Abstract
The exponential growth in the use of dental implants in the last decades has been accompanied by an increase in the prevalence of peri-implant disease. It appears that viruses may have pathogenic potential for the development of this pathology. The objective of this systematic review is to study the possible association between the presence of Epstein–Barr virus and the development of peri-implantitis. An electronic search was conducted in PubMed/MEDLINE, Scielo and Embase databases for cross-sectional and case–control studies in humans published up to and including 4 January 2021. Five studies were included in the qualitative analysis. The meta-analysis did not show a statistically significant difference regarding the prevalence of Epstein–Barr virus in the peri-implant sulcus between implants with peri-implantitis and healthy implants. In conclusion, no association between the human herpesvirus 4 and peri-implantitis was found. Further research on this topic is essential to develop more effective treatments.
1. Introduction
In the last decades, the use of dental implants has increased significantly, suffering an exponential growth since the first decade of the 21st century [1,2,3]. In fact, a study carried out in the United States found that between 1999 and 2016 the prevalence of dental implants increased by 14% per year and projection estimates suggest that it could be as high as 23% by 2026 [3].
According to the scientific literature, dental implants show survival rates of up to 98% at 10 years [4,5,6]. However, the higher use of dental implants has been accompanied by an increase in the prevalence of peri-implant pathology [7]. A recent systematic review and meta-analysis reported an incidence of peri-implantitis ranging from 0.4% over 3 years, to 43.9% within 5 years after implant restoration [8].
Besides minor prosthetic complications (such as crown loosening or ceramic chipping), which are easy to solve, peri-implantitis is the most frequent complication and its resolution is a real challenge, the reason why so much has been published in recent years on this topic [9]. This pathology is defined clinically as the presence of signs of bleeding and/or suppuration in the peri-implant tissues on probing, increased probing depth and loss of 2 or more millimetres of marginal bone compared to previous radiographic recordings [7,10]. Its appearance is the result of a discrepancy between the bacterial challenge and the host response [11]. A large number of risk factors and indicators have been associated with peri-implant disease, like smoking or diabetes mellitus [12,13,14,15], but bacterial infection plays the most important role in its development [8,16,17]. Among the strains most frequently related to peri-implant disease there can be found Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans, Prevotella intermedia, Tannerella forsythia, Treponema denticola, Campylobacter rectus, Treponema socranskii, Porphyromonas gingivalis, Staphylococcus aureus, and Campylobacter gracilis [7,9,18]. However, it has been observed that other pathogens such as Candida spp. or some viruses have an important pathogenic potential in the appearance and evolution of peri-implant disease [7,19,20]. Growing evidence suggests that Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) plays a role in the pathogenesis of periodontitis and peri-implantitis [21]. EBV is an enveloped herpesvirus with double-stranded DNA, and it is estimated to infect more than 90% of the adult population [19]. It is known that EBV is transmitted from host to host by salivary contact and the virus passes through the oropharyngeal epithelium to B lymphocytes, where it establishes a lifelong latent infection [19,22,23,24].
EBV can induce inflammatory process, being related to autoimmune diseases like systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis [25] and is nowadays associated with 1% of global cancers, mostly lymphomas and carcinomas [24].
The hypothesis than EBV may be related to peri-implant disease appears when the presence of EBV is discovered in a high percentage in subgingival plaque samples from periodontal patients [26] or in the peri-implant sulcus [18,21]. Additionally, reduction in subgingival EBV levels following periodontal treatment was demonstrated as well [27]. Therefore, the virus may deteriorate immunologic stability in periodontal/peri-implant disease by contributing to the overgrowth and aggressiveness of inflammophilic bacterial periopathogens, thus favoring the initiation and progression of peri-implant tissues breakdown [27,28]. Actually, the EBV and bacterial periopathogens interaction is bidirectional [29], as specific anaerobic bacteria structural components have the ability to stimulate EBV and the virus may influence pathogenic bacteria overgrowth by affecting potential adhesion to infected host cells and altering the inflammatory cells involved in the immune response [30,31].
The objective of the present systematic review is to study the possible association between EBV and the development of peri-implantitis.
2. Materials and Methods
This systematic review was conducted according to the guidelines of the Preferred Reporting Items of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement [32].
2.1. PECO Question (Population, Exposure, Comparison, Outcome)
P: Patients with at least one dental implant.
E: Peri-implantitis.
C: Healthy implants.
O: Prevalence of Epstein–Barr virus.
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
Studies were eligible for inclusion if they met the following criteria:
- Cross-sectional studies and case–control studies.
- Written in English or Spanish.
- That evaluated the correlation between Epstein–Barr virus and the presence of peri-implantitis.
- Minimum sample of 20 implants.
- Peri-implantitis implants group (test) and healthy implants group (control).
- Peri-implant health diagnosis: radiological evaluation of bone loss and assessment of at least one clinical parameter.
- Systemically healthy subjects.
- No history of antibiotic therapy for at least three months.
2.3. Search Strategy
An electronic search was conducted by two reviewers (E.R.-M. and J.D.-M.) in MEDLINE (PubMed), Embase and Scielo on 4 January 2021 for articles published up to that date. An additional hand search was performed to identify potential articles of interest in the references of the studies found in the electronic search. The following term combination was used: (“epstein barr virus [All Fields]” OR “human herpesvirus 4 [All Fields]”) AND (“peri-implantitis [All Fields]” OR “peri-implant diseases [All Fields]”).
2.4. Study Selection
After discarding duplicate articles, titles and abstracts were read to verify that the identified articles met the inclusion criteria. Finally, the full text of the selected articles was read to corroborate that they met the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Disagreements during the study selection were solved by consulting a third author (J.L.-L.).
2.5. Data Extraction
Data were collected by an author (E.R.-M.) and entered into a data collection form and later they were verified by a second author (J.L.-L.). The following data were extracted: author(s), year of publication, type of study, number of total dental implants, number of healthy implants, number of peri-implantitis implants, number of mucositis implants, Epstein–Barr virus prevalence, sample origin, and main findings.
2.6. Quality Assessment
The Newcastle–Ottawa Quality Assessment Form for Case–Control Studies and the Newcastle–Ottawa Quality Assessment Form Adapted for Cross-sectional Studies were implemented to evaluate the methodological quality of the included articles [33]. Two authors (E.R.-M. and J.D.-M.) independently assessed the studies and any discrepancies were solved consulting a third author (J.L.-L.). The Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS) judges the quality considering three domains: selection of study groups, comparability of the groups and outcome/exposure. The maximum score is 9 points for case–control studies and 10 points for cross-sectional studies.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Review Manager (RevMan) (computer program, version 5.4, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2020) was used to evaluate the association between the presence of EBV in the peri-implant sulcus and the peri-implant tissues health. The Mantel–Haenszel random-effects model was implemented in the meta-analysis. The level of significance was set at p < 0.05. Heterogeneity was assessed with Chi2 and I2 tests.
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection
A total of 28 studies were identified through the electronic and manual searches. Half of them were excluded due to duplication. Of these 14 articles, five were discarded after reading the titles and three after reading the abstract as they did not meet the inclusion criteria. Of the six full-text articles with potential for inclusion [18,19,21,27,34,35], one was excluded as it appeared to be the same study as another included paper but in earlier stage [18]. Finally, a total of five studies were included in the qualitative analysis [19,21,27,34,35] (Figure 1).
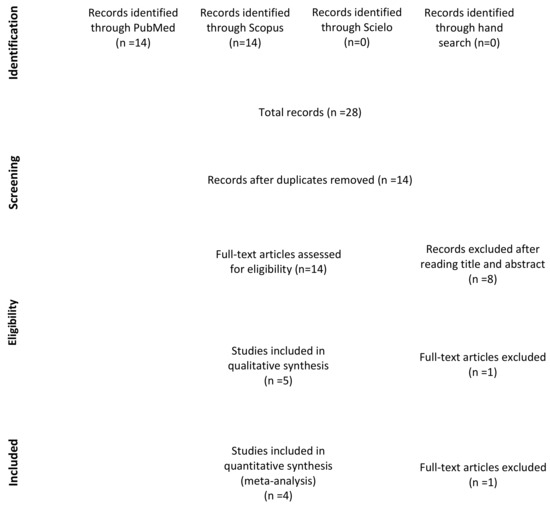
Figure 1.
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) flow diagram of selection process.
3.2. Study Methods and Characteristics
Three of the included articles were cross-sectional studies [21,27,35] and the other two were case–control studies [19,34] (Table 1). The papers were published between 2011 and 2018. Three of them were conducted in training centers [19,21,27], one in a private dental clinic [35] and another one does not specify where it took place [34]. A total of 274 patients (149 women and 125 men) and 388 implants (197 healthy implants, 166 peri-implantitis implants and 25 mucositis implants) were included in the analysis. In all the studies samples were taken to perform a real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to detect the presence of EBV. In two of the articles only subgingival plaque samples of the peri-implant tissues were extracted [19,21], in another one the source of the sample was saliva [34], in another samples were taken both from saliva and subgingival peri-implant tissues [35] and in the last one samples were extracted from subgingival plaque and from the internal implant connection [27]. Only one study differentiated between EBV genotypes (EBV-1 and EBV-2) [21].

Table 1.
Summary of the included studies.
3.3. Quality Assessment
All the studies were assessed using the Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS) [33]. The comparability was the dimension that received the lowest score, while the evaluation of the outcome/exposure was the one that obtained the highest (Table 2). The mean NOS score was 6.6 (±1.34). Two of the studies can be considered of good quality [21,27] and the other three of satisfactory quality [19,34,35].

Table 2.
Quality assessment of the included studies according to the Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS).
3.4. EBV and Peri-Implantitis
In three of the included studies, no statistically significant difference was observed in the prevalence of EBV between patients with peri-implantitis (PI) and patients with healthy implants (HI) [19,27,34]. However, in two of them the PI group presented higher prevalence of EBV [19,34], with no difference in the third study [27].
In the other two works [21,35], statistically significant differences were found in the prevalence of the virus between both groups. The group with PI showed a significantly higher prevalence of EBV compared to the HI group. Jankovic et al. [21] observed this result for EBV-1 genotype not for EBV-2 genotype.
Only one of the studies included also subjects with mucositis, a reversible peri-implant pathology characterized by gingival inflammation without associated bone loss. In that article a statistically significant correlation between the presence of EBV-1 and mucositis was also found [21].
In cases where samples were extracted from two different sites, more EBV positives were obtained from subgingival plaque above the saliva [35] or the internal implant connection [27].
In relation to the association between EBV and other periopathogens, significantly higher median loads of P. intermedia and C. rectus were found in EBV positives compared to EBV negatives [27]. Furthermore, the coexistence between P. gingivalis and EBV was statistically significantly higher in patients with peri-implantitis [19].
Regarding the inflammatory response, a statistically significant association was found between the presence of herpesvirus and the presence in saliva of the markers macrophage inflammatory protein-1β (MIP-1β) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in the PI group [34].
3.5. Quantitative Analysis
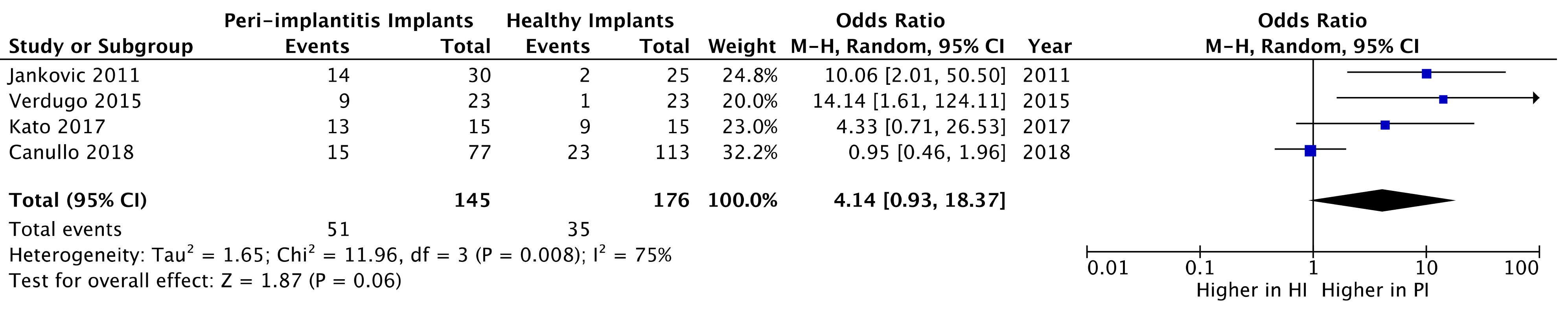
Studies in which subgingival plaque samples were taken were selected for the quantitative analysis [19,21,27,35]. No statistically significant difference was found regarding the presence of EBV in the peri-implant sulcus between PI and HI groups (OR = 4.14; 95% CI: 0.93–18.37; z = 1.87; p = 0.06) (Figure 2). Heterogeneity tests from pooled showed statistical significance (Chi-squared = 11.96, p < 0.008) (Figure 2).
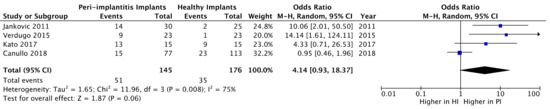
Figure 2.
Forest plot of the prevalence of Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) in peri-implantitis implants versus healthy implants.
4. Discussion
In the present meta-analysis no statistically significant difference was found regarding the presence of EBV in the peri-implant sulcus between implants with peri-implantitis and healthy implants. However, it must be considered that due to the limited literature published on this topic, only four articles [19,21,27,35] could be included in the quantitative analysis and the one with a larger sample and therefore greater weight is the study in which no differences between groups were observed [27].
Only one of the studies evaluated both EBV genotypes, obtaining significantly higher prevalence of the EBV-1 genotype in the PI group, which was not the case with the EBV-2 genotype [21]. This suggests that this genotype could be more present in the development of peri-implant pathology. According to the same study, the development of mucositis could already be encouraged by the presence of EBV-1 [21].
The higher prevalence of the virus in the peri-implant sulcus than in saliva of the same subjects highlights the possible role of EBV in peri-implant diseases [35]. Furthermore, the coexistence of the virus with periopathogenic bacteria such as P. gingivalis [19], P. intermedia or C. rectus [27] could be a key point in the development of peri-implantitis.
Regarding the pathogenesis, it seems that the presence of EBV could be related to an increase in the inflammatory response with the consequent increase in markers such as the macrophage inflammatory protein-1β (MIP-1β) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) [34].
There is no review so far that specifically focused on the relationship between EBV and peri-implantitis, but there are three recent reviews that study the microbiological profile of peri-implantitis [36] or the association of viruses [37], or more explicitly the herpesvirus [38], with the appearance of this pathology.
One of these reviews concluded that the microbiological profile in peri-implantits consists of Gram-negative anaerobic periopathogens and opportunistic microorganisms almost in the same proportion and that is often associated with EBV [36]. Another review concluded that the presence of herpesvirus in the peri-implant subgingival biofilm is an indicator of peri-implant disease [38].
Unlike the present review, the only existing meta-analysis did find a statistically significant difference in the presence of EBV between the PI and HI groups. However, this difference between the two meta-analyses is based solely on the inclusion of a single different article in the quantitative analysis [37].
The main limitation of this review is the limited scientific literature published on this topic, which makes it impossible to draw conclusions about the possible association between EBV and peri-implantitis. Furthermore, some of the included studies analyze small samples or may represent a source of bias, especially due to the lack of information on comparability between groups.
Future research in this area should focus on case–control studies, with large samples, with a higher methodological quality to reduce the risk of bias and in which samples were obtained from the peri-implant sulcus and not from saliva or from the implant connection.
5. Conclusions
No statistically significant difference was found in terms of the prevalence of EBV in the peri-implant sulcus between PI and HI groups. More case–control studies of high methodological quality are necessary to evaluate the possible association between EBV and peri-implantitis. Due to the high prevalence of periodontal disease and its difficult treatment, it is essential to continue researching this topic, since better knowledge of its pathogenesis will allow the development of more effective therapies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.R.-M. and J.D.-M.; methodology, E.R.-M., J.D.-M. and M.S.-S.; validation, E.R.-M., A.E.-D. and J.L.-L.; formal analysis, E.R.-M., J.D.-M.; investigation, E.R.-M. and M.S.-S.; data curation, E.R.-M. and J.L.-L.; writing—original draft preparation, E.R.-M. and J.D.-M.; writing—review and editing, A.E.-D., A.M.-R.; visualization, E.R.-M. and J.L.-L.; supervision, A.E.-D., A.M.-R. and J.L.-L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lambrecht, J.T.; Cardone, E.; Kühl, S. Status report on dental implantology in Switzerland in 2006—A cross-sectional survey. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2010, 3, 71–74. [Google Scholar]
- Sekerci, E.; Lambrecht, J.T.; Mukaddam, K.; Kühl, S. Status report on dental implantology in Switzerland. An updated cross-sectional survey. Swiss Dent. J. 2020, 130, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Elani, H.W.; Starr, J.R.; Da Silva, J.D.; Gallucci, G.O. Trends in dental implant use in the U.S., 1999–2016, and projections to 2026. J. Dent. Res. 2018, 97, 1424–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Jung, U.W.; Cho, K.S.; Lee, J.S. Retrospective radiographic observational study of 1692 Straumann tissue-level dental implants over 10 years: I. Implant survival and loss pattern. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2018, 20, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuchler, U.; Chappuis, V.; Gruber, R.; Lang, N.P.; Salvi, G.E. Immediate implant placement with simultaneous guided bone regeneration in the esthetic zone: 10-year clinical and radiographic outcomes. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2016, 27, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Velzen, F.J.; Ofec, R.; Schulten, E.A.; Bruggenkate, C.M. 10-year survival rate and the incidence of peri-implant disease of 374 titanium dental implants with a SLA surface: A prospective cohort study in 177 fully and partially edentulous patients. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2015, 26, 1121–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kormas, I.; Pedercini, C.; Pedercini, A.; Raptopoulos, M.; Alassy, H.F.; Wolff, L. Peri-implant diseases: Diagnosis, clinical, histological, microbiological characteristics and treatment strategies. A narrative Review. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreyer, H.; Grischke, J.; Tiede, C.; Eberhard, J.; Schweitzer, A.; Toikkanen, S.E. Epidemiology and risk factors of peri-implantitis: A systematic review. J. Periodontal. Res. 2018, 53, 657–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahrmann, P.; Gilli, F.B.; Wiedemeier, D.; Attin, T.R.; Schmidlin, P.; Karygianni, L. The microbiome of peri-implantitis: A systemtic review and meta-analysis. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglundh, T.; Armitage, G.; Araujo, M.G.; Avila-Ortiz, G.; Blanco, J.; Camargo, P.M. Peri-implant diseases and conditions: Consensus report of workgroup 4 of the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89, S313–S318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzsimmons, L.; Kelly, G.L. EBV and apoptosis: The viral master regulator of cell fate? Viruses 2017, 9, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renvert, S.; Persson, G.R.; Pirih, F.Q.; Camargo, P.M. Peri-implant health, peri-implant mucositis, and peri-implantitis: Case definitions and diagnostic considerations. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89, S304–S312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, M.G.; Lindhe, J. Peri-implant health. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89, S249–S256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, J.D. Risk revisited. Commun. Dent. Oral Epidemiol. 1998, 26, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbach, J.; Callaway, A.; Kwon, Y.D.; d’Hoedt, B.; Al-Nawas, B. Comparison of five parameters as risk factors for peri-mucositis. Int J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant 2009, 24, 491–496. [Google Scholar]
- Romandini, M.; Lima, C.; Pedrinaci, I.; Araoz, A.; Soldini, M.C.; Sanz, M. Prevalence and risk/protective indicators of peri-implant diseases: A university-representative cross-sectional study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2021, 32, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, D.H.; Kim, H.J.; Joo, J.Y.; Lee, J.Y. Prevalence and risk factors of peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis after at least 7 years of loading. J. Periodontal. Implant. Sci. 2019, 49, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankovic, S.; Aleksic, Z.; Dimitrijevic, B.; Lekovic, V.; Camargo, P.; Kenney, B. Prevalence of human cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr virus in subgingival plaque at peri-implantitis, mucositis and healthy sites. A pilot study. Int J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 40, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, A.; Imai, K.; Sato, H.; Ogata, Y. Prevalence of Epstein-Barr virus DNA and Porphyromonas gingivalis in Japanese peri-implantitis patients. BMC Oral Health 2017, 17, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, J.G.S.; Bertolini, M.; Thompson, A.; Barão, V.A.R.; Dongari-Bagtzoglou, A. Biofilm Interactions of Candida albicans and Mitis Group Streptococci in a Titanium-Mucosal Interface Model. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e02950-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankovic, S.; Aleksic, Z.; Dimitrijevic, B.; Lekovic, V.; Milinkovic, I.; Kenney, B. Correlation between different genotypes of human cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr virus and peri-implant tissue status. Aust. Dent. J. 2011, 56, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, K.; Inoue, H.; Tamura, M.; Cueno, M.E.; Inoue, H.; Takeichi, O. The periodontal pathogen Porphyromonas gingivalis induces the Epstein-Barr virus lytic switch transactivator ZEBRA by histone modification. Biochimie 2012, 94, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, K.; Kamio, N.; Cueno, M.E.; Saito, Y.; Inoue, H.; Saito, I. Role of the histone H3 lysine 9 methyltransferase Suv39 h1 in maintaining Epstein-Barr virus latency in B95-8 cells. FEBS J. 2014, 281, 2148–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakkalci, D.; Jia, Y.; Winter, J.R.; Lewis, J.E.; Taylor, G.S.; Stagg, H.R. Risk factors for Epstein Barr virus-associated cancers: A systematic review, critical appraisal, and mapping of the epidemiological evidence. J. Glob. Health 2020, 10, 010405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lossius, A.; Johansen, J.N.; Torkildsen, Ø.; Vartdal, F.; Holmøy, T. Epstein-Barr virus in systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis association and causation. Viruses 2012, 4, 3701–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotola, A.; Cassai, E.; Farina, R.; Caselli, E.; Gentili, V.; Lazzarotto, T.; Trombelli, L. Human herpesvirus 7, Epstein-Barr virus and human cytomegalovirus in periodontal tissues of periodontally diseased and healthy subjects. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2008, 35, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canullo, L.; Pesce, P.; Botticelli, D.; Covani, U.; Jankovic, S.; Jovanovic, T.; Rakic, M. What is the impact of epstein-barr virus in peri-implant infection? Int J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2018, 33, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slots, J. Herpesviral-bacterial synergy in the pathogenesis of human periodontitis. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 20, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slots, J. Herpesviral–bacterial interactions in periodontal diseases. Periodontol. 2000. 2010, 52, 117–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugano, N.; Ikeda, K.; Oshikawa, M.; Idesawa, M.; Tanaka, H.; Sato, S.; Ito, K. Relationship between Porphyromonas gingivalis, Epstein–Barr virus infection and reactivation in periodontitis. J. Oral Sci. 2004, 46, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Slots, J.; Saygun, I.; Sabeti, M.; Kubar, A. Epstein–Barr virus in oral diseases. J. Periodontal Res. 2006, 41, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, G.; O’Connell, D.; Peterson, J.; Welch, V.; Losos, M.; Tugwell, P. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomized Studies in Meta-Analyses. 2011. Available online: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (accessed on 8 January 2021).
- Marques Filho, J.S.; Gobara, J., Jr.; da Silva Salomao, G.V.; Sumita, L.M.; Shibli, J.A.; Viana, R.G.; Filho, H.O.S.; Pannuti, C.S.; Braz-Silva, P.H.; Pallos, D. Cytokine levels and human herpesviruses in saliva from clinical periodontal healthy subjects with peri-implantitis: A case-control study. Mediators Inflamm. 2018, 6020625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdugo, F.; Castillo, A.; Castillo, F.; Uribarri, A. Epstein-Barr virus associated peri-implantitis: A Split-mouth study. Clin. Oral Invest. 2015, 19, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakic, M.; Grusovin, M.G.; Canullo, L. The microbiologic profile associated with peri-implantitis in humans: A systematic review. Int J. Oral Maxillofac Implants 2016, 31, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akram, Z.; Al-Aali, K.A.; Alrabiah, M.; Alonaizan, F.A.; Abduljabbar, T.; AlAhmari, F.; Javed, F.; Vohra, F. Current weight of evidence of viruses associated with peri-implantitis and peri-implant health: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev. Med. Virol. 2019, 29, e2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binshabaib, M.; AlHarthi, S.S.; Salehpoor, D.; Michelogiannakis, D.; Javed, F. Contribution of herpesviruses in the progression of periodontal and peri-implant diseases in systemically healthy individuals. Rev. Med. Virol. 2018, 28, e1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).