Characterisation of Peste Des Petits Ruminants Disease in Pastoralist Flocks in Ngorongoro District of Northern Tanzania and Bluetongue Virus Co-Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Outbreak Investigation, PPRV Rapid Diagnostic Test, Sample Collection and Processing
2.3. Antibody Detection by cELISA
2.4. Real-Time Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
2.5. Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.6. Ethical Approval
3. Results
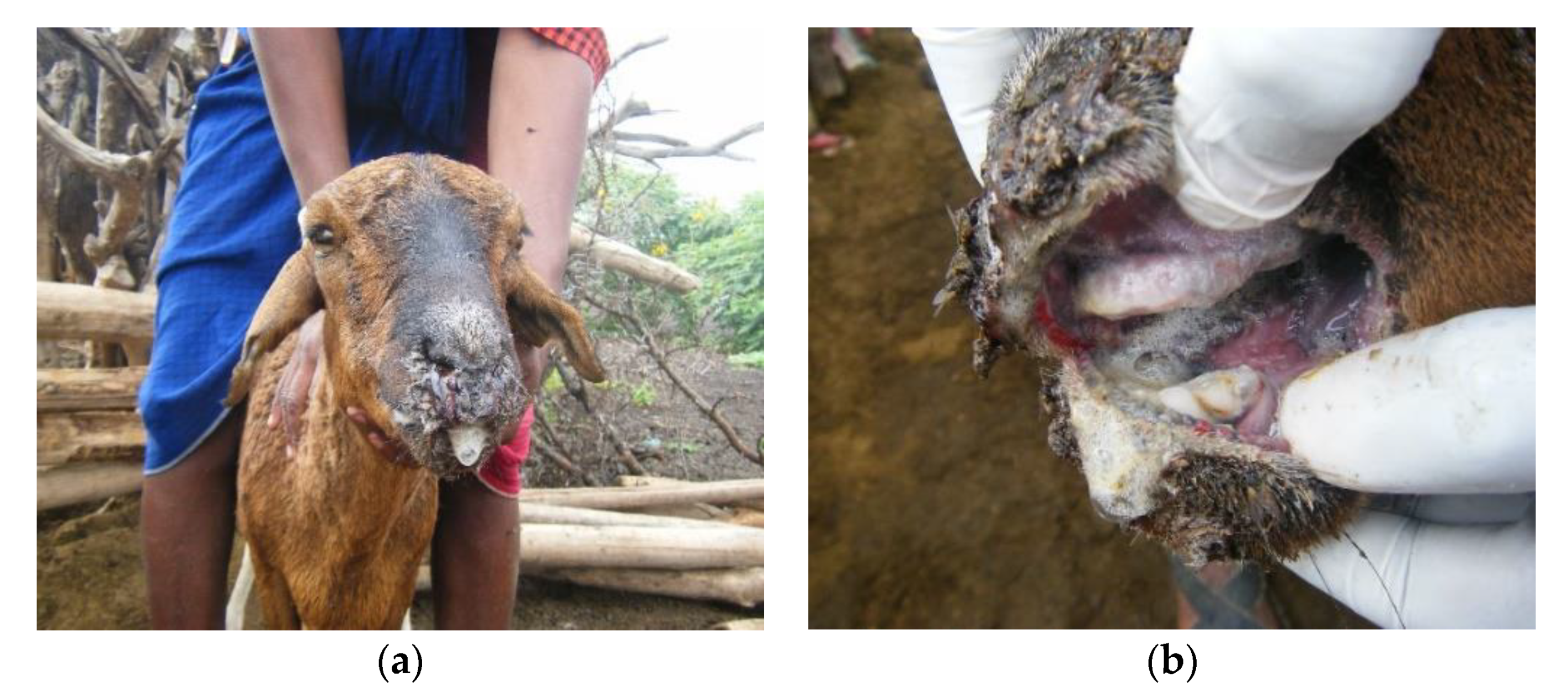
3.1. Outbreak Investigations
3.1.1. Wasso and the Olorien-Magaiduru Ward
Flock 1
Flock 3
Flock 4
Flock 9
3.1.2. Soitsambu and Ololosokwan Wards
Flock 5
Flock 6
Flock 17
Flock 2
3.1.3. Olbalbal Ward
Flock 19
3.1.4. Endulen and Kakesio Wards
Flock 26
Flock 29
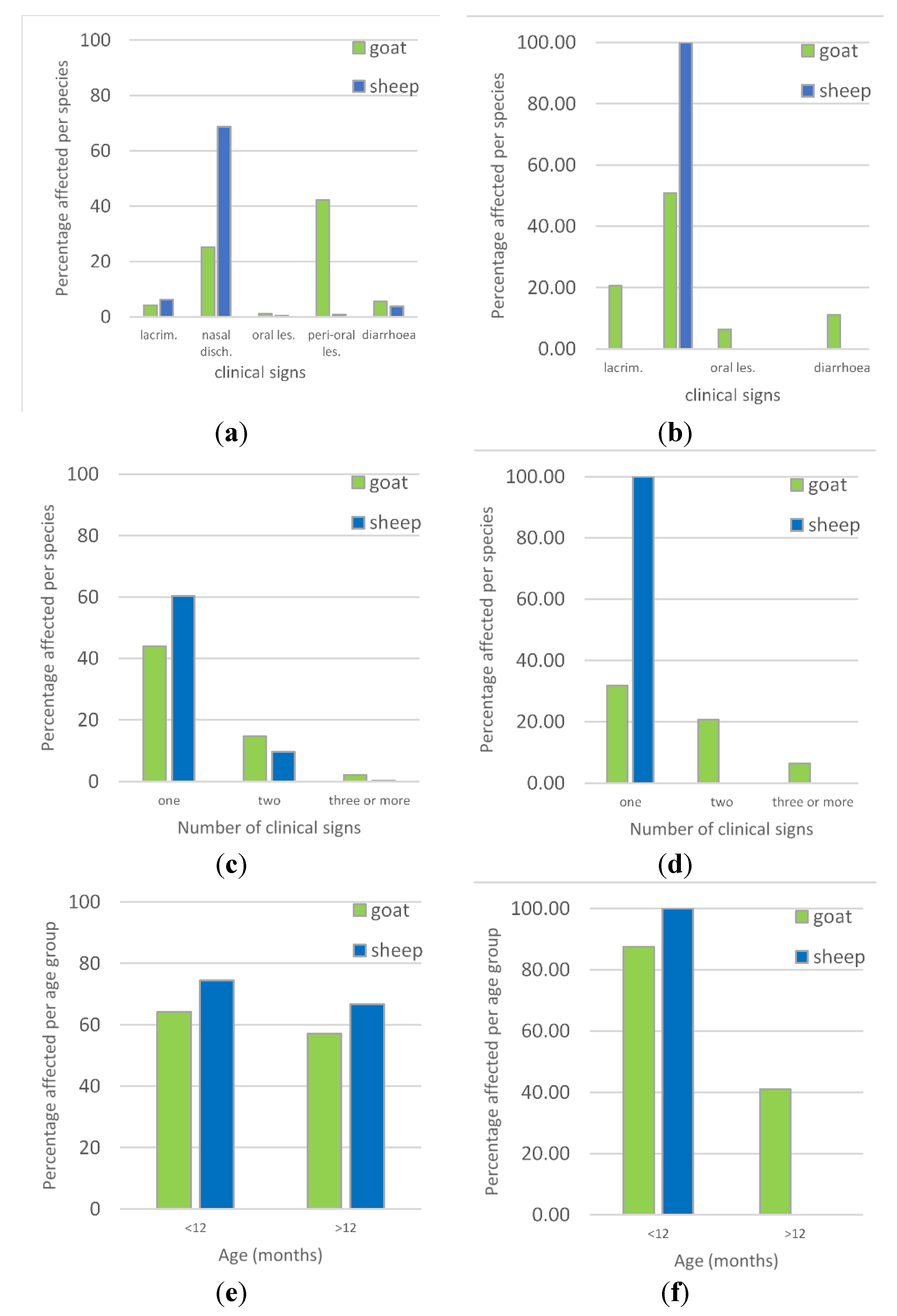
3.2. Overview of Clinical Syndromes and Maa Disease Names
3.3. Comparison of PPRV-RDT and PPRV RT-qPCR Results
3.4. Molecular Sequencing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Banyard, A.C.; Parida, S.; Batten, C.; Oura, C.; Kwiatek, O.; Libeau, G. Global distribution of peste des petits ruminants virus and prospects for improved diagnosis and control. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 2885–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kock, R.; Orynbayev, M.; Sultankulova, K.; Strochkov, V.; Omarova, Z.; Shalgynbayev, E.; Rametov, N.; Sansyzbay, A.; Parida, S. Detection and genetic characterization of lineage IV peste des petits ruminant virus in Kazakhstan. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2015, 62, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, Z. Peste des petits ruminants in China since its first outbreak in 2007: A 10-year review. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 638–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shatar, M.; Khanui, B.; Purevtseren, D.; Khishgee, B.; Loitsch, A.; Unger, H.; Settypalli, T.B.K.; Cattoli, G.; Damdinjav, B.; Dundon, W.G. First genetic characterization of peste des petits ruminants virus from Mongolia. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parida, S.; Muniraju, M.; Mahapatra, M.; Muthuchelvan, D.; Buczkowski, H.; Banyard, A.C. Peste des petits ruminants. Vet. Micro. 2015, 181, 90–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altan, E.; Parida, S.; Mahapatra, M.; Turan, N.; Yilmaz, H. Molecular characterization of Peste des petits ruminants viruses in the Marmara Region of Turkey. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Haan, N.; Kimani, T.; Rushton, J.; Lubroth, J. Chapter 12 Why is small ruminant health important—peste des petits ruminants and its impact on poverty and economics? In Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus; Munir, M., Ed.; Springer-Verlag Berlin and Heidelberg GmbH & Co.: Berlin, Germany, 2015; pp. 195–226. [Google Scholar]
- OIE-FAO. Global Strategy for the Control and Eradication of PPR; World Organisation for Animal Health, United Nations Food and Agriculture Organisation, 2015; p. 255. Available online: http://www.fao.org/emergencies/resources/documents/resources-detail/en/c/282777/ (accessed on 30 March 2020).
- Khalafalla, A.I.; Saeed, I.K.; Ali, Y.H.; Abdurrahman, M.B.; Kwiatek, O.; Libeau, G.; Abu Obeida, A.; Abbas, Z. An outbreak of peste des petits ruminants (PPR) in camels in the Sudan. Acta Trop. 2010, 116, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakian, A.; Nouri, M.; Kahroba, H.; Mohammadian, B.; Mokhber-Dezfouli, M.R. The first report of peste des petits ruminants (PPR) in camels (Camelus dromedarius) in Iran. Trop Anim. Health Prod. 2016, 48, 1215–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, C.; Fast, C.; Schlottau, K.; Hoffmann, B.; Beer, M. Neglected Hosts of Small Ruminant Morbillivirus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 2334–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, C.; Fast, C.; Wernery, U.; Kinne, J.; Joseph, S.; Schlottau, K.; Jenckel, M.; Hoper, D.; Patteril, N.A.G.; Syriac, G.; et al. Camelids and Cattle Are Dead-End Hosts for Peste-des-Petits-Ruminants Virus. Viruses 2019, 11, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefevre, P.C.; Diallo, A. Peste des petits ruminants. Rev. Sci. Tech. 1990, 9, 935–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, W.P. The distribution and epidemiology of peste des petits ruminants. Prev. Vet. Med. 1984, 2, 157–166. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.P.; Saravanan, P.; Sreenivasa, B.P.; Singh, R.K.; Singh, B. Prevalence and distribution of peste des petits ruminants virus infection in small ruminants in India. Rev. Sci. Tech. Oie 2004, 23, 807–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diop, M.; Sarr, J.; Libeau, G. Evaluation of novel diagnostic tools for peste des petits ruminants virus in naturally infected goat herds. Epidemiol. Infect. 2005, 133, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlsein, P.; Saliki, J. Rinderpest and peste des petits ruminants—The diseases: Clinical signs and pathology. In Rinderpest and Peste Des Petits Ruminants: Virus Plagues of Large and Small Ruminants; Barrett, T., Pastoret, P.-P., Taylor, W.P., Eds.; Elsevier Ltd.: London, UK, 2006; pp. 68–85. [Google Scholar]
- Abubakar, M.; Rajput, Z.I.; Arshed, M.J.; Sarwar, G.; Ali, Q. Evidence of peste des petits ruminants virus (PPRV) infection in Sindh Ibex (Capra aegagrus blythi) in Pakistan as confirmed by detection of antigen and antibody. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2001, 43, 745–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, B.; Wiesner, H.; Maltzan, J.; Mustefa, R.; Eschbaumer, M.; Arif, F.A.; Beer, M. Fatalities in wild goats in Kurdistan associated with Peste des Petits Ruminants virus. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2012, 59, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furley, C.W.; Taylor, W.P.; Obi, T.U. An outbreak of peste des petits ruminants in a zoological collection. Vet. Rec. 1987, 121, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinne, J.; Kreutzer, R.; Kreutzer, M.; Wernery, U.; Wohlsein, P. Peste des petits ruminants in Arabian wildlife. Epidemiol. Infect. 2010, 138, 1211–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, M.; Sayalel, K.; Muniraju, M.; Eblate, E.; Fyumagwa, R.; Shilinde, L.; Mdaki, M.; Keyyu, J.; Parida, S.; Kock, R. Spillover of peste des petits ruminants virus from domestic to wild ruminants in the Serengeti ecosystem, Northern Tanzania. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 2230–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asil, R.M.; Ludlow, M.; Ballal, A.; Alsarraj, S.; Ali, W.H.; Mohamed, B.A.; Mutwakil, S.M.; Osman, N.A. First detection and genetic characterization of peste des petits ruminants virus from dorcas gazelles “Gazella dorcas” in the Sudan, 2016–2017. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 2537–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fine, A.E.; Pruvot, M.; Benfield, C.T.O.; Caron, A.; Cattoli, G.; Chardonnet, P.; Dioli, M.; Dulu, T.; Gilbert, M.; Kock, R.; et al. Eradication of Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus and the Wildlife-Livestock Interface. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossiter, P.B. Chapter 50. Peste des petits ruminants. In Infectious Diseases of Livestock, 2nd ed.; Coetzer, J.A.W., Tustin, R.C., Eds.; Oxford University Press Southern Africa: Cape Town, South Africa, 2004; pp. 660–672. [Google Scholar]
- Couacy-Hymann, E.; Bodjo, S.C.; Danho, T.; Koffi, M.Y.; Libeau, G.; Diallo, A. Early detection of viral excretion from experimentally infected goats with peste-des-petits ruminants virus. Prev. Vet. Med. 2007, 78, 85–88. [Google Scholar]
- Parida, S.; Selvaraj, M.; Gubbins, S.; Pope, R.; Banyard, A.; Mahapatra, M. Quantifying Levels of Peste Des Petits Ruminants (PPR) Virus in Excretions from Experimentally Infected Goats and Its Importance for Nascent PPR Eradication Programme. Viruses 2019, 11, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope, R.A.; Parida, S.; Bailey, D.; Brownlie, J.; Barrett, T.; Banyard, A.C. Early Events following Experimental Infection with Peste-Des-Petits Ruminants Virus Suggest Immune Cell Targeting. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajak, K.K.; Sreenivasa, B.P.; Hosamani, M.; Singh, R.P.; Singh, S.K.; Singh, R.K.; Bandyopadhyay, S.K. Experimental studies on immunosuppressive effects of peste des petits ruminants (PPR) virus in goats. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2005, 28, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libeau, G. Chapter 8 Current Advances in Serological Diagnosis of Peste des Petits Ruminants. In Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus; Munir, M., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 133–154. [Google Scholar]
- Ata, F.A.; Al Sumry, H.S.; King, G.J.; Ismaili, S.I.; Ata, A.A. Duration of maternal immunity to peste des petits ruminants. Vet. Rec. 1989, 124, 590–591. [Google Scholar]
- Baron, M.D.; Parida, S.; Oura, C.A.L. Peste des petits ruminants: A suitable candidate for eradication? Vet. Rec. 2011, 169, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeder, P.L.; Abraham, G.; Kenfe, G.; Barrett, T. Peste des petits ruminants in Ethiopian goats. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 1994, 26, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osburn, B.I. 60. Bluetongue. In Diseases of Sheep, 4th ed.; Aitken, I.D., Ed.; Blackwell Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2007; pp. 455–459. [Google Scholar]
- Rajko-Nenow, P.; Golender, N.; Bumbarov, V.; Brown, H.; Frost, L.; Darpel, K.; Tennakoon, C.; Flannery, J.; Batten, C. Complete Coding Sequence of a Novel Bluetongue Virus Isolated from a Commercial Sheeppox Vaccine. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2020, 9, e01539-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.C.; Sherman, D.M. Goat Medicine, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Ames, IA, USA, 2009; pp. 399–404. [Google Scholar]
- Kivaria, F.M.; Kwiatek, O.; Kapaga, A.M.; Swai, E.S.; Libeau, G.; Moshy, W.; Mbyuzi, A.O.; Gladson, J. The incursion, persistence and spread of peste des petits ruminants in Tanzania: Epidemiological patterns and predictions. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2013, 80, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimuribo, E.; Loomu, P.; Mellau, L.; Swai, E. Retrospective study on sero-epidemiology of peste des petits ruminants before its official confirmation in northern Tanzania in 2008. Res. Opin. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2011, 1, 184–187. [Google Scholar]
- Kgotlele, T.; Kasanga, C.J.; Kusiluka, L.J.; Misinzo, G. Preliminary investigation on presence of peste des petits ruminants in Dakawa, Mvomero district, Morogoro region, Tanzania. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2014, 81, E1–E3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misinzo, G.; Kgotlele, T.; Muse, E.A.; Van Doorsselaere, J.; Berg, M.; Munir, M. Peste des petits ruminants virus lineage II and IV from goats in southern Tanzania during an outbreak in 2011. Br. J. Virol. 2014, 2, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Torsson, E.; Kgotlele, T.; Berg, M.; Mtui-Malamsha, N.; Swai, E.S.; Wensman, J.J.; Misinzo, G. History and current status of peste des petits ruminants virus in Tanzania. Infect. Ecol. Epidemiol. 2016, 6, 32701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinclair, A.R.E. Chapter One Dynamics of the Serengeti Ecosystem: Process and Pattern. In Serengeti, Dynamics of an Ecosystem; Sinclair, A.R.E., Norton-Griffiths, M., Eds.; The University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1979; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- NBS National Sample Census of Agriculture 2007/2008 Volume Vb: Regional Report: Arusha Region. National Bureau of Statistics, The United Republic of Tanzania, 2012; pp. 1–457. Available online: https://www.nbs.go.tz/nbs/takwimu/Agriculture/ARUSHA%20REGION%20REPORT.pdf (accessed on 3 March 2020).
- Baron, J.; Fishbourne, E.; Couacy-Hyman, E.; Abubakar, M.; Jones, B.A.; Frost, L.; Herbert, R.; Chibssa, T.R.; Van’t Klooster, G.; Afzal, M.; et al. Development and testing of a field diagnostic assay for peste des petits ruminants virus. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2014, 61, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bataille, A.; Kwiatek, O.; Belfkhi, S.; Mounier, L.; Parida, S.; Mahapatra, M.; Caron, A.; Chubwa, C.C.; Keyyu, J.; Kock, R.; et al. Optimization and evaluation of a non-invasive tool for peste des petits ruminants surveillance and control. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.; McKay, J.A. The detection of antibodies against peste des petits ruminants virus in cattle, sheep and goats and the possible implications to rinderpest control programmes. Epidemiol. Infect. 1994, 112, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batten, C.A.; Banyard, A.C.; King, D.P.; Henstock, M.R.; Edwards, L.; Sanders, A.; Buczkowski, H.; Oura, C.C.; Barrett, T. A real time RT-PCR assay for the specific detection of Peste des petits ruminants virus. J. Virol. Methods 2011, 171, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, M.; Griot, C.; Chaignat, V.; Perler, L.; Thur, B. [Bluetongue disease reaches Switzerland]. Schweiz. Arch. Tierheilkd. 2008, 150, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, T.R.; Babiuk, S.L.; Parkyn, G.R.; Copps, J.S.; Boyle, D.B. Capripoxvirus tissue tropism and shedding: A quantitative study in experimentally infected sheep and goats. Virol. J. 2008, 371, 380–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couacy-Hymann, E.; Bodjo, S.C.; Koffi, M.Y.; Kouakou, C.; Danho, T. The early detection of peste-des-petits-ruminants (PPR) virus antigens and nucleic acid from experimentally infected goats using RT-PCR and immunocapture ELISA techniques. Res. Vet. Sci. 2009, 87, 332–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swai, E.S.; Neselle, M.O. Using participatory epidemiology tools to investigate contagious caprine pleuropneumonia (CCPP) in Maasai flocks, Northern Tanzania. Int. J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2010, 2, 141–147. [Google Scholar]
- Minja, M. Findings of the ethnoveterinary knowledge (EVK) project in Simanjiro District. In Benefits and Risks of Sharing Local Knowledge. Summary Report; FAO Links Project & Vetaid Tanzania: Arusha, Tanzania, 2000; pp. 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- Queenan, K.; Mangesho, P.; Ole-Neselle, M.; Karimuribo, E.; Rweyemamu, M.; Kock, R.; Hasler, B. Using local language syndromic terminology in participatory epidemiology: Lessons for One Health practitioners among the Maasai of Ngorongoro, Tanzania. Prev. Vet. Med. 2017, 139 Pt A, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.A.; Muhammed, A.; Ali, E.T.; Homewood, K.M.; Pfeiffer, D.U. Pastoralist knowledge of sheep and goat disease and implications for peste des petits ruminants virus control in the Afar Region of Ethiopia. Prev. Vet. Med. 2019, 174, 104808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maan, S.; Kumar, A.; Gupta, A.K.; Dalal, A.; Chaudhary, D.; Gupta, T.K.; Bansal, N.; Kumar, V.; Batra, K.; Sindhu, N.; et al. Concurrent infection of Bluetongue and Peste-des-petits-ruminants virus in small ruminants in Haryana State of India. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 65, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, B.; Sen, A.; Chand, K.; Biswas, S.K.; De, A.; Rajak, K.K.; Chakravarti, S. Evidence of mixed infection of peste des petits ruminants virus and bluetongue virus in a flock of goats as confirmed by detection of antigen, antibody and nucleic acid of both the viruses. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2009, 41, 1661–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kgotlele, T.; Chota, A.; Chubwa, C.C.; Nyasebwa, O.; Lyimo, B.; Torsson, E.; Karimuribo, E.; Kasanga, C.J.; Wensman, J.J.; Misinzo, G.; et al. Detection of peste des petits ruminants and concurrent secondary diseases in sheep and goats in Ngorongoro district, Tanzania. Comp. Clin. Path. 2018, 28, 755–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birindwa, B.; George, G.; Ntagereka, B.; Christopher, O.; Lilly, B. Mixed infection of peste-des-petits ruminants and Capripox in goats in South Kivu, Democratic Republic of Congo. J. Adv. Vet. Anim. Res. 2017, 4, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adedeji, A.J.; Dashe, Y.; Akanbi, O.B.; Woma, T.Y.; Jambol, A.R.; Adole, J.A.; Bolajoko, M.B.; Chima, N.; Asala, O.; Tekki, I.S.; et al. Co-infection of peste des petits ruminants and goatpox in a mixed flock of sheep and goats in Kanam, North Central Nigeria. Vet. Med. Sci. 2019, 5, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, A.; Bhattacharjee, U.; Puro, K.; Shakuntala, I.; Sanjukta, R.; Das, S.; Ghatak, S.; Sen, A. Detection of Peste des petits ruminants virus and goatpox virus from an outbreak in goats with high mortality in Meghalaya state, India. Vet. World 2016, 9, 1025–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saravanan, P.; Balamurugan, V.; Sen, A.; Sarkar, J.; Sahay, B.; Rajak, K.K.; Hosamani, M.; Yadav, M.P.; Singh, R.K. Mixed infection of peste des petits ruminants and orf on a goat farm in Shahjahanpur, India. Vet. Rec. 2007, 160, 410–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kgotlele, T.; Macha, E.S.; Kasanga, C.J.; Kusiluka, L.J.; Karimuribo, E.D.; Van Doorsselaere, J.; Wensman, J.J.; Munir, M.; Misinzo, G. Partial genetic characterization of peste des petits ruminants virus from goats in northern and eastern Tanzania. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2014, 61, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couacy-Hymann, E.; Bodjo, C.; Danho, T.; Libeau, G.; Diallo, A. Evaluation of the virulence of some strains of peste-des-petits-ruminants virus (PPRV) in experimentally infected West African dwarf goats. Vet. J. 2007, 173, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dundon, W.G.; Kihu, S.M.; Gitao, G.C.; Bebora, L.C.; John, N.M.; Oyugi, J.O.; Loitsch, A.; Diallo, A. Detection and Genome Analysis of a Lineage III Peste Des Petits Ruminants Virus in Kenya in 2011. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyokwishimira, A.; de D. Baziki, J.; Dundon, W.G.; Nwankpa, N.; Njoroge, C.; Boussini, H.; Wamwayi, H.; Jaw, B.; Cattoli, G.; Nkundwanayo, C.; et al. Detection and molecular characterization of Peste des Petits Ruminants virus from outbreaks in Burundi, December 2017–January 2018. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 2067–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkamwesiga, J.; Coffin-Schmitt, J.; Ochwo, S.; Mwiine, F.N.; Palopoli, A.; Ndekezi, C.; Isingoma, E.; Nantima, N.; Nsamba, P.; Adiba, R.; et al. Identification of Peste des Petits Ruminants Transmission Hotspots in the Karamoja Subregion of Uganda for Targeting of Eradication Interventions. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tshilenge, G.M.; Walandila, J.S.; Kikukama, D.B.; Masumu, J.; Katshay Balowa, L.; Cattoli, G.; Bushu, E.; Mpiana Tshipambe, S.; Dundon, W.G. Peste des petits ruminants viruses of lineages II and III identified in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 239, 108493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, X.F.; Mahapatra, M.; Begovoeva, M.; Kalema-Zikusoka, G.; Driciru, M.; Ayebazibwe, C.; Adwok, D.S.; Kock, M.; Lukusa, J.-P.K.; Muro, J.; et al. Peste des Petits Ruminants at the Wildlife–Livestock Interface in the Northern Albertine Rift and Nile Basin, East Africa. Viruses 2020, 12, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, S.; Moffat, K.; Hill, H.; Flannery, J.T.; Graham, S.P.; Baron, M.D.; Darpel, K.E. Comparison of the Immunogenicities and Cross-Lineage Efficacies of Live Attenuated Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus Vaccines PPRV/Nigeria/75/1 and PPRV/Sungri/96. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01471-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

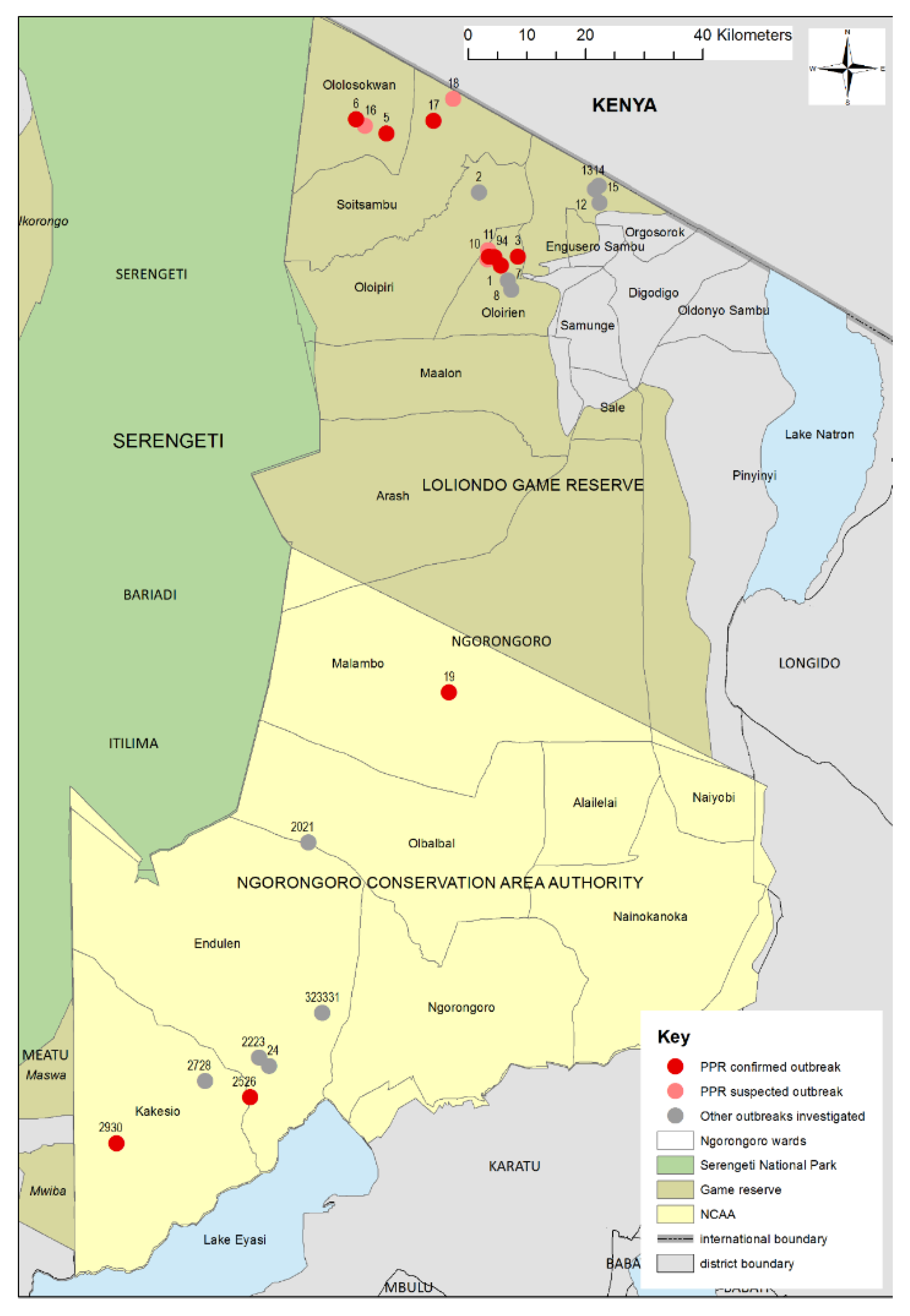
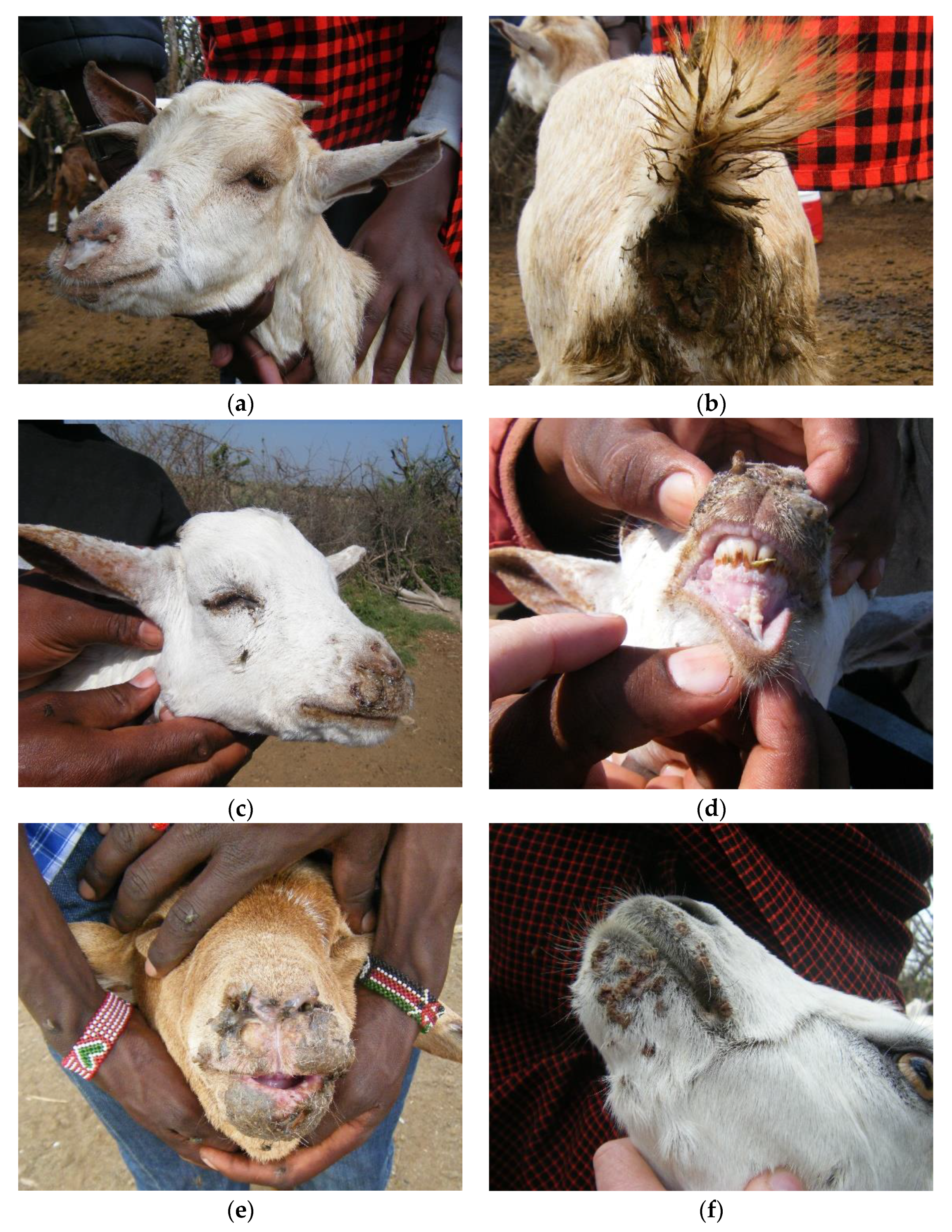
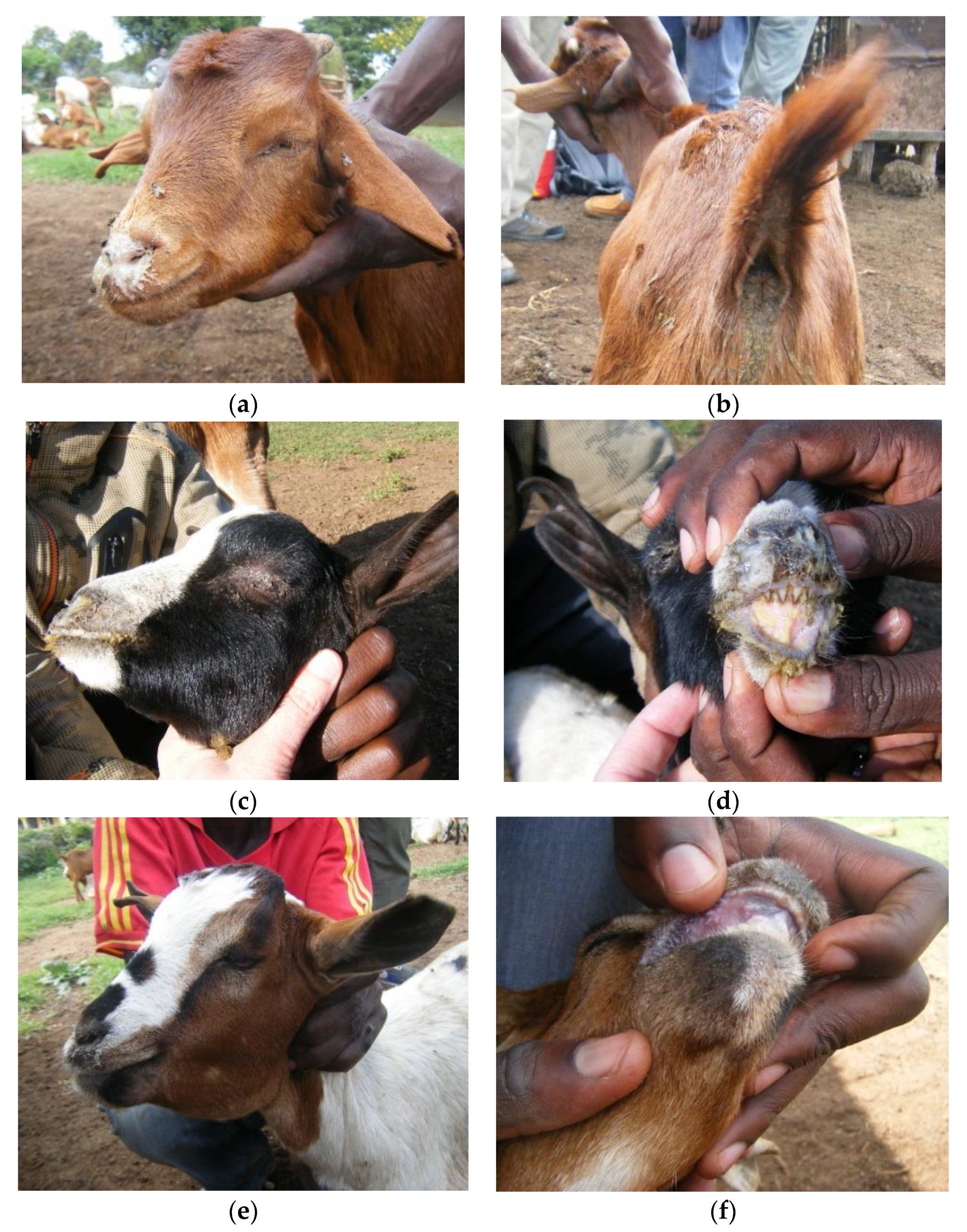

| Ward | Flock No. | Local Disease Name (Maa Language) | Species/Age Groups Affected | Clinical Signs | Flock Mortality (%) | Flock Morbidity † (%) | Diagnostic Test Results Number Positive (Number Tested) | Partial N Gene Sequence | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pyrexia | Lacrimation | Nasal Discharge | Sneezing | Coughing | Dyspnoea | Peri-Oral Lesions | Mouth Lesions | Salivation | Diarrhoea | PPRV-RDT | PPRV RT-qPCR | PPRV cELISA | BTV RT-qPCR | Capripox qPCR | |||||||
| Olorien-Magaiduru | 1 | olodua | sheep and goats, all ages | X | X | X | X | X | - | X | X | - | X | 2.2 | 66.6 | 2 (3) | 4 (7) | 1 (4) | 1 (4) | 0 (4) | TANZANIAGoat3/2015, TANZANIAGoat4/2015 |
| 3 | olkipiei | sheep and goats, all ages | X | X | X | - | X | - | - | X | - | X | 1.5 | 60.0 | 2 (3) | 3 (3) | 2 (2) | -- | -- | TANZANIAGoat10/2015, TANZANIAGoat11/2015 | |
| 4 | olodua | goats | - | - | X | - | - | - | X | - | - | X | 3.0 | 5.5 | 1 (1) | -- | -- | -- | -- | ||
| 9 | oloirobi | sheep and goats (more sheep affected than goats) | X | - | X | X | X | - | X | X | X | X | 9.1 | 15.9 | 0 (3) | 2 (6) | 1 (3) | 1 (1) | 0 (1) | ||
| Soitsambu and Ololosokwan | 5 | olodua | adult sheep | - | - | X | - | - | X | X | X | X | - | 0.2 | 4.3 | 1 (2) | 2 (2) | 1 (2) | -- | -- | TANZANIASheep14/2015 |
| 6 | olodua or olkipiei | sheep and goats, all ages | X | X | X | - | - | X | X | - | X | X | 2.0 | 14.0 | 1 (1) | 2 (2) | 1 (1) | 0 (1) | 0 (1) | TANZANIASheep15/2015 | |
| 17 | none | sheep and goats | - | X | X | - | - | - | X | X | X | - | NA | NA | -- | 2 (3) | 1 (2) | -- | -- | ||
| Olbalbal | 19 | olkipiei | Goats only, mainly young | X | - | X | - | - | X | X | X | - | X | 25.0 | 31.3 | 0 (2) | 1 (5) | 0 (2) | 0 (1) | 0 (1) | |
| Endulen | 26 | NA | - | - | X | - | - | - | - | X | - | X | NA | NA | -- | 1 (3) | 1 (3) | -- | -- | ||
| Kakesio | 29 | enkorotik | - | X | X | - | - | - | - | X | - | X | 4.0 | 4.6 | 1 (2) | 1 (2) | 3 (5) | -- | -- | ||
| Total number positive (total number tested) | 8 (17) | 18 (33) | 11 (24) | 2 (7) | 0 (7) | ||||||||||||||||
| Variable | Category | Number of Animals with Clinical Signs (%) | Total Number of Animals | Univariable Analysis χ2 Test p Value | Adjusted Odds Ratio (95% Confidence Interval) | Multivariable Logistic Regression Wald Test p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flock | 1 | 510 (66.58) | 766 | 0.282 | 1.01 (0.77, 1.33) | 0.95 |
| 3 | 39 (60.00) | 65 | ||||
| Species | Goat | 211 (60.29) | 350 | 0.003 | 1.60 (1.17, 2.17) | 0.003 |
| Sheep | 338 (70.27) | 481 | ||||
| Age | >12 months | 273 (61.35) | 445 | 0.002 | 1.61 (1.20, 2.16) | 0.001 |
| <12 months | 276 (71.50) | 386 |
| Diagnostic Test | PPRV RT-qPCR | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test Result | Positive | Negative | ||
| PPRV rapid detection test (RDT) | Positive | 6 | 0 | 6 |
| Negative | 5 | 4 | 9 | |
| Total | 11 | 4 | 15 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jones, B.A.; Mahapatra, M.; Chubwa, C.; Clarke, B.; Batten, C.; Hicks, H.; Henstock, M.; Keyyu, J.; Kock, R.; Parida, S. Characterisation of Peste Des Petits Ruminants Disease in Pastoralist Flocks in Ngorongoro District of Northern Tanzania and Bluetongue Virus Co-Infection. Viruses 2020, 12, 389. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12040389
Jones BA, Mahapatra M, Chubwa C, Clarke B, Batten C, Hicks H, Henstock M, Keyyu J, Kock R, Parida S. Characterisation of Peste Des Petits Ruminants Disease in Pastoralist Flocks in Ngorongoro District of Northern Tanzania and Bluetongue Virus Co-Infection. Viruses. 2020; 12(4):389. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12040389
Chicago/Turabian StyleJones, Bryony Anne, Mana Mahapatra, Chobi Chubwa, Brian Clarke, Carrie Batten, Hayley Hicks, Mark Henstock, Julius Keyyu, Richard Kock, and Satya Parida. 2020. "Characterisation of Peste Des Petits Ruminants Disease in Pastoralist Flocks in Ngorongoro District of Northern Tanzania and Bluetongue Virus Co-Infection" Viruses 12, no. 4: 389. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12040389
APA StyleJones, B. A., Mahapatra, M., Chubwa, C., Clarke, B., Batten, C., Hicks, H., Henstock, M., Keyyu, J., Kock, R., & Parida, S. (2020). Characterisation of Peste Des Petits Ruminants Disease in Pastoralist Flocks in Ngorongoro District of Northern Tanzania and Bluetongue Virus Co-Infection. Viruses, 12(4), 389. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12040389






