Residual and Late Onset Symptoms Appeared in a Patient with Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia in a Convalescence Stage
Abstract
1. Introduction
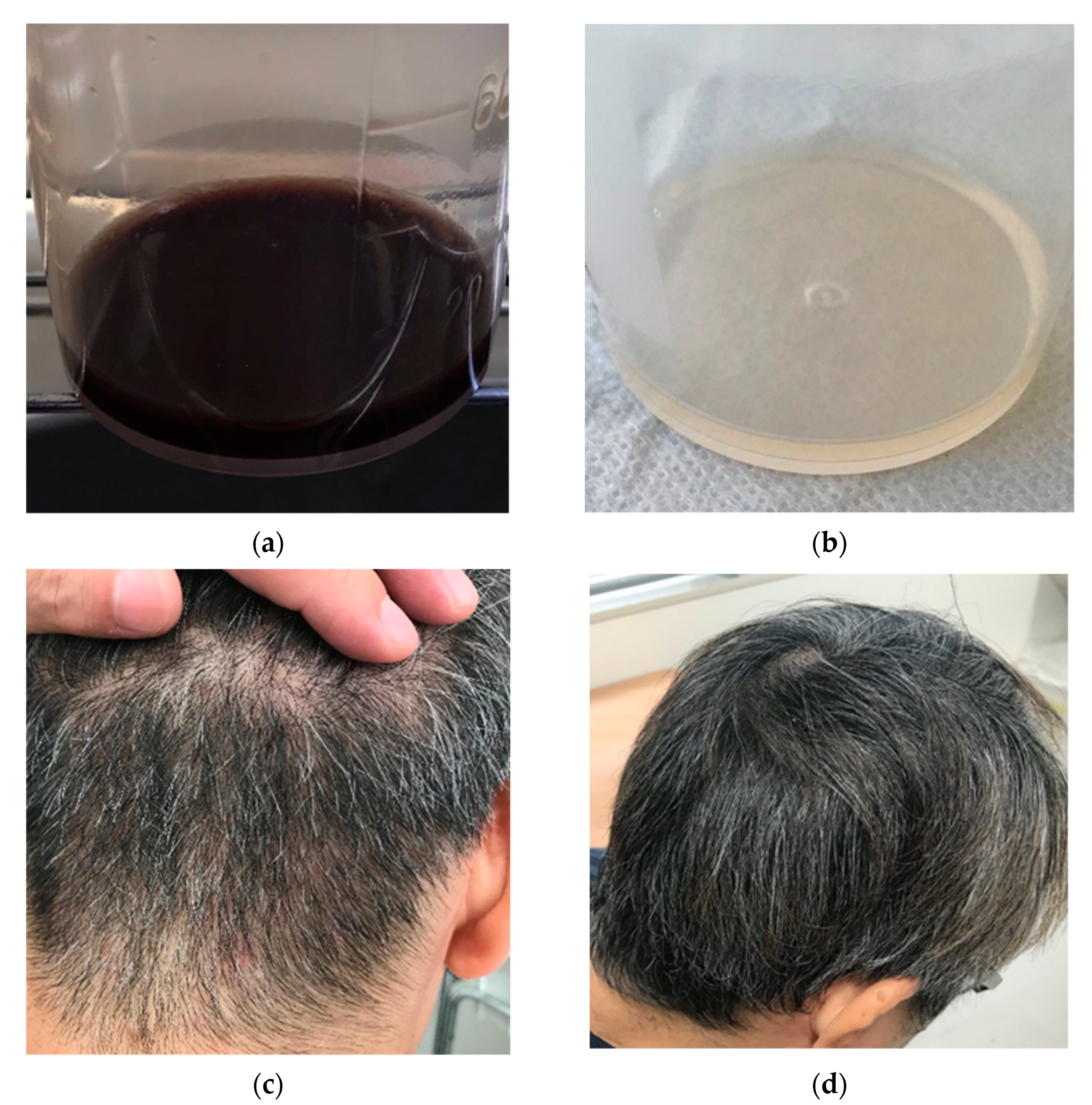
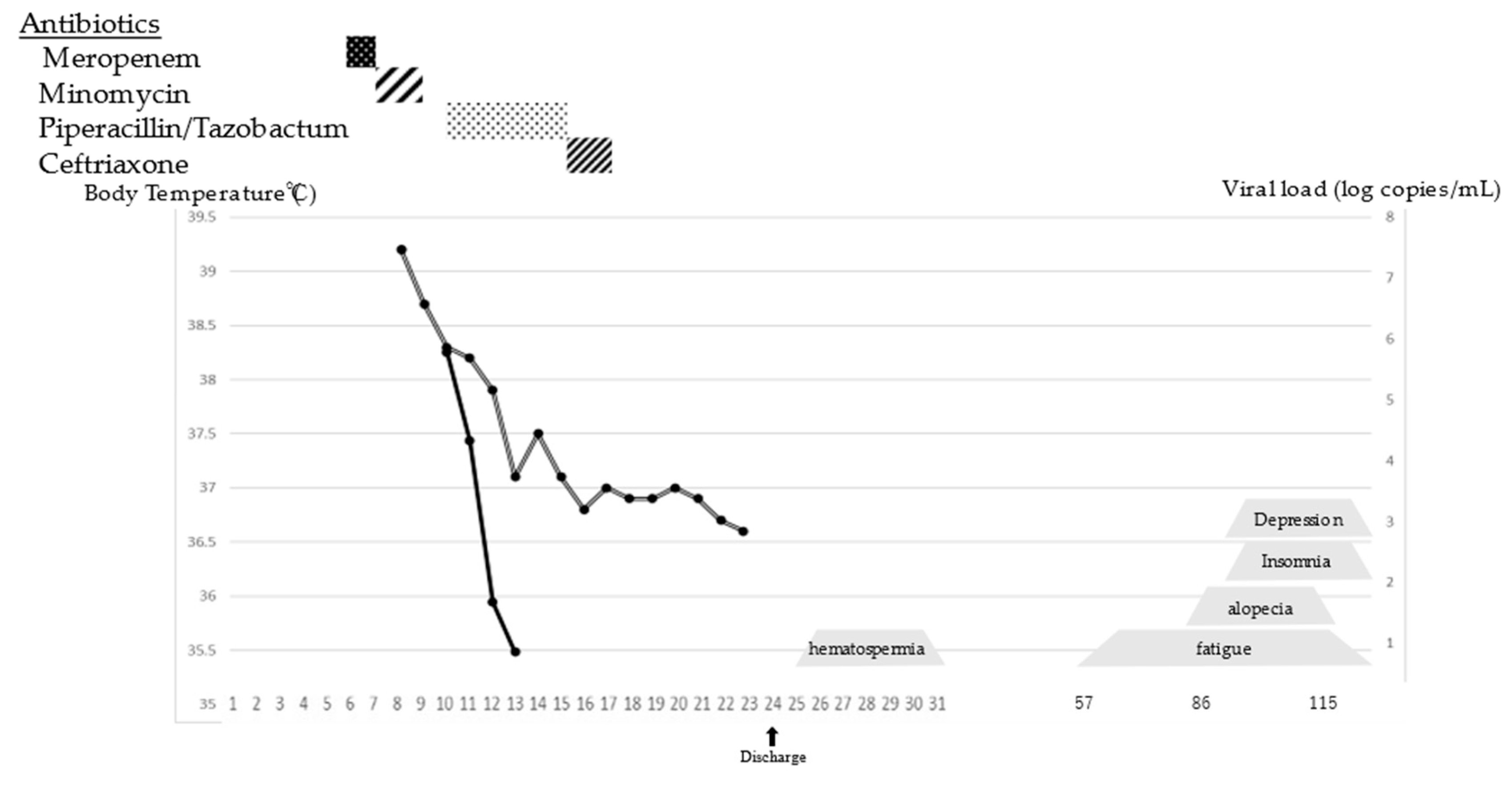
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saijo, M. Pathophysiology of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome and development of specific antiviral therapy. J. Infect. Chemother. 2018, 24, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, T.; Fukushi, S.; Tani, H.; Fukuma, A.; Taniguchi, S.; Toda, S.; Shimazu, Y.; Yano, K.; Morimitsu, T.; Ando, K.; et al. Sensitive and specific PCR systems for detection of both Chinese and Japanese severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus strains and prediction of patient survival based on viral load. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 3325–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, T.; Shimojima, M.; Fukushi, S.; Tani, H.; Fukuma, A.; Taniguchi, S.; Singh, H.; Suda, Y.; Shirabe, K.; Toda, S.; et al. Phylogenetic and geographic relationships of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in China, South Korea, and Japan. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Institute of Infectious Diseases. Summary of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Cases Reported to National Epidemiological Surveillance on Infectious Diseases (NESID). Available online: https://www.niid.go.jp/niid/ja/sfts/sfts-idwrs/7415-sfts-nesid.html (accessed on 3 March 2020). (In Japanese)
- Silvas, J.A.; Aguilar, P.V. The emergence of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 97, 992–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, J.T.; Sesay, F.R.; Massaquoi, T.A.; Idriss, B.R.; Sahr, F.; Semple, M.G. Post-ebola syndrome, Sierra Leone. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howlett, P.; Walder, A.; Lisk, D.; N’jai, A.; Lado, M.M.; Brown, C.; Sevalie, S.; Sesay, F.R.; Semple, M.G.; Scott, J.T. Neurological and psychiatric manifestations of post Ebola syndrome in Sierra Leone. Lancet 2017, 389 (Suppl. 1), S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogstraal, H. The epidemiology of tick-borne Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever in Asia, Europe, and Africa. J. Med. Entomol. 1979, 15, 307–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ergönül, O. Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2006, 6, 203–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houlihan, C.; Behrens, R. Lassa fever. BMJ 2017, 358, j2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, M.P.; Timen, A.; Vossen, A.C.T.M.; van Dissel, J.T. Marburg haemorrhagic fever in returning travellers: An overview aimed at clinicians. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 21, e28–e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rougeron, V.; Feldmann, H.; Grard, G.; Becker, S.; Leroy, E.M. Ebola and Marburg haemorrhagic fever. J. Clin. Virol. 2015, 64, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, S.V.; Law, T.J.; Needham, D.M. Long-term complications of critical care. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 39, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battle, C.E.; Lynch, C.; Thorpe, C.; Biggs, S.; Grobbelaar, K.; Morgan, A.; Roberts, S.; Thornton, E.; Hobrok, M.; Pugh, R. Incidence and risk factors for alopecia in survivors of critical illness: A multi-centre observational study. J. Crit. Care 2019, 50, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujikawa, K.; Koga, T.; Honda, T.; Uchida, T.; Okamoto, M.; Endo, Y.; Mihara, T.; Kondo, A.; Shimada, S.; Hayasaka, D.; et al. Serial analysis of cytokine and chemokine profiles and viral load in severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome: Case report and review of literature. Medicine 2019, 98, e17571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musso, D.; Roche, C.; Robin, E.; Nhan, T.; Teissier, A.; Cao-Lormeau, V.M. Potential sexual transmission of zika virus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gai, Z.; Liang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Jin, C.; Wang, S.W.; Sun, L.; Zhou, N.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, Y.; et al. Person-to-person transmission of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome bunyavirus through blood contact. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuru, M.; Suzuki, T.; Murakami, T.; Matsui, K.; Maeda, Y.; Yoshikawa, T.; Kurosu, T.; Shimojima, M.; Shimada, T.; Hasegawa, H.; et al. Pathological characteristics of a patient with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS) infected with SFTS virus through a sick cat’s bite. Viruses 2021, 13, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, S.; Takazono, T.; Ando, T.; Hayasaka, D.; Tashiro, M.; Saijo, T.; Kurihara, S.; Sekino, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Imamura, Y.; et al. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus RNA in semen, Japan. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 2127–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Test | Value | Reference Range |
|---|---|---|
| Leukocyte count | 1200 /µL | 3300–8600 /µL |
| %Neutrocyte | 61.8 % | |
| %Lymphocyte | 34.4 % | |
| Hemoglobin | 19.4 g/dL | 11.6–14.8 g/dL |
| Thrombocyte | 52,000 /µL | 158,000–348,000 /µL |
| Sodium | 134 mEq/L | 138–145 mEq/L |
| Potassium | 3.5 mEq/L | 3.6–4.8 mEq/L |
| Chloride | 97 mEq/L | 101–108 mEq/L |
| Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) | 44.0 mg/dL | 8.0–22.0 mg/dL |
| Creatinine | 1.97 mg/dL | 0.46–0.79 mg/dL |
| Glucose | 121 mg/dL | 70–109 mg/dL |
| Total bilirubin | 0.8 mg/dL | 0.4–1.5 mg/dL |
| Albumin | 3.6 g/dL | 3.9–5.3 g/dL |
| Alkaline phosphatase | 353 U/L | 106–332 U/L |
| Aspartate aminotransferase | 1019 U/L | 13–30 U/L |
| Alanine aminotransferase | 254 U/L | 7–23 U/L |
| Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase | 56 U/L | 10–80 U/L |
| Creatinine kinase | 14,853 U/L | 57–197 U/L |
| Lactate dehydrogenase | 480 U/L | 124–222 U/L |
| Prothrombin time-international normalized ratio | 1.09 | 0.90–1.10 |
| Activated partial thromboplastin time | 39.0 s | 25.0–40.0 s |
| Fibrinogen | 278 mg/dL | 200.0–400.0 mg/dL |
| D-dimer | 94.1 µg/mL | 0.00–1.00 µg/mL |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kanda, K.; Kinoshita, N.; Kutsuna, S.; Nakamura, K.; Okuhama, A.; Shimomura, A.; Inagaki, T.; Yoshikawa, T.; Kurosu, T.; Shimojima, M.; et al. Residual and Late Onset Symptoms Appeared in a Patient with Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia in a Convalescence Stage. Viruses 2021, 13, 657. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13040657
Kanda K, Kinoshita N, Kutsuna S, Nakamura K, Okuhama A, Shimomura A, Inagaki T, Yoshikawa T, Kurosu T, Shimojima M, et al. Residual and Late Onset Symptoms Appeared in a Patient with Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia in a Convalescence Stage. Viruses. 2021; 13(4):657. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13040657
Chicago/Turabian StyleKanda, Kohei, Noriko Kinoshita, Satoshi Kutsuna, Keiji Nakamura, Ayako Okuhama, Akira Shimomura, Takeshi Inagaki, Tomoki Yoshikawa, Takeshi Kurosu, Masayuki Shimojima, and et al. 2021. "Residual and Late Onset Symptoms Appeared in a Patient with Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia in a Convalescence Stage" Viruses 13, no. 4: 657. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13040657
APA StyleKanda, K., Kinoshita, N., Kutsuna, S., Nakamura, K., Okuhama, A., Shimomura, A., Inagaki, T., Yoshikawa, T., Kurosu, T., Shimojima, M., Saijo, M., & Ohmagari, N. (2021). Residual and Late Onset Symptoms Appeared in a Patient with Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia in a Convalescence Stage. Viruses, 13(4), 657. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13040657






