Immunopathologic Effects of Prednisolone and Cyclosporine A on Feline Immunodeficiency Virus Replication and Persistence
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
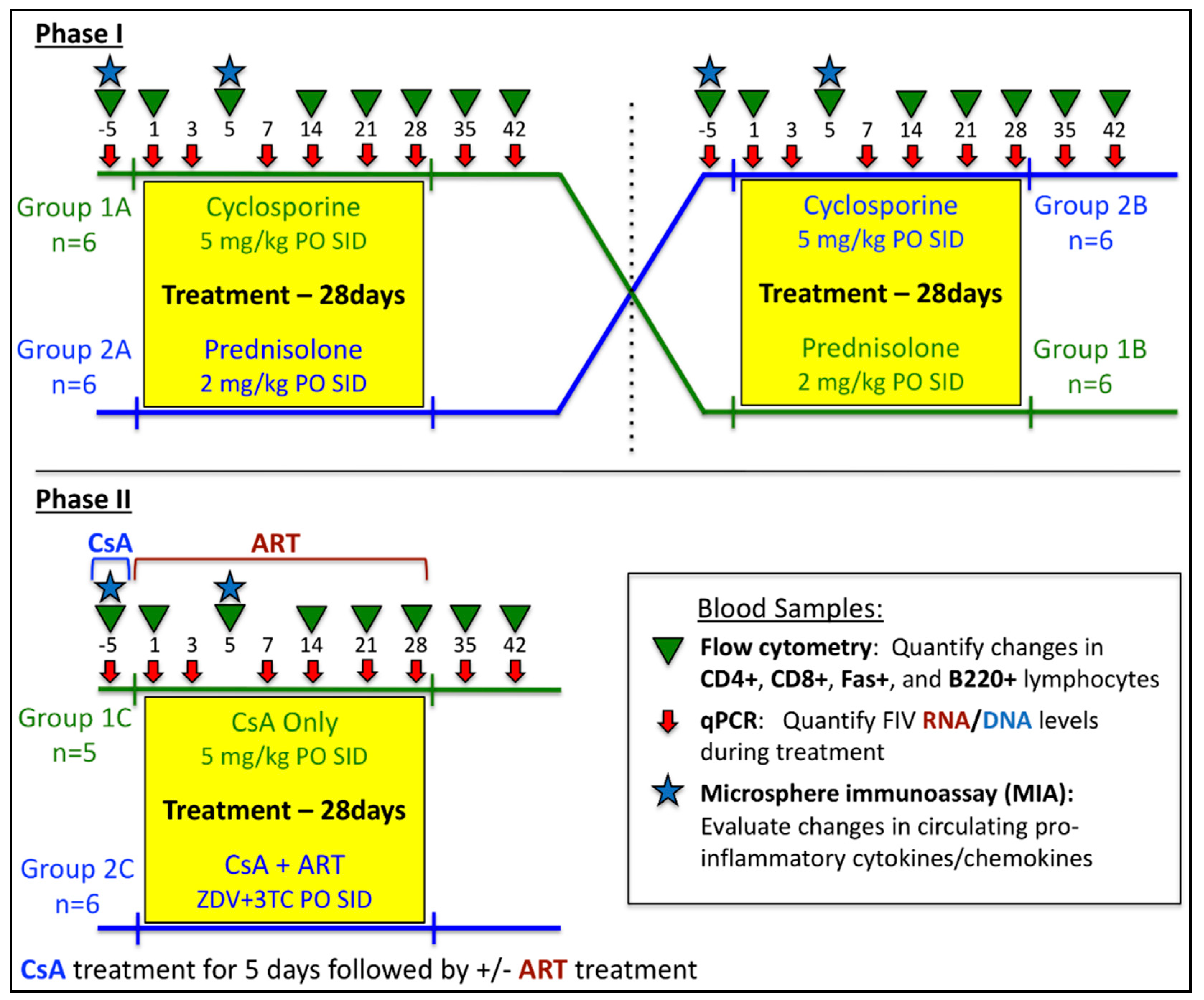
2.1. In vivo Protocols
2.2. Hematologic Analyses
2.3. Quantification of FIV Viral RNA and Proviral DNA in Blood
2.4. Evaluation of Peripheral Cytokine Expression during Immunomodulatory Therapy
2.5. Statistical Analysis
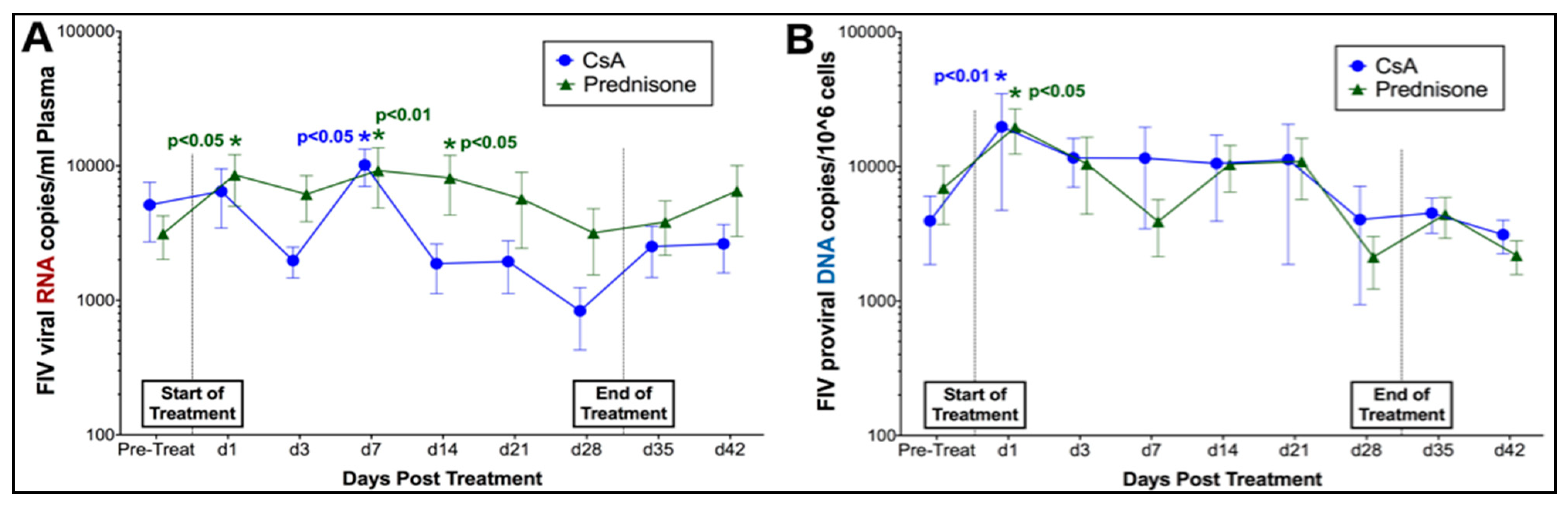
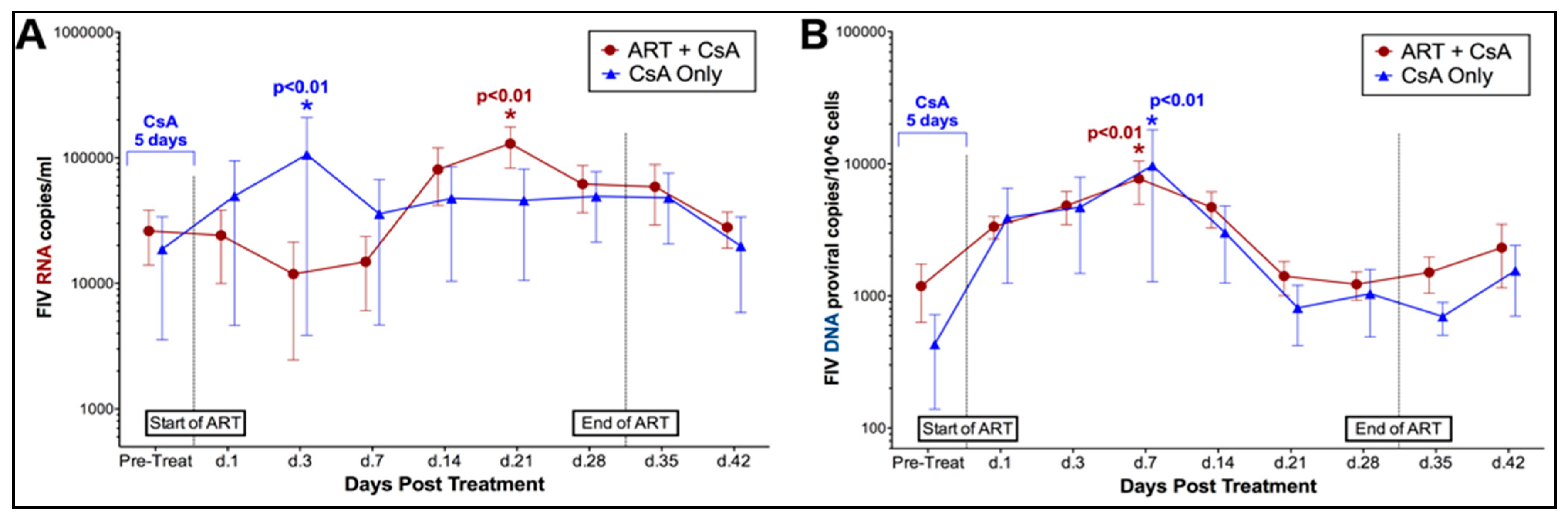
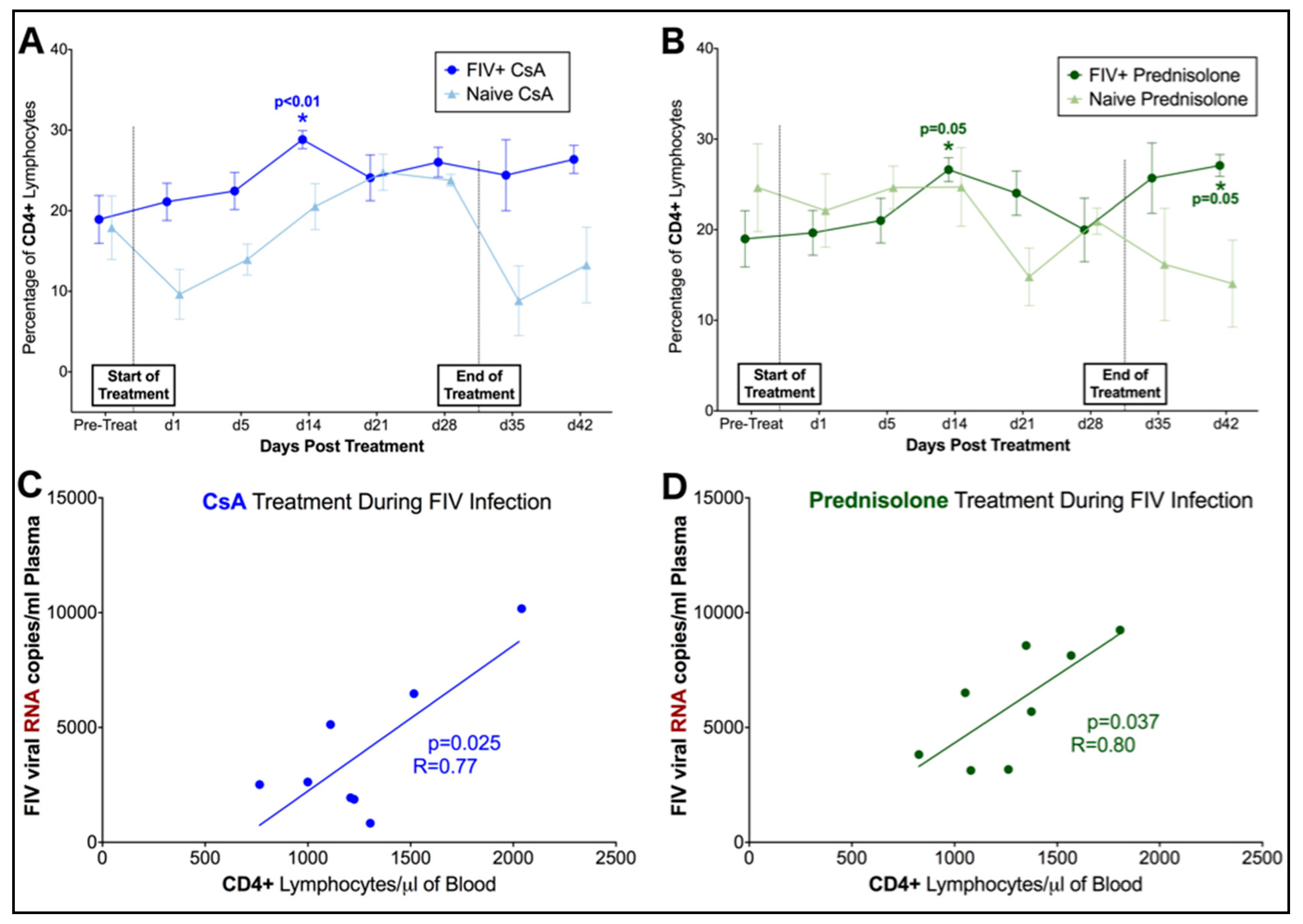
3. Results
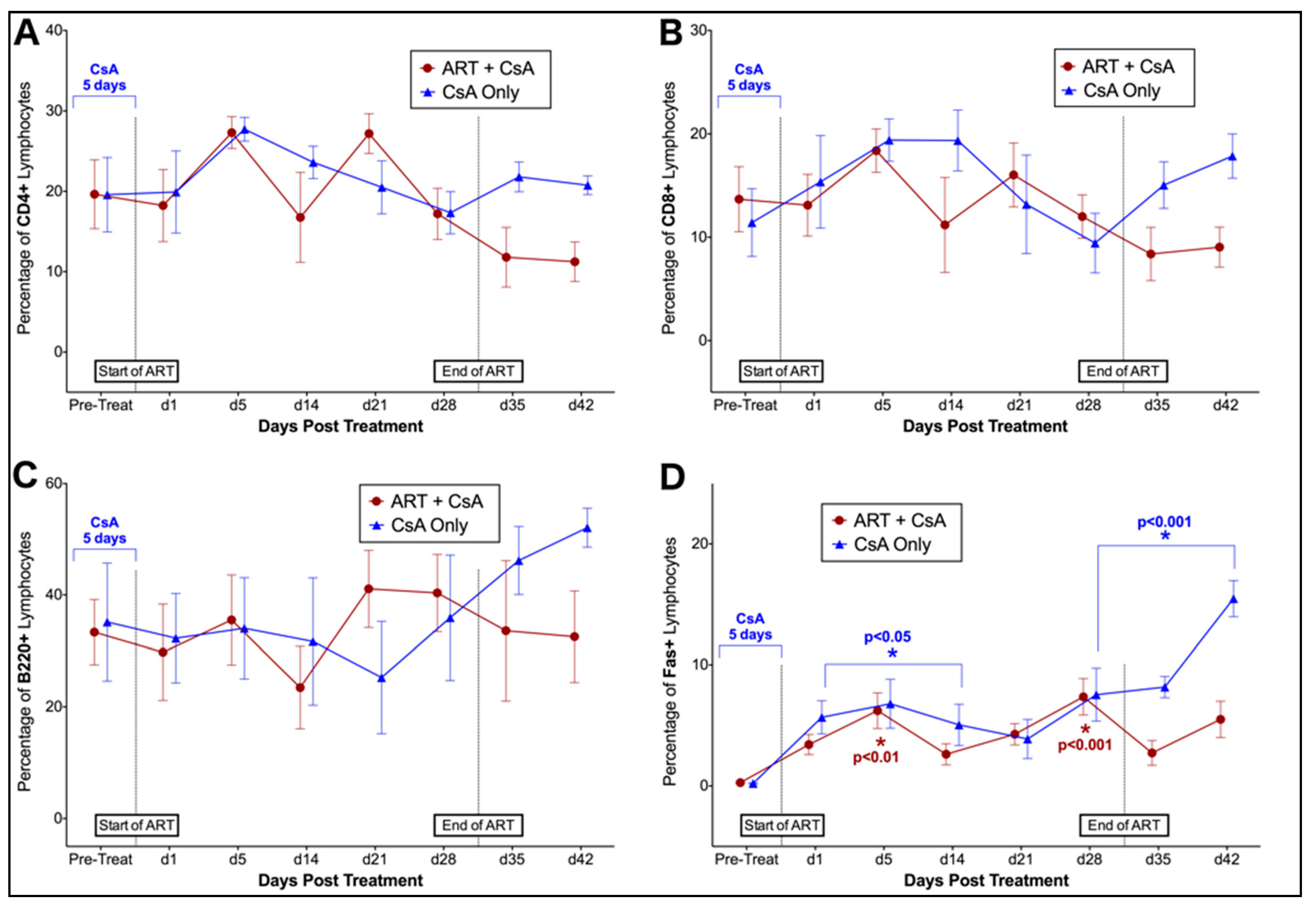
3.1. Prednisolone and Cyclosporine A Induce Acute and Transient Increases in Circulating FIV Viral and Proviral Loads
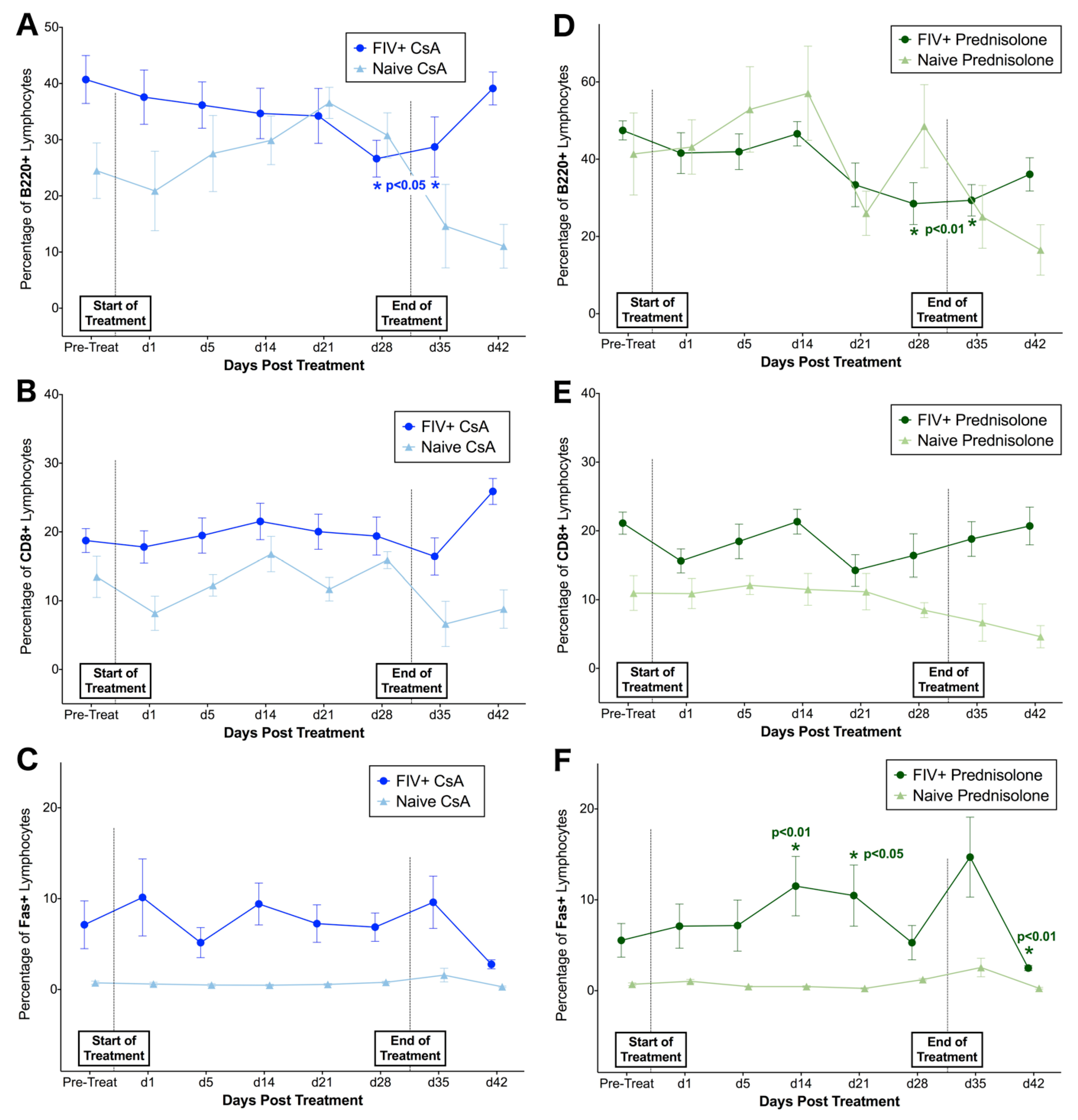
3.2. FIV-Infected Cats Exhibit Divergent Lymphocyte Immunophenotypes during Cyclosporine A and Prednisolone Treatment
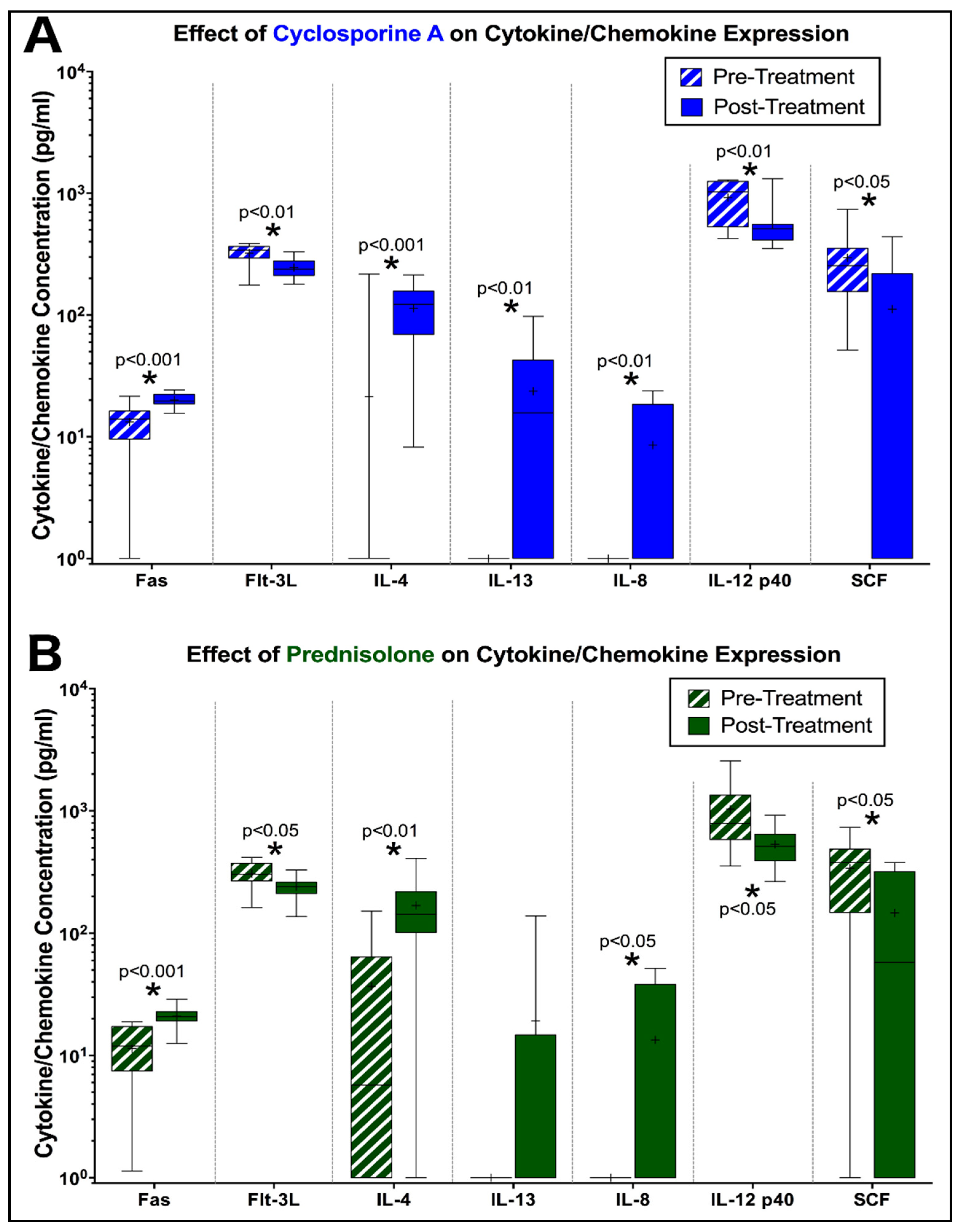
3.3. Peripheral Cytokine Expression is Altered by Prednisolone and CsA during FIV Infection
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siebelink, K.H.; Chu, I.-H.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; Weijer, K.; van Herwijnen, R.; Knell, P.; Egberink, H.F.; Bosch, M.L.; Osterhaus, A.D. Feline immunodeficiency virus (fiv) infection in the cat as a model for hiv infection in man: Fiv-induced impairment of immune function. Aids Res. Hum. Retrovir. 1990, 6, 1373–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkhard, M.; Dean, G.A. Transmission and immunopathogenesis of fiv in cats as a model for HIV. Curr. HIV Res. 2003, 1, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, G.A.; Himathongkham, S.; Sparger, E.E. Differential cell tropism of feline immunodeficiency virus molecular clones in vivo. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 2596–2603. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Elder, J.H.; Lin, Y.-C.; Fink, E.; Grant, C.K. Feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV) as a model for study of lentivirus infections: Parallels with hiv. Curr. HIV Res. 2010, 8, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- English, R.V.; Johnson, C.M.; Gebhard, D.H.; Tompkins, M.B. In vivo lymphocyte tropism of feline immunodeficiency virus. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 5175–5186. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, N.; Yamamoto, J.K.; Ishida, T.; Hansen, H. Feline immunodeficiency virus infection. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1989, 21, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, N.C.; Ho, E.W.; Brown, M.L.; Yamamoto, J.K. Isolation of a t-lymphotropic virus from domestic cats with an immunodeficiency-like syndrome. Science 1987, 235, 790–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torten, M.; Franchini, M.; Barlough, J.E.; George, J.W.; Mozes, E.; Lutz, H.; Pedersen, N.C. Progressive immune dysfunction in cats experimentally infected with feline immunodeficiency virus. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 2225–2230. [Google Scholar]
- Hosie, M.J.; Addie, D.; Belák, S.; Boucraut-Baralon, C.; Egberink, H.; Frymus, T.; Gruffydd-Jones, T.; Hartmann, K.; Lutz, H.; Marsilio, F. Feline immunodeficiency: Abcd guidelines on prevention and management. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2009, 11, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magden, E.; Miller, C.; MacMillan, M.; Bielefeldt-Ohmann, H.; Avery, A.; Quackenbush, S.L.; VandeWoude, S. Acute virulent infection with feline immunodeficiency virus (fiv) results in lymphomagenesis via an indirect mechanism. Virology 2013, 436, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bęczkowski, P.M.; Litster, A.; Lin, T.L.; Mellor, D.J.; Willett, B.J.; Hosie, M.J. Contrasting clinical outcomes in two cohorts of cats naturally infected with feline immunodeficiency virus (fiv). Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 176, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dow, S.W.; Poss, M.L.; Hoover, E.A. Feline immunodeficiency virus: A neurotropic lentivirus. Jaids J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 1990, 3, 658–668. [Google Scholar]
- Hopper, C.; Sparkes, A.; Gruffydd-Jones, T.; Crispin, S.; Muir, P.; Harbour, D.; Stokes, C. Clinical and laboratory findings in cats infected with feline immunodeficiency virus. Vet. Rec. 1989, 125, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, C.; Bielefeldt-Ohmann, H.; MacMillan, M.; Huitron-Resendiz, S.; Henriksen, S.; Elder, J.; VandeWoude, S. Strain-specific viral distribution and neuropathology of feline immunodeficiency virus. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2011, 143, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, C.; Boegler, K.; Carver, S.; MacMillan, M.; Bielefeldt-Ohmann, H.; VandeWoude, S. Pathogenesis of oral fiv infection. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lappin, M. Opportunistic infections associated with retroviral infections in cats. Semin. Vet. Med. Surg. (small Anim.) 1995, 10, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Colitz, C.M. Feline uveitis: Diagnosis and treatment. Clin. Tech. Small Anim. Pract. 2005, 20, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenorio, A.P.; Franti, C.E.; Madewell, B.R.; Pedersen, N.C. Chronic oral infections of cats and their relationship to persistent oral carriage of feline calici-, immunodeficiency, or leukemia viruses. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1991, 29, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callanan, J.; Jones, B.; Irvine, J.; Willett, B.; McCandlish, I.; Jarrett, O. Histologic classification and immunophenotype of lymphosarcomas in cats with naturally and experimentally acquired feline immunodeficiency virus infections. Vet. Pathol. 1996, 33, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egberink, H.; Borst, M.; Niphuis, H.; Balzarini, J.; Neu, H.; Schellekens, H.; de Clercq, E.; Horzinek, M.; Koolen, M. Suppression of feline immunodeficiency virus infection in vivo by 9-(2-phosphonomethoxyethyl) adenine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 3087–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, N.V.; Fontanals, A.; Castillo, V.; Gisbert, M.A.; Suraniti, A.; Mira, G.; Pisano, P.B. Evaluation of different antiretroviral drug protocols on naturally infected feline immunodeficiency virus (fiv) cats in the late phase of the asymptomatic stage of infection. Viruses 2012, 4, 924–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uckun, F.M.; Chen, C.-L.; Samuel, P.; Pendergrass, S.; Venkatachalam, T.; Waurzyniak, B.; Qazi, S. In vivo antiretroviral activity of stampidine in chronically feline immunodeficiency virus-infected cats. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 1233–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, N. An updated approach to chronic feline gingivitis stomatitis syndrome. Vet. Pract. 2012, 44, 34–38. [Google Scholar]
- Lommer, M.J. Efficacy of cyclosporine for chronic, refractory stomatitis in cats: A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blinded clinical study. J. Vet. Dent. 2013, 30, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lommer, M.J. Oral inflammation in small animals. Vet. Clin. Small Anim. Pract. 2013, 43, 555–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyon, K.F. Gingivostomatitis. Vet. Clin. Small Anim. Pract. 2005, 35, 891–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, C.C.; Lappin, M.R. Diagnosis and treatment of feline uveitis. Compendium 2001, 23, 258–269. [Google Scholar]
- Zwahlen, C.; Lucroy, M.; Kraegel, S.; Madewell, B. Results of chemotherapy for cats with alimentary malignant lymphoma: 21 cases (1993–1997). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1998, 213, 1144–1149. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Endo, Y.; Cho, K.-W.; Nishigaki, K.; Momoi, Y.; Nishimura, Y.; Mizuno, T.; Goto, Y.; Watari, T.; Tsujimoto, H.; Hasegawa, A. Molecular characteristics of malignant lymphomas in cats naturally infected with feline immunodeficiency virus. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1997, 57, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunn-Moore, D.; Pearson, G.; Harbour, D.; Whiting, C. Encephalitis associated with giant cells in a cat with naturally occurring feline immunodeficiency virus infection demonstrated by in situ hybridization. Vet. Pathol. 1996, 33, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelton, G.H.; Linenberger, M.L.; Persik, M.T.; Abkowitz, J.L. Prospective hematologic and clinicopathologic study of asymptomatic cats with naturally acquired feline immunodeficiency virus infection. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 1995, 9, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilger, B.; Allen, J. Cyclosporine a in veterinary ophthalmology. Vet. Ophthalmol. 1998, 1, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiber, S.L.; Crabtree, G.R. The mechanism of action of cyclosporin a and fk506. Immunol. Today 1992, 13, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, J.E. Inhibitory effects of cyclosporin a on lymphocyte activation. Cyclosporine Mode Action Clin. Appl. 1989, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.; Clipstone, N.; Timmermann, L.; Northrop, J.; Graef, I.; Fiorentino, D.; Nourse, J.; Crabtree, G.R. The mechanism of action of cyclosporin a and fk506. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1996, 80, S40–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahn, C.; Löwenberg, M.; Hommes, D.W.; Buttgereit, F. Molecular mechanisms of glucocorticoid action and selective glucocorticoid receptor agonists. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2007, 275, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emilie, D.; Etienne, S. Glucocorticoids: Mode of action and pharmacokinetics. Rev. Prat. 1990, 40, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Greenstein, S.; Ghias, K.; Krett, N.L.; Rosen, S.T. Mechanisms of glucocorticoid-mediated apoptosis in hematological malignancies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 1681–1694. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ma, A.; Koka, R.; Burkett, P. Diverse functions of il-2, il-15, and il-7 in lymphoid homeostasis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 24, 657–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Lin, J.-X.; Leonard, W.J. Il-2 family cytokines: New insights into the complex roles of il-2 as a broad regulator of t helper cell differentiation. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2011, 23, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.; Emanuelli, M.; Fink, E.; Musselman, E.; Mackie, R.; Troyer, R.; Elder, J.; VandeWoude, S. FIV vaccine with receptor epitopes results in neutralizing antibodies but does not confer resistance to challenge. npj Vaccines 2018, 3, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.; MacMillan, M.; Boegler, K.; Wood, C.; Elder, J.H.; VandeWoude, S. Pathogenicity and rapid growth kinetics of feline immunodeficiency virus are linked to 3′ elements. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- TerWee, J.A.; Carlson, J.K.; Sprague, W.S.; Sondgeroth, K.S.; Shropshire, S.B.; Troyer, J.L.; VandeWoude, S. Prevention of immunodeficiency virus induced cd4+ t-cell depletion by prior infection with a non-pathogenic virus. Virology 2008, 377, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, N.C.; Leutenegger, C.M.; Woo, J.; Higgins, J. Virulence differences between two field isolates of feline immunodeficiency virus (fiv-apetaluma and fiv-cpgammar) in young adult specific pathogen free cats. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2001, 79, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leutenegger, C.M.; Mislin, C.N.; Sigrist, B.; Ehrengruber, M.U.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R.; Lutz, H. Quantitative real-time pcr for the measurement of feline cytokine mrna. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1999, 71, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meers, J.; Del Fierro, G.; Cope, R.; Park, H.; Greene, W.; Robinson, W. Feline immunodeficiency virus infection: Plasma, but not peripheral blood mononuclear cell virus titer is influenced by zidovudine and cyclosporine. Arch. Virol. 1993, 132, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrieu, J.-M.; Lu, W.; Levy, R. Sustained increases in cd4 cell counts in asymptomatic human immunodeficiency virus type 1-seropositive patients treated with prednisolone for 1 year. J. Infect. Dis. 1995, 171, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayanja-Kizza, H.; Jones-Lopez, E.; Okwera, A.; Wallis, R.S.; Ellner, J.J.; Mugerwa, R.D.; Collaboration, U.C.W.R. Immunoadjuvant prednisolone therapy for hiv-associated tuberculosis: A phase 2 clinical trial in uganda. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 191, 856–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, A.; Wainberg, M.; Coates, R.; Klein, M.; Rachlis, A.; Read, S.; Shepherd, F.; Vellend, H.; Walmsley, S.; Halloran, P. Cyclosporine-induced deterioration in patients with aids. Cmaj: Can. Med. Assoc. J. 1989, 140, 1456. [Google Scholar]
- Kakuda, T.N. Pharmacology of nucleoside and nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitor-induced mitochondrial toxicity. Clin. Ther. 2000, 22, 685–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, M.; Earl, D.D.; Yamamoto, J.K. Is azt/3tc therapy effective against fiv infection or immunopathogenesis? Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2002, 85, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisset, L.R.; Lutz, H.; Böni, J.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R.; Lüthy, R.; Schüpbach, J. Combined effect of zidovudine (zdv), lamivudine (3tc) and abacavir (abc) antiretroviral therapy in suppressing in vitro fiv replication. Antivir. Res. 2002, 53, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, R.R.; Hayakawa, K. B cell development pathways. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2001, 19, 595–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodig, S.J.; Shahsafaei, A.; Li, B.; Dorfman, D.M. The cd45 isoform b220 identifies select subsets of human b cells and b-cell lymphoproliferative disorders. Hum. Pathol. 2005, 36, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, R.G.; Peters, M.G.; Hoofnagle, J.H. Effects of immunosuppressive therapy with prednisolone on b and t lymphocyte function in patients with chronic type b hepatitis. Hepatology 1986, 6, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tareyeva, I.; Shilov, E.; Gordovskaya, N. The effects of azathioprine and prednisolone on t-and b-lymphocytes in patients with lupus nephritis and chronic glomerulonephritis. Clin. Nephrol. 1980, 14, 233–237. [Google Scholar]
- Hannam-Harris, A.C.; Taylor, D.S.; Nowell, P.C. Cyclosporin a directly inhibits human b-cell proliferation by more than a single mechanism. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1985, 38, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lun, M.; Cochi, S.; Fioravanti, D.; Nazzari, C.; Raponi, G.; Mannella, E.; Di, G.T.; Mancini, C.; Filadoro, F. Effect of cyclosporin a on b cell maturation and differentiation. Drugs Under Exp. Clin. Res. 1991, 17, 493–500. [Google Scholar]
- Kunkl, A.; Klaus, G. Selective effects of cyclosporin a on functional b cell subsets in the mouse. J. Immunol. 1980, 125, 2526–2531. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, M.M.; Fogle, J.E.; Tompkins, M.B. Infection with feline immunodeficiency virus directly activates cd4+ cd25+ t regulatory cells. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 9373–9378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahlenkamp, T.W.; Tompkins, M.B.; Tompkins, W.A. Feline immunodeficiency virus infection phenotypically and functionally activates immunosuppressive cd4+ cd25+ t regulatory cells. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 4752–4761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.M.; Petty, C.S.; Tompkins, M.B.; Fogle, J.E. Cd4+ cd25+ t regulatory cells activated during feline immunodeficiency virus infection convert t helper cells into functional suppressors through a membrane-bound tgfβ/garp-mediated mechanism. Virol. J. 2014, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, A.; Ishida, T.; Washizu, T.; Tomoda, I. Humoral immune response to t cell dependent and independent antigens in cats infected with feline immunodeficiency virus. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 1991, 53, 333–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Distelhorst, C. Recent insights into the mechanism of glucocorticosteroid-induced apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2002, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, S.; Rainer, J.; Ploner, C.; Presul, E.; Riml, S.; Kofler, R. Glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis and glucocorticoid resistance: Molecular mechanisms and clinical relevance. Cell Death Differ. 2004, 11, S45–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Healy, E.; Dempsey, M.; Lally, C.; Ryan, M.P. Apoptosis and necrosis: Mechanisms of cell death induced by cyclosporine a in a renal proximal tubular cell line. Kidney Int. 1998, 54, 1955–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naujokat, C.; Daniel, V.; Bauer, T.M.; Sadeghi, M.; Opelz, G. Cell cycle-and activation-dependent regulation of cyclosporin a-induced t cell apoptosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 310, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dropulic, L.K.; Cohen, J.I. Severe viral infections and primary immunodeficiencies. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 53, 897–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuelsson, A.; Broström, C.; van Dijk, N.; Sönnerborg, A.; Chiodi, F. Apoptosis of cd4+ and cd19+ cells during human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection—correlation with clinical progression, viral load, and loss of humoral immunity. Virology 1997, 238, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsikis, P.D.; Wunderlich, E.S.; Smith, C.A.; Herzenberg, L.A. Fas antigen stimulation induces marked apoptosis of t lymphocytes in human immunodeficiency virus-infected individuals. J. Exp. Med. 1995, 181, 2029–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelms, K.; Keegan, A.D.; Zamorano, J.; Ryan, J.J.; Paul, W.E. The il-4 receptor: Signaling mechanisms and biologic functions. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1999, 17, 701–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seder, R.A.; Paul, W.E. Acquisition of lymphokine-producing phenotype by cd4+ t cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1994, 12, 635–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimoto, T.; Paul, W.E. Cd4pos, nk1. 1pos t cells promptly produce interleukin 4 in response to in vivo challenge with anti-cd3. J. Exp. Med. 1994, 179, 1285–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrick, D.A.; Schrenzel, M.D.; Mulvania, T.; Hsieh, B.; Ferlin, W.G.; Lepper, H. Differential production of interferon-γ and interleukin-4 in response to th1-and th2-stimulating pathogens by γδ t cells in vivo. Nature 1995, 373, 255–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynn, T.A. Il-13 effector functions. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 21, 425–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navikas, V.; Link, J.; Wahren, B.; Persson, C.; Link, H. Increased levels of interferon-gamma (ifn-γ), il-4 and transforming growth factor-beta (tgf-β) mrna expressing blood mononuclear cells in human hiv infection. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1994, 96, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyaard, L.; Hovenkamp, E.; Keet, I.; Hooibrink, B.; de Jong, I.; Otto, S.A.; Miedema, F. Single cell analysis of il-4 and ifn-gamma production by t cells from hiv-infected individuals: Decreased ifn-gamma in the presence of preserved il-4 production. J. Immunol. 1996, 157, 2712–2718. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Patella, V.; Florio, G.; Petraroli, A.; Marone, G. Hiv-1 gp120 induces il-4 and il-13 release from human fcεri+ cells through interaction with the vh3 region of ige. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, A.; Hamid, Q.; Robinson, D.; Schotman, E.; Meng, Q.; Assoufi, B.; Kay, A.; Durham, S. Prednisolone treatment in asthma. Reduction in the numbers of eosinophils, t cells, tryptase-only positive mast cells, and modulation of il-4, il-5, and interferon-gamma cytokine gene expression within the bronchial mucosa. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1996, 153, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, D.F.; Fernandez, M.; Caulfield, J.; Hawrylowicz, C.M. Glucocorticoids drive human cd8+ t cell differentiation towards a phenotype with high il-10 and reduced il-4, il-5 and il-13 production. Eur. J. Immunol. 2000, 30, 2344–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Momoi, Y.; Iwasaki, T. Cyclosporine a inhibits the mrna expressions of il-2, il-4 and ifn-γ, but not tnf-α, in canine mononuclear cells. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2007, 69, 887–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warbrick, E.; Thomas, A.; Williams, C. The effects of cyclosporin a, dexamethasone and other immunomodulatory drugs on induced expression of il-3, il-4 and il-8 mrna in a human mast cell line. Toxicology 1997, 116, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jundi, K.; Greene, C.M. Transcription of interleukin-8: How altered regulation can affect cystic fibrosis lung disease. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 1386–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, B.R.; Lore, K.; Bock, P.J.; Andersson, J.; Coffey, M.J.; Strieter, R.M.; Markovitz, D.M. Interleukin-8 stimulates human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication and is a potential new target for antiretroviral therapy. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 8195–8202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osunkalu, V.; Adewumi, A.; Onwuzuluigbo, C.; Olowoselu, O. Interleukin-8 a marker of disease progression and therapeutic response in hiv infection. Niger. Hosp. Pract. 2015, 15, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto, T.; Miike, T.; Nelson, R.; Trudeau, W.; Lockey, R.; Yodoi, J. Elevated serum levels of il-8 in patients with hiv infection. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1993, 93, 149–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gee, K.; Guzzo, C.; Mat, C.; Nor, F.; Ma, W.; Kumar, A. The il-12 family of cytokines in infection, inflammation and autoimmune disorders. Inflamm. Allergy-Drug Targets 2009, 8, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oku, H.; Shimizu, T.; Kawabata, T.; Nagira, M.; Hikita, I.; Ueyama, A.; Matsushima, S.; Torii, M.; Arimura, A. Antifibrotic action of pirfenidone and prednisolone: Different effects on pulmonary cytokines and growth factors in bleomycin-induced murine pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 590, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnotte, B.; Pardoux, C.; Bourhis, J.; Caignard, A.; Burdiles, A.M.; Chehimi, J.; Mami-Chouaib, F.; Chouaib, S. Inhibition of the human allogeneic mixed lymphocyte response by cyclosporin a: Relationship with the il-12 pathway. HLA 1996, 48, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degiannis, D.; Koniavitou, K. In vitro expression of activation markers and lymphocyte proliferation in response to interleukin 12: Effect of immunosuppressive agents. Transplant. Proc. 1996, 28, 3062–3064. [Google Scholar]
- Chehimi, J.; Starr, S.E.; Frank, I.; D’andrea, A.; Ma, X.; MacGregor, R.R.; Sennelier, J.; Trinchieri, G. Impaired interleukin 12 production in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients. J. Exp. Med. 1994, 179, 1361–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wodnar-Filipowicz, A. Flt3 ligand: Role in control of hematopoietic and immune functions of the bone marrow. Physiology 2003, 18, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, D.; Copley, M.; Benz, C.; Dykstra, B.; Bowie, M.; Eaves, C. Regulation of hematopoietic stem cells by the steel factor/kit signaling pathway. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 1926–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Langley, K.E.; Gourley, W.K.; Klimpel, G.R. Stem cell factor (scf) can regulate the activation and expansion of murine intraepithelial lymphocytes. Cytokine 2000, 12, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Alam, R.; Langley, K.E.; Klimpel, G.R. Stem cell factor and il-2 act synergistically in inducing intraepithelial lymphocyte proliferation and cytokine production: Upregulation of the il-2 receptor γ-chain and signaling via jak-3. Cell. Immunol. 2000, 205, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, M.I.; Perez, S.G.; Aarrass, S.; Helder, B.; Broekstra, P.; Gerlag, D.M.; Reedquist, K.A.; Tak, P.P.; Lebre, M.C. Fms-related tyrosine kinase 3 ligand (flt3l)/cd135 axis in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2013, 15, R209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsuka, H.; Kusumi, T.; Kanai, S.; Koyama, M.; Kuno, Y.; Takizawa, R. Stem cell factor mrna expression and production in human nasal epithelial cells: Contribution to the accumulation of mast cells in the nasal epithelium of allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1998, 102, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chklovskaia, E.; Nissen, C.; Landmann, L.; Rahner, C.; Pfister, O.; Wodnar-Filipowicz, A. Cell-surface trafficking and release of flt3 ligand from t lymphocytes is induced by common cytokine receptor γ-chain signaling and inhibited by cyclosporin a. Blood 2001, 97, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miller, C.; Powers, J.; Musselman, E.; Mackie, R.; Elder, J.; VandeWoude, S. Immunopathologic Effects of Prednisolone and Cyclosporine A on Feline Immunodeficiency Virus Replication and Persistence. Viruses 2019, 11, 805. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11090805
Miller C, Powers J, Musselman E, Mackie R, Elder J, VandeWoude S. Immunopathologic Effects of Prednisolone and Cyclosporine A on Feline Immunodeficiency Virus Replication and Persistence. Viruses. 2019; 11(9):805. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11090805
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiller, Craig, Jordan Powers, Esther Musselman, Ryan Mackie, John Elder, and Sue VandeWoude. 2019. "Immunopathologic Effects of Prednisolone and Cyclosporine A on Feline Immunodeficiency Virus Replication and Persistence" Viruses 11, no. 9: 805. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11090805
APA StyleMiller, C., Powers, J., Musselman, E., Mackie, R., Elder, J., & VandeWoude, S. (2019). Immunopathologic Effects of Prednisolone and Cyclosporine A on Feline Immunodeficiency Virus Replication and Persistence. Viruses, 11(9), 805. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11090805





