Adeno-Associated Virus (AAV-DJ)—Cryo-EM Structure at 1.56 Å Resolution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Image Acquisition
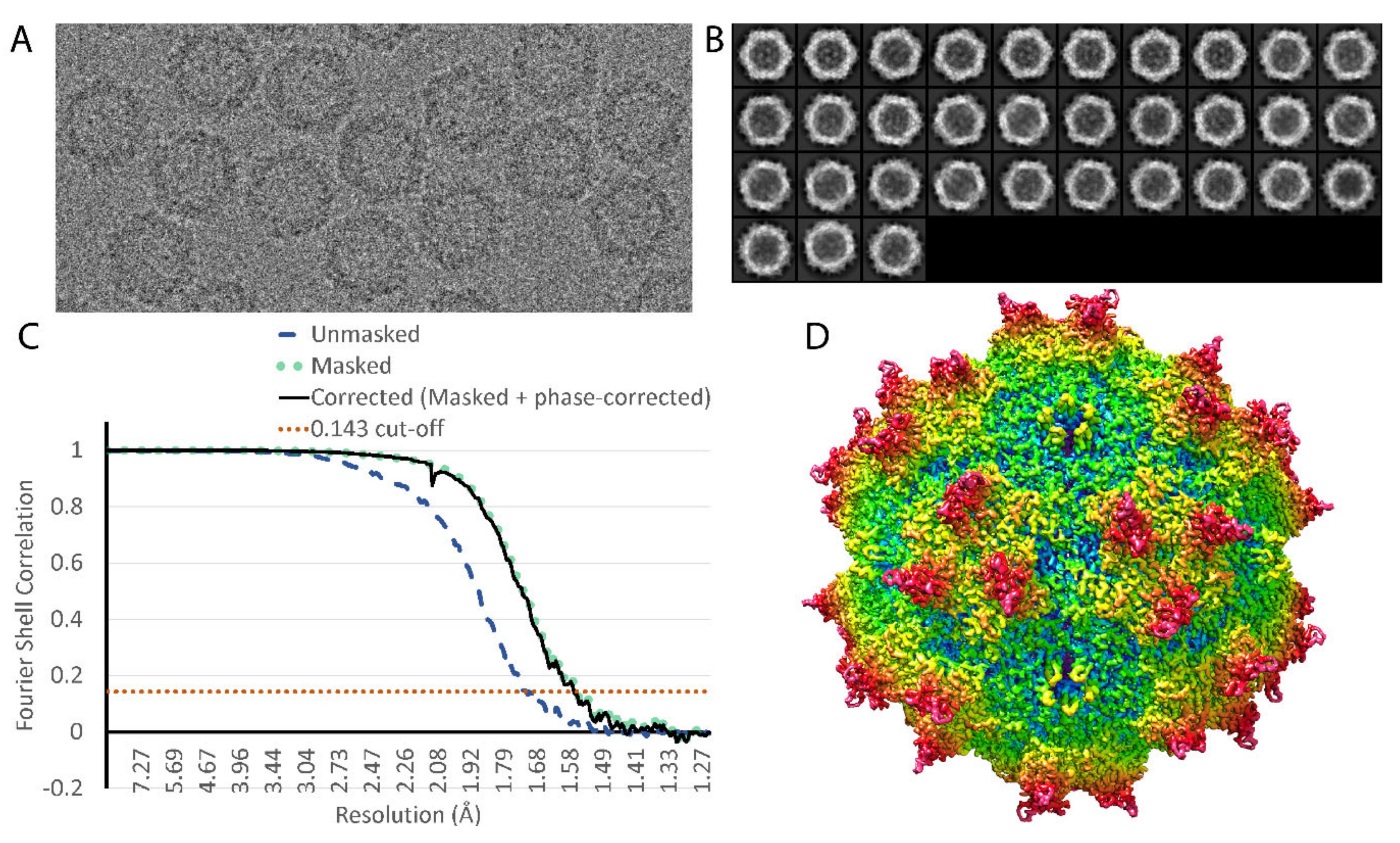
2.3. Image Processing
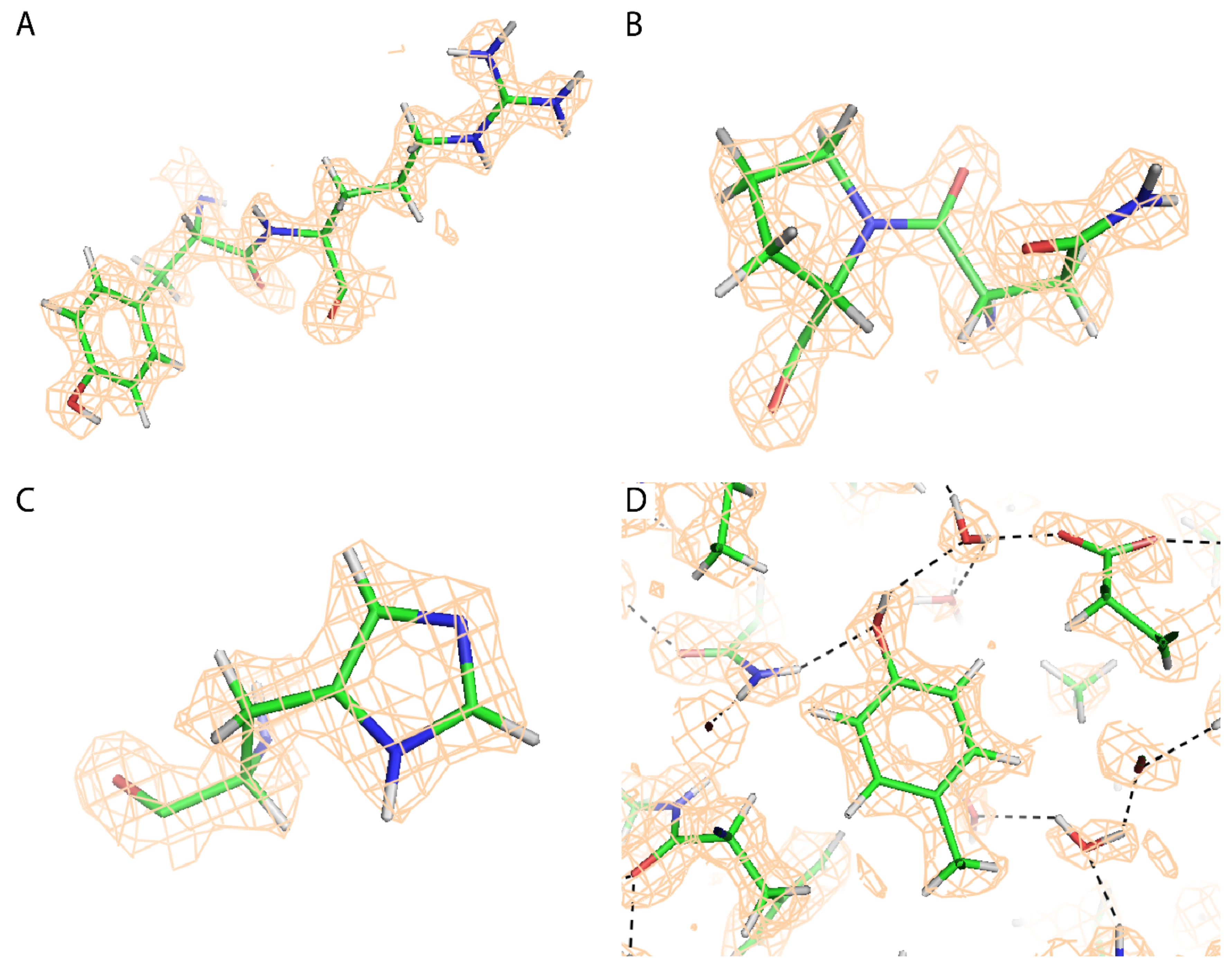
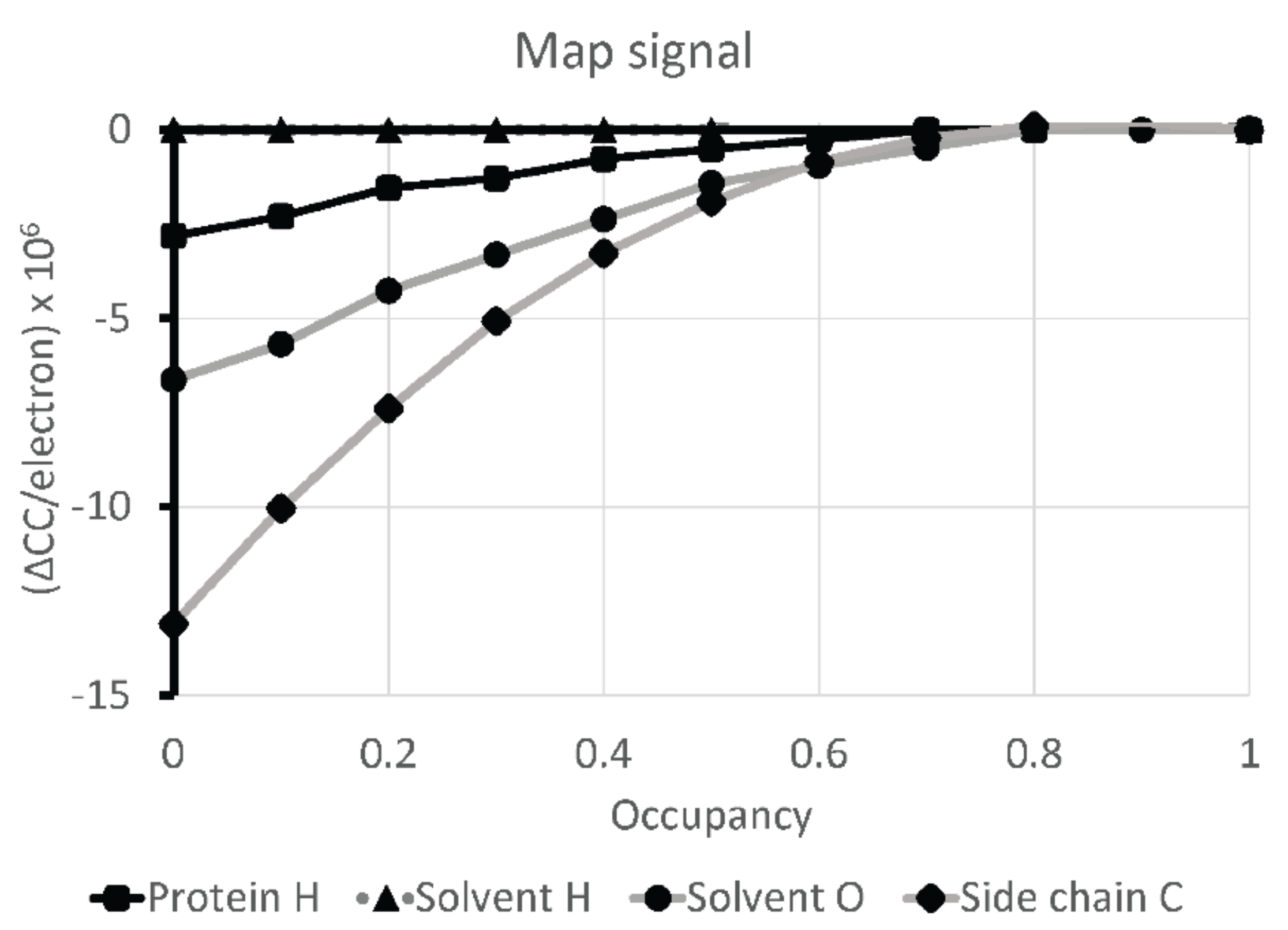
2.4. Atomic Modeling and Refinement
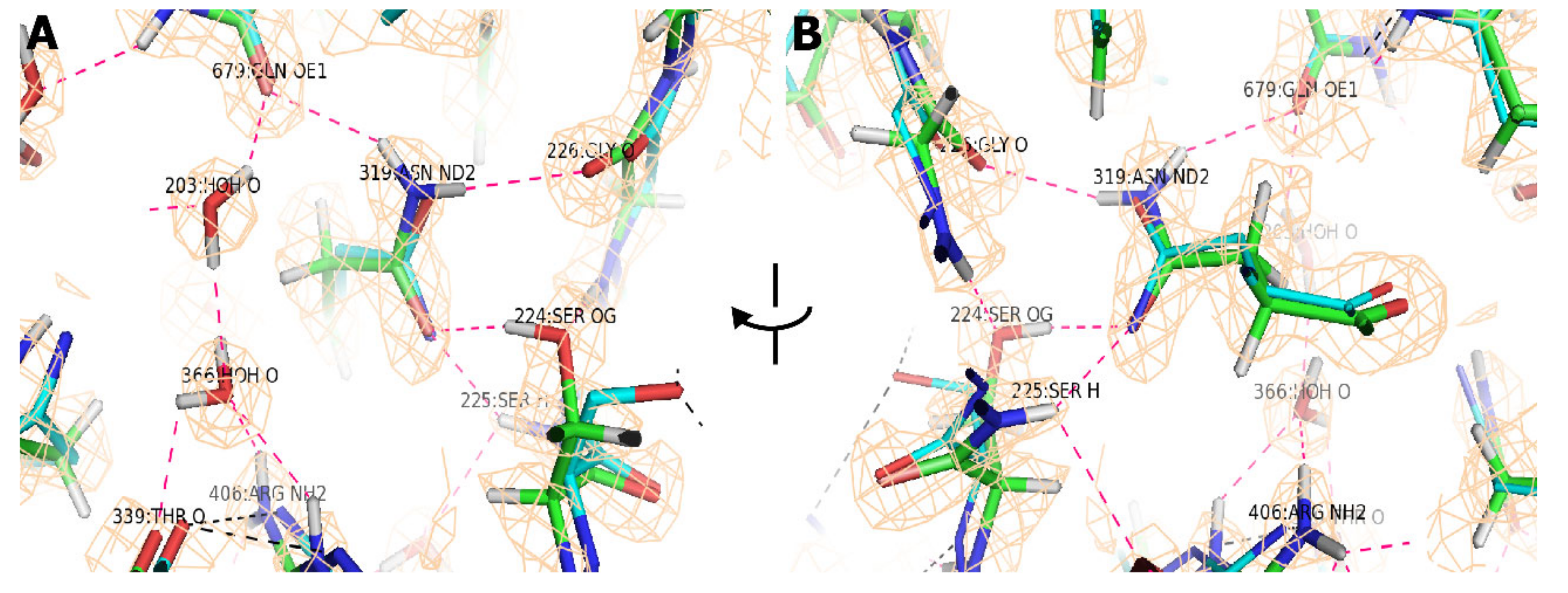
3. Results
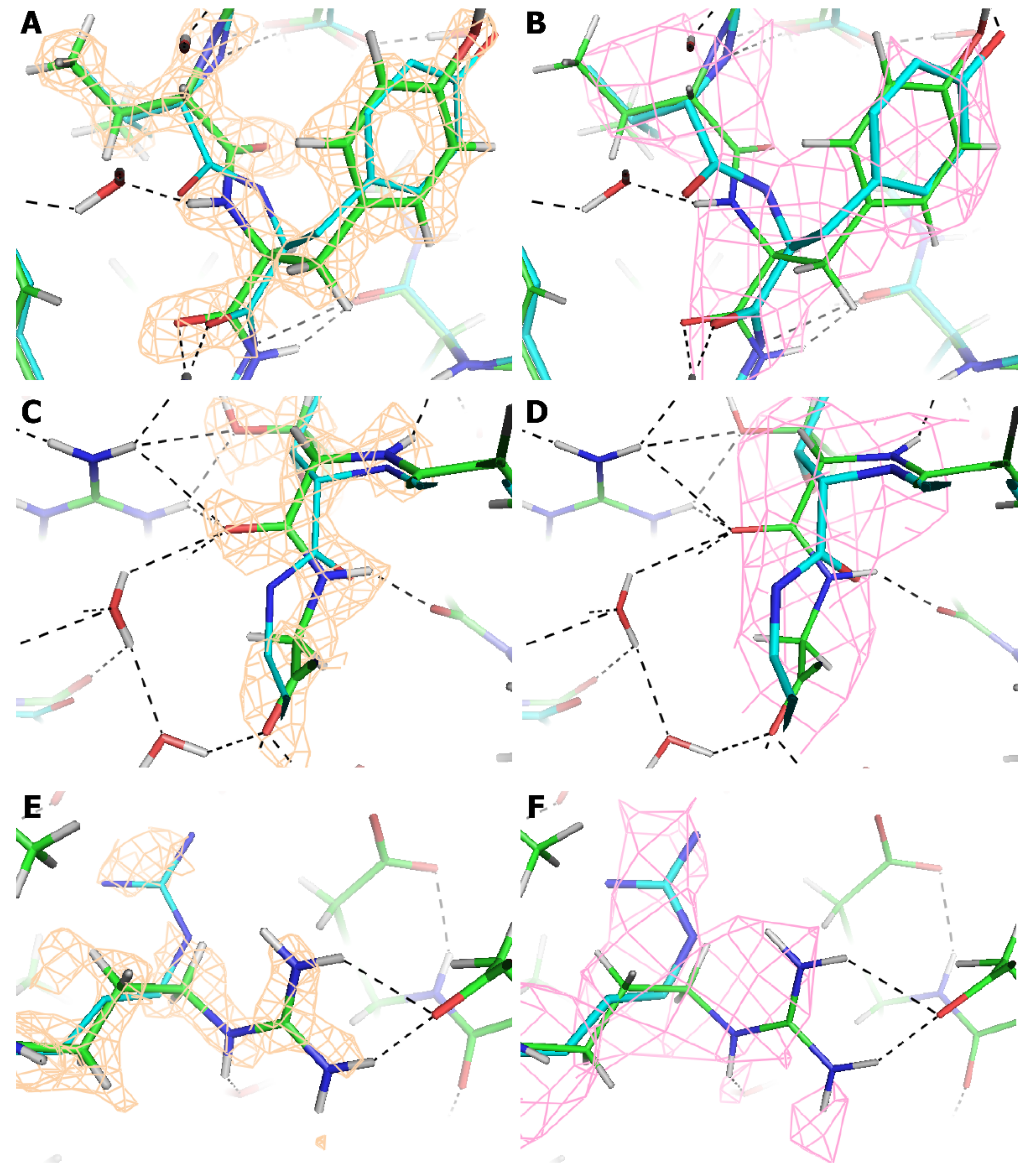
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stanley, W.M. Isolation of a crystalline protein possessing the properties of tobacco-mosaic virus. Science 1935, 81, 644–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendrew, J.C.; Dickerson, R.E.; Strandberg, B.E.; Hart, R.G.; Davies, D.R.; Phillips, D.C.; Shore, V.C. Structure of Myoglobin: A Three-Dimensional Fourier Synthesis at 2 Å. Resolution. Nature 1960, 185, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caspar, D.L.D.; Klug, A. Physical principles in the construction of regular viruses. In Cold Spring Harbor Symposium in Quantitative Biology; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor: New York, NY, USA, 1962; Volume 27, pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann, M.G.; Blow, D.M. Determination of Phases by the Conditions of Non-Crystallgraphic Symmetry. Acta Cryst. 1963, 16, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rosier, D.J.; Klug, A. Reconstruction of Three Dimensional Structures from Electron Micrographs. Nature 1968, 217, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.C.; Olson, A.; Schutt, C.E.; Winkler, F.K.; Bricogne, G. Tomato bushy stunt virus at 2.9 Å resolution. Nature 1978, 276, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad-Zapatero, C.; Abdel-Meguid, S.S.; Johnson, J.E.; Leslie, A.G.W.; Rayment, I.; Rossmann, M.G. Structure of southern bean mosaic virus at 2.8 A resolution. Nature 1980, 286, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, P.L.; Fuller, S.D.; Burnett, R.M. Difference imaging of adenovirus: Bridging the resolution gap between X-ray crystallography and electron microscopy. EMBO J. 1993, 12, 2589–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zocher, G.; Mistry, N.; Frank, M.; Hahnlein-Schick, I.; Ekstrom, J.O.; Arnberg, N.; Stehle, T. A sialic acid binding site in a human picornavirus. PLoS Pathog 2014, 10, e1004401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, S.B.; Day, J.S.; McPherson, A. Satellite tobacco mosaic virus refined to 1.4 Å resolution. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2014, 70, 2316–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, S.W.; Dennis, C.A.; Lane, C.L.; Trinh, C.H.; Rizkallah, P.J.; Stockley, P.G.; Phillips, S.E. Construction and crystal structure of recombinant STNV capsids. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 413, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.Z.; Aiyer, S.; Mietzsch, M.; Hull, J.A.; McKenna, R.; Grieger, J.; Samulski, R.J.; Baker, T.S.; Agbandje-McKenna, M.; Lyumkis, D. Sub-2 Å Ewald curvature corrected structure of an AAV2 capsid variant. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y. Single-Particle Cryo-EM at Crystallographic Resolution. Cell 2015, 161, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirohi, D.; Chen, Z.; Sun, L.; Klose, T.; Pierson, T.C.; Rossmann, M.G.; Kuhn, R.J. The 3.8 Å resolution cryo-EM structure of Zika virus. Science 2016, 352, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, J.R.; Cotmore, S.F.; Bloom, M.E.; Linden, R.M.; Parrish, C.R. (Eds.) Parvoviruses; Hodder Arnold, Ltd.: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Zaidy, S.A.; Kolb, S.J.; Lowes, L.; Alfano, L.N.; Shell, R.; Church, K.R.; Nagendran, S.; Sproule, D.M.; Feltner, D.E.; Wells, C.; et al. AVXS-101 (Onasemnogene Abeparvovec) for SMA1: Comparative Study with a Prospective Natural History Cohort. J. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2019, 6, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoy, S.M. Onasemnogene Abeparvovec: First Global Approval. Drugs 2019, 79, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, D.; Lee, J.S.; Wang, L.; Desai, T.; Akache, B.; Storm, T.A.; Kay, M.A. In vitro and in vivo gene therapy vector evolution via multispecies interbreeding and retargeting of adeno-associated viruses. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 5887–5911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerch, T.F.; O’Donnell, J.K.; Meyer, N.L.; Xie, Q.; Taylor, K.A.; Stagg, S.M.; Chapman, M.S. Structure of AAV-DJ, a retargeted gene therapy vector: Cryo-electron microscopy at 4.5 Å resolution. Structure 2012, 20, 1310–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Spilman, M.; Meyer, N.L.; Lerch, T.F.; Stagg, S.M.; Chapman, M.S. Electron microscopy analysis of a disaccharide analog complex reveals receptor interactions of adeno-associated virus. J. Struct. Biol. 2013, 184, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Spear, J.M.; Noble, A.J.; Sousa, D.R.; Meyer, N.L.; Davulcu, O.; Zhang, F.; Linhardt, R.J.; Stagg, S.M.; Chapman, M.S. The 2.8 Å Electron Microscopy Structure of Adeno-Associated Virus-DJ Bound by a Heparinoid Pentasaccharide. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2017, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Thompson, R.F.; Walker, M.; Siebert, C.A.; Muench, S.P.; Ranson, N.A. An introduction to sample preparation and imaging by cryo-electron microscopy for structural biology. Methods 2016, 100, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.; Bu, W.; Bhatia, S.; Hare, J.; Somasundaram, T.; Azzi, A.; Chapman, M.S. The atomic structure of adeno-associated virus (AAV-2), a vector for human gene therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 10405–10410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, H.J.; Lane, M.D.; Padron, E.; Gurda, B.; McKenna, R.; Kohlbrenner, E.; Aslanidi, G.; Byrne, B.; Muzyczka, N.; Zolotukhin, S.; et al. Structure of adeno-associated virus serotype 8, a gene therapy vector. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 12260–12271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerch, T.F.; Xie, Q.; Chapman, M.S. The structure of adeno-associated virus serotype 3B (AAV-3B): Insights into receptor binding and immune evasion. Virology 2010, 403, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, N.L.; Hu, G.; Davulcu, O.; Xie, Q.; Noble, A.J.; Yoshioka, C.; Gingerich, D.S.; Trzynka, A.; David, L.; Stagg, S.M.; et al. Structure of the gene therapy vector, adeno-associated virus with its cell receptor, AAVR. Elife 2019, 8, e44707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girod, A.; Wobus, C.E.; Zadori, Z.; Ried, M.; Leike, K.; Tijssen, P.; Kleinschmidt, J.A.; Hallek, M. The VP1 capsid protein of adeno-associated virus type 2 is carrying a phospholipase A2 domain required for virus infectivity. J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronenberg, S.; Kleinschmidt, J.A.; Bottcher, B. Electron cryo-microscopy and image reconstruction of adeno-associated virus type 2 empty capsids. EMBO Rep. 2001, 2, 997–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonine, P.V.; Poon, B.K.; Read, R.J.; Sobolev, O.V.; Terwilliger, T.C.; Urzhumtsev, A.; Adams, P.D. Real-space refinement in PHENIX for cryo-EM and crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D Struct. Biol. 2018, 74, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, M.S.; Trzynka, A.; Chapman, B.K. Atomic modeling of cryo-electron microscopy reconstructions--joint refinement of model and imaging parameters. J. Struct. Biol. 2013, 182, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brünger, A.T.; Adams, P.D.; Clore, G.M.; DeLano, W.L.; Gros, P.; Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W.; Jiang, J.-S.; Kuszewski, J.; Nilges, M.; Pannu, N.S.; et al. Crystallography and NMR system: A new software system for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. 1998, 54, 905–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, N.; Davulcu, O.; Xie, Q.; Silveria, M.; Zane, G.; Large, E.; Chapman, M. Expression and Purification of Adeno-associated Virus Virus-like Particles in a Baculovirus System and AAVR Ectodomain Constructs in E. coli. Bio-Protocol 2020, 10, e3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, T.; Grigorieff, N. Automatic estimation and correction of anisotropic magnification distortion in electron microscopes. J. Struct. Biol. 2015, 192, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zivanov, J.; Nakane, T.; Forsberg, B.O.; Kimanius, D.; Hagen, W.J.; Lindahl, E.; Scheres, S.H. New tools for automated high-resolution cryo-EM structure determination in RELION-3. Elife 2018, 7, e42166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.Q.; Palovcak, E.; Armache, J.P.; Verba, K.A.; Cheng, Y.; Agard, D.A. MotionCor2: Anisotropic correction of beam-induced motion for improved cryo-electron microscopy. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 331–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K. Gctf: Real-time CTF determination and correction. J. Struct. Biol. 2016, 193, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, N.R.; Yoshioka, C.K.; Radermacher, M.; Potter, C.S.; Carragher, B. DoG Picker and TiltPicker: Software tools to facilitate particle selection in single particle electron microscopy. J. Struct. Biol. 2009, 166, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, M.; DeRosier, D.J.; Grigorieff, N. Ewald sphere correction for single-particle electron microscopy. Ultramicroscopy 2006, 106, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, T.; Rohou, A.; Grigorieff, N. cisTEM, user-friendly software for single-particle image processing. Elife 2018, 7, e35383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emsley, P.; Lohkamp, B.; Scott, W.G.; Cowtan, K. Features and development of Coot. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 486–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Word, J.M.; Lovell, S.C.; Richardson, J.S.; Richardson, D.C. Asparagine and glutamine: Using hydrogen atom contacts in the choice of side-chain amide orientation. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 285, 1735–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.-M.; Ren, G.; Dudarev, S.L.; Whelan, M.J. Robust Parameterization of Elastic and Absorptive Electron Atomic Scattering Factors. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 1996, 52, 257–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linge, J.; Nilges, M. Influence of non-bonded parameters on the quality of NMR structures: A new force field for NMR structure calculation. J. Biomol. NMR 1999, 13, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriarty, N.W.; Janowski, P.A.; Swails, J.M.; Nguyen, H.; Richardson, J.S.; Case, D.A.; Adams, P.D. Improved chemistry restraints for crystallographic refinement by integrating the Amber force field into Phenix. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D 2020, 76, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butterworth, S. On the Theory of Filter Amplifiers. Wirel. Eng. 1930, 7, 536–541. [Google Scholar]
- Scheres, S.H. Relion: Implementation of a Bayesian approach to cryo-EM structure determination. J. Struct. Biol. 2012, 180, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakane, T.; Kotecha, A.; Sente, A.; McMullan, G.; Masiulis, S.; Brown, P.M.G.E.; Grigoras, I.T.; Malinauskaite, L.; Malinauskas, T.; Miehling, J.; et al. Single-particle cryo-EM at atomic resolution. bioRxiv 2020, 110189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, K.M.; Fischer, N.; Paknia, E.; Chari, A.; Stark, H. Breaking the next Cryo-EM resolution barrier—Atomic resolution determination of proteins! bioRxiv 2020, 106740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penczek, P.A. Fundamentals of three-dimensional reconstruction from projections. Methods Enzymol. 2010, 482, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartesaghi, A.; Merk, A.; Banerjee, S.; Matthies, D.; Wu, X.; Milne, J.L.; Subramaniam, S. Electron microscopy. 2.2 A resolution cryo-EM structure of beta-galactosidase in complex with a cell-permeant inhibitor. Science 2015, 348, 1147–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucukelbir, A.; Sigworth, F.J.; Tagare, H.D. Quantifying the local resolution of cryo-EM density maps. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 63–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, P.B.; Henderson, R. Optimal determination of particle orientation, absolute hand, and contrast loss in single-particle electron cryomicroscopy. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 333, 721–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stagg, S.M.; Noble, A.J.; Spilman, M.; Chapman, M.S. ResLog plots as an empirical metric of the quality of cryo-EM reconstructions. J. Struct. Biol. 2014, 185, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spear, J.M.; Noble, A.J.; Xie, Q.; Sousa, D.R.; Chapman, M.S.; Stagg, S.M. The influence of frame alignment with dose compensation on the quality of single particle reconstructions. J. Struct. Biol. 2015, 192, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, R.F.; Davidson, E.R.; Simpson, W.T. Coherent X-Ray Scattering for the Hydrogen Atom in the Hydrogen Molecule. J. Chem. Phys. 1965, 42, 3175–3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, R.I.; Thompson, A.L.; Watkin, D.J. Crystals enhancements: Dealing with hydrogen atoms in refinement. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2010, 43, 1100–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroud, R.M.; Fauman, E.B. Significance of structural changes in proteins: Expected errors in refined protein structures. Protein Sci. 1995, 4, 2392–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, G.F.; Levitt, M.; Brunger, A.T. Super-resolution biomolecular crystallography with low-resolution data. Nature 2010, 464, 1218–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonine, P.V.; Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W.; Echols, N.; Headd, J.J.; Moriarty, N.W.; Mustyakimov, M.; Terwilliger, T.C.; Urzhumtsev, A.; Zwart, P.H.; Adams, P.D. Towards automated crystallographic structure refinement with phenix.refine. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2012, 68, 352–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabsch, W.; Sander, C. Dictionary of Protein Structure: Pattern Recognition of Hydrogen-Bonded and Geometrical Features. Biopolymers 1983, 22, 2577–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanokura, M. 1H-NMR study on the tautomerism of the imidazole ring of histidine residues. I. Microscopic pK values and molar ratios of tautomers in histidine-containing peptides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1983, 742, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundberg, R.J.; Martin, R.B. Interactions of Histidine and Other Imidazole Derivates with Transition Metal Ions in Chemical and Biological Systems. Chem. Rev. 1973, 74, 471–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, N.; Deniau, C.; Létoffé, S.; Simenel, C.; Kumar, V.; Stojiljkovic, I.; Wandersman, C.; Delepierre, M.; Lecroisey, A. Histidine pK(a) shifts and changes of tautomeric states induced by the binding of gallium-protoporphyrin IX in the hemophore HasA(SM). Protein Sci. 2002, 11, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Williams, J. Electron scattering from atomic hydrogen. III. Absolute differential cross sections for elastic scattering of electrons of energies from 20 to 680 eV. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Phys. 2001, 8, 2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, C.; March, N.H.; Vincent, D. X-ray and Electron Scattering by Molecular Hydrogen. Proc. Phys. Soc. 1958, 71, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Data Collection | |
|---|---|
| Magnification | 155,000× |
| Voltage | 300 kV |
| Electron exposure | 30 e−/Å2 |
| Defocus range | −0.8 to −2.6 μm |
| Pixel size | 0.514 Å |
| (on refinement vs. atomic model:) | 0.5105 Å |
| Data Processing | |
| Motion correction | Relion 3.0 |
| Anisotropic magnification correction | |
| Distortion angle | 5.3° |
| Percent distortion | 0.91% |
| CTF estimation | |
| Resolution range | 30 to 1.56 Å |
| Symmetry imposed | I1 |
| Initial particle images | 85,341 |
| Final particle images | 48,209 |
| Map resolution | 1.56 Å |
| FSC threshold | 0.143 |
| Protein atoms/asymmetric unit (mean B-factor): | 8144 (5.6 Å2) |
| Non hydrogen | 4176 (5.3 Å2) |
| Core β-barrel | 249 (3.3 Å2) |
| Water molecules | 265 (11.9 Å2) |
| RMS bond length deviation from ideal | 0.019 Å |
| RMS bond angle deviation from ideal | 1.4° |
| Ramachandran outliers | 1 (0.2%) |
| Side chains: multiple conformer/outliers | 8/6 (1%) |
| Cross-correlation (model-map) | 0.80 |
| Resolution from model-map refinement (d0.5) | 1.44 Å (core β-barrel) |
| Atoms | Cf. AAV-DJ at 4.5 Å (pdbID: 3J1Q) [20] | Cf. AAV-DJ at 2.8 Å resolution (pdbID: 5UF6) [22] |
| All | 1.39 Å | 0.87 Å |
| All, after rotamer inversion of (pseudo-) symmetrical side chains [58] | 1.36 Å | 0.80 Å |
| After outliers removed (% atoms) | 1.06 (7%) | 0.35 Å (10%) |
| ackbone | 0.96 Å | 0.42 Å |
| After outliers removed (% atoms) | 0.87 (3%) | 0.29 Å (6%) |
| Cα | 0.95 Å | 0.35 Å |
| After outliers removed (% atoms) | 0.86 (3%) | 0.28 Å (5%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, Q.; Yoshioka, C.K.; Chapman, M.S. Adeno-Associated Virus (AAV-DJ)—Cryo-EM Structure at 1.56 Å Resolution. Viruses 2020, 12, 1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12101194
Xie Q, Yoshioka CK, Chapman MS. Adeno-Associated Virus (AAV-DJ)—Cryo-EM Structure at 1.56 Å Resolution. Viruses. 2020; 12(10):1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12101194
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Qing, Craig K. Yoshioka, and Michael S. Chapman. 2020. "Adeno-Associated Virus (AAV-DJ)—Cryo-EM Structure at 1.56 Å Resolution" Viruses 12, no. 10: 1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12101194
APA StyleXie, Q., Yoshioka, C. K., & Chapman, M. S. (2020). Adeno-Associated Virus (AAV-DJ)—Cryo-EM Structure at 1.56 Å Resolution. Viruses, 12(10), 1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12101194





