Expanding the Medfly Virome: Viral Diversity, Prevalence, and sRNA Profiling in Mass-Reared and Field-Derived Medflies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. C. capitata Samples and Cell Line
2.2. Transcriptome Assembly and Virus Discovery
2.3. Annotation of Viral Genomic Structures and Phylogenetic Classification
2.4. Viral Detection and Quantification
2.5. Viral Pre-Purification from Medfly Pupae and Virus Detection and Quantification
2.6. Small RNA Sequencing
2.7. Characterization of Viral sRNA Profiles
3. Results
3.1. RNA Virome Analysis Reveals the Presence of Thirteen RNA Viruses in Medfly
3.2. Prevalence and Viral Abundance Are Variable among Strains
3.3. Small-Interfering RNA Pathway Targets Most of the Analyzed Viruses
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clem, R.J.; Passarelli, A.L. Baculoviruses: Sophisticated Pathogens of Insects. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Yang, L.; Yang, X.; Li, T.; Graham, R.I.; Wu, K.; Wilson, K. Novel partiti-like viruses are conditional mutualistic symbionts in their normal lepidopteran host, African armyworm, but parasitic in a novel host, Fall armyworm. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.; Lin, X.D.; Tian, J.H.; Chen, L.J.; Chen, X.; Li, C.X.; Qin, X.C.; Li, J.; Cao, J.P.; Eden, J.S.; et al. Redefining the invertebrate RNA virosphere. Nature 2016, 540, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Käfer, S.; Paraskevopoulou, S.; Zirkel, F.; Wieseke, N.; Donath, A.; Petersen, M.; Jones, T.C.; Liu, S.; Zhou, X.; Middendorf, M.; et al. Re-assessing the diversity of negative strand RNA viruses in insects. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1008224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haoming, W.; Rui, P.; Tong, C.; Liang, X.; Haiyan, Z.; Tao, L.; Moutong, C.; Shi, W.; Yu, D.; Jumei, Z.; et al. Abundant and Diverse RNA Viruses in Insects Revealed by RNA-Seq Analysis: Ecological and Evolutionary Implications. mSystems 2021, 5, e00039-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Gu, Q.; Niu, J.; Wang, J.J. The RNA Virome and Its Dynamics in an Invasive Fruit Fly, Bactrocera dorsalis, Imply Interactions between Host and Viruses. Microb. Ecol. 2020, 80, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpe, S.R.; Morrow, J.L.; Brettell, L.E.; Shearman, D.C.; Gilchrist, S.; Cook, J.M.; Riegler, M. Tephritid fruit flies have a large diversity of co-occurring RNA viruses. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2021, 186, 107569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, H.; Chiba, S.; Maruyama, K.; Andika, I.B.; Suzuki, N. A novel insect-infecting virga/nege-like virus group and its pervasive endogenization into insect genomes. Virus Res. 2019, 262, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryabov, E. V Invertebrate RNA virus diversity from a taxonomic point of view. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2017, 147, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llopis-Giménez, A.; Maria González, R.; Millán-Leiva, A.; Catalá, M.; Llacer, E.; Urbaneja, A.; Herrero, S. Novel RNA viruses producing simultaneous covert infections in Ceratitis capitata. Correlations between viral titers and host fitness, and implications for SIT programs. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2017, 143, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enkerlin, W.R. Impact of Fruit Fly Control Programmes Using the Sterile Insect Technique BT—Sterile Insect Technique: Principles and Practice in Area-Wide Integrated Pest Management; Dyck, V.A., Hendrichs, J., Robinson, A.S., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 651–676. ISBN 978-1-4020-4051-1. [Google Scholar]
- Maciel-Vergara, G.; Ros, V.I.D. Viruses of insects reared for food and feed. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2017, 147, 60–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertola, M.; Mutinelli, F. A Systematic Review on Viruses in Mass-Reared Edible Insect Species. Viruses 2021, 13, 2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longdon, B.; Jiggins, F.M. Vertically transmitted viral endosymbionts of insects: Do sigma viruses walk alone? Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2012, 279, 3889–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cooper, D.; Eleftherianos, I. Memory and Specificity in the Insect Immune System: Current Perspectives and Future Challenges. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongelli, V.; Saleh, M.-C. Bugs Are Not to Be Silenced: Small RNA Pathways and Antiviral Responses in Insects. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2016, 3, 573–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miesen, P.; Joosten, J.; van Rij, R.P. PIWIs Go Viral: Arbovirus-Derived piRNAs in Vector Mosquitoes. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1006017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gammon, D.B.; Mello, C.C. RNA interference-mediated antiviral defense in insects. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2015, 8, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Asgari, S. MicroRNA functions in insects. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 43, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, R.; Naccache, F.; Ndiaye, E.H.; Fall, G.; Castelli, I.; Lühken, R.; Medlock, J.; Cull, B.; Hesson, J.C.; Montarsi, F.; et al. Identification and RNAi Profile of a Novel Iflavirus Infecting Senegalese Aedes vexans arabiensis Mosquitoes. Viruses 2020, 12, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brennecke, J.; Aravin, A.A.; Stark, A.; Dus, M.; Kellis, M.; Sachidanandam, R.; Hannon, G.J. Discrete small RNA-generating loci as master regulators of transposon activity in Drosophila. Cell 2007, 128, 1089–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonning, B.C.; Saleh, M.-C. The Interplay between Viruses and RNAi Pathways in Insects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2021, 66, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arouri, R.; Le Goff, G.; Hemden, H.; Navarro-Llopis, V.; M’saad, M.; Castañera, P.; Feyereisen, R.; Hernández-Crespo, P.; Ortego, F. Resistance to lambda-cyhalothrin in Spanish field populations of Ceratitis capitata and metabolic resistance mediated by P450 in a resistant strain. Pest Manag. Sci. 2015, 71, 1281–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalloro, R. Establishment of continuously in vitro growing cell lines of med-fly (Ceratitis capitata wied.). Rev. Can. Biol. 1981, 40, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sancho, R.; Guillem-Amat, A.; López-Errasquín, E.; Sánchez, L.; Ortego, F.; Hernández-Crespo, P. Genetic analysis of medfly populations in an area of sterile insect technique applications. J. Pest Sci. 2021, 94, 1277–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grabherr, M.G.; Haas, B.J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Thompson, D.A.; Amit, I.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Raychowdhury, R.; Zeng, Q.; et al. Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Floden, E.W.; Tommaso, P.D.; Chatzou, M.; Magis, C.; Notredame, C.; Chang, J.-M. PSI/TM-Coffee: A web server for fast and accurate multiple sequence alignments of regular and transmembrane proteins using homology extension on reduced databases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W339–W343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New Models and Efficient Methods for Phylogenetic Inference in the Genomic Era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kõressaar, T.; Lepamets, M.; Kaplinski, L.; Raime, K.; Andreson, R.; Remm, M. Primer3_masker: Integrating masking of template sequence with primer design software. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 1937–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warnes, G.R.; Bolker, B.; Bonebakker, L.; Gentleman, R.; Huber, W.; Liaw, A.; Lumley, T.; Maechler, M.; Magnusson, A.; Moeller, S. Gplots: Various R Programming Tools for Plotting Data; R Package Version; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2009; Volume 2, p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, J.T.; Thorvaldsdóttir, H.; Winckler, W.; Guttman, M.; Lander, E.S.; Getz, G.; Mesirov, J.P. Integrative genomics viewer. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lewis, S.H.; Quarles, K.A.; Yang, Y.; Tanguy, M.; Frézal, L.; Smith, S.A.; Sharma, P.P.; Cordaux, R.; Gilbert, C.; Giraud, I.; et al. Pan-arthropod analysis reveals somatic piRNAs as an ancestral defence against transposable elements. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yong, C.Y.; Yeap, S.K.; Omar, A.R.; Tan, W.S. Advances in the study of nodavirus. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasilakis, N.; Forrester, N.L.; Palacios, G.; Nasar, F.; Savji, N.; Rossi, S.L.; Guzman, H.; Wood, T.G.; Popov, V.; Gorchakov, R.; et al. Negevirus: A proposed new taxon of insect-specific viruses with wide geographic distribution. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 2475–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abd-Alla, A.M.M.; Kariithi, H.M.; Mohamed, A.H.; Lapiz, E.; Parker, A.G.; Vreysen, M.J.B. Managing hytrosavirus infections in Glossina pallidipes colonies: Feeding regime affects the prevalence of salivary gland hypertrophy syndrome. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roossinck, M.J. The good viruses: Viral mutualistic symbioses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roossinck, M.J.; Bazán, E.R. Symbiosis: Viruses as Intimate Partners. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2017, 4, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Zhu, J.; Yu, J.; Chen, X.; Kang, L.; Cui, F. A symbiotic virus facilitates aphid adaptation to host plants by suppressing jasmonic acid responses. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2020, 33, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Mierlo, J.T.; Overheul, G.J.; Obadia, B.; van Cleef, K.W.R.; Webster, C.L.; Saleh, M.C.; Obbard, D.J.; van Rij, R.P. Novel Drosophila Viruses Encode Host-Specific Suppressors of RNAi. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
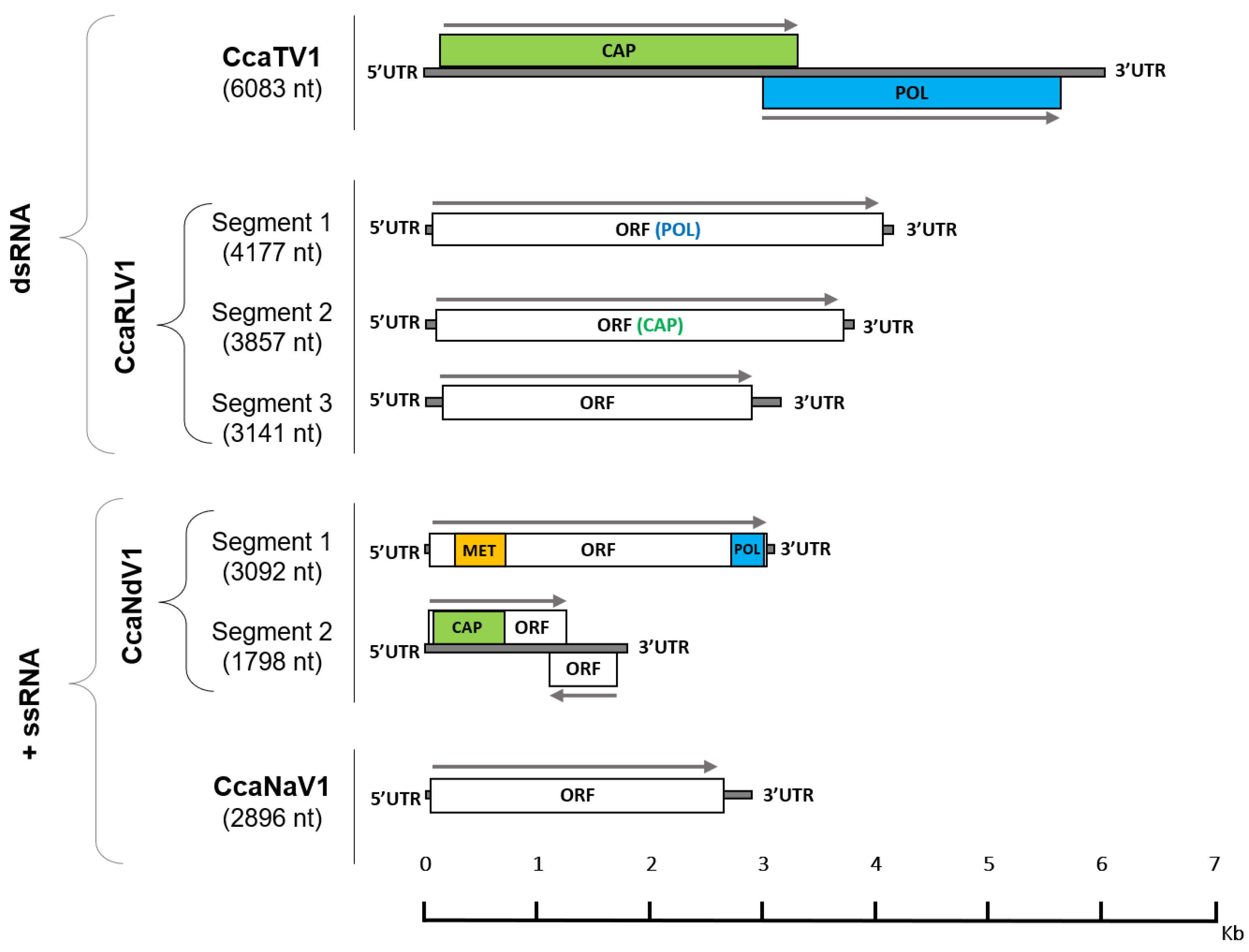
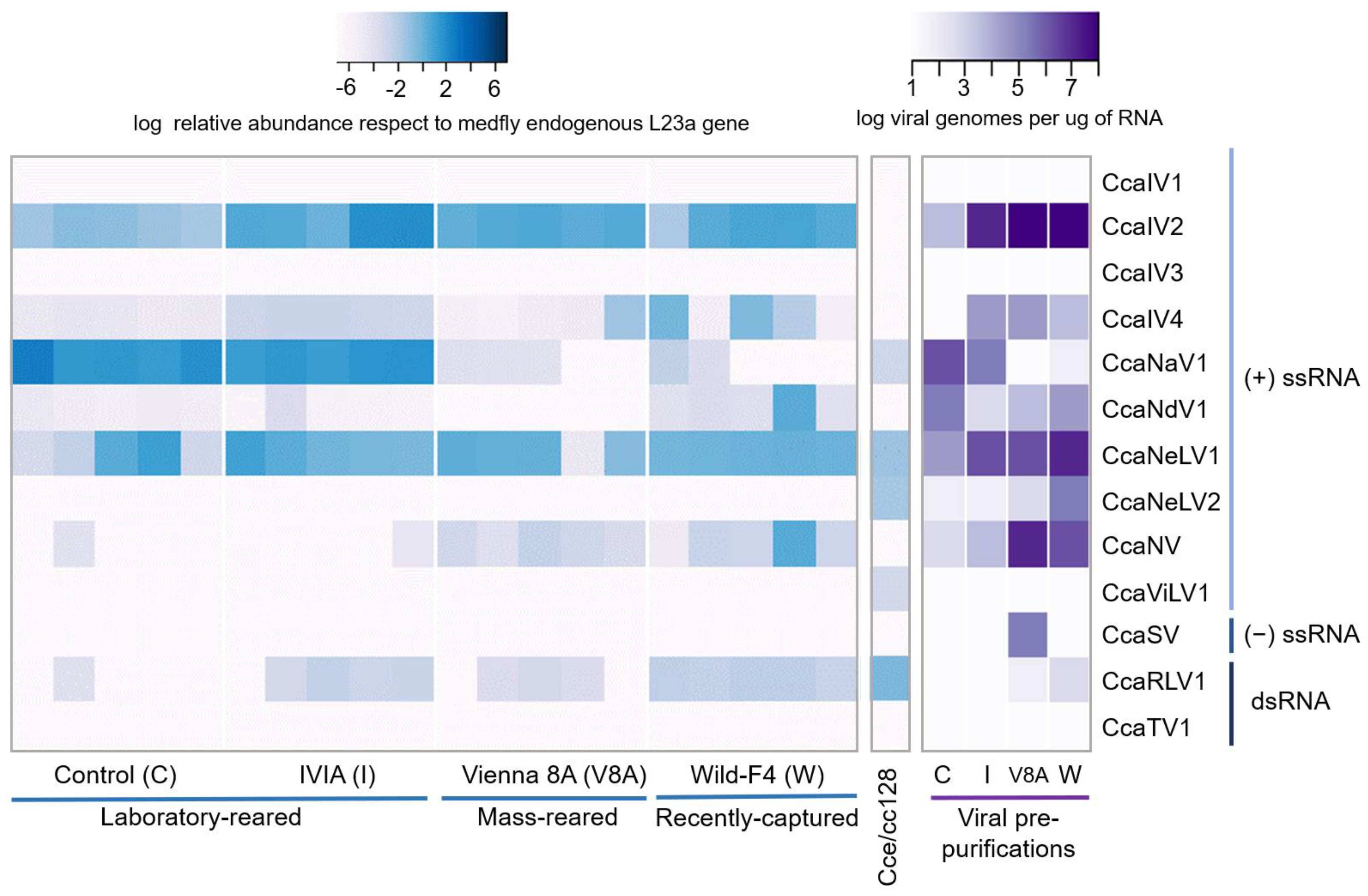
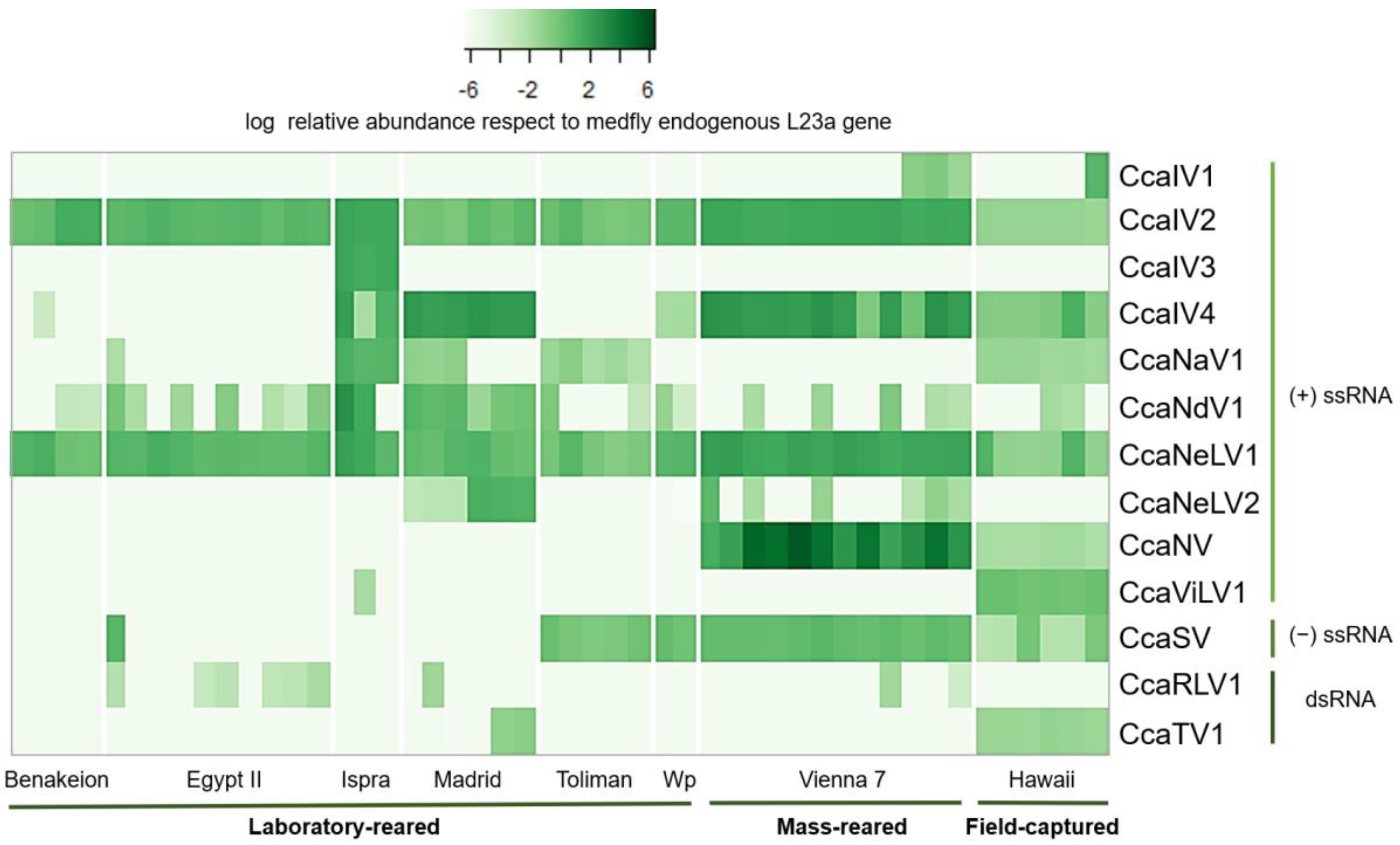
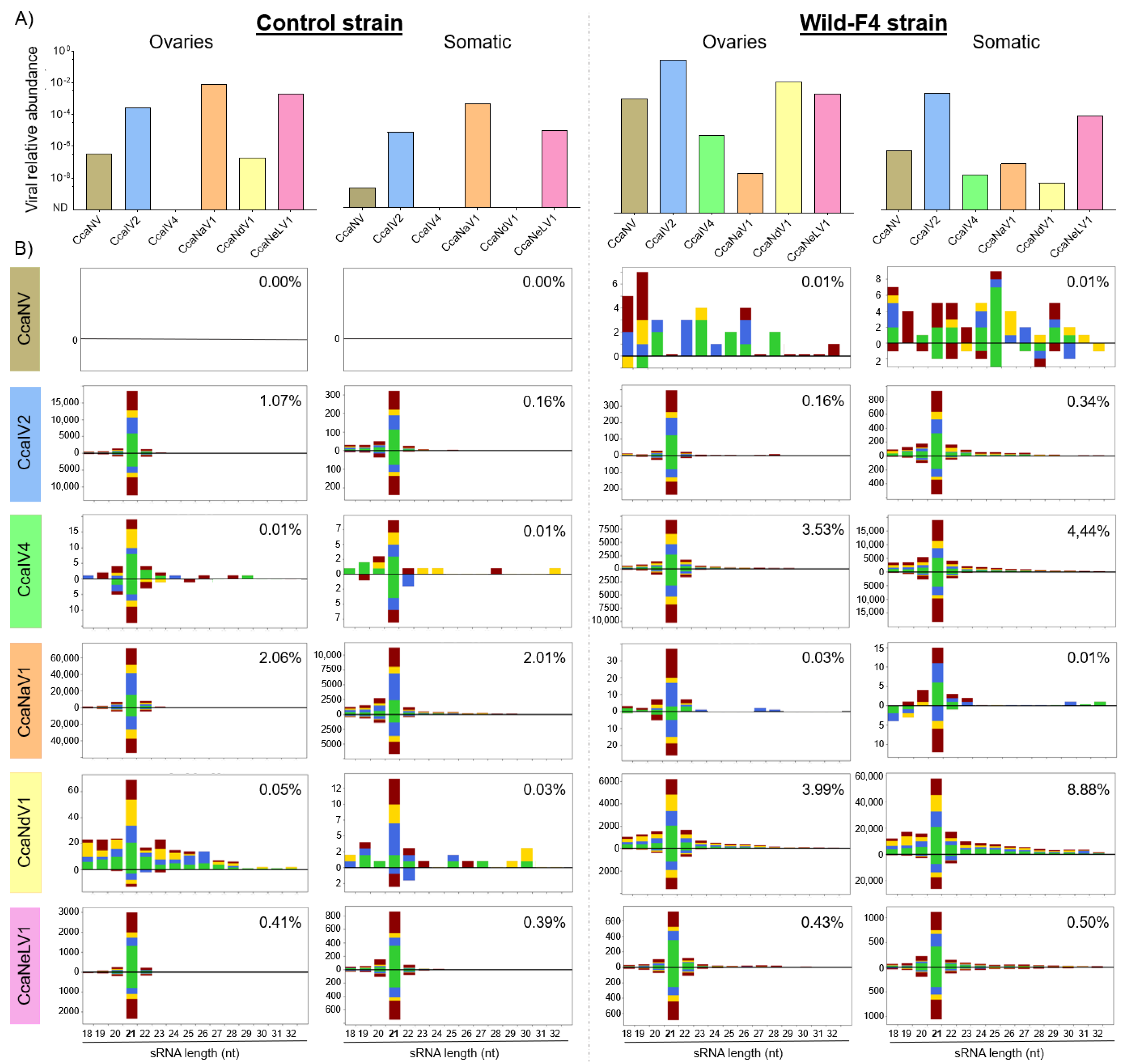
| Virus Type | Virus Family | Virus Full Name | Virus Abbreviation | Genome Length (bp) | Genbank Accession Numbers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| positive ssRNA | Iflaviridae | Ceratitis capitata iflavirus 1 | CcaIV1 | 10,502 | GAMC01001920.1 |
| Ceratitis capitata iflavirus 2 | CcaIV2 | 10,332 | OL957305 | ||
| Ceratitis capitata iflavirus 3 | CcaIV3 | 7370 | HG994137 | ||
| Ceratitis capitata iflavirus 4 | CcaIV4 | 9023 | HG994138 | ||
| Narnaviridae | Ceratitis capitata narnavirus 1 | CcaNaV1 | 2896 | OL957306 | |
| Nodaviridae | Ceratitis capitata nodavirus 1, segment 1 | CcaNdV1_s1 | 3092 | OL957308 | |
| Ceratitis capitata nodavirus 1, segment 2 | CcaNdV1_s2 | 1798 | OL957309 | ||
| Negeviridae | Ceratitis capitata negev-like virus 1 | CcaNeLV1 | 10,258 | HG994139 | |
| Ceratitis capitata negev-like virus 2 | CcaNeLV2 | 10,506 | OL957307 | ||
| Unclassified Riboviria | Ceratitis capitata nora virus | CcaNV | 12,014 | GAMC01015827.1 | |
| Virgaviridae | Ceratits capitata virga-like virus 1 | CcaViLV1 | 9925 | GAMC01017950.1 | |
| negative ssRNA | Rhabdoviridae | Ceratitis capitata sigmavirus | CcaSV | 12,583 | KR822825.1 |
| dsRNA | Reoviridae | Ceratitis capitata reo-like virus 1, segment 1 | CcaRLV1_s1 | 4177 | OL957310 |
| Ceratitis capitata reo-like virus 1, segment 2 | CcaRLV1_s2 | 3857 | OL957311 | ||
| Ceratitis capitata reo-like virus 1, segment 3 | CcaRLV1_s3 | 3141 | OL957312 | ||
| Totiviridae | Ceratitis capitata totivirus 1 | CcaTV1 | 6132 | OL957313 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hernández-Pelegrín, L.; Llopis-Giménez, Á.; Crava, C.M.; Ortego, F.; Hernández-Crespo, P.; Ros, V.I.D.; Herrero, S. Expanding the Medfly Virome: Viral Diversity, Prevalence, and sRNA Profiling in Mass-Reared and Field-Derived Medflies. Viruses 2022, 14, 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14030623
Hernández-Pelegrín L, Llopis-Giménez Á, Crava CM, Ortego F, Hernández-Crespo P, Ros VID, Herrero S. Expanding the Medfly Virome: Viral Diversity, Prevalence, and sRNA Profiling in Mass-Reared and Field-Derived Medflies. Viruses. 2022; 14(3):623. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14030623
Chicago/Turabian StyleHernández-Pelegrín, Luis, Ángel Llopis-Giménez, Cristina Maria Crava, Félix Ortego, Pedro Hernández-Crespo, Vera I. D. Ros, and Salvador Herrero. 2022. "Expanding the Medfly Virome: Viral Diversity, Prevalence, and sRNA Profiling in Mass-Reared and Field-Derived Medflies" Viruses 14, no. 3: 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14030623
APA StyleHernández-Pelegrín, L., Llopis-Giménez, Á., Crava, C. M., Ortego, F., Hernández-Crespo, P., Ros, V. I. D., & Herrero, S. (2022). Expanding the Medfly Virome: Viral Diversity, Prevalence, and sRNA Profiling in Mass-Reared and Field-Derived Medflies. Viruses, 14(3), 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14030623






