Molecular Determinants of Species-Specific Interactions Between Protein Kinase R and Poxvirus K3 Orthologs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Line
2.2. Plasmids
2.3. Luciferase-Based Reporter (LBR) Assay
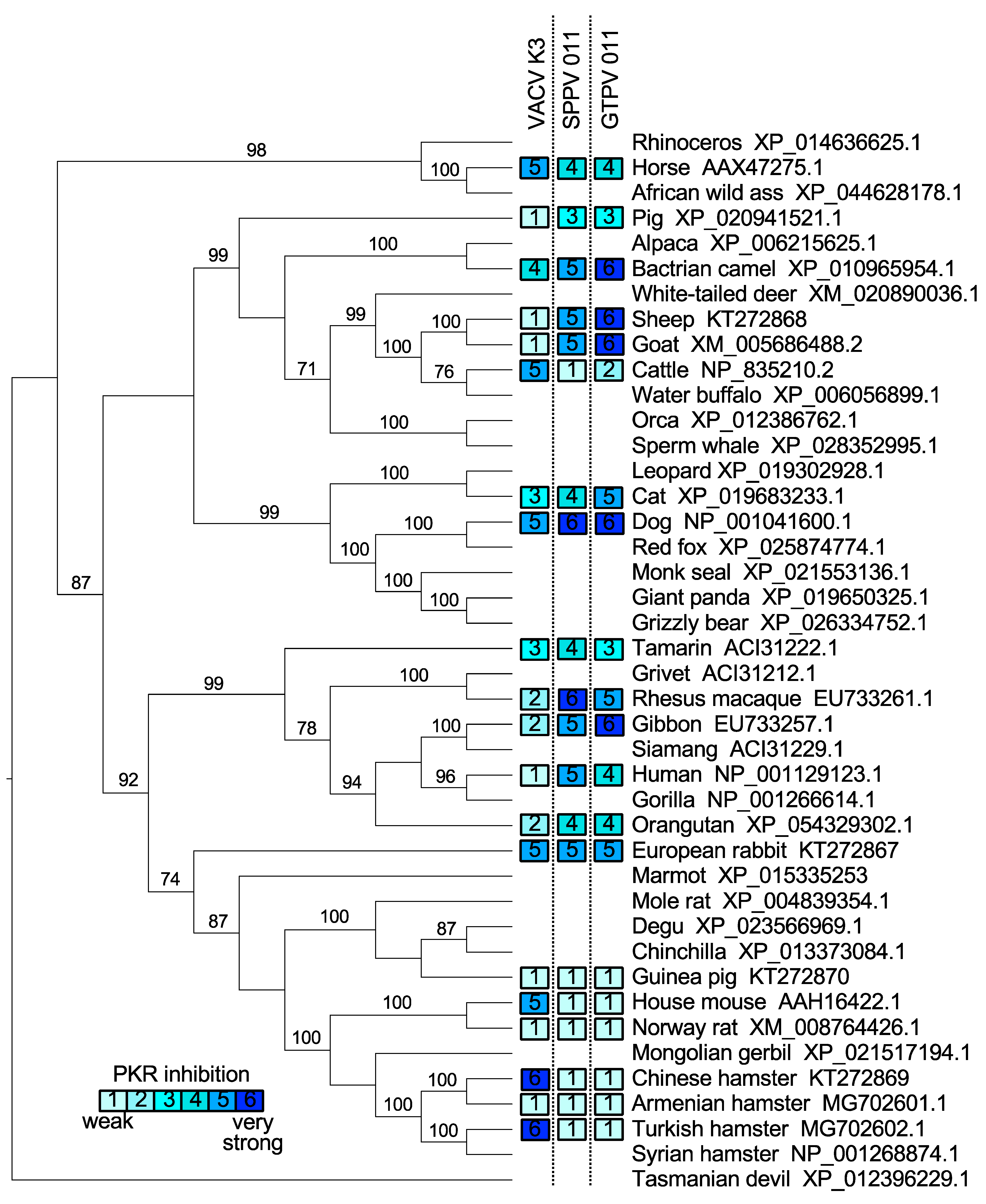
2.4. PKR Phylogeny
2.5. Estimation of Positively Selected Sites in Ruminant PKRs
3. Results
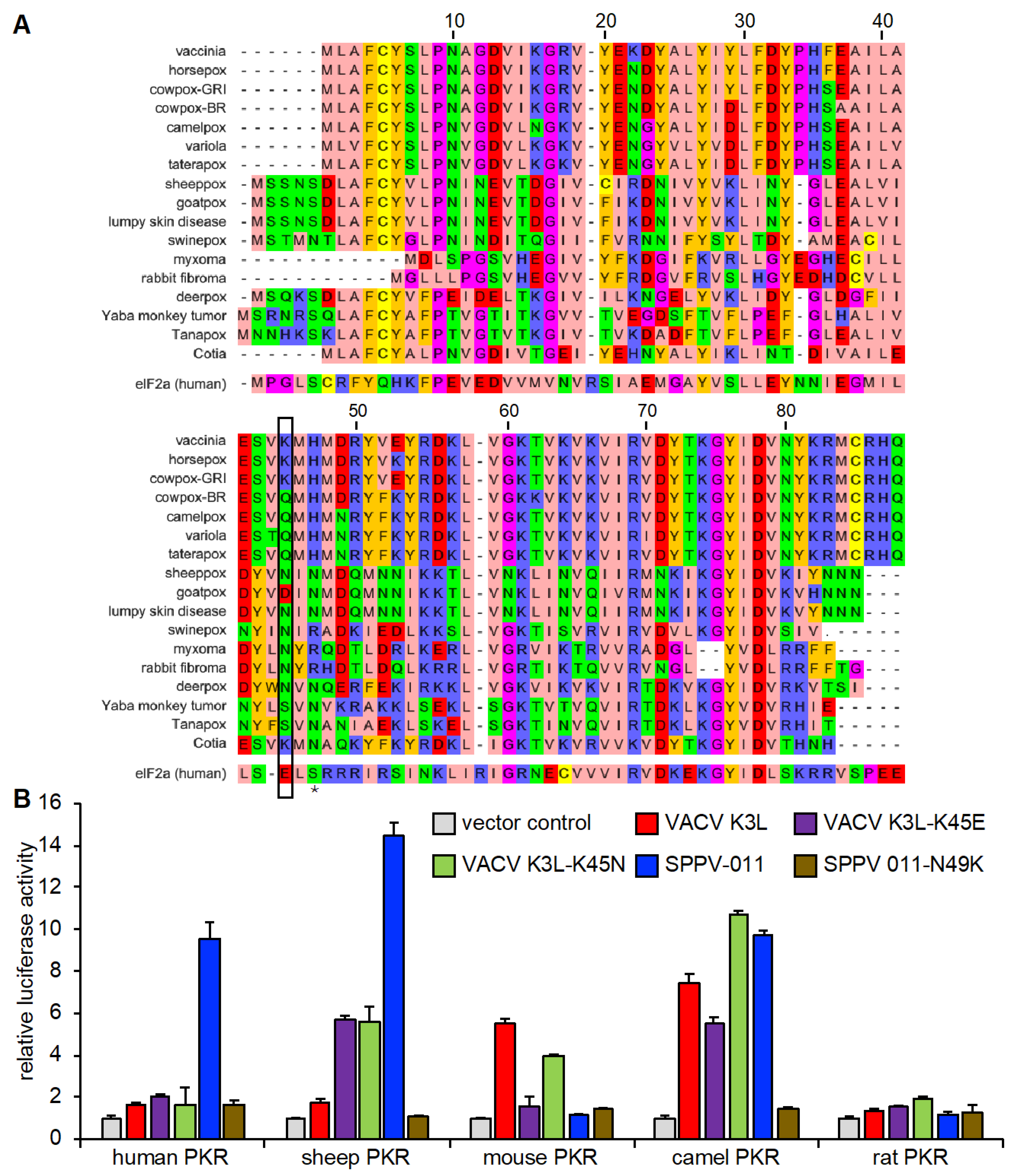
3.1. Species-Specific PKR Inhibition by VACV, SPPV, and GTPV K3 Orthologs
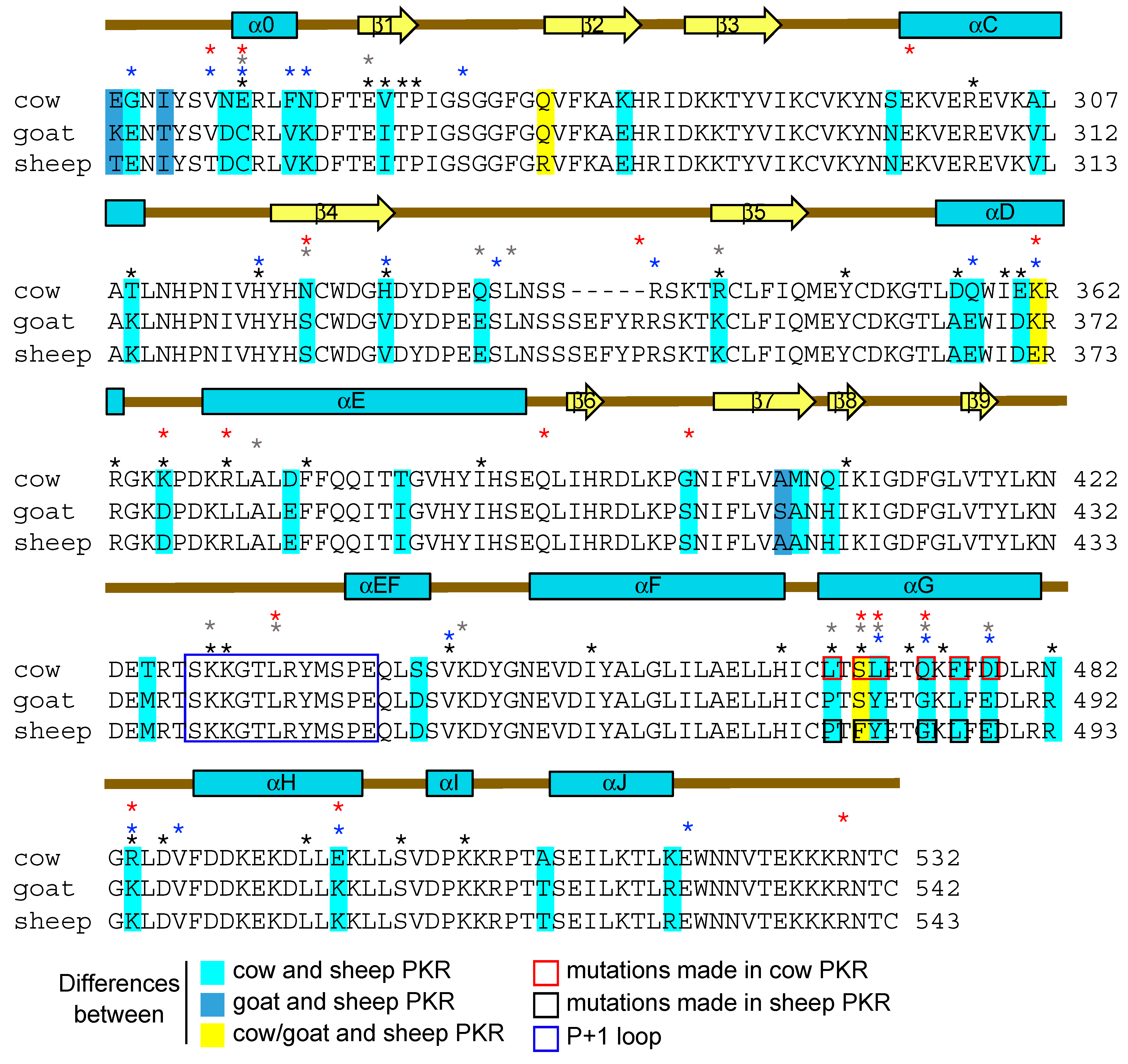
3.2. Differential Inhibition of Cow and Sheep PKRs Is Mediated by the C-Terminal Lobe of the Kinase Domain
3.3. Helix αG Determines the Sensitivity of Cow PKR to VACV and Capripoxvirus K3 Inhibition
3.4. Regions Outside Helix αG in Sheep PKR Contribute to Its Sensitivity to SPPV and GTPV 011
3.5. Species-Specific Modulation of PKR Inhibition by VACV K3 Mutants
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PKR | Protein kinase R |
| eIF2 | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 |
| VACV | Vaccinia virus |
| SPPV | Sheeppox virus |
| GTPV | Goatpox virus |
| ds | Double-stranded |
| LBR | Luciferase-based reporter |
References
- Embry, A.; Gammon, D.B. Abortive Infection of Animal Cells: What Goes Wrong. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2024, 11, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothenburg, S.; Brennan, G. Species-Specific Host-Virus Interactions: Implications for Viral Host Range and Virulence. Trends Microbiol. 2020, 28, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daugherty, M.D.; Malik, H.S. Rules of engagement: Molecular insights from host-virus arms races. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2012, 46, 677–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sironi, M.; Cagliani, R.; Forni, D.; Clerici, M. Evolutionary insights into host-pathogen interactions from mammalian sequence data. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2015, 16, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smart, A.; Gilmer, O.; Caliskan, N. Translation Inhibition Mediated by Interferon-Stimulated Genes during Viral Infections. Viruses 2024, 16, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellen, C.U.T. Viral Strategies and Cellular Countermeasures That Regulate mRNA Access to the Translation Apparatus. Viruses 2025, 17, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Kaufman, R.J. A model for the double-stranded RNA (dsRNA)-dependent dimerization and activation of the dsRNA-activated protein kinase PKR. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 1291–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.A.; Meurs, E.F.; Esteban, M. The dsRNA protein kinase PKR: Virus and cell control. Biochimie 2007, 89, 799–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langland, J.O.; Cameron, J.M.; Heck, M.C.; Jancovich, J.K.; Jacobs, B.L. Inhibition of PKR by RNA and DNA viruses. Virus Res. 2006, 119, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, A.T.; Child, S.J.; Geballe, A.P. Antagonism of Protein Kinase R by Large DNA Viruses. Pathogens 2022, 11, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.V.; Elroy-Stein, O.; Jagus, R.; Moss, B.; Kaufman, R.J. The vaccinia virus K3L gene product potentiates translation by inhibiting double-stranded-RNA-activated protein kinase and phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 1943–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.W.; Watson, J.C.; Jacobs, B.L. The E3L gene of vaccinia virus encodes an inhibitor of the interferon-induced, double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 4825–4829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, M.; Vasconcelos, G.; Dever, T.E. An eIF2alpha-binding motif in protein phosphatase 1 subunit GADD34 and its viral orthologs is required to promote dephosphorylation of eIF2alpha. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E3466–E3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.J.; Tazi, L.; Haller, S.L.; Rothenburg, S. Crocodilepox Virus Protein 157 Is an Independently Evolved Inhibitor of Protein Kinase R. Viruses 2022, 14, 1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratke, K.A.; McLysaght, A.; Rothenburg, S. A survey of host range genes in poxvirus genomes. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2013, 14, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkevich, T.G.; Yutin, N.; Wolf, Y.I.; Koonin, E.V.; Moss, B. Ancient Gene Capture and Recent Gene Loss Shape the Evolution of Orthopoxvirus-Host Interaction Genes. mBio 2021, 12, e0149521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, A.C.; Sicheri, F. X-ray crystal structure and functional analysis of vaccinia virus K3L reveals molecular determinants for PKR subversion and substrate recognition. Mol. Cell 2002, 10, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczerba, M.; Subramanian, S.; Trainor, K.; McCaughan, M.; Kibler, K.V.; Jacobs, B.L. Small Hero with Great Powers: Vaccinia Virus E3 Protein and Evasion of the Type I IFN Response. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langland, J.O.; Jacobs, B.L. The role of the PKR-inhibitory genes, E3L and K3L, in determining vaccinia virus host range. Virology 2002, 299, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haller, S.L.; Park, C.; Bruneau, R.C.; Megawati, D.; Zhang, C.; Vipat, S.; Peng, C.; Senkevich, T.G.; Brennan, G.; Tazi, L.; et al. Host species-specific activity of the poxvirus PKR inhibitors E3 and K3 mediate host range function. J. Virol. 2024, 98, e0133124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothenburg, S.; Seo, E.J.; Gibbs, J.S.; Dever, T.E.; Dittmar, K. Rapid evolution of protein kinase PKR alters sensitivity to viral inhibitors. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2009, 16, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elde, N.C.; Child, S.J.; Geballe, A.P.; Malik, H.S. Protein kinase R reveals an evolutionary model for defeating viral mimicry. Nature 2009, 457, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacquet, S.; Culbertson, M.; Zhang, C.; El Filali, A.; De La Myre Mory, C.; Pons, J.B.; Filippi-Codaccioni, O.; Lauterbur, M.E.; Ngoubangoye, B.; Duhayer, J.; et al. Adaptive duplication and genetic diversification of protein kinase R contribute to the specificity of bat-virus interactions. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eadd7540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.; Haller, S.L.; Rahman, M.M.; McFadden, G.; Rothenburg, S. Myxoma virus M156 is a specific inhibitor of rabbit PKR but contains a loss-of-function mutation in Australian virus isolates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 3855–3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Peng, C.; Zhang, C.; Stoian, A.M.M.; Tazi, L.; Brennan, G.; Rothenburg, S. Maladaptation after a virus host switch leads to increased activation of the pro-inflammatory NF-kappaB pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2115354119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Fernandez, M.E.L.; Peng, C.; Megawati, D.; Brennan, G.; Tazi, L.; Rothenburg, S. Poxvirus K3 Orthologs Regulate NF-kappaB-Dependent Inflammatory Responses by Targeting the PKR-eIF2alpha Axis in Multiple Species. Vaccines 2025, 13, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Peng, C.; Brennan, G.; Rothenburg, S. Species-specific inhibition of antiviral protein kinase R by capripoxviruses and vaccinia virus. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2019, 1438, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megawati, D.; Stroup, J.N.; Park, C.; Clarkson, T.; Tazi, L.; Brennan, G.; Rothenburg, S. Tanapox Virus and Yaba Monkey Tumor Virus K3 Orthologs Inhibit Primate Protein Kinase R in a Species-Specific Fashion. Viruses 2024, 16, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Peng, C.; Rahman, M.J.; Haller, S.L.; Tazi, L.; Brennan, G.; Rothenburg, S. Orthopoxvirus K3 orthologs show virus- and host-specific inhibition of the antiviral protein kinase PKR. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuppurainen, E.S.M.; Venter, E.H.; Shisler, J.L.; Gari, G.; Mekonnen, G.A.; Juleff, N.; Lyons, N.A.; De Clercq, K.; Upton, C.; Bowden, T.R.; et al. Review: Capripoxvirus Diseases: Current Status and Opportunities for Control. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 729–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Varga, J.; Deschambault, Y. Poxvirus encoded eIF2alpha homolog, K3 family proteins, is a key determinant of poxvirus host species specificity. Virology 2020, 541, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Samuel, C.E. Protein kinase PKR plays a stimulus- and virus-dependent role in apoptotic death and virus multiplication in human cells. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 8192–8200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpentier, K.S.; Esparo, N.M.; Child, S.J.; Geballe, A.P. A Single Amino Acid Dictates Protein Kinase R Susceptibility to Unrelated Viral Antagonists. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Megawati, D.; Zheng, C.; Rothenburg, S. Protein Kinase R (PKR) as a Novel dsRNA Sensor in Antiviral Innate Immunity. Methods Mol. Biol. 2025, 2854, 265–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talavera, G.; Castresana, J. Improvement of phylogenies after removing divergent and ambiguously aligned blocks from protein sequence alignments. Syst. Biol. 2007, 56, 564–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefort, V.; Longueville, J.E.; Gascuel, O. SMS: Smart Model Selection in PhyML. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 2422–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z. PAML 4: Phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 1586–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, R.; Yang, Z. Likelihood models for detecting positively selected amino acid sites and applications to the HIV-1 envelope gene. Genetics 1998, 148, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejepinska, J.; Malik, R.; Wagner, S.; Svoboda, P. Reporters transiently transfected into mammalian cells are highly sensitive to translational repression induced by dsRNA expression. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, A.C.; Dever, T.E.; Sicheri, F. Higher-order substrate recognition of eIF2alpha by the RNA-dependent protein kinase PKR. Cell 2005, 122, 887–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpentier, K.S.; Geballe, A.P. An Evolutionary View of the Arms Race between Protein Kinase R and Large DNA Viruses. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 3280–3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawagishi-Kobayashi, M.; Silverman, J.B.; Ung, T.L.; Dever, T.E. Regulation of the protein kinase PKR by the vaccinia virus pseudosubstrate inhibitor K3L is dependent on residues conserved between the K3L protein and the PKR substrate eIF2alpha. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1997, 17, 4146–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elde, N.C.; Child, S.J.; Eickbush, M.T.; Kitzman, J.O.; Rogers, K.S.; Shendure, J.; Geballe, A.P.; Malik, H.S. Poxviruses deploy genomic accordions to adapt rapidly against host antiviral defenses. Cell 2012, 150, 831–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Primer Name | Mutation | Forward Primer Sequences (5′—3′) (Reverse Primers Are Reverse Complement of Forward Primers) | Template |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cm1 | L469P | GAACTTCATATATGTCCCACTTCTTTAGAAACACAG | cow PKR |
| Cm2 | S471F | TCATATATGTCTCACTTTTTTAGAAACACAGAAGTT | cow PKR |
| Cm3 | L472Y | TATGTCTCACTTCTTACGAAACACAGAAGTTCTTTG | cow PKR |
| Cm4 | S471F, L472Y | TTCATATATGTCTCACTTTTTACGAAACACAGAAGTTCTTT | cow PKR |
| Cm5 | L469P, S471F, L472Y | CTTCTTCATATATGTCCCACTTTTTACGAAACACAG | cow PKR |
| Cm6 | Q475G | TCTCACTTCTTTAGAAACAGGGAAGTTCTTTGACGAT | cow PKR |
| Cm7 | F477L | CTTTAGAAACACAGAAGTTATTTGACGATCTAAGGA | cow PKR |
| Cm8 | D479E | TAGAAACACAGAAGTTCTTTGAAGATCTAAGGAATGGC | cow PKR |
| Cm9 | F477L, D479E | TAGAAACACAGAAGTTATTTGAAGATCTAAGGAATGGC | cow PKR |
| Cm10 | Q475G, F477L, D479E | ACTTCTTTAGAAACAGGGAAGTTATTTGAAGATCTA | cow PKR |
| Cm11 | S471F, L472Y, Q475G, F477L, D479E | CATATATGTCTCACTTTTTACGAAACAGGGAAGTTATTT | cow PKR |
| Cm12 | sheep helix αG | CTTCTTCATATATGTCCCACTTTTTACGAAACAGGG | cow PKR |
| Sm1 | Y482L | CATATATGTCCCACTTTTTTAGAAACAGGGAAGTTATTTG | sheep PKR |
| Sm2 | F481S, Y482L | CTTCATATATGTCCCACTAGTTTAGAAACAGGGAAGTT | sheep PKR |
| Sm3 | G485Q | CCCACTTTTTACGAAACACAGAAGTTATTTGAAGATC | sheep PKR |
| Sm4 | P479L | GAACTTCTTCATATATGTCTCACTTTTTACGAAACAGG | sheep PKR |
| Sm5 | L487F, E489D | CGAAACAGGGAAGTTCTTTGATGATCTAAGGAGAGGC | sheep PKR |
| Sm6 | F481S, Y482L, E489D | CGAAACAGGGAAGTTCTTTGATGATCTAAGGAGAGGC | sm2 |
| Sm7 | cow helix αG | CTAGTTTAGAAACACAGAAGTTCTTTGATGATCTAAGGAGAGGC | sheep PKR |
| Sm8 | cow helix αD + E + G | GGAGTGCATTATATACATTCAGAACAGTTAATTCAC | sheep PKR |
| Sm9 | cow helix αG + H+ I + J | GCAGAACTTCTTCATATATGTCTCACTTCTTTAGAAAC | sheep PKR |
| Sm10 | Sm9 + cow helix αD+ E | GGAGTGCATTATATACATTCAGAACAGTTAATTCAC | Sm9 |
| Sm11 | Sm10 + p + 1loop | GGAGTGCATTATATACATTCAGAACAGTTAATTCAC | Sm10 |
| VACV K3L-K45E | K45E | GCTATCTTGGCAGAGAGTGTTGAACTGCATATGGATAGAT | VACV K3L |
| VACV K3L-K49E | K49N | GCTATCTTGGCAGAGAGTGTTGAGATGCATATGGATAGAT | VACV K3L |
| SPPV 011-N49K | N49K | TTGTAATAGATTATGTTGAAATAAACATGGATCAA | SPPV 011 |
| Species | Common Name | Accession | Family | Subfamily |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capra hircus | goat | XM_018055123.1 | Bovidae | Caprinae |
| Capricornis sumatraensis | Sumatran serow | XP_068829084.1 | Bovidae | Caprinae |
| Ovibos moschatus | muskox | KAL1288457.1 | Bovidae | Caprinae |
| Budorcas taxicolor | takin | XP_052505461.1 | Bovidae | Caprinae |
| Ovis aries | sheep | XP_004007349.1 | Bovidae | Caprinae |
| Ovis canadensis | bighorn sheep | XP_069439646 | Bovidae | Caprinae |
| Oryx dammah | scimitar-horned oryx | XP_040080570.1 | Bovidae | Hippotraginae |
| Bos taurus | cattle | XM_005212570.5 | Bovidae | Bovinae |
| Bison bison bison | American bison | XP_010836908.1 | Bovidae | Bovinae |
| Bos mutus | wild yak | XP_070235833.1 | Bovidae | Bovinae |
| Bos javanicus | banteng | XM_061432077.1 | Bovidae | Bovinae |
| Bubalus kerabau | carabao | XP_055395787.1 | Bovidae | Bovinae |
| Bubalus bubalis | water buffalo | XP_044781760.1 | Bovidae | Bovinae |
| Odocoileus virginianus | white-tailed deer | XP_020745697.2 | Cervidae | Capreolinae |
| Rangifer tarandus platyrhynchus | Svalbard reindeer | CAI9174154.1 | Cervidae | Capreolinae |
| Cervus canadensis | elk | XP_043324268.1 | Cervidae | Cervinae |
| Cervus elaphus | red deer | XP_043774162.1 | Cervidae | Cervinae |
| Dama dama | European fallow deer | XP_061011579 | Cervidae | Cervinae |
| Muntiacus reevesi | Reeves’ muntjac | XP_065785502.1 | Cervidae | Muntiacinae |
| Moschus berezovskii | dwarf musk deer | XP_055255352.1 | Moschidae |
| Residue | Posterior Probabilities |
|---|---|
| (Goat PKR) | (pP) |
| 54 K | 0.984 * |
| 74 I | 0.961 * |
| 95 R | 0.992 ** |
| 128 R | 0.976 * |
| 182 A | 0.964 * |
| 225 V | 0.965 * |
| 247 A | 0.998 ** |
| 250 V | 0.961 * |
| 259 V | 0.990 * |
| 261 C | 1.000 ** |
| 303 E | 0.987 * |
| 325 S | 0.956 * |
| 346 R | 0.984 * |
| 371 K | 0.957 * |
| 376 D | 0.975 * |
| 380 L | 0.987 * |
| 400 Q | 0.963 * |
| 409 S | 0.971 * |
| 443 L | 0.981 * |
| 480 S | 0.988 * |
| 481 Y | 0.991 ** |
| 484 G | 0.993 ** |
| 494 K | 0.978 * |
| 507 K | 0.952 * |
| 539 R | 0.971 * |
| PKR/ | Relative Inhibition by | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| PKR Mutant | Mutations | VACV K3 | SPPV 011 |
| Cow PKR | wild type | 6 | 1 |
| Cm1 | L469P | 6 | 1 |
| Cm2 | S471F | 3 | 1 |
| Cm3 | L472Y | 3 | 3 |
| Cm4 | S471F, L472Y | 1 | 3 |
| Cm5 | L469P, S471F, L472Y | 1 | 4 |
| Cm6 | Q475G | 5 | 2 |
| Cm7 | F477L | 3 | 1 |
| Cm8 | D479E | 5 | 1 |
| Cm9 | F477L, D479E | 6 | 4 |
| Cm10 | Q475G, F477L, D479E | 5 | 3 |
| Cm11 | Cm4 + Cm10 | 1 | 6 |
| Cm12 | Helix αG | 1 | 6 |
| Sheep PKR | wild type | 1 | 6 |
| Sm1 | Y482L | 4 | 4 |
| Sm2 | F481S, Y482L | 6 | 4 |
| Sm3 | G485Q | 3 | 6 |
| Sm4 | P479L | 1 | 6 |
| Sm5 | L487F, E489D | 1 | 4 |
| Sm6 | F481S, Y482L, E489D | 6 | 5 |
| Sm7 | helix αG | 6 | 4 |
| Sm8 | helices αD, αE, αG | 6 | 1 |
| Sm9 | helices αG, αH, αI, αJ | 6 | 4 |
| Sm10 | helices αD, αE, αG, αH, αI, αJ | 6 | 2 |
| Sm11 | Sm10 + P + 1 loop | 6 | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, C.; Brennan, G.; Peng, C.; Zhang, C.; Cao, J.; Tazi, L.; Rothenburg, S. Molecular Determinants of Species-Specific Interactions Between Protein Kinase R and Poxvirus K3 Orthologs. Viruses 2025, 17, 1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17121550
Park C, Brennan G, Peng C, Zhang C, Cao J, Tazi L, Rothenburg S. Molecular Determinants of Species-Specific Interactions Between Protein Kinase R and Poxvirus K3 Orthologs. Viruses. 2025; 17(12):1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17121550
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Chorong, Greg Brennan, Chen Peng, Chi Zhang, Jingxin Cao, Loubna Tazi, and Stefan Rothenburg. 2025. "Molecular Determinants of Species-Specific Interactions Between Protein Kinase R and Poxvirus K3 Orthologs" Viruses 17, no. 12: 1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17121550
APA StylePark, C., Brennan, G., Peng, C., Zhang, C., Cao, J., Tazi, L., & Rothenburg, S. (2025). Molecular Determinants of Species-Specific Interactions Between Protein Kinase R and Poxvirus K3 Orthologs. Viruses, 17(12), 1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17121550