Functional Characterization of Replication-Associated Proteins Encoded by Alphasatellites Identified in Yunnan Province, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
2.2. Viral Genomic DNA Extraction and Amplification of Alpha-Rep Genes
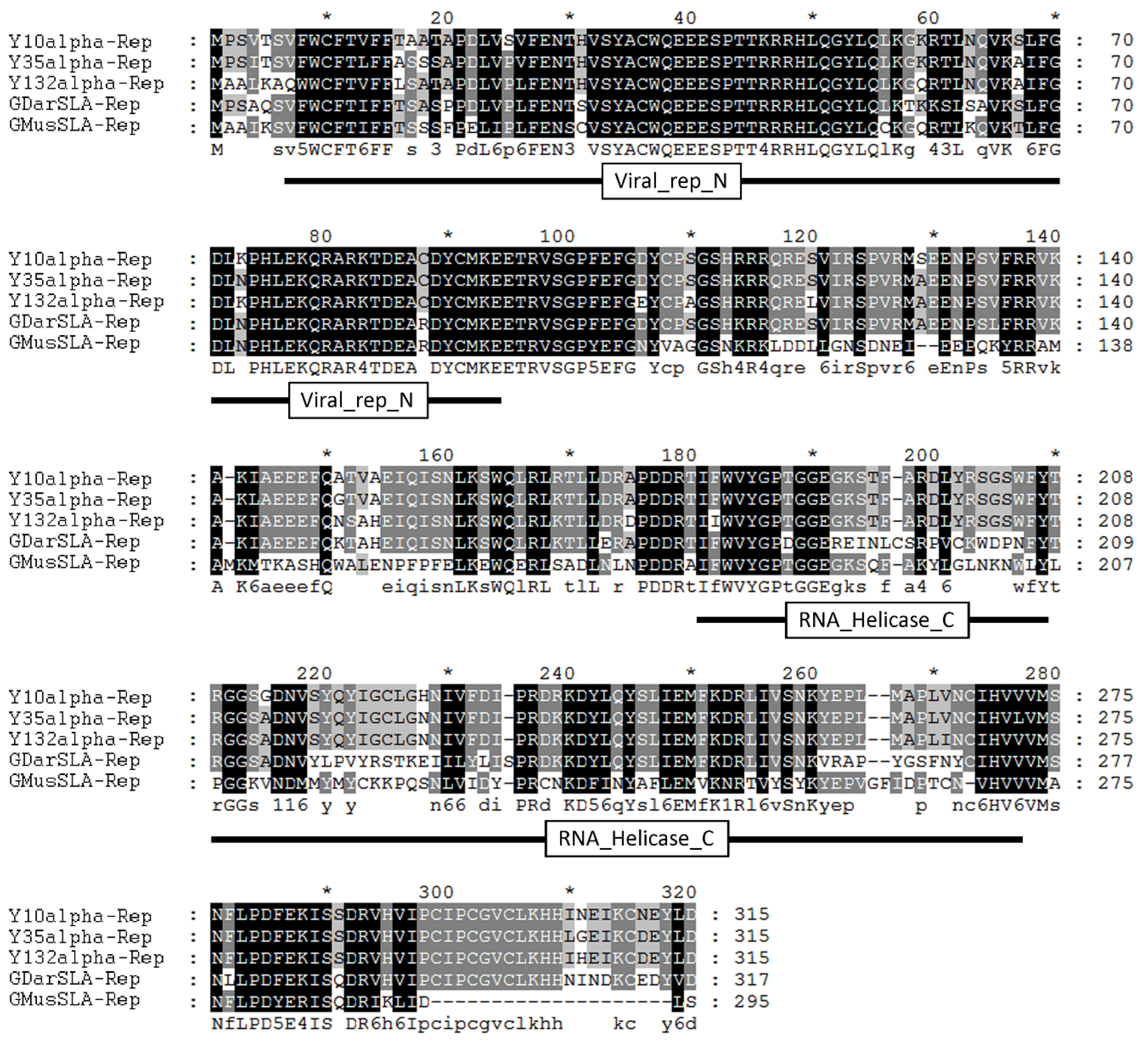
2.3. Sequence Analysis of Alpha-Reps
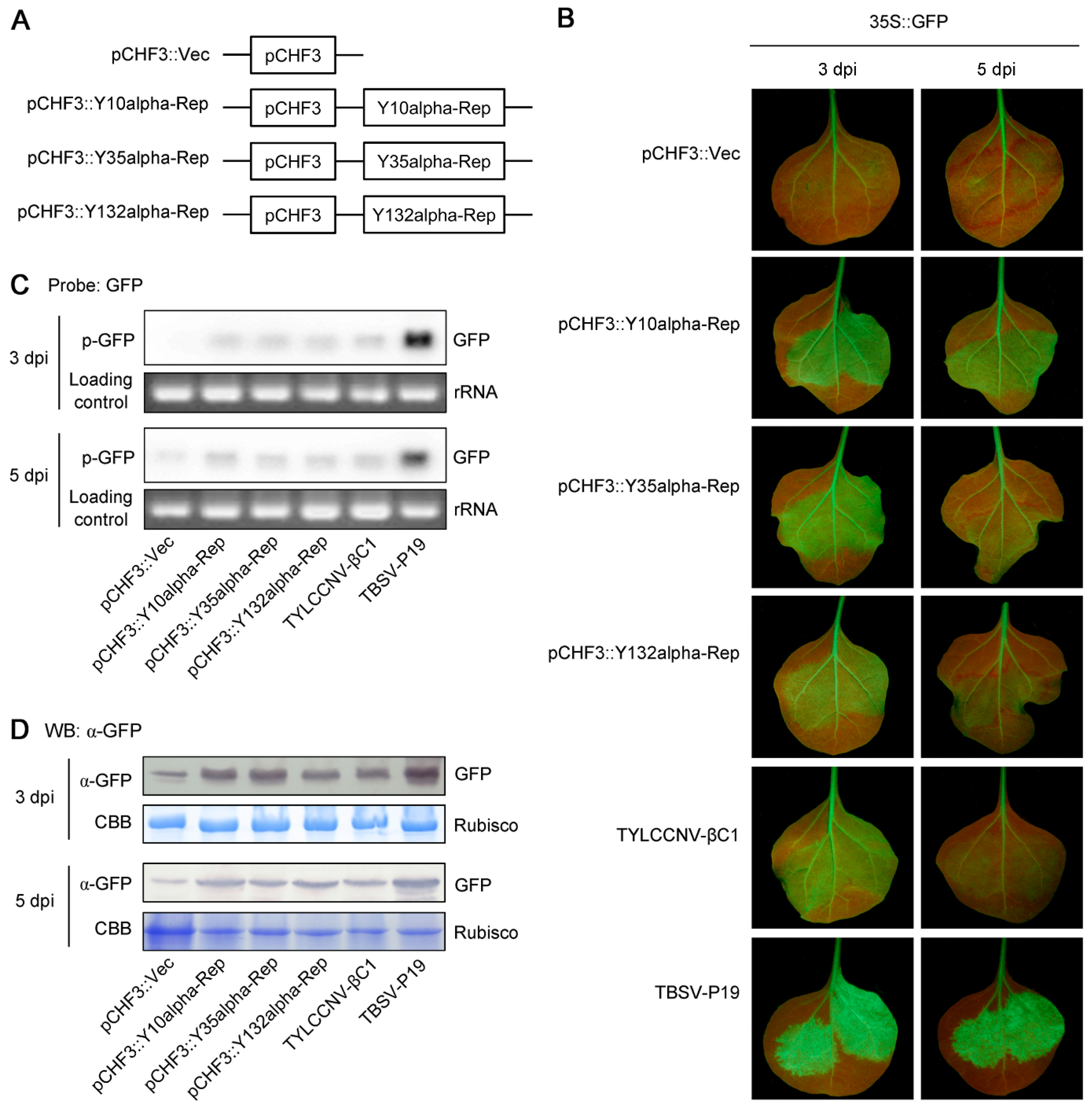
2.4. Recombinant pCHF3 Vectors for PTGS Suppression Analysis
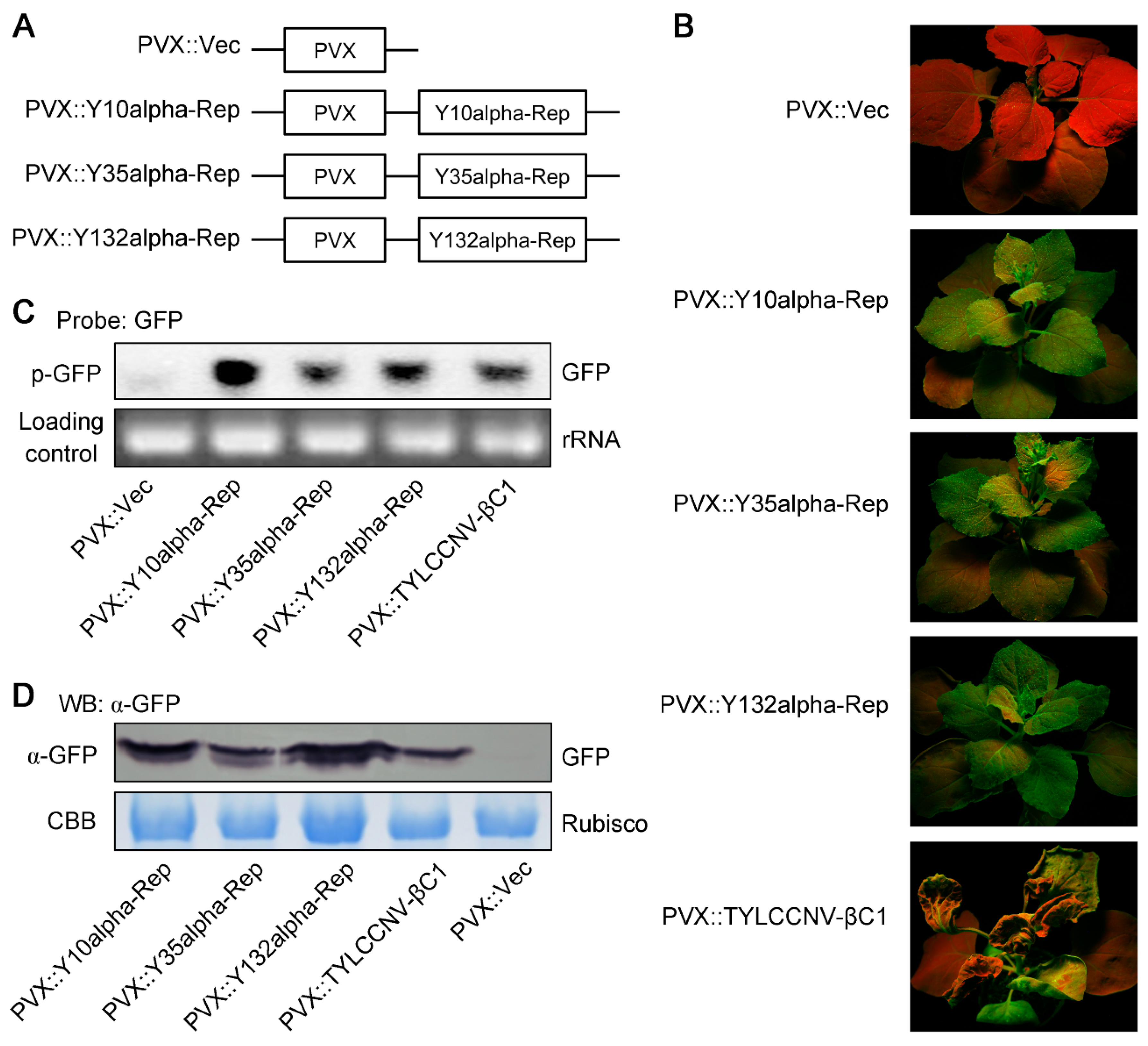
2.5. Recombinant PVX Vectors for TGS Suppression Analysis
2.6. Viral Inoculation and Agroinfiltration
2.7. RNA Extraction and Northern Blot Analysis
2.8. Protein Extraction and Western Blot Analysis
2.9. Southern Blot Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Isolation and Sequence Analysis of Three Types of Alpha-Reps from Yunnan Province, China
3.2. Alpha-Reps Are Suppressors of Local GFP PTGS
3.3. Alpha-Reps Are Suppressors of Systemic GFP PTGS
3.4. Alpha-Reps Can Reverse Established Methylation-Mediated TGS
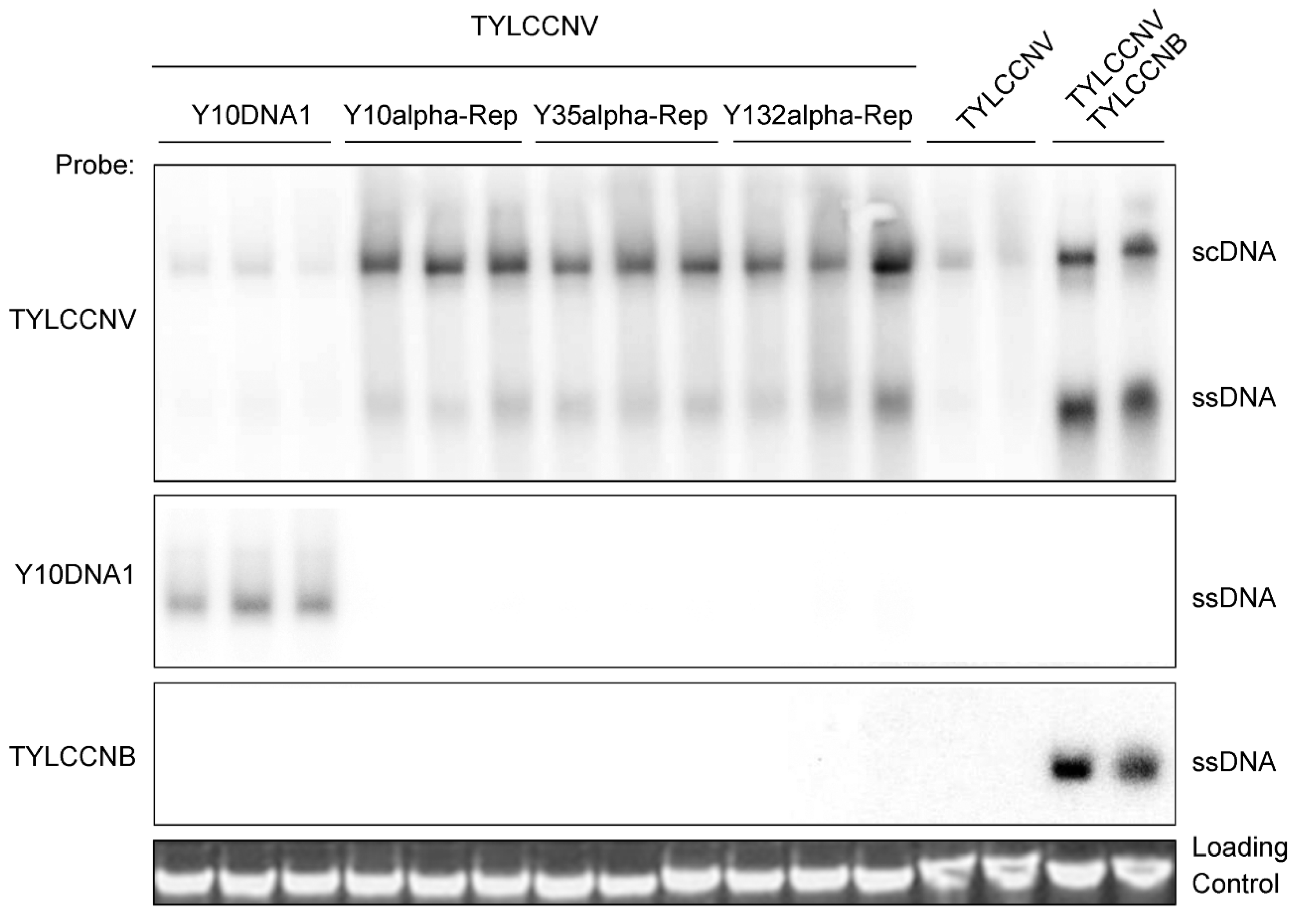
3.5. Alpha-Reps Can Enhance the Accumulation of Their Helper Virus
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rodríguez-Negrete, E.A.; Carrillo-Tripp, J.; Rivera-Bustamante, R.F. RNA Silencing against Geminivirus: Complementary Action of Posttranscriptional Gene Silencing and Transcriptional Gene Silencing in Host Recovery. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 1332–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matzke, M.; Kanno, T.; Daxinger, L.; Huettel, B.; Matzke, A.J. RNA-mediated chromatin-based silencing in plants. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2009, 21, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, J.A.; Jacobsen, S.E. Establishing, maintaining and modifying DNA methylation patterns in plants and animals. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 204–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannon, G.J. RNA interference. Nature 2002, 418, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, S.W.; Voinnet, O. Antiviral Immunity Directed by Small RNAs. Cell 2007, 130, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.W. RNA-based antiviral immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 632–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisaro, D.M. Silencing suppression by geminivirus proteins. Virology 2006, 344, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Fu, S.; Tao, X.; Zhou, X. Rice stripe virus: Exploring Molecular Weapons in the Arsenal of a Negative-Sense RNA Virus. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2021, 59, 351–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, F.; Daròs, J.A. Tobacco etch virus Protein P1 Traffics to the Nucleolus and Associates with the Host 60S Ribosomal Subunits during Infection. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 10725–10737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, L.G.; Crawshaw, S.; Rhee, S.J.; Murphy, A.M.; Canto, T.; Carr, J.P. The cucumber mosaic virus 1a protein regulates interactions between the 2b protein and ARGONAUTE 1 while maintaining the silencing suppressor activity of the 2b protein. PLOS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1009125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismayil, A.; Haxim, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Qian, L.; Han, T.; Chen, T.; Jia, Q.; Liu, A.Y.; Zhu, S.; et al. Cotton Leaf Curl Multan virus C4 protein suppresses both transcriptional and post-transcriptional gene silencing by interacting with SAM synthetase. PLOS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, M.R.; Hagen, C.; Lucas, W.J.; Gilbertson, R.L. Exploiting chinks in the plant’s armor: Evolution and emergence of geminiviruses. Annu Rev. Phytopathol. 2005, 43, 361–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoor, S.; Zafar, Y.; Briddon, R. Geminivirus disease complexes: The threat is spreading. Trends Plant Sci. 2006, 11, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, X.; Wang, Z.Q.; Xiao, R.; Wang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhou, X. iTRAQ analysis of the tobacco leaf proteome reveals that RNA-directed DNA methylation (RdDM) has important roles in defense against geminivirus-betasatellite infection. J. Proteom. 2017, 152, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, K.; Bedford, I.D.; Briddon, R.; Markham, P.G.; Wong, S.M.; Stanley, J. A unique virus complex causes Ageratum yellow vein disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 6890–6895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briddon, R.; Stanley, J. Subviral agents associated with plant single-stranded DNA viruses. Virology 2006, 344, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briddon, R.W.; Brown, J.K.; Moriones, E.; Stanley, J.; Zerbini, M.; Zhou, X.; Fauquet, C.M. Recommendations for the classification and nomenclature of the DNA-beta satellites of begomoviruses. Arch. Virol. 2008, 153, 763–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wu, P.; Liu, P.; Gong, H.; Zhou, X. Characterization of alphasatellites associated with monopartite begomovirus/betasatellite complexes in Yunnan, China. Virol. J. 2010, 7, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Xie, Y.; Zhao, L.; Ren, H.; Li, Z. A Naturally Occurring Defective DNA Satellite Associated with a Monopartite Begomovirus: Evidence for Recombination between Alphasatellite and Betasatellite. Viruses 2013, 5, 2116–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briddon, R.; Mansoor, S.; Bedford, I.; Pinner, M.; Saunders, K.; Stanley, J.; Zafar, Y.; Malik, K.; Markham, P. Identification of DNA Components Required for Induction of Cotton Leaf Curl Disease. Virology 2001, 285, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Xie, Y.; Tao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Fauquet, C.M. Characterization of DNA beta associated with begomoviruses in China and evidence for co-evolution with their cognate viral DNA-A. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84 Pt 1, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X. Advances in Understanding Begomovirus Satellites. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2013, 51, 357–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, K.; Norman, A.; Gucciardo, S.; Stanley, J. The DNA beta satellite component associated with ageratum yellow vein disease encodes an essential pathogenicity protein (βC1). Virology 2004, 324, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Li, G.; Wang, D.; Hu, D.; Zhou, X. A Begomovirus DNAbeta-encoded protein binds DNA, functions as a suppressor of RNA silencing, and targets the cell nucleus. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 10764–10775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, X.; Wang, Z.Q.; Xiao, R.; Cao, L.; Wang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhou, X. Mimic Phosphorylation of a βC1 Protein Encoded by TYLCCNB Impairs Its Functions as a Viral Suppressor of RNA Silencing and a Symptom Determinant. J. Virol. 2017, 91, 00300–00317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briddon, R.W.; Bull, S.E.; Amin, I.; Mansoor, S.; Bedford, I.D.; Rishi, N.; Siwatch, S.S.; Zafar, Y.; Abdel-Salam, A.M.; Markham, P.G. Diversity of DNA 1: A satellite-like molecule associated with monopartite begomovirus-DNA beta complexes. Virology 2004, 324, 462–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinoth Kumar, R.; Singh, D.; Singh, A.K.; Chakraborty, S. Molecular diversity, recombination and population structure of alphasatellites associated with begomovirus disease complexes. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 49, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paprotka, T.; Metzler, V.; Jeske, H. The first DNA 1-like α satellites in association with New World begomoviruses in natural infections. Virology 2010, 404, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stainton, D.; Martin, D.P.; Collings, D.A.; Varsani, A. Comparative analysis of common regions found in babuviruses and alphasatellite molecules. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz-Ul-Rehman, M.S.; Nahid, N.; Mansoor, S.; Briddon, R.W.; Fauquet, C.M. Post-transcriptional gene silencing suppressor activity of two non-pathogenic alphasatellites associated with a begomovirus. Virology 2010, 405, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris, A.M.; Shahid, M.S.; Briddon, R.W.; Khan, A.J.; Zhu, J.K.; Brown, J.K. An unusual alphasatellite associated with monopartite begomoviruses attenuates symptoms and reduces betasatellite accumulation. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92 Pt 3, 706–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mar, T.B.; Mendes, I.R.; Lau, D.; Fiallo-Olivé, E.; Navas-Castillo, J.; Alves, M.S.; Murilo Zerbini, F. Interaction between the New World begomovirus Euphorbia yellow mosaic virus and its associated alphasatellite: Effects on infection and transmission by the whitefly Bemisia tabaci. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 1552–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.; Wang, Z.Q.; Liu, X.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, X.; Xie, Y. Identification and analysis of potential genes regulated by an alphasatellite (TYLCCNA) that contribute to host resistance against tomato yellow leaf curl China virus and its betasatellite (TYLCCNV/TYLCCNB) infection in Nicotiana benthamiana. Viruses 2019, 11, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawaz-Ul-Rehman, M.S.; Fauquet, C.M. Evolution of geminiviruses and their satellites. FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 1825–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voinnet, O.; Baulcombe, D. Systemic signalling in gene silencing. Nature 1997, 389, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchmann, R.C.; Asad, S.; Wolf, J.N.; Mohannath, G.; Bisaro, D.M. Geminivirus AL2 and L2 Proteins Suppress Transcriptional Gene Silencing and Cause Genome-Wide Reductions in Cytosine Methylation. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 5005–5013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Xie, Y.; Raja, P.; Li, S.; Wolf, J.N.; Shen, Q.; Bisaro, D.M.; Zhou, X. Suppression of Methylation-Mediated Transcriptional Gene Silencing by βC1-SAHH Protein Interaction during Geminivirus-Betasatellite Infection. PLOS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Q.; Li, G.Z.; Gong, Q.Q.; Li, G.X.; Zheng, S.J. OsTCTP, encoding a translationally controlled tumor protein, plays an important role in mercury tolerance in rice. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gebali, S.; Mistry, J.; Bateman, A.; Eddy, S.R.; Luciani, A.; Potter, S.C.; Qureshi, M.; Richardson, L.J.; Salazar, G.A.; Smart, A.; et al. The Pfam protein families database in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D427–D432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. 20 years of the SMART protein domain annotation resource. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D493–D496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, R.; Wu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, X. Identification of a Movement Protein of the Tenuivirus Rice Stripe Virus. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 12304–12311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, R.; Malcuit, I.; Moffett, P.; Ruiz, M.T.; Peart, J.; Wu, A.J.; Rathjen, J.P.; Bendahmane, A.; Day, L.; Baulcombe, D.C. High throughput virus-induced gene silencing implicates heat shock protein 90 in plant disease resistance. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 5690–5699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Huang, C.; Li, Z.; Zhou, X. Suppression of RNA Silencing by a Plant DNA Virus Satellite Requires a Host Calmodulin-Like Protein to Repress RDR6 Expression. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1003921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Morris, T.J. Efficient Infection of Nicotiana benthamiana by Tomato bushy stunt virus Is Facilitated by the Coat Protein and Maintained by p19 Through Suppression of Gene Silencing. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2002, 15, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Klahre, U.; Crété, P.; Leuenberger, S.A.; Iglesias, V.A.; Meins, F. High molecular weight RNAs and small interfering RNAs induce systemic posttranscriptional gene silencing in plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11981–11986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voinnet, O. Non-cell autonomous RNA silencing. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 5858–5871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, X.; Fan, Y.; Li, B.; Ryabov, E.; Shi, N.; Zhao, M.; Yu, Z.; Qin, C.; Zheng, Q.; et al. A Genetic Network for Systemic RNA Silencing in Plants. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 2700–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Q.; Amin, I.; Mansoor, S.; Shafiq, M.; Wassenegger, M.; Briddon, R.W. The Rep proteins encoded by alphasatellites restore expression of a transcriptionally silenced green fluorescent protein transgene in Nicotiana benthamiana. Virusdisease 2019, 30, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Tao, X.; Xie, Y.; Fauquet, C.M.; Zhou, X. A DNA beta associated with Tomato yellow leaf curl China virus is required for symptom induction. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 13966–13974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xie, Y.; Zhou, X. Tobacco curly shoot virus DNA beta is not necessary for infection but intensifies symptoms in a host-dependent manner. Phytopathology 2005, 95, 902–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, I.; Hussain, K.; Akbergenov, R.; Yadav, J.S.; Qazi, J.; Mansoor, S.; Hohn, T.; Fauquet, C.M.; Briddon, R.W. Suppressors of RNA silencing encoded by the components of the cotton leaf curl begomovirus-betasatellite complex. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2011, 24, 973–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanitharani, R.; Chellappan, P.; Pita, J.S.; Fauquet, C.M. Differential Roles of AC2 and AC4 of Cassava Geminiviruses in Mediating Synergism and Suppression of Posttranscriptional Gene Silencing. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 9487–9498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raja, P.; Sanville, B.C.; Buchmann, R.C.; Bisaro, D.M. Viral Genome Methylation as an Epigenetic Defense against Geminiviruses. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 8997–9007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, P.; Jackel, J.N.; Li, S.; Heard, I.M.; Bisaro, D.M. Arabidopsis Double-Stranded RNA Binding Protein DRB3 Participates in Methylation-Mediated Defense against Geminiviruses. J. Virol. 2013, 88, 2611–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Yang, X.; Bisaro, D.M.; Zhou, X. The βC1 Protein of Geminivirus–Betasatellite Complexes: A Target and Repressor of Host Defenses. Mol. Plant 2018, 11, 1424–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Guo, W.; Li, F.; Sunter, G.; Zhou, X. Geminivirus-Associated Betasatellites: Exploiting Chinks in the Antiviral Arsenal of Plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2019, 24, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Buckley, K.J.; Yang, X.; Buchmann, R.C.; Bisaro, D.M. Adenosine Kinase Inhibition and Suppression of RNA Silencing by Geminivirus AL2 and L2 Proteins. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 7410–7418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, H.; Huang, X.; Xia, R.; Zhao, Q.; Lai, J.; Teng, K.; Li, Y.; Liang, L.; Du, Q.; et al. BSCTV C2 Attenuates the Degradation of SAMDC1 to Suppress DNA Methylation-Mediated Gene Silencing in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Negrete, E.; Lozano-Durán, R.; Piedra-Aguilera, A.; Cruzado, L.; Bejarano, E.R.; Castillo, A.G. Geminivirus Rep protein interferes with the plant DNA methylation machinery and suppresses transcriptional gene silencing. New Phytol. 2013, 199, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, F.; Huang, C.; Yang, X.; Qian, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhou, X. V2 of tomato yellow leaf curl virus can suppress methylation-mediated transcriptional gene silencing in plants. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinutha, T.; Kumar, G.; Garg, V.; Canto, T.; Palukaitis, P.; Ramesh, S.; Praveen, S. Tomato geminivirus encoded RNAi suppressor protein, AC4 interacts with host AGO4 and precludes viral DNA methylation. Gene 2018, 678, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, F.; Zhou, X. The C4 protein encoded by tomato leaf curl Yunnan virus reverses transcriptional gene silencing by interacting with NbDRM2 and impairing its DNA-binding ability. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakahara, K.S.; Masuta, C. Interaction between viral RNA silencing suppressors and host factors in plant immunity. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2014, 20, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
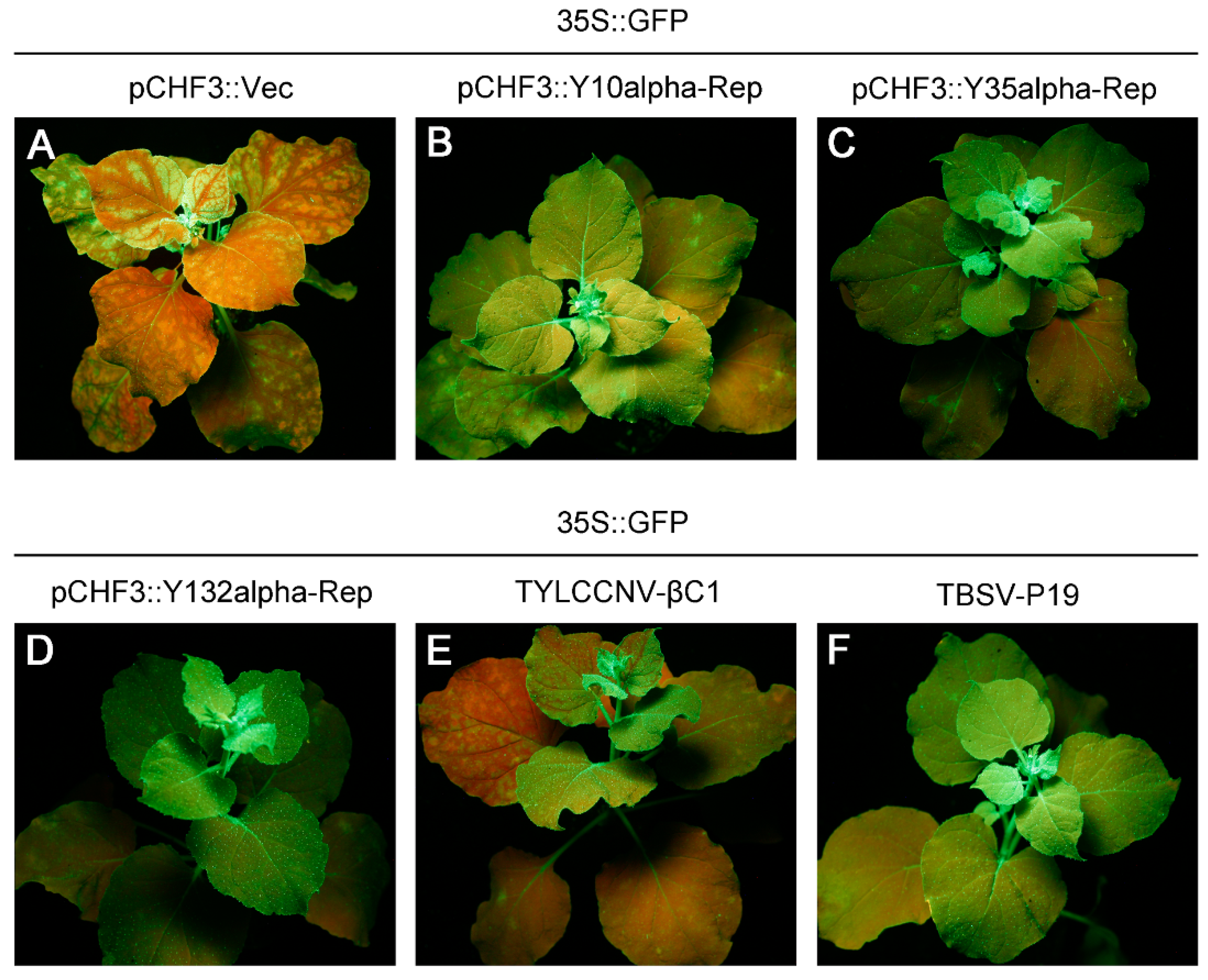
| Treatments | 10 dpi a | 20 dpi a | 30 dpi a | 40 dpi a |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 35S::GFP + pCHF3::Vec | 9/24 | 15/24 | 19/24 | 19/24 |
| 35S::GFP + pCHF3::Y10alpha-Rep | 0/36 | 0/36 | 0/36 | 0/36 |
| 35S::GFP + pCHF3::Y35alpha-Rep | 4/36 | 4/36 | 5/36 | 5/36 |
| 35S::GFP + pCHF3::Y132alpha-Rep | 1/24 | 3/24 | 7/24 | 7/24 |
| 35S::GFP + TYLCCNV-βC1 | 10/20 | 13/20 | 16/20 | 18/20 |
| 35S::GFP + TBSV-P19 | 0/24 | 0/24 | 0/24 | 0/24 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, L.; Che, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Xie, Y. Functional Characterization of Replication-Associated Proteins Encoded by Alphasatellites Identified in Yunnan Province, China. Viruses 2022, 14, 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14020222
Zhao L, Che X, Wang Z, Zhou X, Xie Y. Functional Characterization of Replication-Associated Proteins Encoded by Alphasatellites Identified in Yunnan Province, China. Viruses. 2022; 14(2):222. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14020222
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Liling, Xuan Che, Zhanqi Wang, Xueping Zhou, and Yan Xie. 2022. "Functional Characterization of Replication-Associated Proteins Encoded by Alphasatellites Identified in Yunnan Province, China" Viruses 14, no. 2: 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14020222
APA StyleZhao, L., Che, X., Wang, Z., Zhou, X., & Xie, Y. (2022). Functional Characterization of Replication-Associated Proteins Encoded by Alphasatellites Identified in Yunnan Province, China. Viruses, 14(2), 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14020222







