The Husavirus Posa-Like Viruses in China, and a New Group of Picornavirales
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement and Sample Collection
2.2. Library Preparation and Metagenomic Sequencing
2.3. Quality Control, Assembly, and Analysis
2.4. Detection and Molecular Typing of Novel Husaviruses
2.5. Full-Length Genome Sequencing of Nine Husavirus Strains
2.6. Genome Annotation Characteristics and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.7. Data Availability
3. Results
3.1. Discovery of Husavirus in China
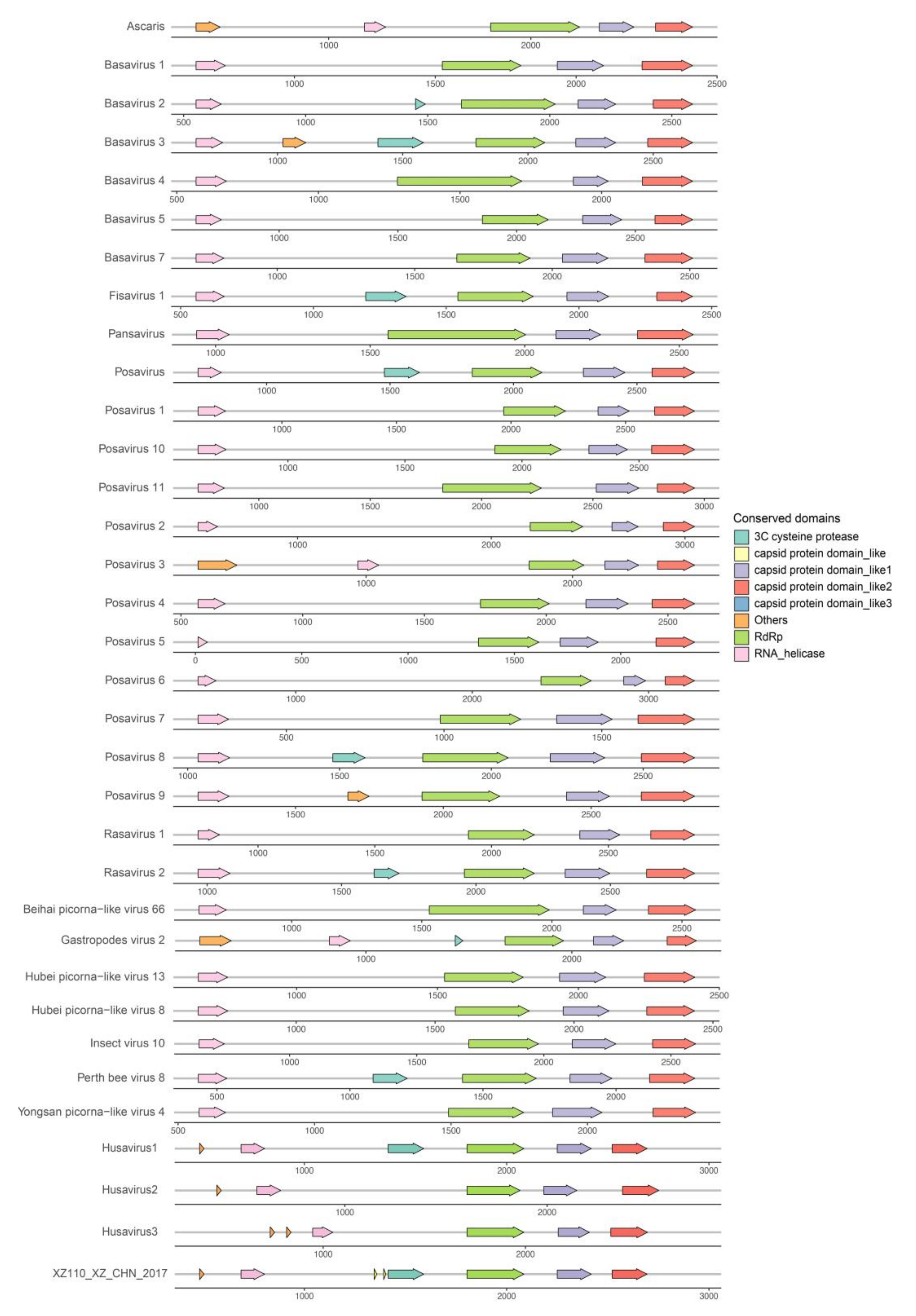
3.2. Full-Length Genomic Characterization of Nine Husavirus Strains
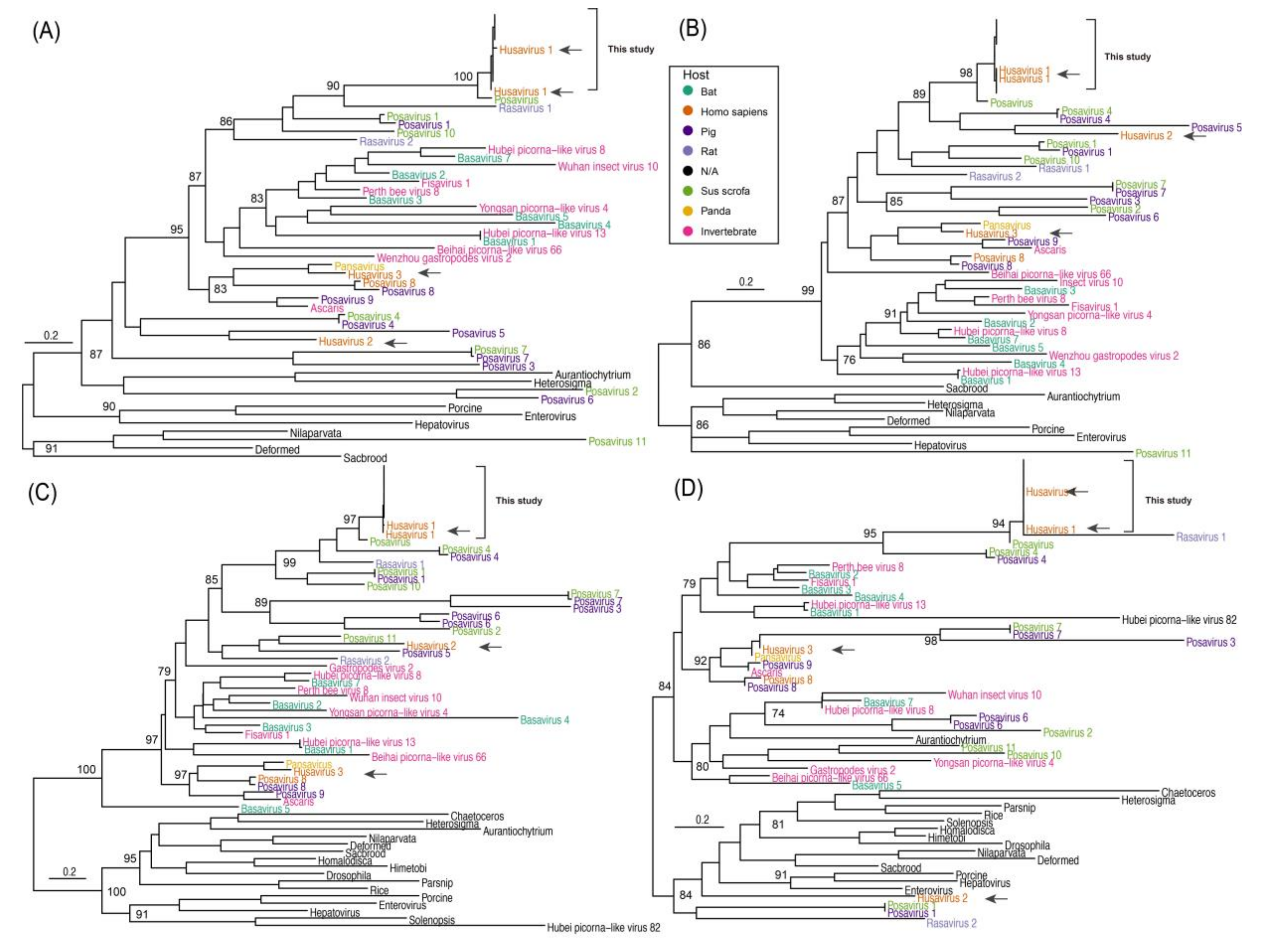
3.3. Phylogenetic Comparison of Husavirus with Other Posa-Like Genomes
3.4. Genomic Organization of the Husaviruses
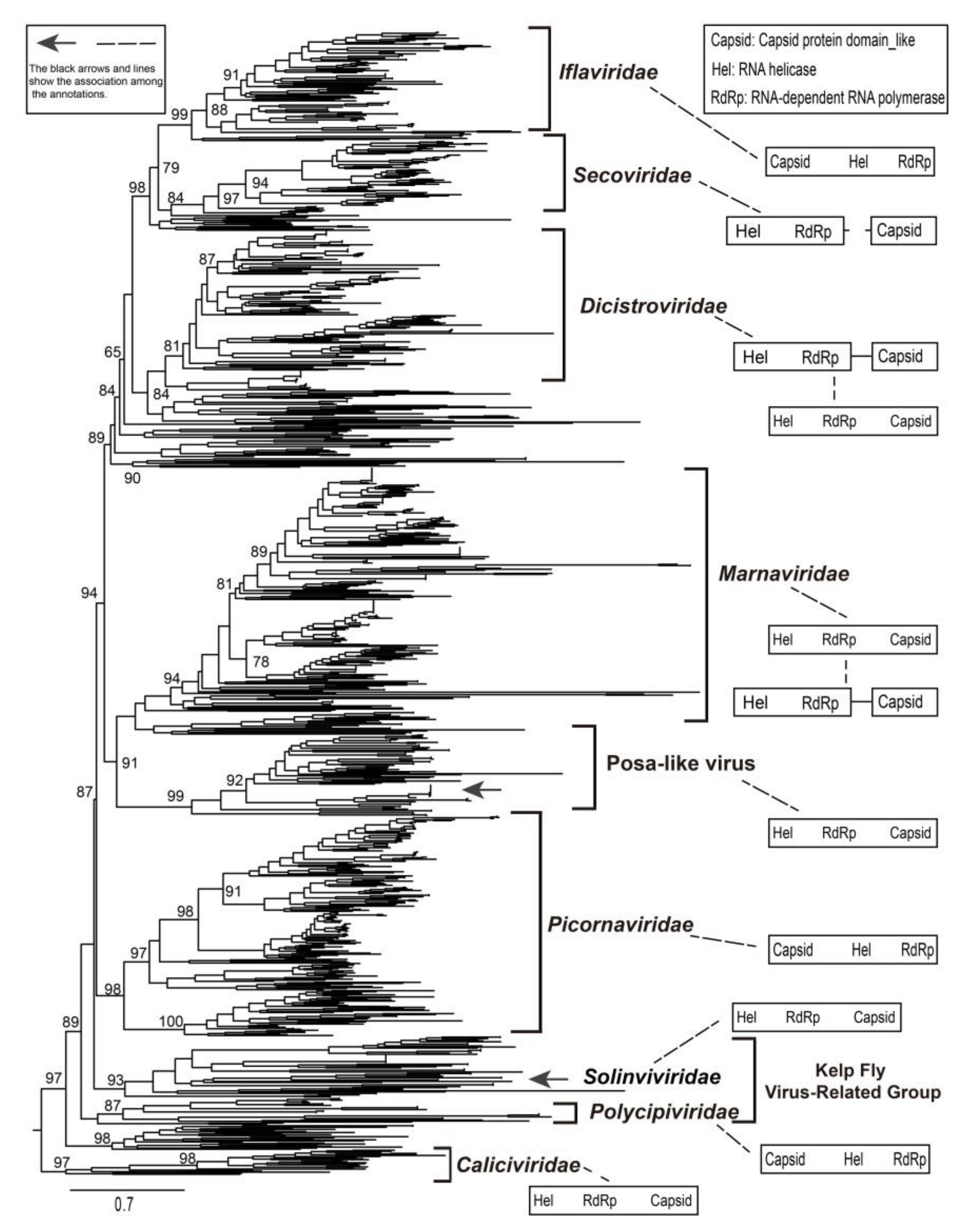
3.5. Identification of a New Group of Picornavirales
3.6. Host and Geographic Clustering Characteristics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adams, M.J.; Lefkowitz, E.J.; King, A.M.Q.; Harrach, B.; Harrison, R.L.; Knowles, N.J.; Kropinski, A.M.; Krupovic, M.; Kuhn, J.; Mushegian, A.; et al. Changes to taxonomy and the International Code of Virus Classification and Nomenclature ratified by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (2017). Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 2505–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Gall, O.; Christian, P.; Fauquet, C.M.; King, A.M.Q.; Knowles, N.J.; Nakashima, N.; Stanway, G.; Gorbalenya, A.E. Picornavirales, a proposed order of positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses with a pseudo-T = 3 virion architecture. Arch. Virol. 2008, 153, 715–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zell, R.; Delwart, E.; Gorbalenya, A.E.; Hovi, T.; King, A.M.Q.; Knowles, N.J.; Lindberg, A.M.; Pallansch, M.A.; Palmenberg, A.C.; Reuter, G.; et al. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Picornaviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 2421–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.; Lin, X.-D.; Chen, X.; Tian, J.-H.; Chen, L.-J.; Li, K.; Wang, W.; Eden, J.-S.; Shen, J.-J.; Liu, L.; et al. The evolutionary history of vertebrate RNA viruses. Nature 2018, 556, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.; Lin, X.-D.; Tian, J.-H.; Chen, L.-J.; Chen, X.; Li, C.-X.; Qin, X.-C.; Li, J.; Cao, J.; Eden, J.-S.; et al. Redefining the invertebrate RNA virosphere. Nature 2016, 540, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauber, C.; Seitz, S.; Mattei, S.; Suh, A.; Beck, J.; Herstein, J.; Börold, J.; Salzburger, W.; Kaderali, L.; Briggs, J.A.; et al. Deciphering the Origin and Evolution of Hepatitis B Viruses by Means of a Family of Non-enveloped Fish Viruses. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 22, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.A.; Taylor, L.J.; Dothard, M.I.; Leiby, J.S.; Fitzgerald, A.S.; Khatib, L.A.; Collman, R.G.; Bushman, F.D. Redondoviridae, a Family of Small, Circular DNA Viruses of the Human Oro-Respiratory Tract Associated with Periodontitis and Critical Illness. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 25, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wille, M.; Shi, M.; Klaassen, M.; Hurt, A.C.; Holmes, E.C. Virome heterogeneity and connectivity in waterfowl and shorebird communities. ISME J. 2019, 13, 2603–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-Z.; Shi, M.; Holmes, E.C. Using Metagenomics to Characterize an Expanding Virosphere. Cell 2018, 172, 1168–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, A.; Victoria, J.; Simmonds, P.; Wang, C.; Shafer, R.W.; Nims, R.; Nielsen, O.; Delwart, E. A Highly Divergent Picornavirus in a Marine Mammal. J. Virol. 2007, 82, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munnink, B.B.O.; Cotten, M.; Deijs, M.; Jebbink, M.F.; Bakker, M.; Farsani, S.M.J.; Canuti, M.; Kellam, P.; Van Der Hoek, L. A novel genus in the order Picornavirales detected in human stool. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 3440–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, T.; Li, L.; Simmonds, P.; Wang, C.; Moeser, A.J.; Delwart, E. The Fecal Virome of Pigs on a High-Density Farm. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 11697–11708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hause, B.M.; Hesse, R.A.; Anderson, G.A. Identification of a novel Picornavirales virus distantly related to posavirus in swine feces. Virus Genes 2015, 51, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siqueira, J.D.; Dominguez-Bello, M.G.; Contreras, M.; Lander, O.; Caballero-Arias, H.; Xutao, D.; Noya-Alarcon, O.; Delwart, E. Complex virome in feces from Amerindian children in isolated Amazonian villages. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hause, B.M.; Palinski, R.; Hesse, R.; Anderson, G. Highly diverse posaviruses in swine faeces are aquatic in origin. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 1362–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munnink, B.B.O.; Phan, M.V.; VIZIONS Consortium; Simmonds, P.; Koopmans, M.P.G.; Kellam, P.; Van Der Hoek, L.; Cotten, M. Characterization of Posa and Posa-like virus genomes in fecal samples from humans, pigs, rats, and bats collected from a single location in Vietnam. Virus Evol. 2017, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Tang, C.; Yue, H.; Ren, Y.; Song, Z. Viral metagenomics analysis demonstrates the diversity of viral flora in piglet diarrhoeic faeces in China. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 1603–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lu, M.; Ma, T.; Cao, L.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, X.; Shi, D.; Shi, H.; Liu, J.; Feng, L. Detection and complete genome characteristics of Posavirus 1 from pigs in China. Virus Genes 2017, 54, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yang, S.; Shan, T.; Hou, R.; Liu, Z.; Li, W.; Guo, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, P.; Wang, X.; et al. Virome comparisons in wild-diseased and healthy captive giant pandas. Microbiome 2017, 5, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strubbia, S.; Phan, M.V.T.; Schaeffer, J.; Koopmans, M.; Cotten, M.; Le Guyader, F.S. Characterization of Norovirus and Other Human Enteric Viruses in Sewage and Stool Samples Through Next-Generation Sequencing. Food Environ. Virol. 2019, 11, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, I.M.; Pons-Salort, M.; Molodecky, N.A.; Diop, O.M.; Chenoweth, P.; Bandyopadhyay, A.S.; Zaffran, M.; Sutter, R.W.; Grassly, N.C. Type 2 Poliovirus Detection after Global Withdrawal of Trivalent Oral Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 834–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, M.A.; Silva, J.M.; Brito, C.R.; Teixeira, D.S.; Melo, F.; Ribeiro, B.M.; Nagata, T.; Campos, F.S. Faecal Virome Analysis of Wild Animals from Brazil. Viruses 2019, 11, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Chen, W.; Chen, J.-P. Viral Metagenomics Revealed Sendai Virus and Coronavirus Infection of Malayan Pangolins (Manis javanica). Viruses 2019, 11, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Song, L.; Breitwieser, F.P.; Salzberg, S.L. Centrifuge: Rapid and sensitive classification of metagenomic sequences. Genome Res. 2016, 26, 1721–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabherr, M.G.; Haas, B.J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Thompson, D.A.; Amit, I.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Raychowdhury, R.; Zeng, Q.; et al. Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, K.; Cui, H.; Hong, M.; Tang, H.; Song, Y.; Yang, Q.; Zhu, S.; Yan, D.; et al. Genetic characterization and molecular epidemiological analysis of novel enterovirus EV-B80 in China. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Wang, J.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Geer, R.C.; Gonzales, N.R.; Gwadz, M.; I Hurwitz, D.; Marchler, G.H.; Song, J.S.; et al. CDD/SPARCLE: The conserved domain database in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D265–D268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, H.; Sunaga, F.; Ochiai, H.; Masuda, T.; Ito, M.; Akagami, M.; Naoi, Y.; Sano, K.; Katayama, Y.; Omatsu, T.; et al. Phylogenetic analysis of novel posaviruses detected in feces of Japanese pigs with posaviruses and posa-like viruses of vertebrates and invertebrates. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 2147–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capella-Gutierrez, S.; Silla-Martínez, J.M.; Gabaldón, T. trimAl: A tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1972–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.-T.; Schmidt, H.A.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A Fast and Effective Stochastic Algorithm for Estimating Maximum-Likelihood Phylogenies. Mol. Boil. Evol. 2014, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.; Von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Gao, F.; Jakovlić, I.; Zou, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.X.; Wang, G.T. PhyloSuite: An integrated and scalable desktop platform for streamlined molecular sequence data management and evolutionary phylogenetics studies. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Lam, T.T.-Y.; Zhu, H.; Guan, Y. Two Methods for Mapping and Visualizing Associated Data on Phylogeny Using Ggtree. Mol. Boil. Evol. 2018, 35, 3041–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jombart, T.; Devillard, S.; Balloux, F. Discriminant analysis of principal components: A new method for the analysis of genetically structured populations. BMC Genet. 2010, 11, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jombart, T.; Ahmed, I. adegenet 1.3-1: New tools for the analysis of genome-wide SNP data. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 3070–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duraisamy, R.; Akiana, J.; Davoust, B.; Mediannikov, O.; Michelle, C.; Robert, C.; Parra, H.-J.; Raoult, D.; Biagini, P.; Desnues, C. Detection of novel RNA viruses from free-living gorillas, Republic of the Congo: Genetic diversity of picobirnaviruses. Virus Genes 2018, 54, 256–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, Z.; Xiao, J.; Song, Y.; Hong, M.; Dai, G.; Lu, H.; Zhang, M.; Liang, Y.; Yan, D.; Zhu, S.; et al. The Husavirus Posa-Like Viruses in China, and a New Group of Picornavirales. Viruses 2020, 12, 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12090995
Han Z, Xiao J, Song Y, Hong M, Dai G, Lu H, Zhang M, Liang Y, Yan D, Zhu S, et al. The Husavirus Posa-Like Viruses in China, and a New Group of Picornavirales. Viruses. 2020; 12(9):995. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12090995
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Zhenzhi, Jinbo Xiao, Yang Song, Mei Hong, Guolong Dai, Huanhuan Lu, Man Zhang, Yueling Liang, Dongmei Yan, Shuangli Zhu, and et al. 2020. "The Husavirus Posa-Like Viruses in China, and a New Group of Picornavirales" Viruses 12, no. 9: 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12090995
APA StyleHan, Z., Xiao, J., Song, Y., Hong, M., Dai, G., Lu, H., Zhang, M., Liang, Y., Yan, D., Zhu, S., Xu, W., & Zhang, Y. (2020). The Husavirus Posa-Like Viruses in China, and a New Group of Picornavirales. Viruses, 12(9), 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12090995




