C-Terminal Binding Protein: Regulator between Viral Infection and Tumorigenesis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
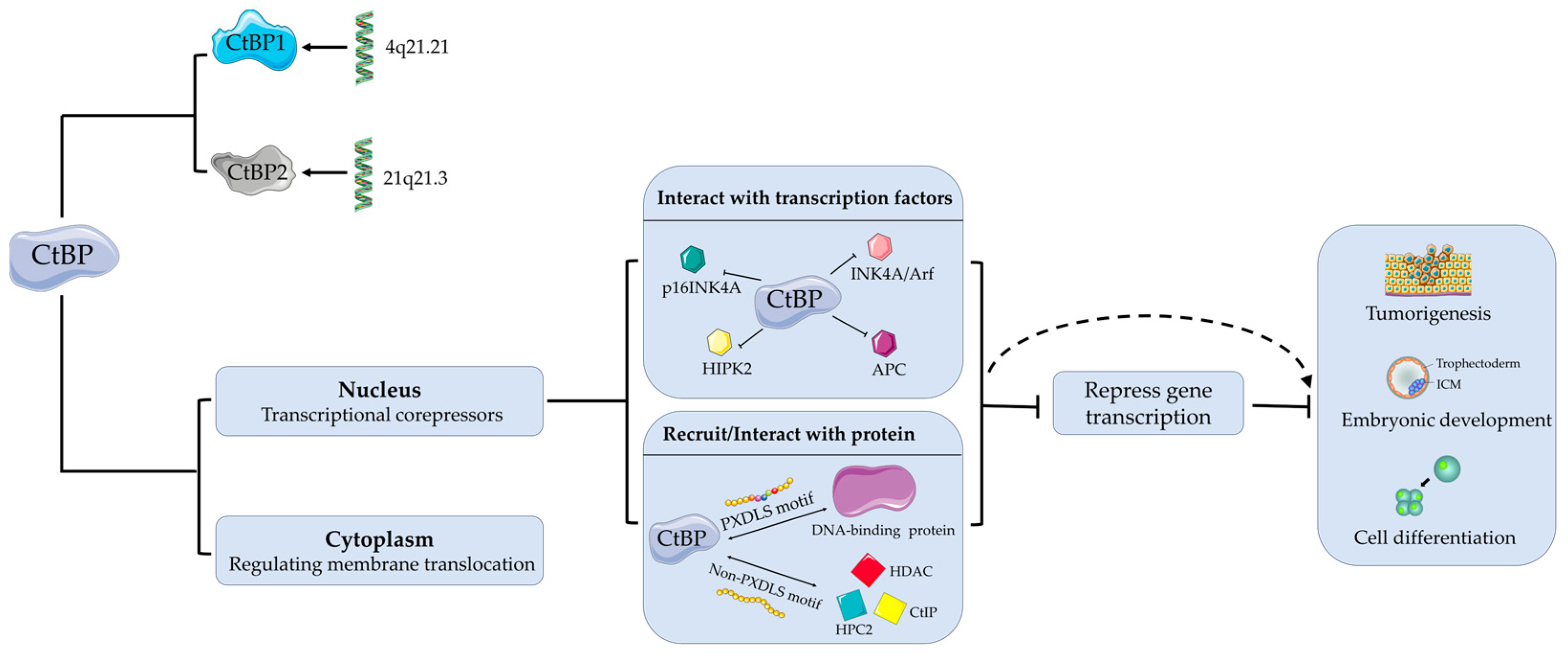
2. Overview of CtBP
2.1. CtBP1
2.2. CtBP2
3. CtBP and Tumors
| Name of Tumor | Role of CtBP |
|---|---|
| Hepatocellular carcinoma | Involving in constituting a transcriptional repression complex to repress E-cadherin [57] |
| Abdominal aortic aneurysm | Modulating inflammatory responses and disrupting the matrix [58] |
| Prostate cancer | Regulating cell proliferation through the c-Myc signaling pathway [59] |
| Gastric cancer | The expression of CtBP2 is inversely correlated with the disease-free progression of gastric cancer [60] |
| Breast cancer | Inhibiting intracellular cholesterol abundance, thus increasing EMT and cell migration [44] |
4. CtBP and Viruses
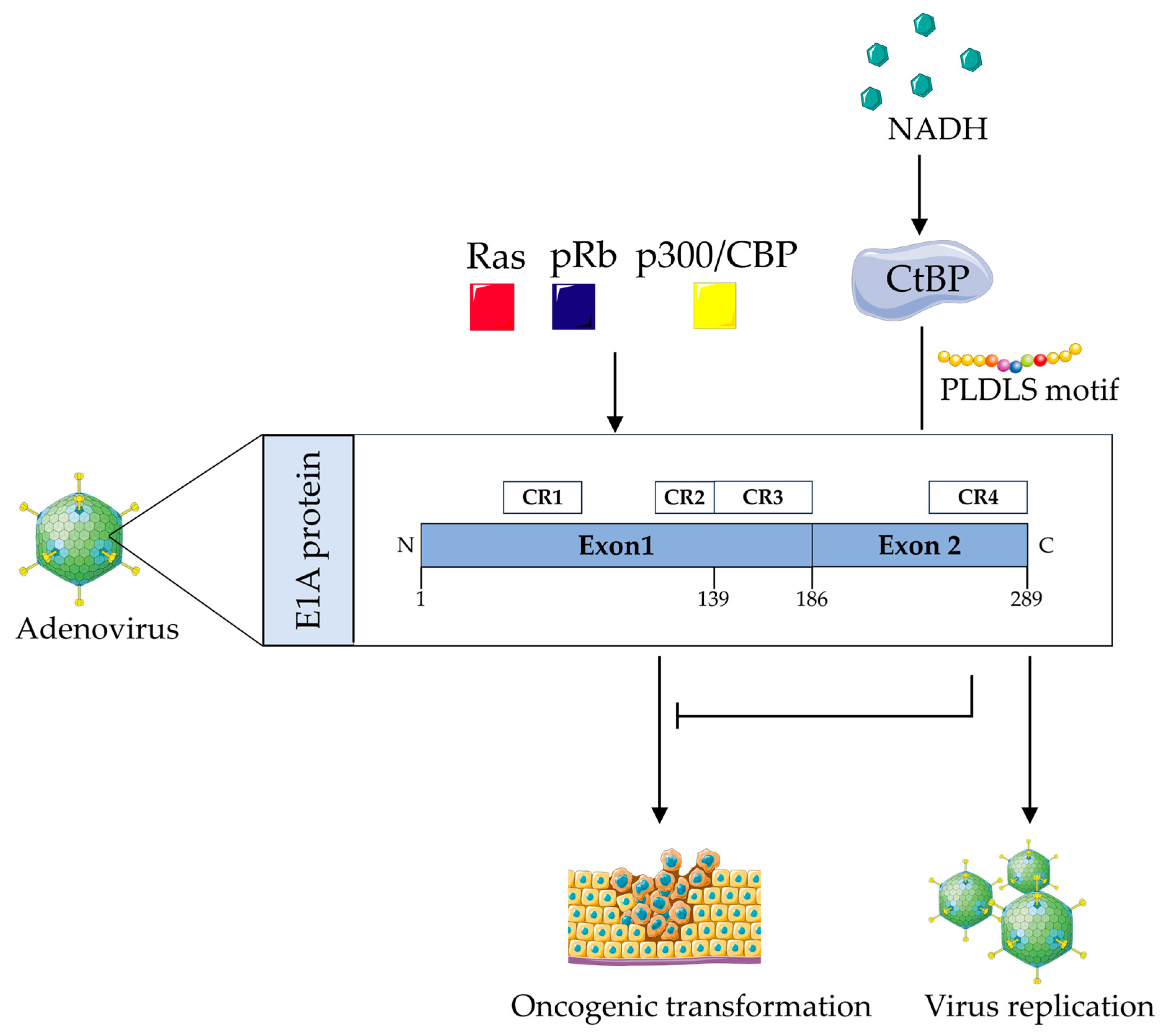
4.1. Adenovirus
4.2. Epstein–Barr Virus
4.3. Hepatitis B Virus
4.4. Human Immunodeficiency Virus
4.5. Marek’s Disease Virus
4.6. Zaire Ebola Virus
5. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boyd, J.M.; Subramanian, T.; Schaeper, U.; La Regina, M.; Bayley, S.; Chinnadurai, G. A region in the C-terminus of adenovirus 2/5 E1a protein is required for association with a cellular phosphoprotein and important for the negative modulation of T24-ras mediated transformation, tumorigenesis and metastasis. EMBO J. 1993, 12, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinnadurai, G. CtBP family proteins: More than transcriptional corepressors. Bioessays 2003, 25, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Birts, C.N.; Darley, M.; Parker, R.; Mirnezami, A.H.; West, J.; Cutress, R.I.; Beers, S.A.; Rose-Zerilli, M.J.J.; Blaydes, J.P. Stem cell-like breast cancer cells with acquired resistance to metformin are sensitive to inhibitors of NADH-dependent CtBP dimerization. Carcinogenesis 2019, 40, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, A.T.; Cororaton, A.D.; Idowu, M.O.; Damle, P.K.; Szomju, B.; Ellis, K.C.; Patel, B.B.; Grossman, S.R. An intestinal stem cell niche in Apc mutated neoplasia targetable by CtBP inhibition. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 32408–32418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raicu, A.M.; Bird, K.M.; Arnosti, D.N. Tête-à-tête with CtBP dimers. Structure 2021, 29, 307–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filograna, A.; De Tito, S.; Monte, M.L.; Oliva, R.; Bruzzese, F.; Roca, M.S.; Zannetti, A.; Greco, A.; Spano, D.; Ayala, I.; et al. Identification and characterization of a new potent inhibitor targeting CtBP1/BARS in melanoma cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 43, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.J.; Kuppuswamy, M.; Vijayalingam, S.; Chinnadurai, G. Interaction of ZEB and histone deacetylase with the PLDLS-binding cleft region of monomeric C-terminal binding protein 2. BMC Mol. Biol. 2009, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagan, J.K.; Arnold, J.; Hanchard, K.J.; Kumar, R.; Bruno, T.; Jones, M.J.; Richard, D.J.; Forrest, A.; Spurdle, A.; Verdin, E.; et al. A novel corepressor, BCoR-L1, represses transcription through an interaction with CtBP. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 15248–15257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.; Crossley, M. The CtBP family: Enigmatic and enzymatic transcriptional co-repressors. Bioessays 2001, 23, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, B.H.; Pearson, R.C.; Crossley, M. C-terminal binding protein: A metabolic sensor implicated in regulating adipogenesis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2011, 43, 693–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mroz, E.A.; Baird, A.H.; Michaud, W.A.; Rocco, J.W. COOH-terminal binding protein regulates expression of the p16INK4A tumor suppressor and senescence in primary human cells. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 6049–6053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Sun, Y.; Li, H.; Shao, Y.; Zhao, D.; Yu, W.; Fu, J. C-terminal binding protein-2 promotes cell proliferation and migration in breast cancer via suppression of p16INK4A. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 26154–26168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumner, E.T.; Chawla, A.T.; Cororaton, A.D.; Koblinski, J.E.; Kovi, R.C.; Love, I.M.; Szomju, B.B.; Korwar, S.; Ellis, K.C.; Grossman, S.R. Transforming activity and therapeutic targeting of C-terminal-binding protein 2 in Apc-mutated neoplasia. Oncogene 2017, 36, 4810–4816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, T.G.; Glas, C.; Bitomsky, N. HIPK2: A tumour suppressor that controls DNA damage-induced cell fate and cytokinesis. Bioessays 2013, 35, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Guo, G.; Huang, J.; Kloeber, J.A.; Zhao, F.; Deng, M.; Tu, X.; Kim, W.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, C.; et al. USP52 regulates DNA end resection and chemosensitivity through removing inhibitory ubiquitination from CtIP. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichikawa, K.; Kubota, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Weng, J.S.; Tomida, T.; Saito, H.; Takekawa, M. MCRIP1, an ERK substrate, mediates ERK-induced gene silencing during epithelial-mesenchymal transition by regulating the co-repressor CtBP. Mol. Cell 2015, 58, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sewalt, R.G.; Gunster, M.J.; van der Vlag, J.; Satijn, D.P.; Otte, A.P. C-Terminal binding protein is a transcriptional repressor that interacts with a specific class of vertebrate Polycomb proteins. Mol. Cell Biol. 1999, 19, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergman, L.M.; Birts, C.N.; Darley, M.; Gabrielli, B.; Blaydes, J.P. CtBPs promote cell survival through the maintenance of mitotic fidelity. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 29, 4539–4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Yu, S.; Lasell, T.K.; Jadhav, A.P.; Macia, E.; Chardin, P.; Melancon, P.; Roth, M.; Mitchison, T.; Kirchhausen, T. Exo1: A new chemical inhibitor of the exocytic pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 6469–6474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grooteclaes, M.; Deveraux, Q.; Hildebrand, J.; Zhang, Q.; Goodman, R.H.; Frisch, S.M. C-terminal-binding protein corepresses epithelial and proapoptotic gene expression programs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 4568–4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraiva, C.; Lopes-Nunes, J.; Esteves, M.; Santos, T.; Vale, A.; Cristóvão, A.C.; Ferreira, R.; Bernardino, L. CtBP Neuroprotective Role in Toxin-Based Parkinson’s Disease Models: From Expression Pattern to Dopaminergic Survival. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 60, 4246–4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dcona, M.M.; Damle, P.K.; Zarate-Perez, F.; Morris, B.L.; Nawaz, Z.; Dennis, M.J.; Deng, X.; Korwar, S.; Singh, S.J.; Ellis, K.C.; et al. Active-Site Tryptophan, the Target of Antineoplastic C-Terminal Binding Protein Inhibitors, Mediates Inhibitor Disruption of CtBP Oligomerization and Transcription Coregulatory Activities. Mol. Pharmacol. 2019, 96, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korwar, S.; Morris, B.L.; Parikh, H.I.; Coover, R.A.; Doughty, T.W.; Love, I.M.; Hilbert, B.J.; Royer, W.E., Jr.; Kellogg, G.E.; Grossman, S.R.; et al. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of substrate-competitive inhibitors of C-terminal Binding Protein (CtBP). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 2707–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilbert, B.J.; Morris, B.L.; Ellis, K.C.; Paulsen, J.L.; Schiffer, C.A.; Grossman, S.R.; Royer, W.E., Jr. Structure-guided design of a high affinity inhibitor to human CtBP. ACS Chem. Biol. 2015, 10, 1118–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsanis, N.; Fisher, E.M. A novel C-terminal binding protein (CTBP2) is closely related to CTBP1, an adenovirus E1A-binding protein, and maps to human chromosome 21q21.3. Genomics 1998, 47, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, L.; Atchison, M.L. YY1 DNA binding and PcG recruitment requires CtBP. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 2596–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnadurai, G. Transcriptional regulation by C-terminal binding proteins. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 1593–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankiewicz, T.R.; Gray, J.J.; Winter, A.N.; Linseman, D.A. C-terminal binding proteins: Central players in development and disease. Biomol. Concepts 2014, 5, 489–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merrill, J.C.; Kagey, M.H.; Melhuish, T.A.; Powers, S.E.; Zerlanko, B.J.; Wotton, D. Inhibition of CtBP1 activity by Akt-mediated phosphorylation. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 398, 657–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.H.; Park, Y.J.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.H. Transcriptional corepressor activity of CtBP1 is regulated by ISG15 modification. Anim. Cells Syst. 2024, 28, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlandsen, H.; Jecrois, A.M.; Nichols, J.C.; Cole, J.L.; Royer, W.E., Jr. NADH/NAD(+) binding and linked tetrameric assembly of the oncogenic transcription factors CtBP1 and CtBP2. FEBS Lett. 2022, 596, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blevins, M.A.; Huang, M.; Zhao, R. The Role of CtBP1 in Oncogenic Processes and Its Potential as a Therapeutic Target. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Guo, W.; Li, G.; Li, S.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Niu, B.; Song, M.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; et al. Protocatechuic Aldehyde Represses Proliferation and Migration of Breast Cancer Cells through Targeting C-terminal Binding Protein 1. J. Breast Cancer 2020, 23, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Li, H.; Yin, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, J.; Guo, D.; Shi, Z. C-Terminal Binding Protein 1 Modulates Cellular Redox via Feedback Regulation of MPC1 and MPC2 in Melanoma Cells. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 7614–7624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Deng, H.; Bi, F.; Liu, J.; Bemis, L.T.; Norris, D.; Wang, X.J.; Zhang, Q. MicroRNA-137 targets carboxyl-terminal binding protein 1 in melanoma cell lines. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2011, 7, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamada, N.; Matsuki, T.; Iwamoto, I.; Nishijo, T.; Noda, M.; Tabata, H.; Nakayama, A.; Nagata, K.I. Expression analyses of C-terminal-binding protein 1 (CtBP1) during mouse brain development. Dev. Neurosci. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.J.; Subramanian, T.; Zhou, Y.; Chinnadurai, G. Acetylation by p300 regulates nuclear localization and function of the transcriptional corepressor CtBP2. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 4183–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, J.; Yang, L.; Guan, C.; Ni, R.; Wang, Y.; Ji, L.; Tian, Y. Interaction with CCNH/CDK7 facilitates CtBP2 promoting esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) metastasis via upregulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) progression. Tumour. Biol. 2015, 36, 6701–6714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, J.C.; Schiffer, C.A.; Royer, W.E., Jr. NAD(H) phosphates mediate tetramer assembly of human C-terminal binding protein (CtBP). J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straza, M.W.; Paliwal, S.; Kovi, R.C.; Rajeshkumar, B.; Trenh, P.; Parker, D.; Whalen, G.F.; Lyle, S.; Schiffer, C.A.; Grossman, S.R. Therapeutic targeting of C-terminal binding protein in human cancer. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 3740–3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhou, F.; Cao, X.; Zhao, P.; Huang, X.; Xie, W.; Zhang, G.; Chen, X. C-terminal binding protein 2 promotes high-glucose-triggered cell proliferation, angiogenesis and cellular adhesion of human retinal endothelial cell line. Int. Ophthalmol. 2022, 42, 2975–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, Q. Knockdown of receptor interacting protein 140 (RIP140) alleviated lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation, apoptosis and permeability in pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells by regulating C-terminal binding protein 2 (CTBP2). Bioengineered 2022, 13, 3981–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekiya, M.; Kainoh, K.; Saito, K.; Yamazaki, D.; Tsuyuzaki, T.; Chen, W.; Kobari, Y.; Nakata, A.; Babe, H.; Shimano, H. C-Terminal Binding Protein 2 Emerges as a Critical Player Linking Metabolic Imbalance to the Pathogenesis of Obesity. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2024, 31, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Hao, D.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Meng, Y.; Li, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, H.; Gardner, K.; et al. CtBP promotes metastasis of breast cancer through repressing cholesterol and activating TGF-β signaling. Oncogene 2019, 38, 2076–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niles, N.R.; Bitensky, L.; Chayen, J.; Cunningham, G.J.; Braimbridge, M.V. The value of histochemistry in the analysis of myocardial dysfunction. Lancet 1964, 1, 963–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susin, S.A.; Lorenzo, H.K.; Zamzami, N.; Marzo, I.; Snow, B.E.; Brothers, G.M.; Mangion, J.; Jacotot, E.; Costantini, P.; Loeffler, M.; et al. Molecular characterization of mitochondrial apoptosis-inducing factor. Nature 1999, 397, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izzotti, A.; Bagnis, A.; Saccà, S.C. The role of oxidative stress in glaucoma. Mutat. Res. 2006, 612, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.M.; Lerner, S.F.; Brunzini, R.; Evelson, P.A.; Llesuy, S.F. Oxidative stress markers in aqueous humor of glaucoma patients. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2004, 137, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballinger, S.W.; Van Houten, B.; Jin, G.F.; Conklin, C.A.; Godley, B.F. Hydrogen peroxide causes significant mitochondrial DNA damage in human RPE cells. Exp. Eye Res. 1999, 68, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dcona, M.M.; Morris, B.L.; Ellis, K.C.; Grossman, S.R. CtBP—An emerging oncogene and novel small molecule drug target: Advances in the understanding of its oncogenic action and identification of therapeutic inhibitors. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2017, 18, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.W.; Paliwal, S.; Draheim, K.; Grossman, S.R.; Lewis, B.C. p19Arf inhibits the invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by binding to C-terminal binding protein. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Ojo, D.; Wei, F.; Wong, N.; Gu, Y.; Tang, D. A Novel Aspect of Tumorigenesis-BMI1 Functions in Regulating DNA Damage Response. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 3396–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovi, R.C.; Paliwal, S.; Pande, S.; Grossman, S.R. An ARF/CtBP2 complex regulates BH3-only gene expression and p53-independent apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2010, 17, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Hao, D.; Li, P.; Su, M.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, T.; Tai, L.; Lu, J.; et al. Metabolic modulation of CtBP dimeric status impacts the repression of DNA damage repair genes and the platinum sensitivity of ovarian cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 19, 2081–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, J.; Baranwal, S.; Love, I.M.; Patel, N.J.; Grossman, S.R.; Patel, B.B. Inhibition of C-terminal binding protein attenuates transcription factor 4 signaling to selectively target colon cancer stem cells. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 3506–3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Ding, X.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Zou, R.; Zhao, M.; Chang, H.; Jiang, C.; La, X.; et al. CtBP modulates Snail-mediated tumor invasion in Drosophila. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Huang, C.X.; Zhang, J.; Inoue, A.; Zeng, S.E.; Xiao, S.J. CtBP1 is involved in epithelial-mesenchymal transition and is a potential therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 809–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Ge, L.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, J.; Liu, L.; Song, Y. CtBP proteins transactivate matrix metalloproteinases and proinflammatory cytokines to mediate the pathogenesis of abdominal aortic aneurysm. Exp. Cell Res. 2022, 421, 113386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Gao, C.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z. CtBP2 could promote prostate cancer cell proliferation through c-Myc signaling. Gene 2014, 546, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, G.; Yang, T.; Liu, S.; Luo, Y.L.; Liu, Y.; Zhong, Q. Epigenetic Regulation of MAP3K8 in EBV-Associated Gastric Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forner, A.; Reig, M.; Bruix, J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 2018, 391, 1301–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Song, T.; Dou, C.; Jia, Y.; Liu, Q. CtBP2 is an independent prognostic marker that promotes GLI1 induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 3752–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakalihasan, N.; Limet, R.; Defawe, O.D. Abdominal aortic aneurysm. Lancet 2005, 365, 1577–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blevins, M.A.; Kouznetsova, J.; Krueger, A.B.; King, R.; Griner, L.M.; Hu, X.; Southall, N.; Marugan, J.J.; Zhang, Q.; Ferrer, M.; et al. Small Molecule, NSC95397, Inhibits the CtBP1-Protein Partner Interaction and CtBP1-Mediated Transcriptional Repression. J. Biomol. Screen 2015, 20, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Asangani, I.A.; Chakravarthi, B.V.; Ateeq, B.; Lonigro, R.J.; Cao, Q.; Mani, R.S.; Camacho, D.F.; McGregor, N.; Schumann, T.E.; et al. Role of transcriptional corepressor CtBP1 in prostate cancer progression. Neoplasia 2012, 14, 905–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Li, S.; Qiao, B.; Yang, K.; Liu, R.; Ma, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, Y. CtBP2 overexpression is associated with tumorigenesis and poor clinical outcome of prostate cancer. Arch. Med. Sci. 2015, 11, 1318–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Lu, C.; Wang, Z.; Feng, G.; Du, E.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Qiao, B.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z. Antimony enhances c-Myc stability in prostate cancer via activating CtBP2-ROCK1 signaling pathway. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 164, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyth, E.C.; Nilsson, M.; Grabsch, H.I.; van Grieken, N.C.; Lordick, F. Gastric cancer. Lancet 2020, 396, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhao, G.; Li, H.; Guo, Q.; Zhu, S.; Li, P.; Min, L.; Zhang, S. RBBP8/CtIP suppresses P21 expression by interacting with CtBP and BRCA1 in gastric cancer. Oncogene 2020, 39, 1273–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhao, H. CTBP1 strengthens the cisplatin resistance of gastric cancer cells by upregulating RAD51 expression. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 22, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbeck, N.; Gnant, M. Breast cancer. Lancet 2017, 389, 1134–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, K.G.; Verger, A.; Kwok, A.; Lee, S.H.; Perdomo, J.; Nardini, M.; Bolognesi, M.; Crossley, M. Role of the C-terminal binding protein PXDLS motif binding cleft in protein interactions and transcriptional repression. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 26, 8202–8213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radkov, S.A.; Touitou, R.; Brehm, A.; Rowe, M.; West, M.; Kouzarides, T.; Allday, M.J. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 3C interacts with histone deacetylase to repress transcription. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 5688–5697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemke, N.R.; Berk, A.J. The Adenovirus E1A C Terminus Suppresses a Delayed Antiviral Response and Modulates RAS Signaling. Cell Host. Microbe. 2017, 22, 789–800.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Chen, M.; Pettersson, U. A new look at adenovirus splicing. Virology 2014, 456–457, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.J.; Subramanian, T.; Chinnadurai, G. Changes in C-terminal binding protein 2 (CtBP2) corepressor complex induced by E1A and modulation of E1A transcriptional activity by CtBP2. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 36613–36623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avvakumov, N.; Kajon, A.E.; Hoeben, R.C.; Mymryk, J.S. Comprehensive sequence analysis of the E1A proteins of human and simian adenoviruses. Virology 2004, 329, 477–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.J.; Subramanian, T.; Chinnadurai, G. Inhibition of transcriptional activation and cell proliferation activities of adenovirus E1A by the unique N-terminal domain of CtBP2. Oncogene 2008, 27, 5214–5222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeper, U.; Boyd, J.M.; Verma, S.; Uhlmann, E.; Subramanian, T.; Chinnadurai, G. Molecular cloning and characterization of a cellular phosphoprotein that interacts with a conserved C-terminal domain of adenovirus E1A involved in negative modulation of oncogenic transformation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 10467–10471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeper, U.; Subramanian, T.; Lim, L.; Boyd, J.M.; Chinnadurai, G. Interaction between a cellular protein that binds to the C-terminal region of adenovirus E1A (CtBP) and a novel cellular protein is disrupted by E1A through a conserved PLDLS motif. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 8549–8552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppuswamy, M.N.; Chinnadurai, G. Relationship between the transforming and transcriptional regulatory functions of adenovirus 2 E1a oncogene. Virology 1987, 159, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, C.; Zhao, H.; Bajak, E.; Granberg, F.; Pettersson, U.; Svensson, C. Impact of the interaction between adenovirus E1A and CtBP on host cell gene expression. Virus Res. 2005, 113, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundqvist, A.; Bajak, E.; Kurup, S.D.; Sollerbrant, K.; Svensson, C. Functional knockout of the corepressor CtBP by the second exon of adenovirus E1a relieves repression of transcription. Exp. Cell Res. 2001, 268, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.J.; Subramanian, T.; Vijayalingam, S.; Chinnadurai, G. PLDLS-dependent interaction of E1A with CtBP: Regulation of CtBP nuclear localization and transcriptional functions. Oncogene 2007, 26, 7544–7551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Sawada, J.; Sui, G.; Affar, E.B.; Whetstine, J.R.; Lan, F.; Ogawa, H.; Luke, M.P.; Nakatani, Y.; Shi, Y. Coordinated histone modifications mediated by a CtBP co-repressor complex. Nature 2003, 422, 735–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, P.; Zhao, L.J.; Chinnadurai, G. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide stimulates oligomerization, interaction with adenovirus E1A and an intrinsic dehydrogenase activity of CtBP. FEBS Lett. 2003, 537, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickherber, M.L.; Garnett-Benson, C. NAD-linked mechanisms of gene de-repression and a novel role for CtBP in persistent adenovirus infection of lymphocytes. Virol. J. 2019, 16, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, A.; Singh, R. CtBP: A global regulator of balancing acts and homeostases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2023, 1878, 188886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, T.; Zhao, L.J.; Chinnadurai, G. Interaction of CtBP with adenovirus E1A suppresses immortalization of primary epithelial cells and enhances virus replication during productive infection. Virology 2013, 443, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damania, B.; Kenney, S.C.; Raab-Traub, N. Epstein-Barr virus: Biology and clinical disease. Cell 2022, 185, 3652–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levhar, N.; Ungar, B.; Kopylov, U.; Fudim, E.; Yavzori, M.; Picard, O.; Amariglio, N.; Chowers, Y.; Shemer-Avni, Y.; Mao, R.; et al. Propagation of EBV-driven Lymphomatous Transformation of Peripheral Blood B Cells by Immunomodulators and Biologics Used in the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel. Dis. 2020, 26, 1330–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, M.; Hayes, M.; McChesney, K.; Johannsen, E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 3C (EBNA3C) interacts with the metabolism sensing C-terminal binding protein (CtBP) repressor to upregulate host genes. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Willox, B.; Zhou, H.; Holthaus, A.M.; Wang, A.; Shi, T.T.; Maruo, S.; Kharchenko, P.V.; Johannsen, E.C.; Kieff, E.; et al. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 3C binds to BATF/IRF4 or SPI1/IRF4 composite sites and recruits Sin3A to repress CDKN2A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fjeld, C.C.; Birdsong, W.T.; Goodman, R.H. Differential binding of NAD+ and NADH allows the transcriptional corepressor carboxyl-terminal binding protein to serve as a metabolic sensor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 9202–9207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touitou, R.; Hickabottom, M.; Parker, G.; Crook, T.; Allday, M.J. Physical and functional interactions between the corepressor CtBP and the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen EBNA3C. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 7749–7755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newbold, J.E.; Xin, H.; Tencza, M.; Sherman, G.; Dean, J.; Bowden, S.; Locarnini, S. The covalently closed duplex form of the hepadnavirus genome exists in situ as a heterogeneous population of viral minichromosomes. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 3350–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Xie, Z.; Cai, D.; Yu, X.; Zhang, H.; Kim, E.S.; Zhou, B.; Hou, J.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Q.; et al. Biogenesis and molecular characteristics of serum hepatitis B virus RNA. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Kim, W.; Kloeber, J.A.; Lou, Z. DNA end resection and its role in DNA replication and DSB repair choice in mammalian cells. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 1705–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, M.Y.; He, X.X.; Chen, M.; Song, Q.L.; Jiang, X.; Xie, Q.H.; Lin, J.S. [The effect of hepatitis B virus X protein on the expression of CtIP in HepG2 Cells]. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi 2011, 19, 577–581. [Google Scholar]
- Glass, J.D.; Johnson, R.T. Human immunodeficiency virus and the brain. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1996, 19, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilliers, K.; Muller, C.J.F. Effect of human immunodeficiency virus on the brain: A review. Anat. Rec. 2021, 304, 1389–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, V.; Bertrand, L.; Luethen, M.; Dabrowski, S.; Lombardi, J.; Morgan, L.; Sharova, N.; Stevenson, M.; Blasig, I.E.; Toborek, M. Occludin controls HIV transcription in brain pericytes via regulation of SIRT-1 activation. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 1234–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Lupiani, B.; Izumiya, Y.; Reddy, S.M. Marek’s disease virus Meq oncoprotein interacts with chicken HDAC 1 and 2 and mediates their degradation via proteasome dependent pathway. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.C.; Baigent, S.J.; Smith, L.P.; Chattoo, J.P.; Petherbridge, L.J.; Hawes, P.; Allday, M.J.; Nair, V. Interaction of MEQ protein and C-terminal-binding protein is critical for induction of lymphomas by Marek’s disease virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 1687–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Kurian, D.; Xu, H.; Petherbridge, L.; Smith, L.P.; Hunt, L.; Nair, V. Interaction of Marek’s disease virus oncoprotein Meq with heat-shock protein 70 in lymphoid tumour cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90 Pt 9, 2201–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardini, M.; Spanò, S.; Cericola, C.; Pesce, A.; Massaro, A.; Millo, E.; Luini, A.; Corda, D.; Bolognesi, M. CtBP/BARS: A dual-function protein involved in transcription co-repression and Golgi membrane fission. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 3122–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, M.F.; Kolokoltsov, A.A.; Albrecht, T.; Davey, R.A. Cellular entry of ebola virus involves uptake by a macropinocytosis-like mechanism and subsequent trafficking through early and late endosomes. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, M.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, S. C-Terminal Binding Protein: Regulator between Viral Infection and Tumorigenesis. Viruses 2024, 16, 988. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16060988
Huang M, Li Y, Li Y, Liu S. C-Terminal Binding Protein: Regulator between Viral Infection and Tumorigenesis. Viruses. 2024; 16(6):988. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16060988
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Meihui, Yucong Li, Yuxiao Li, and Shuiping Liu. 2024. "C-Terminal Binding Protein: Regulator between Viral Infection and Tumorigenesis" Viruses 16, no. 6: 988. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16060988
APA StyleHuang, M., Li, Y., Li, Y., & Liu, S. (2024). C-Terminal Binding Protein: Regulator between Viral Infection and Tumorigenesis. Viruses, 16(6), 988. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16060988





