A Unique Relative of Rotifer Birnavirus Isolated from Australian Mosquitoes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
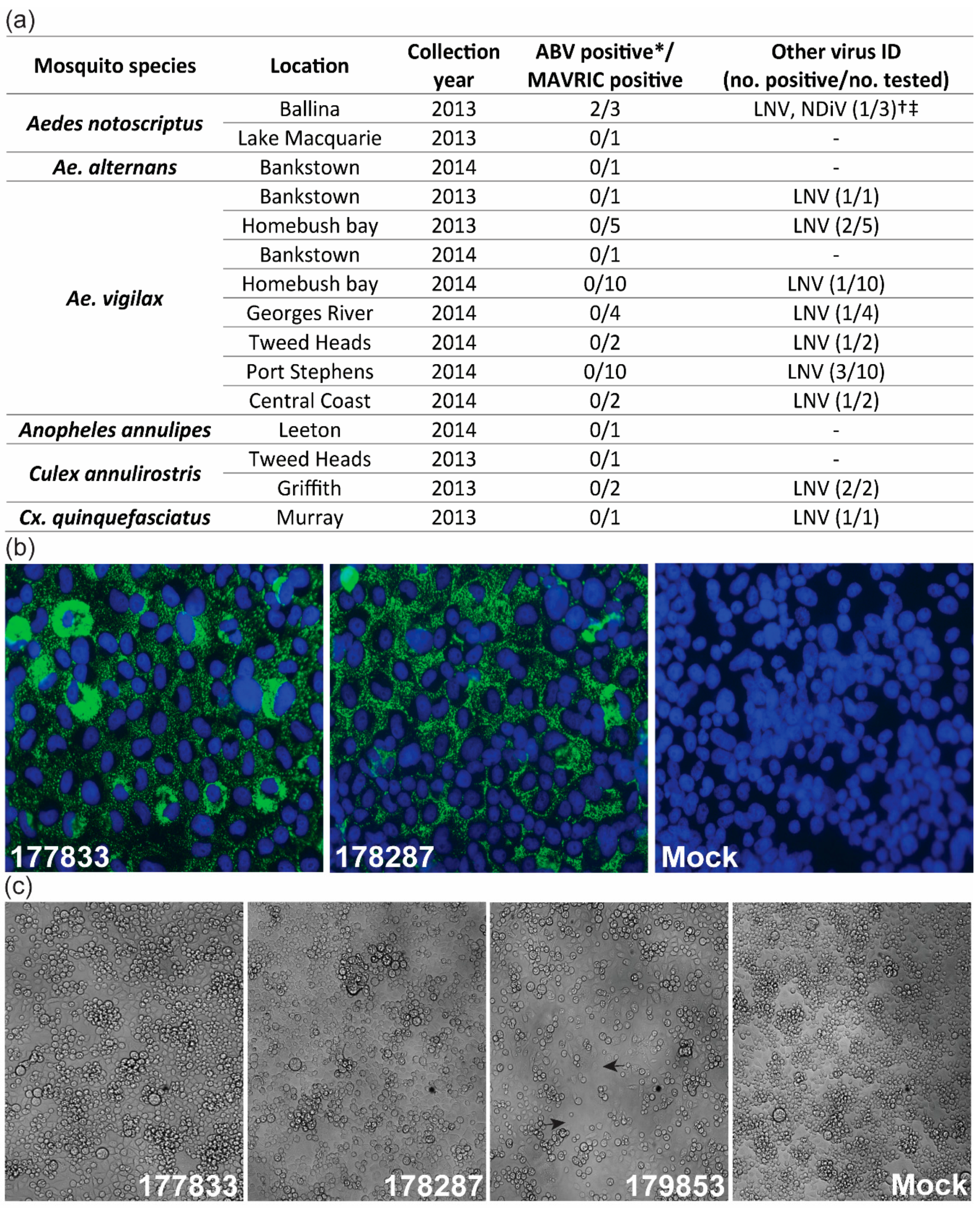
2.1. Mosquito Collection, Processing and Virus Culture
2.2. Next Gneration Sequencing and Bioinformatic Analyses
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. Virus Culture and Antigen Preparation
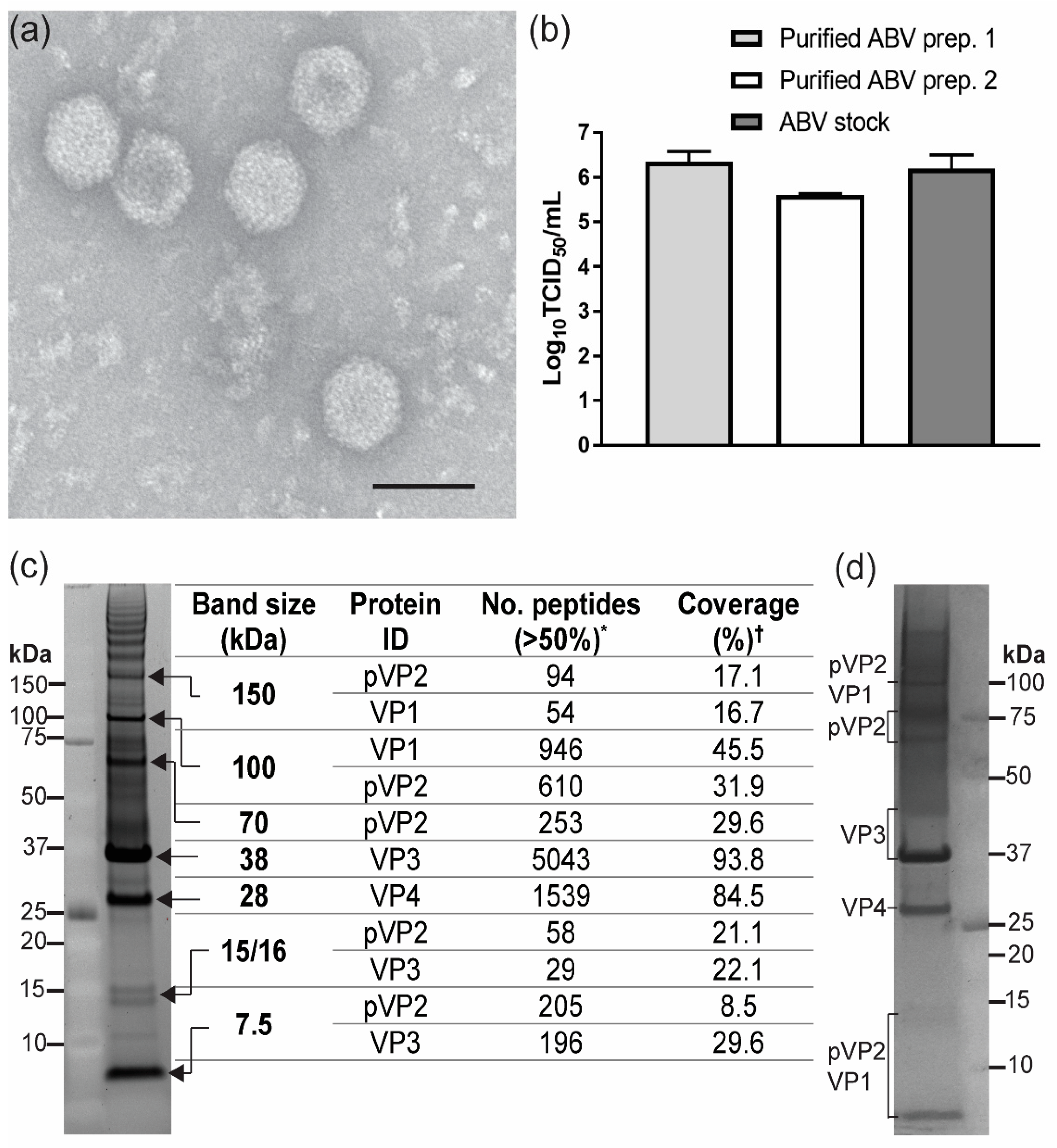
2.5. ABV Purification and Analysis of Virions
2.6. In Vitro Infectivity Assays
2.7. Immunofluorescence Assays
2.8. Generation and Characterization of Monoclonal Antibodies Raised to ABV
2.9. Protein Analysis and Mass Spectrometry for Protein Identification
3. Results
3.1. Detection of Two Isolates of a Novel Virus with Distinctive dsRNA Immunostaining
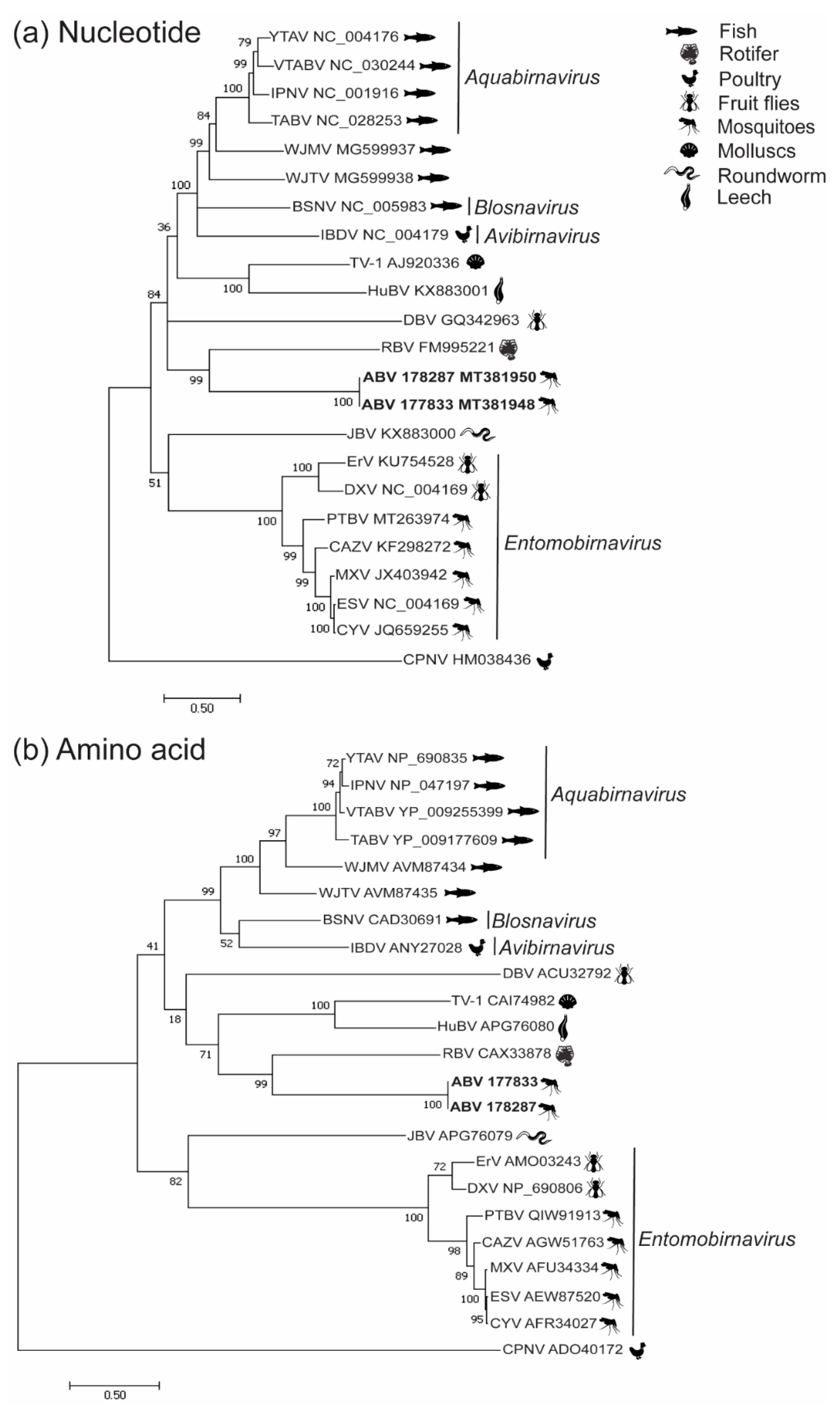
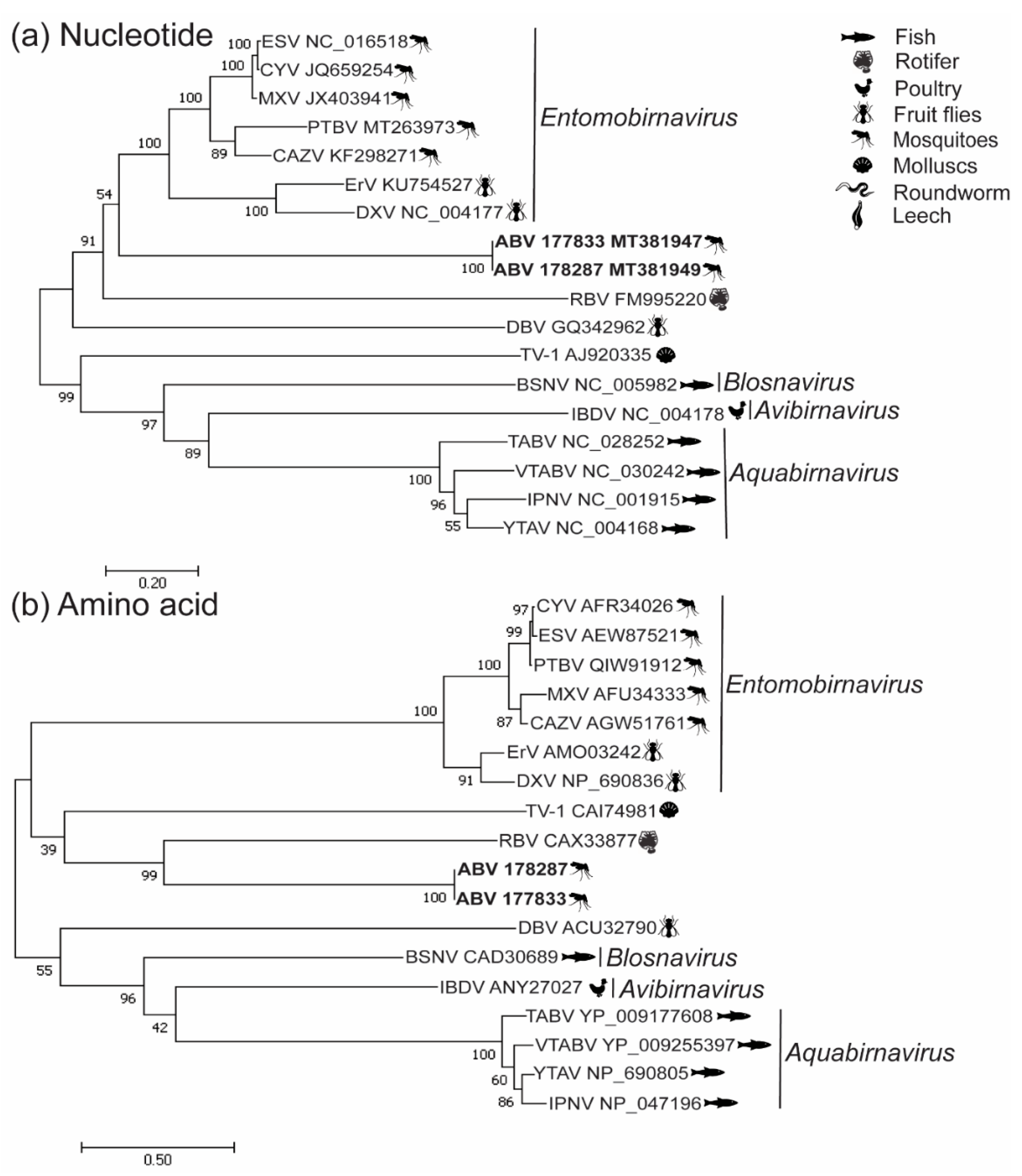
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
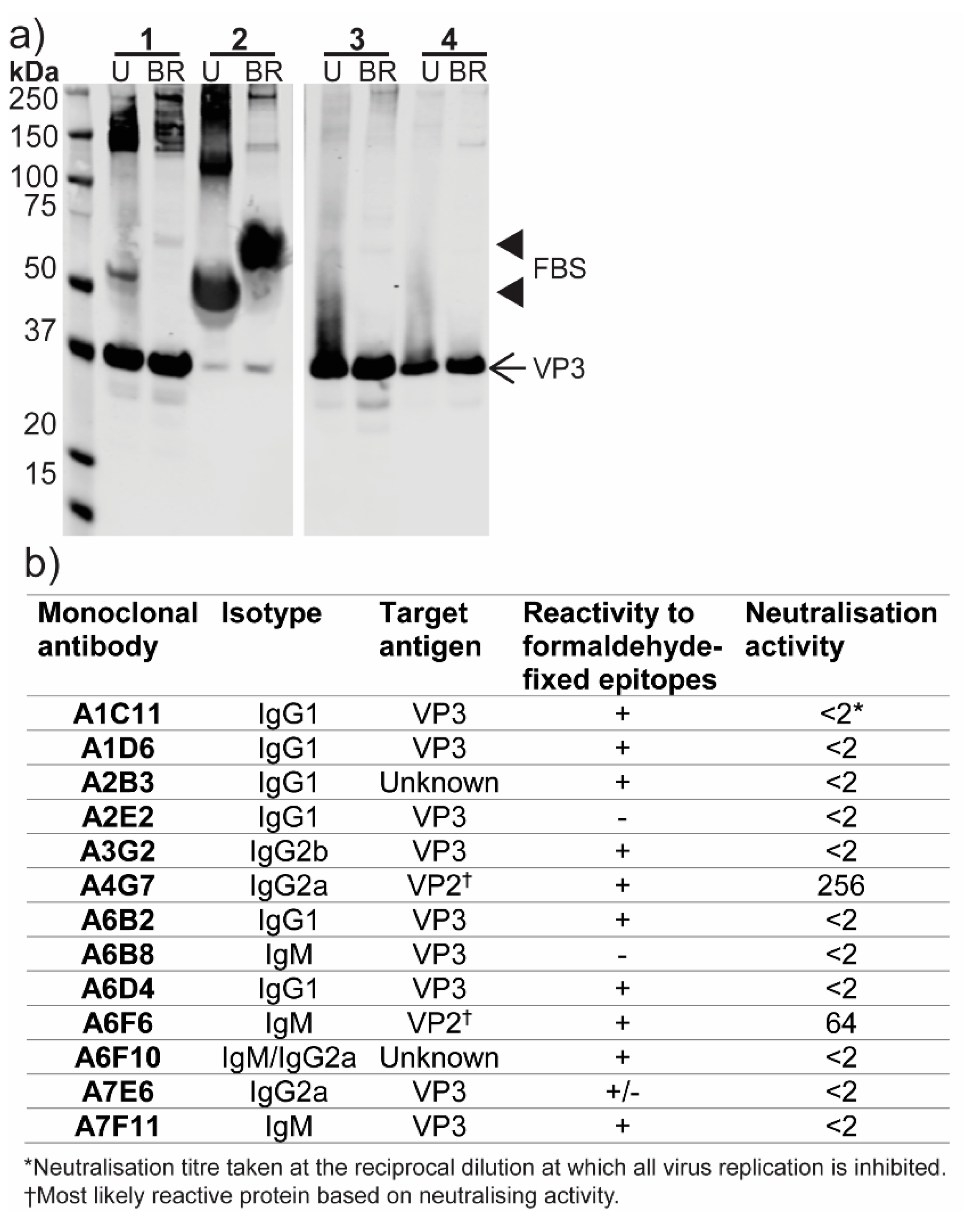
3.3. Analysis of ABV Structural Proteins
3.4. ABV Proteins Demonstrate Trypsin Resistance
3.5. Sequence Analysis of ABV Polyprotein
3.6. Production of Monoclonal Antibodies to ABV
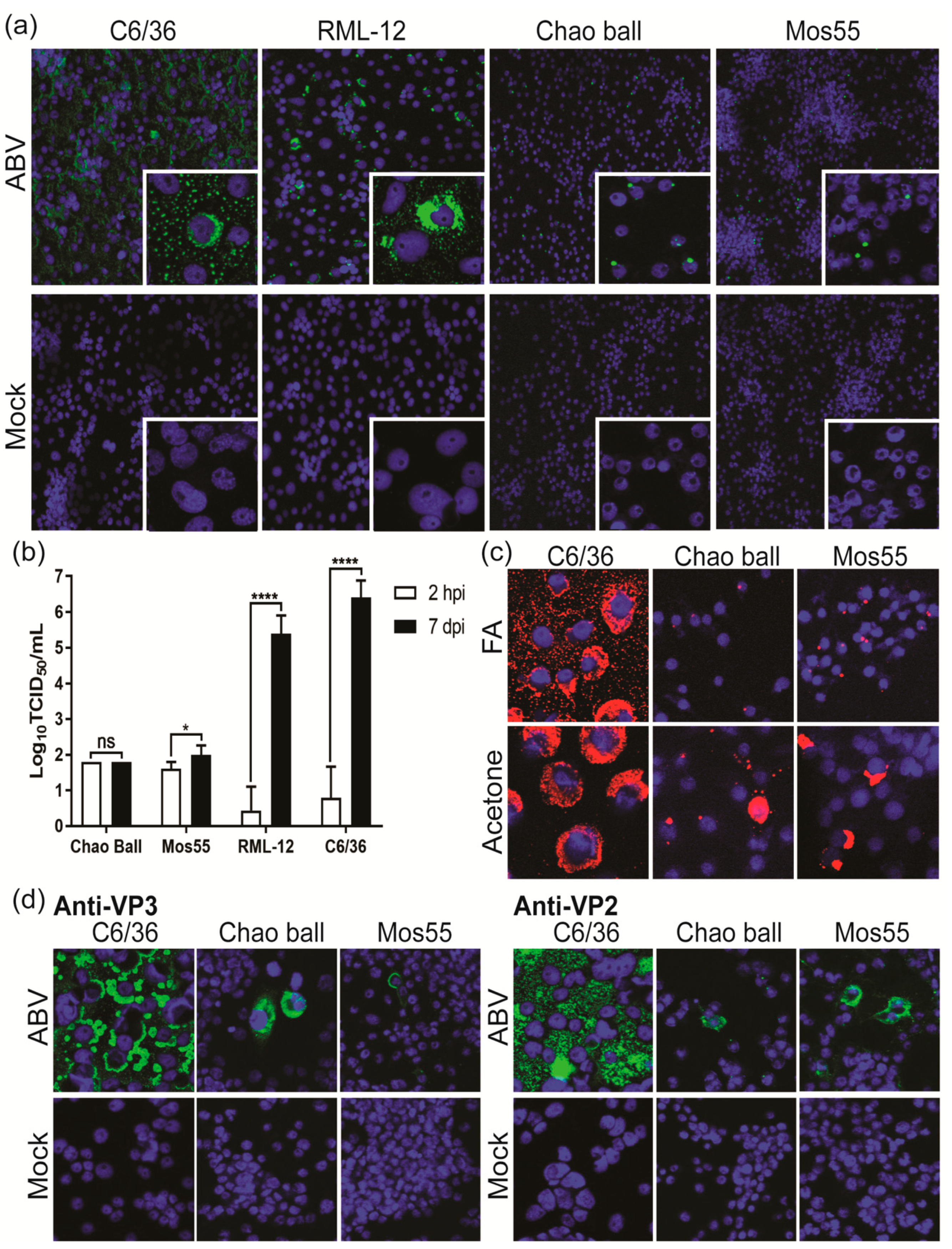
3.7. ABV Does Not Replicate in Vertebrate Cells In Vitro
3.8. ABV Displays Aedes-Specific Tropism In Vitro
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Mass Spectrometry for Glycopeptide Detection
References
- Coulibaly, F.; Chevalier, C.; Gutsche, I.; Pous, J.; Navaza, J.; Bressanelli, S.; Delmas, B.; Rey, F.A. The Birnavirus Crystal Structure Reveals Structural Relationships among Icosahedral Viruses. Cell 2005, 120, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibrat, J.-F.; Mariadassou, M.; Boudinot, P.; Delmas, B. Analyses of the radiation of birnaviruses from diverse host phyla and of their evolutionary affinities with other double-stranded RNA and positive strand RNA viruses using robust structure-based multiple sequence alignments and advanced phylogenetic methods. BMC Evol. Boil. 2013, 13, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmas, B.; Attoui, H.; Ghosh, S.; Malik, Y.S.; Mundt, E.; Vakharia, V.N. ICTV Report Consortium ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Birnaviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2019, 100, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comps, M.; Mari, J.; Poisson, F.; Bonami, J.-R. Biophysical and biochemical properties of an unusual birnavirus pathogenic for rotifers. J. Gen. Virol. 1991, 72, 1229–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Luo, Y.; Lu, R.; Lau, N.C.; Lai, E.C.; Li, W.-X.; Ding, S.-W. Virus discovery by deep sequencing and assembly of virus-derived small silencing RNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 1606–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa, B.; Chevalier, C.; Henry, C.; Huet, J.-C.; Petit, S.; Lepault, J.; Boot, H.; Delmas, B. The Capsid of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus Contains Several Small Peptides Arising from the Maturation Process of pVP2. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 2393–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Vakharia, V.N.; Tao, Y.J. The structure of a birnavirus polymerase reveals a distinct active site topology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 7385–7390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shwed, P.S.; Dobos, P.; Cameron, L.A.; Vakharia, V.N.; Duncan, R. Birnavirus VP1 Proteins Form a Distinct Subgroup of RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerases Lacking a GDD Motif. Virol. 2002, 296, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.-X.; Suzuki, S. Comparison of the RNA polymerase genes of marine birnavirus strains and other birnaviruses. Arch. Virol. 2003, 148, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez, M.C.; Zanetti, F.A.; Terebiznik, M.R.; Colombo, M.I.; Delgui, L.R. Infectious Bursal Disease Virus Hijacks Endosomal Membranes as the Scaffolding Structure for Viral Replication. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01964-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgui, L.R.; Rodríguez, J.F.; Colombo, M.I. The Endosomal Pathway and the Golgi Complex Are Involved in the Infectious Bursal Disease Virus Life Cycle. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 8993–9007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevalier, C.; Lepault, J.; Erk, I.; Da Costa, B.; Delmas, B. The Maturation Process of pVP2 Requires Assembly of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus Capsids. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 2384–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maraver, A.; Oña, A.; Abaitua, F.; González, D.; Clemente, R.; Ruiz-Díaz, J.A.; Castón, J.R.; Pazos, F.; Rodríguez, J.F. The Oligomerization Domain of VP3, the Scaffolding Protein of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus, Plays a Critical Role in Capsid Assembly. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 6438–6449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oña, A.; Luque, D.; Abaitua, F.; Maraver, A.; Castón, J.R.; Rodríguez, J.F. The C-terminal domain of the pVP2 precursor is essential for the interaction between VP2 and VP3, the capsid polypeptides of infectious bursal disease virus. Virology 2004, 322, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villanueva, R.A.; Galaz, J.L.; Valdés, J.A.; Jashés, M.M.; Sandino, A.M. Genome Assembly and Particle Maturation of the Birnavirus Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 13829–13838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vancini, R.; Paredes, A.; Ribeiro, M.; Blackburn, K.; Ferreira, D.; Kononchik, J.P.; Hernandez, R.; Brown, D.T. Espirito Santo Virus: A New Birnavirus That Replicates in Insect Cells. J. Virol. 2011, 86, 2390–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marklewitz, M.; Gloza-Rausch, F.; Kurth, A.; Kümmerer, B.M.; Drosten, C.; Junglen, S. First isolation of an Entomobirnavirus from free-living insects. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 2431–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Mi, Z.; Zhuang, L.; Ma, M.-J.; An, X.; Liu, W.; Cao, W.; Tong, Y. Presence of entomobirnaviruses in Chinese mosquitoes in the absence of Dengue virus co-infection. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, S.; Chung, B.Y.-W.; Bass, D.; Moureau, G.; Tang, S.; McAlister, E.; Culverwell, C.L.; Glücksman, E.; Wang, H.; Brown, T.D.K.; et al. Novel Virus Discovery and Genome Reconstruction from Field RNA Samples Reveals Highly Divergent Viruses in Dipteran Hosts. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesh, R.B.; Bolling, B.G.; Guzman, H.; Popov, V.L.; Wilson, A.; Widen, S.G.; Wood, T.G.; Walker, P.J.; Vasilakis, N. Characterization of Port Bolivar Virus, a Novel Entomobirnavirus (Birnaviridae) Isolated from Mosquitoes Collected in East Texas, USA. Viruses 2020, 12, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, R.A.; Bielefeldt-Ohmann, H.; McLean, B.J.; O’Brien, C.A.; Colmant, A.M.; Piyasena, T.B.; Harrison, J.J.; Newton, N.D.; Barnard, R.T.; Prow, N.A.; et al. Commensal Viruses of Mosquitoes: Host Restriction, Transmission, and Interaction with Arboviral Pathogens. Evol. Bioinform. 2017, 12, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piyasena, T.B.H.; Newton, N.D.; Hobson-Peters, J.; Vet, L.J.; Setoh, Y.X.; Bielefeldt-Ohmann, H.; Khromykh, A.A.; Hall, R.A. Chimeric viruses of the insect-specific flavivirus Palm Creek with structural proteins of vertebrate-infecting flaviviruses identify barriers to replication of insect-specific flaviviruses in vertebrate cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2019, 100, 1580–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall-Mendelin, S.; McLean, B.J.; Bielefeldt-Ohmann, H.; Hobson-Peters, J.; Hall, R.A.; Hurk, A.F.V.D. The insect-specific Palm Creek virus modulates West Nile virus infection in and transmission by Australian mosquitoes. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erasmus, J.H.; Seymour, R.L.; Kaelber, J.T.; Kim, D.Y.; Leal, G.; Sherman, M.B.; Frolov, I.; Chiu, W.; Weaver, S.C.; Nasar, F. Novel insect-specific Eilat virus-based chimeric vaccine candidates provide durable, mono- and multi-valent, single dose protection against lethal alphavirus challenge. J. Virol. 2017, 92, e01274-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobson-Peters, J.; Harrison, J.J.; Watterson, D.; Hazlewood, J.E.; Vet, L.J.; Newton, N.D.; Warrilow, D.; Colmant, A.M.; Taylor, C.; Huang, B.; et al. A recombinant platform for flavivirus vaccines and diagnostics using chimeras of a new insect-specific virus. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaax7888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, C.A.; Hobson-Peters, J.; Yam, A.W.Y.; Colmant, A.M.; McLean, B.J.; Prow, N.A.; Watterson, D.; Hall-Mendelin, S.; Warrilow, D.; Ng, M.-L.; et al. Viral RNA Intermediates as Targets for Detection and Discovery of Novel and Emerging Mosquito-Borne Viruses. PLOS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A O’Brien, C.; McLean, B.J.; Colmant, A.M.; Harrison, J.J.; Hall-Mendelin, S.; Hurk, A.F.V.D.; A Johansen, C.; Watterson, D.; Bielefeldt-Ohmann, H.; Newton, N.D.; et al. Discovery and Characterisation of Castlerea Virus, a New Species ofNegevirusIsolated in Australia. Evol. Bioinform. 2017, 13, 1176934317691269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prow, N.A.; Mah, M.G.; Deerain, J.M.; Warrilow, D.; Colmant, A.M.; O’Brien, C.A.; Harrison, J.J.; McLean, B.J.; Hewlett, E.K.; Piyasena, T.B.H.; et al. New genotypes of Liao ning virus (LNV) in Australia exhibit an insect-specific phenotype. J. Gen. Virol. 2018, 99, 596–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, J.J.; Warrilow, D.; McLean, B.J.; Watterson, D.; O’Brien, C.A.; Colmant, A.M.; Johansen, C.A.; Barnard, R.T.; Hall-Mendelin, S.; Davis, S.S.; et al. A New Orbivirus Isolated from Mosquitoes in North-Western Australia Shows Antigenic and Genetic Similarity to Corriparta Virus but Does Not Replicate in Vertebrate Cells. Viruses 2016, 8, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, B.J.; Hobson-Peters, J.; Webb, C.E.; Watterson, D.; Prow, N.A.; Nguyen, H.D.; Hall-Mendelin, S.; Warrilow, D.; Johansen, C.A.; Jansen, C.C.; et al. A novel insect-specific flavivirus replicates only in Aedes-derived cells and persists at high prevalence in wild Aedes vigilax populations in Sydney, Australia. Virology 2015, 486, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrilow, D.; Huang, B.; Newton, N.D.; Harrison, J.J.; Johnson, K.N.; Chow, W.K.; Hall, R.A.; Hobson-Peters, J. The taxonomy of an Australian nodavirus isolated from mosquitoes. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0210029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colmant, A.M.; O’Brien, C.A.; Newton, N.D.; Watterson, D.; Hardy, J.M.; Coulibaly, F.; Bielefeldt-Ohmann, H.; Warrilow, D.; Huang, B.; Paramitha, D.; et al. Novel monoclonal antibodies against Australian strains of negeviruses and insights into virus structure, replication and host -restriction. J. Gen. Virol. 2020, 101, 440–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warrilow, D.; Watterson, D.; Hall, R.A.; Davis, S.S.; Weir, R.; Kurucz, N.; Whelan, P.; Allcock, R.; Hall-Mendelin, S.; O’Brien, C.A.; et al. A New Species of Mesonivirus from the Northern Territory, Australia. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobson-Peters, J.; Yam, A.W.Y.; Lu, J.; Setoh, Y.X.; May, F.; Kurucz, N.; Walsh, S.; Prow, N.A.; Davis, S.S.; Weir, R.; et al. A New Insect-Specific Flavivirus from Northern Australia Suppresses Replication of West Nile Virus and Murray Valley Encephalitis Virus in Co-infected Mosquito Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.; Pfeiffer, W.; Schwartz, T. Creating the CIPRES Science Gateway for inference of large phylogenetic trees. In Proceedings of the Gateway Computing Environments Workshop (GCE), New Orleans, LA, USA, 14 November 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. A simple method of estimating fifty percent endpoints. Am J Epidemiol 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, L.Y.; Hobson-Peters, J.; Prow, N.A.; Gardner, J.; Bielefeldt-Ohmann, H.; Pyke, A.T.; Suhrbier, A.; Hall, R.A. Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies to the E2 protein of chikungunya virus protects against disease in a mouse model. Clin. Immunol. 2013, 149, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irigoyen, N.; Garriga, D.; Navarro, A.; Verdaguer, N.; Rodríguez, J.F.; Castón, J.R. Autoproteolytic Activity Derived from the Infectious Bursal Disease Virus Capsid Protein. J. Boil. Chem. 2009, 284, 8064–8072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobos, P. The molecular biology of infectious pancreatic necrosis virus (IPNV). Annu. Rev. Fish Dis. 1995, 5, 25–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giansanti, P.; Tsiatsiani, L.; Low, T.Y.; Heck, A.J.R. Six alternative proteases for mass spectrometry–based proteomics beyond trypsin. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 993–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imajoh, M.; Goto, T.; Oshima, S. Characterization of cleavage sites and protease activity in the polyprotein precursor of Japanese marine aquabirnavirus and expression analysis of generated proteins by a VP4 protease activity in four distinct cell lines. Arch. Virol. 2007, 152, 1103–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, S.; Lejal, N.; Huet, J.-C.; Delmas, B. Active Residues and Viral Substrate Cleavage Sites of the Protease of the Birnavirus Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 2057–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobson-Peters, J.; Warrilow, D.; McLean, B.J.; Watterson, D.; Colmant, A.M.; Hurk, A.F.V.D.; Hall-Mendelin, S.; Hastie, M.L.; Gorman, J.J.; Harrison, J.J.; et al. Discovery and characterisation of a new insect-specific bunyavirus from Culex mosquitoes captured in northern Australia. Virology 2016, 489, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pous, J.; Chevalier, C.; Ouldali, M.; Navaza, J.; Delmas, B.; Lepault, J. Structure of birnavirus-like particles determined by combined electron cryomicroscopy and X-ray crystallography. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 2339–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frost, P.; Havarstein, L.S.; Lygren, B.; Ståhl, S.; Endresen, C.; Christie, K.E. Mapping of neutralization epitopes on infectious pancreatic necrosis viruses. J. Gen. Virol. 1995, 76, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahey, K.J.; Erny, K.; Crooks, J. A Conformational Immunogen on VP-2 of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus that Induces Virus-neutralizing Antibodies that Passively Protect Chickens. J. Gen. Virol. 1989, 70, 1473–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCowan, C.; Motha, J.; Crane, M.; Moody, N.; Crameri, S.; Hyatt, A.; Bradley, T. Isolation of a novel aquatic birnavirus from rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss in Australia. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2015, 114, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, D.C.; Ayres, M.D.; Howard, S.C.; Lescott, T.; Arnold, M.K.; Seeley, N.D.; Primrose, S.B. Isolation of a Bisegmented Double-stranded RNA Virus from Thirlmere Reservoir. J. Gen. Virol. 1982, 62, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Falzarano, D.; Misra, V. Caution: Choice of fixative can influence the visualization of the location of a transcription factor in mammalian cells. BioTechniques 2018, 65, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cleef, K.W.; Van Mierlo, J.T.; Miesen, P.; Overheul, G.J.; Fros, J.J.; Schuster, S.; Marklewitz, M.; Pijlman, G.; Junglen, S.; Van Rij, R.P. Mosquito and Drosophila entomobirnaviruses suppress dsRNA- and siRNA-induced RNAi. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 8732–8744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzke, K.; Leggewie, M.; Sreenu, V.B.; Jansen, S.; Heitmann, A.; Welch, S.R.; Brennan, B.; Elliott, R.M.; Tannich, E.; Becker, S.C.; et al. Detection, infection dynamics and small RNA response against Culex Y virus in mosquiot-derived cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2018, 99, 1739–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Protein Identified | Trypsin | Chymotrypsin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. Peptides (50%) * | % Coverage (50) † | No. Peptides (50%) * | % Coverage (50) † | |
| VP1 | 161 | 38.4 | 145 | 43.04 |
| Polyprotein | 605 | 54.7 | 476 | 74.6 |
| pVP2 | 197 | 34.9 | 250 | 70.8 |
| VP3 | 237 | 60.6 | 108 | 82.08 |
| VP4 | 171 | 83.7 | 109 | 84.09 |
| Cell Line | Cell Origin | ABV Replication | Mean Titer Recovered (/mL) † | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 hpi | 5 dpi | |||
| DF-1 | Avian | - | 101.8 | 100.87 |
| Vero | Monkey | - | 101.8 | 101.41 |
| SW13 | Human | - | 101.3 | <101.3 * |
| A549 | Human | - | 101.78 | <101.3 |
| MDCK | Canine | - | 101.05 | <101.3 |
| BSR | Rodent | - | 102.02 | <101.3 |
| MEF IFNAR-/- | Rodent | - | 101.11 | <101.3 |
| VSW | Reptile | - | 101.71 | <101.3 |
| A6 | Amphibian | - | 101.71 | 101.45 # |
| C6/36 | Mosquito | + | 102.13 | 105.8 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
O’Brien, C.A.; Pegg, C.L.; Nouwens, A.S.; Bielefeldt-Ohmann, H.; Huang, B.; Warrilow, D.; Harrison, J.J.; Haniotis, J.; Schulz, B.L.; Paramitha, D.; et al. A Unique Relative of Rotifer Birnavirus Isolated from Australian Mosquitoes. Viruses 2020, 12, 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12091056
O’Brien CA, Pegg CL, Nouwens AS, Bielefeldt-Ohmann H, Huang B, Warrilow D, Harrison JJ, Haniotis J, Schulz BL, Paramitha D, et al. A Unique Relative of Rotifer Birnavirus Isolated from Australian Mosquitoes. Viruses. 2020; 12(9):1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12091056
Chicago/Turabian StyleO’Brien, Caitlin A., Cassandra L. Pegg, Amanda S. Nouwens, Helle Bielefeldt-Ohmann, Bixing Huang, David Warrilow, Jessica J. Harrison, John Haniotis, Benjamin L. Schulz, Devina Paramitha, and et al. 2020. "A Unique Relative of Rotifer Birnavirus Isolated from Australian Mosquitoes" Viruses 12, no. 9: 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12091056
APA StyleO’Brien, C. A., Pegg, C. L., Nouwens, A. S., Bielefeldt-Ohmann, H., Huang, B., Warrilow, D., Harrison, J. J., Haniotis, J., Schulz, B. L., Paramitha, D., Colmant, A. M. G., Newton, N. D., Doggett, S. L., Watterson, D., Hobson-Peters, J., & Hall, R. A. (2020). A Unique Relative of Rotifer Birnavirus Isolated from Australian Mosquitoes. Viruses, 12(9), 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12091056







