Viromics on Honey-Baited FTA Cards as a New Tool for the Detection of Circulating Viruses in Mosquitoes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sampling Strategy
2.2. RNA Extraction from FTA cards for NGS Analysis
2.3. Library Preparation, Sequencing and Bioinformatics Analysis
2.4. Primers Design and Virus Detection by Specific RT-PCRs
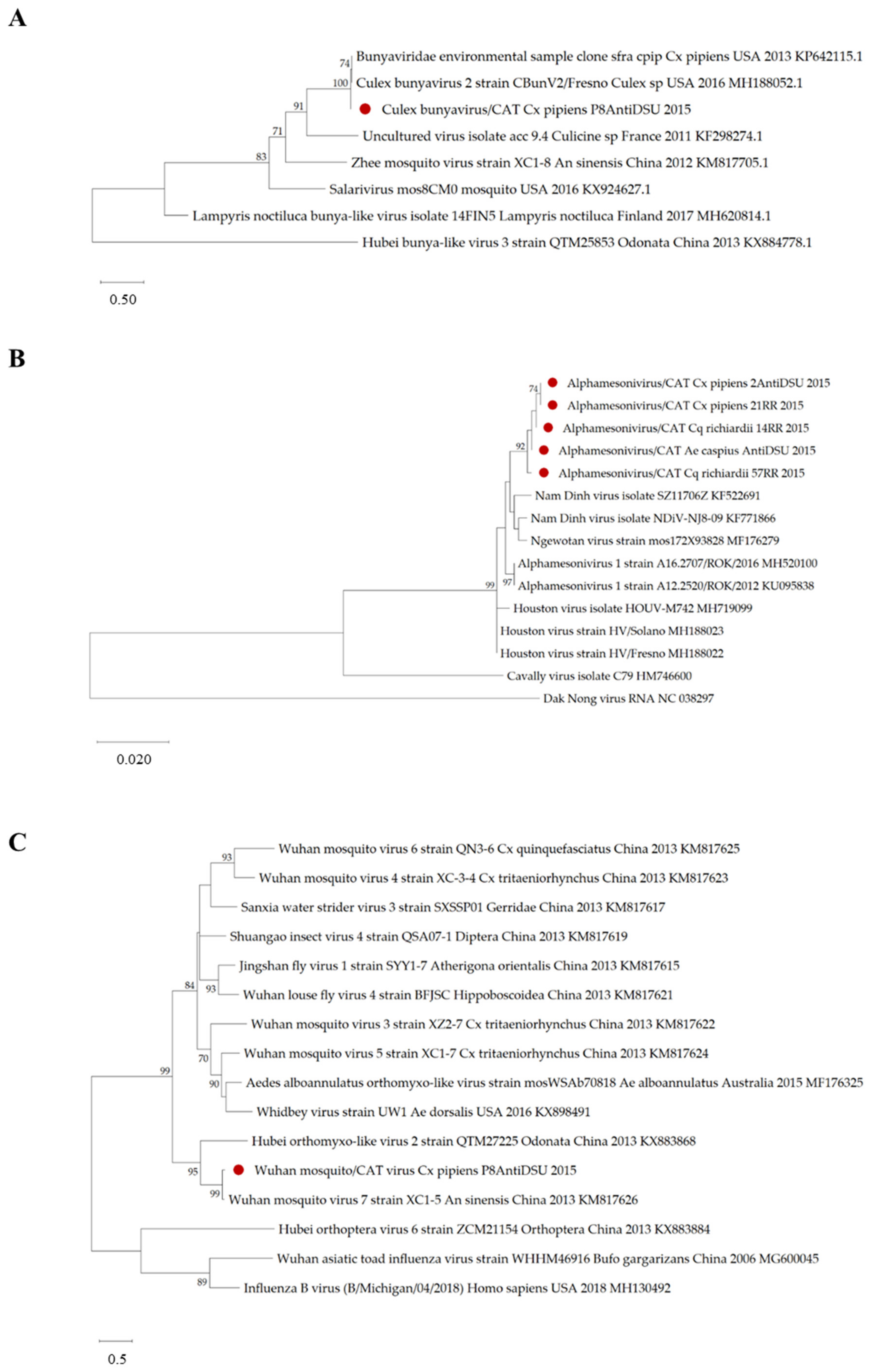
2.5. Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analyses
2.6. Nucleotide Sequences Accession Numbers
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Outputs on NGS on Honey-Baited FTA Cards
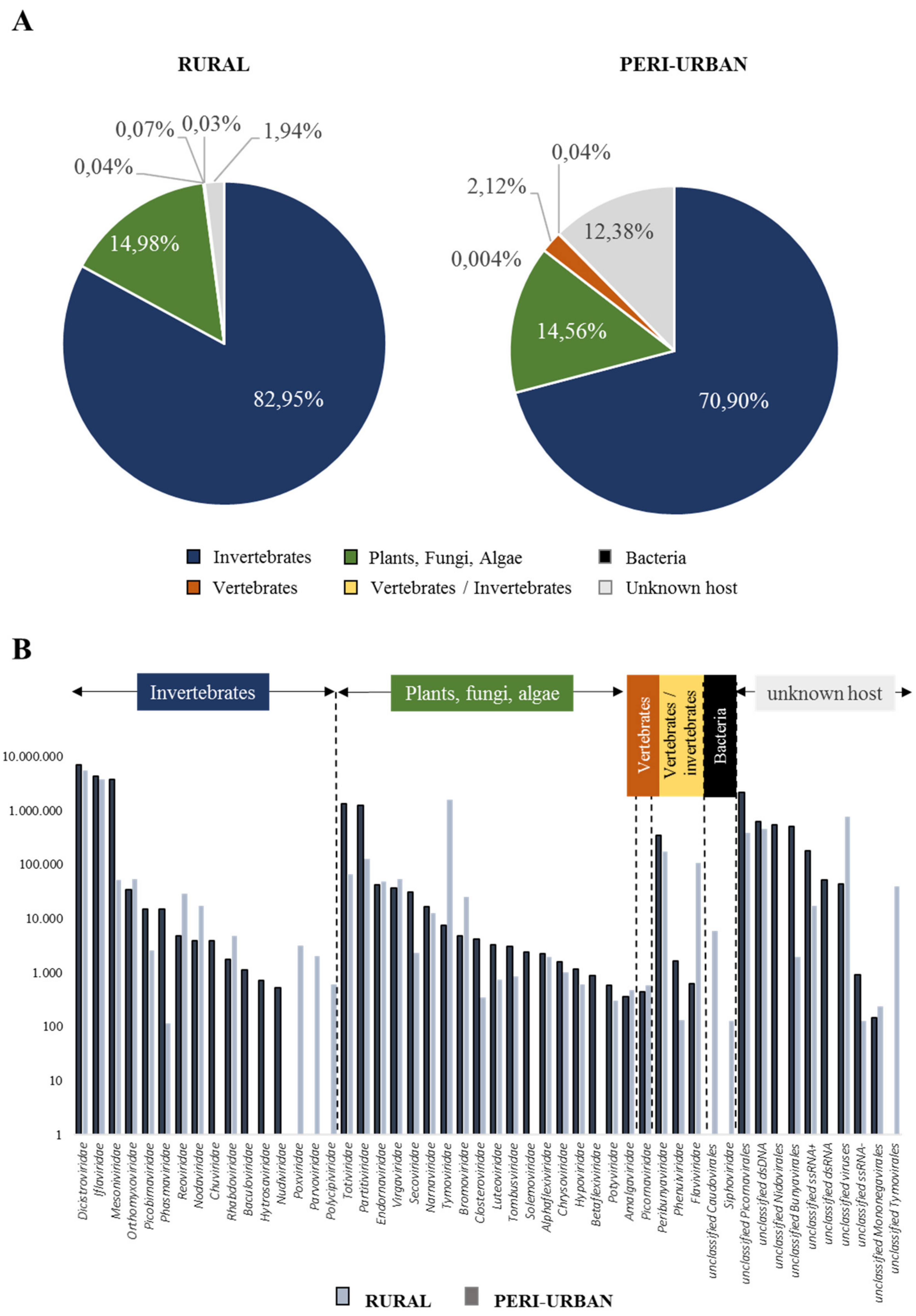
3.2. Virome Composition on Honey-Baited FTA Cards During Entomological Surveys
3.3. Viral Genomes Obtained from Honey-Baited FTA Cards
3.4. Virus Detection by Specific RT-PCRs on Honey-Baited FTA Cards Unexposed to Mosquitoes
3.5. Virus Detection by Specific RT-PCRs on Field-Captured Mosquito Pools
3.6. Overall Remarks of the Approach and Future Perspectives
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nii-Trebi, N.I. Emerging and neglected infectious diseases: Insights, advances and challenges. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, ID5245021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollidge, B.S.; González-Scarano, F.; Soldan, S.S. Arboviral Encephalitides: Transmission, Emergence, and Pathogenesis. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2010, 5, 428–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gubler, D.J. Human arbovirus infections worldwide. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2001, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, S.V. The emergence of arthropod-borne viral diseases: A global prospective, dengue, chikungunya and zika fevers. Acta Trop. 2017, 166, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklinos, L.H.V.; Jones, K.E.; Redding, D.W.; Abubakar, I. The effect of global change in mosquito-borne diseases. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, e302–e312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, J.P.; Brady, O.J.; Scott, T.W.; Zou, C.; Pigott, D.M.; Duda, K.A. Global spread of dengue virus types: Mapping the 70 year history. Trends Microbiol. 2014, 22, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vest, K.G. Zika virus: A basic overview of an emerging arboviral infection in the Western hemisphere. Disaster Med. Public. 2016, 10, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinszer, K.; Morrison, K.; Brownstein, J.S.; Marinho, F.; Santos, A.F.; Nsoesie, E.O. Reconstruction of Zika virus in Brazil. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 92–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, S.C.; Forrester, N.L. Chikungunya: Evolutionary history and recent epidemic spread. Antivir. Res. 2015, 120, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caglioti, C.; Lalle, E.; Castilletti, C.; Carletti, F.; Capobianchi, M.R.; Bordi, L. Chikungunya virus infection: An overview. New Microbiol. 2013, 36, 211–227. [Google Scholar]
- Gubler, D.J. The continuing spread of West Nile virus in the Western hemisphere. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 45, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melanson, V.R.; Jochim, R.; Yarnell, M.; Bingham Ferlez, K.; Shashikumar, S.; Richardson, J.H. Improving Vector-Borne Pathogen Surveillance: A Laboratory-Based Study Exploring the Potential to Dengue Virus and Malaria Parasites in Mosquito Saliva. J. Vector Borne Dis. 2017, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchie, S.A.; Cortis, G.; Paton, C.; Townsend, M.; Shroyer, D.; Zborowski, P.; Hall-Mendelin, S.; van der Hurk, A.F. A Simple Non-Powered Pasive Trap for the Collection of Mosquitoes for Arbovirus Surveillance. J. Med. Entomol. 2013, 50, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, B.J.; Kerlin, T.; Hall-Mendelin, S.; van der Hurk, A.F.; Cortis, G.; Doggett, S.L.; Toi, C.; Fall, K.; McMahon, J.L.; Townsend, M.; et al. Development and Field Evaluation of the Sentinel Mosquito Arbovirus Capture Kit (SMACK). Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Gao, S.; Padmanabhan, C.; Li, R.; Galvez, M.; Gutierrez, D. VirusDetect: An automated pipeline for efficient virus discovery using deep sequencing of small RNAs. Virology 2017, 500, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall-Mendelin, S.; Ritchie, S.A.; Johansen, C.A.; Zborowski, P.; Cortis, G.; Dandridge, S.; Hall, R.A.; van der Hurk, A.F. Exploiting Mosquito Sugar Feeding to Detect Mosquito-Borne Pathogens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 11255–11259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Hurk, A.F.; Hall-Mendelin, S.; Townsend, M.; Kurucz, N.; Edwards, J.; Ehlers, G.; Rodwell, C.; Moore, F.A.; McMahon, J.L.; Northill, J.A.; et al. Applications of a Sugar-Based Surveillance System to Track Arboviruses in Wild Mosquito Populations. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2014, 14, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flies, E.J.; Toi, C.; Weinstein, P.; Doggett, S.L.; Williams, C.R. Converting Mosquito Surveillance to Arbovirus Surveillance with Honey-Baited Nucleic Acid Preservation Cards. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2015, 15, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wipf, N.C.; Guidi, V.; Tonolla, M.; Ruinelli, M.; Müller, P.; Engler, O. Evaluation of honey-baited FTA cards in combination with different mosquito traps in an area of low arbovirus prevalence. Parasite Vectors. 2019, 12, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibby, K. Metagenomic identification of viralpathogens. Trends Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 257–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delwart, E.L. Viral metagenomics. Rev. Med. Virol. 2007, 17, 115–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, D.M.; Mushegian, A.R.; Dolja, V.V.; Koonin, E.V. New dimensions of the virus world discovered by metagenomics. Trends Microbiol. 2010, 18, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greninger, A.L. A decade of RNA virus metagenomics is (not) enough. Virus Res. 2018, 244, 218–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atoni, E.; Zhao, L.; Karungu, S.; Obanda, V.; Agwanda, B.; Xia, H.; Yuan, Z. The discovery and Global Distribution of Novel Mosquito-Associated Viruses in the Last Decade (2007–2017). Rev. Med. Virol 2019, 29, e2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batovska, J.; Mee, P.T.; Lynch, S.E.; Sawbridge, T.I.; Rodoni, B.C. Sensitivity and Specificity of Metatranscriptomics as an Arbovirus Surveillance Tool. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busquets, N.; Alba, A.; Allepuz, A.; Aranda, C.; Nuñez, J.I. Usutu Virus Sequences in Culex pipiens (Diptera: Culicidae), Spain. Emerg Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 861–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Hurk, A.F.; Hall-Mendelin, S.; Johansen, C.A.; Warrilow, D.; Ritchie, S.A. Evolution of Mosquito-Based Arbovirus Surveillance Systems in Australia. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 325659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffner, E.; Angel, G.; Geoffroy, B.; Hervey, J.P.; Rhaiem, A.; Brunhes, J. Les moustiques d’Europe. Logiciel d´identification et d´enseignement; IRD Editions: Paris, France, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Moutailler, S.; Popovici, I.; Devillers, E.; Vayssier-Taussat, M.; Eloit, M. Diversity of Viruses in Ixodes ricinus, and characterization of a neurotropic strain of Eyach virus. New Microbes New Infect. 2016, 11, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vayssier-Taussat, M.; Moutailler, S.; Michelet, L.; Devillers, E.; Bonnet, S.; Cheval, J.; Hebert, C.; Eloit, M. Next Generation Sequencing Uncovers Unexpected Bacterial Pathogens in Ticks in Western Europe. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temmam, S.; Chrétien, D.; Bigot, T.; Dufour, E.; Petres, S.; Desquesnes, M.; Devillers, E.; Dumarest, M.; Yousfi, L.; Moutailler, S.; et al. Monitoring silent spillovers before emergence: A pilot study at the tick/human interface in Thailand. Front. Microbiol. 2019. In press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criscuolo, A.; Brisse, S. AlienTrimmer removes adapter oligonucleotides with high sensitivity in short-insert paired-end reads. Commentary on Turner (2014) Assessment of insert sizes and adapter content in FASTQ data from NexteraXT libraries. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Liu, C.M.; Luo, R.; Sadakane, K.; Lam, T.W. MEGAHIT: An ultra-fast single-node solution for large and complex metagenomics assembly via succinct de Bruijn graph. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1674–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigot, T.; Temmam, S.; Pérot, P.; Eloit, M. RVDB-prot, a reference viral protein database and its HMM profiles [version 1; peer review: Awaiting peer review]. F1000 Res. 2019, 8, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucl. Acids. Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nei, M.; Kumar, S. Molecular Evolution and Phylogenetics; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa, M.; Kishino, H.; Yano, T. Dating the human-ape split by a molecular clock of mitochondrial DNA. J. Mol. Evol. 1985, 22, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Lin, X.-D.; Tian, J.-H.; Chen, L.-J.; Chen, X.; Li, C.-X.; Quin, X.-C.; Li, J.; Cao, J.-P.; Eden, J.-C.; et al. Redefining the Invertebrate RNA Virosphere. Nature 2016, 540, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agboli, E.; Leggewie, M.; Altinli, M.; Schnettler, E. Mosquito-Specific Viruses-Transmission and Interaction. Viruses 2019, 11, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, M.; Altan, E.; Deng, X.; Barker, C.M.; Fang, Y.; Coffey, L.L. Virome of >12 thousand Culex mosquitoes from throughout California. Virology 2018, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, K.G.; Biser, T.; Hamilton, T.; Santos, C.J.; Pimentel, G.; Mokashi, V.P.; Bishop-Lilly, K.A. Bioinformatic characterization of Mosquito Viromes within the Eastern United States and Puerto Rico: Discovery of Novel Viruses. Evol. Bioinform. 2016, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belda, E.; Nanfack-Minkeu, F.; Eiglmeier, K.; Carissimo, G.; Holm, I.; Diallo, M.; Diallo, D.; Vantaux, A.; Kim, S.; Sharakhov, I.V.; et al. De novo profiling of RNA viruses in Anopheles malaria vector mosquitoes from forest ecological zones in Senegal and Cambodia. Bmc Genom. 2019, 20, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, G.; Costa, F.J.; da S Rego, M.O.; D’Athaide, E.S.; Funayama, D.; Montani, M.; Souza, R.; Vasconcelos, S.; Witkin, S.S.; Deng, X.; et al. Detection of RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase of Hubei Reo-like Virus 7 by Next-Generation Sequencing in Aedes aegypti and in Culex quinquefasciatus Mosquitoes from Brazil. Viruses 2019, 11, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öhlund, P.; Hayer, J.; Lundén, H.; Hesson, J.C.; Blomström, A.L. Viromics Reveal a Number of Novel RNA Viruses in Swedish Mosquitoes. Viruses 2019, 11, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Beller, L.; Deboutte, W.; Yinda, K.C.; Delang, L.; Vega-Rua, A. Failloux, A-B. ; Matthijnssens, J. Stable Distinct Core Eukaryotic Viromes in Different Mosquito Species from Guadeloupe, Using Single mosquito Viral Metagenomics. Microbiome 2019, 7, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanborn, M.A.; Klein, T.A.; Kim, H.-C.; Fung, C.K.; Figueroa, K.L.; Yang, Y.; Asafo-adjei, E.A.; Jarman, R.G.; Hang, J. Metagenomics Analysis Reveals Three Novel and Prevalent Mosquito Viruses from a Single Pool of Aedes vexans niponni Collected in the Republic of Korea. Viruses 2019, 11, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, J.H.-O.; Shi, M.; Eden, J.-S.; Holmes, E.C.; Hesson, J.C. Meta-Transcriptomic Comparison of the RNA Viromes of Mosquito Vectors Culex pipiens and Culex torrentium in Northern Europe. Viruses 2019, 11, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atoni, E.; Wang, Y.; Karungu, S.; Waruhiu, C.; Zohaib, A.; Obanda, V.; Agwanda, B.; Mutua, M.; Xia, H.; Yuan, Z. Metagenomic Virome Analysis of Culex Mosquitoes from Kenya and China. Viruses 2018, 10, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholleti, H.; Hayer, j.; Fafetine, J.; Berg, M.; Blomström, A.-L. Genetic Characterization of a Novel Picrona-like Virus in Culex spp. Mosquitoes from Mozambique. Virol J. 2018, 15, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Liu, Y.; Hu, X.; Xiong, J.; Zhang, B.; Yuan, Z. A Metagenomic Survey of Viral Abundance and Diversity in Mosquitoes from Hubei Province. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, S.; Chung, B.Y.-W.; Bass, D.; Moureau, G.; Tang, S.; McAlister, E.; Culverwell, C.L.; Glücksman, E.; Wang, H.; Brown, T.D.K.; et al. Novel Viruses Discovery and Genome Reconstruction form Field RNA Samples Reveals Highly Divergent Viruses in Dipteran Hosts. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Wang, Y.; Shi, C.; Atoni, E.; Zhao, L.; Yuan, Z. Comparative Metagenomic Profiling of Viromes Associated with Four Common Mosquito species in China. Virol Sin. 2018, 33, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habayeb, M.S.; Ekengren, S.K.; Hultmark, D. Nora Virus, a Persistent Virus in Drosophila, Defines a New Picorna-like Virus Family. J. Gen. Virol 2006, 87, 3045–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Lv, X.; Zhai, Y.; Fu, S.; Wang, D.; Rayner, S.; Tang, Q.; Liang, G. Genomic Characterization of a Novel Virus of the Family Tymoviridae Isolated from Mosquitoes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forrester, N.L.; Coffey, L.L.; Weaver, S.C. Arboviral Bottlenecks and Challenges to Maintaining Diversity and Fitness during Mosquito Transmission. Viruses 2014, 6, 3991–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandler, J.A.; Liu, R.M.; Bennett, S.N. RNA Shutgun Metagenomic Sequencing of Northern California (USA) Mosquitoes Uncovers Viruses, Bacteria, and Fungi. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauber, C.; Ziebuhr, J.; Junglen, S.; Drosten, C.; Zirkel, F.; Nga, P.T.; Morita, K.; Snijder, E.J.; Gorbalenya, A.E. Mesoniviridae: A Proposed New Family in the Order Nidovirales formed by a Single Species of Mosquito-Borne Viruses. Arch. Virol. 2012, 157, 1623–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, P.; Rakotoarivony, I.; Etienne, L.; Albane, M.; Benoit, F.; Grégory, L.; Busquets, N.; Birnberg, L.; Talavera, S.; Aranda, C.; et al. First Detection of a Mesonivirus in Culex pipiens in Five Countries Around the Mediterranean Basin. Abstract. In Proceedings of the EPIZONE—11th Annual Meeting ANSES, Paris, France, 19–21 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Vasilakis, N.; Guzman, H.; Firth, C.; Forrester, N.L.; Widen, S.G.; Wood, T.G.; Rossi, S.L.; Ghedin, E.; Popov, V.; Blasdell, K.R.; et al. Mesoniviruses are Mosquito-Specific Viruses with Extensive Geographic Distribution and Host Range. Virol. J. 2014, 11, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, J.; Klein, T.A.; Kim, H.-C.; Yang, Y.; Jima, D.D.; Richardson, J.H.; Jarman, R.G. Genome Sequences of Five Arboviruses in Field-Captured Mosquitoes in a Unique Rural Environment of South Korea. Genome Announc 2016, 4, e01644-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.X.; Shi, M.; Tian, J.-H.; Lin, X.-D.; Kang, Y.-J.; Chen, L.-J.; Qin, X.-C.; Xu, J.; Holmes, E.C.; Zhang, Y.-Z. Unprecedented Genomic Diversity of RNA Viruses in Arthropods Reveals the Ancestry of Negative-Sense RNA Viruses. eLife 2015, 4, e05378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiyasombat, R.; Bolling, B.G.; Brault, A.C.; Bartholomay, L.C.; Blitvich, B.J. Evidence of Efficient Transovarial Transmission of Culex Flavivirus by Culex pipiens (Diptera: Culicidae). J. Med. Entomol 2011, 48, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, S.; Jin, T.; Lin, P.; Huang, Y.; Wu, C.; Peng, B.; Wei, L.; Chu, H.; Wang, M.; et al. Discovery and High Prevalence of Phasi Charoen-like Virus in Field-Captured Aedes aegypti in South China. Virology 2018, 523, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolling, B.G.; Vasilakis, N.; Guzman, H.; Widen, S.G.; Wood, T.G.; Popov, V.L.; Thangamani, S.; Tesh, R.B. Insect-Specific Viruses Detected in Laboratory Mosquito Colonies and Their Potential Implications in Experiments Evaluating Arbovirus vector Competence. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg 2015, 92, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolling, B.G.; Eisen, L.; Moore, C.G.; Blair, C.D. Insect-Specific Flaviviruses from Culex Mosquitoes in Colorado, with Evidence of Vertical Transmission. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg 2011, 85, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolling, B.G.; Weaver, S.C.; Tesh, R.B.; Vasilakis, N. Insect-Specific Virus Discovery: Significance for the Arbovirus Community. Viruses 2015, 7, 4911–4928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudas, G.; Obbard, D.J. Are Arthropods at the Heart of Virus Evolution? eLife 2015, 4, e05378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öhlund, P.; Lundén, H.; Blomström, A.-L. Insect-Specific Virus Evolution and Potential Effects in Vector Competence. Virus Genes 2019, 55, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolling, B.G.; Olea-Popelka, F.J.; Eisen, L.; Moore, C.G.; Blair, C.D. Transmission Dynamics of an Insect-Specific Flavivirus in a Naturally Infected Culex pipiens Laboratory Colony and Effects of Co-Infection on Vector Competence for West Nile Virus. Virology 2012, 427, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baidaliuk, A.; Miot, E.F.; Lequime, S.; Moltini-Conclois, I.; Delaigue, F.; Dabo, S.; Dickson, L.B.; Aubry, F.; Merkling, S.H.; Cao-Lormeau, V.M.; et al. Cell-Fusing Agent Virus Reduces Arbovirus Dissemination in Aedes aegypti Mosquitoes In Vivo. J. Virol 2019, 93, e00705-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnberg, L.; Talavera, S.; Aranda, C.; Núñez, A.I.; Napp, S.; Busquets, N. Field-Captured Aedes vexans (Meigen, 1830) is a Competent Vector for Rift Valley Fever Phlebovirus in Europe. Parasit Vectors 2019, 12, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilakis, N.; Tesh, R.B. Insect-Specific Viruses and their Potential Impact on Arbovirus Transmission. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2015, 15, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Mosquito-Associated Viruses | Primer Code | Primer Nucleotide Sequence (5′→3′) | Tm (°C) | RT-PCR Fragment Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alphamesonivirus 1 | ALPMF | GCGCCATTCTGCAGATCAAC | 58 | 1033 |
| ALPMR | GTGCCAATAAACGCGTGATG | |||
| Bunyaviridae environmental sample | BNYF | GAGTCCTTGTCCATCCCYGC | 57 | 1059 |
| BNYR | GTGCAGGAAGAAGKAGCATGG | |||
| Dezidougou virus | DZGF | GTCCTGTTAAGCTGCAACCC | 56 | 400 |
| DZGR | CGTAACAACGATAAGTGGCG | |||
| Wuhan mosquito virus 7 | WHNF | GCGGAGAGAGGYAAAATGGATC | 57 | 572 |
| WHNR | CATTCCCATCAGGAACCCTG |
| Closest Hit | Gene/Product | Abundance | aa Identity (%) | Max. Contig Length | % Coverage | nt Identity (%) | Accession No. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rural | Alphamesonivirus 1 | Spike protein, hypothetical protein | 3606196 | 53–100 | 1328 | 100 | 99.18 | MF176279.1 |
| Bunyaviridae environmental sample | RNA-dependent RNA polymerase | 335292 | 49–99 | 4354 | 99 | 99.02 | KP642114.1 | |
| Culex bunya-like virus | Hypothetical protein | 289007 | 47–100 | 920 | 98 | 98.45 | MH188002.1 | |
| Culex iflavi-like virus 4 | Polyprotein | 1009175 | 71–100 | 1706 | 99 | 95.77 | NC_040574.1 | |
| Culex picorna-like virus 1 | Polyprotein | 806998 | 64–100 | 1238 | 100 | 96.37 | MH703059.1 | |
| Culex-associated Luteo-like virus | Hypothetical protein, RNA-dependent RNA polymerase | 3285 | 67–100 | 566 | 99 | 95.04 | MK440647.1 | |
| Dezidougou virus | Hypothetical protein 1 | 9366 | 87–100 | 638 | 100 | 94.34 | KY968698.1 | |
| Hubei picorna-like virus 61 | Hypothetical protein | 53578 | 84–100 | 916 | 99 | 95.63 | KX883915.1 | |
| Wenzhou soberno-like virus 4 | Hypothetical proteins 1 and 2 | 668852 | 94–98 | 2284 | 100 | 96.67 | KX882831.1 | |
| Wuhan mosquito virus 5 | PB1 | 5460 | 50 | 580 | 13 | 75.95 | KX898491.1 | |
| Peri-urban | Aedes pseudoscutellaris reovirus | VP1 | 5244 | 69–100 | 667 | 99 | 78.08 | DQ087276.1 |
| Alphamesonivirus 1 | ORF1a, pp1a polyprotein | 22590 | 60–100 | 932 | 100 | 98.18 | MH520106.1 | |
| Culex Hubei-like virus | Hypothetical protein | 5142 | 85–100 | 510 | 91 | 90.34 | MH188025.1 | |
| Culex iflavi-like virus 4 | Polyprotein | 168154 | 97–100 | 2170 | 100 | 96.04 | NC_040574.1 | |
| Culex luteo-like virus | RNA-dependent RNA polymerase | 16686 | 42–67 | 1279 | 65 | 67.49 | MF176386.1 | |
| Culex picorna-like virus 1 | Polyprotein | 102979 | 77–100 | 1290 | 100 | 98.29 | MH703059.1 | |
| Culex pipiens associated Tunisia virus | Replicase | 11319 | 96–100 | 1446 | 98 | 89.11 | NC_040723.1 | |
| Culicine-associated Z virus | VP1, RNA-dependent RNA polymerase | 14584 | 77–97 | 765 | 96 | 83.33 | KF298283.1 | |
| Daeseongdong virus 1 | ORF1, putative RNA-dependent RNA polymerase | 614537 | 75–95 | 5831 | 95 | 82.27 | KU095841.1 | |
| Dezidougou virus | Hypothetical protein 1 | 1424472 | 85–100 | 1882 | 100 | 95.42 | KY968698.1 | |
| Karumba virus | Similar NS5 protein | 96687 | 49 | 3160 | 28 | 76.31 | JF707857.1 | |
| Hubei picorna-like virus 61 | Hypothetical protein | 5815018 | 70–100 | 1252 | 100 | 96.01 | KX883915.1 | |
| Negevirus nona 1 | Hypothetical protein | 190830 | 49–95 | 2765 | 99 | 87.11 | AB972669.1 | |
| Wuhan mosquito virus 6 | Nucleoprotein | 9480 | 72–100 | 468 | 100 | 97.01 | MF176381.1 | |
| Wuhan mosquito virus 7 | PB1 | 43351 | 53–100 | 1846 | 100 | 92.15 | KM817626.1 |
| Sample | Order | Family | Closest virus | No Reads | Mean coverage per nt | Coverage (%) | % Identity (nt) | Accession No |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rural | Picornavirales | Dicistroviridae | Kashmir bee virus | 28080 | 401,29 X | 100 | 96.74 | AY275710.1 |
| Black queen cell virus isolate BQCV_MS | 3112 | 49,85 X | 100 | 93.78 | MH267694.1 | |||
| Iflaviridae | Deformed wing virus isolate Hamilton | 3921 | 51,47 X | 100 | 99.77 | MF623172.1 | ||
| Culex iflavi-like 4 virus strain CIVL/Kern | 17787 | 250,75 X | 100 | 95.78 | NC_040574.1 | |||
| Nidovirales | Mesoniviridae | Ngewotan virus strain mos172×93828 | 9326 | 63,03 X | 100 | 98.88 | MF176279.1 | |
| Unclassified RNA viruses | Wenzhou soberno-like virus 4 strain mosZJ35391 | 12059 | 562,28 X | 99 | 96.79 | KX882831.1 | ||
| Peri-urban | Picornavirales | Dicistroviridae | Aphid lethal paralysis virus isolate ALPV-CE | 572 | 8,42 X | 99 | 94.75 | JX480861.1 |
| Iflaviridae | Deformed wing virus isolate Hamilton | 3670 | 47,57 X | 100 | 99.75 | MF623172.1 | ||
| Culex iflavi-like 4 virus strain CIVL/Kern | 1435 | 20,74 X | 100 | 95.72 | NC_040574.1 | |||
| Unclassified RNA viruses | Hubei picorna-like virus 61 strain mosHB235903 | 147377 | 2384,82 X | 100 | 95.84 | KX883915.1 | ||
| Hubei noda-like virus 11 strain arthropodmix22482 | 210275 | 6 964,36 X | 100 | 97.58 | KX883010.1 | |||
| Dezidougou virus strain DEZI/Aedes africanus/SEN/DAK-AR-41524/1984 | 4939 | 74,39 X | 98 | 95.32 | KY968698.1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Birnberg, L.; Temmam, S.; Aranda, C.; Correa-Fiz, F.; Talavera, S.; Bigot, T.; Eloit, M.; Busquets, N. Viromics on Honey-Baited FTA Cards as a New Tool for the Detection of Circulating Viruses in Mosquitoes. Viruses 2020, 12, 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12030274
Birnberg L, Temmam S, Aranda C, Correa-Fiz F, Talavera S, Bigot T, Eloit M, Busquets N. Viromics on Honey-Baited FTA Cards as a New Tool for the Detection of Circulating Viruses in Mosquitoes. Viruses. 2020; 12(3):274. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12030274
Chicago/Turabian StyleBirnberg, Lotty, Sarah Temmam, Carles Aranda, Florencia Correa-Fiz, Sandra Talavera, Thomas Bigot, Marc Eloit, and Núria Busquets. 2020. "Viromics on Honey-Baited FTA Cards as a New Tool for the Detection of Circulating Viruses in Mosquitoes" Viruses 12, no. 3: 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12030274
APA StyleBirnberg, L., Temmam, S., Aranda, C., Correa-Fiz, F., Talavera, S., Bigot, T., Eloit, M., & Busquets, N. (2020). Viromics on Honey-Baited FTA Cards as a New Tool for the Detection of Circulating Viruses in Mosquitoes. Viruses, 12(3), 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12030274








