The Genotypes/Subtypes and Antiviral Drug Resistance of the Hepatitis C Virus from Patients in a Tertiary Care Hospital in Nepal
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Sample Size and Data Collection Period
2.3. Detection of Hepatitis C Virus Infections and Data Collection
2.4. HCV RNA Extraction and Detection
2.5. Sequencing of HCV RNA
2.6. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.7. Data Management and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. HCV RNA Results and Genotype/Subtype Distribution of HCV
3.2. Genotype Distribution According to Demographic Variables of HCV Patients
3.3. Genotype/Subtype Distribution of HCV Among Self-Reported IV Drug Use and Sexual Route of Transmission
3.4. Phylogenetic Analysis of HCV Genomes from Nepal
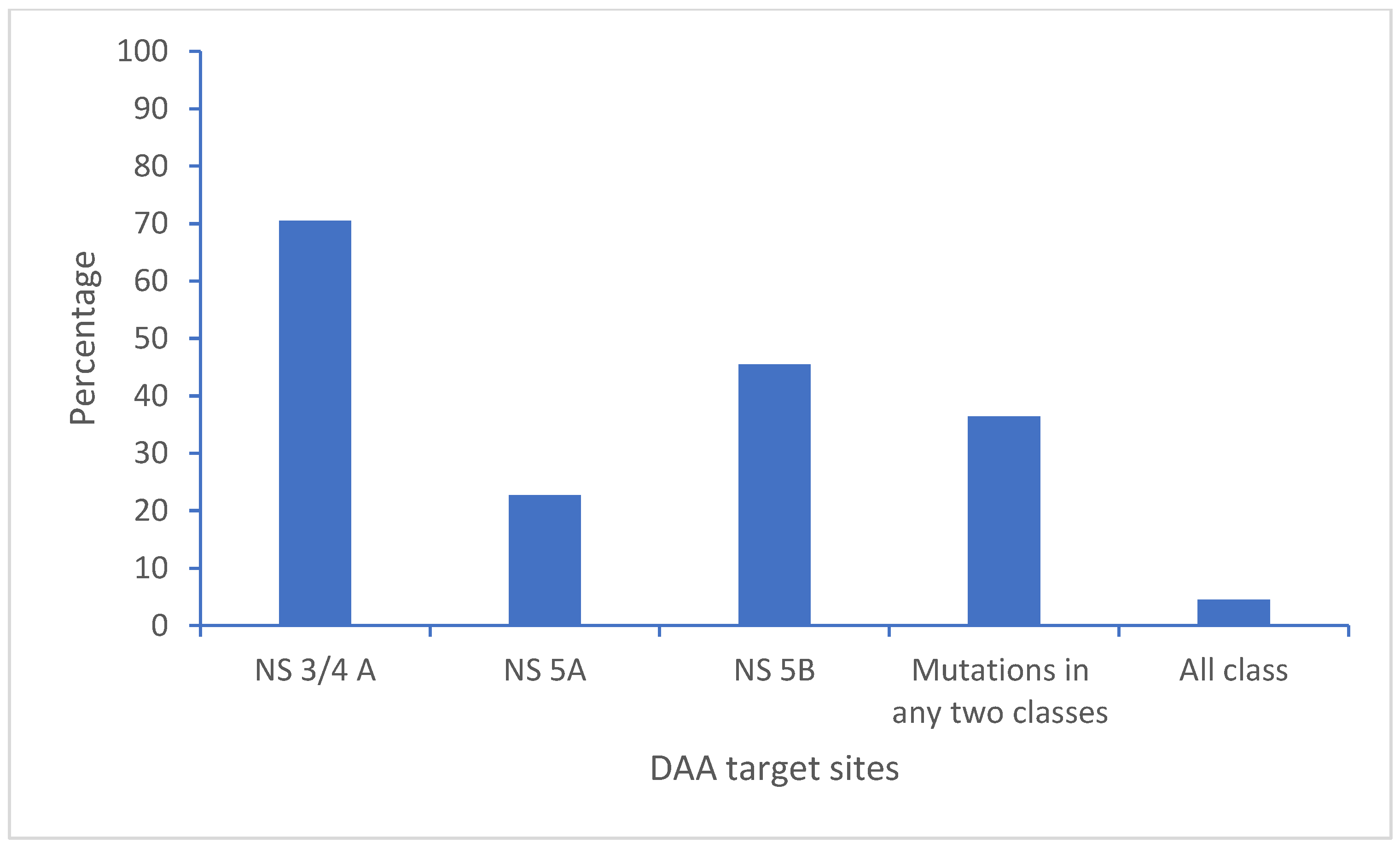
3.5. Polymorphisms and Resistant Mutations on the Direct-Acting Antiviral Drug Target Site of the HCV Genome
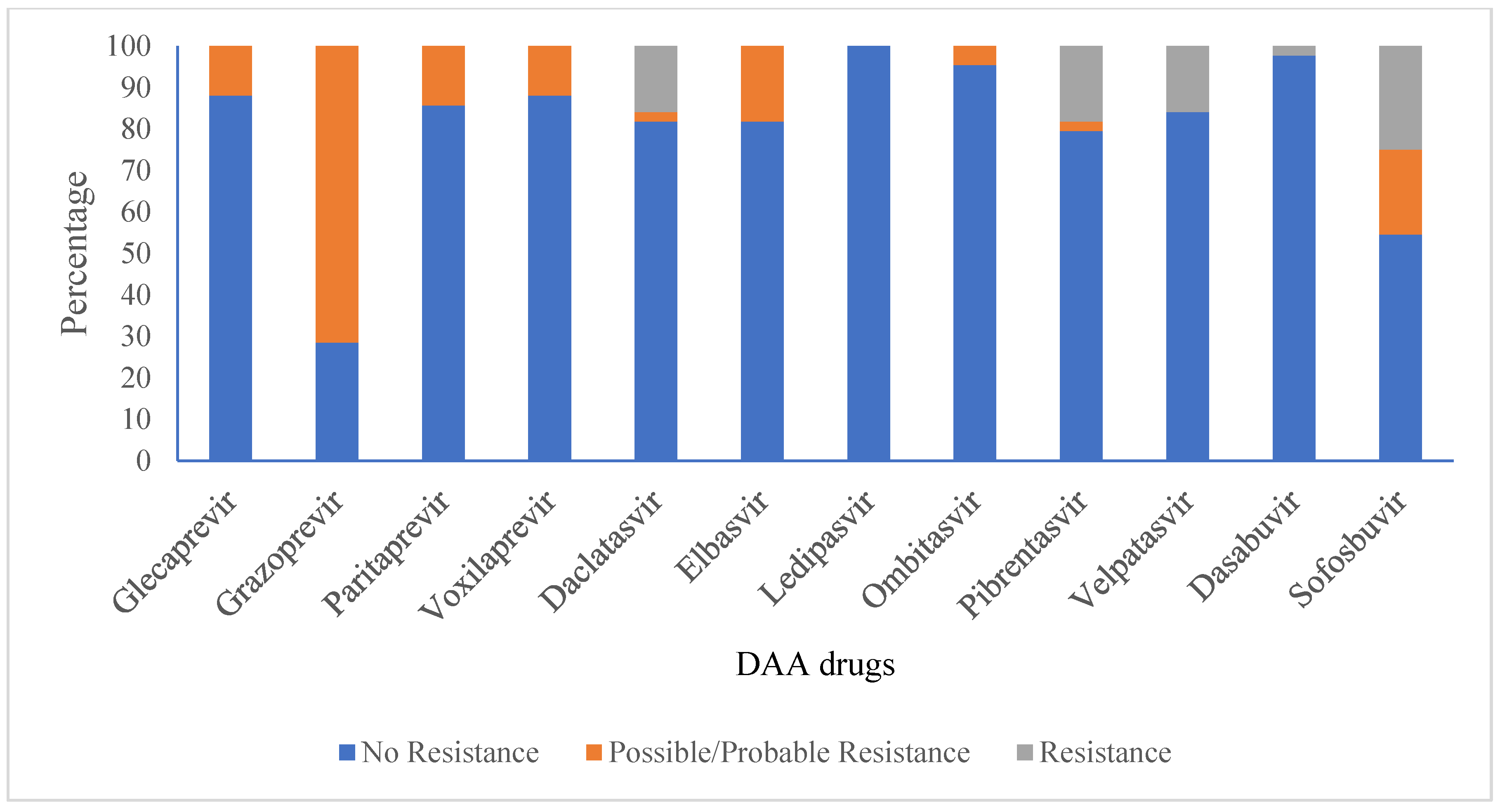
3.6. Anti-Viral Drug Susceptibility Profile for HCV
3.7. Anti-Viral Drug Resistance of Genotypes 3a and 1a
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Hepatitis C Fact Sheet. 2024. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-c (accessed on 21 December 2024).
- Ministry of Health and Population Nepal. National Guideline for Screening, Care and Treatment of Hepatitis C Infection in Nepal. 2020. Available online: https://www.aidsdatahub.org/sites/default/files/resource/nepal-guidelines-hepatitis-2020.pdf (accessed on 21 December 2024).
- Mbisa, J.L.; Lapp, Z.; Bibby, D.F.; Phillips, L.T.; Manso, C.F.; Packer, S.; Simmons, R.; Harris, K.; Mohan, J.; Chinnappan, L.; et al. Identification of 2 Novel Subtypes of Hepatitis C Virus Genotype 8 and a Potential New Genotype Successfully Treated with Direct Acting Antivirals. J. Infect. Dis. 2024, 230, e1254–e1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Borgia, S.M.; Hedskog, C.; Parhy, B.; Hyland, R.H.; Stamm, L.M.; Brainard, D.M.; Subramanian, M.G.; McHutchison, J.G.; Mo, H.; Svarovskaia, E.; et al. Identification of a Novel Hepatitis C Virus Genotype from Punjab, India: Expanding Classification of Hepatitis C Virus into 8 Genotypes. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 218, 1722–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, J.P.; Humphreys, I.; Flaxman, A.; Brown, A.; Cooke, G.S.; Pybus, O.G.; Barnes, E. Global distribution and prevalence of hepatitis C virus genotypes. Hepatology 2015, 61, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokita, H.; Shrestha, S.M.; Okamoto, H.; Sakamoto, M.; Horikita, M.; Iizuka, H.; Shrestha, S.; Miyakawa, Y.; Mayumi, M. Hepatitis C virus variants from Nepal with novel genotypes and their classification into the third major group. J. Gen. Virol. 1994, 75, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, B.K.; Yadav, U.N.; Khatiwada, S.; Tamang, M.K.; Dahal, S.; Li, Y.P. Hepatitis C virus genotype and its correlation with viral load in patients from Kathmandu, Nepal. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2020, 14, 1470–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, K.C.; Poudel-Tandukar, K. High prevalence and genotype distribution of hepatitis C virus in people living with HIV in Kathmandu, Nepal. Infect. Dis. 2021, 53, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geddawy, A.; Ibrahim, Y.F.; Elbahie, N.M.; Ibrahim, M.A. Direct Acting Anti-hepatitis C Virus Drugs: Clinical Pharmacology and Future Direction. J. Transl. Int. Med. 2017, 5, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shah, R.; Ahovegbe, L.; Niebel, M.; Shepherd, J.; Thomson, E.C. Non-epidemic HCV genotypes in low- and middle-income countries and the risk of resistance to current direct-acting antiviral regimens. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 462–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kliemann, D.A.; Tovo, C.V.; da Veiga, A.B.G.; de Mattos, A.A.; Wood, C. Polymorphisms and resistance mutations of hepatitis C virus on sequences in the European hepatitis C virus database. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 8910–8917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garson, J.A.; Ring, C.J.; Tuke, P.W. Improvement of HCV genome detection with “short” PCR products. Lancet 1991, 338, 1466–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briese, T.; Kapoor, A.; Mishra, N.; Jain, K.; Kumar, A.; Jabado, O.J.; Lipkin, W.I. Virome Capture Sequencing Enables Sensitive Viral Diagnosis and Comprehensive Virome Analysis. mBio 2015, 6, e01491-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA 11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartashev, V.; DÃring, M.; Nieto, L.; Coletta, E.; Kaiser, R.; Sierra, S.; HCV EuResist Study group. New findings in HCV genotype distribution in selected West European Russian and Israeli regions. J. Clin. Virol. 2016, 81, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimaldi, E.; Della Pepa, M.E.; Martora, F.; Magliocca, P.; Iovene, M.R.; Coppola, N.; Donnarumma, G.; Galdiero, M. Distribution of Hepatitis C Virus Genotypes and Subtypes in the Metropolitan Area of Naples, Italy, in the Era of Interferon-Free Regimens. Intervirology 2017, 60, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouacida, L.; Suin, V.; Hutse, V.; Boudewijns, M.; Cartuyvels, R.; Debaisieux, L.; De Laere, E.; Hallin, M.; Hougardy, N.; Lagrou, K.; et al. Distribution of HCV genotypes in Belgium from 2008 to 2015. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacka, B.; Bray, B.C.; Applegate, T.L.; Marshall, B.D.L.; Lima, V.D.; Hayashi, K.; DeBeck, K.; Raghwani, J.; Harrigan, P.R.; Krajden, M.; et al. Drug use and phylogenetic clustering of hepatitis C virus infection among people who use drugs in Vancouver, Canada: A latent class analysis approach. J. Viral Hepat. 2018, 25, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tüzüner, U.; Saran Gülcen, B.; Özdemir, M.; Feyzioğlu, B.; Baykan, M. Seven-year Genotype Distribution among Hepatitis C Patients in a City in the Central Anatolia Region of Turkey. Viral Hepat. J. 2018, 24, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, S.C.; Trudeau, S.; Li, J.; Zhou, Y.; Rupp, L.B.; Holmberg, S.D.; Moorman, A.C.; Spradling, P.R.; Teshale, E.H.; Boscarino, J.A.; et al. Race, Age, and Geography Impact Hepatitis C Genotype Distribution in the United States. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2019, 53, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, G.L.C.; Amoras, E.D.G.S.; AraÃjo, M.S.M.; Conde, S.R.S.D.S.; Vallinoto, A.C.R. Hepatitis C virus genotypes and associated risk factors in the state of Pará Northern Brazil. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 24, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenov, N.; Kostyushev, D.; Komarova, S.; Fomicheva, A.; Urtikov, A.; Belaia, O.; Umbetova, K.; Darvina, O.; Tsapkova, N.; Chulanov, V. Epidemiology and Genotype Distribution of Hepatitis C Virus in Russia. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, S.; Iqbal, A. A Review of Hepatitis C in the General Population in Pakistan. Viral Hepatit. Dergisi. 2016, 22, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, A.; Suryaprasad, A.; Trickey, A.; Kanchi, S.; Midha, V.; Foster, M.A.; Bennett, E.; Kamili, S.; Alvarez-Bognar, F.; Shadaker, S.; et al. The burden of hepatitis C virus infection in Punjab, India: A population-based serosurvey. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.A.; Islam, M.M.; Ali, M.E.; Islam, M.A.; Afroze, F.; Hossain, M.S.; Rus’d, A.A. Molecular Epidemiology of HCV RNA Genotype-3 in Dhaka City, Bangladesh. Glob. Med. Genet. 2023, 10, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Medhi, D.; Talukdar, A.J.; Raja, D.; Sarma, K.; Sarma, A.; Saikia, L. Hepatitis C virus genotypes among population with reported risk factors in Assam, north-east India: Emergence of genotype-8. Indian J. Med. Res. 2024, 160, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, W.; Yang, S.; Feng, S.; Wang, Q.; Liu, S.; Xing, H.; Xie, W.; Zhu, L.; Cheng, J. Hepatitis C virus genotype and subtype distribution in Chinese chronic hepatitis C patients: Nationwide spread of HCV genotypes 3 and 6. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Cui, L.; Zhao, W.; Yang, D.; Chen, H.; Wang, R.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; He, T. Molecular epidemiology of hepatitis C infections in Ningxia, China: Genotype, phylogeny and mutation analysis. Virol. J. 2016, 13, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yu, C.; Yin, X.; Guo, X.; Wu, S.; Hou, J. Hepatitis C virus genotypes and subtypes circulating in Mainland China. Emerg. Microbes. Infect. 2017, 6, e95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Chen, J.; Xu, R.; Jiang, X.; Ma, X.; Jia, M.; Wang, M.; Huang, J.; Liao, Q.; Shan, Z.; et al. Molecular evolution of hepatitis C virus in China: A nationwide study. Virology 2018, 516, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, A.; Mondelli, M.U.; ESCMID Study Group for Viral Hepatitis (ESGVH). Hepatitis C: Is eradication possible? Liver Int. 2019, 39, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KC, S.; Murphy, H.; Dixit, S.; Rai, A.; Pradhan, B.; Lagrange-Xelot, M.; Karki, N.; Dureault, A.; Karmacharya, U.; Panthi, S.; et al. Hepatitis C (HCV) therapy for HCV mono-infected and HIV-HCV co-infected individuals living in Nepal. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, D.B.; Jiang, W.; Chen, X.B.; Xiao, G.B.; Wang, Y.H.; Wang, M.L.; Tao, Y.C.; Chen, E.Q. Efficacy and safety of sofosbuvir-based pangenotypic direct-acting antiviral agents for chronic hepatitis C patients without genotype determination: Real-world experience of a retrospective study. Medicine 2020, 99, e22726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.; Magri, A.; Bonsall, D.; Ip, C.L.C.; Trebes, A.; Brown, A.; Piazza, P.; Bowden, R.; Nguyen, D.; Ansari, M.A.; et al. Resistance analysis of genotype 3 hepatitis C virus indicates subtypes inherently resistant to nonstructural protein 5A inhibitors. Hepatology 2019, 69, 1861–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, A.Y.M.; Rodrigo, C.; Cunningham, E.B.; Douglas, M.W.; Dietz, J.; Grebely, J.; Popping, S.; Sfalcin, J.A.; Parczewski, M.; Sarrazin, C.; et al. Characteristics of hepatitis C virus resistance in an international cohort after a decade of direct-acting antivirals. JHEP Rep. 2022, 4, 100462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inzaule, S.; Easterbrook, P.; Latona, A.; Ford, N.P.; Irving, W.; Matthews, P.C.; Vitoria, M.; Duncombe, C.; Giron, A.; McCluskey, S.; et al. Prevalence of Drug Resistance Associated Substitutions in Persons with Chronic Hepatitis C Infection and Virological Failure Following Initial or Re-treatment with Pan-genotypic Direct-Acting Antivirals: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2024, 79, 1437–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paolucci, S.; Premoli, M.; Novati, S.; Gulminetti, R.; Maserati, R.; Barbarini, G.; Sacchi, P.; Piralla, A.; Sassera, D.; Marco, L.D.; et al. Baseline and Breakthrough Resistance Mutations in HCV Patients Failing DAAs. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faiz, S.; Irfan, M.; Farooq, S.; Khan, I.A.; Iqbal, H.; Wahab, A.T.; Shakeel, M.; Gong, P.; Iftner, T.; Choudhary, M.I. Study of drug resistance-associated genetic mutations, and phylo-genetic analysis of HCV in the Province of Sindh, Pakistan. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 12213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Tang, Y.; Xu, D.; Zhang, G.; Xu, P.; Tang, H.; Pang, L. Efficacy and safety of ledipasvir/sofosbuvir for hepatitis C among drug users: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Virol. J. 2021, 18, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, B.C.A.; Ramos, J.A.; Silveira, A.L.D.M.; Nascimento, E.R.D.S.; Ferreira, S.B.; Coelho, H.S.M.; Moura-Neto, R.S.; Villela-Nogueira, C.A.; Hoffmann, L.; Silva, R. Frequency distribution of HCV resistance-associated variants in infected patients treated with direct-acting antivirals. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 115, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variables | Number (N) | Percentage | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 174 | 82.5 |
| Female | 37 | 17.5 | |
| Caste | Janajati | 105 | 49.8 |
| Brahmin/Chhetri | 69 | 32.7 | |
| Madeshi | 19 | 9.0 | |
| Dalit | 14 | 6.6 | |
| Thakuri | 4 | 1.9 | |
| Age | Pediatric group (0–14 yrs) | 1 | 0.5 |
| Young group (15–47 yrs) | 156 | 73.9 | |
| Middle age group (48–63 yrs) | 48 | 22.7 | |
| Elderly group (above 64 yrs) | 6 | 2.8 | |
| Religion | Hindu | 163 | 77.3 |
| Buddhist | 25 | 11.8 | |
| Christian | 18 | 8.5 | |
| Islam | 3 | 1.4 | |
| Kirat | 2 | 0.9 | |
| Alcohol intake | Non-alcoholic | 141 | 66.8 |
| Regular alcoholic | 70 | 33.2 | |
| Smoking | Regular smoker | 135 | 64.0 |
| Non-smoker | 76 | 36.0 | |
| Co-infected with HIV | Non-infected | 197 | 93.4 |
| Co-infected | 14 | 6.6 | |
| Self-reported route of transmission | IV drug use | 96 | 45.5 |
| Sexual | 59 | 28.0 | |
| Unknown | 24 | 11.4 | |
| Blood transfusion | 13 | 6.2 | |
| Haemodialysis | 9 | 4.3 | |
| Professional exposure | 3 | 1.4 | |
| Tattooing | 2 | 0.9 | |
| Blood transfusion or tattooing | 2 | 0.9 | |
| Tattooing or sexual | 2 | 0.9 | |
| Blood transfusion or hemodialysis | 1 | 0.5 |
| Variables | Genotype 1 (1a, 1b) N (%) | Genotype 3 (3a, 3b, 3d, 3e, 3g, 3i) N (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | |||
| Male | 8 (20.5) | 31 (79.5) | 0.9786 |
| Female | 1 (20) | 4 (80) | |
| Caste | |||
| Brahmin/Chhetri | 6 (28.6) | 15 (71.4) | 0.4887 |
| Dalit | 1 (20) | 4 (80) | |
| Janajati | 1 (7.1) | 13 (92.9) | |
| Madeshi | 1 (25) | 3 (75) | |
| Age group | |||
| Pediatric (0–14 yrs) | - | 1 (100) | |
| Young (15–47 yrs) | 8 (25) | 24 (75) | 0.3129 |
| Middle age (48–63 yrs) | 1 (10) | 9 (90) | |
| Elderly (Above 64 yrs) | - | 1 (100) | |
| Religion | |||
| Buddhist | 1 (14.3) | 6 (85.7) | |
| Christian | 1 (33.3) | 2 (66.7) | |
| Hindu | 7 (21.2) | 26 (78.8) | 0.7916 |
| Kirat | - | 1 (100) | |
| Alcohol intake | |||
| Non-alcoholic | 6 (21.2) | 26 (78.8) | 0.6471 |
| Regular alcoholic | 3 (25) | 9 (75) | |
| Smoking | |||
| Non-smoker | 3 (20) | 12 (80) | |
| Regular smoker | 6 (20.7) | 23 (79.3) | 0.9571 |
| Co-infected with HIV | |||
| Co-infected | - | 3 (100) | |
| Non-infected | 9 (21.9) | 32 (78.1) | NA * |
| Antiviral Drug | Polymorphism/Mutation Resistant Associated Substitution (RAS) | Genotype/Subtype | Resistance Type (N) * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NS3/4A Protein | Category II, III | Category I | ||
| Glecaprevir | A166S | 3a | 2 | |
| A166T | 3a | 3 | ||
| Grazoprevir | K/Q80K; K/Q80K + I132I; K/Q80K + A156A; K/Q80K + D168D | 1a | 3 | |
| K/Q80K; K/Q80K + I132I; K/Q80K + A156A; K/Q80K + D168D; I170V | 1a | 1 | ||
| L132I + I/V170I | 3a | 1 | ||
| V55A; I170V | 1a | 1 | ||
| Y56Y + Q168Q + I/V170I | 3a | 18 | ||
| Y56Y + Q168Q + I/V170I; L132I + I/V170I | 3a | 4 | ||
| Y56Y + Q168Q + I170I | 3b, 3d | 2 (1 each) | ||
| Paritaprevir | A166S | 3a | 2 | |
| K/Q80K | 1a | 4 | ||
| Voxilaprevir | K/Q80K | 1a | 4 | |
| V55A | 1a | 1 | ||
| NS5A Protein | ||||
| Daclatasvir | L28I; F/L37L | 1b | 1 | |
| A30K | 3a | 1 | ||
| K/R30K | 3i | 1 | ||
| K30K | 3d, 3e | 2 (1 each) | ||
| K30K; K30K + M/V31M; M/V31M | 3g | 1 | ||
| Y93H | 3a | 2 | ||
| Elbasvir | A30K | 3a | 1 | |
| A30L; Y93H | 3a | 1 | ||
| K/R30K | 3i | 1 | ||
| K30K | 3b, 3d, 3e | 3 (1 each) | ||
| K30K; K30K + M/V31M | 3g | 1 | ||
| Y93H | 3a | 1 | ||
| Ledipasvir | Not found | |||
| Ombitasvir | Y93H | 3a | 1 | |
| Pibrentasvir | P58T | 3a | 1 | |
| A30K | 3a | 1 | ||
| K/R30K | 3i | 1 | ||
| K30K | 3d, 3e | 2 (1 each) | ||
| K30K; M/V31M; K30K + M/V31M | 3g | 1 | ||
| K30K; M31M | 3b | 1 | ||
| Y93H | 3a | 2 | ||
| Velpatasvir | A30K | 3a | 1 | |
| K/R30K | 3i | 1 | ||
| K30K | 3d, 3e | 2 (1 each) | ||
| K30K; K30K + M/V31M; M/V31M | 3g | 1 | ||
| Y93H | 3a | 2 | ||
| NS5B Protein | ||||
| Dasabuvir | C/N316N | 1b | 1 | |
| Sofosbuvir | E/K206E | 3a | 9 | |
| A/T/V150V | 3a | 9 | ||
| A/T/V150V; A/T/V150V + E/K206E; E/K206E | 3a | 1 | ||
| C/N316N | 1b | 1 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kattel, H.P.; Sharma, S.; Alfsnes, K.; Pettersson, J.H.-O.; Pathak, R.; Engebretsen, S.B.; Rijal, K.R.; Ghimire, P.; Andreassen, Å.K.; Banjara, M.R. The Genotypes/Subtypes and Antiviral Drug Resistance of the Hepatitis C Virus from Patients in a Tertiary Care Hospital in Nepal. Viruses 2025, 17, 377. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17030377
Kattel HP, Sharma S, Alfsnes K, Pettersson JH-O, Pathak R, Engebretsen SB, Rijal KR, Ghimire P, Andreassen ÅK, Banjara MR. The Genotypes/Subtypes and Antiviral Drug Resistance of the Hepatitis C Virus from Patients in a Tertiary Care Hospital in Nepal. Viruses. 2025; 17(3):377. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17030377
Chicago/Turabian StyleKattel, Hari Prasad, Sangita Sharma, Kristian Alfsnes, John H.-O. Pettersson, Rahul Pathak, Serina Beate Engebretsen, Komal Raj Rijal, Prakash Ghimire, Åshild K. Andreassen, and Megha Raj Banjara. 2025. "The Genotypes/Subtypes and Antiviral Drug Resistance of the Hepatitis C Virus from Patients in a Tertiary Care Hospital in Nepal" Viruses 17, no. 3: 377. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17030377
APA StyleKattel, H. P., Sharma, S., Alfsnes, K., Pettersson, J. H.-O., Pathak, R., Engebretsen, S. B., Rijal, K. R., Ghimire, P., Andreassen, Å. K., & Banjara, M. R. (2025). The Genotypes/Subtypes and Antiviral Drug Resistance of the Hepatitis C Virus from Patients in a Tertiary Care Hospital in Nepal. Viruses, 17(3), 377. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17030377







