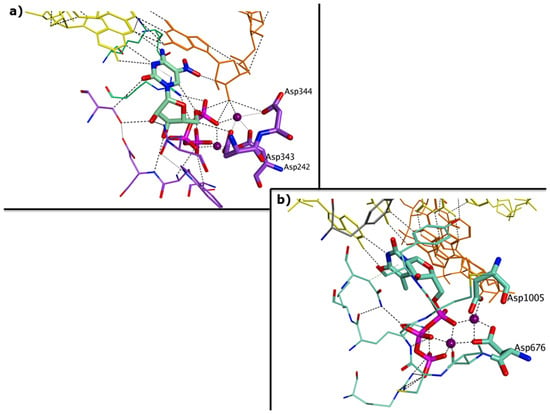
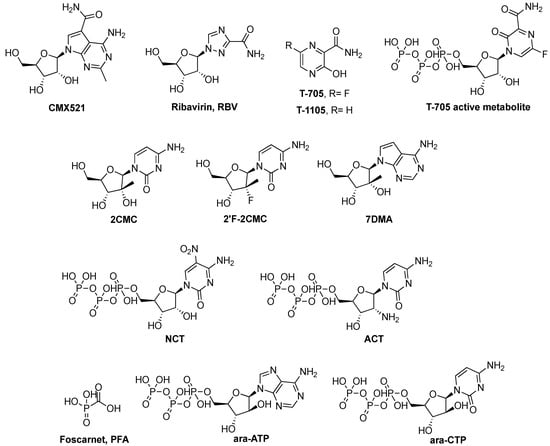
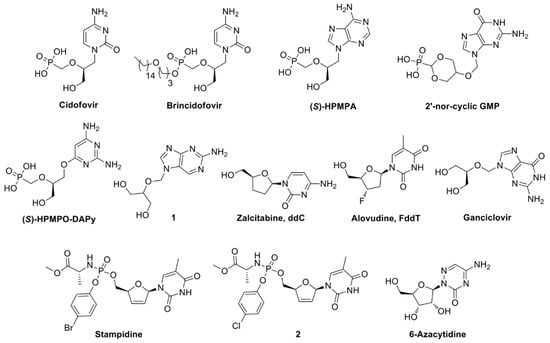
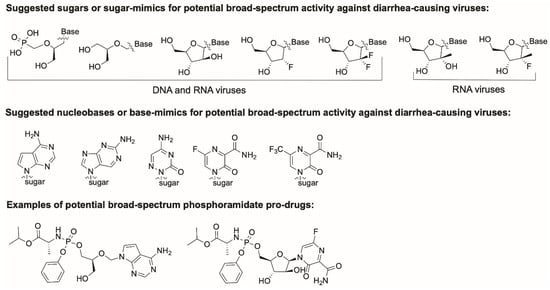
Abstract
Viral gastroenteritis is an important cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, being particularly severe for children under the age of five. The most common viral agents of gastroenteritis are noroviruses, rotaviruses, sapoviruses, astroviruses and adenoviruses, however, no specific antiviral treatment exists today against any of these pathogens. We here discuss the feasibility of developing a broad-spectrum antiviral treatment against these diarrhea-causing viruses. This review focuses on the viral polymerase as an antiviral target, as this is the most conserved viral protein among the diverse viral families to which these viruses belong to. We describe the functional and structural similarities of the different viral polymerases, the antiviral effect of reported polymerase inhibitors and highlight common features that might be exploited in an attempt of designing such pan-polymerase inhibitor.
3. Challenges and Potential Limitations to This Approach
3.1. In Vitro and In Vivo Replication Systems Available for Diarrhea-Causing Viruses
One of the main reasons for the lack of antiviral therapies against viral AGE, is the lack of suitable cell culture systems and/or animal models for the majority of these viruses. The HNoV is not easily cultivated in vitro or in vivo, therefore most antiviral research is being performed on the MNV or the HNoV GI replicon. Only recently it was reported that HNoV can replicate in the human B-cell line BJAB and in stem-cell-derived enteroids [78,79]. These models were a first breakthrough in cultivating the HNoV but further optimization would facilitate their use in drug discovery campaigns. For HSaV there is no in vitro or in vivo replication system available. The porcine SaV Cowden strain can infect gnotobiotic pigs and porcine kidney cells in the presence of bile acids [80,81]. Multiple strains of rotaviruses can be cultivated in vitro in the presence of trypsin; in vivo models to study rotavirus infections are rather limited [82,83,84]. HAdVs type 40 and 41 have limited ability to replicate in cells, when compared to other adenovirus subtypes, plus animal models are lacking [85]. Most HAstV genotypes grow in cell culture [86] but there is no small animal model available. A murine astrovirus model in immunodeficient mice has been reported [87], but the most widely used in vivo model are turkey poults, which are infected with the turkey astrovirus [88].
One advantage of developing polymerase-targeting inhibitors is the availability of enzymatic assays which allow the initial optimization of small molecule inhibitors, which can go into cellular assays at a later stage. These are available for multiple norovirus genotypes, for sapovirus and adenoviruses, but not for astroviruses [19,89]. In the case of rotavirus, polymerase activity can be assessed using purified viroplasms containing the active polymerase-capping enzyme complex VP1-VP3 [59]. Nonetheless, the limited availability of models is a limitation for drug discovery efforts, also because these would help to further understand the viral life cycles thus providing important insights for the development of antiviral therapy.
3.2 Antiviral Drug Resistance
Viral replication usually has a high error rate, causing the generation of resistant mutants able to evade a given treatment, in particular if administered long-term. This has been observed with early anti-HIV reverse transcriptase inhibitors, but later overcome with combination therapies of drugs belonging to different classes, with high genetic barrier to resistance, i.e., requiring multiple mutations for the virus to become resistant [90]. Also for HCV, multi-drug treatment regimens (most of which now include sofosbuvir) are characterized by a high barrier to resistance [91], allowing the suppression of most HCV genotypes [92].
Although all direct-acting antiviral agents can lead to resistance, this issue would have a different impact in the case of the acute infections, as gastroenteritis mostly is. Treatment of acute infections aims to reduce virus replication enough to allow the immune system to clear the virus, and is therefore of short duration [93]. The incidence and clinical impact of resistance development would therefore be different and less likely to occur than for chronic infections.
In addition, resistant viral strains are usually less virulent than the wild type [94], and acute viral infections still resolve in a self-limited manner. Even when treating prolonged/chronic norovirus infections, the treatment course(s) would be expected to be short, potentially rendering the issue of resistance less problematic in this context.
3.3. Mitochondrial Toxicity
Several drugs cause mitochondrial toxicity as a side effect, potentially leading to tissue damage and organ failure. The main risk of mitochondrial toxicity for antivirals acting on the viral polymerase or reverse-transcriptase is due to inhibition of the mitochondrial γDNA-polymerase [95] or RNA-polymerase POLRMT [96]. This side-effect on the γDNA-polymerase is relevant for the anti-HIV nucleoside reverse-transcriptase inhibitors zalzitabine (ddC), didanosine (ddI), stavudine (d4T), zidovudine (AZT), lamivudine (3TC), abacavir (ABC) and tenofovir (TFD) [97,98]. Similarly, different antiviral ribonucleoside analogs show toxic effects due to their affinity for POLRMT. In particular, valopicitabine, an ester prodrug of 2CMC in phase 2 clinical trials for HCV, was not advanced further due to gastrointestinal toxicity [99], while the triphosphate active forms of 2’-C-methyl nucleosides 2CMC, 2CMA and 2CMG inhibit POLRMT by chain termination [100], indicating a potential underlying issue for the development of any 2‘-C-methylated nucleoside into a drug. However, the triphosphate form of 2CMU (uridine) does not impact POLRMT function [96], while sofosbuvir, which combines a 2’-C-methyl feature with a 2’-fluorine substitution on the sugar, does not cause any mitochondrial inhibition [101]. General evidence appears to indicate that 2’-monosusbtitutions, along with 4’-monosubstitutions, on the sugar of antiviral ribonucleosides do not provide selectivity for the viral polymerase over POLRMT, with the associated mitochondrial toxicity mainly due to the core nucleoside rather than the cleaved prodrug moieties [97]. Nonetheless, structure-activity relationships for mitochondrial toxicity remain unpredictable, and this off-target effect can potentially be avoided with tuned modifications at both the sugar and the nucleobase level of selected nucleoside analogues. Potential mitochondrial toxicity should thus be carefully evaluated for each single nucleoside analogue of interest, possibly following a recently developed screening method which combines together multiple biochemical and cellular assays to assess this undesired effect [97].
4. Concluding Remarks
Almost one hundred antivirals have been marketed since 1963, however mostly to treat one specific human viral disease [4]. Given the diversity of human viral pathogens, there is the need to focus on broad-spectrum inhibitors against viral families or even all RNA or DNA viruses. We here explored this approach for rota-, noro-, sapo-, astro-, and adenovirus. In this review, we have emphasized the viral polymerase by studying the functional and structural similarities between the selected polymerases, as in our perspective this offers a starting point for broad-spectrum therapy against diarrhea-causing viruses. The next step would be an in silico structure-based screening of nucleoside and non-nucleoside small-molecules, using a series of molecular docking simulations on the crystal structures or homology models of the five polymerase discussed. This strategy would allow the identification of chemical scaffolds with good predicted affinity for all proteins at the same time, while their subsequent assessment in enzymatic inhibition assays would provide potential broad-spectrum hits for further optimization.
Funding
M.B. is supported by the Sêr Cymru II programme that is part-funded by Cardiff University and the European Regional Development Fund through the Welsh Government. JVD is an SB doctoral fellow of the Scientific Fund for Research of Flanders (FWO). JRP and the research leading to these results has received funding from the People Programme (Marie Curie Actions) of the European Union’s Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013) under REA grant agreement n 608765.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Tate, J.E.; Burton, A.H.; Boschi-Pinto, C.; Parashar, U.D. Regional, and National Estimates of Rotavirus Mortality in Children <5 Years of Age, 2000-2013. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 62 (Suppl. 2), S96–S105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, M.M.; Widdowson, M.A.; Glass, R.I.; Akazawa, K.; Vinjé, J.; Parashar, U.D. Systematic literature review of role of noroviruses in sporadic gastroenteritis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1224–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vega, E.; Barclay, L.; Gregoricus, N.; Shirley, S.H.; Lee, D.; Vinje, J. Genotypic and epidemiologic trends of norovirus outbreaks in the United States, 2009 to 2013. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Clercq, E.; Li, G. Approved Antiviral Drugs over the Past 50 Years. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2016, 29, 695–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angarone, M.P.; Sheahan, A.; Kamboj, M. Norovirus in Transplantation. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2016, 18, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruis, C.; Brown, L.K.; Roy, S.; Atkinson, C.; Williams, R.; Burns, S.O.; Yara-Romero, E.; Jacobs, M.; Goldstein, R.; Breuer, J.; et al. Mutagenesis in Norovirus in Response to Favipiravir Treatment. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2173–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodward, J.M.; Gkrania-Klotsas, E.; Cordero-Ng, A.Y.; Aravinthan, A.; Bandoh, B.N.; Liu, H.; Davies, S.; Zhang, H.; Stevenson, P.; Curran, M.D.; et al. The role of chronic norovirus infection in the enteropathy associated with common variable immunodeficiency. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 110, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CDC. What You Should Know About Flu Antiviral Drugs. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/flu/antivirals/whatyoushould.htm (accessed on 28 January 2019).
- Ng, K.K.; Arnold, J.J.; Cameron, C.E. Structure-function relationships among RNA-dependent RNA polymerases. Curr. Topics Microbiol. Immunol. 2008, 320, 137–156. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Naismith, J.H.; Hay, R.T. Adenovirus DNA replication. Curr. Topics Microbiol. Immunol 2003, 272, 131–164. [Google Scholar]
- DeVincenzo, J.P.; McClure, M.W.; Symons, J.A.; Fathi, H.; Westland, C.; Chanda, S.; Lambkin-Williams, R.; Smith, P.; Zhang, Q.; Beigelman, L.; et al. Activity of Oral ALS-008176 in a Respiratory Syncytial Virus Challenge Study. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2048–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, I.; Lee, J.H.; Cho, K.J.; Han, K.R.; Yang, J.M.; Chung, M.S.; Kim, K.H. Crystal structures of murine norovirus-1 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase in complex with 2-thiouridine or ribavirin. Virology 2012, 426, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohayem, J.; Robel, I.; Jager, K.; Scheffler, U.; Rudolph, W. Protein-primed and de novo initiation of RNA synthesis by norovirus 3Dpol. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 7060–7069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fullerton, S.W.; Blaschke, M.; Coutard, B.; Gebhardt, J.; Gorbalenya, A.; Canard, B.; Tucker, P.A.; Rohayem, J. Structural and functional characterization of sapovirus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 1858–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamyatkin, D.F.; Parra, F.; Alonso, J.M.; Harki, D.A.; Peterson, B.R.; Grochulski, P.; Ng, K.K. Structural insights into mechanisms of catalysis and inhibition in Norwalk virus polymerase. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 7705–7712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamyatkin, D.F.; Parra, F.; Machin, A.; Grochulski, P.; Ng, K.K. Binding of 2′-amino-2′-deoxycytidine-5′-triphosphate to norovirus polymerase induces rearrangement of the active site. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 390, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamyatkin, D.; Rao, C.; Hoffarth, E.; Jurca, G.; Rho, H.; Parra, F.; Grochulski, P.; Ng, K.K. Structure of a backtracked state reveals conformational changes similar to the state following nucleotide incorporation in human norovirus polymerase. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2014, 70, 3099–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
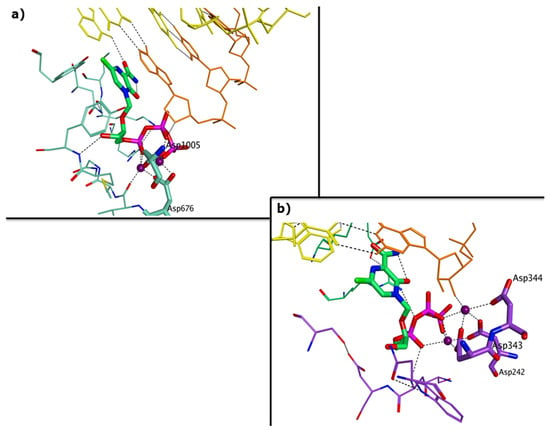
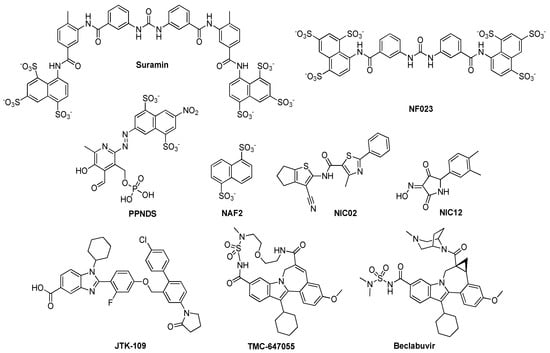
- Croci, R.; Pezzullo, M.; Tarantino, D.; Milani, M.; Tsay, S.C.; Sureshbabu, R.; Tsai, Y.J.; Mastrangelo, E.; Rohayem, J.; Bolognesi, M.; et al. Structural bases of norovirus RNA dependent RNA polymerase inhibition by novel suramin-related compounds. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastrangelo, E.; Pezzullo, M.; Tarantino, D.; Petazzi, R.; Germani, F.; Kramer, D.; Robel, I.; Rohayem, J.; Bolognesi, M.; Milani, M. Structure-based inhibition of Norovirus RNA-dependent RNA polymerases. J. Mol. Biol. 2012, 419, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croci, R.; Tarantino, D.; Milani, M.; Pezzullo, M.; Rohayem, J.; Bolognesi, M.; Mastrangelo, E. PPNDS inhibits murine Norovirus RNA-dependent RNA-polymerase mimicking two RNA stacking bases. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 1720–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruenn, J.A. A structural and primary sequence comparison of the viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 1821–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Reilly, E.K.; Kao, C.C. Analysis of RNA-dependent RNA polymerase structure and function as guided by known polymerase structures and computer predictions of secondary structure. Virology 1998, 252, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkataraman, S.; Prasad, B.; Selvarajan, R. RNA Dependent RNA Polymerases: Insights from Structure, Function and Evolution. Viruses 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarantino, D.; Pezzullo, M.; Mastrangelo, E.; Croci, R.; Rohayem, J.; Robel, I.; Bolognesi, M.; Milani, M. Naphthalene-sulfonate inhibitors of human norovirus RNA-dependent RNA-polymerase. Antiviral. Res. 2014, 102, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butcher, S.J.; Grimes, J.M.; Makeyev, E.V.; Bamford, D.H.; Stuart, D.I. A mechanism for initiating RNA-dependent RNA polymerization. Nature 2001, 410, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawton, J.A.; Estes, M.K.; Prasad, B.V. Mechanism of genome transcription in segmented dsRNA viruses. Adv. Virus Res. 2000, 55, 185–229. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; McDonald, S.M.; Tortorici, M.A.; Tao, Y.J.; Vasquez-Del Carpio, R.; Nibert, M.L.; Patton, J.T.; Harrison, S.C. Mechanism for coordinated RNA packaging and genome replication by rotavirus polymerase VP1. Structure (London, England : 1993) 2008, 16, 1678–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, T.L.; Greenberg, H.B.; Herrmann, J.E.; Smith, L.S.; Matsui, S.M. Analysis of astrovirus serotype 1 RNA, identification of the viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase motif, and expression of a viral structural protein. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Méndez, E.M.; Velàsquez, R.; Burnham, A.; Arias, C.F. Replication cycle of astroviruses. In Astrovirus Research; Schultz-Cherry, S.E., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 19–45. [Google Scholar]
- Guix, S.; Caballero, S.; Bosch, A.; Pinto, R.M. C-terminal nsP1a protein of human astrovirus colocalizes with the endoplasmic reticulum and viral RNA. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 13627–13636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toh, Y.; Harper, J.; Dryden, K.A.; Yeager, M.; Arias, C.F.; Mendez, E.; Tao, Y.J. Crystal Structure of the Human Astrovirus Capsid Protein. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 9008–9017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- York, R.L.; Yousefi, P.A.; Bogdanoff, W.; Haile, S.; Tripathi, S.; DuBois, R.M. Structural, Mechanistic, and Antigenic Characterization of the Human Astrovirus Capsid. J. Virol. 2015, 90, 2254–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Dong, L.; Mendez, E.; Tao, Y. Crystal structure of the human astrovirus capsid spike. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 12681–12686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogdanoff, W.A.; Campos, J.; Perez, E.I.; Yin, L.; Alexander, D.L.; DuBois, R.M. Structure of a Human Astrovirus Capsid-Antibody Complex and Mechanistic Insights into Virus Neutralization. J. Virol. 2017, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consortium, T.U. UniProt: The universal protein knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 2699. [Google Scholar]
- NCBI. Available online: https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov (accessed on 7 December 2018).
- Protein Data Bank. Available online: www.rcsb.org (accessed on 10 December 2018).
- Molecular Operating Environment (MOE). Available online: http://www.chemcomp.com (accessed on 10 December 2018).
- EMBL-EBI. Available online: www.ebi.ac.uk (accessed on 10 December 2018).
- Dufour, E.; Mendez, J.; Lazaro, J.M.; de Vega, M.; Blanco, L.; Salas, M. An aspartic acid residue in TPR-1, a specific region of protein-priming DNA polymerases, is required for the functional interaction with primer terminal protein. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 304, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoeben, R.C.; Uil, T.G. Adenovirus DNA replication. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a013003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salas, M. Protein-priming of DNA replication. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1991, 60, 39–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, A.J.; Kamtekar, S.; Goodman, J.L.; Lazaro, J.M.; de Vega, M.; Blanco, L.; Salas, M.; Steitz, T.A. Structures of phi29 DNA polymerase complexed with substrate: The mechanism of translocation in B-family polymerases. Embo J. 2007, 26, 3494–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.H. Viral polymerases. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2012, 726, 267–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naccache, S.N.; Peggs, K.S.; Mattes, F.M.; Phadke, R.; Garson, J.A.; Grant, P.; Samayoa, E.; Federman, S.; Miller, S.; Lunn, M.P.; et al. Diagnosis of neuroinvasive astrovirus infection in an immunocompromised adult with encephalitis by unbiased next-generation sequencing. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 60, 919–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fremond, M.L.; Perot, P.; Muth, E.; Cros, G.; Dumarest, M.; Mahlaoui, N.; Seilhean, D.; Desguerre, I.; Hebert, C.; Corre-Catelin, N.; et al. Next-Generation Sequencing for Diagnosis and Tailored Therapy: A Case Report of Astrovirus-Associated Progressive Encephalitis. J. Pediatric Infect. Dis. Soc. 2015, 4, e53–e57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohayem, J.; Bergmann, M.; Gebhardt, J.; Gould, E.; Tucker, P.; Mattevi, A.; Unge, T.; Hilgenfeld, R.; Neyts, J. Antiviral strategies to control calicivirus infections. Antiviral Res. 2010, 87, 162–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofia, M.J.; Chang, W.; Furman, P.A.; Mosley, R.T.; Ross, B.S. Nucleoside, nucleotide, and non-nucleoside inhibitors of hepatitis C virus NS5B RNA-dependent RNA-polymerase. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 2481–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanier, R.S.D.; Kolawole, A.; Hosmillo, M.; Nayak, K.; Bae, A.; Gurley, S.; Tippin, T.; Colton, H.; Dunn, J.; Mullin, M.; et al. CMX521: A Nucleoside with Pan-Genotypic Activity against Norovirus. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Antiviral Research, Porto, Portugal, 11–15 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, K.O.; George, D.W. Interferons and ribavirin effectively inhibit Norwalk virus replication in replicon-bearing cells. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 12111–12118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuta, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Shiraki, K.; Sakamoto, K.; Smee, D.F.; Barnard, D.L.; Gowen, B.B.; Julander, J.G.; Morrey, J.D. T-705 (favipiravir) and related compounds: Novel broad-spectrum inhibitors of RNA viral infections. Antiviral Res. 2009, 82, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha-Pereira, J.; Jochmans, D.; Dallmeier, K.; Leyssen, P.; Nascimento, M.S.; Neyts, J. Favipiravir (T-705) inhibits in vitro norovirus replication. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 424, 777–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.; Tucker, K.; Lin, X.; Kao, C.C.; Shaw, K.; Tan, H.; Symons, J.; Behera, I.; Rajwanshi, V.K.; Dyatkina, N.; et al. Biochemical Evaluation of the Inhibition Properties of Favipiravir and 2′-C-Methyl-Cytidine Triphosphates against Human and Mouse Norovirus RNA Polymerases. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 7504–7516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias, A.; Thorne, L.; Goodfellow, I. Favipiravir elicits antiviral mutagenesis during virus replication in vivo. Elife 2014, 3, e03679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha-Pereira, J.; Van Dycke, J.; Neyts, J. Treatment with a Nucleoside Polymerase Inhibitor Reduces Shedding of Murine Norovirus in Stool to Undetectable Levels without Emergence of Drug-Resistant Variants. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 60, 1907–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha-Pereira, J.; Jochmans, D.; Dallmeier, K.; Leyssen, P.; Cunha, R.; Costa, I.; Nascimento, M.S.; Neyts, J. Inhibition of norovirus replication by the nucleoside analogue 2′-C-methylcytidine. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 427, 796–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolawole, A.O.; Rocha-Pereira, J.; Elftman, M.D.; Neyts, J.; Wobus, C.E. Inhibition of human norovirus by a viral polymerase inhibitor in the B cell culture system and in the mouse model. Antiviral Res. 2016, 132, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costantini, V.P.; Whitaker, T.; Barclay, L.; Lee, D.; McBrayer, T.R.; Schinazi, R.F.; Vinjé, J. Antiviral activity of nucleoside analogues against norovirus. Antivir. Ther. 2012, 17, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dycke, J.; Arnoldi, F.; Papa, G.; Vandepoele, J.; Burrone, O.R.; Mastrangelo, E.; Tarantino, D.; Heylen, E.; Neyts, J.; Rocha-Pereira, J. A Single Nucleoside Viral Polymerase Inhibitor Against Norovirus, Rotavirus, and Sapovirus-Induced Diarrhea. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 218, 1753–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harki, D.A.; Graci, J.D.; Edathil, J.P.; Castro, C.; Cameron, C.E.; Peterson, B.R. Synthesis of a universal 5-nitroindole ribonucleotide and incorporation into RNA by a viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Chembiochem 2007, 8, 1359–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smee, D.F.; Sidwell, R.W.; Clark, S.M.; Barnett, B.B.; Spendlove, R.S. Inhibition of rotaviruses by selected antiviral substances: Mechanisms of viral inhibition and in vivo activity. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1982, 21, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rios, M.; Munoz, M.; Spencer, E. Antiviral activity of phosphonoformate on rotavirus transcription and replication. Antiviral Res. 1995, 27, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizarro, J.M.; Pizarro, J.L.; Fernandez, J.; Sandino, A.M.; Spencer, E. Effect of nucleotide analogues on rotavirus transcription and replication. Virology 1991, 184, 768–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, A.; MacMahon, E. Adenovirus infections. Medicine 2017, 45, 777–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Clercq, E. Clinical potential of the acyclic nucleoside phosphonates cidofovir, adefovir, and tenofovir in treatment of DNA virus and retrovirus infections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 16, 569–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimley, M.S.; Chemaly, R.F.; Englund, J.A.; Kurtzberg, J.; Chittick, G.; Brundage, T.M.; Bae, A.; Morrison, M.E.; Prasad, V.K. Brincidofovir for Asymptomatic Adenovirus Viremia in Pediatric and Adult Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplant Recipients: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Phase II Trial. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2017, 23, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, M.; Mori, S.; Shigeta, S.; De Clercq, E. Selective inhibitory effect of (S)-9-(3-hydroxy-2-phosphonylmethoxypropyl)adenine and 2'-nor-cyclic GMP on adenovirus replication in vitro. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1987, 31, 337–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naesens, L.; Lenaerts, L.; Andrei, G.; Snoeck, R.; Van Beers, D.; Holy, A.; Balzarini, J.; De Clercq, E. Antiadenovirus activities of several classes of nucleoside and nucleotide analogues. Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother. 2005, 49, 1010–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uckun, F.M.; Pendergrass, S.; Qazi, S.; Samuel, P.; Venkatachalam, T.K. Phenyl phosphoramidate derivatives of stavudine as anti-HIV agents with potent and selective in-vitro antiviral activity against adenovirus. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 39, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexeeva, I.; Dyachenko, N.; Nosach, L.; Zhovnovataya, V.; Rybalko, S.; Lozitskaya, R.; Fedchuk, A.; Lozitsky, V.; Gridina, T.; Shalamay, A.; et al. 6-azacytidine--compound with wide spectrum of antiviral activity. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2001, 20, 1147–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yates, M.K.; Raje, M.R.; Chatterjee, P.; Spiropoulou, C.F.; Bavari, S.; Flint, M.; Soloveva, V.; Seley-Radtke, K.L. Flex-nucleoside analogues-Novel therapeutics against filoviruses. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 2800–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehellou, Y.; Rattan, H.S.; Balzarini, J. The ProTide Prodrug Technology: From the Concept to the Clinic. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 2211–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofia, M.J.; Bao, D.; Chang, W.; Du, J.; Nagarathnam, D.; Rachakonda, S.; Reddy, P.G.; Ross, B.S.; Wang, P.; Zhang, H.R.; et al. Discovery of a beta-d-2'-deoxy-2'-alpha-fluoro-2'-beta-C-methyluridine nucleotide prodrug (PSI-7977) for the treatment of hepatitis C virus. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 7202–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korb, O.S.T.; Exner, T.E. PLANTS: Application of ant colony optimization to structure-based drug-design. In: Ant colony optimization and swarm intelligence. In Proceedings of the 5th International Workshop, ANTD, Brussels, Belgium, 4–7 September 2006; pp. 245–258. [Google Scholar]
- Eltahla, A.A.; Lim, K.L.; Eden, J.S.; Kelly, A.G.; Mackenzie, J.M.; White, P.A. Nonnucleoside inhibitors of norovirus RNA polymerase: Scaffolds for rational drug design. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3115–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campagnola, G.; Gong, P.; Peersen, O.B. High-throughput screening identification of poliovirus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase inhibitors. Antiviral Res. 2011, 91, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netzler, N.E.; Enosi Tuipulotu, D.; Eltahla, A.A.; Lun, J.H.; Ferla, S.; Brancale, A.; Urakova, N.; Frese, M.; Strive, T.; Mackenzie, J.M.; et al. Broad-spectrum non-nucleoside inhibitors for caliciviruses. Antiviral Res. 2017, 146, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.K.; Watanabe, M.; Zhu, S.; Graves, C.L.; Keyes, L.R.; Grau, K.R.; Gonzalez-Hernandez, M.B.; Iovine, N.M.; Wobus, C.E.; Vinje, J.; et al. Enteric bacteria promote human and mouse norovirus infection of B cells. Science 2014, 346, 755–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettayebi, K.; Crawford, S.E.; Murakami, K.; Broughman, J.R.; Karandikar, U.; Tenge, V.R.; Neill, F.H.; Blutt, S.E.; Zeng, X.L.; Qu, L.; et al. Replication of human noroviruses in stem cell-derived human enteroids. Science 2016, 353, 1387–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flynn, W.T.; Saif, L.J.; Moorhead, P.D. Pathogenesis of porcine enteric calicivirus-like virus in four-day-old gnotobiotic pigs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1988, 49, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chang, K.O.; Sosnovtsev, S.V.; Belliot, G.; Kim, Y.; Saif, L.J.; Green, K.Y. Bile acids are essential for porcine enteric calicivirus replication in association with down-regulation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 8733–8738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, J.L.; Cukor, G.; Blacklow, N.R.; Dambrauskas, R.; Trier, J.S. Susceptibility of mice to rotavirus infection: Effects of age and administration of corticosteroids. Infect. Immune. 1981, 33, 565–574. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, L.A.; Rosen, B.I.; Yuan, L.; Saif, L.J. Pathogenesis of an attenuated and a virulent strain of group A human rotavirus in neonatal gnotobiotic pigs. J. Gen. Virol. 1996, 77 Pt 7, 1431–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.T.; Wei, J.; Guo, H.X.; Han, J.B.; Ye, N.; He, H.Y.; Yu, T.T.; Wu, Y.Z. Development of a human rotavirus induced diarrhea model in Chinese mini-pigs. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 7135–7145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiemessen, C.T.; Kidd, A.H. Adenovirus type 40 and 41 growth in vitro: Host range diversity reflected by differences in patterns of DNA replication. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 1239–1244. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brinker, J.P.; Blacklow, N.R.; Herrmann, J.E. Human astrovirus isolation and propagation in multiple cell lines. Arch. Virol. 2000, 145, 1847–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marvin, S.A.; Huerta, C.T.; Sharp, B.; Freiden, P.; Cline, T.D.; Schultz-Cherry, S. Type I Interferon Response Limits Astrovirus Replication and Protects against Increased Barrier Permeability In Vitro and In Vivo. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 1988–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koci, M.D.; Moser, L.A.; Kelley, L.A.; Larsen, D.; Brown, C.C.; Schultz-Cherry, S. Astrovirus induces diarrhea in the absence of inflammation and cell death. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 11798–11808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferla, S.; Netzler, N.E.; Ferla, S.; Veronese, S.; Tuipulotu, D.E.; Guccione, S.; Brancale, A.; White, P.A.; Bassetto, M. In silico screening for human norovirus antivirals reveals a novel non-nucleoside inhibitor of the viral polymerase. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Peterson, S.; Sedaghat, A.R.; McMahon, M.A.; Callender, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Pitt, E.; Anderson, K.S.; Acosta, E.P.; et al. Dose-response curve slope sets class-specific limits on inhibitory potential of anti-HIV drugs. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 762–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentile, I.; Borgia, F.; Zappulo, E.; Buonomo, A.R.; Spera, A.M.; Castaldo, G.; Borgia, G. Efficacy and Safety of Sofosbuvir in the Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis C: The Dawn of a New Era. Rev. Recent Clin. Trials 2014, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gritsenko, D.; Hughes, G. Ledipasvir/Sofosbuvir (harvoni): Improving options for hepatitis C virus infection. PT 2015, 40, 256–276. [Google Scholar]
- Mason, S.; Devincenzo, J.P.; Toovey, S.; Wu, J.Z.; Whitley, R.J. Comparison of antiviral resistance across acute and chronic viral infections. Antiviral Res. 2018, 158, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omura, N.; Fujii, H.; Yoshikawa, T.; Yamada, S.; Harada, S.; Inagaki, T.; Shibamura, M.; Takeyama, H.; Saijo, M. Association between sensitivity of viral thymidine kinase-associated acyclovir-resistant herpes simplex virus type 1 and virulence. Virol. J. 2017, 14, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, W.; Simpson, J.F.; Meyer, R.R. Cardiac mitochondrial DNA polymerase-gamma is inhibited competitively and noncompetitively by phosphorylated zidovudine. Circ. Res. 1994, 74, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.; Kinkade, A.; Behera, I.; Chaudhuri, S.; Tucker, K.; Dyatkina, N.; Rajwanshi, V.K.; Wang, G.; Jekle, A.; Smith, D.B.; et al. Structure-activity relationship analysis of mitochondrial toxicity caused by antiviral ribonucleoside analogs. Antiviral Res. 2017, 143, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakuda, T.N. Pharmacology of nucleoside and nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitor-induced mitochondrial toxicity. Clin. Ther. 2000, 22, 685–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherry, C.L.; Wesselingh, S.L. Nucleoside analogues and HIV: The combined cost to mitochondria. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 51, 1091–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, N.A. Progress towards improving antiviral therapy for hepatitis C with hepatitis C virus polymerase inhibitors. Part I: Nucleoside analogues. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2009, 18, 709–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, J.J.; Sharma, S.D.; Feng, J.Y.; Ray, A.S.; Smidansky, E.D.; Kireeva, M.L.; Cho, A.; Perry, J.; Vela, J.E.; Park, Y.; et al. Sensitivity of mitochondrial transcription and resistance of RNA polymerase II dependent nuclear transcription to antiviral ribonucleosides. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1003030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.Y.; Xu, Y.; Barauskas, O.; Perry, J.K.; Ahmadyar, S.; Stepan, G.; Yu, H.; Babusis, D.; Park, Y.; McCutcheon, K.; et al. Role of Mitochondrial RNA Polymerase in the Toxicity of Nucleotide Inhibitors of Hepatitis C Virus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 806–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).