Turnip Mosaic Virus Coat Protein Deletion Mutants Allow Defining Dispensable Protein Domains for ‘in Planta’ eVLP Formation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
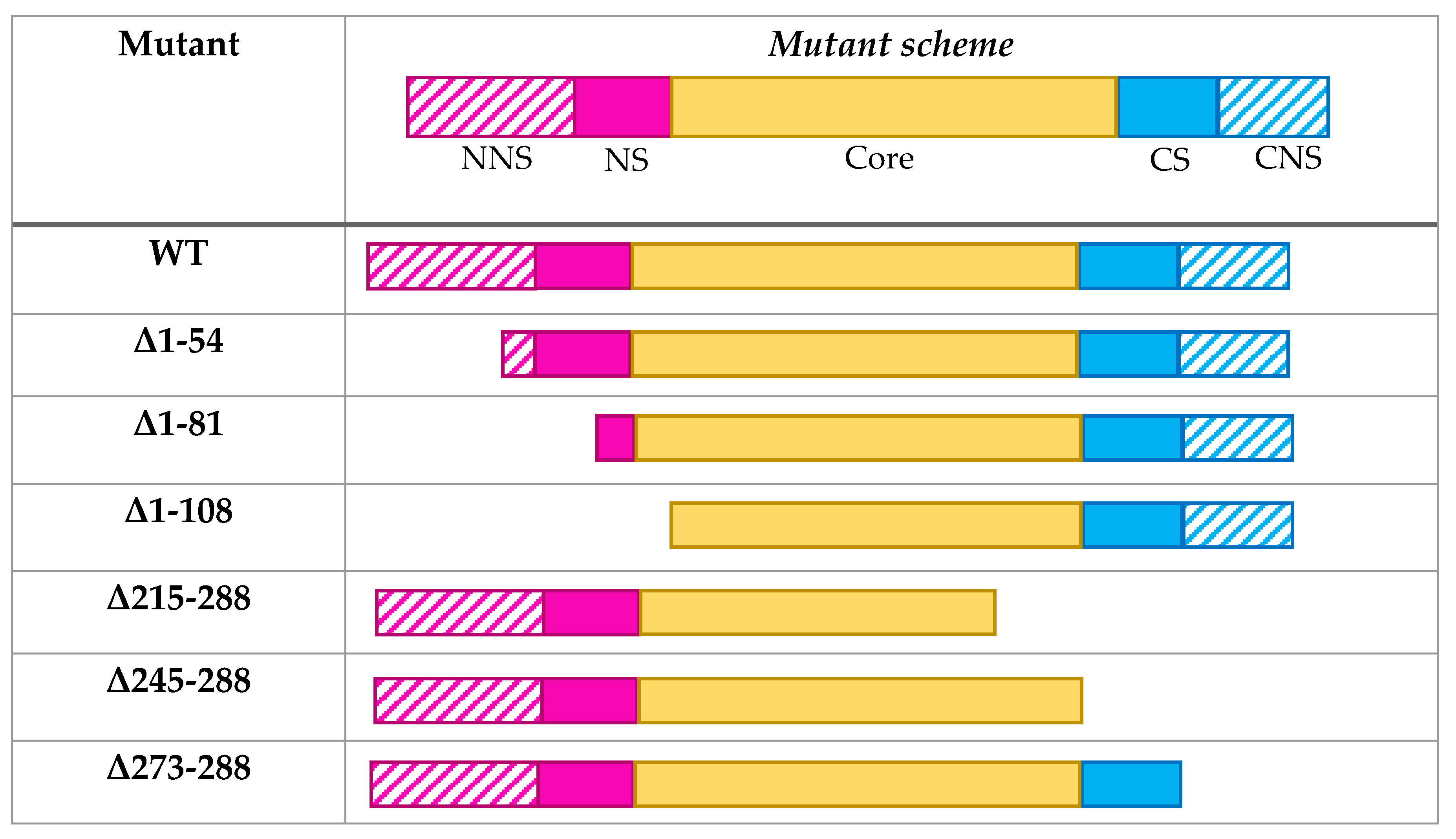
2.1. Construction of Expression Plasmids
2.2. Production and Purification
2.3. Immunoassays
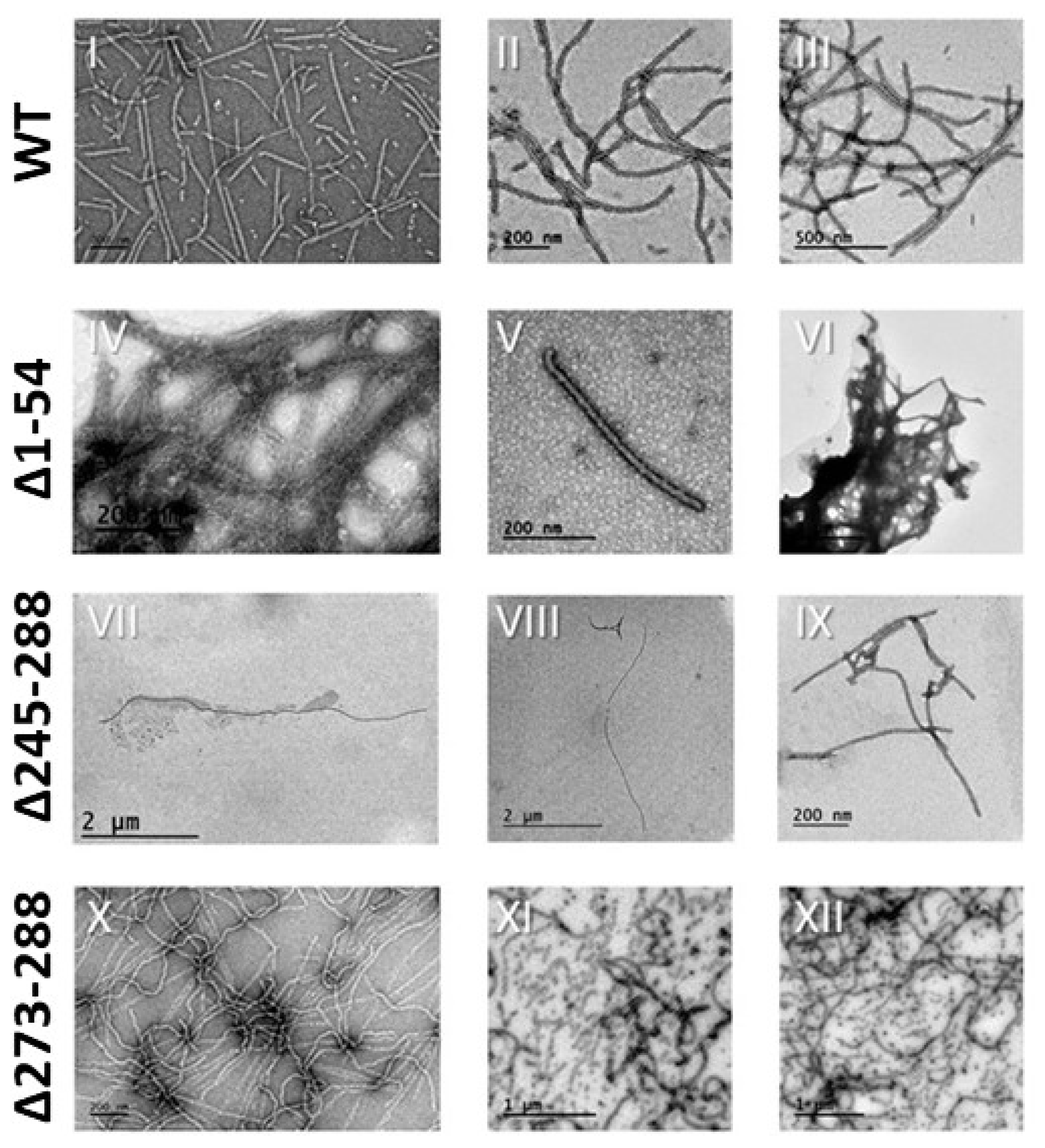
2.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
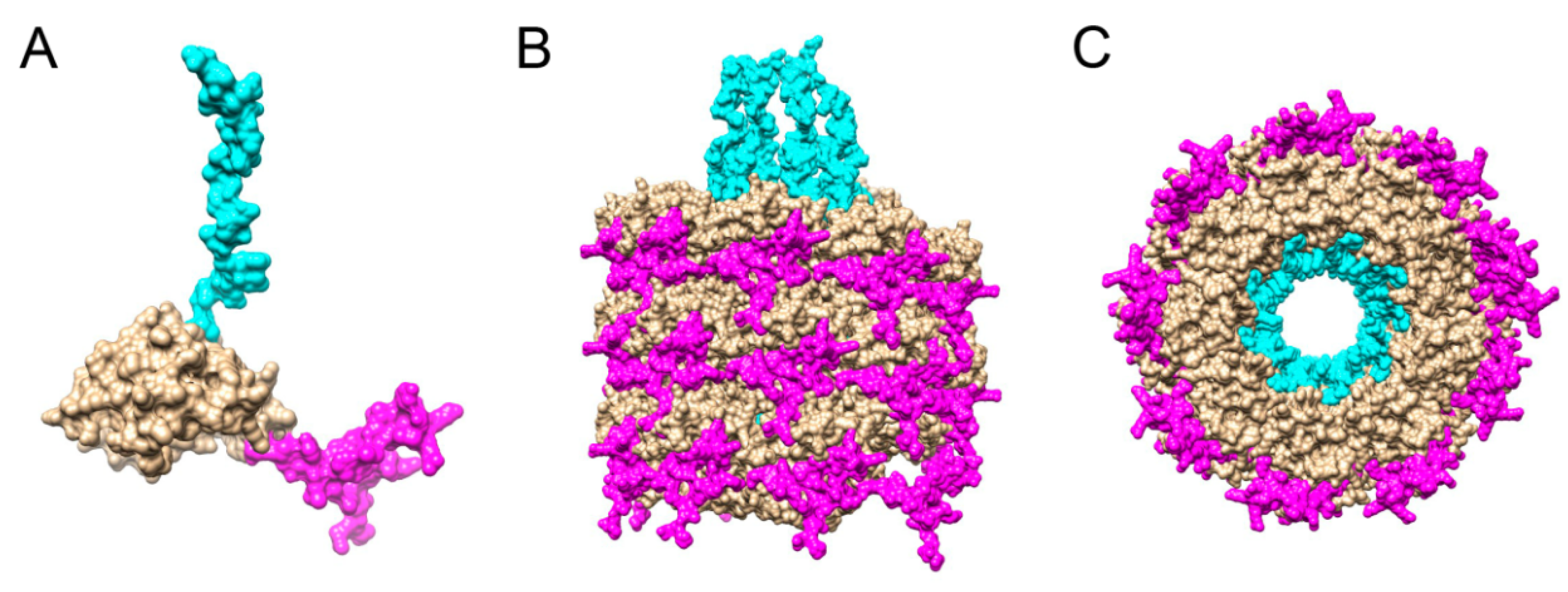
3. Results and Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klug, A. The Tobacco mosaic virus particle: Structure and assembly. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1999, 354, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomonossoff, G.P.; Wege, C. TMV Particles: The journey from fundamental studies to bionanotechnology applications. Adv. Virus Res. 2018, 102, 149–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grinzato, A.; Kandiah, E.; Lico, C.; Betti, C.; Baschieri, S.; Zanotti, G. Atomic structure of potato virus X, the prototype of the Alphaflexiviridae family. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2020, 16, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitek, A.S.; Hu, H.; Shukla, S.; Steinmetz, N.F. Cancer theranostic applications of albumin-coated Tobacco mosaic virus nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 39468–39477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, D.H.T.; Hu, H.; Commandeur, U.; Steinmetz, N.F. Chemical addressability of Potato virus X for its applications in bio/nanotechnology. J. Struct. Biol. 2017, 200, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lico, C.; Benvenuto, E.; Baschieri, S. The two-faced Potato virus X: From plant pathogen to smart nanoparticle. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, N.F.; Mertens, M.E.; Taurog, R.E.; Johnson, J.E.; Commandeur, U.; Fischer, R.; Manchester, M. Potato virus X as a novel platform for potential biomedical applications. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiben, S.; Koch, C.; Altintoprak, K.; Southan, A.; Tovar, G.; Laschat, S.; Weiss, I.M.; Wege, C. Plant virus-based materials for biomedical applications: Trends and prospects. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 145, 96–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittner, A.M. TMV-templated formation of metal and polymer nanotubes. In Virus-Derived Nanoparticles for Advanced Technologies: Methods and Protocols; Wege, C., Lomonossoff, G.P., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkhipenko, M.V.; Petrova, E.K.; Nikitin, N.A.; Protopopova, A.D.; Dubrovin, E.V.; Yaminskii, I.V.; Rodionova, N.P.; Karpova, O.V.; Atabekov, J.G. Characteristics of artificial virus-like particles assembled in vitro from Potato virus X coat protein and foreign viral RNAs. Acta Nat. 2011, 3, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, R.M.; McDonald, J.G.; Horne, R.W.; Bancroft, J.B. Assembly of flexuous plant viruses and their proteins. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1976, 276, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culver, J.N. Tobacco mosaic virus assembly and disassembly: Determinants in pathogenicity and resistance. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2002, 40, 287–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kegel, W.K.; van der Schoot, P. Physical regulation of the self-assembly of Tobacco mosaic virus coat protein. Biophys. J. 2006, 91, 1501–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Cui, Z. Virus-like particles as theranostic platforms. Adv. Ther. 2020, 1900194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybicki, E.P. Plant molecular farming of virus-like nanoparticles as vaccines and reagents. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 12, e1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porta, C.; Spall, V.E.; Findlay, K.C.; Gergerich, R.C.; Farrance, C.E.; Lomonossoff, G.P. Cowpea mosaic virus-based chimaeras—Effects of inserted peptides on the phenotype, host range, and transmissibility of the modified viruses. Virology 2003, 310, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, J.F.C.; Peyret, H.; Saunders, K.; Castells-Graells, R.; Marsian, J.; Meshcheriakova, Y.; Lomonossoff, G.P. Synthetic plant virology for nanobiotechnology and nanomedicine. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 9, e1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donchenko, E.K.; Pechnikova, E.V.; Mishyna, M.Y.; Manukhova, T.I.; Sokolova, O.S.; Nikitin, N.A.; Atabekov, J.G.; Karpova, O.V. Structure and properties of virions and virus-like particles derived from the coat protein of Alternanthera mosaic virus. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Gamboa, I.; Manrique, P.; Sánchez, F.; Ponz, F. Plant-made potyvirus-like particles used for log-increasing antibody sensing capacity. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 254, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuste-Calvo, C.; Lopez-Santalla, M.; Zurita, L.; Cruz-Fernandez, C.F.; Sanchez, F.; Garin, M.I.; Ponz, F. Elongated flexuous plant virus-derived nanoparticles functionalized for autoantibody detection. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potyvirus~ViralZone Page (SIB Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics). Available online: https://viralzone.expasy.org/50 (accessed on 28 April 2020).
- Wylie, S.J.; Adams, M.; Chalam, C.; Kreuze, J.; López-Moya, J.J.; Ohshima, K.; Praveen, S.; Rabenstein, F.; Stenger, D.; Wang, A.; et al. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Potyviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 352–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora, M.; Méndez-López, E.; Agirrezabala, X.; Cuesta, R.; Lavín, J.L.; Sánchez-Pina, M.A.; Aranda, M.A.; Valle, M. Potyvirus virion structure shows conserved protein fold and RNA binding site in ssRNA viruses. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, eaao2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kezar, A.; Kavcic, L.; Polak, M.; Novacek, J.; Gutierrez-Aguirre, I.; Znidaric, M.T.; Coll, A.; Stare, K.; Gruden, K.; Ravnikar, M.; et al. Structural basis for the multitasking nature of the potato virus Y coat protein. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaaw3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuesta, R.; Yuste-Calvo, C.; Gil-Carton, D.; Sanchez, F.; Ponz, F.; Valle, M. Structure of Turnip mosaic virus and its viral-like particles. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, F.; Sáez, M.; Lunello, P.; Ponz, F. Plant viral elongated nanoparticles modified for log-increases of foreign peptide immunogenicity and specific antibody detection. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 168, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velázquez-Lam, E.; Imperial, J.; Ponz, F. Polyphenol-functionalized plant viral-derived nanoparticles exhibit strong antimicrobial and antibiofilm formation activities. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 2040–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuenca, S.; Mansilla, C.; Aguado, M.; Yuste-Calvo, C.; Sánchez, F.; Sánchez-Montero, J.M.; Ponz, F. Nanonets derived from Turnip mosaic virus as scaffolds for increased enzymatic activity of immobilized Candida antarctica lipase B. Front. Plant. Sci. 2016, 7, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuste-Calvo, C.; González-Gamboa, I.; Pacios, L.F.; Sánchez, F.; Ponz, F. Structure-based multifunctionalization of mlexuous elongated viral nanoparticles. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 5019–5028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Aoust, M.A.; Lavoie, P.O.; Couture, M.M.; Trepanier, S.; Guay, J.M.; Dargis, M.; Mongrand, S.; Landry, N.; Ward, B.J.; Vezina, L.P. Influenza virus-like particles produced by transient expression in Nicotiana benthamiana induce a protective immune response against a lethal viral challenge in mice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2008, 6, 930–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainsbury, F.; Liu, L.; Lomonossoff, G.P. Cowpea mosaic virus-based systems for the expression of antigens and antibodies in plants. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 483, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, D.D.; Tribbick, G.; Mason, T.J.; Hewish, D.R.; Geysen, H.M.; Ward, C.W. Localization of virus-specific and group-specific epitopes of plant potyviruses by systematic immunochemical analysis of overlapping peptide fragments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 8192–8196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, D.D.; Strike, P.M.; Tracy, S.L.; Gough, K.H.; Ward, C.W. The N-termini and C-termini of the coat proteins of potyviruses are surface-located and the N-terminus contains the major virus-specific epitopes. J. Gen. Virol. 1988, 69, 1497–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touriño, A.; Sánchez, F.; Fereres, A.; Ponz, F. High expression of foreign proteins from a biosafe viral vector derived from Turnip mosaic virus. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2008, 6, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimalov, B.; Gal-On, A.; Stav, R.; Belausov, E.; Arazi, T. Maintenance of coat protein N-terminal net charge and not primary sequence is essential for Zucchini yellow mosaic virus systemic infectivity. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 3421–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voloudakis, A.E.; Aleman-Verdaguer, M.E.; Padgett, H.S.; Beachy, R.N. Characterization of resistance in transgenic Nicotiana benthamiana encoding N-terminal deletion and assembly mutants of the tobacco etch potyvirus coat protein. Arch. Virol. 2005, 150, 2567–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatineni, S.; Kovacs, F.; French, R. Wheat streak mosaic virus infects systemically despite extensive coat protein deletions: Identification of virion assembly and cell-to-cell movement determinants. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 1366–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybicki, E.P.; Shukla, D.D. Coat protein phylogeny and systematics of potyviruses. In Archives of Virology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1992; Volume 5, pp. 139–170. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, D.D.; Ward, C.W.; Brunt, A.A. The Potyviridae; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 1994; p. xii. 516p. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, S.H.; Lim, W.S.; Hwang, S.H.; Park, J.W.; Choi, H.S.; Kim, K.H. Importance of the C-terminal domain of Soybean mosaic virus coat protein for subunit interactions. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukashina, E.; Ksenofontov, A.; Fedorova, N.; Badun, G.; Mukhamedzhanova, A.; Karpova, O.; Rodionova, N.; Baratova, L.; Dobrov, E. Analysis of the role of the coat protein N-terminal segment in Potato virus X virion stability and functional activity. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2012, 13, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuste-Calvo, C.; Ibort, P.; Sánchez, F.; Ponz, F. Turnip Mosaic Virus Coat Protein Deletion Mutants Allow Defining Dispensable Protein Domains for ‘in Planta’ eVLP Formation. Viruses 2020, 12, 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12060661
Yuste-Calvo C, Ibort P, Sánchez F, Ponz F. Turnip Mosaic Virus Coat Protein Deletion Mutants Allow Defining Dispensable Protein Domains for ‘in Planta’ eVLP Formation. Viruses. 2020; 12(6):661. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12060661
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuste-Calvo, Carmen, Pablo Ibort, Flora Sánchez, and Fernando Ponz. 2020. "Turnip Mosaic Virus Coat Protein Deletion Mutants Allow Defining Dispensable Protein Domains for ‘in Planta’ eVLP Formation" Viruses 12, no. 6: 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12060661
APA StyleYuste-Calvo, C., Ibort, P., Sánchez, F., & Ponz, F. (2020). Turnip Mosaic Virus Coat Protein Deletion Mutants Allow Defining Dispensable Protein Domains for ‘in Planta’ eVLP Formation. Viruses, 12(6), 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12060661





