Targeting Latent HIV Reservoirs: Effectiveness of Combination Therapy with HDAC and PARP Inhibitors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plasmid DNA Construction
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Virus Production and Infection
2.4. Inhibitors
2.5. Immunostaining
2.6. NK-Cell Assays
2.7. Flow Cytometry
3. Results
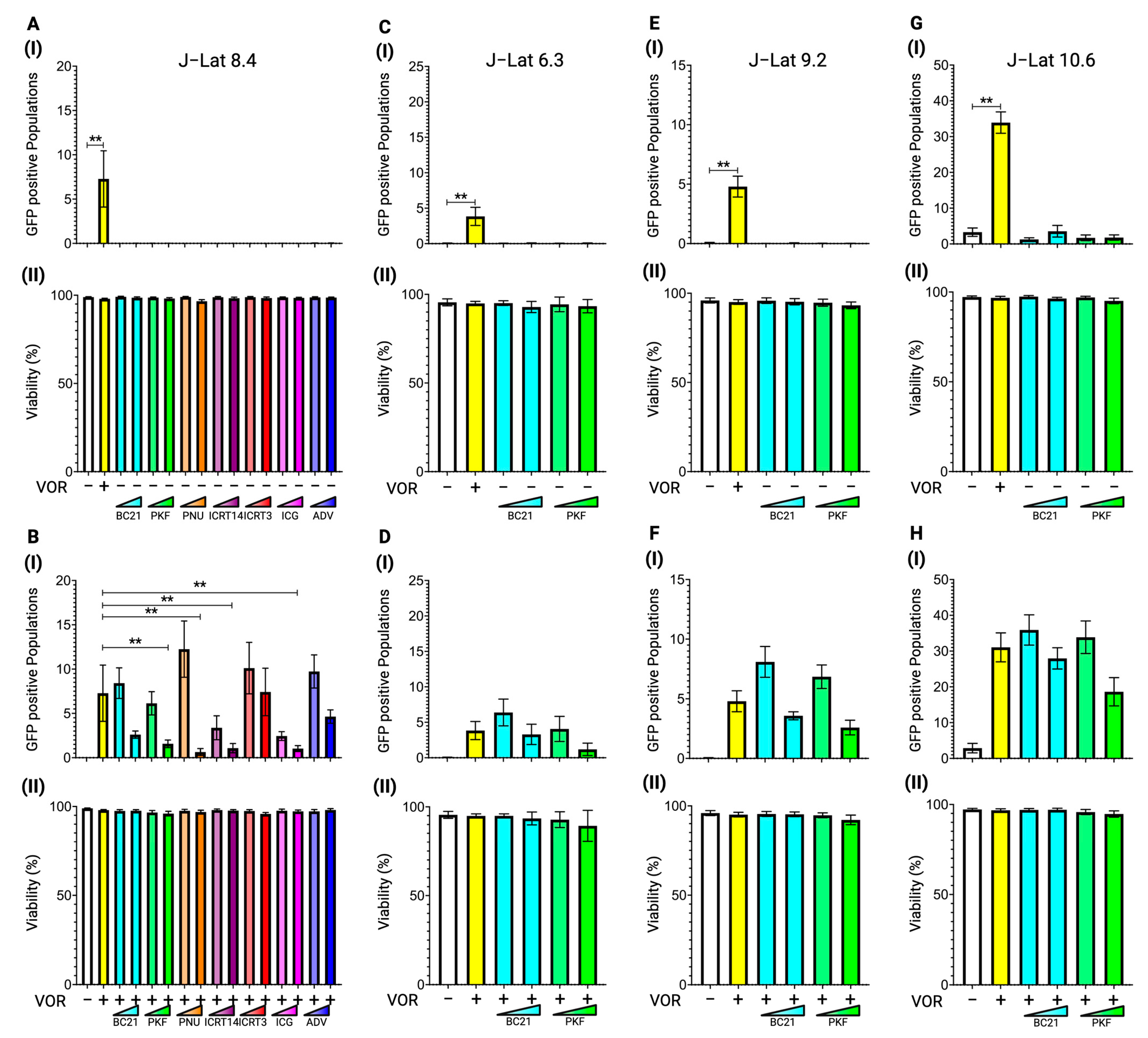
3.1. Latency Reversal Efficacy of β-Catenin Inhibitors in J-Lat Cell Line Models
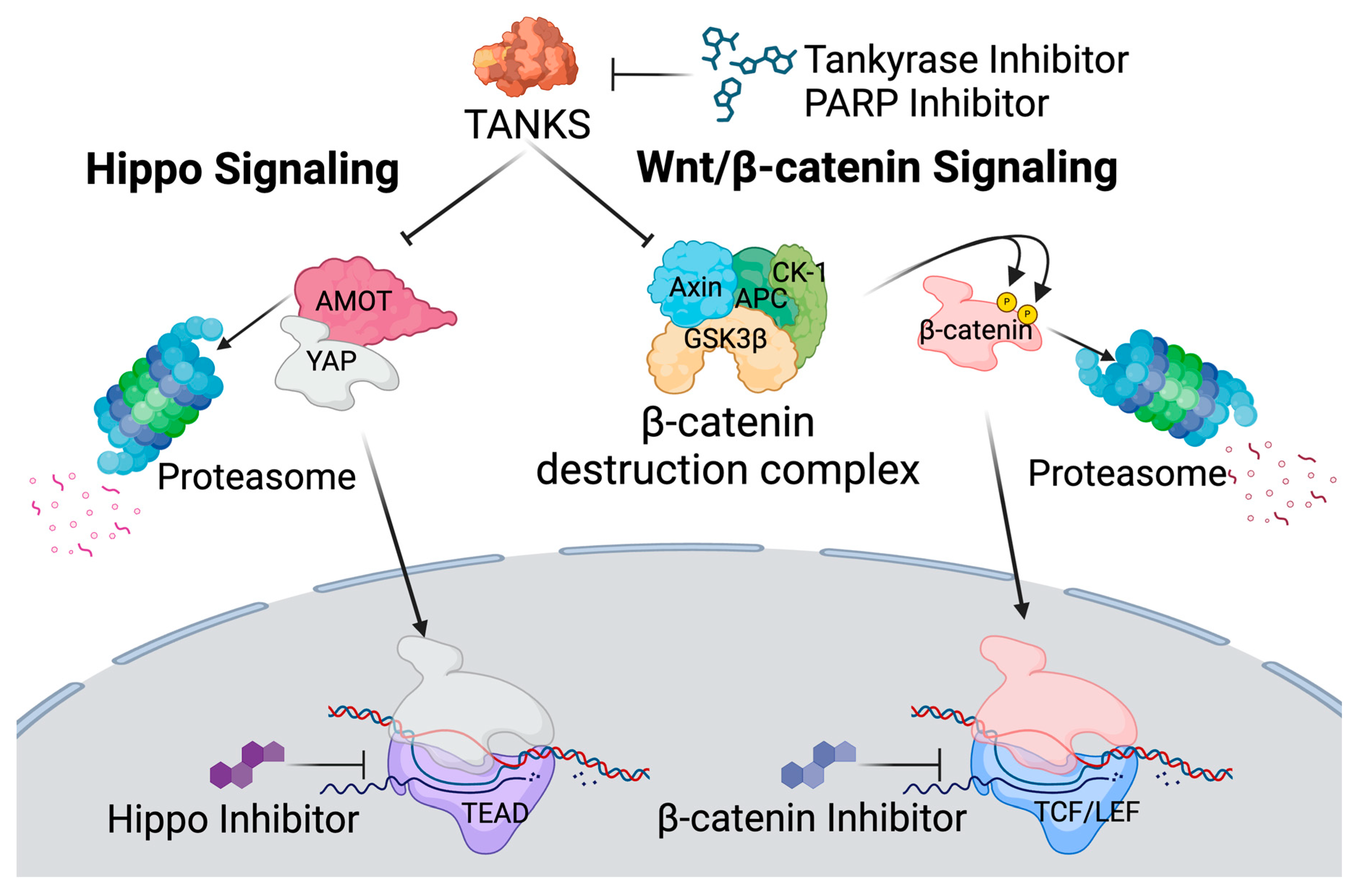
3.2. Latency Reversal Efficacy of Tankyrase Inhibitors in J-Lat Cell Line Models
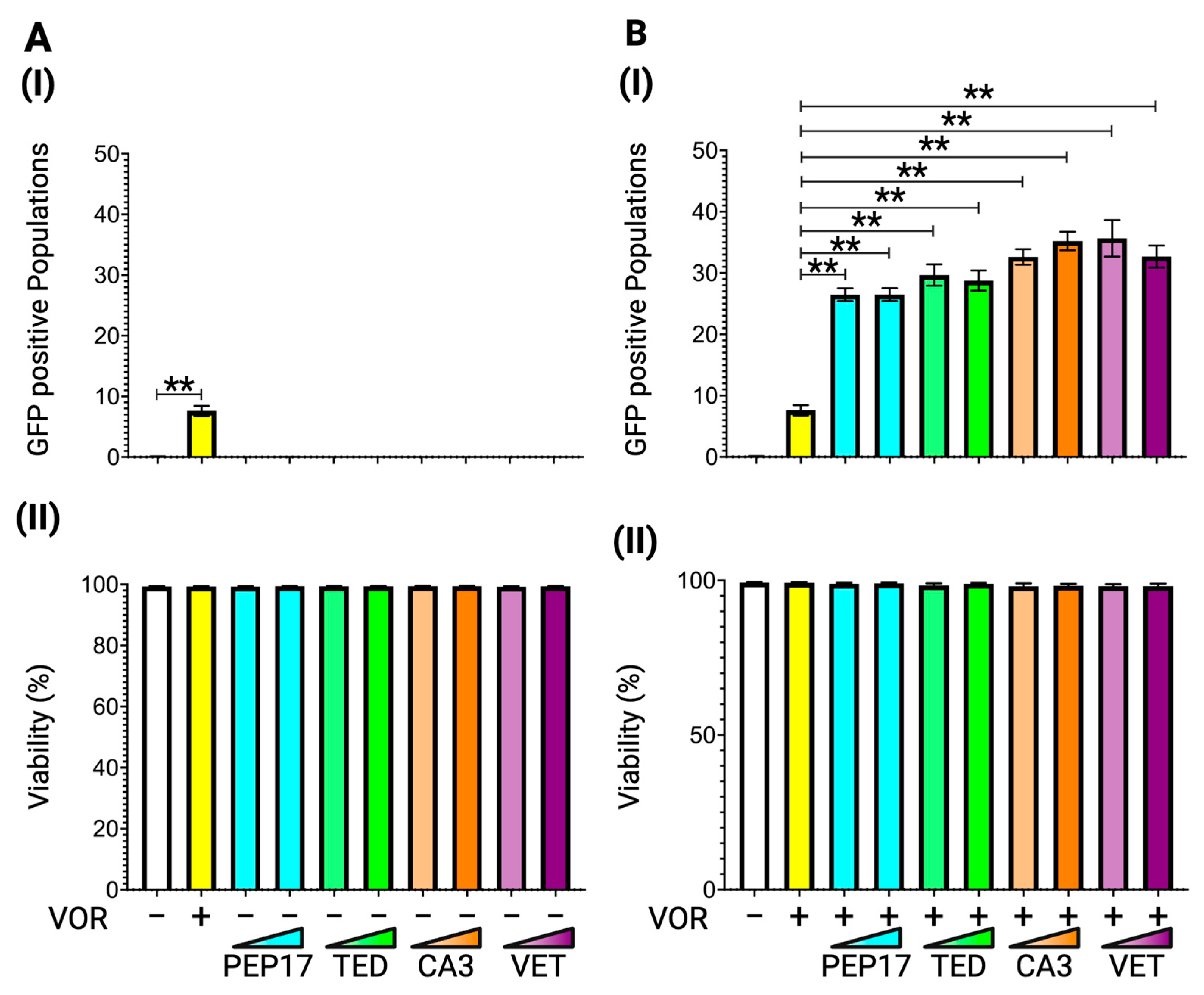
3.3. Latency Reversal Efficacy of Hippo Inhibitors in J-Lat Cell Line Models
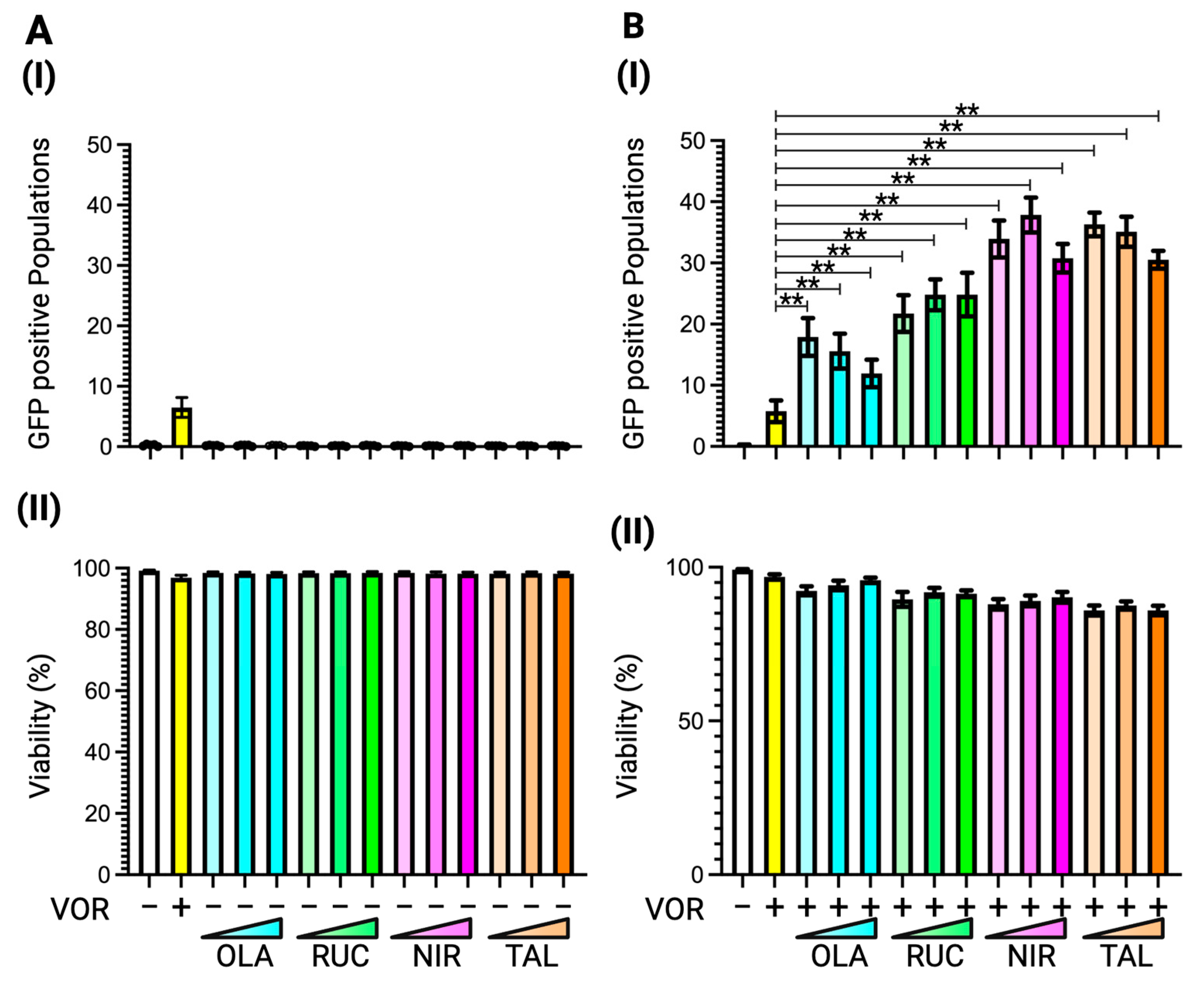
3.4. Latency Reversal Efficacy of PARP Inhibitors in J-Lat Cell Line Models
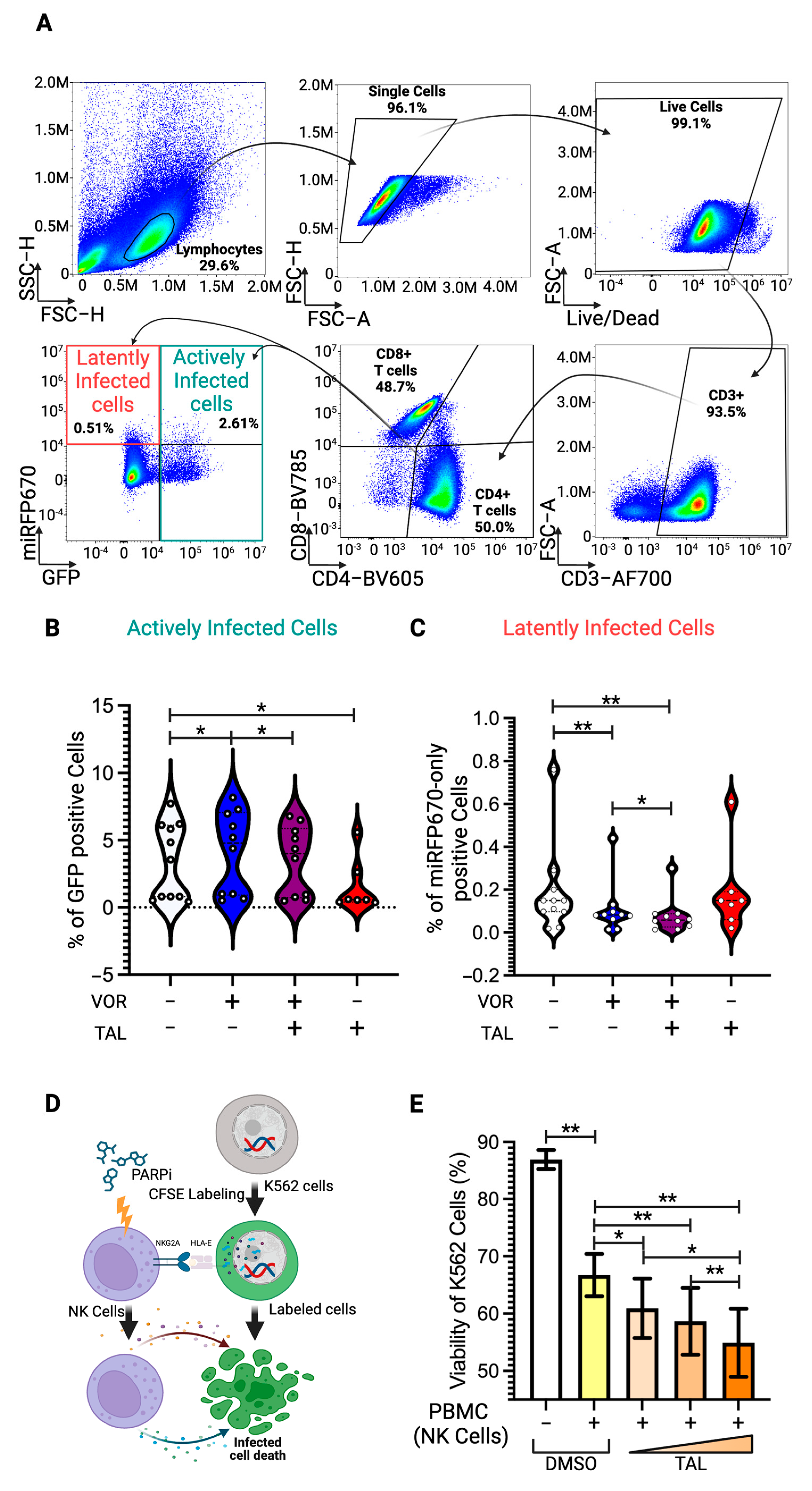
3.5. Latency Reversal Efficacy of PARP Inhibitor in Human Primary Cell Model and Immune Activation
3.6. Enhancement of NK-Cell Cytotoxic Activity by PARP Inhibitor
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saez-Cirion, A.; Mamez, A.C.; Avettand-Fenoel, V.; Nabergoj, M.; Passaes, C.; Thoueille, P.; Decosterd, L.; Hentzien, M.; Perdomo-Celis, F.; Salgado, M.; et al. Sustained HIV remission after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with wild-type CCR5 donor cells. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 3544–3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, B.O.; Knops, E.; Cords, L.; Lubke, N.; Salgado, M.; Busman-Sahay, K.; Estes, J.D.; Huyveneers, L.E.P.; Perdomo-Celis, F.; Wittner, M.; et al. In-depth virological and immunological characterization of HIV-1 cure after CCR5Delta32/Delta32 allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrios-Navas, A.; Nguyen, T.L.; Gallo, J.E.; Marino-Ramirez, L.; Soto, J.M.S.; Sanchez, A.; Jordan, I.K.; Valderrama-Aguirre, A. Unveiling ancestral threads: Exploring CCR5 ∆32 mutation frequencies in Colombian populations for HIV/AIDS therapeutics. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2024, 125, 105680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGraw, A.; Hillmer, G.; Choi, J.; Narayan, K.; Mehedincu, S.M.; Marquez, D.; Tibebe, H.; DeCicco-Skinner, K.L.; Izumi, T. Evaluating HIV-1 Infectivity and Virion Maturation across Varied Producer Cells with a Novel FRET-Based Detection and Quantification Assay. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarca, A.D.; Sardo, L.; Fukuda, H.; Matsui, H.; Shirakawa, K.; Horikawa, K.; Takaori-Kondo, A.; Izumi, T. FRET-Based Detection and Quantification of HIV-1 Virion Maturation. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 647452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGraw, A.; Hillmer, G.; Medehincu, S.M.; Hikichi, Y.; Gagliardi, S.; Narayan, K.; Tibebe, H.; Marquez, D.; Mei Bose, L.; Keating, A.; et al. Exploring HIV-1 Maturation: A New Frontier in Antiviral Development. Viruses 2024, 16, 1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ta, T.M.; Malik, S.; Anderson, E.M.; Jones, A.D.; Perchik, J.; Freylikh, M.; Sardo, L.; Klase, Z.A.; Izumi, T. Insights Into Persistent HIV-1 Infection and Functional Cure: Novel Capabilities and Strategies. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 862270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardo, L.; Parolin, C.; Yoshida, T.; Garzino-Demo, A.; Izumi, T. Editorial: Novel Insights Into a Functional HIV Cure. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 797570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorlund, K.; Horwitz, M.S.; Fife, B.T.; Lester, R.; Cameron, D.W. Landscape review of current HIV ‘kick and kill’ cure research—some kicking, not enough killing. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdigao, P.; Gaj, T.; Santa-Marta, M.; Barbas, C.F., 3rd; Goncalves, J. Reactivation of Latent HIV-1 Expression by Engineered TALE Transcription Factors. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cary, D.C.; Peterlin, B.M. Targeting the latent reservoir to achieve functional HIV cure. F1000Research 2016, 5, F1000 Faculty Rev-1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barouch, D.H.; Deeks, S.G. Immunologic strategies for HIV-1 remission and eradication. Science 2014, 345, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Euler, Z.; Alter, G. Exploring the potential of monoclonal antibody therapeutics for HIV-1 eradication. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2015, 31, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leth, S.; Schleimann, M.H.; Nissen, S.K.; Hojen, J.F.; Olesen, R.; Graversen, M.E.; Jorgensen, S.; Kjaer, A.S.; Denton, P.W.; Mork, A.; et al. Combined effect of Vacc-4x, recombinant human granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor vaccination, and romidepsin on the HIV-1 reservoir (REDUC): A single-arm, phase 1B/2A trial. Lancet HIV 2016, 3, e463–e472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debrabander, Q.; Hensley, K.S.; Psomas, C.K.; Bramer, W.; Mahmoudi, T.; van Welzen, B.J.; Verbon, A.; Rokx, C. The efficacy and tolerability of latency-reversing agents in reactivating the HIV-1 reservoir in clinical studies: A systematic review. J. Virus Erad. 2023, 9, 100342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, L.E.; Avila, D.E.; Spallanzani, R.G.; Ziblat, A.; Fuertes, M.B.; Lapyckyj, L.; Croci, D.O.; Rabinovich, G.A.; Domaica, C.I.; Zwirner, N.W. Histone deacetylase inhibitors impair NK cell viability and effector functions through inhibition of activation and receptor expression. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2012, 91, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R.B.; O’Connor, R.; Mueller, S.; Foley, M.; Szeto, G.L.; Karel, D.; Lichterfeld, M.; Kovacs, C.; Ostrowski, M.A.; Trocha, A.; et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors impair the elimination of HIV-infected cells by cytotoxic T-lymphocytes. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, J.A.; Lam, S.; Garrido, C.; Archin, N.; Rooney, C.M.; Bollard, C.M.; Margolis, D.M. Expanded cytotoxic T-cell lymphocytes target the latent HIV reservoir. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogbomo, H.; Michaelis, M.; Kreuter, J.; Doerr, H.W.; Cinatl, J., Jr. Histone deacetylase inhibitors suppress natural killer cell cytolytic activity. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 1317–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Breckenridge, C.A.; Yu, J.; Price, R.; Wei, M.; Wang, Y.; Nowicki, M.O.; Ha, Y.P.; Bergin, S.; Hwang, C.; Fernandez, S.A.; et al. The histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid lessens NK cell action against oncolytic virus-infected glioblastoma cells by inhibition of STAT5/T-BET signaling and generation of gamma interferon. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 4566–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hottiger, M.O.; Hassa, P.O.; Luscher, B.; Schuler, H.; Koch-Nolte, F. Toward a unified nomenclature for mammalian ADP-ribosyltransferases. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2010, 35, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palazzo, L.; Mikoc, A.; Ahel, I. ADP-ribosylation: New facets of an ancient modification. FEBS J. 2017, 284, 2932–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, N.; Li, X.; Tran, M.K.; Han, X.; Chen, J. Tankyrase Inhibitors Target YAP by Stabilizing Angiomotin Family Proteins. Cell Rep. 2015, 13, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.M.; Mishina, Y.M.; Liu, S.; Cheung, A.; Stegmeier, F.; Michaud, G.A.; Charlat, O.; Wiellette, E.; Zhang, Y.; Wiessner, S.; et al. Tankyrase inhibition stabilizes axin and antagonizes Wnt signalling. Nature 2009, 461, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanconato, F.; Forcato, M.; Battilana, G.; Azzolin, L.; Quaranta, E.; Bodega, B.; Rosato, A.; Bicciato, S.; Cordenonsi, M.; Piccolo, S. Genome-wide association between YAP/TAZ/TEAD and AP-1 at enhancers drives oncogenic growth. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 1218–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.; Azzolin, L.; Di Biagio, D.; Zanconato, F.; Battilana, G.; Lucon Xiccato, R.; Aragona, M.; Giulitti, S.; Panciera, T.; Gandin, A.; et al. The SWI/SNF complex is a mechanoregulated inhibitor of YAP and TAZ. Nature 2018, 563, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanconato, F.; Battilana, G.; Forcato, M.; Filippi, L.; Azzolin, L.; Manfrin, A.; Quaranta, E.; Di Biagio, D.; Sigismondo, G.; Guzzardo, V.; et al. Transcriptional addiction in cancer cells is mediated by YAP/TAZ through BRD4. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1599–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, R.T.; Brown, J.D.; Torres, M. WNTs modulate cell fate and behavior during vertebrate development. Trends Genet. 1997, 13, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.R.; Moon, R.T. Signal transduction through beta-catenin and specification of cell fate during embryogenesis. Genes. Dev. 1996, 10, 2527–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGraw, A.; Tibebe, H.; Marquez, D.; Gagliardi, S.; Hillmer, G.; Sullivan, C.; Haidery, H.; Hotchikin, T.; Keating, A.; Izumi, C. PP1. 9–00102 Targeting Latent HIV Reservoirs: Effectiveness of Combination Therapy with HDAC and PARP Inhibitors. J. Virus Erad. 2024, 10, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battivelli, E.; Dahabieh, M.S.; Abdel-Mohsen, M.; Svensson, J.P.; Tojal Da Silva, I.; Cohn, L.B.; Gramatica, A.; Deeks, S.; Greene, W.C.; Pillai, S.K.; et al. Distinct chromatin functional states correlate with HIV latency reactivation in infected primary CD4(+) T cells. Elife 2018, 7, e34655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliinyk, O.S.; Shemetov, A.A.; Pletnev, S.; Shcherbakova, D.M.; Verkhusha, V.V. Smallest near-infrared fluorescent protein evolved from cyanobacteriochrome as versatile tag for spectral multiplexing. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shemetov, A.A.; Oliinyk, O.S.; Verkhusha, V.V. How to Increase Brightness of Near-Infrared Fluorescent Proteins in Mammalian Cells. Cell Chem. Biol. 2017, 24, 758–766 e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbian, H.J.; Seaton, M.S.; Narasipura, S.D.; Wallace, J.; Rajan, R.; Sha, B.E.; Al-Harthi, L. beta-catenin regulates HIV latency and modulates HIV reactivation. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, V.; Hu, H.; Barroga, C.; Bossard, C.; Kc, S.; Dellamary, L.; Stewart, J.; Chiu, K.; Ibanez, M.; Pedraza, M.; et al. A small-molecule inhibitor of the Wnt pathway (SM04690) as a potential disease modifying agent for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2018, 26, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Wang, X.; Jia, T.; Wei, W.; Chua, M.S.; So, S. Tankyrase inhibitors attenuate WNT/beta-catenin signaling and inhibit growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 25390–25401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarabia, I.; Novis, C.L.; Macedo, A.B.; Takata, H.; Nell, R.; Kakazu, J.C.; Furler, R.L.; Shakya, B.; Schubert, H.L.; Hill, C.P.; et al. Activation of the Anti-Oxidative Stress Response Reactivates Latent HIV-1 Through the Mitochondrial Antiviral Signaling Protein Isoform MiniMAVS. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 682182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsell, A.G.; Ekblad, T.; Karlberg, T.; Low, M.; Pinto, A.F.; Tresaugues, L.; Moche, M.; Cohen, M.S.; Schuler, H. Structural Basis for Potency and Promiscuity in Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerase (PARP) and Tankyrase Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 1262–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Stigt Thans, T.; Akko, J.I.; Niehrs, A.; Garcia-Beltran, W.F.; Richert, L.; Sturzel, C.M.; Ford, C.T.; Li, H.; Ochsenbauer, C.; Kappes, J.C.; et al. Primary HIV-1 Strains Use Nef To Downmodulate HLA-E Surface Expression. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e00719-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandarian, F.; Sunga, G.M.; Arango-Saenz, D.; Rossetti, M. A Flow Cytometry-Based Cytotoxicity Assay for the Assessment of Human NK Cell Activity. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 126, 56191. [Google Scholar]
- Rose, M.; Burgess, J.T.; O’Byrne, K.; Richard, D.J.; Bolderson, E. PARP Inhibitors: Clinical Relevance, Mechanisms of Action and Tumor Resistance. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 564601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Qian, W.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, L.; Chen, S.; Xia, Y. A new wave of innovations within the DNA damage response. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedes, K.J.; Wilkerson, P.M.; Wetterskog, D.; Weigelt, B.; Ashworth, A.; Reis-Filho, J.S. Synthetic lethality of PARP inhibition in cancers lacking BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 1192–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, C.J.; Ashworth, A. PARP inhibitors: Synthetic lethality in the clinic. Science 2017, 355, 1152–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyman, B.; Jamieson, C. To PARP or not to PARP?-Toward sensitizing acute myeloid leukemia stem cells to immunotherapy. EMBO J. 2019, 38, e103479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padella, A.; Ghelli Luserna Di Rora, A.; Marconi, G.; Ghetti, M.; Martinelli, G.; Simonetti, G. Targeting PARP proteins in acute leukemia: DNA damage response inhibition and therapeutic strategies. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paczulla, A.M.; Rothfelder, K.; Raffel, S.; Konantz, M.; Steinbacher, J.; Wang, H.; Tandler, C.; Mbarga, M.; Schaefer, T.; Falcone, M.; et al. Absence of NKG2D ligands defines leukaemia stem cells and mediates their immune evasion. Nature 2019, 572, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, K.; Perez, C.; Rojas, L.B.P.; Burke, B.; Guevara-Patino, J.A. Functions of NKG2D in CD8(+) T cells: An opportunity for immunotherapy. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2018, 15, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzese, O.; Graziani, G. Role of PARP Inhibitors in Cancer Immunotherapy: Potential Friends to Immune Activating Molecules and Foes to Immune Checkpoints. Cancers 2022, 14, 5633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Han, D.; Fan, X.; Zhao, L. Ovarian cancer treatment and natural killer cell-based immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1308143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Li, L.; Lu, Q.; Wang, L.H.; Liu, C.Y.; Lei, Q.; Guan, K.L. Angiomotin is a novel Hippo pathway component that inhibits YAP oncoprotein. Genes. Dev. 2011, 25, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.S.; Dang, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, G.; Wang, E.; Xia, H.; Zhou, W.; Wu, S.; Liu, X. The Hippo signaling component LATS2 enhances innate immunity to inhibit HIV-1 infection through PQBP1-cGAS pathway. Cell Death Differ. 2022, 29, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, R.J.; Fozouni, P.; Thomas, S.; Sy, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, M.M.; Ott, M. The Short Isoform of BRD4 Promotes HIV-1 Latency by Engaging Repressive SWI/SNF Chromatin-Remodeling Complexes. Mol. Cell 2017, 67, 1001–1012 e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Guo, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, Q. The BET bromodomain inhibitor JQ1 activates HIV latency through antagonizing Brd4 inhibition of Tat-transactivation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Gaiha, G.D.; John, S.P.; Pertel, T.; Chin, C.R.; Gao, G.; Qu, H.; Walker, B.D.; Elledge, S.J.; Brass, A.L. Reactivation of latent HIV-1 by inhibition of BRD4. Cell Rep. 2012, 2, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Mbonye, U.; Feng, Z.; Wang, X.; Gao, X.; Karn, J.; Zhou, Q. The KAT5-Acetyl-Histone4-Brd4 axis silences HIV-1 transcription and promotes viral latency. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callow, M.G.; Tran, H.; Phu, L.; Lau, T.; Lee, J.; Sandoval, W.N.; Liu, P.S.; Bheddah, S.; Tao, J.; Lill, J.R.; et al. Ubiquitin ligase RNF146 regulates tankyrase and Axin to promote Wnt signaling. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Mickanin, C.; Feng, Y.; Charlat, O.; Michaud, G.A.; Schirle, M.; Shi, X.; Hild, M.; Bauer, A.; et al. RNF146 is a poly(ADP-ribose)-directed E3 ligase that regulates axin degradation and Wnt signalling. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Garcia, O.; Valdez-Alarcon, J.J.; Baizabal-Aguirre, V.M. Wnt/beta-Catenin Signaling as a Molecular Target by Pathogenic Bacteria. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Liang, X.; Cui, W.; Ober-Blobaum, J.L.; Vazzana, J.; Shrikant, P.A.; Lee, K.P.; Clausen, B.E.; Mellman, I.; Jiang, A. beta-Catenin in dendritic cells exerts opposite functions in cross-priming and maintenance of CD8+ T cells through regulation of IL-10. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 2823–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattinoni, L.; Ji, Y.; Restifo, N.P. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in T-cell immunity and cancer immunotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 4695–4701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swafford, D.; Manicassamy, S. Wnt signaling in dendritic cells: Its role in regulation of immunity and tolerance. Discov. Med. 2015, 19, 303–310. [Google Scholar]
- Spranger, S.; Gajewski, T.F. A new paradigm for tumor immune escape: Beta-catenin-driven immune exclusion. J. Immunother. Cancer 2015, 3, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willinger, T.; Freeman, T.; Herbert, M.; Hasegawa, H.; McMichael, A.J.; Callan, M.F. Human naive CD8 T cells down-regulate expression of the WNT pathway transcription factors lymphoid enhancer binding factor 1 and transcription factor 7 (T cell factor-1) following antigen encounter in vitro and in vivo. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 1439–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gattinoni, L.; Zhong, X.S.; Palmer, D.C.; Ji, Y.; Hinrichs, C.S.; Yu, Z.; Wrzesinski, C.; Boni, A.; Cassard, L.; Garvin, L.M.; et al. Wnt signaling arrests effector T cell differentiation and generates CD8+ memory stem cells. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 808–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavigner, M.; Zanoni, M.; Tharp, G.K.; Habib, J.; Mattingly, C.R.; Lichterfeld, M.; Nega, M.T.; Vanderford, T.H.; Bosinger, S.E.; Chahroudi, A. Pharmacological Modulation of the Wnt/beta-Catenin Pathway Inhibits Proliferation and Promotes Differentiation of Long-Lived Memory CD4(+) T Cells in Antiretroviral Therapy-Suppressed Simian Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected Macaques. J. Virol. 2019, 94, e01094-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Sharma, A.; Oh, S.Y.; Moon, H.G.; Hossain, M.Z.; Salay, T.M.; Leeds, K.E.; Du, H.; Wu, B.; Waterman, M.L.; et al. T cell factor 1 initiates the T helper type 2 fate by inducing the transcription factor GATA-3 and repressing interferon-gamma. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 992–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, M.; Al-Yahya, S.; Al-Alwan, M.; BinEssa, H.A.; Khabar, K.S.A.; Almohanna, F.; Assiri, A.M.; Altaweel, A.; Qattan, A.; Meyer, B.F.; et al. beta-catenin attenuation leads to up-regulation of activating NKG2D ligands and tumor regression in Braf(V600E)-driven thyroid cancer cells. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1171816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Name | Catalog Number | Vendor |
|---|---|---|
| HDAC Inhibitor | ||
| Vorinostat | SML0061 | Sigma-Aldrich |
| ß-catenin Inhibitor | ||
| BC21 | 219334 | Sigma-Aldrich |
| PKF118-310 | 219331 | Sigma-Aldrich |
| PNU-74654 | S8429 | Selleckchem |
| ICRT14 | SML0203 | Sigma-Aldrich |
| iCRT3 | 219332 | Sigma-Aldrich |
| ICG-001 | S2662 | Selleckchem |
| Adavivint | SM04690 | Sigma-Aldrich |
| Tankyrase Inhibitor | ||
| IWR-1-endo | 681669 | Sigma-Aldrich |
| XAV-939 | S1180 | Sellecchem |
| Hippo Inhibitor | ||
| Peptide-17 | S8164 | Selleckchem |
| TED-347 | S8951 | Selleckchem |
| Verteporfin | S1786 | Selleckchem |
| CA3 (CIL56) | S8661 | Selleckchem |
| PARP Inhibitor | ||
| Olaparib | S1060 | Selleckchem |
| Rucaparib | S4948 | Selleckchem |
| Niraparib | S2741 | Selleckchem |
| Talazoparib | S7048 | Selleckchem |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tibebe, H.; Marquez, D.; McGraw, A.; Gagliardi, S.; Sullivan, C.; Hillmer, G.; Narayan, K.; Izumi, C.; Keating, A.; Izumi, T. Targeting Latent HIV Reservoirs: Effectiveness of Combination Therapy with HDAC and PARP Inhibitors. Viruses 2025, 17, 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17030400
Tibebe H, Marquez D, McGraw A, Gagliardi S, Sullivan C, Hillmer G, Narayan K, Izumi C, Keating A, Izumi T. Targeting Latent HIV Reservoirs: Effectiveness of Combination Therapy with HDAC and PARP Inhibitors. Viruses. 2025; 17(3):400. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17030400
Chicago/Turabian StyleTibebe, Hasset, Dacia Marquez, Aidan McGraw, Sophia Gagliardi, Cailyn Sullivan, Grace Hillmer, Kedhar Narayan, Coco Izumi, Adleigh Keating, and Taisuke Izumi. 2025. "Targeting Latent HIV Reservoirs: Effectiveness of Combination Therapy with HDAC and PARP Inhibitors" Viruses 17, no. 3: 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17030400
APA StyleTibebe, H., Marquez, D., McGraw, A., Gagliardi, S., Sullivan, C., Hillmer, G., Narayan, K., Izumi, C., Keating, A., & Izumi, T. (2025). Targeting Latent HIV Reservoirs: Effectiveness of Combination Therapy with HDAC and PARP Inhibitors. Viruses, 17(3), 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17030400








