Abstract
The cosmopolitan fungus Rhizoctonia solani has a wide host range and is the causal agent of numerous crop diseases, leading to significant economic losses. To date, no cultivars showing complete resistance to R. solani have been identified and it is imperative to develop a strategy to control the spread of the disease. Fungal viruses, or mycoviruses, are widespread in all major groups of fungi and next-generation sequencing (NGS) is currently the most efficient approach for their identification. An increasing number of novel mycoviruses are being reported, including double-stranded (ds) RNA, circular single-stranded (ss) DNA, negative sense (−)ssRNA, and positive sense (+)ssRNA viruses. The majority of mycovirus infections are cryptic with no obvious symptoms on the hosts; however, some mycoviruses may alter fungal host pathogenicity resulting in hypervirulence or hypovirulence and are therefore potential biological control agents that could be used to combat fungal diseases. R. solani harbors a range of dsRNA and ssRNA viruses, either belonging to established families, such as Endornaviridae, Tymoviridae, Partitiviridae, and Narnaviridae, or unclassified, and some of them have been associated with hypervirulence or hypovirulence. Here we discuss in depth the molecular features of known viruses infecting R. solani and their potential as biological control agents.
1. Introduction
The genus Rhizoctonia was initially described by French mycologist Augustin Pyramus de Candolle in 1815 [1] and belongs to the order Cantharellales, phylum Basidiomycota. Rhizoctonia species are assigned into three main groups based on the number of nuclei in the fungal cells: Uninucleate Rhizoctonia, binucleate Rhizoctonia (teleomorphs: Ceratobasidium spp. and Tulasnella spp.) and multinucleate Rhizoctonia (teleomorphs: Thanatephorus spp. and Waitea spp.). Rhizoctonia solani Kühn (teleomorph: Thanatephorus cucumeris) is the most widely known species within the group of multinucleate Rhizoctonia and is classified into fourteen anastomosis groups (AGs) based on hyphal fusion experiments (Table 1) [2,3,4,5,6]. R. solani is a soil-borne plant pathogen with widespread geographical distribution and a wide host range, known to cause various important crop diseases, leading to significant agricultural and economic losses. For instance, R. solani is the causative agent of rice sheath blight leading up to 50% yield losses in Asia [4]. The symptoms caused by R. solani infection vary depending on the host plant and include damping-off of seedlings, stem canker, and root or stem rots [7].

Table 1.
R. solani anastomosis groups (AGs) and subgroups with their reported hosts or habitats.
The establishment of R. solani infection in a suitable host occurs following the attachment of fungal mycelia or sclerotia on the host root. A sclerotium is an aggregate of a dense structure of clustered mycelium with the ability to overwinter several years in host plant tissue, plant debris or soil and germinate in the presence of root exudates emitted by the plant when climatic condition are favorable [5]. The fungus then proliferates on the root and produces specialised T-shaped structures named “infection pads”. These infection pads produce enzymes capable of digesting the plant cell wall so that the fungus penetrates and colonizes the intercellular and intracellular spaces of the root tissue. As it develops, the fungus diverts the cellular reserves of the plant for its own growth. Gradually, the mycelium invades the cells and kills them, while producing survival structures, and the plant begins to wither when its conducting vessels are attacked [5,8].
Attempts to control R. solani by agronomic approaches, such as breeding strategies, crop rotation or chemical fungicides, proved ineffective due to the wide host range, soil-borne nature and the saprotrophitic nature of the fungus. Even in cases of extensive use of chemical fungicides due to substantial crop losses, R. solani proved persistent. Notably, R. solani does not produce conidia (asexual spores), therefore its ability to spread long distances is limited, despite being considered ubiquitous in soil [9,10]. Therefore, it is imperative to find new alternatives, preferably with minimal impact on the environment, to protect crops from R. solani while reducing the use of chemical fungicides [11]. Moreover, it is known that R. solani hosts a range of viruses, some of them still unclassified [7,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22].
A virus is an infectious agent requiring a host, such as a cell, whose metabolism and constituents it uses to replicate. A mycovirus is a virus that specifically infects fungi. The first mycovirus was found in the edible mushroom Agaricus bisporus (phylum: Basidiomycota) in 1962 [23]. Since then mycoviruses have been found in all major fungal taxa, namely Basidiomycota, Ascomycota, Chytridiomycota, Deuteromycota, and Zygomycota [13]. However, it is considered that only a fraction of the extant mycoviruses have been described so far and next-generation sequencing (NGS) techniques are currently being used to identify novel unknown mycoviruses [9]. The majority of mycoviruses reported have dsRNA genomes, although ssRNA and DNA viruses have been reported [13]. According to the International Committee for the Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV; 2018b), mycoviruses are currently classified in nineteen officially recognized families and a floating genus not classified in a family, accommodating linear dsRNA viruses (Amalgaviridae, Botybirnavirus, Chrysoviridae, Megabirnaviridae, Partitiviridae, Quadriviridae, Reoviridae, Totiviridae), linear positive-sense (+)ssRNA families (Alphaflexiviridae, Barnaviridae, Botourmiaviridae, Deltaflexiviridae, Endornaviridae, Gammaflexiviridae, Hypoviridae, Narnaviridae), reverse transcribing linear ssRNA families (Metaviridae, Pseudoviridae), linear negative-sense (−)ssRNA families (Mymonaviridae) and circular ssDNA viruses (Genomoviridae) [24,25]. Generally, mycoviruses lack an extracellular phase in their replication cycle [9,23]; nevertheless, a novel ssDNA virus related to plant geminiviruses and conferring hypovirulence to its host, is transmitted in aerosols [26]. Fungi infected by viruses often present unusual characteristics such as abnormal pigmentation, irregular growth, and altered sexual reproduction. Potential hypovirulent effects of mycoviruses on their fungal hosts may be used for biological control of fungal diseases, similar to the application of a hypovirus found in the plant pathogenic fungus Cryphonectria parasitica used to control chestnut blight in Europe [12].
2. The Diversity of Viruses Infecting Rhizoctonia solani
The first dsRNA element in R. solani was initially described by Butler and Castano [13]. Since then numerous thorough studies were performed to explore the diversity of viruses infecting R. solani. To date, approximately 100 viruses have been found in R. solani isolates, including members of established families accommodating dsRNA, (+)ssRNA, and (−)ssRNA together with members of proposed families and unclassified RNA elements (Figure 1). Some of the viruses reported to infect R. solani belong to well-studied mycovirus families, such as Barnaviridae, Botourmiaviridae, Deltaflexiviridae, Endornaviridae, Hypoviridae, Megabirnaviridae, Narnaviridae, and Partitiviridae (Table 2 and Table S1). Others belong or are closely related to families traditionally known to infect plants, such as CMV [7] and proposed members of the orders Bunyavirales, Serpentovirales, and Tymovirales [6,27,28,29].
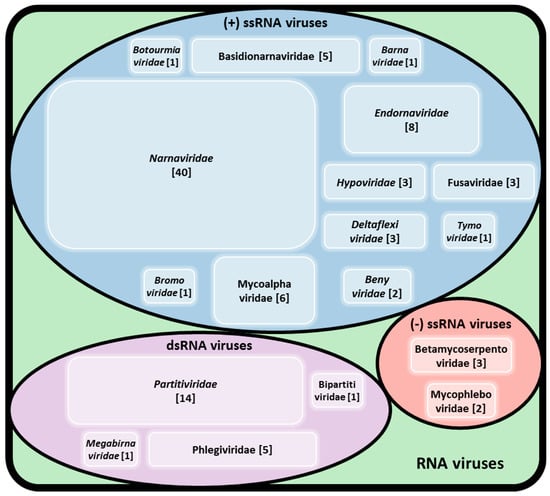
Figure 1.
Virus families reported infecting R. solani. The numbers in brackets refer to the number of different viruses belonging to each family and reported to infect R. solani.

Table 2.
Representative viruses known to infect Rhizoctonia solani.
In general, recent large-scale metatranscriptomic analyses of plant pathogenic fungi has led to the discovery of several (−)ssRNA mycoviruses including mymonaviruses [19,30,31,32] and other mycoviruses related to the bi- and tri-segmented peribunyaviruses and phenuiviruses, and the multi-segmented ophioviruses [19,33,34]. Since whole transcriptome shotgun sequencing is widely utilized to identify and quantify mycoviruses in biological samples, the majority of reported sequences are partial while verification of full length genomic sequences is not always feasible. To our knowledge, the mycoviruses infecting R. solani whose complete genome sequences have been reported so far belong to the established families Deltaflexiviridae, Endornavirdae, and Partitiviridae [15] but several partial genomes of viruses have been described (Table 2 and Table S1) [6,19]. Only the betapartitivirus Rhizoctonia solani virus 717 and the magoulivirus Rhizoctonia solani ourmia-like virus have been approved by ICTV so far, even though the genome of the latter has not been fully sequenced.
To date, numerous different viruses have been reported to infect R. solani AG-1 IA, isolated from rice: Rhizoctonia solani dsRNA virus 1 (RsRV1) in 2013 [16], Rhizoctonia solani partitivirus 2 (RsPV2) in 2014 [17], Rhizoctonia solani RNA virus 2 (RsRV2-HN008) in 2015 [12] and more recently Rhizoctonia solani dsRNA virus 3 (RsRV3) [35], Rhizoctonia solani partitivirus 3 to 8 (RsPV3 to 8, respectively) [36,37,38] and Rhizoctonia solani endornavirus 1 (RsEV1) [39]. Multiple co-infections of R. solani isolates are not uncommon; for instance R. solani AG2-2 IV DC17 has been reported to harbor an endornavirus, a megabirnavirus, a mitovirus, two flexiviruses, and three closely related mycoalphaviruses [9,15]. Similarly, R. solani AG-3PT RS002 infecting potato harbors an endornavirus [14] and a mitovirus [18]. Furthermore, a cross-kingdom viral infection has been discovered when a plant virus, cucumber mosaic virus (CMV), was found in an R. solani strain isolated from potato plants [7]. In addition, five unrelated dsRNA elements (L1, L2, M1, M2, and S1) were found to occur in DNA form in R. solani AG3 from North America [40,41].
2.1. Double-Stranded RNA Viruses
DsRNA viruses have a wide host range including animals, plants, protozoa, and fungi [42]. Mycoviruses with dsRNA genomes are mostly encapsidated in isometric particles [43] and are currently classified into eight families: Amalgaviridae (1 genomic segment, 3.5 kbp in length), Chrysoviridae (3–7 genomic segments, 2.4–3.6 kbp in length), Megabirnaviridae (2 genomic segments, 7.0–9.0 kbp in length), Partitiviridae (2–3 genomic segments, 1.4–2.3 kbp in length), Quadriviridae (4 genomic segments, 3.7–4.9 kbp in length), Reoviridae (Spinareovirinae subfamily, 10–12 genomic segments, 0.7–5.0 kbp in length) and Totiviridae (non-segmented, 4.6–7 kbp in length) [42,44,45,46]. Moreover, a dsRNA virus named Botrytis porri RNA virus 1 (BpRV1) belonging to the genus Botybirnavirus has been described [47]. Mycovirus taxonomy regularly changes with the discovery of novel viruses [48] and additional families, such as Alternaviridae (4 genomic segments 1.4–3.6 kbp in length), have been proposed recently. Generally, dsRNA viruses form spherical and not filamentous virions, the latter being a common characteristic of several (+)ssRNA plant and fungal viruses including Alphaflexiviridae, Betaflexiviridae, Gammaflexiviridae, Potyviridae, and Closteroviridae; nevertheless, a novel dsRNA virus from Colletotrichum camelliae isolated from tea plants in China was found to form flexuous and elongated virions [42,44]. Some dsRNA viruses form no true virions but are associated with and coated by viral proteins, as reported recently for Aspergillus fumigatus tetramycovirus-1 (AfuTmV-1) and Beauveria bassiana polymycovirus-1 (BbPmV-1), from the human pathogen A. fumigatus and the insect pathogen B. bassiana, respectively [49,50]. BbPmV-1 appears to be associated with hypovirulence in its host which is uncommon for mycoviruses [51].
2.1.1. Megabirnaviridae and Phlegiviridae
Megabirnaviridae is a family known to infect fungi and currently accommodates one genus Megabirnavirus [52], while a second related genus Phlegivirus has been proposed [9]. Members of the family contain linear bi-segmented dsRNA genomes, with two linear segments sizing each from 7 to 8.9 kbp and comprising 16.1 kbp in total length. The dsRNAs genomes are separately packaged into isometric particles [43,53,54]. The exemplar of the only officially recognized species RnMV1/W779 for each segment two tandem non-overlapping ORFs in each segment [52]. The ORFs in the largest segment encode a putative RdRp and a capsid protein (CP), whereas the ORFs in the smallest segment encode two proteins of unknown function [53,54]. Other unclassified members of the family include Sclerotinia sclerotiorum megabirnavirus 1 (SsMBV1) [55], Rosellinia necatrix megabirnavirus 2 (RnMBV2) [56], Pleospora megabirnavirus 1 (PMBV1) [57], and Entoleuca megabirnavirus 1 (EnMBV1) [27]. Virus transmission occurs either horizontally through anastomosis or vertically via sporulation [53]. Additionally, recent NGS approaches revealed more dsRNA viruses related to the Megabirnaviridae family (Table S1) [6,9]. The partial sequence of Rhizoctonia solani megabirnavirus 1 (RsMBV1; Table 2) is 975 bp in length and encodes a putative RdRp (Pfam02123, E-value 7e-13). More partial ORFs have been reported and named Rhizoctonia solani dsRNA virus 6-10 (RsRV6-10; Table S1), which are related to the previously proposed genus Phlegivirus [58] in the family Phlegiviridae [6].
2.1.2. Partitiviridae and Bipartitiviridae
Members of the Partitiviridae family have two linear, individually encapsidated monocistronic dsRNA segments, while an additional satellite or defective dsRNA segment may also be present. Each dsRNA segment is from 1.4 to 2.4 kbp in size and contains one large ORF encoding and RdRp or CP [59]. The family accommodates five genera: Alphapartitivirus, Betapartitivirus, Cryspovirus, Deltapartitivirus, and Gammapartitivirus [59]. The genera Alphapartitivirus and Betapartitivirus are known to infect plants, ascomycetes or basidiomycetes, whereas the genus Gammapartitivirus infect ascomycetes [59] and oomycetes [60]. The genera Deltapartitivirus and Cryspovirus infect exclusively plants and protozoa, respectively [59]. Fungal partitiviruses are transmitted either horizontally via hyphal fusion or vertically via spores [61].
To date, members of the genera Alphapartitivirus and Betapartitivirus have been found in R. solani. a putative alphapartitivirus named Rhizoctonia solani partitivirus 2 (RsPV2) was isolated from the causal agent of rice sheath blight, R. solani AG-1 IA GD-11. RsPV2/GD-11 contains two segments 2020 bp and 1790 bp in length, respectively (Figure 2; Table 2). The protein encoded by dsRNA1 is an RdRp (Pfam02123, E-value 5e-05) similar to that of partitiviruses such as Diuris peduncolata cryptic virus (DpCV; accession number JX156424, identity 63.77%, E-value 0.0), while dsRNA2 encodes a CP [17]. The betapartitivirus Rhizoctonia solani virus 717 (RsV717), isolated from R. solani AG-2 Rhs 717 has two genomic segments, 2363 bp and 2206 bp in length (Figure 2; Table 2). DsRNA1 encodes a putative RdRp (Pfam00680, E-value 0.002) with high similarity to that of Fusarium poae virus 1 (FpV1; accession number LC150606, identity 46.81%, E-value 0.0); while dsRNA2 encodes a putative CP [20]. In addition, the complete genomes of four other alphapartitiviruses, Rhizoctonia solani dsRNA virus 3 (RsRV3/A105), Rhizoctonia solani partitivirus 3 (RsPV3/HG81), Rhizoctonia solani partitivirus 4 (RsPV4/HG81), and Rhizoctonia solani partitivirus 5 (RsPV5/C24), were also determined [35,36,38]. Furthermore, the complete genomes of three betapartitiviruses isolated from R. solani YNBB-111, Rhizoctonia solani partitivirus 6 to 8 (RsPV6-8/YNBB-111), were also characterized [37]. Moreover, the complete coding sequences of Rhizoctonia solani dsRNA virus 2 (RsDSRV2/A; Table 2) and Rhizoctonia solani partitivirus 6 to 8 (RsPV6/BR5, RsPV7/BR6 and RsPV8/BR16; Table S1) (RsPV6-8; Table S1), isolated from R. solani AG2-2 LP, have been determined using NGS. RsDSRV2/A, RsPV7/BR6 and RsPV8/BR16 RdRps belong to the genus Alphapartitivirus, while RsPV6/BR5 belongs to the genus Betapartitivirus [6]. Finally, a partial sequence of the Rhizoctonia solani partitivirus 1 from R. solani OA-1 has been determined (Table 2). In total, fourteen members of the family Partitiviridae have been found to infect R. solani, together with Rhizoctonia solani bipartite-like virus 1 (RsBPV1; Table 2), a member of the proposed family Bipartitiviridae [6].
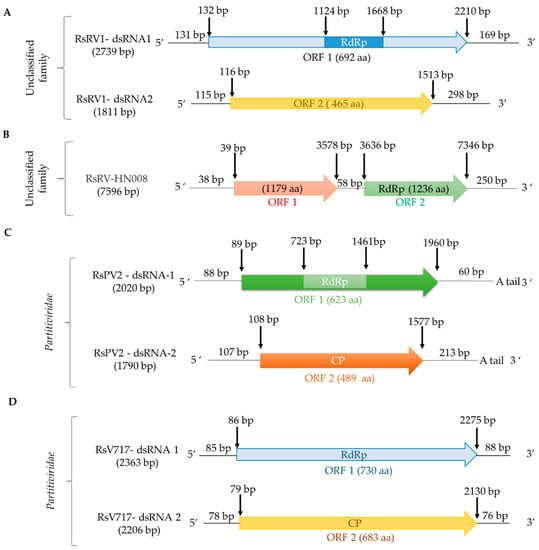
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the genomic organization of double-stranded (ds)RNA viruses infecting R. solani: (A) unclassified RsRV1/B275; (B) unclassified RsRV-HN008/HN008; (C) betapartitivirus RsV717/Rhs 717; (D) alphapartitivirus RsPV2/GD-11.
2.1.3. Unclassified dsRNA Viruses
To our knowledge, few studies characterized unclassified dsRNA viruses infecting R. solani. Rhizoctonia solani dsRNA virus 1 (RsRV1) (Figure 2; Table 2), found in the Chinese R. solani AG-1 IA B275 isolate from rice in 2007, was fully sequenced and analyzed. RsRV1 consists of two segments named RsRV1-dsRNA1 and RsRV1-dsRNA2, 2379 and 1811 bp in length, respectively, each containing a single open reading frame (ORF). RsRV1-dsRNA1 encodes an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp; Pfam00680, E-value 1e-04), whereas RsRV1-dsRNA2 encodes a protein of unknown function. Both proteins are closely related to the unclassified Fusarium graminearum dsRNA mycovirus-4 (FgV-4) [16].
Rhizoctonia solani RNA virus HN008 (RsRV-HN008) (Figure 2; Table 2) was fully sequenced and characterized. RsRV-HN008 has a genome 7596 bp in length, containing two non-overlapping ORFs. ORF1 has no significant similarity to any protein in the databases, whereas ORF2 encodes an RdRp (Pfam02123, E-value 4e-14) with low similarity to that of Rosellinia necatrix megabirnavirus 1-W779 (RnMV1/W779; accession number LC333756, identity 29.06%, E-value 9e-71) [17].
M1 and M2 dsRNAs were found in R. solani Rhs 1A together with the genetically distinct dsRNAs L1 (25 kbp), L2 (23 kbp) and S1 (1.2 kbp), and represent the first well-described dsRNA elements in R. solani (Table 2) [40,62]. M1 is homologous to the recently described Rhizoctonia solani putative virus 1 (RsV1/BR4, Table 2; E-value 45.64%); it contains two putative ORFs on the positive strand, while four more have been reported on the negative strand [62]. M2 contains one main ORF which encodes an RdRp (Pfam05919; 4e-170) closely related to that of mitoviruses, such as the Rhizoctonia solani mitovirus 22 (RsMV22, Table S1; E-value 79.57%) and similar to the pentafunctional AROM polypeptide of the shikimate pathway, which synthesizes the five central steps of the shikimate pathway in filamentous fungi and yeast [40].
2.2. Single-Stranded RNA Viruses
In addition to dsRNA viruses, ssRNA viruses are also prevalent in R. solani [63]. Some viruses with the smallest and simplest genomes have ssRNA as their genetic material [64]. The ssRNA viruses may be classified as positive-sense (+) or negative-sense (−), based on the polarity of their RNA genome [65]. The (+)ssRNA viruses have a simple RNA replication and expression mechanism [66], while the (−)ssRNA viruses initiate replication by packaging their transcription and replication machinery into virions [67]. The majority of ssRNA mycoviruses reported have a linear monopartite (+)ssRNA genome [68]. According to the ICTV, (+)ssRNA mycoviruses are assigned in 8 families [69], including Alphaflexiviridae (5.4–9 kb in length), Barnaviridae (4 kb in length), Botourmiaviridae (2.9 kb in length), Deltaflexiviridae (6–8 kb in length), Endornaviridae (14–17.6 kb in length), Gammaflexiviridae (6.8 kb in length), Hypoviridae (9–13 kb in length) and Narnaviridae (1.7–2.9 kb in length). Only one (−)ssRNA mycovirus is officially recognized by the ICTV, Sclerotinia sclerotiorum negative-stranded RNA virus 1, which is closely related to nyaviruses and bornaviruses and was recently assigned to the family Mymonaviridae [70].
2.2.1. (+)ssRNA Viruses: Barnaviridae
The Barnaviridae family currently accommodates genus Barnavirus and one species, Mushroom bacilliform virus [71] The exemplar of the species, mushroom bacilliform virus (MBV; accession number NC_001633) has a monopartite (+)ssRNA genome 4.0 kbp in length. The genome has four ORFs, encoding a protein of unknown function (P1), a polyprotein that includes protease and VPg domains (P2), RdRp (P3), and CP (P4), respectively. Few viruses related to genus Barnavirus have been discovered so far, including Colobanthus quitensis associated barnavirus 1 (CqBV1; accession number MG686618) and Rhizoctonia solani barnavirus 1 (RsBV1) [19]. RsBarV1 is 3915 bp in length and contains three ORFs, encoding a polyprotein with protease (Pfam02122, E-value 9e-06) and VPg domains, an RdRp (Pfam02123; E-value 5e-30) similar to that of MBV (identity 47%, E-value 1e-124), and a CP. The ORF encoding the protein of unknown function is missing, suggesting that the 5′ terminal sequence of RsBV1 is incomplete.
2.2.2. (+)ssRNA Viruses: Benyviridae
The family Benyviridae accommodates (+)ssRNA plant viruses with rod-shaped virions, whose genome is capped and polyadenylated, comprises four to five segments and ranges from 1.3 to 6.7 kb in length [46]. Benyviridae accommodates four species within the genus Benyvirus and its members are associated with cell-to-cell movement [46,72,73]. Two distinct viruses, both named Rhizoctonia solani Beny-like virus 1 (RsBenV1; Table 2) were found in R. solani 42304-9a [19] and R. solani AG-2.2 LP BR2 [6], respectively, and were partially characterized. In each case, only one segment of the genome was identified, encoding a putative RdRp related to benyviruses and benylike-viruses; more specifically RsBenV1/42304-9a is closely related to beet soil-borne mosaic virus (BSBMV; accession number AF280539, identity 39.13%, E-value 1e-09), an official member of the Benyviridae family, while RsBenV1/BR2 is closely related to Sclerotium rolfsii beny-like virus 1 (SrBLV1; accession number MH766487, identity 40.74%, E-value 0.0).
2.2.3. (+)ssRNA Viruses: Botourmiaviridae and Basidionarnaviridae
Botourmiaviridae is a family of plant and fungal viruses with (+)ssRNA genomes. The family Botourmiaviridae currently accommodates ten species and four genera: Botoulivirus (1 segment, 2.9 kbp in length), Magoulivirus (1 segment, 2.3 kbp in length), Ourmiavirus (3 segments, approximately 0.9 kbp, 1.0 kbp and 2.8 kbp in length, respectively), and Scleroulivirus (1 segment, 3 kbp in length). NGS has led to the identification of new viruses infecting R. solani which are related to Botourmiaviridae, Rhizoctonia solani ourmia-like virus (RsOLV) 1-5 [6,19]. Only 59%–87% of the RsOLV1 genome was sequenced and the original analysis revealed similarity to the RdRps of members of the genus Ourmiavirus such as Cassava virus C (CVC; accession number NC_013111, identity 33.73%, E-value 2e-07), Epirus cherry virus (EcV; accession number NC_011065, identity 33.61%, E-value 2e-09) and Ourmia melon virus (OmV; accession number NC_011068, identity 32.61%, E-value 9e-09) [19].
Plant viruses of the genus Ourmiavirus are tripartite with each segment encoding a single protein: RdRp, CP and movement protein (MP), respectively, and are believed to have evolved by reassorting genomic segments of viruses infecting fungi and plants [74]. In contrast, the RsOLV1 genome does not appear to encode the CP or the MP [19]. Currently, RsOLV1 is the exemplar of the officially recognized species Rhizoctonia magoulivirus 1, genus Magoulivirus, family Botourmiaviridae. In contrast, evolutionary phylogenetic tree clustered RsOLV 2 to 5 together Agaricus bisporus virus 15 (AbV15/003; accession number AQM49945) into a potential novel genus within the family Botourmiaviridae or even a novel closely related family (Figure 3) provisionally named Basidionarnaviridae since it currently accommodates only viruses infecting basidiomycetes [6]. The RsOLV2/Rs, RsOLV2, and RsOLV3 RdRp sequences are over 70% identical, therefore they are likely different isolates of the same species [6].
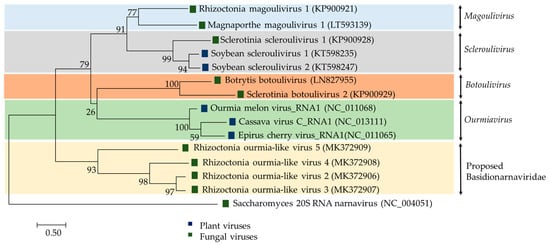
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic analysis of viruses related to the family Botourmiaviridae. The phylogenetic tree was built using the maximum likelihood method; substitution model LG+G+I. 1000 bootstrap replications were applied.
2.2.4. (+)ssRNA Viruses: Bromoviridae
Bromoviridae is a family of viruses with worldwide distribution that naturally infects plants. There are currently six genera in the family, including Alfamovirus, Anulavirus, Bromovirus, Cucumovirus, Ilarvirus, and Oleavirus. Bromoviridae possess a tripartite linear (+)ssRNA genome [75], approximately 8 kb in length [76]. RNA1 and RNA2 encode RdRp 1a and 2a, respectively, both involved in genome replication and transcription of ssRNA4 from the minus-strand copy of RNA3. RNA3 produces a MP and a CP. Members of the genera Cucumovirus and Ilarvirus have an additional overlapping ORF [75]. Members of the family Bromoviridae form virions, either spherical or quasi-spherical for the members of the genera Cucumovirus, Ilarvirus, Anulavirus, and Bromovirus, or bacilliform for the members of the genera Ilarvirus, Alfamovirus, and Oleavirus [76].
Natural cross-kingdom virus transmission between plants and fungi has been speculated for some time and recently transmission of CMV to R. solani was reported [7]. CMV-infected R. solani AG-3 (Figure 4) was isolated from potato plants (Solanum tuberosum L.) in Inner Mongolia, China. CMV transmission can occur in both directions from plant to R. solani and R. solani to plant, while CMV can be transmitted horizontally via hyphal fusion but not vertically via basidiospores [7]. CMV is a member of the genus Cucumovirus, family Bromoviridae [7] and has three genomic segments 3309 nt, 3053 nt, and 2214 nt in length, respectively, encapsidated in isometric particles [7].
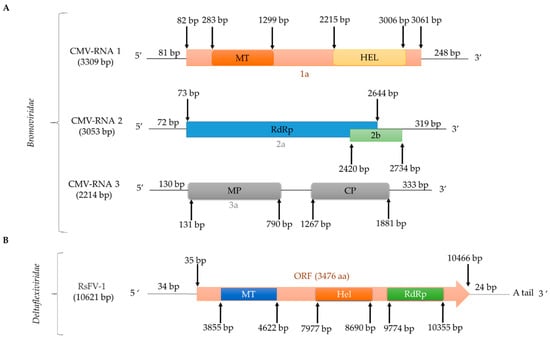
Figure 4.
Schematic representation of the genomic organization of single-stranded (ss)RNA viruses infecting R. solani: (A) bromovirus CMV; CMV-RNA 1 encodes 1a (replicase component; Pfam12467, E-value 1e-73), CMV-RNA 2 encodes 2a (replicase component; Pfam00978, E-value 0.0) and 2b (RNA-silencing suppressor), and CMV-RNA 3 encodes 3a (MP; Pfam00803, E-value 1e-88) and coat protein (CP); (B) deltaflexivirus RsFV-1/DC717.
2.2.5. (+)ssRNA Viruses: Deltaflexiviridae and Tymoviridae, Tymovirales
The general term flexiviruses refers to members of the order Tymovirales, families Alphaflexiviridae, Betaflexiviridae, Deltaflexiviridae, and Gammaflexiviridae. Flexiviruses have a monopartite (+)ssRNA polyadenylated genome 6.5–9.5 kb in length and filamentous virions, which encode a replication-associated polyprotein 150–250 kDa in size [68] and are known to infect both plants and fungi [77,78]. The first mycovirus reported in the order Tymovirales was Botrytis virus F (BotV-F), which belongs to the family Gammaflexiviridae, genus Mycoflexivirus [79]. Within the family Deltaflexiviridae, three species belonging to the genus Deltaflexivirus have been reported: Sclerotinia deltaflexivirus 1 (SsDFV1) [80], soybean-associated deltaflexivirus 1 (SlaMFV1) [81], and Fusarium deltaflexivirus 1 (FgDFV1) [68]. Only one flexivirus infecting R. solani has been fully sequenced in, tentatively named Rhizoctonia solani flexivirus 1 (RsFV1; Figure 4; Table 2) [15]. RsFV-1 was isolated from R. solani AG2-2IV/DC17 and its (+)ssRNA genome consists of 10,621 nt excluding the poly (A) tail. RsFV-1 encodes a single protein similar to that of other members of the order Tymovirales, most notably the deltaflexiviruses SsDFV1 (accession number NC_038977, identity 35.5%, E-value 2e-104), SlaMFV1 (accession number NC_038979, identity 34.32%, E-value 9e-110) and FgDFV1 (accession number NC_030654, identity 38.8 %, E-value 2e-111) [15]. Additionally, the RsFV-1 protein has three conserved domains, including a viral methyltransferase (Pfam01660, E-value 3.65e-29), a viral helicase (Pfam01443, E-value 2.04e-08), and an RdRp (Pfam00978, E-value 2.46e-08). Two more flexiviruses, Rhizoctonia solani flexivirus 2 (RsFV2; Table S1) and Rhizoctonia solani flexi-like virus 1 (RsFLV1; Table 2) were detected in R. solani AG2-2IV/DC17 and R. solani AG-2.2 LP BR9, respectively, and have been partially sequenced.
Tymoviridae is a family of (+)ssRNA viruses in the order Tymovirales which range from 6.0 to 7.5 kb in length [82]. The family Tymoviridae currently accommodates three genera Maculavirus, Marafivirus, and Tymovirus and 41 officially recognized species [69]. However, more viruses related to Tymoviridae have been reported but not classified thus far [76], including Rhizoctonia solani positive-stranded RNA virus 1 (RsPSV1; Figure 2) [19], the only known tymovirus infecting R. solani. The partial genome sequence of RsPSV1 contains a large ORF and several small ORFs, similar to the bee Macula-like virus (MlV; accession number NC_027631, identity 30%, E-value 4e-56) in the family Tymoviridae.
2.2.6. (+)ssRNA Viruses: Endornaviridae
Endornaviridae is a family of viruses with non-encapsidated RNA genomes that range in size from 9.7–17.6 kb and contains a single ORF encoding a polyprotein [83,84]; the polyprotein has an RNA helicase domain at the N-terminus and conserved RdRp motifs at the C-terminus [85]. Endornaviruses naturally infect fungi, plants, and oomycetes, which are persistent and do not cause obvious symptoms in their host [85,86,87]. In fungal hosts, endornaviruses are transmitted vertically via sporulation and horizontally via anastomosis [88], whereas in plant hosts they rely on vertical transmission via pollen and ova, since they lack a MP and cannot move from cell to cell [89,90,91]. Endornaviruses are not encapsidated and do not form true viral particles [85]. The family accommodates two genera, Alphaendornavirus and Betaendornavirus.
An endornavirus, tentatively named Rhizoctonia solani endornavirus (Table 2) and isolated from R. solani AG-3PT strain RS002 (RsEV-RS002), was partially sequenced. The RsEV-RS002 partial genome (14964 nt) includes a partial 5′ untranslated region (5′-UTR) but not the 3′-UTR. The RsEV-RS002 genome shows low similarity to the genomic sequence of bell pepper alphaendornavirus (BPEV-YW; accession number NC_015781, identity 29.8%, E-value 1e-71). A conserved domain search in Pfam [92] showed that the RsEV-RS002 protein has three conserved domain motifs including a viral methyltransferase (MT; Pfam01660, E-value 5e-05), a viral helicase (Hel; Pfam01443, E-value 7e-11), both located at the N-terminus, and an RdRp (Pfam00978, E-value 3e-16) located at the C-terminus. The putative RdRp domain is located at the C-terminus whereas the putative viral helicase and MT are both located at the N-terminus [14]. Rhizoctonia solani endornavirus 1 (RsEV1/GD-2; Table S1), Rhizoctonia solani endornavirus 2 (RsEV2/Illinois1; Table 2), Rhizoctonia solani endornavirus 3 (RsEV3/DC17; Table S1), and Rhizoctonia solani endornavirus 4 to 7 (RsEV4-7; Table S1) have also been reported [6]. RsEV4, 5, 6, and 7 each contain a single putative ORF of 6719, 5300, 5077 and 4757 aa, respectively. RsEV4, RsEV6 and RsEV7 encode an RdRp (Pfam00978; E-value 9e-23, 9e-22, and 1e-25, respectively) and a Hel (Pfam01443; E-value 7e-12, 3e-06, and 1e-25, respectively) domain. RsEV5 encodes an MT (Pfam01660; E-value 4e-05) domain in addition to the RdRp (Pfam00978; E-value 5e-17); however, no Hel domain was detected. Additionally, a complete genome sequence of an endornavirus from R. cerealis, another species of the genus Rhizoctonia, has been described [93] and is the exemplar of an officially recognized species Rhizoctonia cerealis alphaendornavirus 1. RsEV-RS002, RsEV1/GD-2 and RsEV5 belong to genus Alphaendornavirus as well, while a new genus Gammaendornavirus within the family Endornaviridae was recently proposed to accommodate RsEV2/Illinois1, RsEV3/DC17, RsEV4, RsEV6, and RsEV7 [6].
2.2.7. (+)ssRNA Viruses: Hypoviridae and Fusariviridae
The family Hypoviridae accommodates a single genus, Hypovirus, and four recognized species, Cryphonectria hypovirus 1 to 4, with capsidless monosegmented (+)ssRNA genomes ranging from 12.7 to 9.2 Kbp in length [94,95,96,97,98]. Each genome has either one or two ORFs, encoding at least putative RdRp and Hel domains [98] and occasionally additional domains including glucosyltransferase (UGT), papain like protease (PRO) and permuted papain-fold peptidase of dsRNA viruses and eukaryotes (PPPDE) [99,100]. The primary interest in hypoviruses stemmed from their ability to mitigate the fungal host virulence (hypovirulence), of the chestnut blight fungus Cryphonectria parasitica. Hypoviruses can be transmitted horizontally to virulent isolates via hyphal anastomosis [99].
To our knowledge, a complete hypovirus genome from R. solani has not been reported so far, but the complete ORF of Rhizoctonia solani hypovirus 1 (RsHV1; Table 2) and partial ORFs for Rhizoctonia solani hypovirus 2 and 3 (RsHV2 and 3, respectively; Table S1) were recently described using NGS [6]. The RsHV1 segment is 18 kbp in length, representing one of the longest hypovirus genomes known so far, and encodes a large putative protein of 5344 aa where only a helicase conserved domain (cd00046, E-value 6.99e-06) was detected; neither an RdRp domain nor the GDD motif, hallmark of most viral RdRps, was found in the protein sequence. Nevertheless, BLAST analysis revealed that the RsHV1 protein was homologous to other hypoviruses such as Sclerotinia sclerotiorum hypovirus 2 (SsHV2; accession number QBA69886, identity 26.64%, E-value 4e-81) [101]. The RsHV2 and 3 sequences are 9 and 5 kbp in length, respectively, with two ORFs each. The two RsHV2 ORFs encode proteins homologous to those of hypoviruses but lacking any conserved motifs, while one of the RsHV3 ORFs has a helicase conserved domain (cd00046, E-value 3.62e-10). A new genus Megahypovirus within the family Hypoviridae was proposed to accommodate RsHV1 and SsHV2, whose genomes are large, together with Agaricus bisporus virus 2 (AbV2/003; accession number KY357506), RsHV2 and RsHV3 [6].
Furthermore, three fusariviruses Rhizoctonia solani fusarivirus 1, 2 and 3 (RsFV1, 2 and 3, respectively) were described [6] related to the members of the proposed family Fusariviridae [102]. The RsFV1 genomic segment is 11 kbp in length containing four putative ORFs: the largest ORF3 encodes a protein with an RdRp (Pfam00680; E-value 7e-20) and a Hel (Pfam00270; E-value 1.2e-06) domain; ORF1 encodes a viral helicase (Pfam04851; E-value 3.7e-09); the smallest ORF2 and ORF4 encode proteins of unknown function. RsFV2 has similar genomic organization, while the RsFV3 partial genomic sequence encodes for an RdRp (Pfam00680; E-value 1.2e-06) and a Hel (cd00046; E-value 2e-06) domain [6]. It has been proposed to subdivide the currently described fusariviruses into at least two further genera, based on the sequence length and genome organization, and in this case RsFV1 and RsFV2 would cluster together while RsFV3 would belong to a different genus [6].
2.2.8. (+)ssRNA Viruses: Narnaviridae
Members of the family Narnaviridae are the simplest viruses with a linear (+)ssRNA genome 1.7–3.6 kb in length, a single ORF, which encodes an RdRp [103,104], and no capsid. The family Narnaviridae accommodates two genera, Mitovirus and Narnavirus [103]. All known members of genus Mitovirus infect filamentous fungi and plants [104,105], whereas members of the genus Narnavirus have been also found in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae and in the oomycete Phytophthora infestans [43]. Mitoviruses have genomes 2.3–3.1 kb in length [106] and do not form true virions but are associated with lipid membrane-bound vesicles [107]. Mitoviruses replicate in the mitochondria of the host cell, in contrast to narnaviruses that are known to replicate in the cytosol. Since the discovery of the first mitovirus in C. parasitica, many mitoviruses have been detected in phytopathogenic fungi [106], most of them from ascomycetes, a few from basidiomycetes and one from arbuscular mycorrhiza [108]. Some mitoviruses have been reported to confer hypovirulence to their host, such as Sclerotinia sclerotiorum mitovirus 4 (SsMV4) isolated from S. sclerotiorum strain AH16 [109].
To our knowledge, there are no complete mitovirus genomes described from R. solani, however, forty partial genome sequences of mitoviruses infecting R. solani have been reported [6,9,21]. A novel mitovirus infecting R. solani AG-3PT strain RS002 [18] was characterized and tentatively named Rhizoctonia solani mitovirus 1 (RMV1-RS002; Table 2). The partial genome sequence of RMV1-RS002 is 2797 nt and shows similarity to the tuber excavatum mitovirus (TeMV; accession number JN222389, identity 25.6%, E-value 4e-106) [18]. The protein encoded by RMV1-RS002 is similar to Glomus sp. RF1 small virus (GRF1V-S; accession number NC_040656, identity 49.55%, E-value 7e-94) [18]. The partial 5′-UTR of RMV1-RS002 was shown to form at least three stem-loop structures [18], as is typical for viral UTRs in general. In addition to of RMV1-RS002, several partial mitovirus genomes sequences have been reported (Table S1) [6,9,19]. A new family Mitoviridae, closely related to but distinct from the family Narnaviridae, has been proposed to accommodate current members of the genus Mitovirus and other mitoviruses. This new family would be subdivided into a number of genera, including plant and fungal mitoviruses [6,105,110]. Moreover, a new order would be established to include the Narnaviridae and the proposed Mitoviridae families [95].
2.2.9. (+)ssRNA Viruses: Mycoalphaviridae
The Togaviridae family accommodates genus Alphavirus and 31 species, including several important human pathogens such as Eastern equine encephalitis virus (EEEV) [111], Western equine encephalitis virus (WEEV) [112], Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus (VEEV) [113], Sindbis virus (SINV) [114], Ross River virus (RRV) [115], Semliki Forest virus (SFV) [116], and Chikungunya virus [117]. Alphaviruses are arboviruses that are transmitted alternatively between insect vectors and vertebrate hosts [118,119]. Members of the Togaviridae family are small enveloped (+)ssRNA viruses ranging from 10 to 2 Kbp in size [119], with a methylguanosine cap and a poly(A) stretch at the 5′ end and 3′ end, respectively, and a genome encoding both non-structural and structural proteins [118]. The virion consists of a nucleocapsid core, a lipid bilayer and surface glycoproteins [120].
To our knowledge, there is no member of the genus Alphavirus infecting R. solani. However, partial genomic sequences related to Togaviridae family were recently reported in R. solani AG-2.2 LP, including Rhizoctonia solani alphavirus-like 1, 2, and 3 (RsALV1/BR15, Table 2; RsALV2/BR14 and RsALV3/BR8, Table S1) [6]. The RsAVL2 partial ORF encodes RdRp (Pfam00978, E-value 2.9e-21), whereas both RdRp (Pfam00978, E-values 3.8e-18 and 2.1e-19, respectively) and viral helicase (Pfam01443, E-values 8.5e-05 and 6.6e-11, respectively) domains can be detected in RsAVL1 and RsAVL3 [6]. A new family Mycoalphaviridae was proposed to accommodate RsALV1, RsALV 2, and RsALV3, together with Rhizoctonia solani RNA virus 1, 2, and 3 (RsRV1-3/DC17; Table S1) detected in R. solani AG 2-2IV DC17 and Sclerotinia sclerotiorum RNA virus L (SsRVL; accession number EU779934) [6].
2.2.10. (−)ssRNA Viruses: Betamycoserpentoviridae, Serpentovirales
Aspiviridae, formerly known as Ophioviridae, is a family of flexible filamentous viruses known to infect plants [121] and belongs to the order Serpentovirales. The family Aspiviridae currently accommodates one genus Ophiovirus and 7 species. The members of the family Aspirividae contain a (−)ssRNA genome ranging from 11.3 to 12.5 kb in length separated into 3 to 4 segments [121]. Recently, unclassified partial virus sequences related to ophioviruses were reported infecting soil-borne R. solani strains and named Rhizoctonia solani negative-stranded RNA virus 1 to 3 (RsNSRV1-3; Table 2). Analysis of the sequences revealed a large ORF with significant similarity to the L proteins encoded by RNA1 of the lettuce ring necrosis ophiovirus and other members of the family Aspiviridae. A new family Betamycoserpentoviridae within the order Serpentovirales has been proposed to accommodate these viruses, together with Fusarium poae negative-stranded RNA virus 1 (FpNSV1) from the fungal plant pathogen Fusarium poae [19,34].
2.2.11. (−)ssRNA Viruses: Mycophleboviridae, Bunyavirales
The order Bunyavirales accommodates twelve families: Arenaviridae, Cruliviridae, Fimoviridae, Hantaviridae, Leishbuviridae, Mypoviridae, Nairoviridae, Peribunyaviridae, Phasmaviridae, Phenuiviridae, Tospoviridae, and Wupedeviridae. Metatranscriptomics analyses of plant pathogenic fungi revealed the presence of several (−)ssRNA mycoviruses, related to bi- and tri-segmented (−)ssRNA viruses, such as peribunyaviruses and phenuiviruses [19,33,34]. For instance, Lentinula edodes negative-strand RNA virus 2 (LeNSRV2) infecting Lentinula edodes is a phenui-like virus and the first segmented (−)ssRNA virus found to infect fungi [28], while more viruses related to the order Bunyavirales were reported in fungi associated with the marine organism Holothuria polii [29] and the ascomycete Entoleuca sp. [27]. Recently, two viruses infecting R. solani and related to bunyaviruses were reported: Rhizoctonia solani bunya/phlebo-like virus 1 (RsBPLV1; Table 2) [6] and Rhizoctonia solani negative-stranded virus 4 (RsNSV4; Table S1). Analysis of the protein encoded by the RsBPLV1 segment revealed the presence of RdRp motifs (Pfam04196; E-value 1e-09). Subsequently, the new family Mycophleboviridae was proposed within the order Bunyavirales to accommodate RsBPLV1 and RsNSRV1 together with Ixodes scapularis associated virus 6 (IsV6; accession number MG256514).
3. Transmission of Viruses Infecting Rhizoctonia solani
Mycovirus transmission is a significant process that needs to be addressed in any mycovirus-mediated biological control approach to alleviate fungal diseases. Specifically, it is necessary for the mycovirus to acquire some functions before being considered as a potential biological control agent, including limitation of host range to prevent the spread to undesirable hosts and the ability to establish and spread within the targeted host population [122]. Two principal pathways of transmission are known: Horizontal transmission via hyphal anastomosis and heterokaryosis, and vertical transmission through sporulation [123]. The effectiveness and success of biological control may vary depending on the mycovirus mode of transmission. Horizontal transmission is generally linked to increased biocontrol efficiency, since it leads to widespread coverage of the biocontrol agent, whereas vertical transmission is associated with lower efficiency [124]. Mycoviruses are completely dependent on their host due to their inability to survive in the environment and vertical transmission may have evolved in cases of mutualism. Nevertheless, some cases of horizontal transmission in mutualistic symbiosis have been reported [125]. The replication cycle of mycoviruses, in general, lacks an extracellular phase and infectious virions; one notable exception is the novel circular ssDNA virus, Sclerotinia sclerotiorum hypovirulence associated DNA virus 1 (SsHADV-1), which can be transmitted extracellularly and use a mycophagous insect (Lycoriella ingénue) as a vector for transmission [43,106]. This suggests the potential existence of other undiscovered mycoviruses that might be transmitted extracellularly.
In R. solani, few studies have been reported on mycovirus transmission. Successful transfection protocols were previously established for some mycoviruses, including members of the families Partitiviridae, Megabirnaviridae, Reoviridae, and Totiviridae. This approach is generally based on the use of polyethylene glycol (PEG) 4000 that promotes protoplast fusion and subsequent regeneration of the virus-transfected protoplasts and contributes substantially to the understanding of virus-host interaction and mycovirus-mediated biological control [17]. For instance, the alphapartitivirus RsPV2/GD-11 was successfully introduced into protoplasts of the virus-free R. solani strain GD-118 creating the derivative virus-transfected strain GD-118T [17]. Despite the complexity of fungal cell walls which are considered to be a substantial barrier to their spread, mycoviruses are generally capable of transmission from one fungal isolate to another in nature [25]. Purified RsPV2/GD-11 particles were successfully transmitted horizontally or vertically, although in some cases transmission via hyphal fusion failed between different genotypes within the same R. solani anastomosis group [22]. In addition, members of the family Endornaviridae, which do not produce virus particles, are transmissible at high rates horizontally as well as vertically [14]. For instance, a betaendornavirus identified in R. solani Ra1 has the ability to be transmitted vertically via basidiospores [7], while the alphaendornavirus RsEV1/GD-2 could be transmitted horizontally via hyphal anastomosis [39]. Furthermore, the M2 dsRNA and the betapartitiviruses RsPV6/YNBB-111, RsPV7/YNBB-111 and RsPV8/YNBB-111 could be transmitted horizontally via hyphal anastomiosis [37,40]. Moreover, CMV infecting R. solani was transmitted horizontally through hyphal fusion, but not vertically via basidiospores [7].
4. Effects of Virus Infection on Rhizoctonia solani
Mycovirus infections are often cryptic (symptomless) but investigations focus on potential hypovirulence, a phenomenon that may be exploited in the context of sustainable biological control of fungal diseases. The prime example is Cryphonectria hypovirus 1 (CHV1), used to successfully control the plant pathogen Cryphonectria parasitica, the causal agent of chestnut blight, in Europe [122]. This discovery revolutionized the world of fungal biological control and led to the term hypovirulence [126]. Additionally, Rosellinia necatrix megabirnavirus 1 (RnMBV1) was isolated from Rosellinia necatrix the causative agent of a worldwide devastating disease. RnMBV1 belongs to the family Megabirnaviridae, has a bi-segmented genome and is a potential virocontrol agent since it confers hypovirulence by significantly reducing the virulence and mycelial growth of its host [53,69]. The main effects include a decrease in the host growth rate, attenuation of host virulence, lack of sporulation and reduction of basidiospore germination [127,128]. In addition, other mycoviruses may have more deleterious effects, including the ‘La France’ disease of Agaricus biporus caused by the ‘La France’ isometric virus (LIV) and the mushroom diseases caused by oyster mushroom isometric virus (OMIV) and oyster mushroom spherical virus (OMSV) [21]. To investigate the effect of mycoviruses on their hosts it is important to construct a virus-free isogenic line, either by transmitting the mycovirus into a virus-free strain or by curing the virus-infected one [25]. For instance, protoplast transfection of RsPV2/GD-11 into the R. solani virus-free strain GD-118 resulted in darker mycelial pigmentation on potato dextrose agar (PDA) plates, and a reduction of mycelial growth rate, sclerotia size and numbers [17]. Furthermore, RsPV2/GD-11 diminished lesion sizes on rice leaves, indicating hypovirulence [17]. Similarly, horizontal transmission of RsEV5/GD-2 resulted in host hypovirulence [39]. In contrast to RsPV2/GD-11 and RsEV5/GD-2, infection of R. solani with CMV does not affect the growth rate and morphology of the fungus on PDA under laboratory conditions [7]. Additionally, M1 dsRNA is associated with enhanced virulence in the parental R. solani Rhs 1A, while sectors of the parental strain harboring the M2 dsRNA and the derivative strains showed reduced pigmentation and growth rate [41]. The RNA titers of M1 and M2 dsRNAs appear to be inversely correlated [40]; the former can be found mainly in mitochondria [62] while the latter in the cytosol [40]. All these studies clearly illustrate the phenotypic variation of mycovirus infection.
5. Conclusions and Future Prospects
Viruses infecting R. solani are less well studied as compared to those in other fungal genera such as C. parasitica. However, a range of RNA viruses infecting R. solani was described including members of the families Barnaviridae, Benyviridae, Botourmiaviridae, Bromoviridae, Deltaflexiviridae, Endornaviridae, Hypoviridae, Megabirnaviridae, Narnaviridae, Partitiviridae, Togaviridae, and Tymoviridae, together with unclassified mycoviruses related to the orders Serpentovirales and Bunyavirales. These families include dsRNA viruses, (+)ssRNA viruses and (−)ssRNA viruses and the majority of the viruses infecting R. solani have dsRNA or (+)ssRNA genomes.
In addition to the discovery of novel viruses, future research on mycoviruses needs to focus on the molecular mechanisms of mycovirus–host interactions and provide a better understanding of mycovirus transmission mechanisms. Efficient mycovirus detection relies on NGS technology. NGS allows the determination of mycoviruses previously unreported and contributes considerably to the clarification of unknown molecular mechanisms of host-virus interactions since it can be used to examine in detail changes in the R. solani transcriptome following mycovirus infection. Viruses infecting R. solani are transmissible horizontally via anastomosis hyphal fusion or vertically via sporulation [129], while successful transmission depends on the particular mycovirus under study. For example, endornaviruses use both routes of transmission, horizontal and vertical [14], whereas CMV was efficiently transmitted horizontally in R. solani CMV-free strains via hyphal fusion but failed to transmit through basidiospores [7]. No specific vectors facilitating mycovirus transmission have been reported although it is believed that yet undetermined insect vectors may play a key role and these should be identified in the future. Mycovirus-related research focuses especially on the identification of potential biological agents to combat plant pathogenic fungi. In the case of R. solani, some viruses such as CMV have no discernible effects on their host, while others such as RsPV2/GD-11 were shown to cause hypovirulence and therefore are promising biocontrol agents and should be studied extensively in the future.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4915/11/12/1113/s1, Table S1: Additional mycoviruses reported to infect R. solani.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.H.A., I.K.-L. and M.F.F.; validation, A.H.A., I.K.-L. and M.F.F.; writing—original draft preparation, A.H.A.; writing—review and editing, A.H.A., M.F.F., and I.K.-L.; project administration, M.F.F.; funding acquisition, M.F.F. All authors listed have made a direct, substantial and intellectual contribution to this work, therefore, approved it for publication.
Funding
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the National Nature Science Foundation of China, Grant No. (31750110464), and Huazhong Agricultural University, Talented Young Scientist Program (TYSP Grant No.42000481-7).
Acknowledgments
A.H.A would like to acknowledge Jiang Daohong, Ph.D., Xie Jiatao, Ph.D., and all the professors and associate professors at State Key Laboratory of Agricultural Microbiology, College of Plant Science and Technology, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan 430070, People’s Republic of China. M.F.F. also would like to thank the National Nature Science Foundation of China for the financial support, China Postdoctoral Science Foundation and Shaobo Xiao, DMV, Ph.D at State Key Laboratory of Agricultural Microbiology, Laboratory of Infectious Diseases, College of Veterinary Medicine, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan 430070, Hubei, the People’s Republic of China for their encouragement. I.K.-L. thanks Robert Coutts, Ph.D. for critical reading of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors herein declare no potential competition of interest.
References
- Ram, R.M.; Singh, H. Rhizoctonia bataticola: A serious threat to chickpea production. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2018, 6, 715–723. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, G.K.H.; Bertier, L.; Soltaninejad, S.; Höfte, M. Cropping systems and cultural practices determine the Rhizoctonia anastomosis groups associated with Brassica spp. in Vietnam. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsatly, J.; Copley, T.R.; Jabaji, S.H. Antioxidant genes of plants and fungal pathogens are distinctly regulated during disease development in different Rhizoctonia solani pathosystems. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Fei, B.; He, J.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, D.; Pan, L.; Li, S.; Liang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhu, J. Transcriptome analysis reveals the host selection fitness mechanisms of the Rhizoctonia solani AG1IA pathogen. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouzai, Y.; Kimura, M.; Watanabe, M.; Kusunoki, K.; Osaka, D.; Suzuki, T.; Matsui, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Ichinose, Y.; Toyoda, K. Salicylic acid-dependent immunity contributes to resistance against Rhizoctonia solani, a necrotrophic fungal agent of sheath blight, in rice and Brachypodium distachyon. New Phytol. 2018, 217, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picarelli, M.A.S.; Forgia, M.; Rivas, E.B.; Nerva, L.; Chiapello, M.; Turina, M.; Colariccio, A. Extreme diversity of mycoviruses present in isolates of Rhizoctonia solani AG2-2 LP from Zoysia japonica from Brazil. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andika, I.B.; Wei, S.; Cao, C.; Salaipeth, L.; Kondo, H.; Sun, L. Phytopathogenic fungus hosts a plant virus: A naturally occurring cross-kingdom viral infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 12267–12272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrios, G.N. Plant Pathology, 5th ed.; Department of Plant Pathology, University of Florida: Gainesville, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bartholomäus, A.; Wibberg, D.; Winkler, A.; Pühler, A.; Schlüter, A.; Varrelmann, M. Deep sequencing analysis reveals the mycoviral diversity of the virome of an avirulent isolate of Rhizoctonia solani AG-2-2 IV. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, N.; Yong, X.; Yang, X.; Shen, Q. Biocontrol of Rhizoctonia solani damping-off disease in cucumber with Bacillus pumilus SQR-N43. Microbiol. Res. 2012, 167, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, M.; Xie, J.; Wu, S.; Maria, S.; Zheng, D.; Assane, H.A.; Wang, Q.; Cheng, J.; Fu, Y.; Jiang, D. A Novel Deltaflexivirus that Infects the Plant Fungal Pathogen, Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, Can Be Transmitted Among Host Vegetative Incompatible Strains. Viruses 2018, 10, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Chen, C.-Y.; Gao, B.-D. Genome sequence of a novel mycovirus of Rhizoctonia solani, a plant pathogenic fungus. Virus Genes 2015, 51, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, L.; Meiling, Z.; Mei, Y.; Erxun, Z. Diversity of dsRNA viruses infecting rice sheath blight fungus Rhizoctonia solani AG-1 IA. Rice Sci. 2018, 25, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Falloon, R.E.; Stewart, A.; Pitman, A.R. Molecular characterisation of an endornavirus from Rhizoctonia solani AG-3PT infecting potato. Fungal Biol. 2014, 118, 924–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartholomäus, A.; Wibberg, D.; Winkler, A.; Pühler, A.; Schlüter, A.; Varrelmann, M. Identification of a novel mycovirus isolated from Rhizoctonia solani (AG 2-2 IV) provides further information about genome plasticity within the order Tymovirales. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Liu, H.; Zhang, M.; Cao, X.; Zhou, E. The complete genomic sequence of a novel mycovirus from Rhizoctonia solani AG-1 IA strain B275. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 1609–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Q.; Zhu, M.; Zhou, E. A novel mycovirus closely related to viruses in the genus Alphapartitivirus confers hypovirulence in the phytopathogenic fungus Rhizoctonia solani. Virology 2014, 456, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Falloon, R.E.; Stewart, A.; Pitman, A.R. Novel mitoviruses in Rhizoctonia solani AG-3PT infecting potato. Fungal Biol. 2016, 120, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzano, S.-Y.L.; Nelson, B.D.; Ajayi-Oyetunde, O.; Bradley, C.A.; Hughes, T.J.; Hartman, G.L.; Eastburn, D.M.; Domier, L.L. Identification of diverse mycoviruses through metatranscriptomics characterization of the viromes of five major fungal plant pathogens. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 6846–6863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, E.E.; Lakshman, D.K.; Tavantzis, S.M. Molecular characterization of the genome of a partitivirus from the basidiomycete Rhizoctonia solani. J. Gen. Virol. 2000, 81, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S. Rhizoctonia Solani on Potato in New Zealand: Pathogen Characterisation and Identification of Double-Stranded RNA Viruses that may Affect their Virulence. Ph.D. Thesis, Lincoln University, Lincoln, New Zealand, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Jian, J.; Lakshman, D.K.; Tavantzis, S.M. Association of distinct double-stranded RNAs with enhanced or diminished virulence in Rhizoctonia solani infecting potato. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact 1997, 10, 1002–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, M.; Yu, J.; Kim, K.-H. Five questions about mycoviruses. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, A. A Review Paper on Mycoviruses. J. Plant Pathol. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotta-Loizou, I.; Coutts, R.H. Mycoviruses in Aspergilli: A comprehensive review. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Li, B.; Fu, Y.; Jiang, D.; Ghabrial, S.A.; Li, G.; Peng, Y.; Xie, J.; Cheng, J.; Huang, J. A geminivirus-related DNA mycovirus that confers hypovirulence to a plant pathogenic fungus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 8387–8392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco, L.; Arjona-Girona, I.; Cretazzo, E.; López-Herrera, C. Viromes in Xylariaceae fungi infecting avocado in Spain. Virology 2019, 532, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-H.; Fujita, M.; Chiba, S.; Hyodo, K.; Andika, I.B.; Suzuki, N.; Kondo, H. Two novel fungal negative-strand RNA viruses related to mymonaviruses and phenuiviruses in the shiitake mushroom (Lentinula edodes). Virology 2019, 533, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerva, L.; Forgia, M.; Ciuffo, M.; Chitarra, W.; Chiapello, M.; Vallino, M.; Varese, G.; Turina, M. The mycovirome of a fungal collection from the sea cucumber Holothuria polii. Virus Res. 2019, 273, 197737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, F.; Wu, M.; Li, G. Molecular characterization and geographic distribution of a mymonavirus in the population of Botrytis cinerea. Viruses 2018, 10, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, F.; Xie, J.; Cheng, S.; You, M.P.; Barbetti, M.J.; Jia, J.; Wang, Q.; Cheng, J.; Fu, Y.; Chen, T. Virome Characterization of a Collection of S. sclerotiorum from Australia. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; He, H.; Wang, S.; Chen, X.; Qiu, D.; Kondo, H.; Guo, L. Evidence for a novel negative-stranded RNA mycovirus isolated from the plant pathogenic fungus Fusarium graminearum. Virology 2018, 518, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaire, L.; Pagán, I.; Ayllón, M.A. Characterization of Botrytis cinerea negative-stranded RNA virus 1, a new mycovirus related to plant viruses, and a reconstruction of host pattern evolution in negative-sense ssRNA viruses. Virology 2016, 499, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osaki, H.; Sasaki, A.; Nomiyama, K.; Tomioka, K. Multiple virus infection in a single strain of Fusarium poae shown by deep sequencing. Virus Genes 2016, 52, 835–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zheng, L.; Liu, C.; Shu, C.; Zhou, E. Characterization of a novel dsRNA mycovirus isolated from strain A105 of Rhizoctonia solani AG-1 IA. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Zeng, M.; Zhang, M.; Shu, C.; Zhou, E. Complete nucleotide sequence of a partitivirus from Rhizoctonia solani AG-1 IA strain C24. Viruses 2018, 10, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gai, X.T.; Chen, R.X.; Li, C.X.; Zhao, G.K.; Xia, Z.Y.; Zou, C.M.; Zhong, J. Characterization of three novel betapartitiviruses co-infecting the phytopathogenic fungus Rhizoctonia solani. Virus Res. 2019, 270, 197649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, Q.; Li, Y.; Cheng, J.; Fu, Y.; Chen, T.; Jiang, D.; Xie, J. Two alphapartitiviruses co-infecting a single isolate of the plant pathogenic fungus Rhizoctonia solani. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Shu, C.; Zhang, M.; Yang, M.; Zhou, E. Molecular Characterization of a Novel Endornavirus Conferring Hypovirulence in Rice Sheath Blight Fungus Rhizoctonia solani AG-1 IA Strain GD-2. Viruses 2019, 11, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshman, D.K.; Jian, J.; Tavantzis, S.M. A double-stranded RNA element from a hypovirulent strain of Rhizoctonia solani occurs in DNA form and is genetically related to the pentafunctional AROM protein of the shikimate pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 6425–6429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshman, D.; Tavantzis, S. Spontaneous appearance of genetically distinct double-stranded RNA elements in Rhizoctonia solani. Phytopathol 1994, 84, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Dong, K.; Zhou, L.; Wang, G.; Hong, N.; Jiang, D.; Xu, W. A dsRNA virus with filamentous viral particles. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghabrial, S.A.; Castón, J.R.; Jiang, D.; Nibert, M.L.; Suzuki, N. 50-plus years of fungal viruses. Virology 2015, 479, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, S.K.; Lo, G.C.; Chow, F.W.; Fan, R.Y.; Cai, J.J.; Yuen, K.-Y.; Woo, P.C. Novel Partitivirus Enhances Virulence of and Causes Aberrant Gene Expression in Talaromyces marneffei. mBio 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Depierreux, D.; Vong, M.; Nibert, M.L. Nucleotide sequence of Zygosaccharomyces bailii virus Z: Evidence for+ 1 programmed ribosomal frameshifting and for assignment to family Amalgaviridae. Virus Res. 2016, 217, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilmer, D.; Ratti, C.; Consortium, I.R. ICTV Virus taxonomy profile: Benyviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Jin, F.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L.; Jiang, D.; Li, G. Characterization of a novel bipartite double-stranded RNA mycovirus conferring hypovirulence in the phytopathogenic fungus Botrytis porri. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 6605–6619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, L.; Zhang, M.; Hong, N.; Xiao, F.; Fu, M.; Xiang, J.; Wang, G. Identification and characterization of a novel hepta-segmented dsRNA virus from the phytopathogenic fungus Colletotrichum fructicola. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanhayuwa, L.; Kotta-Loizou, I.; Özkan, S.; Gunning, A.P.; Coutts, R.H. A novel mycovirus from Aspergillus fumigatus contains four unique dsRNAs as its genome and is infectious as dsRNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 9100–9105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotta-Loizou, I.; Coutts, R.H. Studies on the virome of the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana reveal novel dsRNA elements and mild hypervirulence. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Jiang, D. New insights into mycoviruses and exploration for the biological control of crop fungal diseases. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2014, 52, 45–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Miyazaki, N.; Kanematsu, S.; Xie, J.; Ghabrial, S.A.; Hillman, B.I.; Suzuki, N.; Consortium, I.R. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Megabirnaviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2019, 100, 1269–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, S.; Salaipeth, L.; Lin, Y.-H.; Sasaki, A.; Kanematsu, S.; Suzuki, N. A novel bipartite double-stranded RNA mycovirus from the white root rot fungus Rosellinia necatrix: Molecular and biological characterization, taxonomic considerations, and potential for biological control. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 12801–12812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanematsu, S.; Shimizu, T.; Salaipeth, L.; Yaegashi, H.; Sasaki, A.; Ito, T.; Suzuki, N. Genome rearrangement of a mycovirus Rosellinia necatrix megabirnavirus 1 affecting its ability to attenuate virulence of the host fungus. Virology 2014, 450, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Sun, X.; Cheng, J.; Fu, Y.; Liu, H.; Jiang, D.; Ghabrial, S.A.; Xie, J. Characterization of a novel megabirnavirus from Sclerotinia sclerotiorum reveals horizontal gene transfer from single-stranded RNA virus to double-stranded RNA virus. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 8567–8579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, A.; Nakamura, H.; Suzuki, N.; Kanematsu, S. Characterization of a new megabirnavirus that confers hypovirulence with the aid of a co-infecting partitivirus to the host fungus, Rosellinia necatrix. Virus Res. 2016, 219, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nerva, L.; Ciuffo, M.; Vallino, M.; Margaria, P.; Varese, G.; Gnavi, G.; Turina, M. Multiple approaches for the detection and characterization of viral and plasmid symbionts from a collection of marine fungi. Virus Res. 2016, 219, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrzik, K.; Sarkisova, T.; Starý, J.; Koloniuk, I.; Hrabáková, L.; Kubešová, O. Molecular characterization of a new monopartite dsRNA mycovirus from mycorrhizal Thelephora terrestris (Ehrh.) and its detection in soil oribatid mites (Acari: Oribatida). Virology 2016, 489, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vainio, E.J.; Chiba, S.; Ghabrial, S.A.; Maiss, E.; Roossinck, M.; Sabanadzovic, S.; Suzuki, N.; Xie, J.; Nibert, M. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Partitiviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2018, 99, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiba, K.; Hatta, C.; Sasai, S.; Tojo, M.; Ohki, S.T.; Mochizuki, T. Genome sequence of a novel partitivirus identified from the oomycete Pythium nunn. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 2561–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Cheng, J.; Tang, J.; Fu, Y.; Jiang, D.; Baker, T.S.; Ghabrial, S.A.; Xie, J. A novel partitivirus that confers hypovirulence on plant pathogenic fungi. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 10120–10133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, J.; Lakshman, D.K.; Tavantzis, S.M. A virulence-associated, 6.4-kb, double-stranded RNA from Rhizoctonia solani is phylogenetically related to plant bromoviruses and electron transport enzymes. Mol. Plant. Microbe Interact. 1998, 11, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoll, J.; Verweij, P.E.; Melchers, W.J. Discovery and characterization of novel Aspergillus fumigatus mycoviruses. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usui, K.; Ichihashi, N.; Yomo, T. A design principle for a single-stranded RNA genome that replicates with less double-strand formation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 8033–8043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baltimore, D. Expression of animal virus genomes. Bacteriol. Rev. 1971, 35, 235. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koonin, E.V.; Dolja, V.V.; Morris, T.J. Evolution and taxonomy of positive-strand RNA viruses: Implications of comparative analysis of amino acid sequences. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1993, 28, 375–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reguera, J.; Gerlach, P.; Cusack, S. Towards a structural understanding of RNA synthesis by negative strand RNA viral polymerases. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2016, 36, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; He, H.; Yang, X.; Zeng, H.; Qiu, D.; Guo, L. The complete genome sequence of a novel Fusarium graminearum RNA virus in a new proposed family within the order Tymovirales. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 2899–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, A.J. Journal of General Virology–Introduction to ‘ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profiles’. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xie, J.; Cheng, J.; Fu, Y.; Li, G.; Yi, X.; Jiang, D. Fungal negative-stranded RNA virus that is related to bornaviruses and nyaviruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 12205–12210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revill, P.A.; Davidson, A.D.; Wright, P.J. The nucleotide sequence and genome organization of mushroom bacilliform virus: A single-stranded RNA virus of Agaricus bisporus (Lange) Imbach. Virology 1994, 202, 904–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, M.; Kiguchi, T.; Kusume, T.; Tamada, T. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Japanese isolate S of beet necrotic yellow vein virus RNA and comparison with European isolates. Arch. Virol. 1996, 141, 2163–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, H.; Hirano, S.; Chiba, S.; Andika, I.B.; Hirai, M.; Maeda, T.; Tamada, T. Characterization of burdock mottle virus, a novel member of the genus Benyvirus, and the identification of benyvirus-related sequences in the plant and insect genomes. Virus Res. 2013, 177, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turina, M.; Hillman, B.I.; Izadpanah, K.; Rastgou, M.; Rosa, C.; Consortium, I.R. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Ourmiavirus. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sztuba-Solińska, J.; Bujarski, J.J. Insights into the single-cell reproduction cycle of members of the family Bromoviridae: Lessons from the use of protoplast systems. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 10330–10340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, A.M.; Lefkowitz, E.; Adams, M.J.; Carstens, E.B. Virus Taxonomy: Ninth Report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 9. [Google Scholar]
- Sabanadzovic, S.; Ghanem-Sabanadzovic, N.A.; Tzanetakis, I.E. Blackberry virus E: An unusual flexivirus. Arch. Virol. 2011, 156, 1665–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanem-Sabanadzovic, N.A.; Tzanetakis, I.E.; Sabanadzovic, S. Rubus canadensis virus 1, a novel betaflexivirus identified in blackberry. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howitt, R.L.; Beever, R.E.; Pearson, M.N.; Forster, R.L. Genome characterization of Botrytis virus F, a flexuous rod-shaped mycovirus resembling plant ‘potex-like’viruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2001, 82, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zheng, D.; Cheng, J.; Chen, T.; Fu, Y.; Jiang, D.; Xie, J. Characterization of a novel Sclerotinia sclerotiorum RNA virus as the prototype of a new proposed family within the order Tymovirales. Virus Res. 2016, 219, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzano, S.-Y.L.; Domier, L.L. Novel mycoviruses discovered from metatranscriptomics survey of soybean phyllosphere phytobiomes. Virus Res. 2016, 213, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, J.; Tangudu, C.S.; Hurt, S.L.; Tumescheit, C.; Firth, A.E.; Garcia-Rejon, J.E.; Machain-Williams, C.; Blitvich, B.J. Discovery of a novel Tymoviridae-like virus in mosquitoes from Mexico. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 649–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde, R.A.; Khalifa, M.E.; Okada, R.; Fukuhara, T.; Sabanadzovic, S. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Endornaviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2019, 100, 1204–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roossinck, M.J.; Sabanadzovic, S.; Okada, R.; Valverde, R.A. The remarkable evolutionary history of endornaviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 2674–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, R.; Kiyota, E.; Moriyama, H.; Fukuhara, T.; Valverde, R.A. Molecular and biological properties of an endornavirus infecting winged bean (Psophocarpus tetragonolobus). Virus Genes 2017, 53, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Z.; Lin, W.; Qiu, P.; Liu, X.; Guo, L.; Wu, K.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Z. Complete sequence of a double-stranded RNA from the phytopathogenic fungus Erysiphe cichoracearum that might represent a novel endornavirus. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 2343–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, R.; Kiyota, E.; Moriyama, H.; Toshiyuki, F.; Valverde, R.A. A new endornavirus species infecting Malabar spinach, Basellaalba, L., Ed. Arch. Virol. 2014, 159, 807–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, R.; Yong, C.K.; Valverde, R.A.; Sabanadzovic, S.; Aoki, N.; Hotate, S.; Kiyota, E.; Moriyama, H.; Fukuhara, T. Molecular characterization of two evolutionarily distinct endornaviruses co-infecting common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris). J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, K.-i.; Nakamura, H.; Matsumoto, N. Hypovirulent strain of the violet root rot fungus Helicobasidium mompa. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2003, 69, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuomivirta, T.T.; Kaitera, J.; Hantula, J. A novel putative virus of Gremmeniella abietina type B (Ascomycota: Helotiaceae) has a composite genome with endornavirus affinities. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 2299–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, J.W.; Li, H.; Sivasithamparam, K.; Dixon, K.W.; Jones, M.G.; Wylie, S.J. Novel Endorna-like viruses, including three with two open reading frames, challenge the membership criteria and taxonomy of the Endornaviridae. Virology 2016, 499, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchler-Bauer, A.; Lu, S.; Anderson, J.B.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; DeWeese-Scott, C.; Fong, J.H.; Geer, L.Y.; Geer, R.C.; Gonzales, N.R. CDD: A Conserved Domain Database for the functional annotation of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 39, D225–D229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, T.; Sun, H.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, A.; Chen, H.; Wang, K. Complete genome sequence of a novel endornavirus in the wheat sharp eyespot pathogen Rhizoctonia cerealis. Arch. Virol. 2014, 159, 1213–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, N.; Ghabrial, S.A.; Kim, K.-H.; Pearson, M.; Marzano, S.-Y.L.; Yaegashi, H.; Xie, J.; Guo, L.; Kondo, H.; Koloniuk, I. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Hypoviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2018, 99, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapira, R.; Choi, G.H.; Nuss, D.L. Virus-like genetic organization and expression strategy for a double-stranded RNA genetic element associated with biological control of chestnut blight. EMBO J. 1991, 10, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillman, B.I.; Halpern, B.T.; Brown, M.P. A viral dsRNA element of the chestnut blight fungus with a distinct genetic organization. Virology 1994, 201, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smart, C.; Yuan, W.; Foglia, R.; Nuss, D.; Fulbright, D.; Hillman, B. Cryphonectria hypovirus 3, a virus species in the family Hypoviridae with a single open reading frame. Virology 1999, 265, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linder-Basso, D.; Dynek, J.N.; Hillman, B.I. Genome analysis of Cryphonectria hypovirus 4, the most common hypovirus species in North America. Virology 2005, 337, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Xiao, X.; Fu, Y.; Liu, H.; Cheng, J.; Ghabrial, S.A.; Li, G.; Jiang, D. A novel mycovirus closely related to hypoviruses that infects the plant pathogenic fungus Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Virology 2011, 418, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulia, A.; Andika, I.B.; Kondo, H.; Hillman, B.I.; Suzuki, N. A symptomless hypovirus, CHV4, facilitates stable infection of the chestnut blight fungus by a coinfecting reovirus likely through suppression of antiviral RNA silencing. Virology 2019, 533, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, M.E.; Pearson, M.N. Characterisation of a novel hypovirus from Sclerotinia sclerotiorum potentially representing a new genus within the Hypoviridae. Virology 2014, 464, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, S.; Chiba, S.; Kondo, H.; Kanematsu, S.; Suzuki, N. A novel single-stranded RNA virus isolated from a phytopathogenic filamentous fungus, Rosellinia necatrix, with similarity to hypo-like viruses. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Mao, J.; Yang, Z.; Cao, Q.; Zhang, T.; Wang, S.; Liu, D. Characterization of two novel mycoviruses from Penicillium digitatum and the related fungicide resistance analysis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruenn, J.A.; Warner, B.E.; Yerramsetty, P. Widespread mitovirus sequences in plant genomes. PeerJ 2015, 3, e876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nerva, L.; Vigani, G.; Di Silvestre, D.; Ciuffo, M.; Forgia, M.; Chitarra, W.; Turina, M. Biological and Molecular Characterization of Chenopodium quinoa Mitovirus 1 Reveals a Distinct Small RNA Response Compared to Those of Cytoplasmic RNA Viruses. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e01998-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.-J.; Chan, D.; Xiang, Y.; Williams, H.; Li, X.-R.; Sniezko, R.A.; Sturrock, R.N. Characterization of Five Novel Mitoviruses in the White Pine Blister Rust Fungus Cronartium ribicola. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marais, A.; Nivault, A.; Faure, C.; Theil, S.; Comont, G.; Candresse, T.; Corio-Costet, M.-F. Determination of the complete genomic sequence of Neofusicoccum luteum mitovirus 1 (NLMV1), a novel mitovirus associated with a phytopathogenic Botryosphaeriaceae. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 2477–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turina, M.; Ghignone, S.; Astolfi, N.; Silvestri, A.; Bonfante, P.; Lanfranco, L. The virome of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Gigaspora margarita reveals the first report of DNA fragments corresponding to replicating non-retroviral RNA viruses in fungi. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 2012–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, H.; Liu, L.; Li, B.; Cheng, J.; Fu, Y.; Jiang, D.; Xie, J. Co-infection of a hypovirulent isolate of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum with a new botybirnavirus and a strain of a mitovirus. Virol. J. 2016, 13, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nibert, M.L.; Vong, M.; Fugate, K.K.; Debat, H.J. Evidence for contemporary plant mitoviruses. Virology 2018, 518, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volchkov, V.; Volchkova, V.; Netesov, S. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Eastern equine encephalomyelitis virus genome. Mol. Genet. Mikrobiol. Virusol. 1991, 5, 8–15. [Google Scholar]
- Netolitzky, D.J.; Schmaltz, F.L.; Parker, M.D.; Rayner, G.A.; Fisher, G.R.; Trent, D.W.; Bader, D.E.; Nagata, L.P. Complete genomic RNA sequence of western equine encephalitis virus and expression of the structural genes. J. Gen. Virol. 2000, 81, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinney, R.M.; Tsuchiya, K.R.; Sneider, J.M.; Trent, D.W. Genetic evidence that epizootic Venezuelan equine encephalitis (VEE) viruses may have evolved from enzootic VEE subtype ID virus. Virology 1992, 191, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, E.G.; Rice, C.M.; Strauss, J.H. Complete nucleotide sequence of the genomic RNA of Sindbis virus. Virology 1984, 133, 92–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faragher, S.; Meek, A.; Rice, C.; Dalgarno, L. Genome sequences of a mouse-avirulent and a mouse-virulent strain of Ross River virus. Virology 1988, 163, 509–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kääriäinen, L.; Takkinen, K.; Keränen, S.; Söderlund, H. Replication of the genome of alphaviruses. J. Cell Sci. 1987, 1987, 231–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.H.; Morita, K.; del Carmen Parquet, M.; Hasebe, F.; Mathenge, E.G.; Igarashi, A. Complete nucleotide sequence of chikungunya virus and evidence for an internal polyadenylation site. J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83, 3075–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contigiani, M.S.; Diaz, L.A. Togaviridae. In Arthropod Borne Diseases; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 115–135. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Merits, A.; Bolling, B.; Nasar, F.; Coffey, L.L.; Powers, A.; Weaver, S.C. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Togaviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2018, 99, 761–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Jose, J.; Xiang, Y.; Kuhn, R.J.; Rossmann, M.G. Structural changes of envelope proteins during alphavirus fusion. Nature 2010, 468, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, M.L.; Dal Bó, E.; da Graça, J.V.; Gago-Zachert, S.; Hammond, J.; Moreno, P.; Natsuaki, T.; Pallás, V.; Navarro, J.A.; Reyes, C.A. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Ophioviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feau, N.; Dutech, C.; Brusini, J.; Rigling, D.; Robin, C. Multiple introductions and recombination in C ryphonectria hypovirus 1: Perspective for a sustainable biological control of chestnut blight. Evol. Appl. 2014, 7, 580–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusini, J.; Robin, C. Mycovirus transmission revisited by in situ pairings of vegetatively incompatible isolates of Cryphonectria parasitica. J. Virol. Methods 2013, 187, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilio, G.; Thiévent, K.; Koella, J.C. Host genotype and environment affect the trade-off between horizontal and vertical transmission of the parasite Edhazardia aedis. BMC Evol. Biol. 2018, 18, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, A.; Saldierna Guzmán, J.; Shay, J. Transmission of bacterial endophytes. Microorganisms 2017, 5, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawe, A.L.; Nuss, D.L. Hypovirus molecular biology: From Koch’s postulates to host self-recognition genes that restrict virus transmission. In Advances in Virus Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 86, pp. 109–147. [Google Scholar]
- Moleleki, N.; van Heerden, S.W.; Wingfield, M.J.; Wingfield, B.D.; Preisig, O. Transfection of Diaporthe perjuncta with Diaporthe RNA virus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 3952–3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihrmark, K.; Stenström, E.; Stenlid, J. Double-stranded RNA transmission through basidiospores of Heterobasidion annosum. Mycol. Res. 2004, 108, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, M.N.; Beever, R.E.; Boine, B.; Arthur, K. Mycoviruses of filamentous fungi and their relevance to plant pathology. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2009, 10, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).