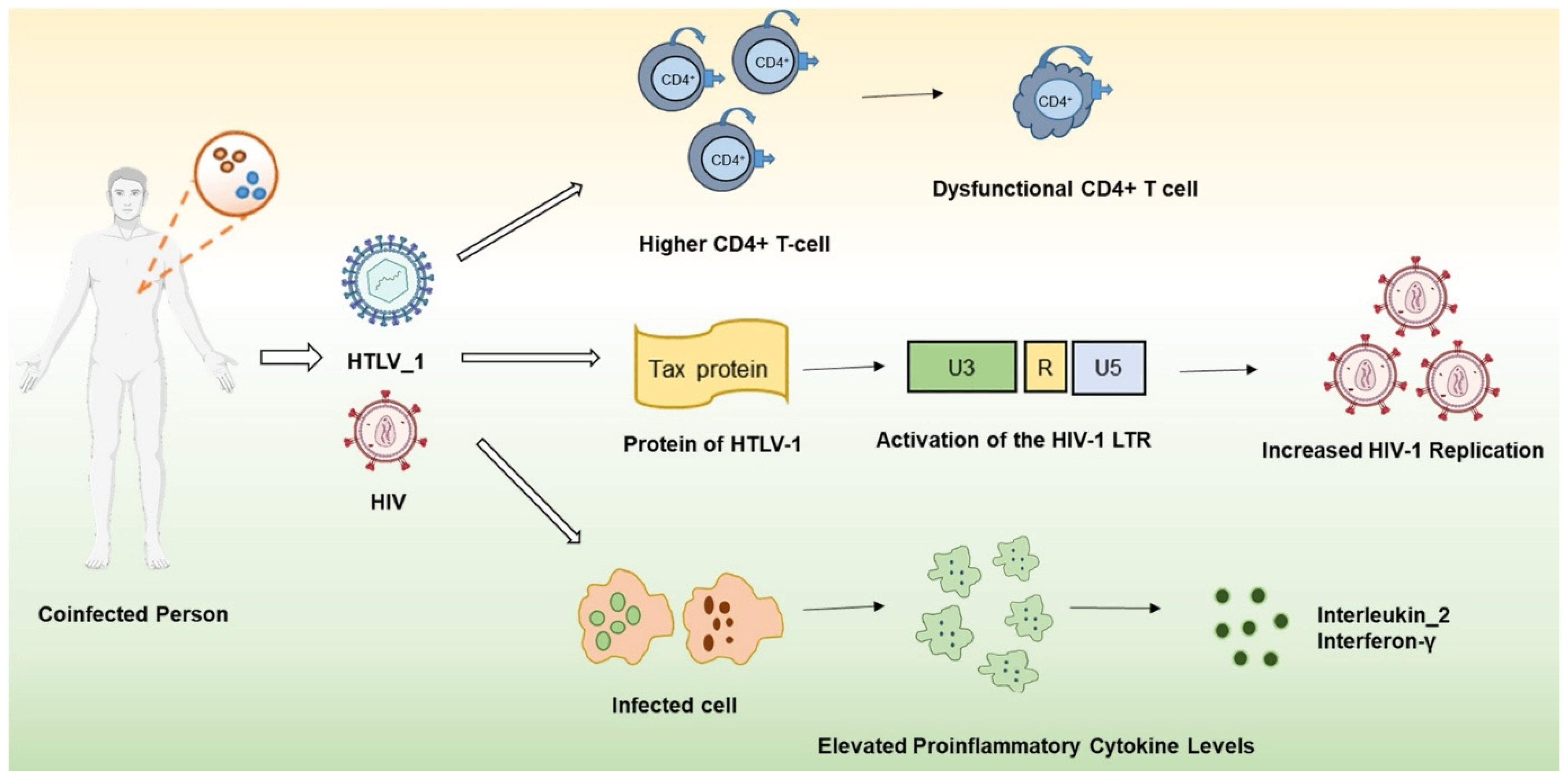
2. Effects of Co-Infection on Immune System Dynamics
3. Viral Interplay and Synergistic Pathogenesis: Mechanisms of Co-Infection Between HIV and HTLV-1
4. Longitudinal Patterns in HIV and HTLV-1 Co-Infection: Viral Loads, Immune Responses, and Disease Trajectories
5. Antiretroviral Therapy in HIV/HTLV-1 Co-Infection: Mechanisms, Efficacy, and Side Effects
6. Therapeutic Efficacy of Antiretroviral Regimens in HIV and HTLV-1 Co-Infected Patients
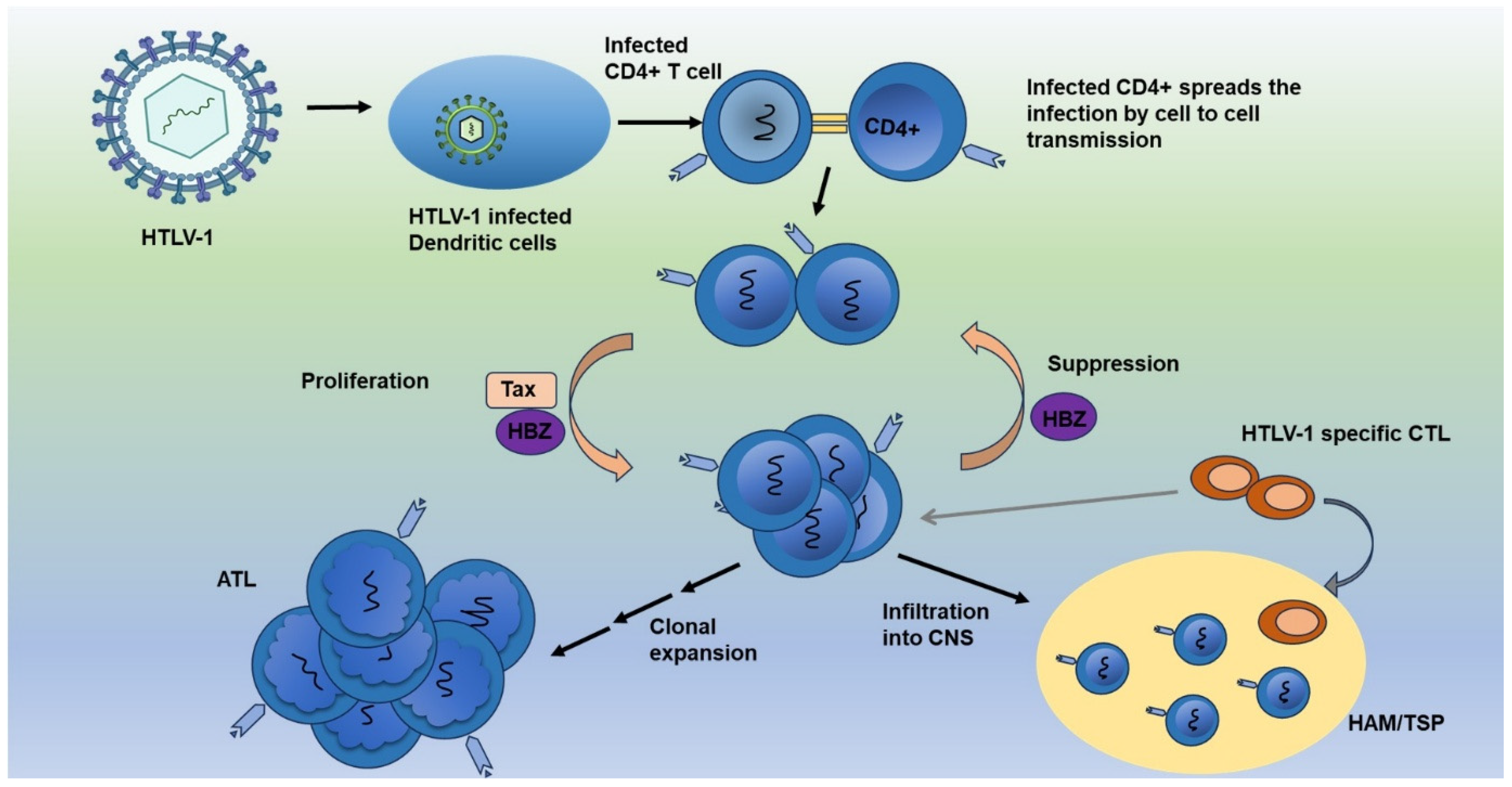
7. HIV-1 and HTLV-1 Reservoirs: Mechanisms of Persistence, Immune Evasion, and Implications for Treatment
8. Comparative Impact on Morbidity and Mortality in Co-Infected Versus Mono-Infected
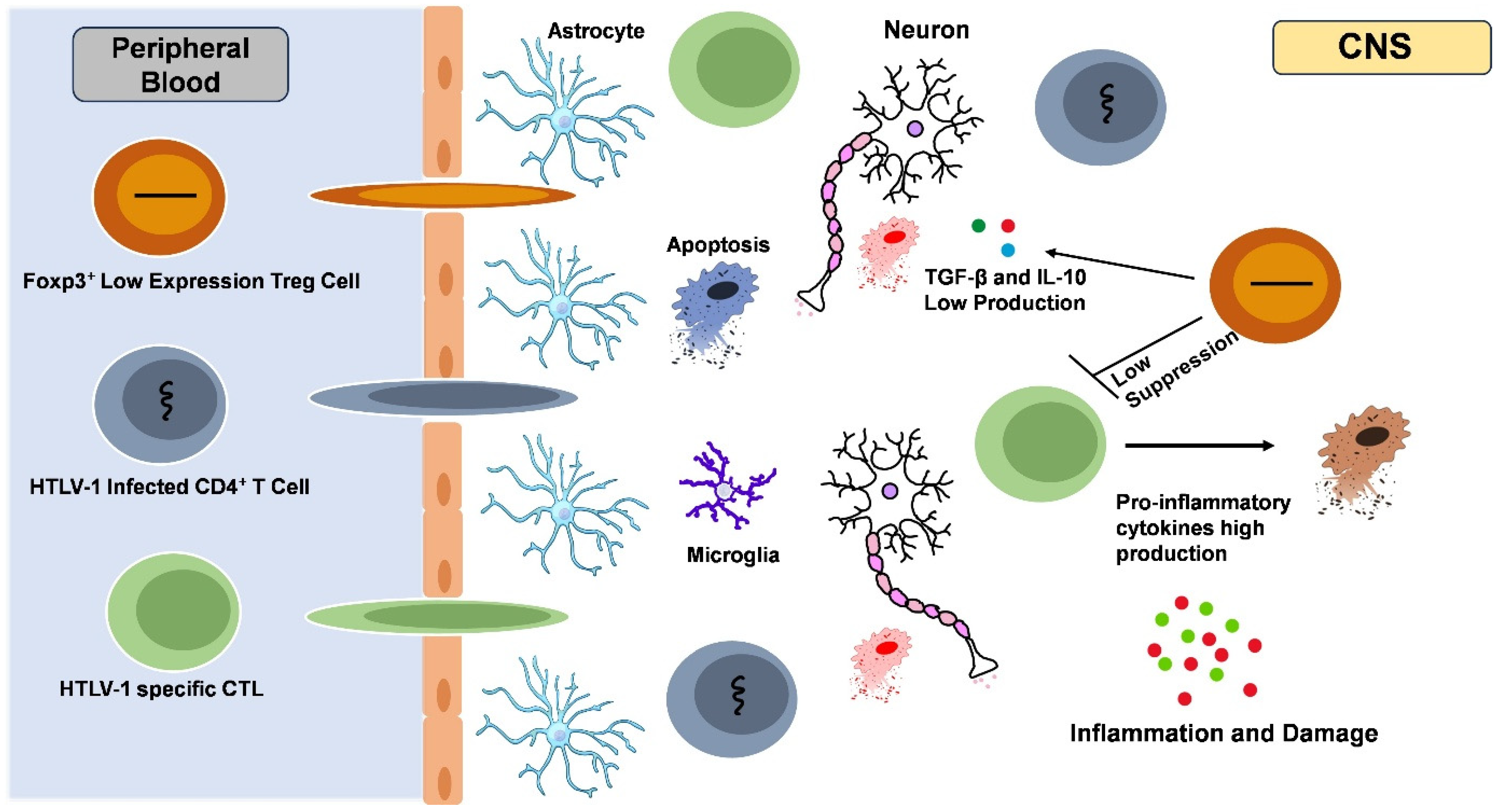
9. Neurological Effect
9.1. Neurological Complications in Patients Co-Infected with HIV and HTLV-1
9.2. HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorders (HAND): Pathogenesis, Impact, and the Role of the CNS
9.3. The Prevalence and Impact of HAM/TSP in HIV/HTLV-1 Co-Infected Patients
9.4. Management Strategies for HAM/TSP in the Context of ART
10. Public Health Implications of HIV/HTLV-1 Co-Infection
10.1. Epidemiology of Co-Infection in Different Geographic Regions
10.2. Strategies for Public Health to Manage and Prevent Co-Infections
10.3. Diagnostic Challenges in Identifying and Managing HIV/HTLV-1 Co-Infection
10.4. Barriers to Effective Treatment and Management, Especially in Resource-Limited Settings
11. Perspectives and Future Challenges
12. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nadler, J.P.; Bach, M.C.; Godofsky, E. Management of coinfection with human immunodeficiency virus and human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1996, 23, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, R.C. The discovery of the first human retrovirus: HTLV-1 and HTLV-2. Retrovirology 2005, 2, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bangham, C.R.M. The immune control and cell-to-cell spread of human T-lymphotropic virus type 1. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 3177–3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gout, O.; Baulac, M.; Gessain, A.; Semah, F.; Saal, F.; Peries, J.; Cabrol, C.; Foucault-Fretz, C.; Laplane, D.; Sigaux, F.; et al. Rapid development of myelopathy after HTLV-I infection acquired by transfusion during cardiac transplantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 322, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osame, M.; Arimura, K.; Nakagawa, M.; Umehara, F.; Usuku, K.; Ijichi, S. HTLV-I associated myelopathy (HAM): Review and recent studies. Leukemia 1997, 11 (Suppl. S3), 63–64. [Google Scholar]
- Enose-Akahata, Y.; Vellucci, A.; Jacobson, S. Role of HTLV-1 Tax and HBZ in the Pathogenesis of HAM/TSP. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brites, C.; Sampalo, J.; Oliveira, A. HIV/human T-cell lymphotropic virus coinfection revisited: Impact on AIDS progression. AIDS Rev. 2009, 11, 8–16. [Google Scholar]
- Brites, C.; Alencar, R.; Gusmao, R.; Pedroso, C.; Netto, E.M.; Pedral-Sampaio, D.; Badaro, R. Co-infection with HTLV-1 is associated with a shorter survival time for HIV-1-infected patients in Bahia, Brazil. Aids 2001, 15, 2053–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elaiw, A.M.; AlShamrani, N.H. Modeling and analysis of a within-host HIV/HTLV-I co-infection. Bol. Soc. Mat. Mex. 2021, 27, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montano-Castellon, I.; Marconi, C.S.C.; Saffe, C.; Brites, C. Clinical and Laboratory Outcomes in HIV-1 and HTLV-1/2 Coinfection: A Systematic Review. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 820727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulherkar, T.H.; Gomez, D.J.; Sandel, G.; Jain, P. Co-Infection and Cancer: Host-Pathogen Interaction between Dendritic Cells and HIV-1, HTLV-1, and Other Oncogenic Viruses. Viruses 2022, 14, 2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilotti, E.; Bianchi, M.V.; De Maria, A.; Bozzano, F.; Romanelli, M.G.; Bertazzoni, U.; Casoli, C. HTLV-1/-2 and HIV-1 co-infections: Retroviral interference on host immune status. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starling, A.L.B.; Pereira, S.R.S.; Peruhype-Magalhaes, V.; Coelho-Dos-Reis, J.G.A.; Bicalho, K.A.; de Paiva, L.P.; Martins, J.P.; Trindade, B.C.; Labanca, L.; Faccioli, L.H.; et al. Impact of HIV co-infection on immunological biomarker profile of HTLV-1 infected patients. Immunol. Lett. 2021, 236, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrahao, M.H.; Lima, R.G.; Netto, E.; Brites, C. Short communication: Human lymphotropic virus type 1 coinfection modulates the synthesis of cytokines by peripheral blood mononuclear cells from HIV type 1-infected individuals. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2012, 28, 806–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisco, A.; Vanpouille, C.; Margolis, L. Coinfecting viruses as determinants of HIV disease. Curr. HIV AIDS Rep. 2009, 6, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, H.; Rezaee, S.A.; Valizade, N.; Vakili, R.; Rafatpanah, H. Assessment of HTLV-I proviral load, HIV viral load and CD4 T cell count in infected subjects; with an emphasis on viral replication in co-infection. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2014, 17, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Assone, T.; Paiva, A.; Fonseca, L.A.; Casseb, J. Genetic Markers of the Host in Persons Living with HTLV-1, HIV and HCV Infections. Viruses 2016, 8, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marconi, C.S.C.; Lins-Kusterer, L.; Brites, C.; Gomes-Neto, M. Comparison of functioning and health-related quality of life among patients with HTLV-1, HIV, and HIV-HTLV-1-coinfection. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2021, 54, e0759-2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.T.; Neves, E.S.; Grinsztejn, B.; de Melo Espindola, O.; Schor, D.; Araujo, A. Neurological manifestations of coinfection with HIV and human T-lymphotropic virus type 1. Aids 2012, 26, 521–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert-Guroff, M.; Blayney, D.W.; Safai, B.; Lange, M.; Gelmann, E.P.; Gutterman, J.W.; Mansell, P.W.; Goedert, J.L.; Groopman, J.E.; Steigbigel, N.H.; et al. HTLV-I-specific antibody in AIDS patients and others at risk. Lancet 1984, 2, 128–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khabbaz, R.F.; Onorato, I.M.; Cannon, R.O.; Hartley, T.M.; Roberts, B.; Hosein, B.; Kaplan, J.E. Seroprevalence of HTLV-1 and HTLV-2 among intravenous drug users and persons in clinics for sexually transmitted diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 1992, 326, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schechter, M.; Moulton, L.H.; Harrison, L.H. HIV viral load and CD4+ lymphocyte counts in subjects coinfected with HTLV-I and HIV-1. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. Hum. Retrovirol. 1997, 15, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessinger, R.; Beilke, M.; Kissinger, P.; Jarrott, C.; Tabak, O.F. Retroviral coinfections at a New Orleans HIV outpatient clinic. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. Hum. Retrovirol. 1997, 14, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobesky, M.; Couppie, P.; Pradinaud, R.; Godard, M.C.; Alvarez, F.; Benoit, B.; Carme, B.; Lebeux, P. Coinfection with HIV and HTLV-I infection and survival in AIDS stage. French Guiana Study. GECVIG (Clinical HIV Study Group in Guiana). Presse Med. 2000, 29, 413–416. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vandormael, A.; Rego, F.; Danaviah, S.; Alcantara, L.C., Jr.; Boulware, D.R.; de Oliveira, T. CD4+ T-cell Count may not be a Useful Strategy to Monitor Antiretroviral Therapy Response in HTLV-1/HIV Co-infected Patients. Curr. HIV Res. 2017, 15, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibu, M.A.; Lin, Y.J.; Chiang, C.Y.; Lu, C.Y.; Goswami, D.; Sundhar, N.; Agarwal, S.; Islam, M.N.; Lin, P.Y.; Lin, S.Z.; et al. Novel anti-aging herbal formulation Jing Si displays pleiotropic effects against aging associated disorders. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 146, 112427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.N.; Mishra, V.K.; Munalisa, R.; Parveen, F.; Ali, S.F.; Akter, K.; Ahmed, T.; Ho, T.-J.; Huang, C.-Y. Mechanistic insight of mitochondrial dysfunctions in cardiovascular diseases with potential biomarkers. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 2024, 20, 441–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockwood, N.; Cook, L.; Kagdi, H.; Basnayake, S.; Bangham, C.R.M.; Pozniak, A.L.; Taylor, G.P. Immune Compromise in HIV-1/HTLV-1 Coinfection With Paradoxical Resolution of CD4 Lymphocytosis During Antiretroviral Therapy: A Case Report. Medicine 2015, 94, e2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbett, E.L.; Watt, C.J.; Walker, N.; Maher, D.; Williams, B.G.; Raviglione, M.C.; Dye, C. The growing burden of tuberculosis: Global trends and interactions with the HIV epidemic. Arch. Intern Med. 2003, 163, 1009–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdonck, K.; Gonzalez, E.; Van Dooren, S.; Vandamme, A.M.; Vanham, G.; Gotuzzo, E. Human T-lymphotropic virus 1: Recent knowledge about an ancient infection. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2007, 7, 266–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norrgren, H.; Bamba, S.; Da Silva, Z.J.; Koivula, T.; Andersson, S. Higher mortality in HIV-2/HTLV-1 co-infected patients with pulmonary tuberculosis in Guinea-Bissau, West Africa, compared to HIV-2-positive HTLV-1-negative patients. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 14 (Suppl. S3), e142–e147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machuca, A.; Rodes, B.; Soriano, V. The effect of antiretroviral therapy on HTLV infection. Virus Res. 2001, 78, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, J.S.; Jaberolansar, N.; Chappell, K.J. Human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 and antiretroviral therapy: Practical considerations for pre-exposure and post-exposure prophylaxis, transmission prevention, and mitigation of severe disease. Lancet Microbe 2024, 5, e400–e408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Futsch, N.; Mahieux, R.; Dutartre, H. HTLV-1, the Other Pathogenic Yet Neglected Human Retrovirus: From Transmission to Therapeutic Treatment. Viruses 2017, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volberding, P.A.; Deeks, S.G. Antiretroviral therapy and management of HIV infection. Lancet 2010, 376, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, R.M.; Currier, J.S. Management of antiretroviral treatment-related complications. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2007, 21, 103–132, ix. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regis, C.; Oliveira, A.; Brites, C. Onset of opportunistic infections in patients co-infected by HTLV-1 and HIV-1, with high CD4+ cells count. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 13, 311–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, A.Q. Neurological Aspects of HIV-1/HTLV-1 and HIV-1/HTLV-2 Coinfection. Pathogens 2020, 9, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanzo-Vargas, M.P.; Arellano-Veintemilla, T.; Gonzalez-Lagos, E.; Echevarria, J.; Mejia, F.; Grana, A.; Gotuzzo, E. Socio-Demographic, Clinical, and Mortality Differences between HIV-Infected and HIV/HTLV-1 Co-Infected Patients in Peru. Pathogens 2023, 12, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomier, C.; Rabaaoui, S.; Pouliquen, J.F.; Couppie, P.; El Guedj, M.; Nacher, M.; Lacoste, V.; Wattel, E.; Kazanji, M.; Mortreux, F. Antiretroviral therapy promotes an inflammatory-like pattern of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1) replication in human immunodeficiency virus type 1/HTLV-1 co-infected individuals. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 753–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreider, E.F.; Bar, K.J. HIV-1 Reservoir Persistence and Decay: Implications for Cure Strategies. Curr. HIV/AIDS Rep. 2022, 19, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierson, T.; McArthur, J.; Siliciano, R.F. Reservoirs for HIV-1: Mechanisms for viral persistence in the presence of antiviral immune responses and antiretroviral therapy. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2000, 18, 665–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chomont, N.; El-Far, M.; Ancuta, P.; Trautmann, L.; Procopio, F.A.; Yassine-Diab, B.; Boucher, G.; Boulassel, M.R.; Ghattas, G.; Brenchley, J.M.; et al. HIV reservoir size and persistence are driven by T cell survival and homeostatic proliferation. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Lian, X.; Gao, C.; Sun, X.; Einkauf, K.B.; Chevalier, J.M.; Chen, S.M.Y.; Hua, S.; Rhee, B.; Chang, K.; et al. Distinct viral reservoirs in individuals with spontaneous control of HIV-1. Nature 2020, 585, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melamed, A.; Fitzgerald, T.W.; Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Birney, E.; Bangham, C.R.M. Selective clonal persistence of human retroviruses in vivo: Radial chromatin organization, integration site, and host transcription. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabm6210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Sanchez, M.A.; Mestre de Juan, M.J.; Gomez-Pajuelo, C.; Lopez, J.I.; Diaz de Atauri, M.J.; Martinez-Tello, F.J. Pulmonary hypertension due to toxic oil syndrome. A clinicopathologic study. Chest 1989, 95, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloney, E.M.; Cleghorn, F.R.; Morgan, O.S.; Rodgers-Johnson, P.; Cranston, B.; Jack, N.; Blattner, W.A.; Bartholomew, C.; Manns, A. Incidence of HTLV-I-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP) in Jamaica and Trinidad. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. Hum. Retrovirol. 1998, 17, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.K.; Ramesh, S.; Islam, M.N.; Shibu, M.A.; Kuo, C.H.; Hsieh, D.J.; Lin, S.Z.; Kuo, W.W.; Huang, C.Y.; Ho, T.J. Artemisia argyi mitigates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by inhibiting mitochondrial dysfunction through the IGF-IIR/Drp1/GATA4 signaling pathway. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2025, 72, 388–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, L.H.; Vaz, B.; Taveira, D.M.; Quinn, T.C.; Gibbs, C.J.; de Souza, S.H.; McArthur, J.C.; Schechter, M. Myelopathy among Brazilians coinfected with human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I and HIV. Neurology 1997, 48, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulius Silva, M.; de Melo Espindola, O.; Bezerra Leite, A.C.; Araujo, A. Neurological aspects of HIV/human T lymphotropic virus coinfection. AIDS Rev. 2009, 11, 71–78. [Google Scholar]
- Leite, A.C.; Mendonca, G.A.; Serpa, M.J.; Nascimento, O.J.; Araujo, A.Q. Neurological manifestations in HTLV-I-infected blood donors. J. Neurol. Sci. 2003, 214, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.K.; Ramesh, S.; Islam, M.N.; Shibu, M.A.; Kuo, C.H.; Hsieh, D.J.; Lin, S.Z.; Kuo, W.W.; Huang, C.Y.; Ho, T.J. Ohwia caudata inhibits doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by regulating mitochondrial dynamics via the IGF-IIR/p-Drp1/PARP signaling pathway. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2024, 71, 1181–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saylor, D.; Dickens, A.M.; Sacktor, N.; Haughey, N.; Slusher, B.; Pletnikov, M.; Mankowski, J.L.; Brown, A.; Volsky, D.J.; McArthur, J.C. HIV-associated neurocognitive disorder—Pathogenesis and prospects for treatment. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 12, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elendu, C.; Aguocha, C.M.; Okeke, C.V.; Okoro, C.B.; Peterson, J.C. HIV-related neurocognitive disorders: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Mental Health Implications: A Review. Medicine 2023, 102, e35652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.B.; Spudich, S.S. Global Health Neurology: HIV/AIDS. Semin. Neurol. 2018, 38, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, D.U.; Proietti, F.A.; Ribas, J.G.; Araujo, M.G.; Pinheiro, S.R.; Guedes, A.C.; Carneiro-Proietti, A.B. Epidemiology, treatment, and prevention of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1-associated diseases. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etzel, A.; Shibata, G.Y.; Rozman, M.; Jorge, M.L.; Damas, C.D.; Segurado, A.A. HTLV-1 and HTLV-2 infections in HIV-infected individuals from Santos, Brazil: Seroprevalence and risk factors. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2001, 26, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osame, M.; Usuku, K.; Izumo, S.; Ijichi, N.; Amitani, H.; Igata, A.; Matsumoto, M.; Tara, M. HTLV-I associated myelopathy, a new clinical entity. Lancet 1986, 1, 1031–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan Hsieh, D.J.; Islam, M.N.; Kuo, W.W.; Shibu, M.A.; Lai, C.H.; Lin, P.Y.; Lin, S.Z.; Chen, M.Y.; Huang, C.Y. A combination of isoliquiritigenin with Artemisia argyi and Ohwia caudata water extracts attenuates oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis by modulating Nrf2/Ho-1 signaling pathways in SD rats with doxorubicin-induced acute cardiotoxicity. Environ. Toxicol. 2023, 38, 3026–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brites, C.; Weyll, M.; Pedroso, C.; Badaro, R. Severe and Norwegian scabies are strongly associated with retroviral (HIV-1/HTLV-1) infection in Bahia, Brazil. Aids 2002, 16, 1292–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schechter, M.; Harrison, L.H.; Halsey, N.A.; Trade, G.; Santino, M.; Moulton, L.H.; Quinn, T.C. Coinfection with human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I and HIV in Brazil. Impact on markers of HIV disease progression. JAMA 1994, 271, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Slater, C.M.; Ribeiro, L.C.; Puccioni-Sohler, M. Difficulties in HAM/TSP diagnosis. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2012, 70, 686–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwasaki, Y.; Ohara, Y.; Kobayashi, I.; Akizuki, S. Infiltration of helper/inducer T lymphocytes heralds central nervous system damage in human T-cell leukemia virus infection. Am. J. Pathol. 1992, 140, 1003–1008. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nagai, M.; Usuku, K.; Matsumoto, W.; Kodama, D.; Takenouchi, N.; Moritoyo, T.; Hashiguchi, S.; Ichinose, M.; Bangham, C.R.; Izumo, S.; et al. Analysis of HTLV-I proviral load in 202 HAM/TSP patients and 243 asymptomatic HTLV-I carriers: High proviral load strongly predisposes to HAM/TSP. J. Neurovirol. 1998, 4, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessain, A.; Barin, F.; Vernant, J.C.; Gout, O.; Maurs, L.; Calender, A.; de Thé, G. Antibodies to human T-lymphotropic virus type-I in patients with tropical spastic paraparesis. Lancet 1985, 2, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradshaw, D.; Taylor, G.P. HTLV-1 Transmission and HIV Pre-exposure Prophylaxis: A Scoping Review. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 881547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olindo, S.; Belrose, G.; Gillet, N.; Rodriguez, S.; Boxus, M.; Verlaeten, O.; Asquith, B.; Bangham, C.; Signate, A.; Smadja, D.; et al. Safety of long-term treatment of HAM/TSP patients with valproic acid. Blood 2011, 118, 6306–6309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isache, C.; Sands, M.; Guzman, N.; Figueroa, D. HTLV-1 and HIV-1 co-infection: A case report and review of the literature. IDCases 2016, 4, 53–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galetto, L.R.; Lunge, V.R.; Beria, J.U.; Tietzmann, D.C.; Stein, A.T.; Simon, D. Short communication: Prevalence and risk factors for human T cell lymphotropic virus infection in Southern Brazilian HIV-positive patients. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2014, 30, 907–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beilke, M.A. Retroviral coinfections: HIV and HTLV: Taking stock of more than a quarter century of research. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2012, 28, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, F.M.; Santos, F.L.N.; Silva, A.A.O.; Nascimento, N.M.; Almeida, M.; Carreiro, R.P.; Galvao-Castro, B.; Rios Grassi, M.F. Distribution of Human Immunodeficiency Virus and Human T-Leukemia Virus Co-infection in Bahia, Brazil. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 788176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mendoza, C.; Caballero, E.; Aguilera, A.; Benito, R.; Macia, D.; Garcia-Costa, J.; Soriano, V.; Spanish, H.N. HIV co-infection in HTLV-1 carriers in Spain. Virus Res. 2019, 266, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augusto, A.; Augusto, O.; Taquimo, A.; Nhachigule, C.; Siyawadya, N.; Tembe, N.; Bhatt, N.; Mbofana, F.; Gudo, E.S. First description of HTLV-1/2 seroprevalence in HIV-infected inmates in Mozambique. J. Med. Virol. 2017, 89, 1498–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansson, F.; Camara, C.; Biai, A.; Monteiro, M.; da Silva, Z.J.; Dias, F.; Alves, A.; Andersson, S.; Fenyo, E.M.; Norrgren, H.; et al. High prevalence of HIV-1, HIV-2 and other sexually transmitted infections among women attending two sexual health clinics in Bissau, Guinea-Bissau, West Africa. Int. J. STD AIDS 2010, 21, 631–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhasmana, D.; Taylor, G.P. Human T-lymphotropic virus/HIV co-infection: A clinical review. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 27, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, L.H.; Schechter, M. Coinfection with HTLV-I and HIV: Increase in HTLV-I-related outcomes but not accelerated HIV disease progression? AIDS Patient Care STDS 1998, 12, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costin, J.M. Cytopathic mechanisms of HIV-1. Virol. J. 2007, 4, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroso, C.; Netto, E.M.; Weyll, N.; Brites, C. Coinfection by HIV-1 and human lymphotropic virus type 1 in Brazilian children is strongly associated with a shorter survival time. J. Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 2011, 57 (Suppl. S3), S208–S211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beilke, M.A.; Japa, S.; Moeller-Hadi, C.; Martin-Schild, S. Tropical spastic paraparesis/human T leukemia virus type 1-associated myelopathy in HIV type 1-coinfected patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 41, e57–e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, M.L.; Vreeman, R.C. Current strategies for improving access and adherence to antiretroviral therapies in resource-limited settings. HIV AIDS 2013, 5, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crum, N.F.; Riffenburgh, R.H.; Wegner, S.; Agan, B.K.; Tasker, S.A.; Spooner, K.M.; Armstrong, A.W.; Fraser, S.; Wallace, M.R.; Triservice, A.C.C. Comparisons of causes of death and mortality rates among HIV-infected persons: Analysis of the pre-, early, and late HAART (highly active antiretroviral therapy) eras. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2006, 41, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong, M.; Rane, M.S.; Govere, S.; Galagan, S.R.; Moosa, M.Y.; Stoep, A.V.; Celum, C.; Drain, P.K. Depression and anxiety as barriers to art initiation, retention in care, and treatment outcomes in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. EClinicalMedicine 2021, 31, 100621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, C.; Beljanski, V.; Yin, K.; Olagnier, D.; Ben Yebdri, F.; Steel, C.; Goulet, M.L.; DeFilippis, V.R.; Streblow, D.N.; Haddad, E.K.; et al. Sequence-Specific Modifications Enhance the Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Response Activated by RIG-I Agonists. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 8011–8025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugata, K.; Yasunaga, J.; Mitobe, Y.; Miura, M.; Miyazato, P.; Kohara, M.; Matsuoka, M. Protective effect of cytotoxic T lymphocytes targeting HTLV-1 bZIP factor. Blood 2015, 126, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frangione-Beebe, M.; Albrecht, B.; Dakappagari, N.; Rose, R.T.; Brooks, C.L.; Schwendeman, S.P.; Lairmore, M.D.; Kaumaya, P.T. Enhanced immunogenicity of a conformational epitope of human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 using a novel chimeric peptide. Vaccine 2000, 19, 1068–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Islam, M.N.; Mili, M.A.; Jahan, I.; Chakma, C.; Munalisa, R. Immunological and Neurological Signatures of the Co-Infection of HIV and HTLV: Current Insights and Future Perspectives. Viruses 2025, 17, 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17040545
Islam MN, Mili MA, Jahan I, Chakma C, Munalisa R. Immunological and Neurological Signatures of the Co-Infection of HIV and HTLV: Current Insights and Future Perspectives. Viruses. 2025; 17(4):545. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17040545
Chicago/Turabian StyleIslam, Md. Nazmul, Masuma Akter Mili, Israt Jahan, Cotton Chakma, and Rina Munalisa. 2025. "Immunological and Neurological Signatures of the Co-Infection of HIV and HTLV: Current Insights and Future Perspectives" Viruses 17, no. 4: 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17040545
APA StyleIslam, M. N., Mili, M. A., Jahan, I., Chakma, C., & Munalisa, R. (2025). Immunological and Neurological Signatures of the Co-Infection of HIV and HTLV: Current Insights and Future Perspectives. Viruses, 17(4), 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17040545






