Kiwira Virus, a Newfound Hantavirus Discovered in Free-tailed Bats (Molossidae) in East and Central Africa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
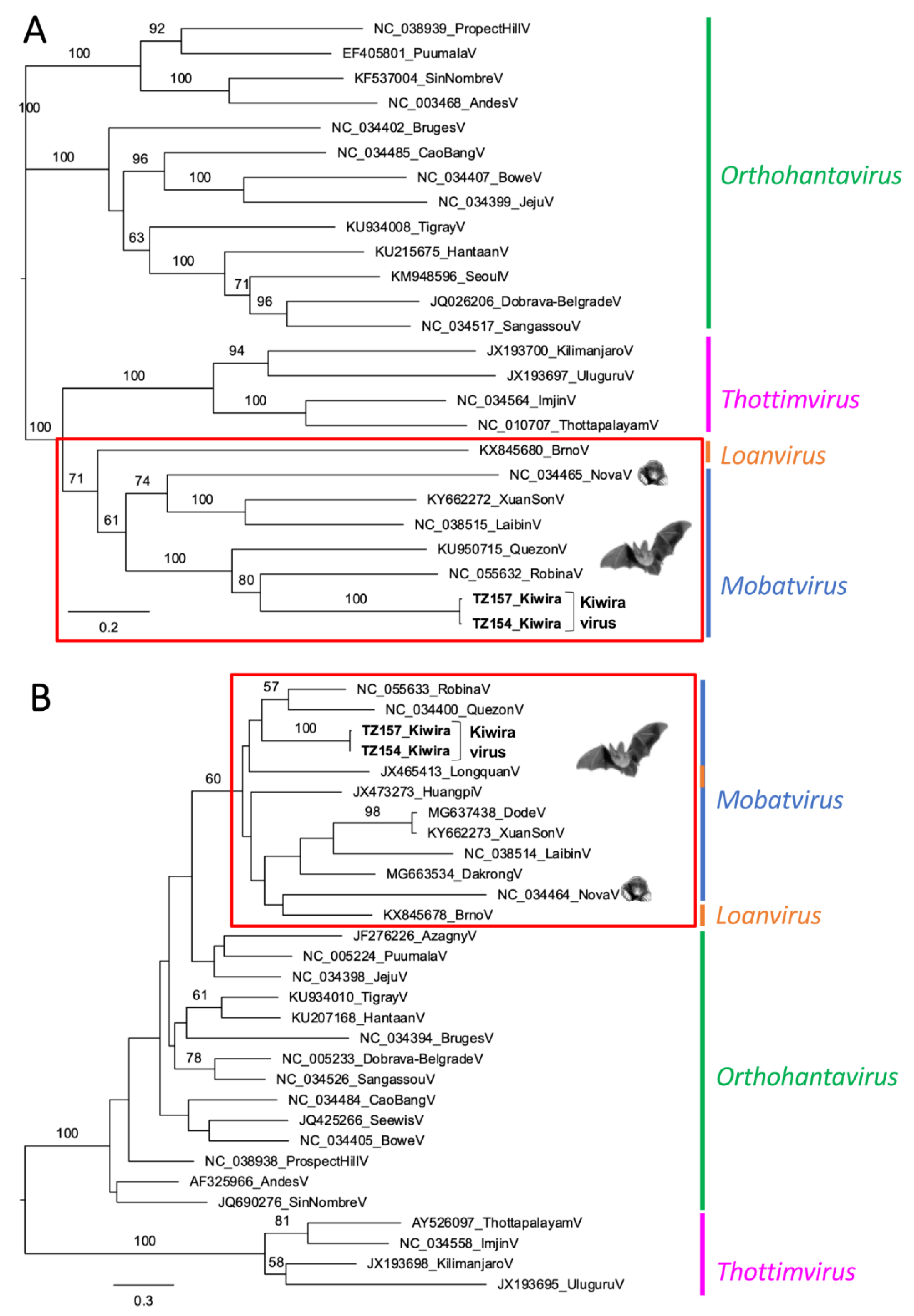
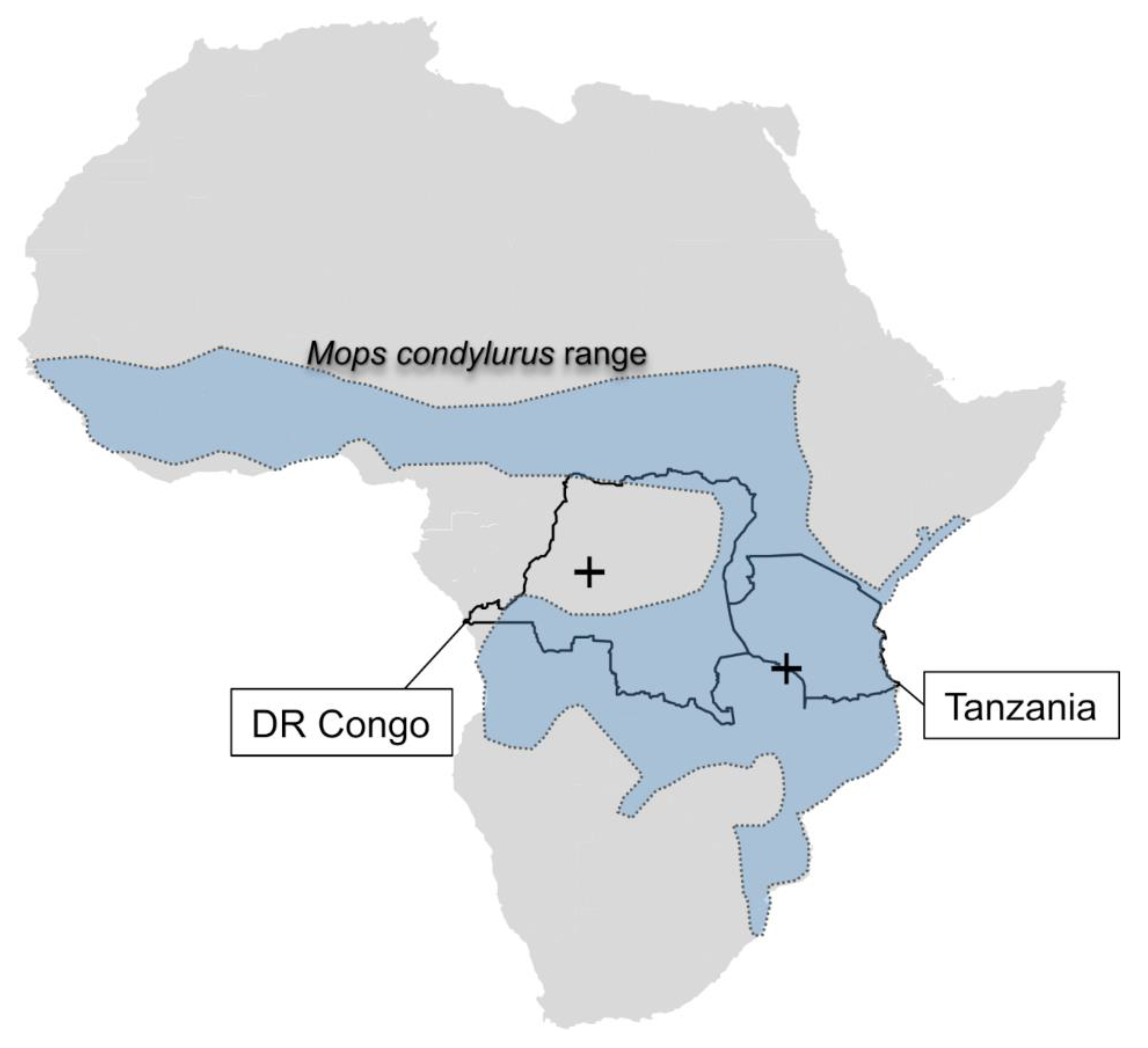
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vaheri, A.; Strandin, T.; Hepojoki, J.; Sironen, T.; Henttonen, H.; Mäkelä, S.; Mustonen, J. Uncovering the Mysteries of Hantavirus Infections. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruger, D.H.; Figueiredo, L.T.M.; Song, J.-W.; Klempa, B. Hantaviruses—Globally Emerging Pathogens. J. Clin. Virol. 2015, 64, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klempa, B.; Fichet-Calvet, E.; Lecompte, E.; Auste, B.; Aniskin, V.; Meisel, H.; Denys, C.; Koivogui, L.; ter Meulen, J.; Krüger, D.H. Hantavirus in African Wood Mouse, Guinea. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 838–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klempa, B.; Fichet-Calvet, E.; Lecompte, E.; Auste, B.; Aniskin, V.; Meisel, H.; Barrière, P.; Koivogui, L.; ter Meulen, J.; Krüger, D.H. Novel Hantavirus Sequences in Shrew, Guinea. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 520–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, S.; Witkowski, P.T.; Auste, B.; Nowak, K.; Weber, N.; Fahr, J.; Mombouli, J.-V.; Wolfe, N.D.; Drexler, J.F.; Drosten, C.; et al. Hantavirus in Bat, Sierra Leone. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumibcay, L.; Kadjo, B.; Gu, S.H.; Kang, H.J.; Lim, B.K.; Cook, J.A.; Song, J.-W.; Yanagihara, R. Divergent Lineage of a Novel Hantavirus in the Banana Pipistrelle (Neoromicia nanus) in Côte d’Ivoire. Virol. J. 2012, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klempa, B.; Koivogui, L.; Sylla, O.; Koulemou, K.; Auste, B.; Krüger, D.H.; ter Meulen, J. Serological Evidence of Human Hantavirus Infections in Guinea, West Africa. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 201, 1031–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowski, P.T.; Leendertz, S.A.J.; Auste, B.; Akoua-Koffi, C.; Schubert, G.; Klempa, B.; Muyembe-Tamfum, J.-J.; Karhemere, S.; Leendertz, F.H.; Krüger, D.H. Human Seroprevalence Indicating Hantavirus Infections in Tropical Rainforests of Côte d’Ivoire and Democratic Republic of Congo. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinemann, P.; Tia, M.; Alabi, A.; Anon, J.-C.; Auste, B.; Essbauer, S.; Gnionsahe, A.; Kigninlman, H.; Klempa, B.; Kraef, C.; et al. Human Infections by Non-Rodent-Associated Hantaviruses in Africa. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 214, 1507–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, S.; Yanagihara, R. Genetic Diversity and Geographic Distribution of Bat-Borne Hantaviruses. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2020, 39, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laenen, L.; Vergote, V.; Calisher, C.H.; Klempa, B.; Klingström, J.; Kuhn, J.H.; Maes, P. Hantaviridae: Current Classification and Future Perspectives. Viruses 2019, 11, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H. Aligning Sequence Reads, Clone Sequences and Assembly Contigs with BWA-MEM. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1303.3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castresana, J. Selection of Conserved Blocks from Multiple Alignments for Their Use in Phylogenetic Analysis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000, 17, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouy, M.; Guindon, S.; Gascuel, O. SeaView Version 4: A Multiplatform Graphical User Interface for Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Tree Building. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.-F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New Algorithms and Methods to Estimate Maximum-Likelihood Phylogenies: Assessing the Performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefort, V.; Longueville, J.-E.; Gascuel, O. SMS: Smart Model Selection in PhyML. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 2422–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelan, S.; Goldman, N. A General Empirical Model of Protein Evolution Derived from Multiple Protein Families Using a Maximum-Likelihood Approach. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2001, 18, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, H.A.; Strimmer, K.; Vingron, M.; von Haeseler, A. TREE-PUZZLE: Maximum Likelihood Phylogenetic Analysis Using Quartets and Parallel Computing. Bioinformatics 2002, 18, 502–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.E.; Purvis, A.; MacLarnon, A.; Bininda-Emonds, O.R.P.; Simmons, N.B. A Phylogenetic Supertree of the Bats (Mammalia: Chiroptera). Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2002, 77, 223–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, S.; Taniguchi, S.; Aoki, K.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Kyuwa, S.; Tanaka-Taya, K.; Masangkay, J.S.; Omatsu, T.; Puentespina, R.; Watanabe, S.; et al. Molecular Phylogeny of a Genetically Divergent Hantavirus Harbored by the Geoffroy’s Rousette (Rousettus amplexicaudatus), a Frugivorous Bat Species in the Philippines. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 45, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, J.H.; Adkins, S.; Agwanda, B.R.; Al Kubrusli, R.; Alkhovsky, S.V.; Amarasinghe, G.K.; Avšič-Županc, T.; Ayllón, M.A.; Bahl, J.; Balkema-Buschmann, A.; et al. 2021 Taxonomic Update of Phylum Negarnaviricota (Riboviria: Orthornavirae), Including the Large Orders Bunyavirales and Mononegavirales. Arch. Virol. 2021, 166, 3513–3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witkowski, P.T.; Drexler, J.F.; Kallies, R.; Ličková, M.; Bokorová, S.; Maganga, G.D.; Szemes, T.; Leroy, E.M.; Krüger, D.H.; Drosten, C.; et al. Phylogenetic Analysis of a Newfound Bat-Borne Hantavirus Supports a Laurasiatherian Host Association for Ancestral Mammalian Hantaviruses. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 41, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Těšíková, J.; Bryjová, A.; Bryja, J.; Lavrenchenko, L.A.; Goüy de Bellocq, J. Hantavirus Strains in East Africa Related to Western African Hantaviruses. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2017, 17, 278–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariwa, H.; Fujiki, M.; Yoshimatsu, K.; Arikawa, J.; Takashima, I.; Hashimoto, N. Urine-Associated Horizontal Transmission of Seoul Virus among Rats. Arch. Virol. 1998, 143, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safronetz, D.; Lindsay, R.; Dibernardo, A.; Hjelle, B.; Xiao, R.; Artsob, H.; Drebot, M.A. A Preliminary Study of the Patterns of Sin Nombre Viral Infection and Shedding in Naturally Infected Deer Mice (Peromyscus maniculatus). Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2005, 5, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monadjem, A.; Cotterill, F.; Hutson, A.M.; Mickleburgh, S.; Bergmans, W. Mops condylurus. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2017: E.T13838A22075340. Available online: https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-2.RLTS.T13838A22075340.en (accessed on 27 September 2022).
- Goldstein, T.; Anthony, S.J.; Gbakima, A.; Bird, B.H.; Bangura, J.; Tremeau-Bravard, A.; Belaganahalli, M.N.; Wells, H.L.; Dhanota, J.K.; Liang, E.; et al. The Discovery of Bombali Virus Adds Further Support for Bats as Hosts of Ebolaviruses. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 1084–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareinen, L.; Ogola, J.; Kivistö, I.; Smura, T.; Aaltonen, K.; Jääskeläinen, A.J.; Kibiwot, S.; Masika, M.M.; Nyaga, P.; Mwaengo, D.; et al. Range Expansion of Bombali Virus in Mops condylurus Bats, Kenya, 2019. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 3007–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.J.; Stanley, W.T.; Esselstyn, J.A.; Gu, S.H.; Yanagihara, R. Expanded Host Diversity and Geographic Distribution of Hantaviruses in Sub-Saharan Africa. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 7663–7667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.-P.; Lin, X.-D.; Wang, W.; Tian, J.-H.; Cong, M.-L.; Zhang, H.-L.; Wang, M.-R.; Zhou, R.-H.; Wang, J.-B.; Li, M.-H.; et al. Phylogeny and Origins of Hantaviruses Harbored by Bats, Insectivores, and Rodents. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, S.; Nguyen, S.T.; Boldgiv, B.; Fukui, D.; Araki, K.; Dang, C.N.; Ohdachi, S.D.; Nguyen, N.X.; Pham, T.D.; Boldbaatar, B.; et al. Novel Bat-Borne Hantavirus, Vietnam. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 1159–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, S.; Kikuchi, F.; Bawm, S.; Sơn, N.T.; Lin, K.S.; Tú, V.T.; Aoki, K.; Tsuchiya, K.; Tanaka-Taya, K.; Morikawa, S.; et al. Molecular Phylogeny of Mobatviruses (Hantaviridae) in Myanmar and Vietnam. Viruses 2019, 11, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Sample ID | Sex | Location | GPS | Lung | Liver | Kidney | Spleen | Intestine |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TZ117 | male | Kajunjumele | −9.609889, 33.913750 | + | - | - | - | NA |
| TZ120 | male | Kajunjumele | −9.609889, 33.913750 | + | + | NA | ||
| TZ123 | male | Kajunjumele | −9.609889, 33.913750 | NA | NA | |||
| TZ154 | male | Kyela | −9.602364, 33.925929 | + | + | + | ++ | + |
| TZ157 | female | Kyela | −9.602364, 33.925929 | ++ | + | + | +++ | + |
| TZ161 | male | Kyela | −9.602364, 33.925929 | |||||
| DRC348 | NA | Lompole | −2.5881744, 20.3696069 | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| NC_034401 Quezon Virus | NC_005632 Robina Virus | DRC348 Lompole | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TZ117 | 82.1 | 80.0 | 98.6 |
| TZ120 | 81.4 | 80.0 | 98.6 |
| TZ123 | 82.1 | 80.7 | 98.6 |
| TZ154 | 82.1 | 80.0 | 98.6 |
| TZ157 | 82.1 | 80.7 | 98.6 |
| TZ161 | 82.1 | 80.7 | 98.6 |
| DRC348 | 82.9 | 81.4 |
| Kiwira Virus Samples | Pairwise Identity [%] to Quezon Virus 2 | Pairwise Identity [%] to Robina Virus 3 | Number of Mapped Reads |
|---|---|---|---|
| TZ154S | 87.4 | 88.3 | 39,234 |
| TZ157S | 85.4 | 86.4 | 2480 |
| TZ154L | 82.9 | 83.7 | 1,997,514 |
| TZ157L | 80.4 | 81.6 | 1,478,369 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weiss, S.; Sudi, L.E.; Düx, A.; Mangu, C.D.; Ntinginya, N.E.; Shirima, G.M.; Köndgen, S.; Schubert, G.; Witkowski, P.T.; Muyembe, J.-J.; et al. Kiwira Virus, a Newfound Hantavirus Discovered in Free-tailed Bats (Molossidae) in East and Central Africa. Viruses 2022, 14, 2368. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14112368
Weiss S, Sudi LE, Düx A, Mangu CD, Ntinginya NE, Shirima GM, Köndgen S, Schubert G, Witkowski PT, Muyembe J-J, et al. Kiwira Virus, a Newfound Hantavirus Discovered in Free-tailed Bats (Molossidae) in East and Central Africa. Viruses. 2022; 14(11):2368. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14112368
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeiss, Sabrina, Lwitiho E. Sudi, Ariane Düx, Chacha D. Mangu, Nyanda Elias Ntinginya, Gabriel M. Shirima, Sophie Köndgen, Grit Schubert, Peter T. Witkowski, Jean-Jacques Muyembe, and et al. 2022. "Kiwira Virus, a Newfound Hantavirus Discovered in Free-tailed Bats (Molossidae) in East and Central Africa" Viruses 14, no. 11: 2368. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14112368
APA StyleWeiss, S., Sudi, L. E., Düx, A., Mangu, C. D., Ntinginya, N. E., Shirima, G. M., Köndgen, S., Schubert, G., Witkowski, P. T., Muyembe, J.-J., Ahuka, S., Klempa, B., Leendertz, F. H., & Krüger, D. H. (2022). Kiwira Virus, a Newfound Hantavirus Discovered in Free-tailed Bats (Molossidae) in East and Central Africa. Viruses, 14(11), 2368. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14112368








