Tomato Chlorotic Spot Virus (TCSV) Putatively Incorporated a Genomic Segment of Groundnut Ringspot Virus (GRSV) Upon a Reassortment Event
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation and Sequencing
2.2. De Novo Assembly of Virus Genomes
2.3. Phylogenetic Analyses
2.4. Evaluation of Synonymous-Site Variability and Nucleotide Diversity
2.5. TMRCA Calculation
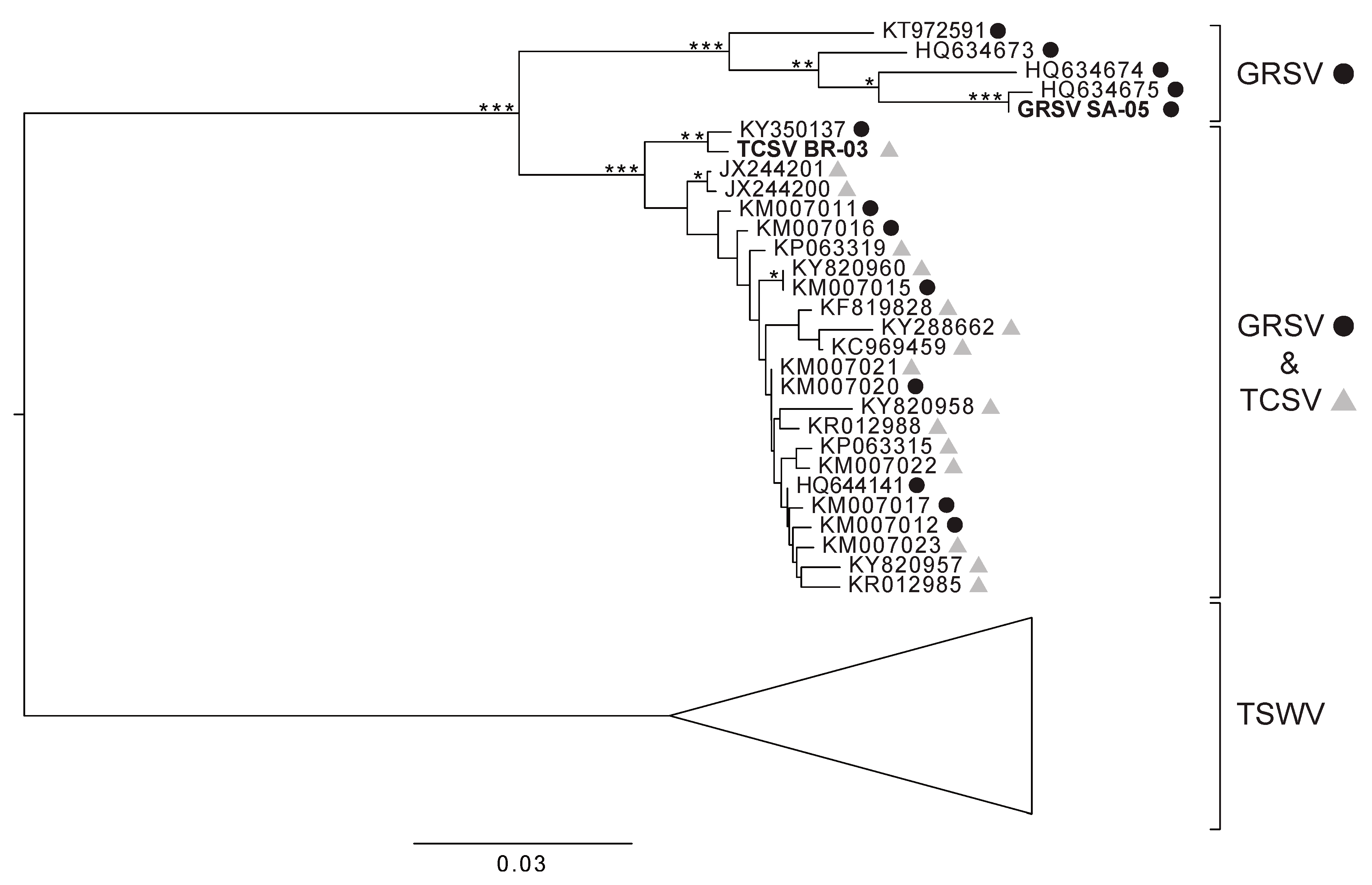
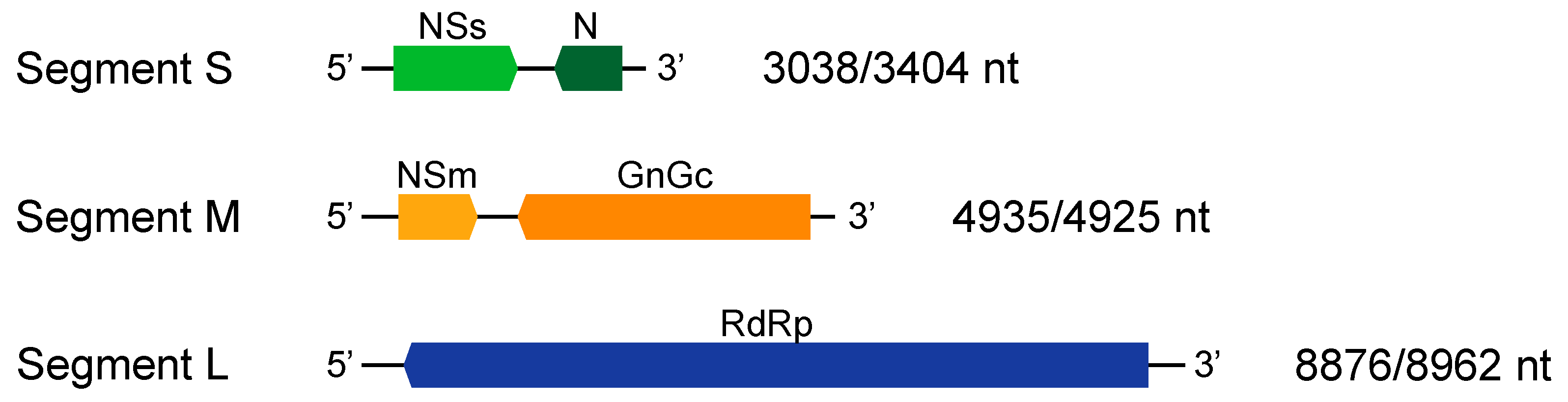
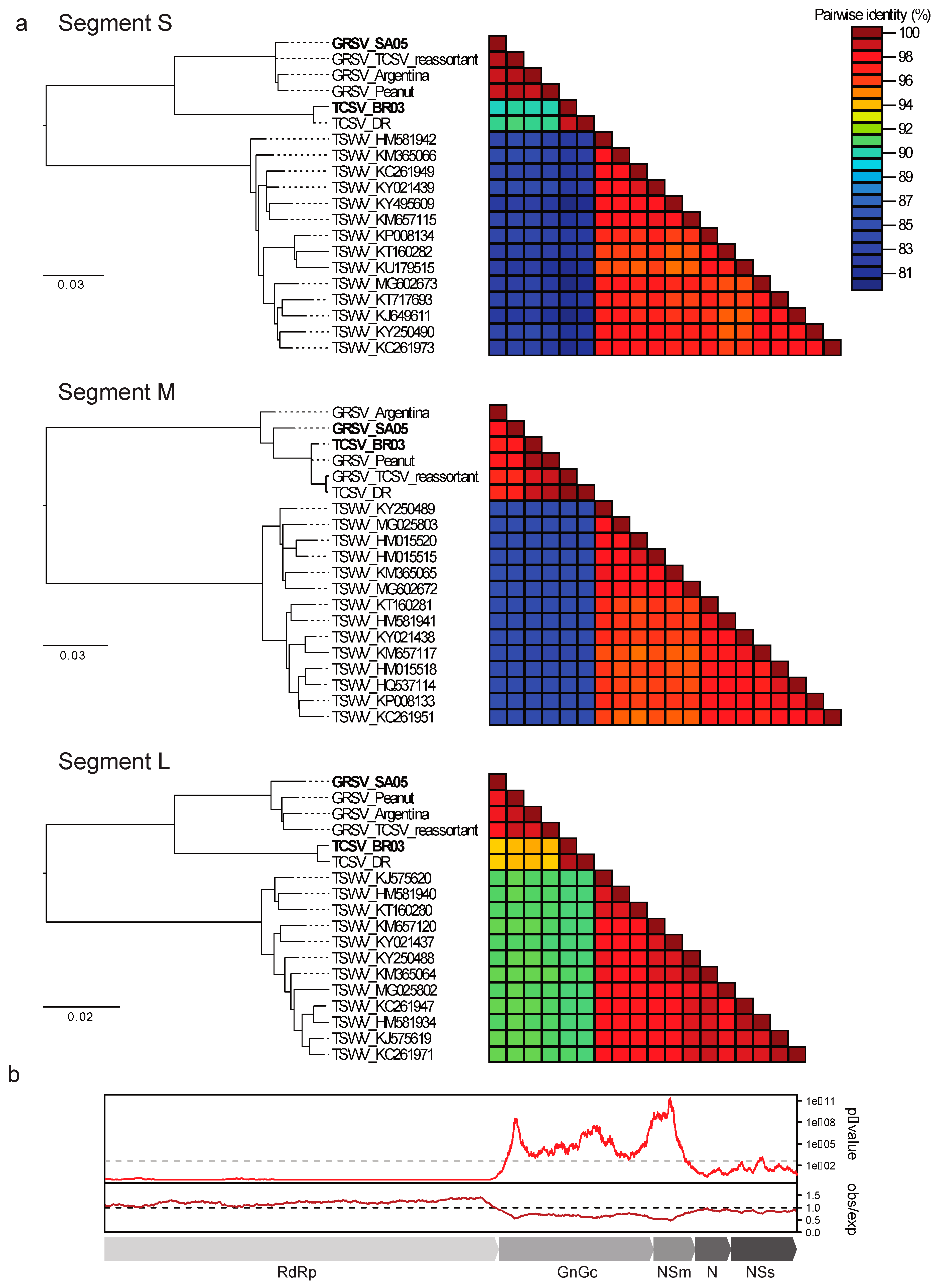
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pappu, H.R.; Jones, R.A.; Jain, R.K.; Jain, R.K. Global status of tospovirus epidemics in diverse cropping systems: Successes achieved and challenges ahead. Virus Res. 2009, 141, 219–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maes, P.; Adkins, S.; Alkhovsky, S.V.; Avšič-Županc, T.; Ballinger, M.J.; Bente, D.A.; Beer, M.; Bergeron, É.; Blair, C.D.; Briese, T.; et al. Taxonomy of the order Bunyavirales: second update 2018. Arch. Virol. 2019, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotenberg, D.; Jacobson, A.L.; Schneweis, D.J.; Whitfield, A.E. Thrips transmission of tospoviruses. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2015, 15, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turina, M.; Kormelink, R.; Resende, R.O. Resistance to Tospoviruses in Vegetable Crops: Epidemiological and Molecular Aspects. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2016, 54, 347–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plyusnin, A.; Beaty, B.J.; Elliott, R.M.; Goldbach, R.; Kormelink, R.; Lundkvist, K.A.; Schmaljohn, C.S.; Tesh, R.B. Family – Bunyaviridae. In Virus Taxonomy: classification and nomenclature of viruses: ninth report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses; King, A.M.Q., Adams, M.J., Carstens, E.B., Lefkowitz, E.J., Eds.; Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 2012; pp. 725–741. [Google Scholar]
- Takeda, A.; Sugiyama, K.; Nagano, H.; Mori, M.; Kaido, M.; Mise, K.; Tsuda, S.; Okuno, T. Identification of a novel RNA silencing suppressor, NSs protein of Tomato spotted wilt virus. FEBS Lett. 2002, 532, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kormelink, R.; Storms, M.; Vanlent, J.; Peters, D.; Goldbach, R. Expression and subcellular location of the NSM protein of tomato spotted wilt virus (TSWV), a putative viral movement protein. Virology 1994, 200, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adkins, S.; Quadt, R.; Choi, T.J.; Ahlquist, P.; German, T. An RNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity associated with virions of tomato spotted wilt virus, a plant- and insect-infecting bunyavirus. Virology 1995, 207, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, A.S.; Melo, F.L.; Inoue-Nagata, A.K.; Nagata, T.; Kitajima, E.W.; Resende, R.O. Characterization of bean necrotic mosaic virus: a member of a novel evolutionary lineage within the Genus Tospovirus. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Avila, A.C.; de Haan, P.; Kormelink, R.; Resende, R.O.; Goldbach, R.W.; Peters, D. Classification of tospoviruses based on phylogeny of nucleoprotein gene sequences. J. Gen. Virol. 1993, 74, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovato, F.A.; Nagata, T.; de Oliveira Resende, R.; de Avila, A.C.; Inoue-Nagata, A.K. Sequence analysis of the glycoproteins of Tomato chlorotic spot virus and Groundnut ringspot virus and comparison with other tospoviruses. Virus Genes 2004, 29, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, C.G.; Reitz, S.R.; Perry, K.L.; Adkins, S. A natural M RNA reassortant arising from two species of plant- and insect-infecting bunyaviruses and comparison of its sequence and biological properties to parental species. Virology 2011, 413, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Avila, A.C.; Dehaan, P.; Smeets, M.L.L.; Resende, R.D.; Kormelink, R.; Kitajima, E.W.; Goldbach, R.W.; Peters, D. Distinct levels of relationships between tospovirus isolates. Arch. Virol. 1993, 128, 211–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. ProtTest 3: fast selection of best-fit models of protein evolution. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1164–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhire, B.M.; Varsani, A.; Martin, D.P. SDT: A virus classification tool based on pairwise sequence alignment and identity calculation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firth, A.E. Mapping overlapping functional elements embedded within the protein-coding regions of RNA viruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 12425–12439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Librado, P.; Rozas, J. DnaSP v5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1451–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouckaert, R.; Heled, J.; Kühnert, D.; Vaughan, T.; Wu, C.H.; Xie, D.; Suchard, M.A.; Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J. BEAST 2: A software platform for Bayesian evolutionary analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2014, 10, e1003537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A.; Lam, T.T.; Max Carvalho, L.; Pybus, O.G. Exploring the temporal structure of heterochronous sequences using TempEst (formerly Path-O-Gen). Virus Evol. 2016, 2, vew007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, A.J.; Ho, S.Y.; Phillips, M.J.; Rambaut, A. Relaxed phylogenetics and dating with confidence. PLoS Biol. 2006, 4, e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, A.J.; Rambaut, A.; Shapiro, B.; Pybus, O.G. Bayesian coalescent inference of past population dynamics from molecular sequences. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 22, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouckaert, R.R.; Drummond, A.J. bModelTest: Bayesian phylogenetic site model averaging and model comparison. BMC Evol. Biol. 2017, 17, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Breuil, S.; Cañizares, J.; Blanca, J.M.; Bejerman, N.; Trucco, V.; Giolitti, F.; Ziarsolo, P.; Lenardon, S. Analysis of the coding-complete genomic sequence of groundnut ringspot virus suggests a common ancestor with tomato chlorotic spot virus. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 2311–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, C.G.; Frantz, G.; Reitz, S.R.; Funderburk, J.E.; Mellinger, H.C.; McAvoy, E.; Turechek, W.W.; Marshall, S.H.; Tantiwanich, Y.; McGrath, M.T.; et al. Emergence of Groundnut ringspot virus and Tomato chlorotic spot virus in Vegetables in Florida and the Southeastern United States. Phytopathology 2015, 105, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, M.M.S.; Orilio, A.F.; Melo, F.L.; Rodriguez, R.; Feliz, A.; Cayetano, X.; Martinez, R.T.; Resende, R.O. The First Report of Tomato chlorotic spot virus (TCSV) Infecting Long Beans and Chili Peppers in the Dominican Republic. Plant Dis. 2014, 98, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, R.T.; de Almeida, M.M.S.; Rodriguez, R.; de Oliveira, A.S.; Melo, F.L.; Resende, R.O. Identification and genome analysis of tomato chlorotic spot virus and dsRNA viruses from coinfected vegetables in the Dominican Republic by high-throughput sequencing. Virol. J. 2018, 15, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, C.G.; Rivera-Vargas, L.I.; Rodrigues, J.C.V.; Mercado, W.; Mellinger, H.C.; Adkins, S. First report of tomato chlorotic spot virus (TCSV) in tomato, pepper, and jimsonweed in Puerto Rico. Plant Health Prog. 2013, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.; McGrath, M.T.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Z.; Ling, K.S. First report of tomato chlorotic spot virus infecting tomato in New York. Plant Dis. 2018, 102, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Londoño, A.; Capobianco, H.; Zhang, S.; Polston, J.E. First record of Tomato chlorotic spot virus in the USA. Trop. Plant Pathol. 2012, 37, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Protein | Virus | Number of Isolates | Number of Segregating Sites (S) | Average Number of Differences (K) | Nucleotide Diversity (π) | Nucleotide Diversity with Jukes Cantor Correction (π JC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N (212 nt) | TCSV | 28 | 43 | 5.26190 | 0.02482 | 0.02554 |
| GRSV | 25 | 57 | 9.64333 | 0.04549 | 0.04742 | |
| TCSV and GRSV | 53 | 96 | 22.98621 | 0.10843 | 0.12246 | |
| NSm (381 nt) | TCSV | 16 | 27 | 4.28333 | 0.01124 | 0.01135 |
| GRSV | 13 | 48 | 16.69231 | 0.04381 | 0.04581 | |
| TCSV and GRSV | 29 | 66 | 11.20936 | 0.02942 | 0.03066 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, J.M.F.; de Oliveira, A.S.; de Almeida, M.M.S.; Kormelink, R.; Nagata, T.; Resende, R.O. Tomato Chlorotic Spot Virus (TCSV) Putatively Incorporated a Genomic Segment of Groundnut Ringspot Virus (GRSV) Upon a Reassortment Event. Viruses 2019, 11, 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11020187
Silva JMF, de Oliveira AS, de Almeida MMS, Kormelink R, Nagata T, Resende RO. Tomato Chlorotic Spot Virus (TCSV) Putatively Incorporated a Genomic Segment of Groundnut Ringspot Virus (GRSV) Upon a Reassortment Event. Viruses. 2019; 11(2):187. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11020187
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, João Marcos Fagundes, Athos Silva de Oliveira, Mariana Martins Severo de Almeida, Richard Kormelink, Tatsuya Nagata, and Renato Oliveira Resende. 2019. "Tomato Chlorotic Spot Virus (TCSV) Putatively Incorporated a Genomic Segment of Groundnut Ringspot Virus (GRSV) Upon a Reassortment Event" Viruses 11, no. 2: 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11020187
APA StyleSilva, J. M. F., de Oliveira, A. S., de Almeida, M. M. S., Kormelink, R., Nagata, T., & Resende, R. O. (2019). Tomato Chlorotic Spot Virus (TCSV) Putatively Incorporated a Genomic Segment of Groundnut Ringspot Virus (GRSV) Upon a Reassortment Event. Viruses, 11(2), 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11020187





