Molecular Characterization and Seroprevalence of Hepatitis E Virus in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients and Solid Organ Transplant Recipients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Serum Samples
- Patients hospitalized in Hospital of Lithuanian University Health Sciences Kaunas Clinics (HLUHSKC) Gastroenterology clinic and diagnosed with IBD (n = 203). All samples were assigned into 2 groups based on clinical characteristics, namely patients with diagnosed UC (n = 156) or CD (n = 47). In addition, all IBD patients were assigned into groups based on whether they have (n = 42) or have not (n = 161) received biological therapy (anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF) (infliximab/adalimumab) antibody protocol). Samples from anti-TNF therapy group patients were collected during the maintenance stage of the treatment. Samples were collected from 2015 to 2020, stored, and retrospectively tested for the presence of anti-HEV antibodies and HEV RNA.
- SOT recipients were hospitalized in HLUHSKC Nephrology clinic and Gastroenterology clinic (n = 63). Samples were collected during post-transplantation visitations. All samples were assigned into 2 groups based on allograft type, namely kidney (n = 58) and liver (n = 5). Samples were collected from 2019 to 2020 and tested immediately after collection.
- Healthy control group (n = 100) of individuals without clinical IBD diagnosis or SOT. Sufficient representation of different age groups and genders was achieved by the inclusion of an equal number of samples from each category. Samples were collected from 2015 to 2017, stored, and retrospectively tested for the presence of anti-HEV antibodies and HEV RNA.
2.2. Serological Testing
2.3. Molecular Diagnostics
2.4. Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. Viral Stock Preparation and Cell Line Infection
2.6. Immunofluorescence Assay and Confocal Microscopy
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
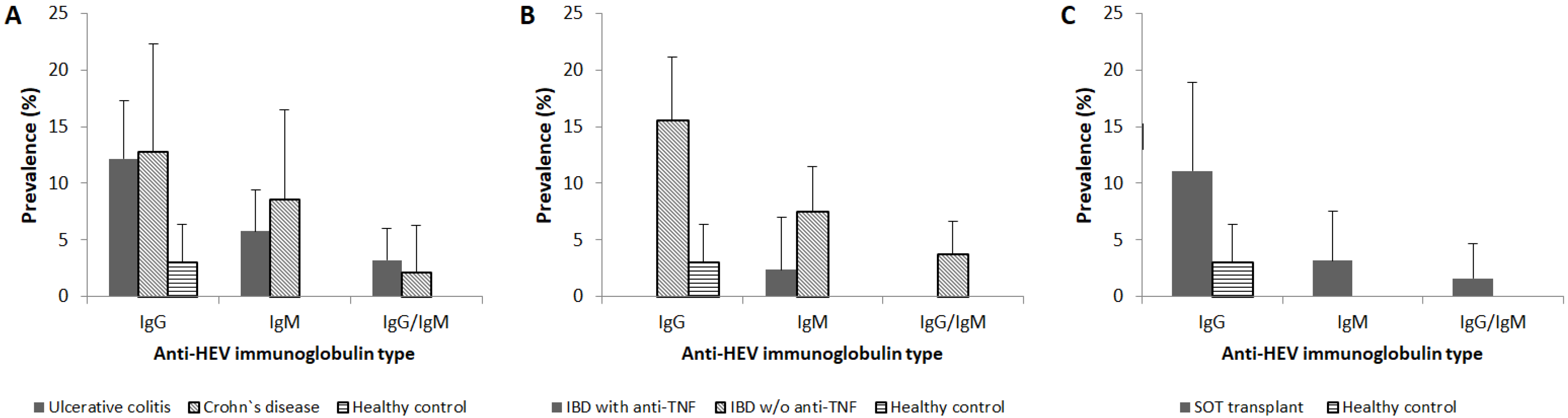
3.1. HEV Seroprevalence in IBD Patients and SOT Recipients
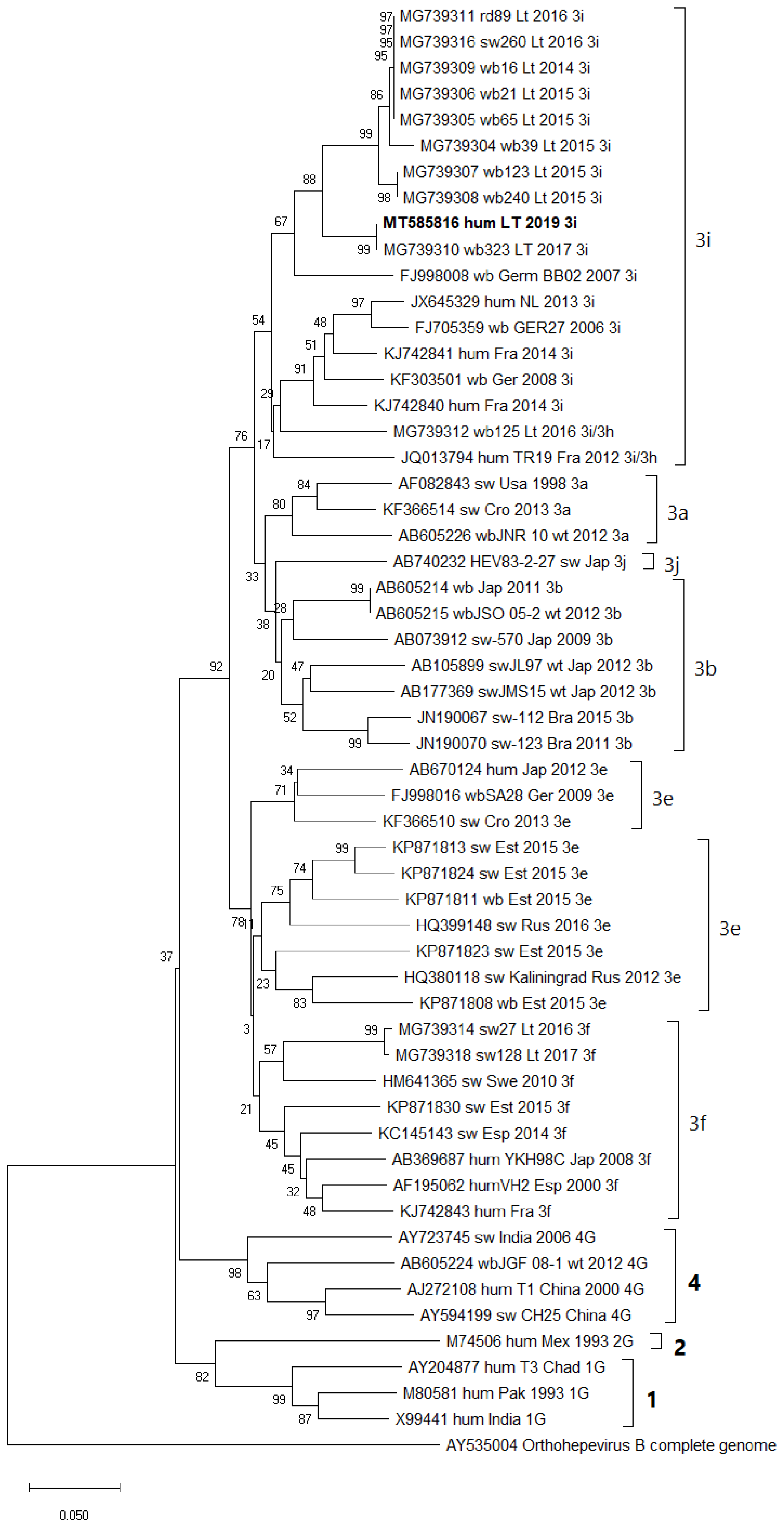
3.2. RNA Detection and Molecular Characteristics of HEV in Lithuanian IBD Patients and SOT Recipients
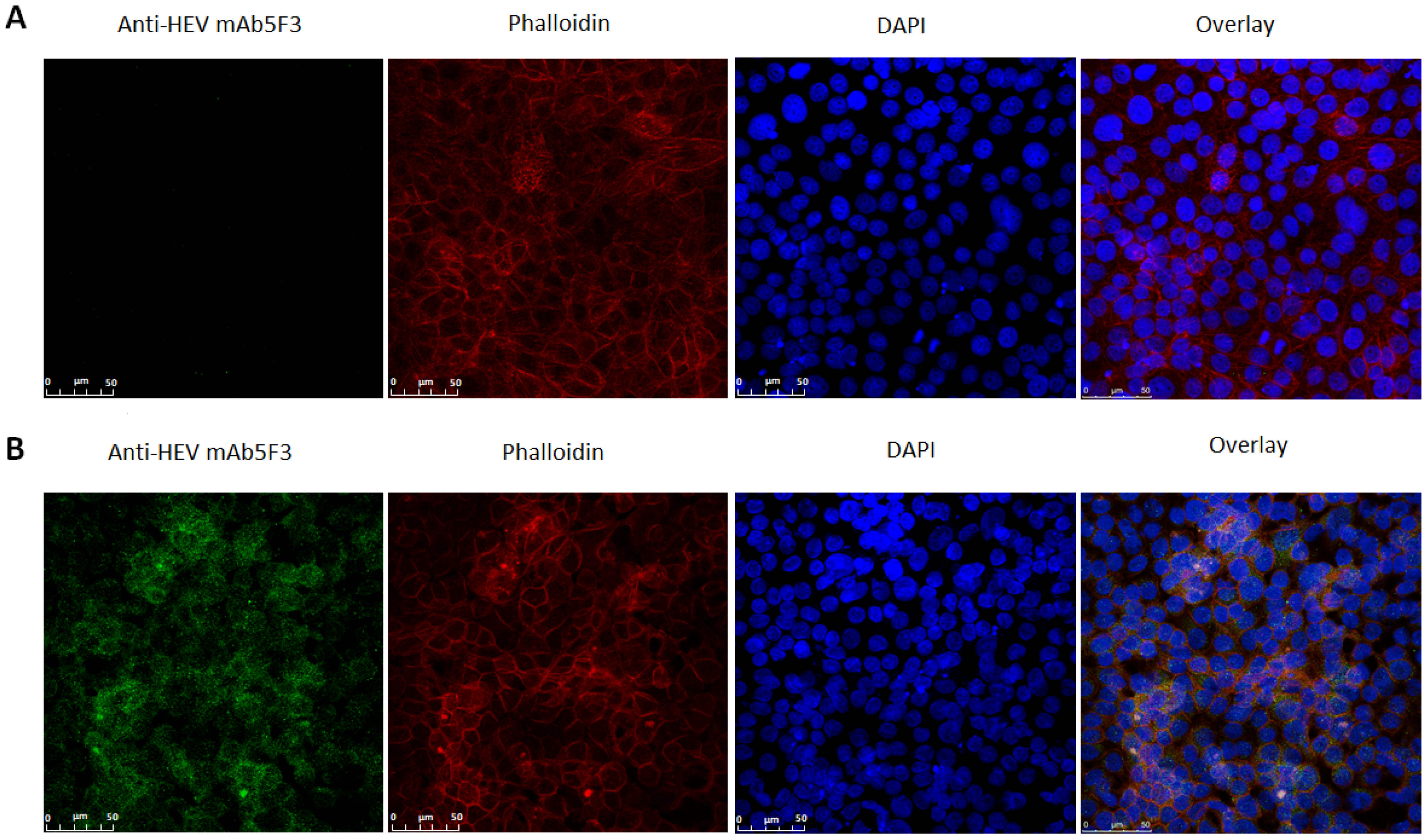
3.3. HEV Isolate Propagation in MARC-145 Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spahr, C.; Knauf-Witzens, T.; Vahlenkamp, T.; Ulrich, R.G.; Johne, R. Hepatitis E virus and related viruses in wild, domestic and zoo animals: A review. Zoonoses Public Health 2018, 65, 11–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruso, C.; Peletto, S.; Rosamilia, A.; Modesto, P.; Chiavacci, L.; Sona, B.; Balsamelli, F.; Ghisetti, V.; Acutis, P.L.; Pezzoni, G.; et al. Hepatitis E virus: A cross-sectional serological and virological study in pigs and humans at zoonotic risk within a high-density pig farming area. Transbound Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 1443–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlosser, J.; Eiden, M.; Vina-Rodriguez, A.; Fast, C.; Dremsek, P.; Lange, E.; Rainer, G.U.; Groschup, M.H. Natural and experimental hepatitis E virus genotype 3-infection in European wild boar is transmissible to domestic pigs. Vet. Res. 2014, 45, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ek, W.E.; D’Amato, M.; Halfvarson, J. The history of genetics in inflammatory bowel disease. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2014, 27, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abegunde, A.T.; Muhammad, B.H.; Bhatti, O.; Ali, T. Environmental risk factors for inflammatory bowel diseases: Evidence based literature review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 6296–6317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciccocioppo, R.; Racca, F.; Paolucci, S.; Campanini, G.; Pozzi, L.; Betti, E.; Riboni, R.; Alessandro, V.; Baldanti, F.; Corazza, G.R. Human cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr virus infection in inflammatory bowel disease: Need for mucosal viral load measurement. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 1915–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biancone, L.; Pavia, M.; Del Vecchio Blanco, G.; D’Incà, R.; Castiglione, F.; De Nigris, F.; Doldo, P.; Cosco, C.; Vavassori, P.; Bresci, G.P.; et al. Hepatitis B and C virus infection in Crohn’s disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2001, 7, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevaux, J.-B.; Nani, A.; Oussalah, A.; Venard, V.; Bensenane, M.; Belle, A.; Gueant, J.L.; Bigard, M.A.; Bronowicki, J.P.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L. Prevalence of hepatitis B and C and risk factors for nonvaccination in inflammatory bowel disease patients in Northeast France. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2010, 16, 916–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loras, C.; Saro, C.; Gonzalez-Huix, F.; Mínguez, M.; Merino, O.; Gisbert, J.P.; Barrio, J.; Bernal, A.; Gutiérrez, A.; Piqueras, A.; et al. Prevalence and factors related to hepatitis B and C in inflammatory bowel disease patients in Spain: A nationwide, multicenter study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 104, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krain, L.J.; Nelson, K.E.; Labrique, A.B. Host immune status and response to hepatitis E virus infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 139–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Kumagai, I.; Yoshida, Y.; Miyasaka, A.; Takikawa, Y.; Kamiya, R.; Kondo, K.; Kato, A.; Chiba, T.; Okamoto, H. Asymptomatic acute hepatitis E in a female patient with ulcerative colitis. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 10, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haagsma, E.B.; van den Berg, A.P.; Porte, R.J.; Benne, C.A.; Vennema, H.; Reimerink, J.H.J.; Koopmans, M.P.G. Chronic hepatitis E virus infection in liver transplant recipients. Liver Dis. Int. Liver Transpl. Soc. 2008, 14, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komolmit, P.; Oranrap, V.; Suksawatamnuay, S.; Thanapirom, K.; Sriphoosanaphan, S.; Srisoonthorn, N.; Posuwan, N.; Thongmee, T.; Treeprasertsuk, S.; Poovorawan, Y. Clinical significance of post-liver transplant hepatitis E seropositivity in high prevalence area of hepatitis E genotype 3: A prospective study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartl, J.; Otto, B.; Madden, R.G.; Webb, G.; Woolson, K.L.; Kriston, L.; Vettorazzi, E.; Lohse, A.W.; Dalton, H.R.; Pischke, S. Hepatitis E seroprevalence in Europe: A meta-analysis. Viruses 2016, 8, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlosser, B.; Stein, A.; Neuhaus, R.; Pahl, S.; Ramez, B.; Krüger, D.H.; Berg, T.; Hofmann, J. Liver transplant from a donor with occult HEV infection induced chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis in the recipient. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 500–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adlhoch, C.; Wolf, A.; Meisel, H.; Kaiser, M.; Ellerbrok, H.; Pauli, G.; High, H.E.V. Presence in four different wild boar populations in East and West Germany. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 139, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spancerniene, U.; Buitkuviene, J.; Grigas, J.; Pampariene, I.; Salomskas, A.; Cepuliene, R.; Zymantiene, J.; Stankevicius, A. Seroprevalence of hepatitis E virus in Lithuanian domestic pigs and wildlife. Acta Vet. Brno. 2017, 85, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, T.V.; Ivanova-Pozdejeva, A.; Reshetnjak, I.; Geller, J.; Värv, K.; Rumvolt, R.; Vikentjeva, M.; Trubnikova, E.V.; Pozdniakova, N.; Shevelev, A.B.; et al. Hepatitis E virus infection in different groups of Estonian patients and people who inject drugs. J. Clin. Virol. Off. Public Pan. Am. Soc. Clin. Virol. 2018, 104, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bura, M.; Łagiedo, M.; Michalak, M.; Sikora, J.; Mozer-Lisewska, I. Hepatitis E virus IgG seroprevalence in HIV patients and blood donors, west-central Poland. Int. J. Infect. Dis. Off. Public Int. Soc. Infect. Dis. 2017, 61, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haagsman, A.; Reuter, G.; Duizer, E.; Nagy, G.; Herremans, T.; Koopmans, M.; Szücs, G. Seroepidemiology of hepatitis E virus in patients with non-A, non-B, non-C hepatitis in Hungary. J. Med. Virol. 2007, 79, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steponaitiene, R.; Kupcinskas, J.; Survilaite, S.; Varkalaite, G.; Jonaitis, L.; Kiudelis, G.; Denapiene, G.; Valantinas, J.; Skieceviciene, J.; Kupcinskas, L. TPMT and ITPA genetic variants in Lithuanian inflammatory bowel disease patients: Prevalence and azathioprine-related side effects. Adv. Med. Sci. 2016, 61, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burisch, J.; Bergemalm, D.; Halfvarson, J.; Domislovic, V.; Krznaric, Z.; Goldis, A.; Dahlerup, J.F.; Oksanen, P.; Collin, P.; de Castro, L.; et al. The use of 5-aminosalicylate for patients with Crohn’s disease in a prospective European inception cohort with 5 years follow-up—An Epi-IBD study. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2020, 8, 949–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burisch, J.; Vardi, H.; Schwartz, D.; Friger, M.; Kiudelis, G.; Kupčinskas, J.; Fumery, M.; Gower-Rousseau, C.; Lakatos, L.; Lakatos, P.L.; et al. Health-care costs of inflammatory bowel disease in a pan-European, community-based, inception cohort during 5 years of follow-up: A population-based study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basyte-Bacevice, V.; Skieceviciene, J.; Valantiene, I.; Sumskiene, J.; Petrenkiene, V.; Kondrackiene, J.; Petrauskas, D.; Lammert, F.; Kupcinskas, J. SERPINA1 and HSD17B13 gene variants in patients with liver fibrosis and cirrhosis. J. Gastrointest. Liver Dis. 2019, 28, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupcinskas, J.; Valantiene, I.; Varkalaitė, G.; Steponaitiene, R.; Skieceviciene, J.; Sumskiene, J.; Petrenkiene, V.; Kondrackiene, J.; Kiudelis, G.; Lammert, F.; et al. PNPLA3 and RNF7 gene variants are associated with the risk of developing liver fibrosis and cirrhosis in an eastern European population. J. Gastrointest. Liver Dis. 2017, 26, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basyte-Bacevice, V.; Skieceviciene, J.; Valantiene, I.; Sumskiene, J.; Petrenkiene, V.; Kondrackiene, J.; Petrauskas, D.; Lammert, F.; Kupcinskas, J. TM6SF2 and MBOAT7 gene variants in liver fibrosis and cirrhosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelman, S.; Salteniene, V.; Pranculis, A.; Skieceviciene, J.; Zykus, R.; Petrauskas, D.; Kupcinskas, L.; Canbay, A.; Link, A.; Kupcinskas, J. Plasma Nogo-A and placental growth factor levels are associated with portal hypertension in patients with liver cirrhosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 2935–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spancerniene, U.; Grigas, J.; Buitkuviene, J.; Zymantiene, J.; Juozaitiene, V.; Stankeviciute, M.; Razukevicius, D.; Zienius, D.; Stankevicius, A. Prevalence and phylogenetic analysis of hepatitis E virus in pigs, wild boars, roe deer, red deer and moose in Lithuania. Acta Vet. Scand. 2018, 60, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, M.; Bendall, R.; Grierson, S.; Heath, G.; Mitchell, J.; Dalton, H. Human and porcine hepatitis E virus strains, United Kingdom. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 953–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigas, J.; Simkute, E.; Simanavicius, M.; Pautienius, A.; Streimikyte-Mockeliune, Z.; Razukevicius, D.; Stankevicius, A. Hepatitis E genotype 3 virus isolate from wild boar is capable of replication in non-human primate and swine kidney cells and mouse neuroblastoma cells. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simanavicius, M.; Tamosiunas, P.L.; Petraityte-Burneikiene, R.; Johne, R.; Ulrich, R.G.; Zvirbliene, A.; Kucinskaite-Kodze, I. Generation in yeast and antigenic characterization of hepatitis E virus capsid protein virus-like particles. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Serrano, P.; Pérez-Calle, J.L.; Sánchez-Tembleque, M.D. Hepatitis B and inflammatory bowel disease: Role of antiviral prophylaxis. World J Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 1342–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomba, R.; Liang, T.J. Hepatitis B reactivation associated with immune suppressive and biological modifier therapies: Current concepts, management strategies and future directions. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 1297–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morisco, F.; Castiglione, F.; Rispo, A.; Stroffolini, T.; Vitale, R.; Sansone, S.; Granata, R.; Orlando, A.; Marmo, R.; Riegler, G.; et al. Hepatitis B virus infection and immunosuppressive therapy in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Dig. Liver Dis. 2011, 43, S40–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owada, Y.; Oshiro, Y.; Inagaki, Y.; Harada, H.; Fujiyama, N.; Kawagishi, N.; Yagisawa, T.; Usui, J.; Akutsu, N.; Itabashi, Y.; et al. A nationwide survey of hepatitis E virus infection and chronic hepatitis in heart and kidney transplant recipients in Japan. Transplantation 2020, 104, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahluwalia, B.; Moraes, L.; Magnusson, M.K.; Öhman, L. Immunopathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease and mechanisms of biological therapies. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goetz, M.; Atreya, R.; Ghalibafian, M.; Galle, P.R.; Neurath, M.F. Exacerbation of ulcerative colitis after rituximab salvage therapy. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2007, 13, 1365–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neurath, M.F. Cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buescher, G.; Ozga, A.-K.; Lorenz, E.; Pischke, S.; May, J.; Addo, M.M.; Horvatits, T. Hepatitis E seroprevalence and viremia rate in immunocompromised patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Liver Int. 2021, 41, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamar, N.; Selves, J.; Mansuy, J.-M.; Ouezzani, L.; Péron, J.-M.; Guitard, J.; Cointault, O.; Esposito, L.; Abravanel, F.; Danjoux, M.; et al. Hepatitis E virus and chronic hepatitis in organ-transplant recipients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; de Man, R.A.; de Knegt, R.J.; Metselaar, H.J.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Pan, Q. Epidemiology and management of chronic hepatitis E infection in solid organ transplantation: A comprehensive literature review. Rev. Med. Virol. 2013, 23, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scotto, G.; Aucella, F.; Grandaliano, G.; Martinelli, D.; Querques, M.; Gesuete, A.; Infante, B.; Carri, P.D.; Massa, S.; Salatino, G.; et al. Hepatitis E in hemodialysis and kidney transplant patients in south-east Italy. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 3266–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamar, N.; Garrouste, C.; Haagsma, E.B.; Garrigue, V.; Pischke, S.; Chauvet, C.; Dumortier, J.; Cannesson, A.; Cassuto-Viguier, E.; Thervet, E.; et al. Factors associated with chronic hepatitis in patients with hepatitis E virus infection who have received solid organ transplants. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 1481–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinakos, Ε.; Gioula, G.; Liava, C.; Papa, A.; Papadopoulou, E.; Tsakni, E.; Fouzas, I.; Akriviadis, E. Prevalence of hepatitis E in liver transplant recipients in Greece. Epidemiol. Infect. 2018, 146, 1619–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, Y.; Oshiro, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Yoshizumi, T.; Okajima, H.; Ishiyama, K.; Nakanishi, C.; Hidaka, M.; Wada, H.; Hibi, T.; et al. A nationwide survey of hepatitis E virus infection and chronic hepatitis e in liver transplant recipients in Japan. EBioMedicine 2015, 2, 1607–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riveiro-Barciela, M.; Buti, M.; Homs, M.; Campos-Varela, I.; Cantarell, C.; Crespo, M.; Castells, L.; Tabernero, D.; Quer, J.; Rafael, E.; et al. Cirrhosis, liver transplantation and HIV infection are risk factors associated with hepatitis E virus infection. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harritshøj, L.H.; Hother, C.E.; Sengeløv, H.; Daugaard, G.; Sørensen, S.S.; Jacobsen, S.; Perch, M.; Holm, D.K.; Sækmose, S.G.; Aagaard, B.; et al. Epidemiology of hepatitis E virus infection in a cohort of 4023 immunocompromised patients. Int. J. Infect. Dis. Off. Public Int. Soc. Infect. Dis. 2020, 91, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cangin, C.; Focht, B.; Harris, R.; Strunk, J.A. Hepatitis E seroprevalence in the United States: Results for immunoglobulins IGG and IGM. J. Med. Virol. 2019, 91, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ditah, I.; Ditah, F.; Devaki, P.; Ditah, C.; Kamath, P.S.; Charlton, M. Current epidemiology of hepatitis E virus infection in the United States: Low seroprevalence in the National Health and Nutrition Evaluation Survey. Hepatol. Baltim. Md. 2014, 60, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heil, J.; Hoebe, C.J.P.A.; Loo IHM van Cals, J.W.L.; van Liere, G.A.F.S.; Dukers-Muijrers, N.H.T.M. Hepatitis E prevalence in a sexual high-risk population compared to the general population. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191798. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, B.C.; Lyra, A.C.; Rocha, R.; Santana, G.O. Epidemiology, demographic characteristics and prognostic predictors of ulcerative colitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 9458–9467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, H.J. Natural history and long-term clinical course of Crohn’s disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, E.; Takeda, N.; Tian-Chen, L.; Orii, K.; Ichijo, T.; Matsumoto, A.; Yoshizawa, K.; Iijima, T.; Takayama, T.; Miyamura, T.; et al. Seroepidemiological study of hepatitis E virus infection in Japan using a newly developed antibody assay. J. Gastroenterol. 2001, 36, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himmelsbach, K.; Bender, D.; Hildt, E. Life cycle and morphogenesis of the hepatitis E virus. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyson, D.A. A comprehensive review of apples and apple components and their relationship to human health. Adv. Nutr. 2011, 2, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Li, C.; Hagedorn, C.H. Phylogenetic analysis of global hepatitis E virus sequences: Genetic diversity, subtypes and zoonosis. Rev. Med. Virol. 2006, 16, 5–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, N.; D’Agostino, M.; Johne, R. Potential approaches to assess the infectivity of hepatitis E virus in pork products: A review. Food Environ. Virol. 2017, 9, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaussade, H.; Rigaud, E.; Allix, A.; Carpentier, A.; Touzé, A.; Delzescaux, D.; Choutet, P.; Garcia-Bonnet, N.; Coursaget, P. Hepatitis E virus seroprevalence and risk factors for individuals in working contact with animals. J. Clin. Virol. Off. Public Pan. Am. Soc. Clin. Virol. 2013, 58, 504–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krumbholz, A.; Mohn, U.; Lange, J.; Motz, M.; Wenzel, J.J.; Jilg, W.; Walther, M.; Straube, E.; Wutzler, P.; Zell, R. Prevalence of hepatitis E virus-specific antibodies in humans with occupational exposure to pigs. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2012, 201, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Diagnosis | Sample Size (# Tested) | Age Range (Years) | Mean Age ± SD a (Years) | Gender (#M/#F b) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inflammatory bowel disease | 203 | 18–80 | 40 ± 15 | 118/85 |
| Ulcerative colitis | 156 | 18–80 | 40 ± 15 | 89/67 |
| W c anti-TNF treatment | 29 | 18–57 | 34 ± 12 | 16/13 |
| w/o d anti-TNF treatment | 127 | 19–80 | 43 ± 16 | 73/54 |
| Crohn’s disease | 47 | 18–67 | 36 ± 13 | 29/18 |
| w anti-TNF treatment | 13 | 19–55 | 34 ± 12 | 9/4 |
| w/o anti-TNF treatment | 34 | 18–67 | 38 ± 14 | 20/14 |
| Solid organ transplant recipients | 63 | 19–76 | 52 ± 14 | 48/15 |
| Liver allograft | 5 | 21–54 | 43 ± 13 | 3/2 |
| Kidney allograft | 58 | 19–76 | 52 ± 14 | 45/13 |
| Healthy control | 100 | 20–85 | 53 ± 19 | 50/50 |
| Total | 366 | 18–85 | 46 ± 17 | 216/150 |
| Healthy Control | Test Group Total | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| % IgG a Positive | (95%CI b) | % IgG Positive | (95%CI) | |
| Total | 3.0 | (0–6.3) | 12.0 | (8.1–15.9) |
| Age (years) | ||||
| <29 | 0 | 4.6 | (0–9.6) | |
| 30–39 | 0 | 18.0 | (7.4–28.7) | |
| 40–49 | 7.1 | (0–20.6) | 5.0 | (0–10.5) |
| 50–59 | 0 | 13.3 | (3.4–23.3) | |
| 60–69 | 0 | 29.0 | (13.1–45.0) | |
| ≥70 | 6.9 | (0–16.1) | 14.3 | (0–32.6) |
| Gender | ||||
| Male | 6.0 | (0–12.6) | 10.8 | (6.1–15.6) |
| Female | 0 | 14.0 | (7.2–20.8) | |
| Diagnosis | % IgG a Positive (95%CI b) | % IgM c Positive (95%CI) | % IgG/IgM Positive (95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inflammatory bowel disease | 12.3 (7.8–16.8) | 6.4 (3.0–9.8) | 3.0 (0.6–5.3) |
| Ulcerative colitis | |||
| ≤29 | 6.8 (0–14.3) | 2.3 (0–6.7) | 2.3 (0–6.7) |
| 30–39 | 18.8 (5.2–32.3) | 6.3 (0–14.6) | 3.1 (0–9.2) |
| 40–49 | 5.4 (0–12.7) | 8.1 (0–16.9) | 2.7 (0–7.9) |
| 50–59 | 0 | 4.6 (0–13.3) | 0 |
| 60–69 | 50.0 (23.8–76.2) | 14.3 (0–32.6) | 14.3 (0–32.6) |
| ≥70 | 14.3 (0–40.2) | 0 | 0 |
| Crohn’s disease | |||
| ≤29 | 0 | 12.5 (0–28.7) | 0 |
| 30–39 | 30.0 (1.6–58.4) | 20.0 (0–44.8) | 10.0 (0–28.6) |
| 40–49 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 50–59 | 25.0 (0–67.4) | 0 | 0 |
| 60–69 | 66.7 (13.3–100.0) | 0 | 0 |
| Solid organ transplant recipients | 11.1 (3.4–18.9) | 3.2 (0–7.5) | 1.6 (0–4.7) |
| ≤29 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 30–39 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 40–49 | 11.1 (0–31.6) | 0 | 0 |
| 50–59 | 26.3 (6.5–16.1) | 5.3 (0–15.3) | 5.3 (0–15.3) |
| 60–69 | 0 | 7.1 (0–20.6) | 0 |
| Factors | Anti-HEV a IgG b | |
|---|---|---|
| Odds Ratio (95% CI c) | p | |
| Age (years) | 1.032 (1.007–1.057) | <0.01 |
| Anti-TNF therapy | 0 | >0.05 |
| Inflammatory bowel disease | 4.541 (1.337–15.426) | <0.01 |
| Ulcerative colitis | 5.688 (1.633–19.817) | <0.01 |
| Crohn’s disease | 6.929 (1.628–29.487) | <0.01 |
| Solid organ transplant received | 4.042 (1.005–16.258) | <0.05 |
| Kidney allograft | 4.222 (0.979–18.213) | <0.05 |
| Liver allograft | 12.432 (0.992–155.757) | <0.05 |
| Gender | 0.958 (0.450–2.038) | >0.05 |
| No. | Patient ID | Age | Gender | Diagnosis | HEV ORF1 Positive | HEV ORF2 Positive | Anti-HEV a IgG b Positive | Anti-HEV IgM c Positive |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | BT1 | 22 | Female | UC d with anti-TNF treatment | + | + | − | − |
| 2 | KA1 | 45 | Female | Kidney allograft recipient | − | + | − | − |
| 3 | KA2 | 57 | Male | Kidney allograft recipient | + | − | + | − |
| 4 | KA3 | 76 | Male | Kidney allograft recipient | + | − | − | − |
| 5 | KA4 | 44 | Male | Kidney allograft recipient | + | − | − | − |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grigas, J.; Montoya, M.; Simkute, E.; Buitkus, M.; Zagrabskaite, R.; Pautienius, A.; Razukevicius, D.; Jonaitis, L.V.; Kiudelis, G.; Skieceviciene, J.; et al. Molecular Characterization and Seroprevalence of Hepatitis E Virus in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients and Solid Organ Transplant Recipients. Viruses 2021, 13, 670. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13040670
Grigas J, Montoya M, Simkute E, Buitkus M, Zagrabskaite R, Pautienius A, Razukevicius D, Jonaitis LV, Kiudelis G, Skieceviciene J, et al. Molecular Characterization and Seroprevalence of Hepatitis E Virus in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients and Solid Organ Transplant Recipients. Viruses. 2021; 13(4):670. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13040670
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrigas, Juozas, Maria Montoya, Evelina Simkute, Marius Buitkus, Ruta Zagrabskaite, Arnoldas Pautienius, Dainius Razukevicius, Laimas Virginijus Jonaitis, Gediminas Kiudelis, Jurgita Skieceviciene, and et al. 2021. "Molecular Characterization and Seroprevalence of Hepatitis E Virus in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients and Solid Organ Transplant Recipients" Viruses 13, no. 4: 670. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13040670
APA StyleGrigas, J., Montoya, M., Simkute, E., Buitkus, M., Zagrabskaite, R., Pautienius, A., Razukevicius, D., Jonaitis, L. V., Kiudelis, G., Skieceviciene, J., Vaiciuniene, R., Stankuviene, A., Bumblyte, I. A., Kupcinskas, J., & Stankevicius, A. (2021). Molecular Characterization and Seroprevalence of Hepatitis E Virus in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients and Solid Organ Transplant Recipients. Viruses, 13(4), 670. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13040670







