TREX1 531C>T Polymorphism is Associated with High Proviral Load Levels in HTLV-1-Infected Persons
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Sample Collection and Storage
2.3. DNA Extraction
2.4. Quantification of HTLV-1 Proviral Load
2.5. Genotyping of TREX1 531C/T (rs11797)
2.6. ANA Screening in HEp-2 Cells
2.7. Quantification of Plasma Cytokines
2.8. Statistical Analysis
2.9. Ethics Statement
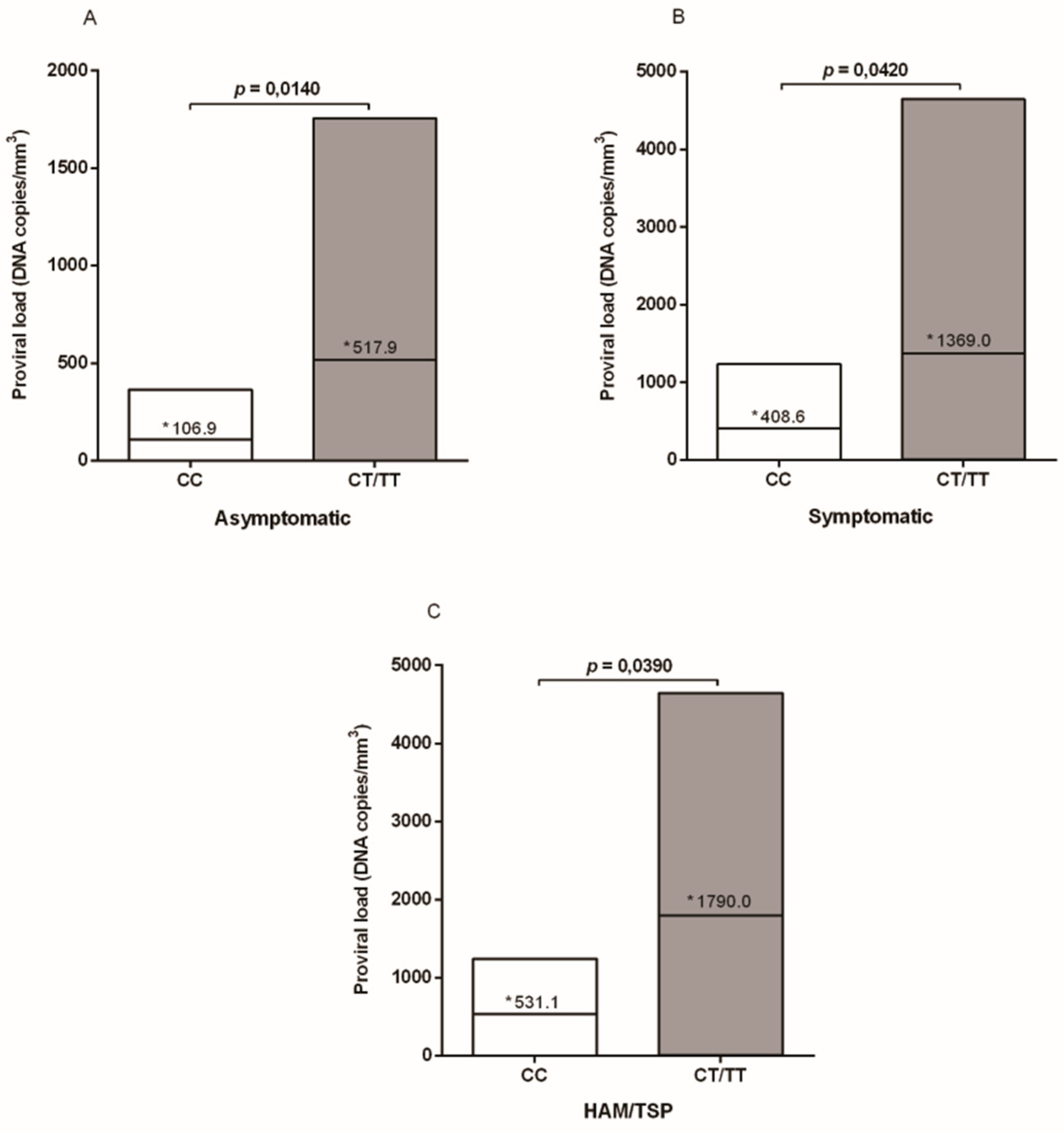
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kalyanaraman, V.S.; Sarngadharan, M.G.; Nakao, Y.; Ito, Y.; Aoki, T.; Gallo, R.C. Natural antibodies to the structural core protein (p24) of the human T-cell leucemia (lymphoma) retrovírus found in sera of leucemia in Japan. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 1653–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osame, M.; Usuku, K.; Izumo, S. HTLV-I associated myelopathy, a new clinical entity. Lancet 1986, 1, 1031–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakova, M.; Lézin, A.; Dantin, F.; Lagathu, G.; Olindo, S.; Jean-Baptiste, G.; Arfi, S.; Césaire, R. Increased proviral load in HTLV-1-infected patients with rheumatoid arthritis or connective tissue disease. Retrovirology 2005, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okajima, R.; Oliveira, A.C.; Smid, J.; Casseb, J.; Sanches, J.A. High prevalence of skin disorders among HTLV-1 infected individuals independent of clinical status. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassar, O.; Gessain, A. Serological and Molecular Methods to Study Epidemiological Aspects of human T-cell lymphotropi vírus type 1 infection. Methods Mol. Boil. 2017, 1582, 3–24. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, M.; Bangham, C.R. Immunopathogenesis of human T-cell leukemia virus type-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis: Recent perspectives. Leuk. Res. Treat. 2012, 2012, 259045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Montfoort, N.; Olagnier, D.; Hiscott, J. Unmasking immune sensing of retroviruses: Interplay between innate sensors and host effectors. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014, 25, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sze, A.; Olagnier, D.; Lin, R.; van Grevenynghe, J.; Hiscott, J. SAMHD1 host restriction factor: A link with innate immune sensing of retrovirus infection. J. Mol. Biol. 2013, 425, 4981–4994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.; Regalado-Magdos, A.D.; Stiggelbout, B.; Lee-Kirsch, M.A.; Lieberman, J. The cytosolic exonuclease TREX1 inhibits the innate immune response to human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindahl, T.; Barnes, D.; Yang, Y.; Robins, P. Biochemical properties of mammalian TREX1 and its association with DNA replication and inherited inflammatory disease. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2009, 37, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stetson, D.B.; Ko, J.S.; Heidmann, T.; Medzhitov, R. Trex1 prevents cell-intrinsic initiation of autoimmunity. Cell 2008, 134, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namjou, B.; Kothari, P.H.; Kelly, J.A.; Glenn, S.B.; Ojwang, J.O.; Adler, A.; Alarcón-Riquelme, M.E.; Gallant, C.J.; Boackle, S.A.; Criswell, L.A.; et al. Evaluation of the TREX1 gene in a large multi-ancestral lupus cohort. Genes Immun. 2011, 12, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontillo, A.; Girardelli, M.; Catamo, E.; Duarte, A.J.; Crovella, S. Polymorphisms in TREX1 and susceptibility to HIV-1 infection. Int. J. Immunogenet. 2013, 40, 492–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koumakis, E.; Giraud, M.; Dieudé, P.; Cohignac, V.; Cuomo, G.; Airò, P.; Hachulla, E.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Diot, E.; Caramaschi, P.; et al. Brief report: Candidate gene study in systemic sclerosis identifies a rare and functional variant of the TNFAIP3 locus as a risk factor for polyautoimmunity. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 2746–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredi, M.; Bianchi, M.; Andreoli, L.; Greco, G.; Olivieri, I.; Orcesi, S.; Fazzi, E.; Cereda, C.; Tincani, A. Typing TREX1 gene in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Reumatismo 2015, 67, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barizzone, N.; Monti, S.; Mellone, S.; Godi, M.; Marchini, M.; Scorza, R.; Danieli, M.G.; D’Alfonso, S. Rare variants in the TREX1 gene and susceptibility to autoimmune diseases. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 471703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamegão-Lopes, B.P.; Rezende, P.R.; Maradei-Pereira, L.M.C.; Lemos, J.A.R. HTLV-1 and HTLV-2 proviral load: A simple method using quantitative real-time PCR. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2006, 39, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruvinel, W.M.; Andrade, L.E.C.; von Mühlen, C.A.; Dellavance, A.; Ximenes, A.C.; Bichara, C.D.; Bueno, C.; Mangueira, C.L.P.; Bonfá, E.; de Almeida Brito, F.; et al. V Brazilian consensus guidelines for detection of anti-cell autoantibodies on hep-2 cells. Adv. Rheumatol. 2019, 59, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayres, M.; Ayres, J.R.; Ayres, D.L.; Santos, A.S. BioEstat 5.3: Aplicações estatísticas nas áreas das Ciências Biológicas e Médicas; Editora Sociedade Civil Mamirauá: Belém, PA, Brasil, 2011; p. 364. [Google Scholar]
- Derse, D.; Hill, S.A.; Lloyd, P.A.; Chung, H.K.; Morse, B.A. Examining human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 infection and replication by cell-free infection with recombinant virus vectors. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 8461–8468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pique, C.; Jones, K.S. Pathways of cell-cell transmission of HTLV-1. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha-Júnior, M.C.; Haddad, R.; Alves, D.C.; de Deus Wagatsuma, V.M.; Mendes-Junior, C.T.; Deghaide, N.H.; Takayanagui, O.M.; Covas, D.T.; Donadi, E.A.; Kashima, S. Interleukin-18 and interferon-gamma polymorphisms are implicated on proviral load and susceptibility to human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 infection. Tissue Antigens 2012, 80, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assone, T.; Malta, F.M.; Bakkour, S.; Montalvo, L.; Paiva, A.M.; Smid, J.; de Oliveira, A.C.P.; de Toledo Gonçalves, F.; do Carmo Luiz, O.; Fonseca, L.A.M.; et al. Polymorphisms in HLA-C and KIR alleles are not associated with HAM/TSP risk in HTLV-1-infected subjects. Virus Res. 2018, 244, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NCBI (National Center for Biotechnology Information). Reference SNP (rs): Rs11797. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/snp/rs11797#frequency_tab (accessed on 22 January 2019).
- Santos, N.P.; Ribeiro-Rodrigues, E.M.; Ribeiro-Dos-Santos, A.K.; Pereira, R.; Gusmão, L.; Amorim, A.; Guerreiro, J.F.; Zago, M.A.; Matte, C.; Hutz, M.H.; et al. Assessing individual interethnic admixture and population substructure using a 48-insertion-deletion (INSEL) ancestry-informative marker (AIM) panel. Hum. Mutat. 2009, 31, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booiman, T.; Setiawan, L.C.; Kootstra, N.A. Genetic variation in Trex1 affects HIV-1 disease progression. Aids 2014, 28, 2517–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, M.; Usuku, K.; Matsumoto, W.; Kodama, D.; Takenouchi, N.; Moritoyo, T.; Hashiguchi, S.; Ichinose, M.; Bangham, C.R.; Izumo, S.; et al. Analysis Of HTLV-I Proviral Load In 202 HAM/TSP Patients And 243 Asymptomatic HTLV-I Carriers: High Proviral Load Strongly Predisposes To HAM/TSP. J. Neurovirol. 1998, 4, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi Ghezeldasht, A.; Hedayati-Moghaddam, M.R.; Habibi, M.; Mollahosseini, F.; Rafatpanah, H.; Miri, R.; Hatef Fard, M.; Sahebari, M. Rate of positive autoimmune markers in Human T lymphotropic virus type 1 carriers: A case-control study from Iran. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 21, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Eguchi, K.; Nakamura, T.; Mizokami, A.; Shirabe, S.; Kawakami, A. High prevalence of Sjögren’s syndrome in patients with HTLV-I associated myelopathy. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1997, 56, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, M.C.; Torres, M.; Tamayo, O.; Criollo, W.; Quintana, M.; Sánchez, A.; García, F. Autoimmune syndrome in the tropical spastic paraparesis/myelopathy associated with human T-lymphotropic virus infections. Biomedica 2008, 28, 510–522. [Google Scholar]
- Dellavance, A.; Gabriel, J.A.; Nuccitelli, B.; Taliberti, B.H.; von Mühlen, C.A.; Bichara, C.D.A.; Santos, C.H.R.; Bueno, C.; Yano, C.M.; Mangueira, C.L.P.; et al. 3° Consenso Brasileiro para pesquisa de autoanticorpos em células HEp-2 (FAN): Recomendações para padronização do ensaio de pesquisa de autoanticorpos em células HEp-2, controle de qualidade e associações clínicas. Rev. Bras. Reumatol. 2009, 49, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Levin, M.C.; Lee, S.M.; Kalume, F.; Morcos, Y.; Dohan Jr, F.C.; Hasty, K.A.; Callaway, J.C.; Zunt, J.; Desiderio, D.; Stuart, J.M. Autoimmunity due to molecular mimicry as a cause of neurological disease. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 509–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivashkiv, L.B.; Donlin, L.T. Regulation of type I interferon responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Genotypes and Alleles | HTLV-1 n = 151 n (%) | Control n = 100 n (%) | p * |
|---|---|---|---|
| CC | 83 (54.97) | 60 (60.00) | 0.6095 |
| CT | 56 (37.09) | 31 (31.00) | |
| TT | 12 (7.94) | 9 (9.00) | |
| C | 0.74 | 0.75 | 0.7243 |
| T | 0.26 | 0.25 |
| Genotypes and Alleles | Asymptomatic n = 91 n (%) | Symptomatic n = 58 n (%) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| CC | 48 (52.74) | 32 (57.63) | 0.2151 # |
| CT | 38 (41.76) | 18 (30.51) | |
| TT | 5 (5.50) | 8 (11.86) | |
| C | 0.74 | 0.72 | 0.8735 * |
| T | 0.26 | 0.28 |
| Genotypes and Alleles | Asymptomatic n = 91 n (%) | HAM/TSP n = 32 n (%) | Rheumatologic Manifestations n = 19 n (%) | p1 | p2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC | 48 (52.74) | 19 (59.38) | 8 (42.10) | 0.0339 # | 0.6241 # |
| CT | 38 (41.76) | 7 (21.87) | 9 (47.37) | ||
| TT | 5 (5.50) | 6 (18.75) | 2 (10.53) | ||
| C | 0.74 | 0.75 | 0.69 | 1.000 * | 0.5309 * |
| T | 0.26 | 0.25 | 0.31 |
| Genotypes and Alleles | Asymptomatic n = 10 n (%) | HAM/TSP n = 10 n (%) |
|---|---|---|
| ANA POS | 0 (0.0) | 3 (30.0) |
| ANA NEG | 10 (100.0) | 7 (70.0) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, D.d.C.; Amoras, E.d.S.G.; Moura, T.C.F.; Lopes, F.T.; Gomes, S.T.M.; Costa, C.A.d.; Sousa, M.S.; Ishak, R.; Vallinoto, A.C.R.; Queiroz, M.A.F. TREX1 531C>T Polymorphism is Associated with High Proviral Load Levels in HTLV-1-Infected Persons. Viruses 2020, 12, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12010007
Silva DdC, Amoras EdSG, Moura TCF, Lopes FT, Gomes STM, Costa CAd, Sousa MS, Ishak R, Vallinoto ACR, Queiroz MAF. TREX1 531C>T Polymorphism is Associated with High Proviral Load Levels in HTLV-1-Infected Persons. Viruses. 2020; 12(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Denis de Castro, Ednelza da Silva Graça Amoras, Tuane Carolina Ferreira Moura, Felipe Teixeira Lopes, Samara Tatielle Monteiro Gomes, Carlos A. da Costa, Maísa Silva Sousa, Ricardo Ishak, Antonio Carlos Rosário Vallinoto, and Maria Alice Freitas Queiroz. 2020. "TREX1 531C>T Polymorphism is Associated with High Proviral Load Levels in HTLV-1-Infected Persons" Viruses 12, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12010007
APA StyleSilva, D. d. C., Amoras, E. d. S. G., Moura, T. C. F., Lopes, F. T., Gomes, S. T. M., Costa, C. A. d., Sousa, M. S., Ishak, R., Vallinoto, A. C. R., & Queiroz, M. A. F. (2020). TREX1 531C>T Polymorphism is Associated with High Proviral Load Levels in HTLV-1-Infected Persons. Viruses, 12(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12010007






