Whole Genome Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis of Rabies Viruses from Bats in Connecticut, USA, 2018–2019
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bat Samples and Rabies Diagnostic Tests
2.2. RNA Extraction and SISPA
2.3. Whole Genome Sequencing
2.4. Assembly of Sequencing Reads
2.5. Bat Species Identification
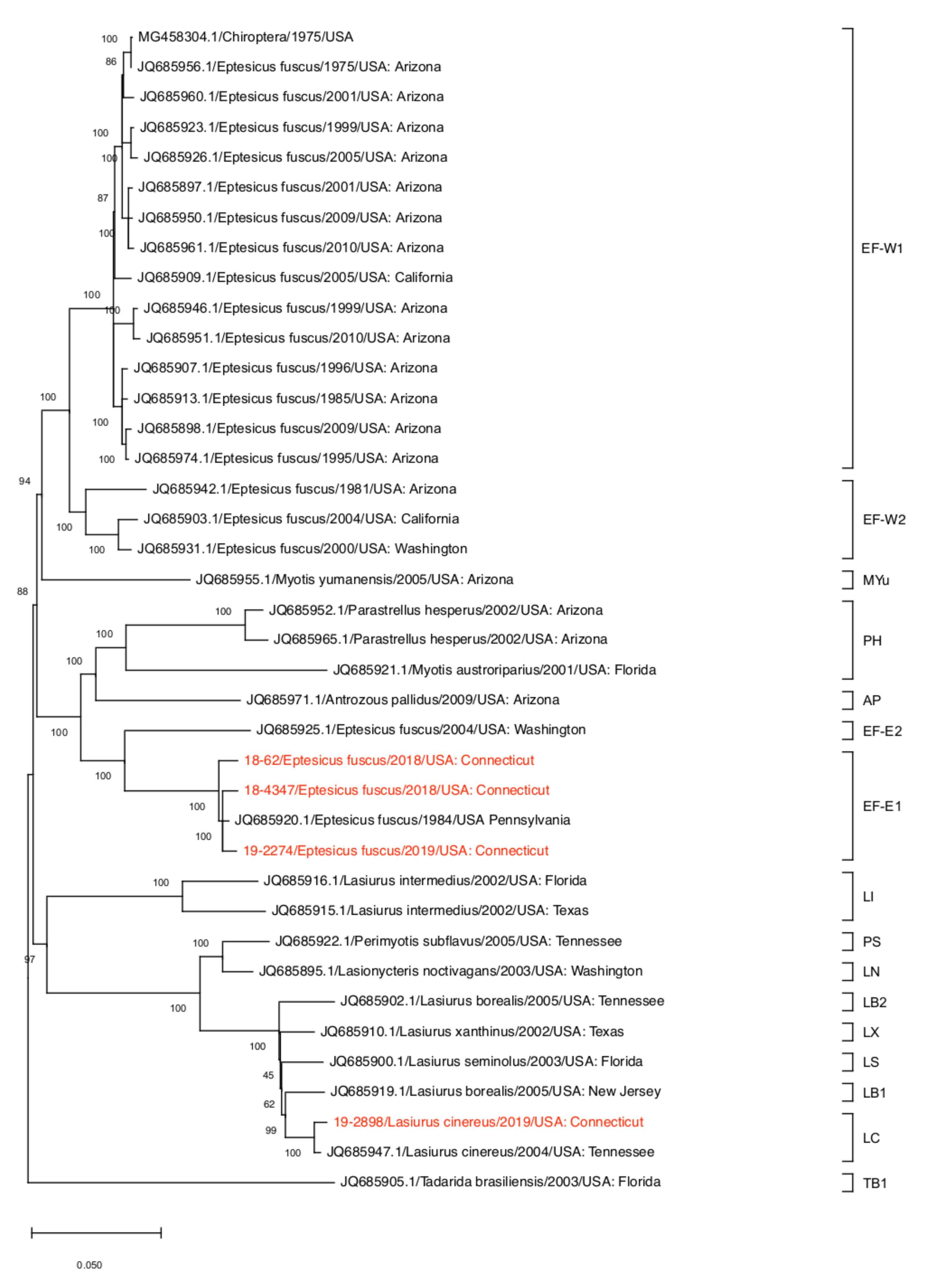
2.6. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Virus Taxonomy: 2019 Release. Available online: https://talk.ictvonline.org/ictv-reports/ictv_online_report/negative-sense-rna-viruses/w/rhabdoviridae/795/genus-lyssavirus (accessed on 1 September 2021).
- Hampson, K.; Coudeville, L.; Lembo, T.; Sambo, M.; Kieffer, A.; Attlan, M.; Barrat, J.; Blanton, J.D.; Briggs, D.J.; Cleaveland, S.; et al. Estimating the global burden of endemic canine rabies. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003709. [Google Scholar]
- Fooks, A.R.; Jackson, A.C. Rabies: Scientific Basis of the Disease and Its Management, 4th ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Monroe, B.P.; Cleaton, J.M.; Orciari, L.A.; Gigante, C.M.; Kirby, J.D.; Chipman, R.B.; Fehlner-Gardiner, C.; Gutierrez Cedillo, V.; Petersen, B.W.; et al. Public Veterinary Medicine: Public Health: Rabies surveillance in the United States during 2018. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2020, 256, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Singh, K.P.; Cherian, S.; Saminathan, M.; Kapoor, S.; Manjunatha Reddy, G.B.; Panda, S.; Dhama, K. Rabies—Epidemiology, pathogenesis, public health concerns and advances in diagnosis and control: A comprehensive review. Vet. Q. 2017, 37, 212–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadin-Davis, S.; Alnabelseya, N.; Knowles, M.K. The phylogeography of Myotis bat-associated rabies viruses across Canada. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velasco-Villa, A.; Mauldin, M.R.; Shi, M.; Escobar, L.E.; Gallardo-Romero, N.F.; Damon, I.; Olson, V.A.; Streicker, D.G.; Emerson, G. The history of rabies in the Western Hemisphere. Antivir. Res. 2017, 146, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, M.J.; Altenbach, J.S.; Best, T.L. Bats of the United States and Canada; The Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Connecticut Department of Energy and Environmental Protection. Bats. Available online: https://portal.ct.gov/DEEP/Wildlife/Fact-Sheets/Bats (accessed on 19 October 2021).
- Pieracci, E.G.; Brown, J.A.; Bergman, D.L.; Gilbert, A.; Wallace, R.M.; Blanton, J.D.; Velasco-Villa, A.; Morgan, C.N.; Lindquist, S.; Chipman, R.B. Evaluation of species identification and rabies virus characterization among bat rabies cases in the United States. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2020, 256, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieracci, E.G.; Pearson, C.M.; Wallace, R.M.; Blanton, J.D.; Whitehouse, E.R.; Ma, X.; Stauffer, K.; Chipman, R.B.; Olson, V. Vital Signs: Trends in Human Rabies Deaths and Exposures—United States, 1938–2018. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2019, 68, 524–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzmin, I.V.; Shi, M.; Orciari, L.A.; Yager, P.A.; Velasco-Villa, A.; Kuzmina, N.A.; Streicker, D.G.; Bergman, D.L.; Rupprecht, C.E. Molecular inferences suggest multiple host shifts of rabies viruses from bats to mesocarnivores in Arizona during 2001–2009. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, N.; Arechiga-Ceballos, N.; Aguilar-Setien, A. Vampire bat rabies: Ecology, epidemiology and control. Viruses 2014, 6, 1911–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McElhinney, L.M.; Marston, D.A.; Freuling, C.M.; Cragg, W.; Stankov, S.; Lalosevic, D.; Lalosevic, V.; Muller, T.; Fooks, A.R. Molecular diversity and evolutionary history of rabies virus strains circulating in the Balkans. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 2171–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Velasco-Villa, A.; Orciari, L.A.; Juarez-Islas, V.; Gomez-Sierra, M.; Padilla-Medina, I.; Flisser, A.; Souza, V.; Castillo, A.; Franka, R.; Escalante-Mane, M.; et al. Molecular diversity of rabies viruses associated with bats in Mexico and other countries of the Americas. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 1697–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunt, S.; Solomon, H.; Leavitt, H.; Lasek-Nesselquist, E.; LaPierre, P.; Shudt, M.; Bigler, L.; Singh, N.; Davis, A.D. Origin of 3 Rabid Terrestrial Animals in Raccoon Rabies Virus-Free Zone, Long Island, New York, USA, 2016–2017. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1315–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Eitan, L.N.; Wu, G.; Golding, M.; Tang, Y.; Goharriz, H.; Marston, D.A.; Fooks, A.R.; McElhinney, L.M. Whole-genome sequencing and phylogenetic analysis of rabies viruses from Jordan. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupprecht, C.E.; Fooks, A.R.; Abela-Ridder, B. Chapter 11: Laboratory Techniques in Rabies, 5th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Gigante, C.M.; Dettinger, L.; Powell, J.W.; Seiders, M.; Condori, R.E.C.; Griesser, R.; Okogi, K.; Carlos, M.; Pesko, K.; Breckenridge, M.; et al. Multi-site evaluation of the LN34 pan-lyssavirus real-time RT-PCR assay for post-mortem rabies diagnostics. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrzastek, K.; Lee, D.H.; Smith, D.; Sharma, P.; Suarez, D.L.; Pantin-Jackwood, M.; Kapczynski, D.R. Use of Sequence-Independent, Single-Primer-Amplification (SISPA) for rapid detection, identification, and characterization of avian RNA viruses. Virology 2017, 509, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalili, V.; Afgan, E.; Gu, Q.; Clements, D.; Blankenberg, D.; Goecks, J.; Taylor, J.; Nekrutenko, A. The Galaxy platform for accessible, reproducible and collaborative biomedical analyses: 2020 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, W395–W402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streicker, D.G.; Turmelle, A.S.; Vonhof, M.J.; Kuzmin, I.V.; McCracken, G.F.; Rupprecht, C.E. Host phylogeny constrains cross-species emergence and establishment of rabies virus in bats. Science 2010, 329, 676–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klug, B.J.; Turmelle, A.S.; Ellison, J.A.; Baerwald, E.F.; Barclay, R.M. Rabies prevalence in migratory tree-bats in Alberta and the influence of roosting ecology and sampling method on reported prevalence of rabies in bats. J. Wildl. Dis. 2011, 47, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szanto, A.G.; Nadin-Davis, S.A.; Rosatte, R.C.; White, B.N. Genetic tracking of the raccoon variant of rabies virus in eastern North America. Epidemics 2011, 3, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.S.; Orciari, L.A.; Yager, P.A. Molecular epidemiology of rabies in the United States. Semin. Virol. 1995, 6, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, T.J.; Castle, K.T.; Liechti, F.; Hein, C.D.; Schirmacher, M.R.; Cryan, P.M. First Direct Evidence of Long-distance Seasonal Movements and Hibernation in a Migratory Bat. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Year | Bat Species | No. of Bats Tested for Rabies | No. of RABV Positive Samples (Sample ID) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | Eptesicus fuscus | 8 | 3 (18-62, 18-3792, 18-4347) |
| Lasionycteris noctivagans | 1 | 0 | |
| Unidentified | 44 | 1 * | |
| 2019 | Eptesicus fuscus | 13 | 1 (19-2274) |
| Lasiurus borealis | 1 | 0 | |
| Lasiurus cinereus | 2 | 1 (19-2898) | |
| Myotis lucifugus | 2 | 0 | |
| Unidentified | 19 | 0 | |
| Total | 88 | 6 |
| Sample | Ct Value | Total NGS Reads | Q/C Passed | Assembled Reads (%) | Complete CDS (Mean Depth of Coverage) | Identified Species by DNA Barcoding (Top Hit %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18-62 | 26.29 | 797,418 | 687,856 | 3108 (0.45) | Yes (37.4) | Big brown bat (99.85%) |
| 18-3792 | 36.0 | 726,524 | 609,074 | 14 (0.003) | No (0.1) | Big brown bat (100%) |
| 18-4347 | 24.57 | 607,824 | 53,2362 | 3887 (0.73) | Yes (47) | Big brown bat (99.17%) |
| 19-2274 | 21.05 | 722,642 | 638,616 | 2348 (0.37) | Yes (28.4) | Big brown bat (99.85%) |
| 19-2898 | 29.39 | 661,854 | 578,494 | 2459 (0.43) | Yes (29.6) | Hoary bat (100%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hyeon, J.-Y.; Risatti, G.R.; Helal, Z.H.; McGinnis, H.; Sims, M.; Hunt, A.; Chung, D.H.; Kim, J.; Desiato, J.; Lee, D.-H. Whole Genome Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis of Rabies Viruses from Bats in Connecticut, USA, 2018–2019. Viruses 2021, 13, 2500. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13122500
Hyeon J-Y, Risatti GR, Helal ZH, McGinnis H, Sims M, Hunt A, Chung DH, Kim J, Desiato J, Lee D-H. Whole Genome Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis of Rabies Viruses from Bats in Connecticut, USA, 2018–2019. Viruses. 2021; 13(12):2500. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13122500
Chicago/Turabian StyleHyeon, Ji-Yeon, Guillermo R. Risatti, Zeinab H. Helal, Holly McGinnis, Maureen Sims, Amelia Hunt, David H. Chung, Junwon Kim, Julia Desiato, and Dong-Hun Lee. 2021. "Whole Genome Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis of Rabies Viruses from Bats in Connecticut, USA, 2018–2019" Viruses 13, no. 12: 2500. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13122500
APA StyleHyeon, J.-Y., Risatti, G. R., Helal, Z. H., McGinnis, H., Sims, M., Hunt, A., Chung, D. H., Kim, J., Desiato, J., & Lee, D.-H. (2021). Whole Genome Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis of Rabies Viruses from Bats in Connecticut, USA, 2018–2019. Viruses, 13(12), 2500. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13122500






