Detection of Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus in House Mouse (Mus musculus) in Brazil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Areas and Rodent Sampling
2.2. Serological Analysis
2.3. RT-PCR and Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Serological Results
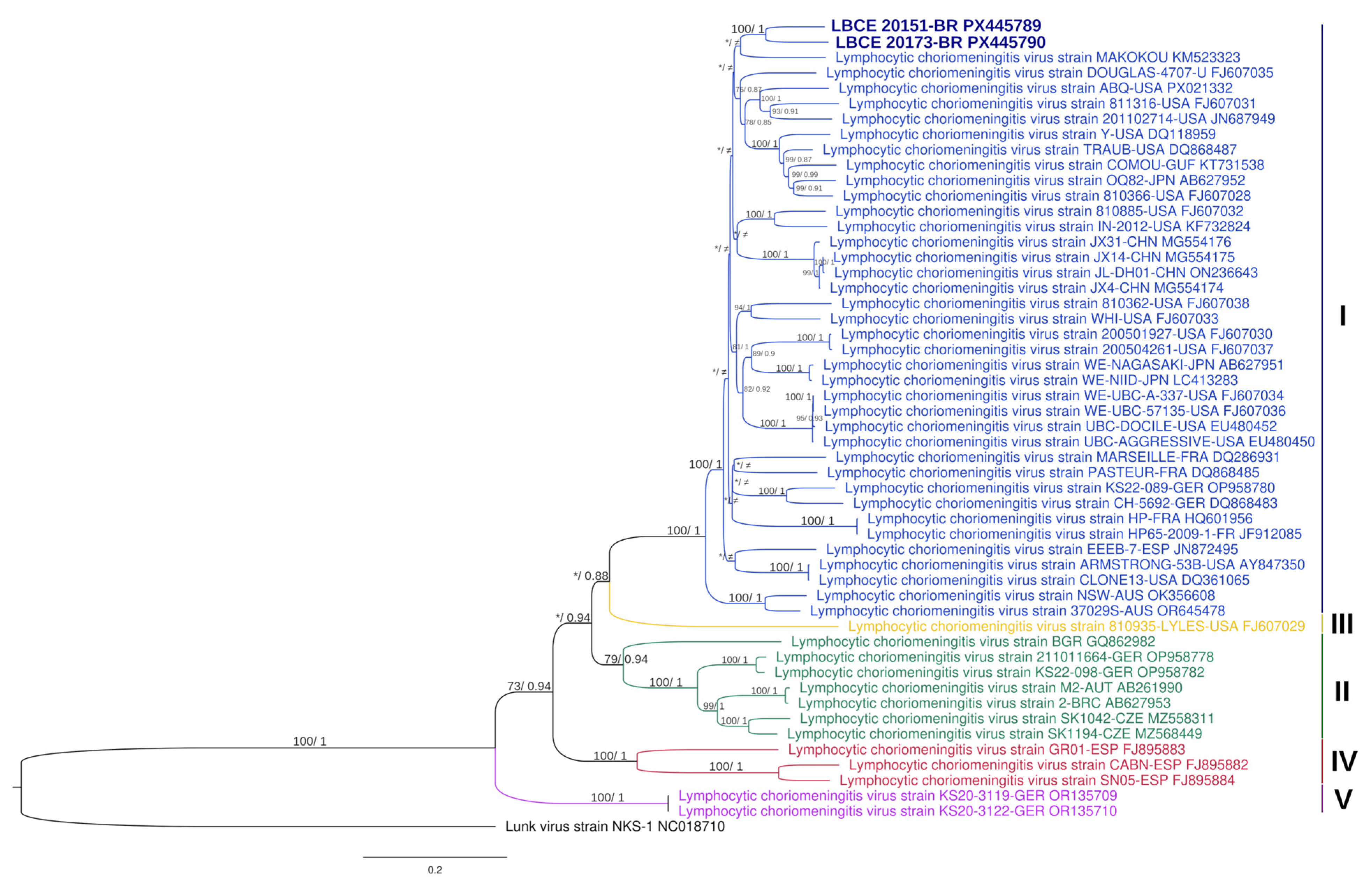
3.2. Virus Characterization
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LCMV | Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| RT-PCR | Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal Fluid |
| TORCH | Toxoplasmose, Rubeola, Citomegalovirus, Herpes Virus |
| GPC | Glycoprotein Precursor Complex |
| NP | Nucleoprotein |
| nt | Nucleotide |
| aa | Amino Acid |
| CTL | Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte |
References
- Hallam, S.J.; Koma, T.; Maruyama, J.; Paessler, S. Review of Mammarenavirus Biology and Replication. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.J.; Novella, I.S.; Teng, M.N.; Oldstone, M.B.A.; de la Torre, J.C. NP and L Proteins of Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus (LCMV) Are Sufficient for Efficient Transcription and Replication of LCMV Genomic RNA Analogs. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 3470–3477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radoshitzky, S.R.; Buchmeier, M.J.; de la Torre, J.C. Arenaviridae: The Viruses and Their Replication. In Fields Virology, 7th ed.; Howley, P.M., Knipe, D.M., Whelan, S.P.J., Eds.; Wolters Kluwer: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 784–809. [Google Scholar]
- Charrel, R.N.; de Lamballerie, X.; Emonet, S. Phylogeny of the Genus Arenavirus. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2008, 11, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonthius, D.J. Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus: An Underrecognized Cause of Neurologic Disease in the Fetus, Child, and Adult. Semin. Pediatr. Neurol. 2012, 19, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasdell, K.R.; Becker, S.D.; Hurst, J.; Begon, M.; Bennett, M. Host Range and Genetic Diversity of Arenaviruses in Rodents, United Kingdom. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1455–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skinner, H.H.; Knight, E.H. The Potential Role of Syrian Hamsters and Other Small Animals as Reservoirs of Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus. J. Small Anim. Pract. 1979, 20, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilibic-Cavlek, T.; Savic, V.; Ferenc, T.; Mrzljak, A.; Barbic, L.; Bogdanic, M.; Stevanovic, V.; Tabain, I.; Ferencak, I.; Zidovec-Lepej, S. Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis—Emerging Trends of a Neglected Virus: A Narrative Review. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2021, 6, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deibel, R.; Woodall, J.P.; Decher, W.J.; Schryver, G.D. Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus in Man: Serologic Evidence of Association with Pet Hamsters. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1975, 232, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaine, M.; Weingertner, A.S.; Nougairede, A.; Lepiller, Q.; Fafi-Kremer, S.; Favre, R.; Charrel, R. Microcephaly Caused by Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 1548–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacNeil, A.; Ströher, U.; Farnon, E.; Campbell, S.; Cannon, D.; Paddock, C.D.; Drew, C.P.; Kuehnert, M.; Knust, B.; Gruenenfelder, R.; et al. Solid Organ Transplant-Associated Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis, United States, 2011. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1256–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, F.d.P.; Woodall, J.P.; Rosa, A.P.d.A.T.d.; Rosa, J.F.S.T.d. Studies on Arenaviruses in Brazil. Medicina 1997, 37, 175–181. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, J.; Guterres, A.; De Oliveira, R.C.; Chamberlain, J.; Lewandowski, K.; Teixeira, B.R.; Coelho, T.A.; Crisóstomo, C.F.; Bonvicino, C.R.; D’Andrea, P.S.; et al. Xapuri Virus, a Novel Mammarenavirus: Natural Reassortment and Increased Diversity between New World Viruses. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, J.; de Oliveira, R.C.; Guterres, A.; Barreto-Vieira, D.F.; Terças, A.C.P.; Teixeira, B.R.; da Silva, M.A.N.; Caldas, G.C.; de Oliveira Coelho, J.M.C.; Barth, O.M.; et al. Detection of Latino Virus (Arenaviridae: Mammarenavirus) Naturally Infecting Calomys Callidus. Acta Trop. 2018, 179, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coimbra, T.L.M.; Nassar, E.S.; de Souza, L.T.M.; Ferreira, I.B.; Rocco, I.M.; Burattini, M.N.; Travassos da Rosa, A.P.A.; Vasconcelos, P.F.C.; Pinheiro, F.P.; LeDuc, J.W.; et al. New Arenavirus Isolated in Brazil. Lancet 1994, 343, 391–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riera, L.; Castillo, E.; Saavedra, M.D.C.; Priotto, J.; Sottosanti, J.; Polop, J.; Ambrosio, A.M. Serological Study of the Lymphochoriomeningitis Virus (LCMV) in an Inner City of Argentina. J. Med. Virol. 2005, 76, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellar, A.; Guevara, M.; Rodas, J.D.; Londoño, A.F.; Arroyave, E.; Díaz, F.J.; Levis, S.; Blanco, P.J. Primera Evidencia de Infección Por El Virus de La Coriomeningitis Linfocítica (Arenavirus) En Roedores Mus Musculus Capturados En La Zona Urbana Del Municipio de Sincelejo, Sucre, Colombia. Biomedica 2017, 37, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavergne, A.; de Thoisy, B.; Tirera, S.; Donato, D.; Bouchier, C.; Catzeflis, F.; Lacoste, V. Identification of Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Mammarenavirus in House Mouse (Mus Musculus, Rodentia) in French Guiana. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 37, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saavedra, M.d.C.; Ambrosio, A.M.; Riera, L.; Levis, S.; Sottosanti, J.; Sabattini, M. Aislamiento del virus de la coriomeningitis linfocitaria de seres humanos. Medicina 2001, 61, 837–842. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, J.; Oliveira, R.C.; Rosa, G.C.; Guterres, A.; Lima, M.R.Q.; Horta, M.A.P.; Bóia, M.N.; Lemos, E.R.S. Condições de Saúde Dos Profissionais Que Manuseiam Animais No Brasil e a Prevalência de Infecção Por Robovírus, Rickettsia Do Grupo Da Febre Maculosa e Bartonella. In Vigilância em Saúde: Interfaces Entre a Saúde Pública e a Pesquisa Científica; COLAB: Uberlândia, Brazil, 2021; pp. 121–140. [Google Scholar]
- De Masi, E.; Vilaça, P.; Razzolini, M.T.P. Environmental Conditions and Rodent Infestation in Campo Limpo District, São Paulo Municipality, Brazil. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2009, 19, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masi, E.; Pino, F.A.; Santos, M.d.G.S.; Genehr, L.; Albuquerque, J.O.M.; Bancher, A.M.; Alves, J.C.M. Socioeconomic and Environmental Risk Factors for Urban Rodent Infestation in Sao Paulo, Brazil. J. Pest Sci. 2010, 83, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, N.d.J.; Sousa, E.; Reis, M.G.; Ko, A.I.; Costa, F. Rat Infestation Associated with Environmental Deficiencies in an Urban Slum Community with High Risk of Leptospirosis Transmission. Cad. Saúde Pública 2017, 33, e00132115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (IBGE) Censo Demográfico 2022. Available online: https://censo2022.ibge.gov.br/ (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Püttker, T.; Pardini, R.; Meyer-Lucht, Y.; Sommer, S. Responses of Five Small Mammal Species to Micro-Scale Variations in Vegetation Structure in Secondary Atlantic Forest Remnants, Brazil. BMC Ecol. 2008, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, E.R.S.d.; D’Andrea, P.S. Trabalho de Campo com Animais: Procedimentos, Riscos e Biossegurança; Editora Fiocruz: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2014; p. 77. [Google Scholar]
- Bonvicino, C.R.; Oliveira, J.d.; D’Andrea, P.S. Guia Dos Roedores Do Brasil, Com Chaves Para Gêneros Baseadas Em Caracteres Externos; Manuais Técnicos; Centro Pan-Americano de Febre Aftosa—OPAS/OMS: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2008; pp. 68–69. [Google Scholar]
- Corrêa, M.M.d.O.; Ribeiro, M.C.S.; de Oliveira, M.B.; Bonvicino, C.R. Técnicas e Avanços na Identificação de Cromossomos de Mamíferos. Braz. J. Mammal. 2023, E92, e922023116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, J.N.; Childs, J.E.; Ksiazek, T.G.; Peters, C.J.; Velleca, W.M. Methods for Trapping and Sampling Small Mammals for Virologic Testing; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 1995.
- Riera, L.M.; Feuillade, M.R.; Saavedra, M.C.; Ambrosio, A.M. Evaluation of an Enzyme Immunosorbent Assay for the Diagnosis of Argentine Haemorrhagic Fever. Acta Virol. 1997, 41, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Emonet, S.; Retornaz, K.; Gonzalez, J.P.; De Lamballerie, X.; Charrel, R.N. Mouse-to-Human Transmission of Variant Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 472–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claro, I.M.; Ramundo, M.S.; Coletti, T.M.; da Silva, C.A.M.; Valenca, I.N.; Candido, D.S.; Sales, F.C.S.; Manuli, E.R.; de Jesus, J.G.; de Paula, A.; et al. Rapid Viral Metagenomics Using SMART-9N Amplification and Nanopore Sequencing. Wellcome Open Res. 2023, 6, 17170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilsker, M.; Moosa, Y.; Nooij, S.; Fonseca, V.; Ghysens, Y.; Dumon, K.; Pauwels, R.; Alcantara, L.C.; Vanden Eynden, E.; Vandamme, A.M.; et al. Genome Detective: An Automated System for Virus Identification from High-Throughput Sequencing Data. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 871–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, D.T.; Chernomor, O.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q.; Vinh, L.S. UFBoot2: Improving the Ultrafast Bootstrap Approximation. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; Von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast Model Selection for Accurate Phylogenetic Estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.K.F.; Ly-Trong, N.; Ren, H.; Baños, H.; Roger, A.J.; Susko, E.; Bielow, C.; Maio, N.D.; Goldman, N.; Hahn, M.W.; et al. IQ-TREE 3: Phylogenomic Inference Software Using Complex Evolutionary Models. Preprints (EcoEvoRxiv) 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozewicki, J.; Li, S.; Amada, K.M.; Standley, D.M.; Katoh, K. MAFFT-DASH: Integrated Protein Sequence and Structural Alignment. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W5–W10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; Van Der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. Mrbayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian Phylogenetic Inference and Model Choice across a Large Model Space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Suleski, M.; Sanderford, M.; Sharma, S.; Tamura, K. MEGA12: Molecular Evolutionary Genetic Analysis Version 12 for Adaptive and Green Computing. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2024, 41, msae263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albariño, C.G.; Palacios, G.; Khristova, M.L.; Erickson, B.R.; Carrol, S.A.; Comer, J.A.; Hui, J.; Briese, T.; St. George, K.; Ksiazek, T.G.; et al. High Diversity and Ancient Common Ancestry of Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- N′Dilimabaka, N.; Berthet, N.; Rougeron, V.; Mangombi, J.B.; Durand, P.; Maganga, G.D.; Bouchier, C.; Schneider, B.S.; Fair, J.; Renaud, F.; et al. Evidence of Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus (LCMV) in Domestic Mice in Gabon: Risk of Emergence of LCMV Encephalitis in Central Africa. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 1456–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gass, J.T.; Nofchissey, R.A.; Twohig, F.M.; Ye, C.; Goodfellow, S.M.; Mentore, K.; Burgos, M.; Negrete, O.; Whitmer, S.; Klena, J.D.; et al. Discovery of a Novel Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus Strain Associated with Severe Human Disease in Immunocompetent Patient, New Mexico. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2025, 14, 2542250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosio, A.; Saavedra, M.C.; Gamboa, G.S.; Maiza, A.S.; Mariani, M.A. Ecological and Epidemiological Features of Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus Activity in Argentina. Curr. Top. Virol. 2014, 12, 53–63. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, A.J.; Ribeiro, R.R.; Maia-Júnior, J.A.; Silva, V.C.; Borges, I.C.V.; Gonçalves, P.R.; Rangel, K.S.; Dias, H.V.R.; Godinho, A.B.F.R. Small Mammals in the Diet of Barn Owls (Tyto Furcata) in an Urban Area in Rio de Janeiro State, Brazil, with a New Record of the Dwarf Mouse Opossum (Cryptonanus). Braz. J. Biol. 2022, 82, e237675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucio, C.d.S.; Gentile, R.; Cardoso, T.d.S.; de Oliveira Santos, F.; Teixeira, B.R.; Maldonado Júnior, A.; D’Andrea, P.S. Composition and Structure of the Helminth Community of Rodents in Matrix Habitat Areas of the Atlantic Forest of Southeastern Brazil. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2021, 15, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheler-Costa, C.; Vettorazzi, C.A.; Pardini, R.; Verdade, L.M. The Distribution and Abundance of Small Mammals in Agroecosystems of Southeastern Brazil. Mammalia 2012, 76, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliapietra, V.; Rosà, R.; Hauffe, H.C.; Laakkonen, J.; Voutilainen, L.; Vapalahti, O.; Vaheri, A.; Henttonen, H.; Rizzoli, A. Spatial and Temporal Dynamics of Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus in Wild Rodents, Northern Italy. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duh, D.; Hasic, S.; Buzan, E. The Impact of Illegal Waste Sites on a Transmission of Zoonotic Viruses. Virol. J. 2017, 14, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehl, C.; Adeyemi, O.A.; Wylezich, C.; Höper, D.; Beer, M.; Triebenbacher, C.; Heckel, G.; Ulrich, R.G. Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus Lineage V in Wood Mice, Germany. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2024, 30, 399–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, S.; Huang, S.J.; Wang, Z.D.; Wei, F.; Feng, X.M.; Jiang, D.X.; Liu, Q. Isolation and Genomic Characterization of Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus in Ticks from Northeastern China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 1733–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvato, M.; Borrow, P.; Shimomaye, E.; Oldstone, M.B. Molecular Basis of Viral Persistence: A Single Amino Acid Change in the Glycoprotein of Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus Is Associated with Suppression of the Antiviral Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte Response and Establishment of Persistence. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 1863–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, B.M.; Emonet, S.F.; Welch, M.J.; Lee, A.M.; Campbell, K.P.; De La Torre, J.C.; Oldstone, M.B. Point Mutation in the Glycoprotein of Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus Is Necessary for Receptor Binding, Dendritic Cell Infection, and Long-Term Persistence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevilla, N.; Kunz, S.; McGavern, D.; Oldstone, M.B.A. Infection of Dendritic Cells by Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2003, 276, 125–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz-Riaño, E.; Yee, B.; Cheng, H.; Carlos De La Torre, J.; Martínez-Sobrido, L. The C-Terminal Region of Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus Nucleoprotein Contains Distinct and Segregable Functional Domains Involved in NP-Z Interaction and Counteraction of the Type I Interferon Response. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 13038–13048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Sobrido, L.; Emonet, S.; Giannakas, P.; Cubitt, B.; García-Sastre, A.; de la Torre, J.C. Identification of Amino Acid Residues Critical for the Anti-Interferon Activity of the Nucleoprotein of the Prototypic Arenavirus Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 11330–11340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, K.M.; Kimberlin, C.R.; Zandonatti, M.A.; MacRae, I.J.; Saphire, E.O. Structure of the Lassa Virus Nucleoprotein Reveals a dsRNA-Specific 3′ to 5′ Exonuclease Activity Essential for Immune Suppression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2396–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camp, J.V.; Nowotny, N.; Aberle, S.W.; Redlberger-Fritz, M. Retrospective Screening for Zoonotic Viruses in Encephalitis Cases in Austria, 2019–2023, Reveals Infection with Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus but Not with Rustrela Virus or Tahyna Virus. Viruses 2025, 17, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knust, B.; Ströher, U.; Edison, L.; Albariño, C.G.; Lovejoy, J.; Armeanu, E.; House, J.; Cory, D.; Horton, C.; Fowler, K.L.; et al. Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus in Employees and Mice at Multipremises Feeder-Rodent Operation, United States, 2012. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobec, M.; Dzelalija, B.; Punda-Polic, V.; Zoric, I. High Prevalence of Antibodies to Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus in a Murine Typhus Endemic Region in Croatia. J. Med. Virol. 2006, 78, 1643–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
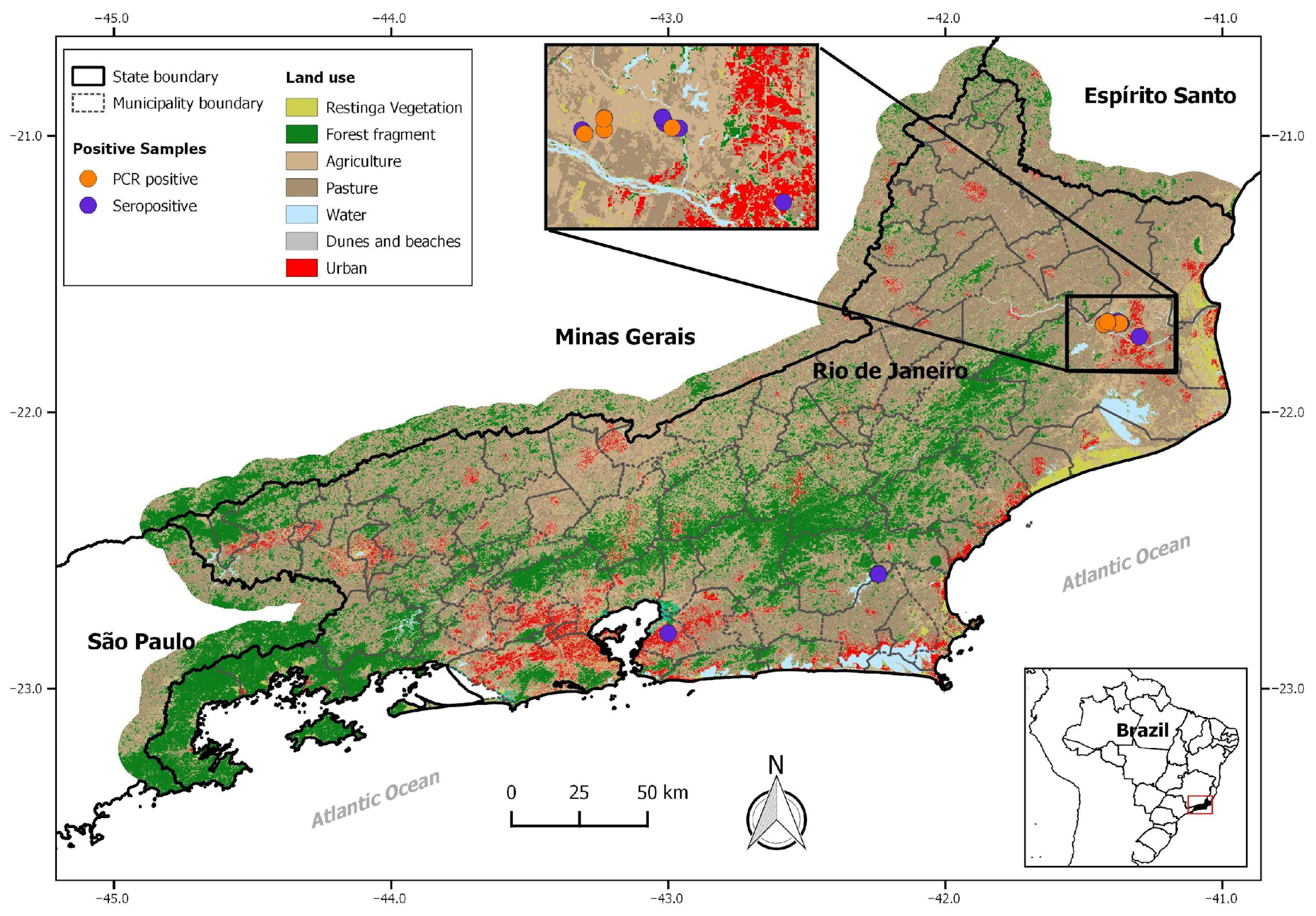
| Municipalities and Rodent Species | LCMV Antibodies | RT-Nested PCR | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Positive/N Total (%) | Positive/N Total (%) | ||
| Rio de Janeiro | |||
| R. norvegicus | 0/4 | NA | |
| Campos dos Goytacazes | |||
| M. musculus | 38/68 (55) | 14/64 (21) | |
| R. norvegicus | 1/2 (50) | 0/1 | |
| R. rattus | 2/5 (40) | 0/4 | |
| Silva Jardim | |||
| M. musculus | 7/37 (19) | 0/2 | |
| São Gonçalo | |||
| M. musculus | 0/1 | NA | |
| R. norvegicus | 1/93 (1) | NA | |
| Valença | |||
| M. musculus | 0/17 | NA | |
| Casimiro de Abreu | |||
| M. musculus | 0/8 | 0/6 | |
| R. rattus | 0/1 | 0/1 | |
| Total | 49/236 (20) | 14/78 (18) | |
| Strain_Country_Lineage | Accession Number | (%) Nucleotides and Amino Acids Similarities | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LBCE20151 | LBCE20173 | ||||||||
| NT | AA | NT | AA | ||||||
| GPC | NP | GPC | NP | GPC | NP | GPC | NP | ||
| COMOU_GUF_I | KT731538 | 86 | 85 | 95 | 96 | 83 | 84 | 93 | 95 |
| MAKOKOU_GABN_I | KM523323 | 85 | 86 | 93 | 97 | 84 | 86 | 93 | 96 |
| IN-2012_USA_I | KF732824 | 85 | 86 | 95 | 97 | 84 | 86 | 94 | 97 |
| 810885_USA_I | FJ607032 | 84 | 86 | 95 | 97 | 84 | 86 | 94 | 97 |
| DOUGLAS_4707_USA_I | FJ607035 | 85 | 87 | 95 | 98 | 85 | 86 | 94 | 97 |
| UBC_DOCILE_USA_I | EU480452 | 85 | 85 | 94 | 97 | 85 | 86 | 93 | 95 |
| UBC_AGGRESSIVE_USA_I | EU480450 | 85 | 85 | 94 | 97 | 85 | 86 | 93 | 96 |
| ARMSTRONG_53B_USA_I | AY847350 | 85 | 86 | 95 | 97 | 84 | 84 | 95 | 95 |
| WE_UBC_57135_USA_I | FJ607036 | 85 | 85 | 94 | 97 | 85 | 86 | 93 | 96 |
| JX31_CHN_I | MG554176 | 84 | 87 | 93 | 97 | 84 | 85 | 93 | 97 |
| CLONE13_USA_I | DQ361065 | 85 | 86 | 95 | 97 | 84 | 84 | 96 | 95 |
| TRAUB_USA_I | DQ868487 | 85 | 86 | 95 | 97 | 85 | 86 | 94 | 97 |
| 2_BRC_II | AB627953 | 78 | 81 | 90 | 93 | 78 | 80 | 89 | 93 |
| CABN_ESP_IV | FJ895882 | 73 | 80 | 80 | 91 | 73 | 78 | 80 | 90 |
| KS20-3122_GER_V | OR135710 | 75 | 79 | 85 | 93 | 75 | 78 | 84 | 92 |
| 810935_LYLES_USA_III | FJ607029 | 78 | 80 | 89 | 92 | 78 | 79 | 89 | 92 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cavalcanti, G.R.; Fernandes, J.; Santos, F.d.O.; Teixeira, B.R.; Guterres, A.; Brignone, J.; Levis, S.; Lucio, C.d.S.; Costa-Neto, S.F.d.; Fonseca, V.; et al. Detection of Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus in House Mouse (Mus musculus) in Brazil. Viruses 2025, 17, 1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17121544
Cavalcanti GR, Fernandes J, Santos FdO, Teixeira BR, Guterres A, Brignone J, Levis S, Lucio CdS, Costa-Neto SFd, Fonseca V, et al. Detection of Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus in House Mouse (Mus musculus) in Brazil. Viruses. 2025; 17(12):1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17121544
Chicago/Turabian StyleCavalcanti, Gabriel Rosa, Jorlan Fernandes, Fernando de Oliveira Santos, Bernardo Rodrigues Teixeira, Alexandro Guterres, Julia Brignone, Silvana Levis, Camila dos Santos Lucio, Sócrates Fraga da Costa-Neto, Vagner Fonseca, and et al. 2025. "Detection of Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus in House Mouse (Mus musculus) in Brazil" Viruses 17, no. 12: 1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17121544
APA StyleCavalcanti, G. R., Fernandes, J., Santos, F. d. O., Teixeira, B. R., Guterres, A., Brignone, J., Levis, S., Lucio, C. d. S., Costa-Neto, S. F. d., Fonseca, V., Giovanetti, M., Alcantara, L. C. J., D’Andrea, P. S., de Lemos, E. R. S., & Oliveira, R. C. d. (2025). Detection of Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus in House Mouse (Mus musculus) in Brazil. Viruses, 17(12), 1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17121544








