Shared Common Ancestry of Rodent Alphacoronaviruses Sampled Globally
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Nucleic Acid Preparation
2.3. High-Throughput Sequencing
2.4. Genome Retrieval with PCR
2.5. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.6. Analysis of the Virus-Host Co-Divergence
3. Results
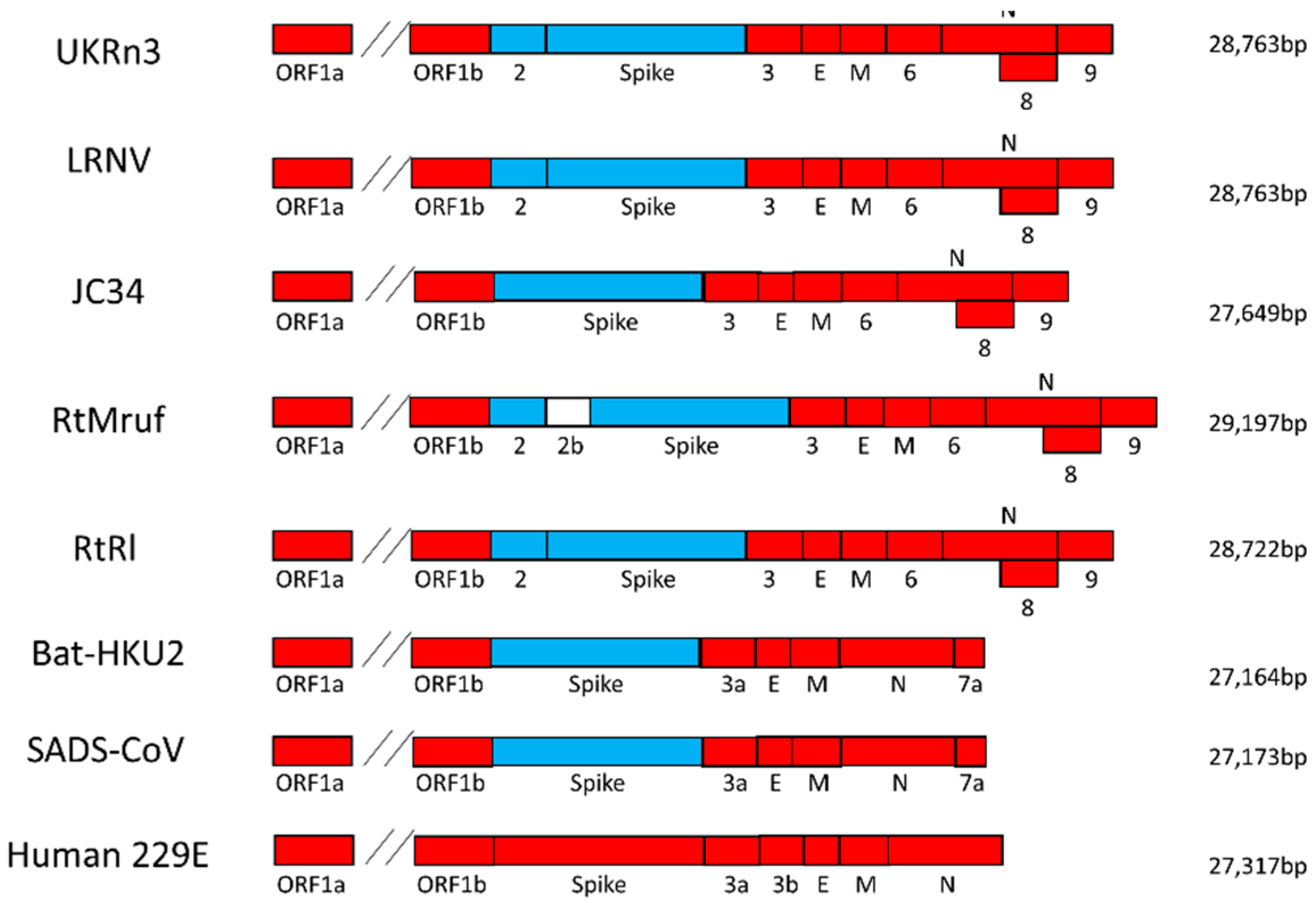
3.1. Genome Retrieval of Rodent and Rabbit Alphacoronaviruses
3.2. Virus Genome Characterization
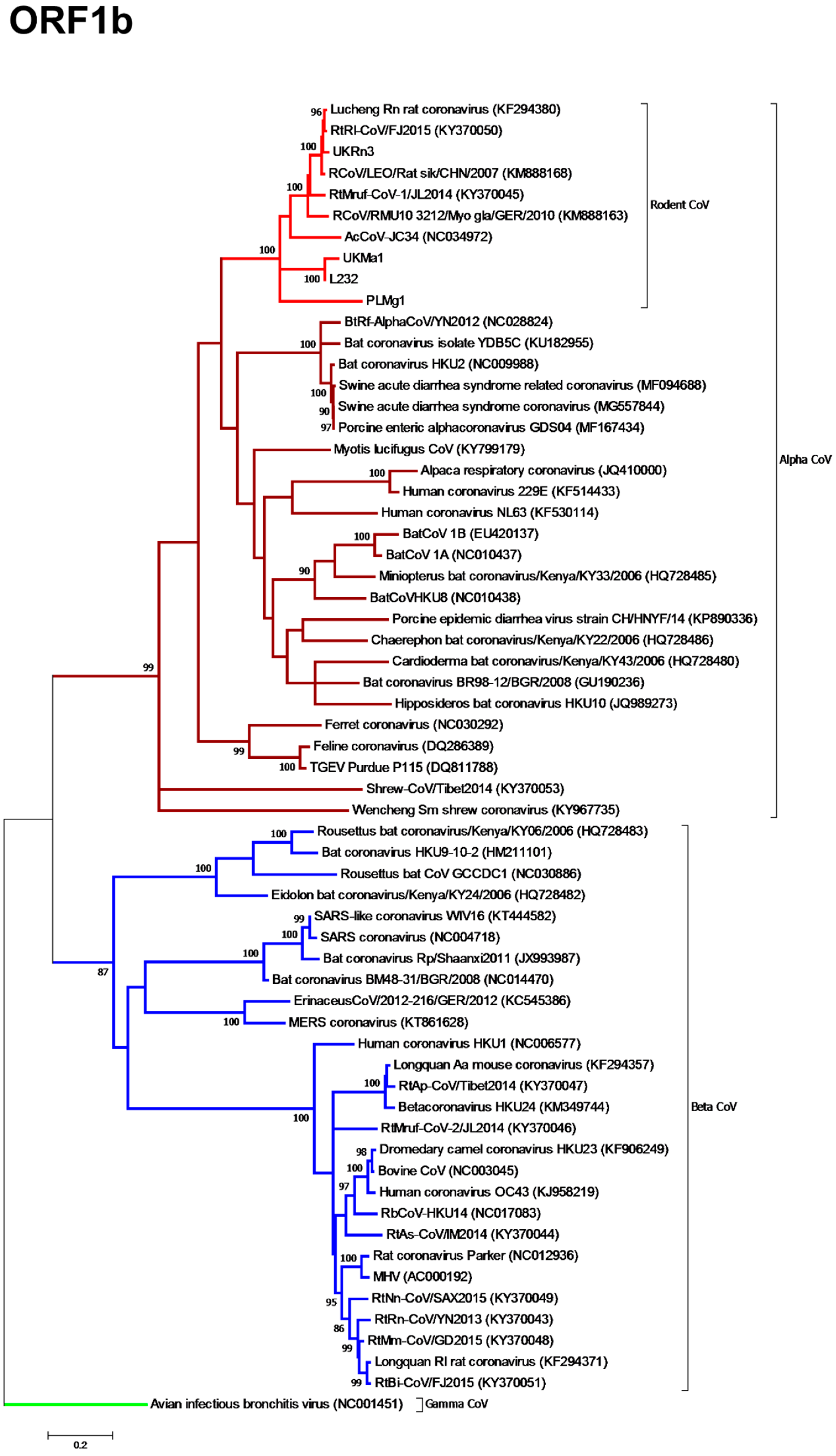
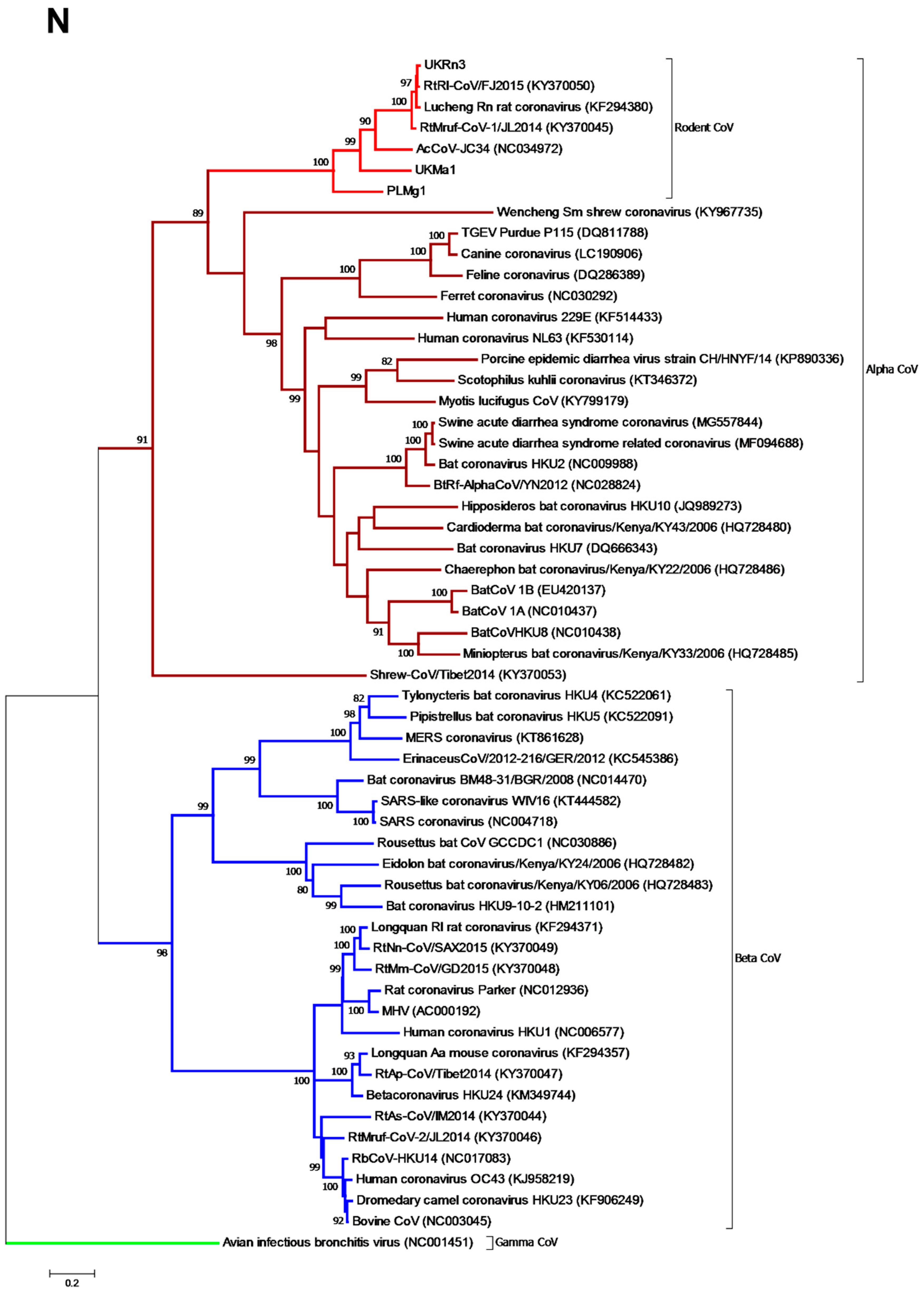
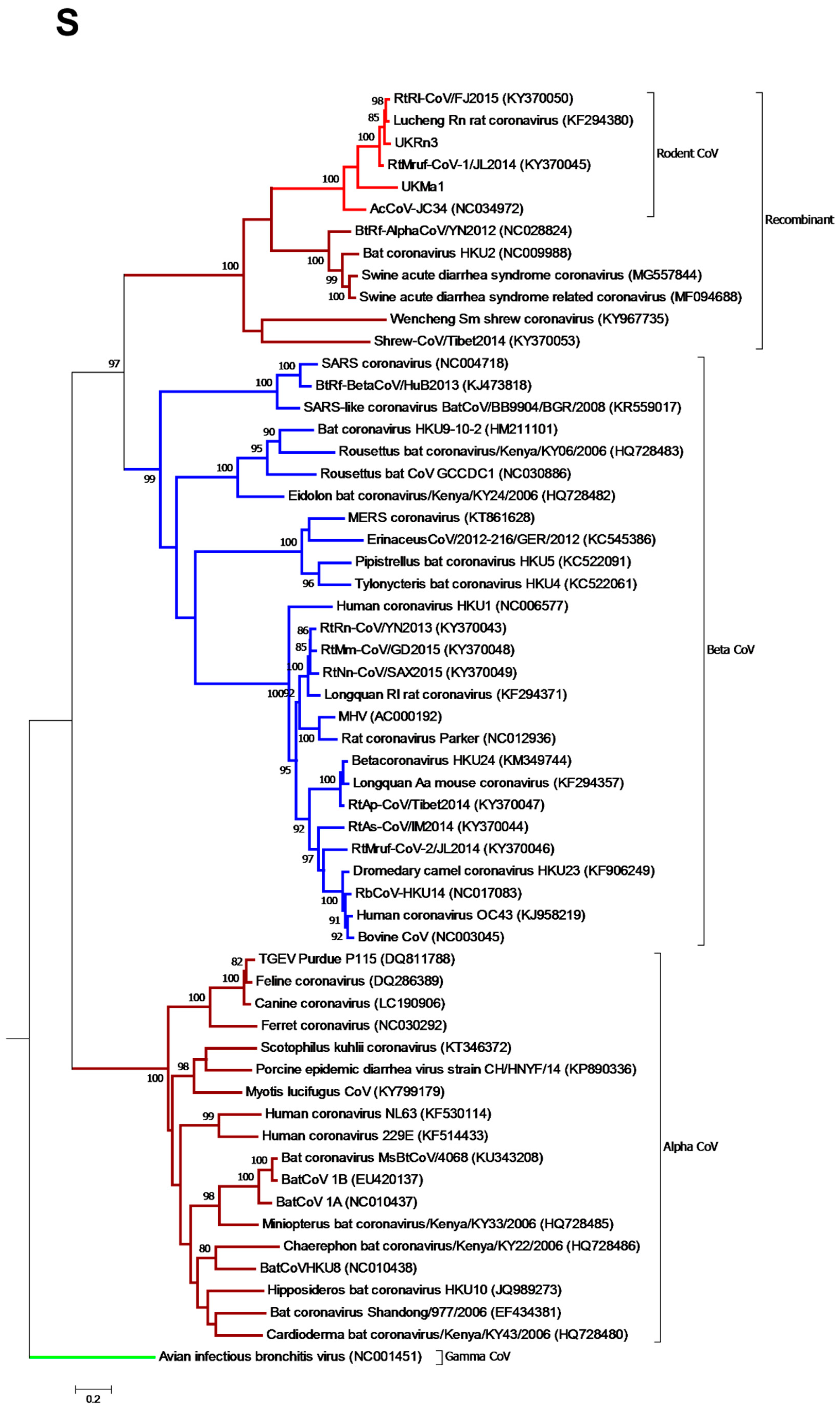
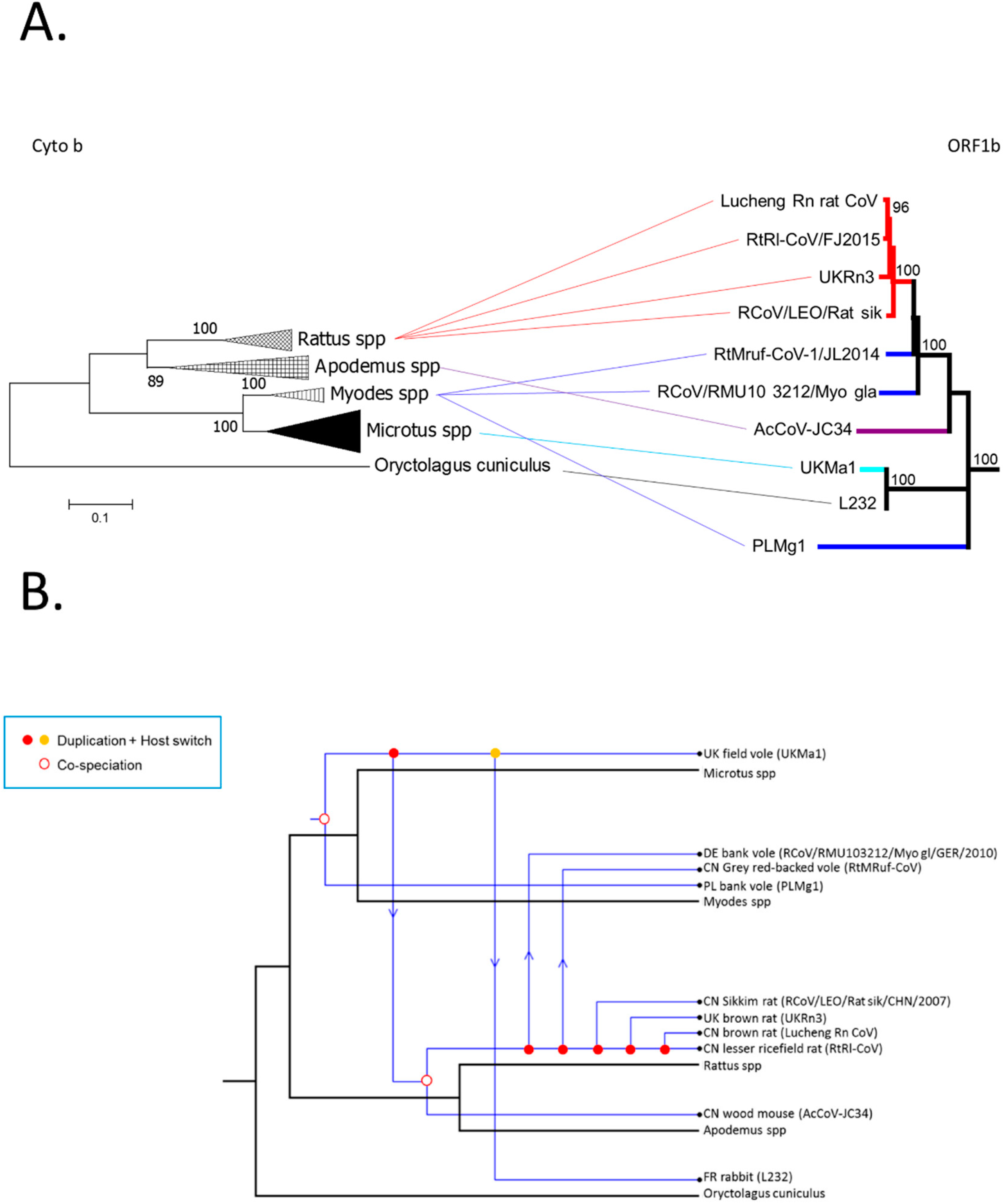
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of Rodent Alphacoronaviruses Suggests a Shared Common Ancestry
3.4. Comparison of Virus and Host Phylogenies
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hudson, C.; Beaudette, F.R. Infection of the cloaca with the virus of infectious bronchitis. Science 1932, 76, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamre, D.; Procknow, J.J. A new virus isolated from the human respiratory tract. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1966, 121, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, S.; Navas-Martin, S. Coronavirus pathogenesis and the emerging pathogen severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2005, 69, 635–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luis, A.D.; Hayman, D.T.; O’Shea, T.J.; Cryan, P.M.; Gilbert, A.T.; Pulliam, J.R.; Mills, J.N.; Timonin, M.E.; Willis, C.K.; Cunningham, A.A.; et al. A comparison of bats and rodents as reservoirs of zoonotic viruses: Are bats special? Proc. Biol. Sci. 2013, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huchon, D.; Madsen, O.; Sibbald, M.J.; Ament, K.; Stanhope, M.J.; Catzeflis, F.; de Jong, W.W.; Douzery, E.J. Rodent phylogeny and a timescale for the evolution of Glires: Evidence from an extensive taxon sampling using three nuclear genes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2002, 19, 1053–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.G.; Kapusinszky, B.; Wang, C.; Rose, R.K.; Lipton, H.L.; Delwart, E.L. The fecal viral flora of wild rodents. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheever, F.S.; Daniels, J.B.; Pappenheimer, A.M.; Bailey, O.T. A murine virus (JHM) causing disseminated encephalomyelitis with extensive destruction of myelin. J. Exp. Med. 1949, 90, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, J.C.; Cross, S.S.; Rowe, W.P. Rat coronavirus (RCV): A prevalent, naturally occurring pneumotropic virus of rats. Arch. Gesamte Virusforsch. 1970, 31, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoleridis, T.; Onianwa, O.; Horncastle, E.; Dayman, E.; Zhu, M.; Danjittrong, T.; Wachtl, M.; Behnke, J.M.; Chapman, S.; Strong, V.; et al. Discovery of Novel Alphacoronaviruses in European Rodents and Shrews. Viruses 2016, 8, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, X.Y.; Yang, W.H.; Zhou, J.H.; Li, B.; Zhang, W.; Shi, Z.L.; Zhang, Y.Z. Detection of alpha- and betacoronaviruses in rodents from Yunnan, China. Virol. J. 2017, 14, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Zhu, C.; Wang, Y.; Ai, L.; Yang, L.; Ye, F.; Ding, C.; Chen, J.; He, B.; Zhu, J.; et al. Virome analysis for identification of novel mammalian viruses in bats from Southeast China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monchatre-Leroy, E.; Boué, F.; Boucher, J.-M.; Renault, C.; Moutou, F.; Ar Gouilh, M.; Umhang, G. Identification of Alpha and Beta Coronavirus in Wildlife Species in France: Bats, Rodents, Rabbits, and Hedgehogs. Viruses 2017, 9, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Lin, X.D.; Tian, J.H.; Chen, L.J.; Chen, X.; Li, C.X.; Qin, X.C.; Li, J.; Cao, J.P.; Eden, J.S.; et al. Redefining the invertebrate RNA virosphere. Nature 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conow, C.; Fielder, D.; Ovadia, Y.; Libeskind-Hadas, R. Jane: A new tool for the cophylogeny reconstruction problem. Algorithms for Mol. Biol. 2010, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lin, X.D.; Guo, W.P.; Zhou, R.H.; Wang, M.R.; Wang, C.Q.; Ge, S.; Mei, S.H.; Li, M.H.; Shi, M.; et al. Discovery, diversity and evolution of novel coronaviruses sampled from rodents in China. Virology 2015, 474, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, S.K.; Woo, P.C.; Li, K.S.; Tsang, A.K.; Fan, R.Y.; Luk, H.K.; Cai, J.P.; Chan, K.H.; Zheng, B.J.; Wang, M.; et al. Discovery of a novel coronavirus, China Rattus coronavirus HKU24, from Norway rats supports the murine origin of Betacoronavirus 1 and has implications for the ancestor of Betacoronavirus lineage A. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 3076–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geoghegan, J.L.; Duchene, S.; Holmes, E.C. Comparative analysis estimates the relative frequencies of co-divergence and cross-species transmission within viral families. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, S.K.; Woo, P.C.; Li, K.S.; Huang, Y.; Wang, M.; Lam, C.S.; Xu, H.; Guo, R.; Chan, K.H.; Zheng, B.J.; et al. Complete genome sequence of bat coronavirus HKU2 from Chinese horseshoe bats revealed a much smaller spike gene with a different evolutionary lineage from the rest of the genome. Virology 2007, 367, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Fan, H.; Lan, T.; Yang, X.-L.; Shi, W.-F.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.-W.; Xie, Q.-M.; Mani, S.; et al. Fatal swine acute diarrhoea syndrome caused by an HKU2-related coronavirus of bat origin. Nature 2018, 556, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lin, X.D.; Liao, Y.; Guan, X.Q.; Guo, W.P.; Xing, J.G.; Holmes, E.C.; Zhang, Y.Z. Discovery of a highly divergent coronavirus in the Asian house shrew from China illuminates the origin of the alphacoronaviruses. J. Virol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Yang, L.; Ren, X.; He, G.; Zhang, J.; Yang, J.; Qian, Z.; Dong, J.; Sun, L.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Deciphering the bat virome catalog to better understand the ecological diversity of bat viruses and the bat origin of emerging infectious diseases. ISME J. 2016, 10, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyrc, K.; Jebbink, M.F.; Berkhout, B.; van der Hoek, L. Genome structure and transcriptional regulation of human coronavirus NL63. Virol. J. 2004, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dye, C.; Siddell, S.G. Genomic RNA sequence of Feline coronavirus strain FIPV WSU-79/1146. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 2249–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiscox, J.A.; Mawditt, K.L.; Cavanagh, D.; Britton, P. Investigation of the control of coronavirus subgenomic mRNA transcription by using T7-generated negative-sense RNA transcripts. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 6219–6227. [Google Scholar]
- De Wit, E.; van Doremalen, N.; Falzarano, D.; Munster, V.J. SARS and MERS: Recent insights into emerging coronaviruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol 2016, 14, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Ming, C.; Li, Y.; Su, L.-Y.; Su, Y.-H.; Otecko, N.O.; Dalecky, A.; Donnellan, S.; Aplin, K.; Liu, X.-H.; et al. Out of Southern East Asia of the Brown Rat Revealed by Large-Scale Genome Sequencing. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Name | Species | Country | Organ | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UKRn3 | Rattus norvegicus | United Kingdom | Liver | [9] |
| UKMa1 | Microtus agrestis | United Kingdom | Gut | [9] |
| PLMg1 | Myodes glareolus | Poland | Liver | [9] |
| L232 | Oryctolagus cuniculus | France | Intestinal fluid | [12] |
| Gene | Number of Sequences | Length (nt) | Corresponding Positions on Lucheng CoV Genome |
|---|---|---|---|
| ORF1b | 46 | 576 | 14,140–14,715 |
| S | 31 | 1398 | 23,242–24,639 |
| N | 32 | 1170 | 26,977–28,146 |
| Virus | Genes | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ORF1ab | ORF2 | S | ORF3 | E | M | ORF6 | N | ORF8 | ORF9 | |
| UKRn3 | AACUAA | AACUUUAA | AACUAA | UACUAA | AACUAA | AACUAA | AACUAA | AACUAA | AACUAA | AACUAA |
| LRNV | AACUAA | AACUAA | AACUAA | UACUAA | AACUAA | AACUAA | AACUAA | AACUAA | AACUAA | AACUAA |
| UKMa1 | N/A | AACUUUAA | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | AACUAA | AACUAA | CACUAA | AACUAA |
| RtRl | AACUAA | AACUUUAA | AACUAA | AACUAA | AACUAA | AACUAA | AACUAA | AACUAA | AACUAA | AACUAA |
| RtMruf | AACUAA | AACUUUAA | AACUAA | UACUAA | AACUAA | AACUAA | AACUAA | AACUAA | GACUAA | AACUAA |
| JC34 | AACUAA | N/A | AACUUA | UACUAAA | AACUAA | AACUAA | AACUAA | AACUAA | CACUAA | AACUAA |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsoleridis, T.; Chappell, J.G.; Onianwa, O.; Marston, D.A.; Fooks, A.R.; Monchatre-Leroy, E.; Umhang, G.; Müller, M.A.; Drexler, J.F.; Drosten, C.; et al. Shared Common Ancestry of Rodent Alphacoronaviruses Sampled Globally. Viruses 2019, 11, 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11020125
Tsoleridis T, Chappell JG, Onianwa O, Marston DA, Fooks AR, Monchatre-Leroy E, Umhang G, Müller MA, Drexler JF, Drosten C, et al. Shared Common Ancestry of Rodent Alphacoronaviruses Sampled Globally. Viruses. 2019; 11(2):125. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11020125
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsoleridis, Theocharis, Joseph G. Chappell, Okechukwu Onianwa, Denise A. Marston, Anthony R. Fooks, Elodie Monchatre-Leroy, Gérald Umhang, Marcel A. Müller, Jan F. Drexler, Christian Drosten, and et al. 2019. "Shared Common Ancestry of Rodent Alphacoronaviruses Sampled Globally" Viruses 11, no. 2: 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11020125
APA StyleTsoleridis, T., Chappell, J. G., Onianwa, O., Marston, D. A., Fooks, A. R., Monchatre-Leroy, E., Umhang, G., Müller, M. A., Drexler, J. F., Drosten, C., Tarlinton, R. E., McClure, C. P., Holmes, E. C., & Ball, J. K. (2019). Shared Common Ancestry of Rodent Alphacoronaviruses Sampled Globally. Viruses, 11(2), 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11020125





