Seroprevalence of Enterovirus 71 Among Children in Western India
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design, Ethical Approval, and Serum Sample Collection
2.2. EV71 Antibody Testing
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
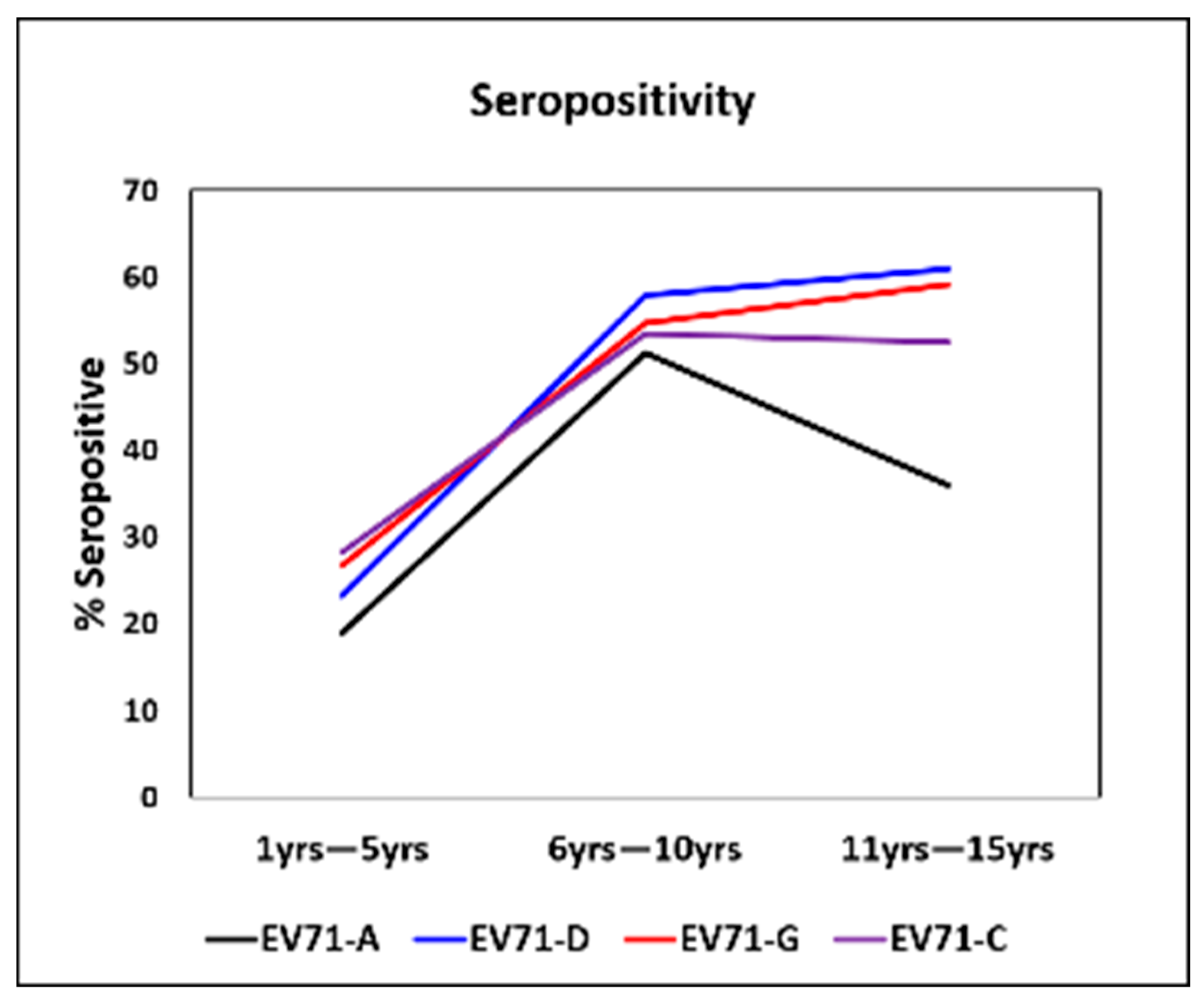
3.1. Age-Stratified Seropositivity Against EV71 C, D, and G Genotypes
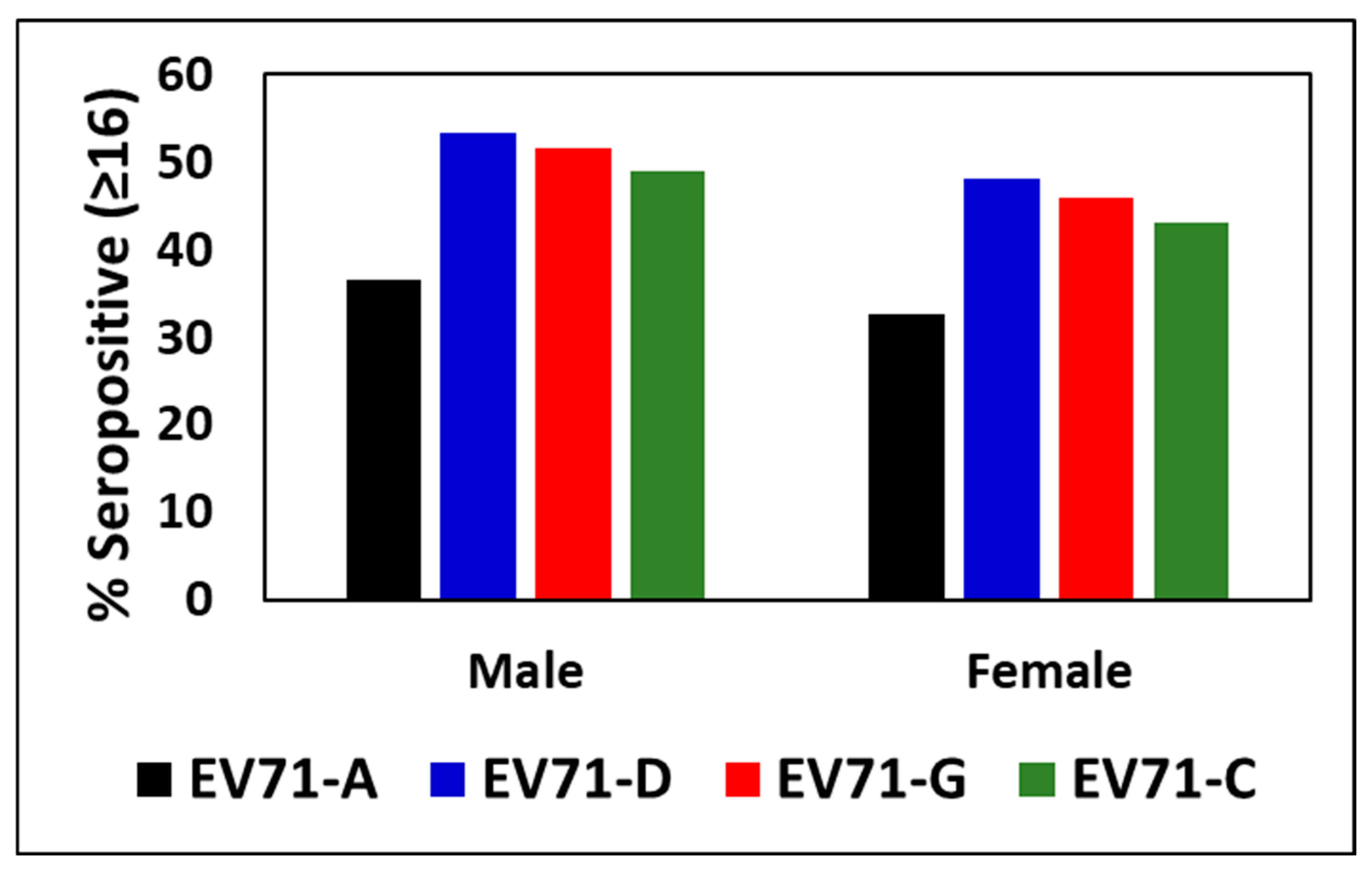
3.2. Percentage Seropositivity to EV71 Genotypes Between Males and Females
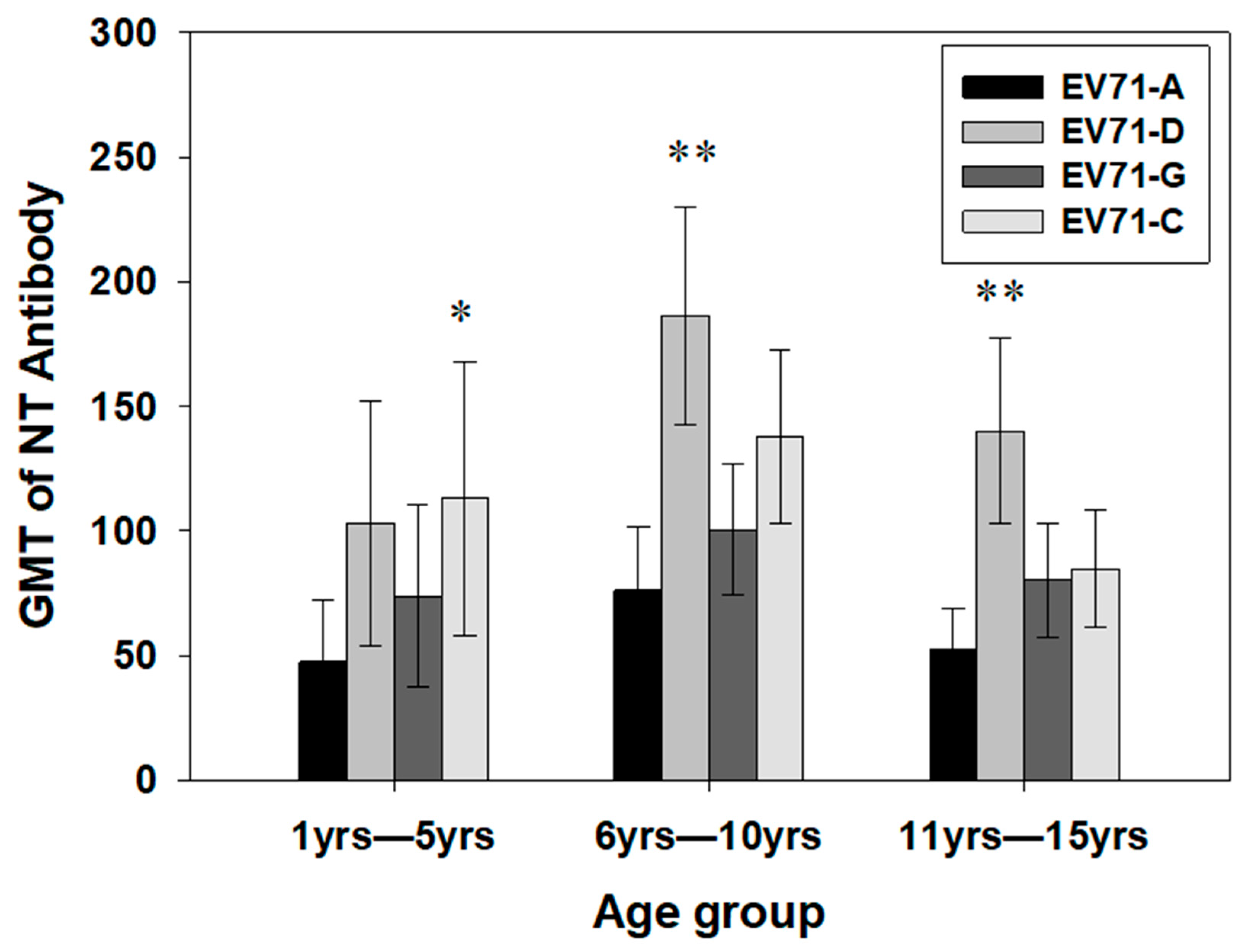
3.3. Geometric Mean Titers (GMTs) of Antibodies Against EV71 Genotypes Between the Age Groups
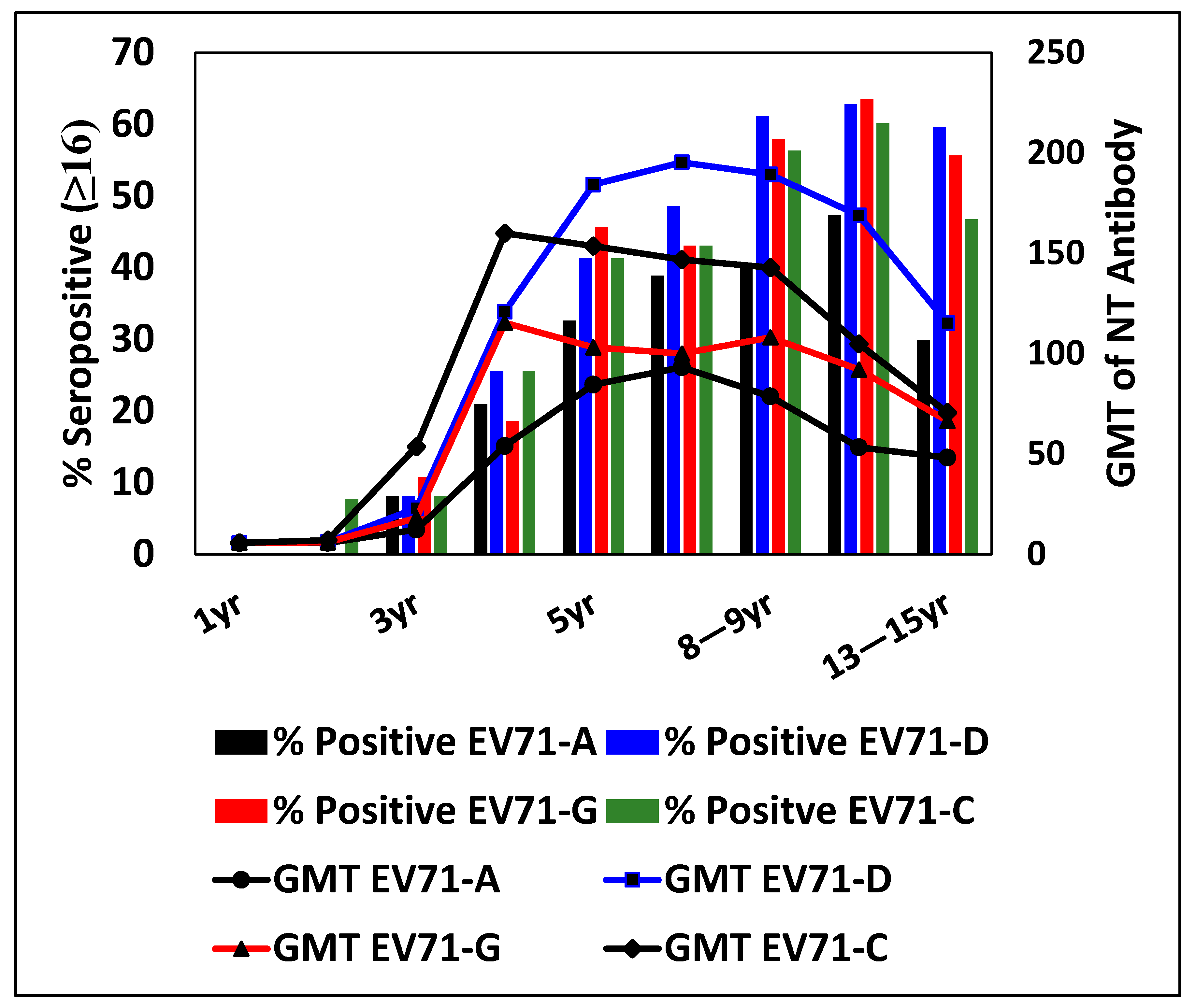
3.4. Percentage Seropositivity and GMT for EV71 Genotypes at Different Ages
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Puenpa, J.; Wanlapakorn, N.; Vongpunsawad, S.; Poovorawan, Y. The History of Enterovirus A71 Outbreaks and Molecular Epidemiology in the Asia-Pacific Region. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 26, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Deshpande, J.M.; Nadkarni, S.S.; Francis, P.P. Enterovirus 71 isolated from a case of acute flaccid paralysis in India represents a new genotype. Curr. Sci. 2003, 84, 1350–1353. [Google Scholar]
- Saxena, V.K.; Sane, S.; Nadkarni, S.S.; Sharma, D.K.; Deshpande, J.M. Genetic diversity of enterovirus A71, India. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 1, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mohanty, M.C.; Varose, S.Y.; Saxena, V.K. Susceptibility and cytokine responses of human neuronal cells to multiple circulating EV-A71 genotypes in India. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Brown, B.A.; Oberste, M.S.; Alexander, J.P.; Kennett, M.L.; Pallansch, M.A. Molecular Epidemiology and Evolution of Enterovirus 71 Strains Isolated from 1970 to 1998. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 9969–9975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomar, S.J.; Alagarasu, K.; More, A.; Nadkarni, M.; Bachal, R.; Bote, M.; Patil, J.; Venkatesh, V.; Parashar, D.; Tandale, B.V. Decadal Change in Seroprevalence of Chikungunya Virus Infection in Pune City, India. Viruses 2022, 14, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Deshpande, J.M. Enterovirus Research Center, ICMR, Parel, Mumbai, India. Unpublished work. 2002.
- Weldon, W.C.; Oberste, M.S.; Pallansch, M.A. Standardized Methods for Detection of Poliovirus Antibodies. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1387, 145–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. A simple method of estimating fifty percent endpoints. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yi, L.; Su, J.; Lu, J.; Ke, C.; Zeng, H.; Guan, D.; Ma, C.; Zhang, W.; Xiao, H.; et al. Seroprevalence of human enterovirus 71 and coxsackievirus A16 in Guangdong, China, in pre- and post-2010 HFMD epidemic period. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Huang, K.Y.A.; Huang, P.N.; Huang, Y.C.; Yang, S.L.; Tsao, K.C.; Chiu, C.H.; Shih, S.R.; Lin, T.Y. Emergence of genotype C1 Enterovirus A71 and its link with antigenic variation of virus in Taiwan. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Si, F.; Wang, D.; Ji, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, S.; Li, J.; Xu, W.; Tao, Z.; Yan, D. Identification of the first C1 subgenotype of enterovirus 71 in the Chinese mainland in a retrospective study. Virol. J. 2022, 19, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- van der Sanden, S.M.; Koen, G.; van Eijk, H.; Koekkoek, S.M.; de Jong, M.D.; Wolthers, K.C. Prediction of Protection against Asian Enterovirus 71 Outbreak Strains by Cross-neutralizing Capacity of Serum from Dutch Donors, The Netherlands. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 1562–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Akhmadishina, L.V.; Eremeeva, T.P.; Trotsenko, O.E.; Ivanova, O.E.; Mikhailov, M.I.; Lukashev, A.N. Seroepidemiology and molecular epidemiology of enterovirus 71 in Russia. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kamau, E.; Nguyen, D.; Celma, C.; Blomqvist, S.; Horby, P.; Simmonds, P.; Harvala, H. Seroprevalence and Virologic Surveillance of Enterovirus 71 and Coxsackievirus A6, United Kingdom, 2006-2017. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 9, 2261–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Linsuwanon, P.; Puenpa, J.; Huang, S.W.; Wang, Y.F.; Mauleekoonphairoj, J.; Wang, J.R.; Poovorawan, Y. Epidemiology and seroepidemiology of human enterovirus 71 among Thai populations. J. Biomed. Sci. 2014, 21, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ang, L.W.; Phoon, M.C.; Wu, Y.; Cutter, J.; James, L.; Chow, V.T. The changing seroepidemiology of enterovirus 71 infection among children and adolescents in Singapore. BMC Infect. Dis. 2011, 11, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shi, Y.; Chen, P.; Bai, Y.; Xu, X.; Liu, Y. Seroprevalence of coxsackievirus A6 and enterovirus A71 infection in humans: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Virol. 2023, 168, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lerdsamran, H.; Prasertsopon, J.; Mungaomklang, A.; Klinmalai, C.; Noisumdaeng, P.; Sangsiriwut, K.; Tassaneetrithep, B.; Guntapong, R.; Iamsirithaworn, S.; Puthavathana, P. Seroprevalence of antibodies to enterovirus 71 and coxsackievirus A16 among people of various age groups in a northeast province of Thailand. Virol. J. 2018, 15, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rabenau, H.F.; Richter, M.; Doerr, H.W. Hand, foot and mouth disease: Seroprevalence of Coxsackie A16 and Enterovirus 71 in Germany. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2010, 199, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diedrich, S.; Weinbrecht, A.; Schreier, E. Seroprevalence and molecular epidemiology of enterovirus 71 in Germany. Arch. Virol. 2009, 154, 1139–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhu, S.; Guo, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, D.; Yan, D.; Tan, X.; Tang, L.; Zhu, H.; Yang, Z.; et al. Retrospective seroepidemiology indicated that human enterovirus 71 and coxsackievirus A16 circulated wildly in central and southern China before large-scale outbreaks from 2008. Virol J. 2010, 7, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chang, L.Y.; King, C.C.; Hsu, K.H.; Ning, H.C.; Tsao, K.C.; Li, C.C.; Huang, Y.C.; Shih, S.R.; Chiou, S.T.; Chen, P.Y.; et al. Risk factors of enterovirus 71 infection and associated hand, foot, and mouth disease/herpangina in children during an epidemic in Taiwan. Pediatrics 2002, 109, e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.C.; Huang, L.M.; Kao, C.L.; Lu, C.Y.; Shao, P.L.; Cheng, A.L.; Fan, T.Y.; Chi, H.; Chang, L.Y. Seroprevalence of enterovirus 71 and no evidence of crossprotection of enterovirus 71 antibody against the other enteroviruses in kindergarten children in Taipei city. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2012, 45, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ooi, E.E.; Phoon, M.C.; Ishak, B.; Chan, S.H. Seroepidemiology of human enterovirus 71, Singapore. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 995–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Girsang, R.T.; Rusmil, K.; Fadlyana, E.; Setiabudiawan, B.; Adrizain, R.; Mulyadi, R.P.; Budiman, A.; Utami, R.K.; Mardiah, B.Z.; Dwi Putra, M.G.; et al. A serosurvey study of hand, foot and mouth disease in healthy children aged 6 to 71 months old in West Bandung and Bandung Region, Indonesia. BMC Infect. Dis. 2025, 25, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
| Age Group (Years) | Age in years as Mean (SD) | Male n (%) | Female n (%) | Total n |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1–5 | 3.8 (1.06) | 69 (48.6) | 73 (51.40) | 142 |
| 6–10 | 8.3 (1.29) | 131 (53.47) | 114 (46.53) | 245 |
| 11–15 | 12.9 (1.45) | 142 (63.11) | 83 (36.89) | 225 |
| 1–15 | 342 (55.88) | 270 (44.12) | 612 |
| EV71 Genotypes | Origin | Year | Age/Sex | Clinical Sample | Clinical Condition | Diagnosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A (Prototype BrCr) | USA | 1969 | Infant | Feces | Encephalitis | |
| G | Jaunpur, Uttar Pradesh | 2011 | 40 m/F | Feces | AFP | Not known |
| C | Thane, Maharashtra | 2012 | 42 m/M | Cerebrospinal fluid | Encephalitis | Viral Enc |
| D | Faridabad, Haryana | 2001 | 60 m/M | Feces | AFP | GBS |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohanty, M.C.; Varose, S.Y.; Rane, S.V.; Pawar, S.D.; Tandale, B.V. Seroprevalence of Enterovirus 71 Among Children in Western India. Viruses 2025, 17, 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17030356
Mohanty MC, Varose SY, Rane SV, Pawar SD, Tandale BV. Seroprevalence of Enterovirus 71 Among Children in Western India. Viruses. 2025; 17(3):356. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17030356
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohanty, Madhu Chhanda, Swapnil Y. Varose, Sneha V. Rane, Shailesh D. Pawar, and Babasaheb V. Tandale. 2025. "Seroprevalence of Enterovirus 71 Among Children in Western India" Viruses 17, no. 3: 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17030356
APA StyleMohanty, M. C., Varose, S. Y., Rane, S. V., Pawar, S. D., & Tandale, B. V. (2025). Seroprevalence of Enterovirus 71 Among Children in Western India. Viruses, 17(3), 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17030356









