The Intrinsic Innate Immunity of Hepatocytes Suppresses HBV Replication and Is Antagonized by HBx
Abstract
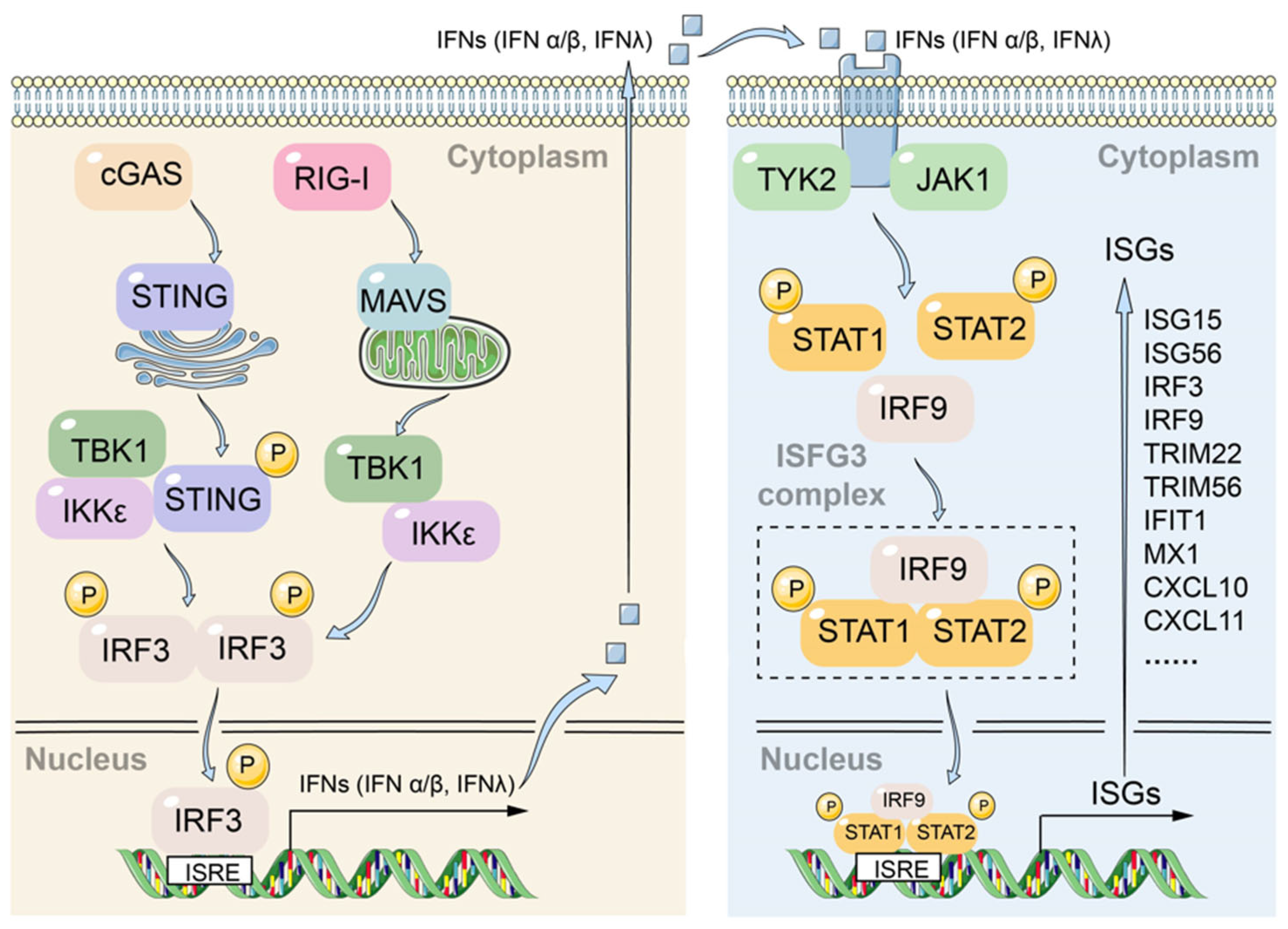
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
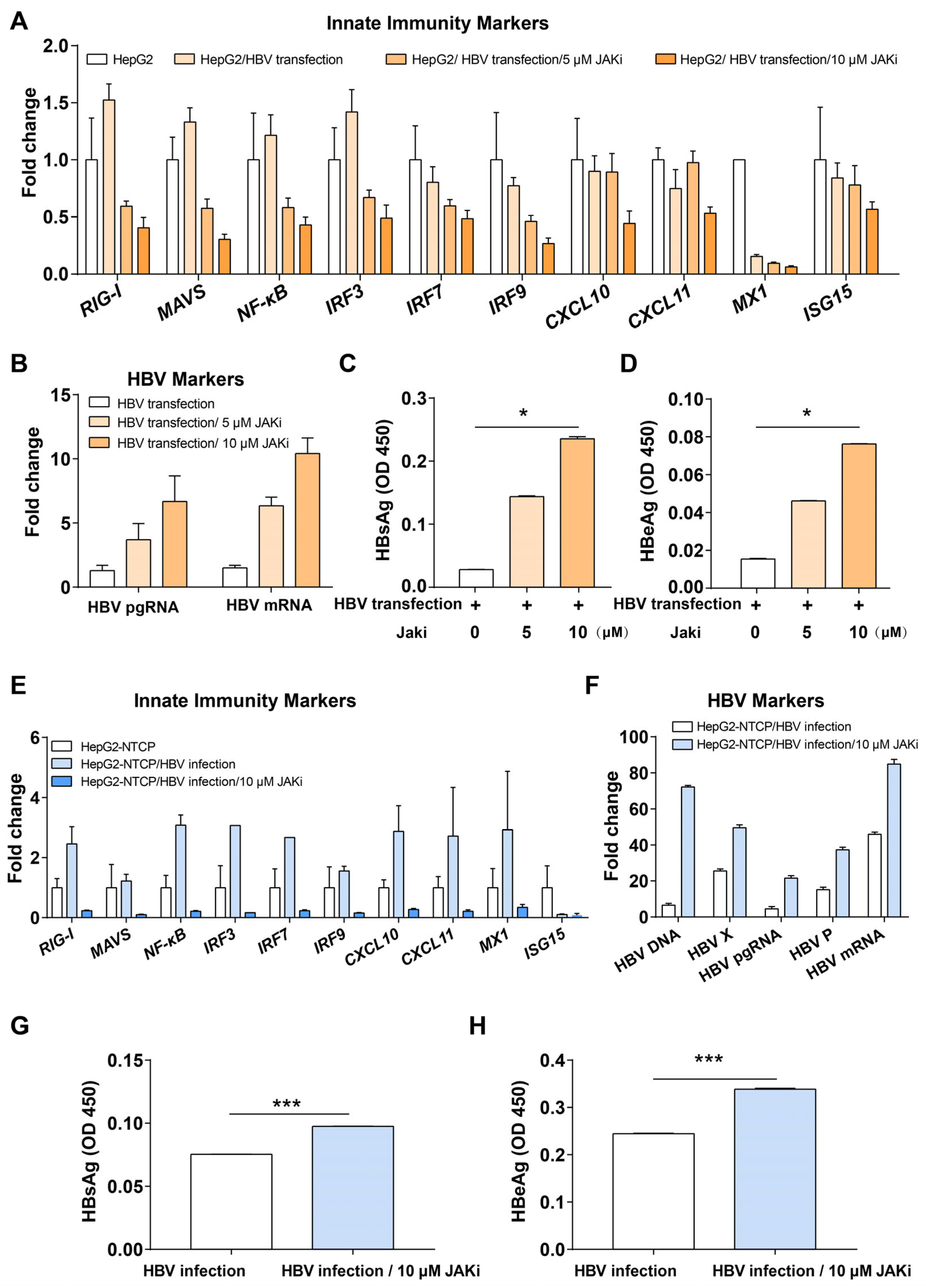
3.1. Modulation of Intrinsic Innate Immunity Increases HBV Replication in HepG2 and HepG2-NTCP
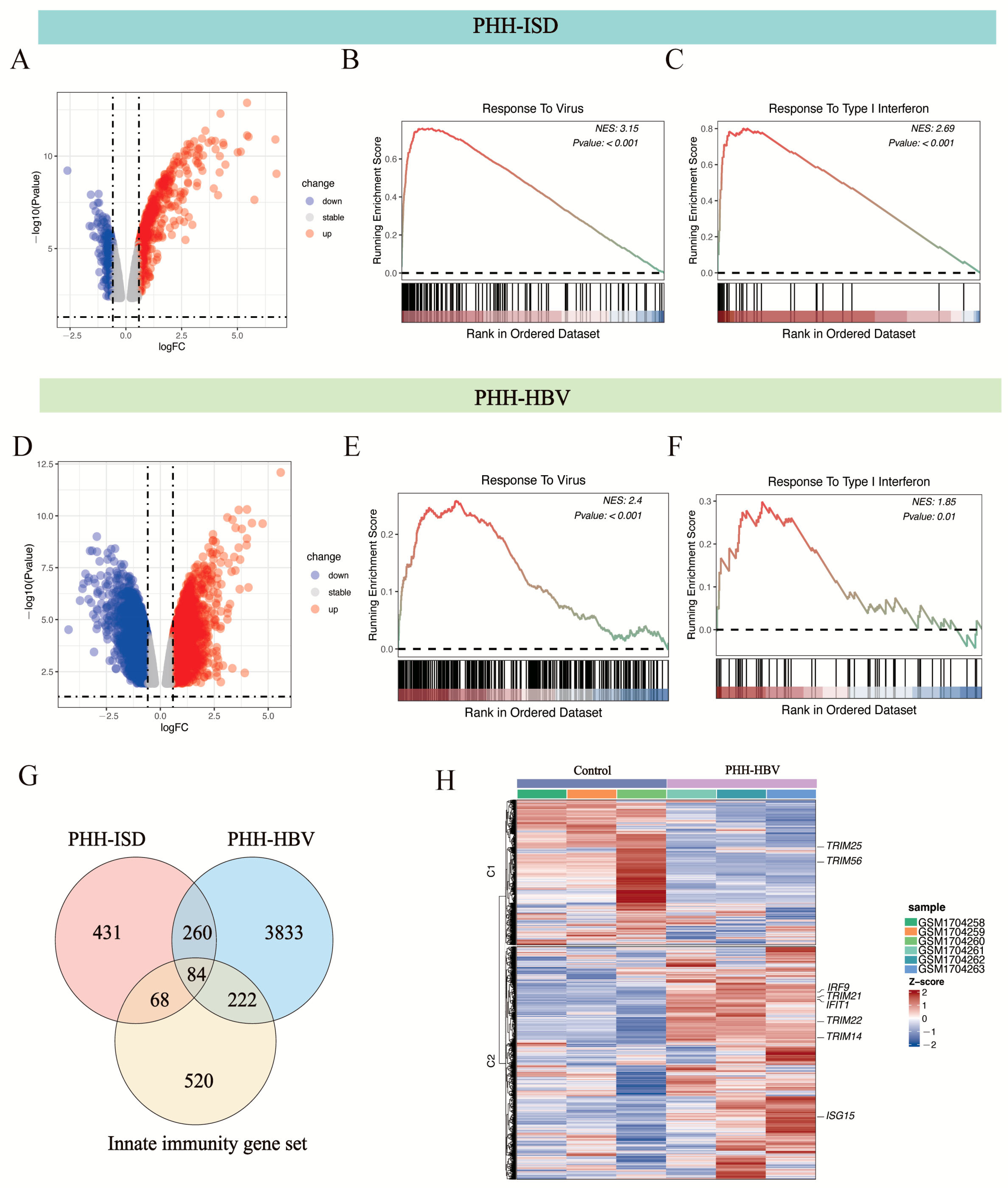
3.2. Innate Immunity Genes Involved in HBV Infection
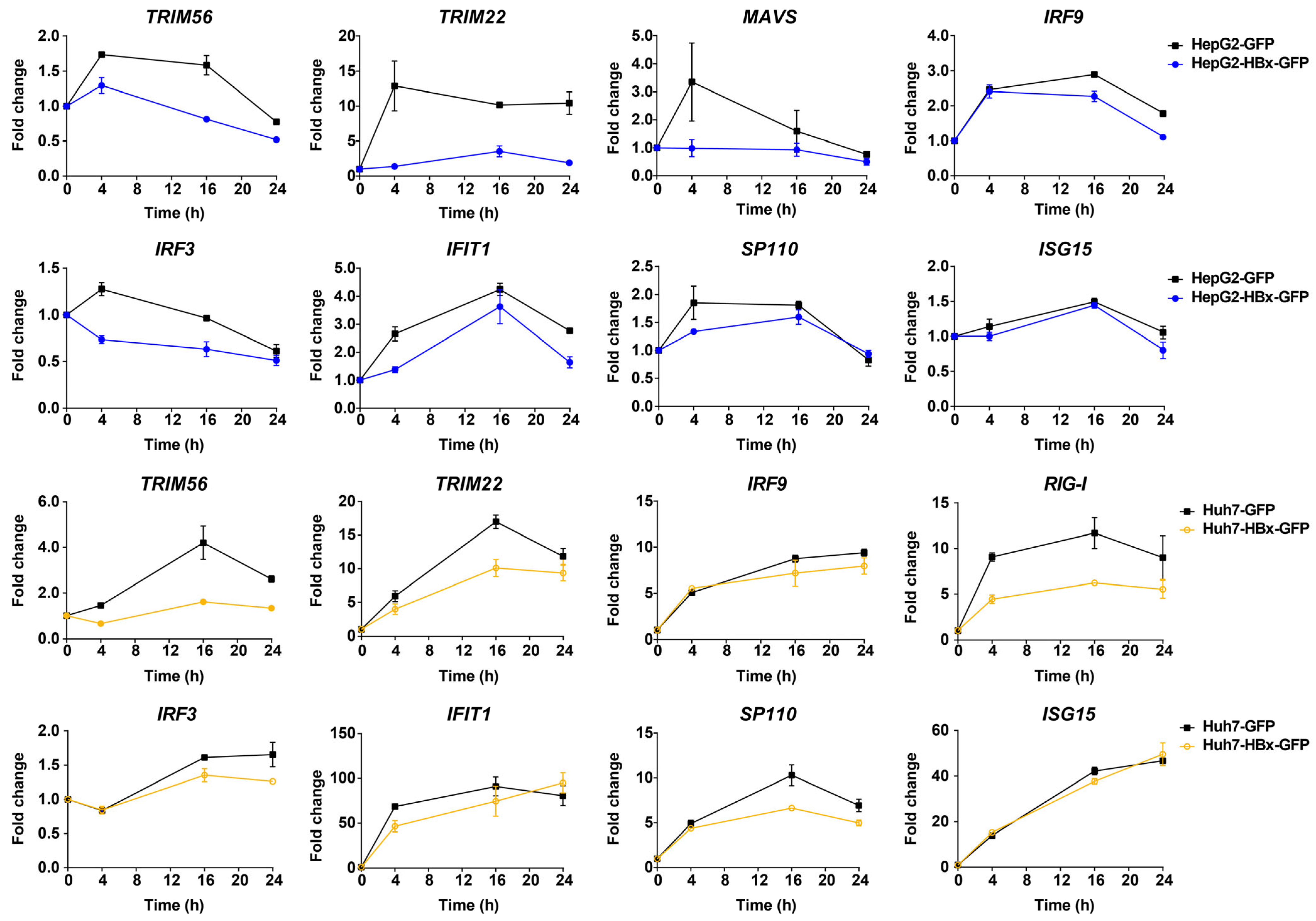
3.3. HBx Interrupts the Induction of ISGs in IFN-λ1-Treated Hepatocytes
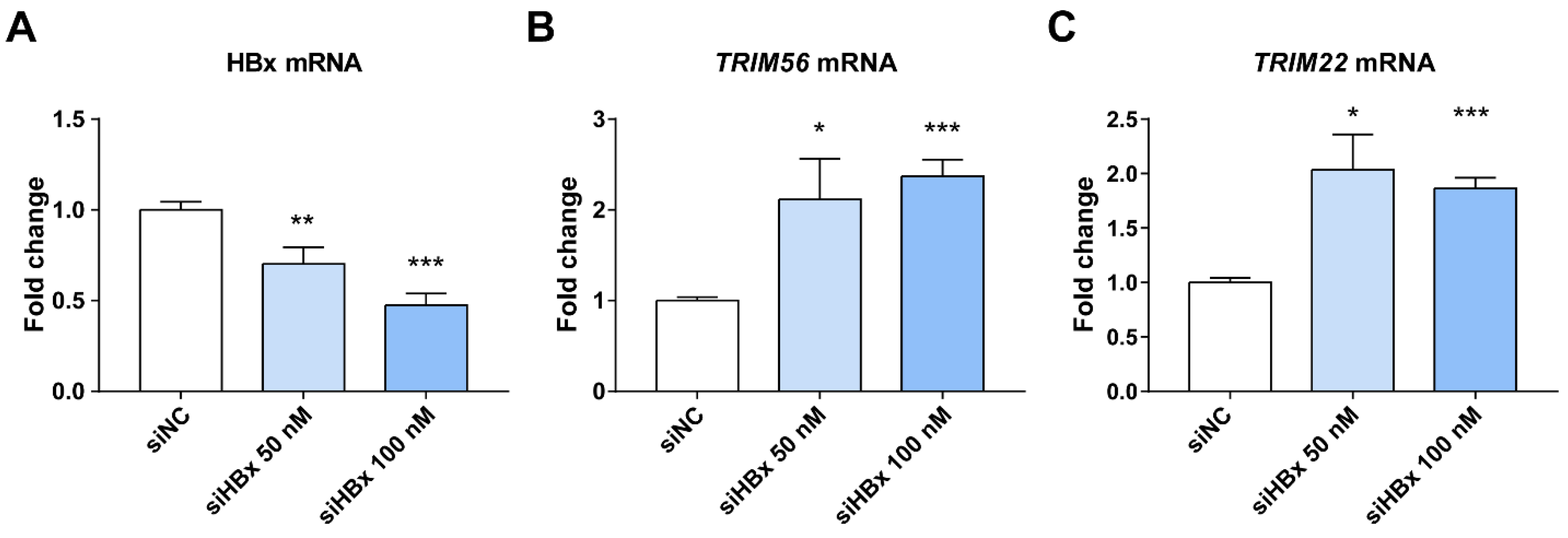
3.4. Suppression of HBx Increases TRIM22/TRIM56 in HepG2.2.15
3.5. Down-Regulation of TRIM22 or TRIM56 Increases the Expression of HBV pgRNA
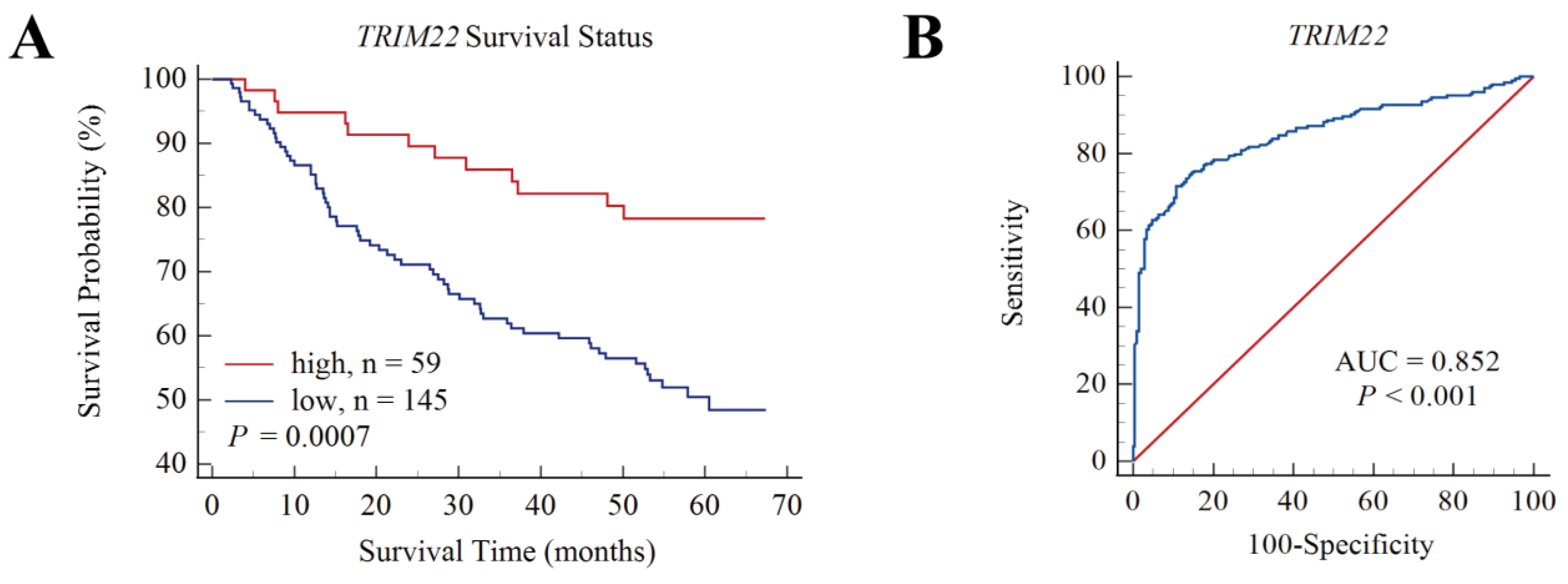
3.6. Expression of TRIM22 and TRIM56 in the Tissues and Cells of HBV-Related HCC Patients
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Torre, L.A.; Siegel, R.L.; Ward, E.M.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Incidence and Mortality Rates and Trends--An Update. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2016, 25, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plummer, M.; de Martel, C.; Vignat, J.; Ferlay, J.; Bray, F.; Franceschi, S. Global burden of cancers attributable to infections in 2012: A synthetic analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2016, 4, e609–e616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iavarone, M.; Colombo, M. HBV infection and hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Liver Dis. 2013, 17, 375–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minor, M.M.; Slagle, B.L. Hepatitis B virus HBx protein interactions with the ubiquitin proteasome system. Viruses 2014, 6, 4683–4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoletti, A.; Gehring, A.J. The immune response during hepatitis B virus infection. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 1439–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehermann, B.; Nascimbeni, M. Immunology of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infection. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, C.; Peppa, D.; Khanna, P.; Nebbia, G.; Jones, M.; Brendish, N.; Lascar, R.M.; Brown, D.; Gilson, R.J.; Tedder, R.J.; et al. Temporal analysis of early immune responses in patients with acute hepatitis B virus infection. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 1289–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Xia, Y.; Serti, E.; Block, P.D.; Chung, M.; Chayama, K.; Rehermann, B.; Liang, T.J. Hepatitis B virus evades innate immunity of hepatocytes but activates cytokine production by macrophages. Hepatology 2017, 66, 1779–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shlomai, A.; Schwartz, R.E.; Ramanan, V.; Bhatta, A.; de Jong, Y.P.; Bhatia, S.N.; Rice, C.M. Modeling host interactions with hepatitis B virus using primary and induced pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocellular systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 12193–12198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoneda, M.; Hyun, J.; Jakubski, S.; Saito, S.; Nakajima, A.; Schiff, E.R.; Thomas, E. Hepatitis B Virus and DNA Stimulation Trigger a Rapid Innate Immune Response through NF-kappaB. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 630–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, S.; Li, K.; Kameyama, T.; Hayashi, T.; Ishida, Y.; Murakami, S.; Watanabe, T.; Iijima, S.; Sakurai, Y.; Watashi, K.; et al. The RNA sensor RIG-I dually functions as an innate sensor and direct antiviral factor for hepatitis B virus. Immunity 2015, 42, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; tenOever, B.R.; Grandvaux, N.; Zhou, G.P.; Lin, R.; Hiscott, J. Triggering the interferon antiviral response through an IKK-related pathway. Science 2003, 300, 1148–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zevini, A.; Olagnier, D.; Hiscott, J. Crosstalk between Cytoplasmic RIG-I and STING Sensing Pathways. Trends Immunol. 2017, 38, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.L.; Liao, F. Melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 senses hepatitis B virus and activates innate immune signaling to suppress virus replication. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 3264–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dansako, H.; Ueda, Y.; Okumura, N.; Satoh, S.; Sugiyama, M.; Mizokami, M.; Ikeda, M.; Kato, N. The cyclic GMP-AMP synthetase-STING signaling pathway is required for both the innate immune response against HBV and the suppression of HBV assembly. FEBS J. 2016, 283, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickensheets, H.; Sheikh, F.; Park, O.; Gao, B.; Donnelly, R.P. Interferon-lambda (IFN-lambda) induces signal transduction and gene expression in human hepatocytes, but not in lymphocytes or monocytes. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2013, 93, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Sun, P.; Lucendo-Villarin, B.; Angus, A.G.; Szkolnicka, D.; Cameron, K.; Farnworth, S.L.; Patel, A.H.; Hay, D.C. Modulating innate immunity improves hepatitis C virus infection and replication in stem cell-derived hepatocytes. Stem Cell Rep. 2014, 3, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ryu, W.S. Hepatitis B virus polymerase blocks pattern recognition receptor signaling via interaction with DDX3: Implications for immune evasion. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Chen, J.; Wu, M.; Chen, H.; Kato, N.; Yuan, Z. Hepatitis B virus polymerase inhibits RIG-I- and Toll-like receptor 3-mediated beta interferon induction in human hepatocytes through interference with interferon regulatory factor 3 activation and dampening of the interaction between TBK1/IKKepsilon and DDX3. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 2080–2090. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Wu, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, L.; He, J.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, C.; Wang, F.; et al. Hepatitis B virus polymerase impairs interferon-alpha-induced STA T activation through inhibition of importin-alpha5 and protein kinase C-delta. Hepatology 2013, 57, 470–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Ni, C.; Song, T.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Zheng, Z.; Jia, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Guan, K.; Xu, Y.; et al. The hepatitis B virus X protein disrupts innate immunity by downregulating mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 1158–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Jung, S.Y.; Hodgson, A.J.; Madden, C.R.; Qin, J.; Slagle, B.L. Hepatitis B virus regulatory HBx protein binds to adaptor protein IPS-1 and inhibits the activation of beta interferon. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.H.; Park, E.S.; Kim, D.H.; Cho, K.C.; Kim, K.P.; Park, Y.K.; Ahn, S.H.; Park, S.H.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, C.W.; et al. Suppression of interferon-mediated anti-HBV response by single CpG methylation in the 5’-UTR of TRIM22. Gut 2018, 67, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Zhou, L.; Xie, H.; Zheng, S. Innate immune evasion by hepatitis B virus-mediated downregulation of TRIF. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 463, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, M.; Quiroga, J.A.; Carreno, V. Hepatitis B virus downregulates the human interferon-inducible MxA promoter through direct interaction of precore/core proteins. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 2073–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Meng, Z.; Jiang, M.; Pei, R.; Trippler, M.; Broering, R.; Bucchi, A.; Sowa, J.P.; Dittmer, U.; Yang, D.; et al. Hepatitis B virus suppresses toll-like receptor-mediated innate immune responses in murine parenchymal and nonparenchymal liver cells. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visvanathan, K.; Skinner, N.A.; Thompson, A.J.; Riordan, S.M.; Sozzi, V.; Edwards, R.; Rodgers, S.; Kurtovic, J.; Chang, J.; Lewin, S.; et al. Regulation of Toll-like receptor-2 expression in chronic hepatitis B by the precore protein. Hepatology 2007, 45, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, T.; Lo, C.; Skinner, N.; Locarnini, S.; Visvanathan, K.; Mansell, A. The hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) targets and suppresses activation of the toll-like receptor signaling pathway. J. Hepatol. 2011, 55, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.L.; Chen, P.J.; Lin, M.H.; Chen, D.S. Temporal aspects of major viral transcript expression in Hep G2 cells transfected with cloned hepatitis B virus DNA: With emphasis on the X transcript. Virology 1991, 185, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, C.; Livingston, C.M.; Li, L.; Beran, R.K.; Daffis, S.; Ramakrishnan, D.; Burdette, D.; Peiser, L.; Salas, E.; Ramos, H.; et al. The Smc5/6 Complex Restricts HBV when Localized to ND10 without Inducing an Innate Immune Response and Is Counteracted by the HBV X Protein Shortly after Infection. PloS ONE 2017, 12, e0169648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornyeyev, D.; Ramakrishnan, D.; Voitenleitner, C.; Livingston, C.M.; Xing, W.; Hung, M.; Kwon, H.J.; Fletcher, S.P.; Beran, R.K. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Hepatitis B Virus X Protein in Primary Human Hepatocytes. J. Virol. 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.K.; Kim, S.Y.; Seong, J.K.; Cheong, J. Hepatitis B virus X increases immune cell recruitment by induction of chemokine SDF-1. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Dai, X.; Huang, J.; Han, T.; Liao, X.; Cheng, K.; Sun, X.; Xie, Q.; Sun, P.; Zhou, X. The influence of male HBV infection on sperm quality, embryonic development, and assisted reproductive outcomes. Hum. Reprod. 2024, 39, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.; Domrachev, M.; Lash, A.E. Gene Expression Omnibus: NCBI gene expression and hybridization array data repository. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, T.; Wilhite, S.E.; Ledoux, P.; Evangelista, C.; Kim, I.F.; Tomashevsky, M.; Marshall, K.A.; Phillippy, K.H.; Sherman, P.M.; Holko, M.; et al. NCBI GEO: Archive for functional genomics data sets--update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D991–D995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breuer, K.; Foroushani, A.K.; Laird, M.R.; Chen, C.; Sribnaia, A.; Lo, R.; Winsor, G.L.; Hancock, R.E.; Brinkman, F.S.; Lynn, D.J. InnateDB: Systems biology of innate immunity and beyond--recent updates and continuing curation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D1228–D1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Wang, J.; Jaehnig, E.J.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, B. WebGestalt 2019: Gene set analysis toolkit with revamped UIs and APIs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W199–W205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardou, P.; Mariette, J.; Escudie, F.; Djemiel, C.; Klopp, C. jvenn: An interactive Venn diagram viewer. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.Y. clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, W.; Brouwer, C. Pathview: An R/Bioconductor package for pathway-based data integration and visualization. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1830–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camp, R.L.; Dolled-Filhart, M.; Rimm, D.L. X-tile: A new bio-informatics tool for biomarker assessment and outcome-based cut-point optimization. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 7252–7259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Liang, X.; Liu, Y.; Qu, Z.; Gao, L.; Han, L.; Liu, S.; Cui, M.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Hepatitis B virus core protein inhibits TRAIL-induced apoptosis of hepatocytes by blocking DR5 expression. Cell Death Differ. 2009, 16, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.Q.; Cai, W.W.; Sun, X.Y.; Bi, Y.W.; Zeng, C.; Zhao, X.Y.; Zhou, Q.; Xu, T.; Xie, Q.D.; Sun, P.N.; et al. Defined host factors support HBV infection in non-hepatic 293T cells. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 2507–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nisole, S.; Stoye, J.P.; Saib, A. TRIM family proteins: Retroviral restriction and antiviral defence. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meroni, G.; Diez-Roux, G. TRIM/RBCC, a novel class of ‘single protein RING finger’ E3 ubiquitin ligases. Bioessays 2005, 27, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchil, P.D.; Quinlan, B.D.; Chan, W.T.; Luna, J.M.; Mothes, W. TRIM E3 ligases interfere with early and late stages of the retroviral life cycle. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, B.; Wang, N.; Lee, Y.M.; Liu, C.; Li, K. TRIM56 is a virus- and interferon-inducible E3 ubiquitin ligase that restricts pestivirus infection. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 3733–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Gao, B.; Xu, W.; Xiong, S. Identification of TRIM22 as a RING finger E3 ubiquitin ligase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 374, 502–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, T.; Zou, J.; Saitoh, T.; Kumar, H.; Abe, T.; Matsuura, Y.; Kawai, T.; Akira, S. The ubiquitin ligase TRIM56 regulates innate immune responses to intracellular double-stranded DNA. Immunity 2010, 33, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, G.J.; Kim, C.; Shin, W.J.; Sklan, E.H.; Eoh, H.; Jung, J.U. TRIM56-mediated monoubiquitination of cGAS for cytosolic DNA sensing. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Li, N.L.; Wang, J.; Liu, B.; Lester, S.; Li, K. TRIM56 is an essential component of the TLR3 antiviral signaling pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 36404–36413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roessler, S.; Jia, H.L.; Budhu, A.; Forgues, M.; Ye, Q.H.; Lee, J.S.; Thorgeirsson, S.S.; Sun, Z.; Tang, Z.Y.; Qin, L.X.; et al. A unique metastasis gene signature enables prediction of tumor relapse in early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 10202–10212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Huo, X.; Yang, X.R.; He, J.; Cheng, L.; Wang, N.; Deng, X.; Jin, H.; Wang, C.; Zhao, F.; et al. STAT3-mediated upregulation of lncRNA HOXD-AS1 as a ceRNA facilitates liver cancer metastasis by regulating SOX4. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.M.; Ooi, L.L.; Hui, K.M. Identification and validation of a novel gene signature associated with the recurrence of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 6275–6283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melis, M.; Diaz, G.; Kleiner, D.E.; Zamboni, F.; Kabat, J.; Lai, J.; Mogavero, G.; Tice, A.; Engle, R.E.; Becker, S.; et al. Viral expression and molecular profiling in liver tissue versus microdissected hepatocytes in hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Chen, Y.; Lu, M. Advances in Targeting the Innate and Adaptive Immune Systems to Cure Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dusheiko, G.; Agarwal, K.; Maini, M.K. New Approaches to Chronic Hepatitis B. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takaoka, A.; Yanai, H. Interferon signalling network in innate defence. Cell Microbiol. 2006, 8, 907–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpentier, A.; Sheldon, J.; Vondran, F.W.R.; Brown, R.J.; Pietschmann, T. Efficient acute and chronic infection of stem cell-derived hepatocytes by hepatitis C virus. Gut 2020, 69, 1659–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suslov, A.; Boldanova, T.; Wang, X.; Wieland, S.; Heim, M.H. Hepatitis B Virus Does Not Interfere With Innate Immune Responses in the Human Liver. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 1778–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutz, P.; Metz, P.; Lempp, F.A.; Bender, S.; Qu, B.; Schoneweis, K.; Seitz, S.; Tu, T.; Restuccia, A.; Frankish, J.; et al. HBV Bypasses the Innate Immune Response and Does Not Protect HCV from Antiviral Activity of Interferon. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 1791–1804.e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauterbach-Riviere, L.; Bergez, M.; Monch, S.; Qu, B.; Riess, M.; Vondran, F.W.R.; Liese, J.; Hornung, V.; Urban, S.; Konig, R. Hepatitis B Virus DNA is a Substrate for the cGAS/STING Pathway but is not Sensed in Infected Hepatocytes. Viruses 2020, 12, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; He, R.; Fang, P.; Li, M.; Yu, H.; Wang, Q.; Yu, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, A.; et al. Hepatitis B virus rigs the cellular metabolome to avoid innate immune recognition. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Sun, L.; Mu, T.; Yi, J.; Ma, C.; Xie, H.; Liu, M.; Tang, H. An HBV-encoded miRNA activates innate immunity to restrict HBV replication. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 12, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luangsay, S.; Gruffaz, M.; Isorce, N.; Testoni, B.; Michelet, M.; Faure-Dupuy, S.; Maadadi, S.; Ait-Goughoulte, M.; Parent, R.; Rivoire, M.; et al. Early inhibition of hepatocyte innate responses by hepatitis B virus. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 1314–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.L.; Zhang, C.Z.; Liu, L.L.; Lu, S.X.; Pan, Y.H.; Wang, C.H.; He, Y.F.; Lin, C.S.; Yang, X.; Xie, D.; et al. A GYS2/p53 Negative Feedback Loop Restricts Tumor Growth in HBV-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 534–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.Z.; Mu, D. Multi-scale modeling identifies the role of p53-Gys2 negative feedback loop in cellular homeostasis. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2020, 17, 3260–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariffianto, A.; Deng, L.; Abe, T.; Matsui, C.; Ito, M.; Ryo, A.; Aly, H.H.; Watashi, K.; Suzuki, T.; Mizokami, M.; et al. Oxidative stress sensor Keap1 recognizes HBx protein to activate the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway, thereby inhibiting hepatitis B virus replication. J. Virol. 2023, 97, e0128723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Zhao, J.; Chen, N.K.; Chen, Z.Y. Hepatocyte-intrinsic innate immunity in hepatitis B virus infection: A focused review. World J. Hepatol. 2025, 17, 104533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Tian, Z. The role of innate immunity in HBV infection. Semin. Immunopathol. 2013, 35, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Sun, Y.; Song, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Peng, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Gao, C.; et al. Hepatitis B virus evades immune recognition via RNA adenosine deaminase ADAR1-mediated viral RNA editing in hepatocytes. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 1871–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatakeyama, S. TRIM proteins and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 792–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieland, S.; Thimme, R.; Purcell, R.H.; Chisari, F.V. Genomic analysis of the host response to hepatitis B virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 6669–6674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.S.; Ko, E.; Yoon, E.L.; Jung, Y.K.; Kim, J.H.; Seo, Y.S.; Yim, H.J.; Kim, K.H.; Kwon, S.Y.; Yeon, J.E.; et al. Multiplexed Proteomic Approach for Identification of Serum Biomarkers in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients with Normal AFP. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, B.; Duan, Z.; Xu, W.; Xiong, S. Tripartite motif-containing 22 inhibits the activity of hepatitis B virus core promoter, which is dependent on nuclear-located RING domain. Hepatology 2009, 50, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, M.; Zang, T.M.; Rihn, S.J.; Zhang, F.; Kueck, T.; Alim, M.; Schoggins, J.; Rice, C.M.; Wilson, S.J.; Bieniasz, P.D. Identification of Interferon-Stimulated Genes with Antiretroviral Activity. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 20, 392–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Du, X.; Song, W.; Zhang, W.; Lin, L.; Yuan, Z. Hepatitis B virus polymerase disrupts K63-linked ubiquitination of STING to block innate cytosolic DNA-sensing pathways. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 2287–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Dong, H.; Lai, X.; Ou, G.; Cao, J.; Shi, J.; Xiang, C.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, K.; et al. TRIM56 impairs HBV infection and replication by inhibiting HBV core promoter activity. Antivir. Res. 2022, 207, 105406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Guo, J.T.; Wu, J.Z.; Yang, G. Identification and characterization of multiple TRIM proteins that inhibit hepatitis B virus transcription. PloS One 2013, 8, e70001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furutani, Y.; Hirano, Y.; Toguchi, M.; Higuchi, S.; Qin, X.Y.; Yanaka, K.; Sato-Shiozaki, Y.; Takahashi, N.; Sakai, M.; Kongpracha, P.; et al. A small molecule iCDM-34 identified by in silico screening suppresses HBV DNA through activation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furutani, Y.; Toguchi, M.; Shiozaki-Sato, Y.; Qin, X.Y.; Ebisui, E.; Higuchi, S.; Sudoh, M.; Suzuki, H.; Takahashi, N.; Watashi, K.; et al. An interferon-like small chemical compound CDM-3008 suppresses hepatitis B virus through induction of interferon-stimulated genes. PloS One 2019, 14, e0216139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Megahed, F.A.K.; Zhou, X.; Sun, P. The Interactions between HBV and the Innate Immunity of Hepatocytes. Viruses 2020, 12, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| GSE14520 [52] Tissue | GSE84402 [53] Tissue | GSE121248 [54] Tissue | GSE55092 [55] Tissue | GSE55092 [55] Cell | Padj | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRIM22(logFC) | −1.81 | −1.51 | −0.94 | −1.57 | −1.57 | <0.05 |
| TRIM56(logFC) | 0.38 | <0.05 |
| GSE180646 [80] | GSE163042 | GSE126090 [81] | GSE52752 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRIM22(logFC) | 2.7284365 | 2.0612795 | 3.26 | 2.3469416 |
| Padj.(TRIM22) | 1.16 × 10−17 | 0.0155509 | 2.20 × 10−11 | 2.50 × 10−6 |
| TRIM56(logFC) | 0.2710238 | 0.69630274 | 0.949 | 0.9618422 |
| Padj.(TRIM56) | 0.0403 | 0.4714832 | 8.00E-07 | 0.00102 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, C.; Megahed, F.A.K.; Guo, Y.; Sun, D.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Bi, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, Q.; Xie, Q.; et al. The Intrinsic Innate Immunity of Hepatocytes Suppresses HBV Replication and Is Antagonized by HBx. Viruses 2025, 17, 1599. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17121599
Zeng C, Megahed FAK, Guo Y, Sun D, Wang Y, Liu Q, Bi Y, Li J, Zhou Q, Xie Q, et al. The Intrinsic Innate Immunity of Hepatocytes Suppresses HBV Replication and Is Antagonized by HBx. Viruses. 2025; 17(12):1599. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17121599
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Chui, Fayed Attia Koutb Megahed, Yiqiong Guo, Dongmei Sun, Yaru Wang, Qin Liu, Yanwei Bi, Jinghang Li, Qi Zhou, Qingdong Xie, and et al. 2025. "The Intrinsic Innate Immunity of Hepatocytes Suppresses HBV Replication and Is Antagonized by HBx" Viruses 17, no. 12: 1599. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17121599
APA StyleZeng, C., Megahed, F. A. K., Guo, Y., Sun, D., Wang, Y., Liu, Q., Bi, Y., Li, J., Zhou, Q., Xie, Q., Sun, P., & Zhou, X. (2025). The Intrinsic Innate Immunity of Hepatocytes Suppresses HBV Replication and Is Antagonized by HBx. Viruses, 17(12), 1599. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17121599





