Molecular Epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2 in Tunisia (North Africa) through Several Successive Waves of COVID-19
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Whole-Genome Sequencing
2.3. Genome Assembly
2.4. Variant Detection by Partial Sequencing of the S Gene
2.5. Variant Detection by Real-Time RT-PCR
2.6. Clade and Lineage Assignment
2.7. Phylogenetic Analysis
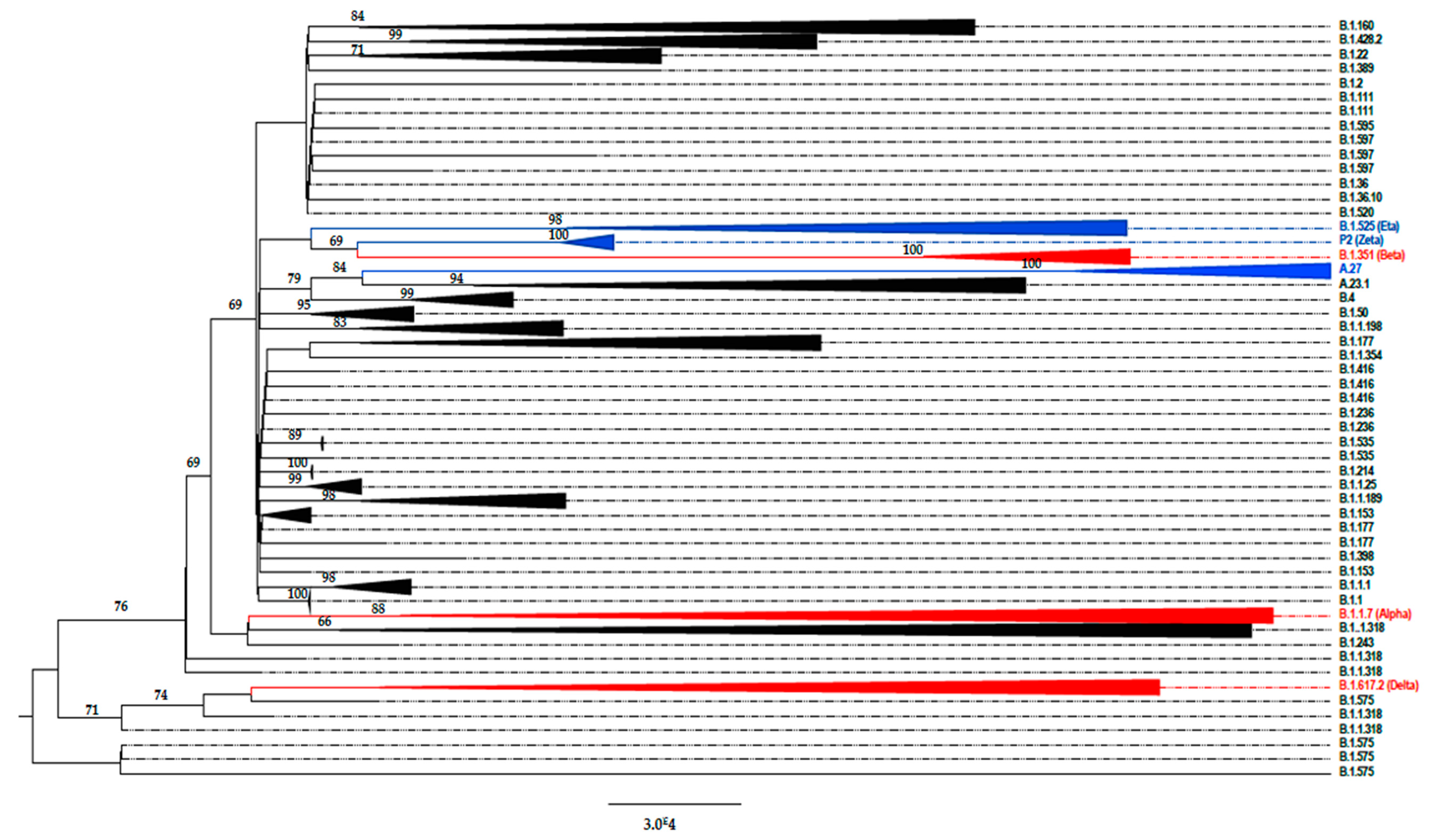
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coronaviridae Study Group of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. The species Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: Classifying 2019-nCoV and naming it SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, F.; Zhao, S.; Yu, B.; Chen, Y.M.; Wang, W.; Song, Z.G.; Hu, Y.; Tao, Z.W.; Tian, J.H.; Pei, Y.Y.; et al. A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature 2020, 579, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. China Novel Coronavirus Investigating and Research Team. A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- Elbe, S.; Buckland-Merrett, G. Data, disease and diplomacy: GISAID’s innovative contribution to global health. Glob Chall. 2017, 1, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Tracking SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Available online: https://www.who.int/en/activities/tracking-SARS-CoV-2-variants/ (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (eCDC). SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/covid-19/variants-concern (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- GOV-UK. Investigation of SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern: Technical Briefings. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/investigation-of-novel-sars-cov-2-variant-variant-of-concern-20201201 (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- Challen, R.; Brooks-Pollock, E.; Read, J.M.; Dyson, L.; Tsaneva-Atanasova, K.; Danon, L. Risk of mortality in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern 202012/1: Matched cohort study. BMJ (Clin. Res. Ed.) 2021, 372, n579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksamentov, I.; Roemer, C.; Hodcroft, E.B.; Neher, R.A. Nextclade: Clade assignment, mutation calling and quality control for viral genomes. J. Open Source Softw. 2021, 6, 3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegally, H.; Wilkinson, E.; Althaus, C.L.; Giovanetti, M.; San, J.E.; Giandhari, J.; Pillay, S.; Naidoo, Y.; Ramphal, U.; Msomi, N.; et al. Rapid replacement of the Beta variant by the Delta variant in South Africa. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earnest, R.; Uddin, R.; Matluk, N.; Renzette, N.; Siddle, K.J.; Loreth, C.; Adams, G.; Tomkins-Tinch, C.H.; Petrone, M.E.; Rothman, J.E.; et al. Comparative transmissibility of SARS-CoV-2 variants Delta and Alpha in New England, USA. medRxiv 2021, 100583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, N.R.; Mellan, T.A.; Whittaker, C.; Claro, I.M.; Candido, D.D.S.; Mishra, S.; Crispim, M.A.E.; Sales, F.C.S.; Hawryluk, I.; McCrone, J.T.; et al. Genomics and epidemiology of the P.1 SARS-CoV-2 lineage in Manaus, Brazil. Science 2021, 372, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S. E484K and N501Y SARS-CoV 2 spike mutants Increase ACE2 recognition but reduce affinity for neutralizing antibody. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 102, 108424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Van Blargan, L.A.; Bloyet, L.M.; Rothlauf, P.W.; Chen, R.E.; Stumpf, S.; Zhao, H.; Errico, J.M.; Theel, E.S.; Liebeskind, M.J.; et al. Identification of SARS-CoV-2 spike mutations that attenuate monoclonal and serum antibody neutralization. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 477–488.E4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization: Home/News/ Classification of Omicron (B.1.1.529): SARS-CoV-2 Variant of Concern. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/26-11-2021-classification-of-omicron-(b.1.1.529)-sars-cov-2-variant-of-concern (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- Saxena, S.K.; Kumar, S.; Ansari, S.; Paweska, J.T.; Maurya, V.K.; Tripathi, A.K.; Abdel-Moneim, A.S. Characterization of the novel SARS-CoV-2 Omicron (B.1.1.529) variant of concern and its global perspective. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 94, 1738–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO Health Emergency Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/region/emro/country/tn (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- Bhoyar, R.C.; Jain, A.; Sehgal, P.; Divakar, M.K.; Sharma, D.; Imran, M.; Jolly, B.; Ranjan, G.; Rophina, M.; Sharma, S.; et al. High throughput detection and genetic epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2 using COVIDSeq next-generation sequencing. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, C.-C.; Shakya, M.; Davenport, K.; Flynn, M.; Gutiérrez, A.M.; Hu, B.; Li, P.-E.; Jackson, E.P.; Xu, Y.; Chain, P.S.G. EDGE COVID-19: A Web Platform to generate submission-ready genomes for SARS-CoV-2 sequencing efforts. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2006.08058v4. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, C.C.; Chain, P.S. Rapid evaluation and quality control of next generation sequencing data with FaQCs. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H. Aligning sequence reads, clone sequences and assembly contigs with BWA-MEM. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1303.3997. [Google Scholar]
- Rambaut, A.; Holmes, E.C.; O’Toole, Á.; Hill, V.; McCrone, J.T.; Ruis, C.; du Plessis, L.; Pybus, O.G. A dynamic nomenclature proposal for SARS-CoV-2 lineages to assist genomic epidemiology. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 1403–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fares, W.; Ghedira, K.; Gdoura, M.; Chouikha, A.; Haddad-Boubaker, S.; Khedhiri, M.; Ayouni, K.; Lamari, A.; Touzi, H.; Hammemi, W.; et al. Sequencing Using a Two-Step Strategy Reveals High Genetic Diversity in the S Gene of SARS-CoV-2 after a High-Transmission Period in Tunis, Tunisia. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e0063921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pangolin COVID-19 Lineage Assigner. Available online: https://pangolin.cog-uk.io/ (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trifinopoulos, J.; Nguyen, L.T.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. W-IQ-TREE: A fast online phylogenetic tool for maximum likelihood analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W232–W235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klempt, P.; Brzoň, O.; Kašný, M.; Kvapilová, K.; Hubáček, P.; Briksi, A.; Bezdíček, M.; Koudeláková, V.; Lengerová, M.; Hajdúch, M.; et al. Distribution of SARS-CoV-2 Lineages in the Czech Republic, Analysis of Data from the First Year of the Pandemic. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, J.; Fanis, P.; Tryfonos, C.; Koptides, D.; Krashias, G.; Bashiardes, S.; Hadjisavvas, A.; Loizidou, M.; Oulas, A.; Alexandrou, D.; et al. Molecular epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2 in Cyprus. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du Plessis, L.; McCrone, J.T.; Zarebski, A.E.; Hill, V.; Ruis, C.; Gutierrez, B.; Raghwani, J.; Ashworth, J.; Colquhoun, R.; Connor, T.R.; et al. Establishment and lineage dynamics of the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic in the UK. Science 2021, 371, 708–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsvay, A.; Klink, G.V.; Safina, K.R.; Nabieva, E.; Garushyants, S.K.; Biba, D.; Bazykin, G.A.; Mikhaylov, I.M.; Say, A.V.; Zakamornaya, A.I.; et al. Genomic epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2 in Russia reveals recurring cross-border transmission throughout 2020. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelbrecht, S.; Delaney, K.; Kleinhans, B.; Wilkinson, E.; Tegally, H.; Stander, T.; van Zyl, G.; Preiser, W.; de Oliveira, T. Multiple Early Introductions of SARS-CoV-2 to Cape Town, South Africa. Viruses 2021, 13, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallam, M.; Mahafzah, A. Molecular Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Genetic Lineages in Jordan: Tracking the Introduction and Spread of COVID-19 UK Variant of Concern at a Country Level. Pathogens 2021, 10, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burki, T. China’s successful control of COVID-19. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 20, 1240–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Xia, F.; Bragazzi, N.L.; McCarthy, Z.; Wang, X.; He, S.; Sun, X.; Tang, S.; Xiao, Y.; Wu, J. Lessons drawn from China and South Korea for managing COVID-19 epidemic: Insights from a comparative modeling study. ISA Trans. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Lun, W.; Chen, Z.; Lu, X.; Li, J.; Qiu, F.; Li, S.; Mao, C.; Lu, Y.; et al. Transmission dynamics and successful control measures of SARS-CoV-2 in the mega-size city of Guangzhou, China. Medicine 2021, 100, e27846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, L.; Marogi, E.; Moss, C.B.; Murphy, R.L.; Ison, M.G.; Achenbach, C.J.; Resnick, D.; Singh, L.; White, J.; Boctor, M.J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Surveillance in the Middle East and North Africa: Longitudinal Trend Analysis. J. Med. Internet Res. 2021, 23, e25830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallam, M.; Ababneh, N.A.; Dababseh, D.; Bakri, F.G.; Mahafzah, A. Temporal increase in D614G mutation of SARS-CoV-2 in the Middle East and North Africa. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fourati, S.; Decousser, J.W.; Khouider, S.; N’Debi, M.; Demontant, V.; Trawinski, E.; Gourgeon, A.; Gangloff, C.; Destras, G.; Bal, A.; et al. Novel SARS-CoV-2 Variant Derived from Clade 19B, France. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 5, 1540–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alpert, T.; Brito, A.F.; Lasek-Nesselquist, E.; Rothman, J.; Valesano, A.L.; MacKay, M.J.; Petrone, M.E.; Breban, M.I.; Watkins, A.E.; Vogels, C.B.F.; et al. Early introductions and community transmission of SARS-CoV-2 variant B.1.1.7 in the United States. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolze, A.; Cirulli, E.T.; Luo, S.; White, S.; Wyman, D.; Dei Rossi, A.; Cassens, T.; Jacobs, S.; Nguyen, J.; Ramirez, J.M., III; et al. Rapid displacement of SARS-CoV-2 variant B.1.1.7 by B.1.617.2 and P.1 in the United States. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SARS-CoV-2 Lineages. Available online: https://cov-lineages.org/lineage_list.html (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- Hodcroft, E.B.; Zuber, M.; Nadeau, S.; Crawford, K.H.D.; Bloom, J.D.; Veesler, D.; Mateo, D.; Hernando, A.; Comas, I.; Candelas, F.G. SeqCOVID-SPAIN consortium, Stadler, T.; Neher, R.A. Emergence and spread of a SARS-CoV-2 variant through Europe in the summer of 2020. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center of Diseases Control and Prevention (CDC). Delta Variant: What We Know About the Science. 2021. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/variants/delta-variant.html (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- Challen, R.; Dyson, L.; Overton, C.E.; Guzman-Rincon, L.M.; Hill, E.M.; Stage, H.B.; Brooks-Pollock, E.; Pellis, L.; Scarabel, F.; Pascall, D.J.; et al. Early epidemiological signatures of novel SARS-CoV2 variants: Establishment of B.1.617.2 in England. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

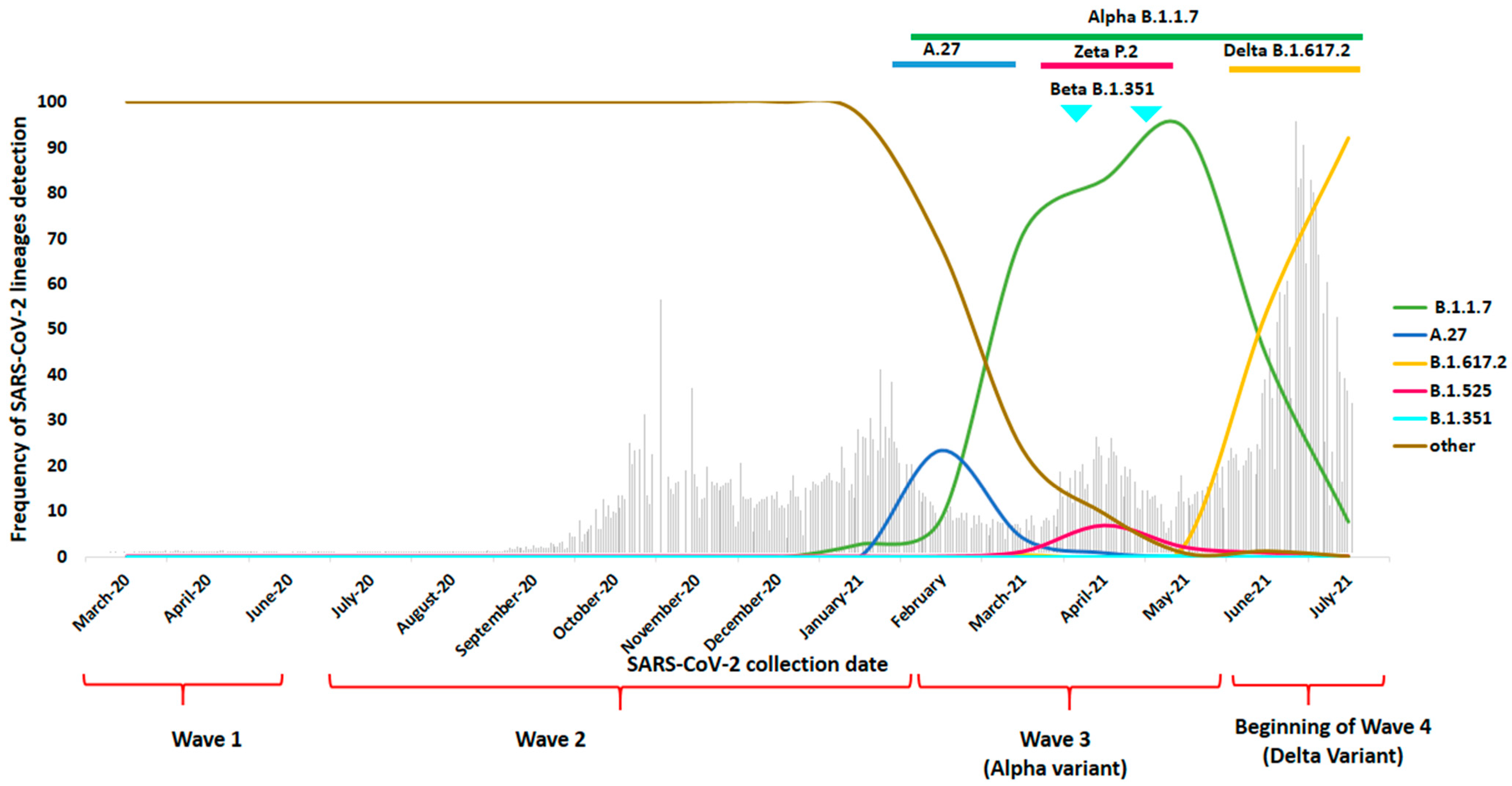
| Wave 1 | Wave 2 | Wave 3 | Begining of Wave 4 | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WHO | GISAID Clade | Nextstrain Clade | Methodolgy | Pango Lineage | Mar-20 | Apr-20 | Jun-20 | Jul-20 | Aug-20 | Sep-20 | Oct-20 | Nov-20 | Dec-20 | Jan-21 | Feb-21 | Mar-21 | Apr-21 | May-21 | Jun-21 | Jul-21 | Total |
| WGS | B.1.153 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |||||||||||||||||
| WGS | B.1.1 * | 1 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 1 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 26 | ||||||||||
| 20A | WGS | B.1.36.10 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| WGS | B.1 * | 12 | 9 | 2 | 1 | 7 | 4 | 4 | 13 | 1 | 12 | 5 | 7 | 8 | 7 | 92 | |||||
| WGS | B.1.520 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 19A | WGS | B.4 | 3 | 3 | |||||||||||||||||
| 20A | WGS | B.1.36 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| 20A | WGS | B.1.398 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| 20A | WGS | B.1.214 | 2 | 2 | |||||||||||||||||
| 20B | WGS | B.1.1.50 | 6 | 1 | 7 | ||||||||||||||||
| 20C | WGS | B.1.597 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||
| 20D | WGS | B.1.1.1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||
| 20A | WGS | B.1.22 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 5 | |||||||||||||||
| 20C | WGS | B.1.428.2 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 16 | ||||||||||||
| 20B | WGS | B.1.1.25 | 2 | 2 | |||||||||||||||||
| 20B | WGS | B.1.1.198 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 | |||||||||||||
| 20B | WGS | B.1.1.189 | 1 | 3 | 4 | ||||||||||||||||
| WGS | B.1.1.354 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 20E | WGS | B.1.177 | 2 | 7 | 6 | 2 | 6 | 4 | 7 | 4 | 38 | ||||||||||
| 20A | WGS | B.1.160 | 3 | 15 | 15 | 3 | 11 | 13 | 26 | 1 | 1 | 88 | |||||||||
| WGS | B.1.111 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |||||||||||||||||
| 20A | WGS | B.1.389 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| WGS | B.1.575 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 4 | ||||||||||||||||
| 20A | WGS | B.1.473 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| 20C | WGS | B.1.595 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| WGS | B.1.623 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 20A | WGS | B.1.236 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||
| WGS | B.1.535 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 20A | WGS | B.1.533 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||
| Alpha | GRY | 20I | WGS | B.1.1.7 | 1 | 25 | 79 | 11 | 6 | 1 | 713 | ||||||||||
| PS/qRT-PCR | 1 | 3 | 113 | 79 | 277 | 112 | 5 | ||||||||||||||
| 20A | WGS | B.1.416 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||
| WGS | B * | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 20A | WGS | B.1.243 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| Zeta | 20B | WGS | P.2 | 4 | 1 | 5 | |||||||||||||||
| 19B | WGS | A.27 | 8 | 6 | 3 | 23 | |||||||||||||||
| PS | 3 | 2 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 19B | WGS | A.23.1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||
| WGS | B.1.415.1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Eta | G/484K.V3 | 21D | WGS | B.1.525 | 2 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 20 | ||||||||||||
| PS | 3 | 5 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 20A | WGS | B.1.160.14 | 2 | 2 | |||||||||||||||||
| 20A | WGS | B.1.160.28 | 2 | 2 | |||||||||||||||||
| Beta | GH/501Y.V2 | 20H | WGS | B.1.351 | 1 | 2 | |||||||||||||||
| PS | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| WGS | B.1.1.178 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| G | 20A/S:126A | WGS | B.1.620 | 2 | 1 | 3 | |||||||||||||||
| 20E | WGS | B.1.1.318 | 2 | 6 | 1 | 9 | |||||||||||||||
| 20G | WGS | B.1.2 | 2 | 2 | |||||||||||||||||
| Delta | G/478K.V1 | 21A,21I,21J | WGS | B.1.617.2 | 4 | 84 | 16 | 253 | |||||||||||||
| PS | 6 | 92 | 51 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 20C/S:80Y | WGS | B.1.367 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| WGS | B.1.629 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 15 | 18 | 6 | 7 | 20 | 21 | 43 | 49 | 10 | 36 | 46 | 197 | 193 | 313 | 310 | 74 | 1359 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chouikha, A.; Fares, W.; Laamari, A.; Haddad-Boubaker, S.; Belaiba, Z.; Ghedira, K.; Kammoun Rebai, W.; Ayouni, K.; Khedhiri, M.; Ben Halima, S.; et al. Molecular Epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2 in Tunisia (North Africa) through Several Successive Waves of COVID-19. Viruses 2022, 14, 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14030624
Chouikha A, Fares W, Laamari A, Haddad-Boubaker S, Belaiba Z, Ghedira K, Kammoun Rebai W, Ayouni K, Khedhiri M, Ben Halima S, et al. Molecular Epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2 in Tunisia (North Africa) through Several Successive Waves of COVID-19. Viruses. 2022; 14(3):624. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14030624
Chicago/Turabian StyleChouikha, Anissa, Wasfi Fares, Asma Laamari, Sondes Haddad-Boubaker, Zeineb Belaiba, Kais Ghedira, Wafa Kammoun Rebai, Kaouther Ayouni, Marwa Khedhiri, Samar Ben Halima, and et al. 2022. "Molecular Epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2 in Tunisia (North Africa) through Several Successive Waves of COVID-19" Viruses 14, no. 3: 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14030624
APA StyleChouikha, A., Fares, W., Laamari, A., Haddad-Boubaker, S., Belaiba, Z., Ghedira, K., Kammoun Rebai, W., Ayouni, K., Khedhiri, M., Ben Halima, S., Krichen, H., Touzi, H., Ben Dhifallah, I., Guerfali, F. Z., Atri, C., Azouz, S., Khamessi, O., Ardhaoui, M., Safer, M., ... Triki, H. (2022). Molecular Epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2 in Tunisia (North Africa) through Several Successive Waves of COVID-19. Viruses, 14(3), 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14030624








