Metagenomic Analysis of Virioplankton from the Pelagic Zone of Lake Baikal
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Sequencing
2.2. Water Chemistry Analyses
2.3. Microbial Enumeration
2.4. Bioinformatics Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Environmental Characteristics
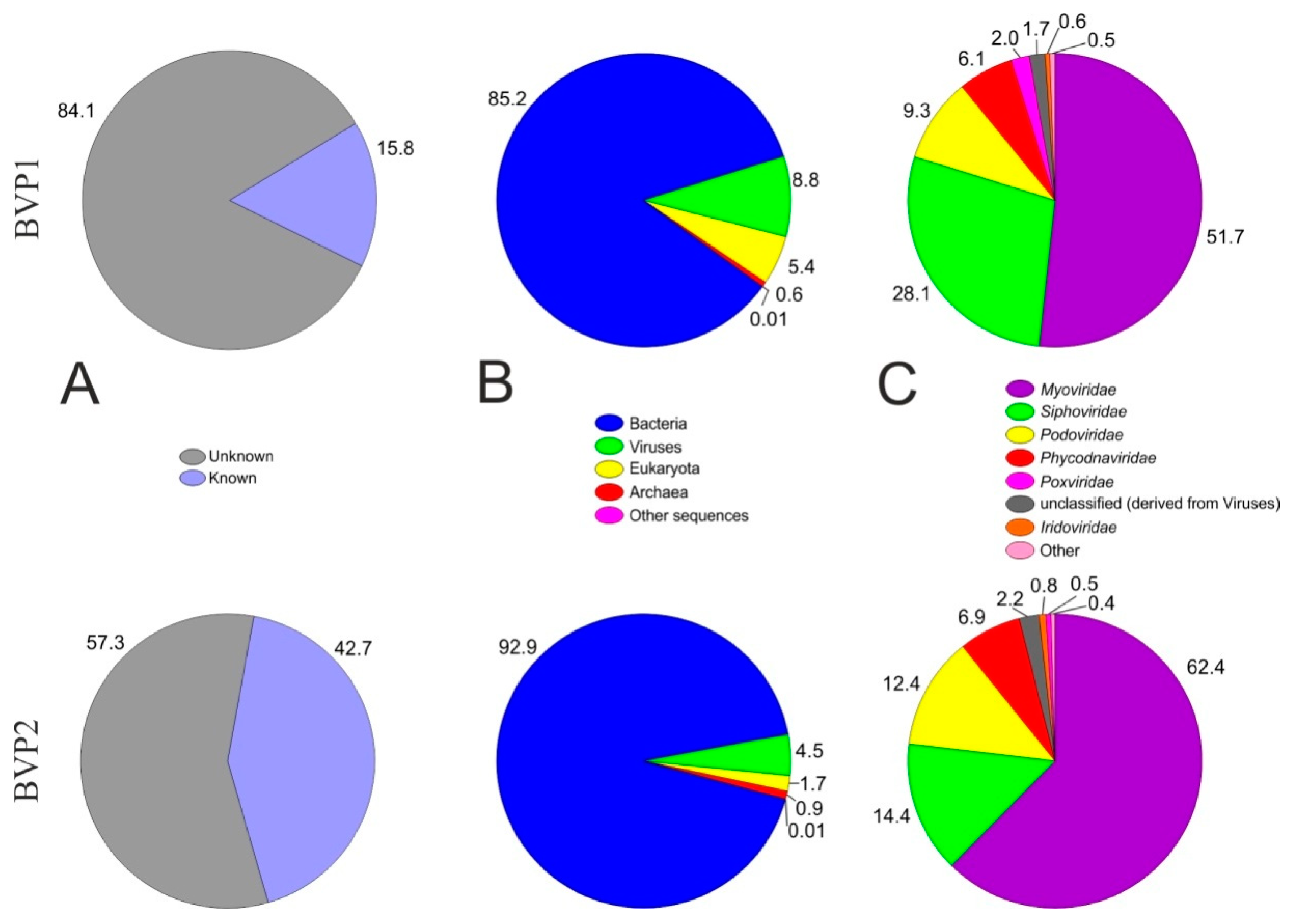
3.2. Overview of the Lake Baikal Virome
3.3. Taxonomic Composition
3.4. Analysis of Sequences at the Genus Level
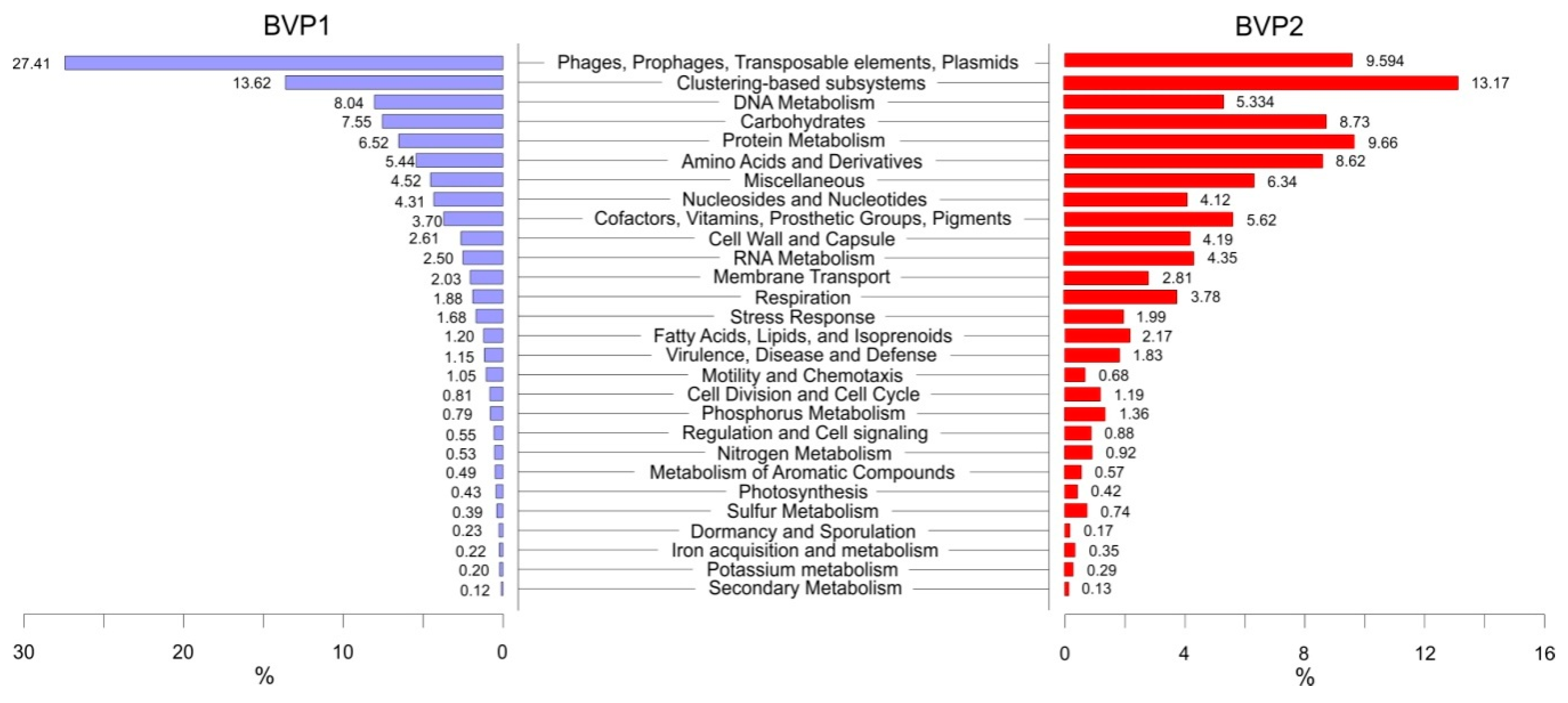
3.5. Functional Analysis
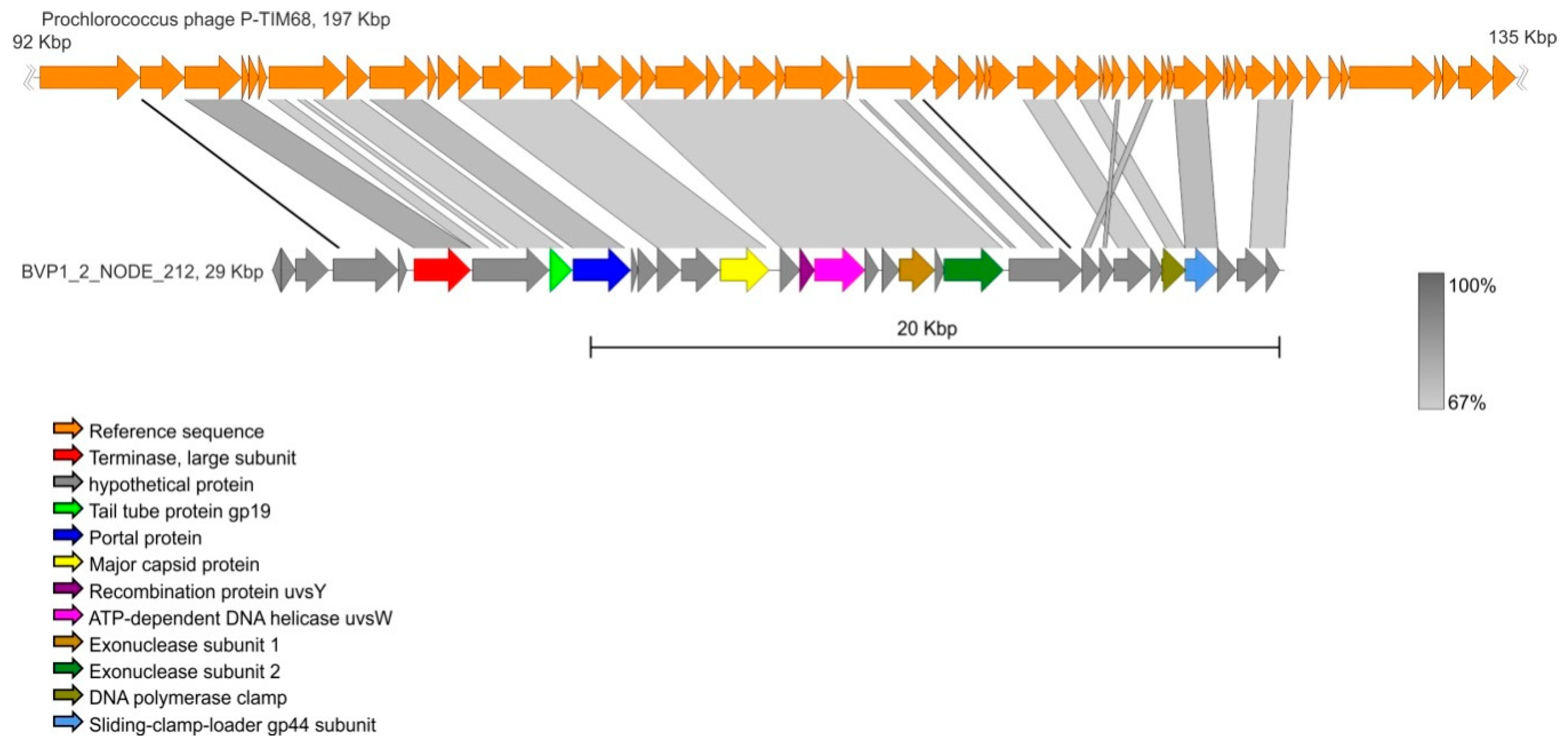
3.6. Contig Analysis
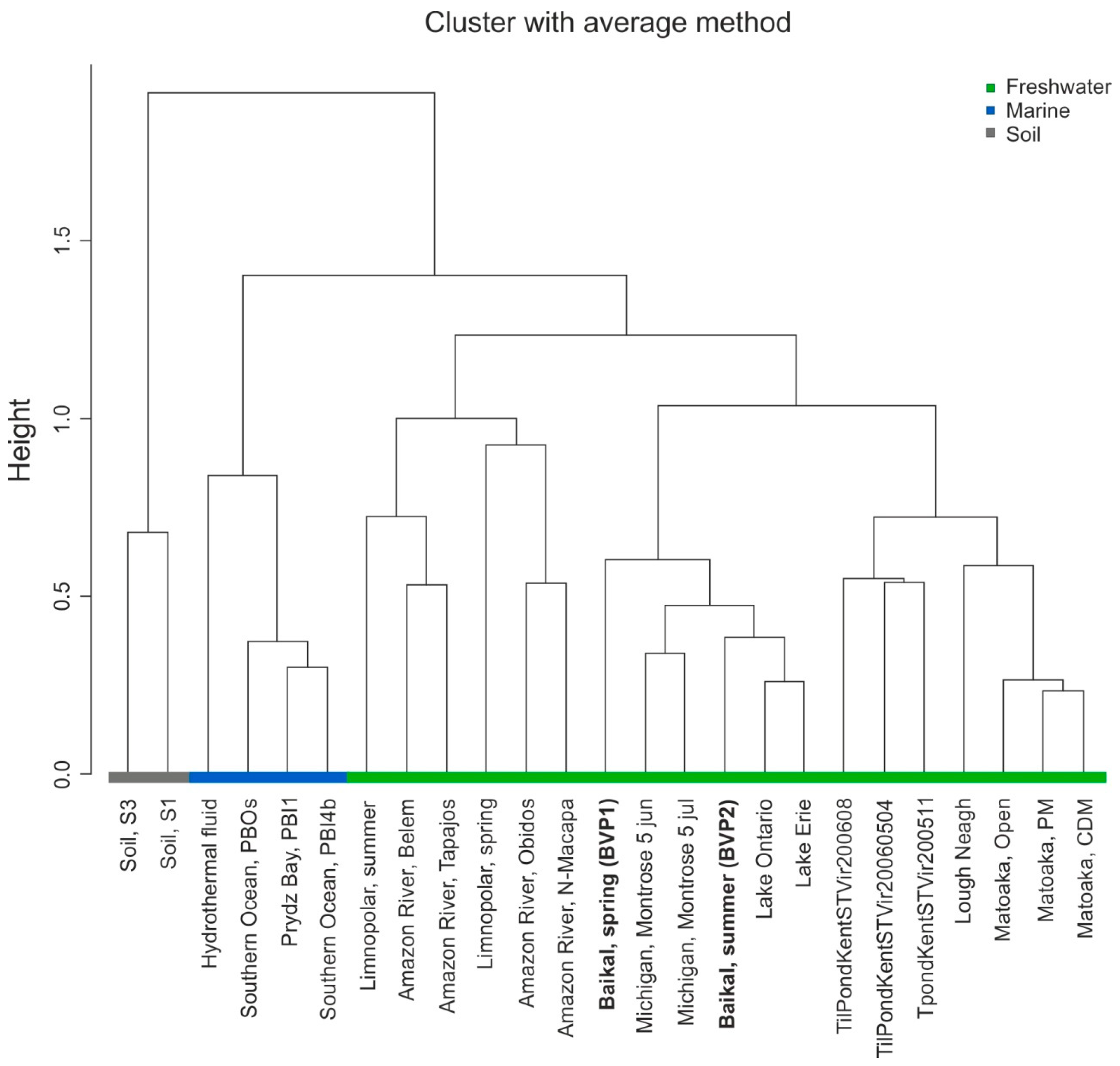
3.7. Comparative Analysis of Viromes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Steward, G.F.; Culley, A.I.; Mueller, J.A.; Wood-Charlson, E.M.; Belcaid, M.; Poisson, G. Are we missing half of the viruses in the ocean? ISME J. 2013, 7, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackermann, H.-W. Bacteriophages: Tailed. In Encyclopedia of Life Sciences; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Schwalbach, M.; Hewson, I.; Fuhrman, J. Viral effects on bacterial community composition in marine plankton microcosms. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2004, 34, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, N.J.; Wilson, W.H.; Joint, I.R.; Mann, N.H. Occurrence of a sequence in marine cyanophages similar to that of T4 g20 and its application to PCR-based detection and quantification techniques. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 2051–2060. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Chen, F.; Wilhelm, S.W.; Poorvin, L.; Hodson, R.E. phylogenetic diversity of marine cyanophage isolates and natural virus communities as revealed by sequences of viral capsid assembly protein gene g20. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 1576–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filee, J.; Tetart, F.; Suttle, C.A.; Krisch, H.M. Marine T4-type bacteriophages, a ubiquitous component of the dark matter of the biosphere. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 12471–12476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitbart, M.; Miyake, J.H.; Rohwer, F. Global distribution of nearly identical phage-encoded DNA sequences. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2004, 236, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Suttle, C.A. Amplification of DNA polymerase gene fragments from viruses infecting microalgae. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 1274–1278. [Google Scholar]
- Culley, A.I.; Lang, A.S.; Suttle, C.A. High diversity of unknown picorna-like viruses in the sea. Nature 2003, 424, 1054–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culley, A.I.; Mueller, J.A.; Belcaid, M.; Wood-Charlson, E.M.; Poisson, G.; Steward, G.F. The characterization of rna viruses in tropical seawater using targeted PCR and metagenomics. mBio 2014, 5, e01210–e01214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinsdale, E.A.; Edwards, R.A.; Hall, D.; Angly, F.; Breitbart, M.; Brulc, J.M.; Furlan, M.; Desnues, C.; Haynes, M.; Li, L.; et al. Functional metagenomic profiling of nine biomes. Nature 2008, 452, 629–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djikeng, A.; Kuzmickas, R.; Anderson, N.G.; Spiro, D.J. Metagenomic analysis of RNA viruses in a fresh water lake. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Bueno, A.; Tamames, J.; Velázquez, D.; Moya, A.; Quesada, A.; Alcamí, A. High diversity of the viral community from an Antarctic lake. Science 2009, 326, 858–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Brito, B.; Li, L.; Wegley, L.; Furlan, M.; Angly, F.; Breitbart, M.; Buchanan, J.; Desnues, C.; Dinsdale, E.; Edwards, R.; et al. Viral and microbial community dynamics in four aquatic environments. ISME J. 2010, 4, 739–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roux, S.; Enault, F.; Robin, A.; Ravet, V.; Personnic, S.; Theil, S.; Colombet, J.; Sime-Ngando, T.; Debroas, D. Assessing the diversity and specificity of two freshwater viral communities through metagenomics. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fancello, L.; Trape, S.; Robert, C.; Boyer, M.; Popgeorgiev, N.; Raoult, D.; Desnues, C. Viruses in the desert: A metagenomic survey of viral communities in four perennial ponds of the Mauritanian Sahara. ISME J. 2012, 7, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.-H.; Chiang, P.-W.; Shiah, F.-K.; Chen, Y.-L.; Liou, J.-R.; Hsu, T.-C.; Maheswararajah, S.; Saeed, I.; Halgamuge, S.; Tang, S.-L. Microbial and viral metagenomes of a subtropical freshwater reservoir subject to climatic disturbances. ISME J. 2013, 7, 2374–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Wu, L.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Z. Viral metagenomics analysis of planktonic viruses in East Lake, Wuhan, China. Virol. Sin. 2013, 28, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre de Cárcer, D.; López-Bueno, A.; Pearce, D.A.; Alcamí, A. Biodiversity and distribution of polar freshwater DNA viruses. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1400127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohiuddin, M.; Schellhorn, H.E. Spatial and temporal dynamics of virus occurrence in two freshwater lakes captured through metagenomic analysis. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, J.C.; Rahman, F.; Saxton, M.A.; Williamson, K.E. Metagenomic assessment of viral diversity in lake matoaka, a temperate, eutrophic freshwater lake in southeastern Virginia, USA. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 75, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, S.C.; Kuehnle, N.; Ruggeri, C.A.; Malki, K.; Bruder, K.; Elayyan, J.; Damisch, K.; Vahora, N.; O’Malley, P.; Ruggles-Sage, B.; et al. Assessment of a metaviromic dataset generated from nearshore Lake Michigan. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2016, 67, 1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skvortsov, T.; De Leeuwe, C.; Quinn, J.P.; McGrath, J.W.; Allen, C.C.R.; McElarney, Y.; Watson, C.; Arkhipova, K.; Lavigne, R.; Kulakov, L.A. Metagenomic characterisation of the viral community of lough neagh, the largest freshwater lake in Ireland. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arkhipova, K.; Skvortsov, T.; Quinn, J.P.; McGrath, J.W.; Allen, C.C.R.; Dutilh, B.E.; McElarney, Y.; Kulakov, L.A. Temporal dynamics of uncultured viruses: A new dimension in viral diversity. ISME J. 2018, 12, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butina, T.V.; Potapov, S.A.; Belykh, O.I.; Damdinsuren, N.; Choidash, B. Genetic diversity of the family Myoviridae cyanophages in Lake Baikal. Seriya Biologiya. Ekol. Izvestiya Irkutsk. Gos. Univ. 2012, 5, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Potapov, S.; Belykh, O.; Krasnopeev, A.; Gladkikh, A.; Kabilov, M.; Tupikin, A.; Butina, T. Assessing the diversity of the g23 gene of T4-like bacteriophages from Lake Baikal with high-throughput sequencing. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2018, 365, fnx264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butina, T.V.; Belykh, O.I.; Maksimenko, S.Y.; Belikov, S.I. Phylogenetic diversity of T4-like bacteriophages in Lake Baikal, East Siberia. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2010, 309, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kozhova, O.M.; Izmest’eva, L.R. Lake Baikal: Evolution and Biodiversity, 2nd ed.; Backhuys Publishers: Leiden, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Potapov, S.A.; Krasnopeev, A.Y.; Tikhonova, I.V.; Galachyants, A.D.; Podlesnaya, G.V.; Khanaev, I.V.; Belykh, O.I. Characterization of the genetic diversity of T4-like bacteriophages in benthic biofilms of Lake Baikal. Bull. Irkutsk State Univ. Ser. Biol. Ecol. 2018, 25, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butina, T.V.; Belykh, O.I.; Belikov, S.I. Molecular-genetic identification of T4 bacteriophages in Lake Baikal. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 433, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straškrábová, V.; Izmest’yeva, L.R.; Maksimova, E.A.; Fietz, S.; Nedoma, J.; Borovec, J.; Kobanova, G.I.; Shchetinina, E.V.; Pislegina, E.V. Primary production and microbial activity in the euphotic zone of Lake Baikal (Southern Basin) during late winter. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2005, 46, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovskaya, G. Ecological monitoring of phytoplankton in Lake Baikal. Aquat. Ecosyst. Heal. Manag. 2000, 3, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondarenko, N.A.; Ozersky, T.; Obolkina, L.A.; Tikhonova, I.V.; Sorokovikova, E.G.; Sakirko, M.V.; Potapov, S.A.; Blinov, V.V.; Zhdanov, A.A.; Belykh, O.I. Recent changes in the spring microplankton of Lake Baikal, Russia. Limnologica 2019, 75, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozhov, M.M. Biologiya ozera Baikal (Biology of Lake Baikal); Akad. Nauk SSSR: Moscow, Russia, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Thurber, R.V.; Haynes, M.; Breitbart, M.; Wegley, L.; Rohwer, F. Laboratory procedures to generate viral metagenomes. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 470–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brosius, J.; Dull, T.J.; Sleeter, D.D.; Noller, H.F. Gene organization and primary structure of a ribosomal RNA operon from Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol. 1981, 148, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, K.G.; Feig, Y.S. The use of DAPI for identifying and counting aquatic microflora1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1980, 25, 943–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, F.; Paarmann, D.; D’Souza, M.; Olson, R.; Glass, E.; Kubal, M.; Paczian, T.; Rodriguez, A.; Stevens, R.; Wilke, A.; et al. The metagenomics RAST server–a public resource for the automatic phylogenetic and functional analysis of metagenomes. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, S.; Enault, F.; Hurwitz, B.L.; Sullivan, M.B. VirSorter: Mining viral signal from microbial genomic data. PeerJ 2015, 3, e985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Lomsadze, A.; Borodovsky, M. Ab initio gene identification in metagenomic sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, M.J.; Petty, N.K.; Beatson, S.A. Easyfig: A genome comparison visualizer. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1009–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. Unpublished Work, The BWA-MEM Algorithm is Based on an Algorithm Finding Super-Maximal Exact Matches (SMEMs), Which was First Published with the Fermi Assembler Paper in 2012. Available online: http://bio-bwa.sourceforge.net/bwa.shtml (accessed on 28 October 2019).
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.T.; Thorvaldsdóttir, H.; Winckler, W.; Guttman, M.; Lander, E.S.; Getz, G.; Mesirov, J.P. Integrative genomics viewer. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mcminn, A.; Gong, Z.; Liang, Y.; Wang, M.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Xia, J. Viral diversity and its relationship with environmental factors at the surface and deep sea of Prydz Bay, Antarctica. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, B.S.; Coutinho, F.H.; Gregoracci, G.B.; Leomil, L.; Oliveira, L.S.; Froés, A.; Tschoeke, D.A.; Soares, A.C.; Cabral, A.S.; Ward, N.D.; et al. Virioplankton assemblage structure in the Lower River and ocean continuum of the Amazon. mSphere 2017, 2, e00366–e00417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; Han, L. Diversity and distribution characteristics of viruses in soils of a marine-terrestrial ecotone in East China. Microb. Ecol. 2018, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, R.; Abe, T.; Takeyama, H.; Naganuma, T. Metagenomic analysis of 0.2-μm-passable microorganisms in deep-sea hydrothermal fluid. Mar. Biotechnol. 2011, 13, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollenweider, R.A.; Kerekes, J. Eutrophication of waters. Monitoring Assessment and Control; OECD Coope.: Paris, France, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Guiry, M.D.; Guiry, G.M. AlgaeBase. World-Wide Electronic Publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. Available online: http://www.algaebase.org (accessed on 20 July 2018).
- Khodzher, T.V.; Domysheva, V.M.; Sorokovikova, L.M.; Sakirko, M.V.; Tomberg, I.V. Current chemical composition of Lake Baikal water. Inl. Waters 2017, 7, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potapov, S.A.; Butina, T.V.; Belykh, O.I. Mezhgodovaya dinamika chislennosti i vertikal’noye raspredeleniye virusnykh chastits v planktone oz. Baykal (The interannual dynamics and vertical distribution of virus-like particles of Lake Baikal). Monit. Syst. Environ. 2016, 6, 120–124. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, X.; Xiang, Q.; Tay, M.; Harn, S.; Saeidi, N.; Giek, S.; Kushmaro, A.; Thompson, J.R.; Gin, K.Y. Geospatial distribution of viromes in tropical freshwater ecosystems. Water Res. 2018, 137, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruder, K.; Malki, K.; Cooper, A.; Sible, E.; Shapiro, J.W.; Watkins, S.C.; Putonti, C. Freshwater metaviromics and bacteriophages: A current assessment of the state of the art in relation to Bioinformatic challenges. Evol. Bioinform. 2016, 12, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Bae, J.W. Amplification methods bias metagenomic libraries of uncultured single-stranded and double-stranded DNA viruses. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 7663–7668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, S.; Solonenko, N.E.; Dang, V.T.; Poulos, B.T.; Schwenck, S.M.; Goldsmith, D.B.; Coleman, M.L.; Breitbart, M.; Sullivan, M.B. Towards quantitative viromics for both double-stranded and single-stranded DNA viruses. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes, A.; Semenkovich, N.P.; Whiteson, K.; Rohwer, F.; Gordon, J.I. Going viral: Next-generation sequencing applied to phage populations in the human gut. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, M.B.; Coleman, M.L.; Weigele, P.; Rohwer, F.; Chisholm, S.W. Three Prochlorococcus cyanophage genomes: Signature features and ecological interpretations. PLoS Biol. 2005, 3, e144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mida, J.L.; Scavia, D.; Fahnenstiel, G.L.; Pothoven, S.A.; Vanderploeg, H.A.; Dolan, D.M. Long-term and recent changes in southern Lake Michigan water quality with implications for present trophic status. J. Great Lakes Res. 2010, 36, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, S.G.; Mendez, C.B.; Deng, L.; Poulos, B.; Kauffman, A.K.M.; Kern, S.; Brum, J.; Polz, M.F.; Boyle, E.A.; Sullivan, M.B. A simple and efficient method for concentration of ocean viruses by chemical flocculation. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2011, 3, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Water Property | BVP1 | BVP2 |
|---|---|---|
| Water temperature (°C) | 0.4–1.3 (0.75*) | 2.7–2.8 (2.76) |
| pH | 7.92–7.98 (7.95) | 7.75–7.82 (7.79) |
| Ntotal (mg/L) | 0.17–0.31 (0.23) | 0.20–0.34 (0.29) |
| Ptotal (µg/L) | 11–15 (13) | 10–12 (11) |
| TOC (mg/L) | 0.7–1.3 (1.07) | 1.7–1.9 (1.8) |
| NO2− (mg/L) | 0.001 (the entire layer) | 0.001–0.003 (0.002) |
| NO3− (mg/L) | 0.34–0.45 (0.39) | 0.37–0.40 (0.39) |
| O2 (mg/L) | 13.5–14.8 (14.3) | 12.6–12.8 (12.7) |
| PO43− (µg/L) | 24–40 (30) | 22–26 (24) |
| Chla (µg/L) | 0.65–3.42 (1.83) | 1.31–1.59 (1.40) |
| Viruses (VLPs mL−1) | 2 (±1) × 106 | 1.9 (±0.8) ×106 |
| Bacteria (cell mL−1) | 1.5 (±0.7) × 106 | 0.19 (±0.3) × 106 |
| Transparency, m | 11 | 16 |
| Sample | Raw Data | Uploaded to MG-RAST | Annotated, RefSeq | Sequences Containing Ribosomal RNA Genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BVP1 | 3223426 | 1474135 | 233310 | 929 |
| BVP2 | 4136035 | 1956295 | 835350 | 2675 |
| Virus Family | Primary Host | Relative Abundance (% of Viral Sequences) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BVP1 | BVP2 | ||
| Myoviridae | Bacteria | 51.7 | 62.4 |
| Siphoviridae | Bacteria | 28.1 | 14.4 |
| Podoviridae | Bacteria | 9.3 | 12.4 |
| Phycodnaviridae | Algae | 6.1 | 6.9 |
| Poxviridae | Birds, mammals, humans | 2 | 0.5 |
| Unclassified viruses | - | 1.7 | 2.2 |
| Iridoviridae | Insects, amphibians, fish, invertebrates | 0.5 | 0.8 |
| Unclassified (Caudovirales) | Bacteria | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Baculoviridae | Insects | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| Marseilleviridae | Amoeba | 0.08 | 0.09 |
| Microviridae | Bacteria | 0.02 | 0.003 |
| Nimaviridae | Crustaceans | 0.02 | 0.01 |
| Herpesviridae | Animals, including humans | 0.02 | 0.04 |
| Polydnaviridae | Insects | 0.02 | - |
| Ascoviridae | Invertebrates | 0.01 | 0.003 |
| Asfarviridae | Insects, pigs | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Lipothrixviridae | Archaea | 0.01 | 0.003 |
| Circoviridae | Birds, mammals | 0.005 | - |
| Parvoviridae | Warm-blooded animals, humans | 0.005 | - |
| Alloherpesviridae | Fish, amphibians | 0.005 | 0.008 |
| Sample | Number of Contigs Assembled | Max Length (bp) | Median | Number of Contigs ≥ 5 Kbp |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BVP1 | 25,5462 | 127,498 | 326 | 1383 |
| BVP2 | 388,735 | 1,129,755 | 425 | 3041 |
| BVP1_2 | 544,501 | 1,129,000 | 367 | 4438 |
| Contig | Length (bp) | Number of Identified Open Reading Frames (ORFs) | Best BLAST Hit Affiliation | Accession Number | % Identity | Query Cover (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BVP1_NODE_544 | 9190 | 8 | Yellowstone Lake virophage 7 | NC_028257 | 75.92 | 34 |
| BVP1_NODE_724 | 7752 | 9 | Pelagibacter phage HTVC010P | NC_020481 | 73.05 | 88 |
| BVP1_NODE_937 | 6565 | 8 | Synechococcus phage S-SM2 | NC_015279 | 70.20 | 89 |
| BVP1_NODE_1041 | 6082 | 6 | Synechococcus phage S-RIP2 | NC_020838 | 71.18 | 69 |
| BVP1_NODE_1110 | 5801 | 8 | Synechococcus phage S-SM2 | NC_015279 | 72.93 | 84 |
| BVP1_NODE_667 | 8107 | 18 | Synechococcus phage S-CBS4 | NC_016766 | 67.78 | 65 |
| BVP1_NODE_697 | 7967 | 12 | Flavobacterium phage 11b | NC_006356 | 71.85 | 48 |
| BVP1_NODE_1160 | 5626 | 12 | Staphylococcus phage G1 | NC_007066 | 99.77 | 99 |
| BVP1_NODE_1162 | 5621 | 7 | Synechococcus phage S-SM2 | NC_015279 | 72.23 | 82 |
| BVP1_NODE_1352 | 5081 | 9 | Staphylococcus phage Sb-1 | NC_023009 | 99.98 | 100 |
| BVP2_NODE_1582 | 7385 | 10 | Synechococcus phage S-SM2 | NC_015279 | 74.52 | 90 |
| BVP2_NODE_1722 | 7059 | 8 | Synechococcus phage S-SM2 | NC_015279 | 70.49 | 88 |
| BVP2_NODE_1766 | 6972 | 10 | Synechococcus phage S-CBS4 | NC_016766 | 72.36 | 55 |
| BVP2_NODE_2275 | 5991 | 4 | Prochlorococcus phage P-SSM2 | NC_006883 | 74.59 | 73 |
| BVP2_NODE_2795 | 5268 | 7 | Synechococcus phage S-SM2 | NC_015279 | 71.99 | 74 |
| BVP2_NODE_2816 | 5244 | 7 | Prochlorococcus phage P-SSM2 | NC_006883 | 73.91 | 81 |
| BVP2_NODE_3036 | 5004 | 7 | Pelagibacter phage HTVC010P | NC_020481 | 80.00 | 89 |
| BVP2_NODE_344 | 17331 | 10 | Synechococcus phage S-SM2 | NC_015279 | 72.75 | 55 |
| BVP2_NODE_721 | 11566 | 20 | Synechococcus phage S-CAM9 | NC_031922 | 67.18 | 40 |
| BVP2_NODE_969 | 9692 | 9 | Synechococcus phage S-SKS1 | NC_020851 | 70.84 | 82 |
| BVP1_2_NODE_831 | 13691 | 17 | Synechococcus phage S-SM2 | NC_015279 | 74.40 | 85 |
| BVP1_2_NODE_1425 | 10187 | 9 | Synechococcus phage S-SM2 | NC_015279 | 70.55 | 78 |
| BVP1_2_NODE_1820 | 8894 | 9 | Synechococcus phage S-RIP2 | NC_020838 | 71.18 | 55 |
| BVP1_2_NODE_3506 | 5863 | 11 | Synechococcus phage S-CBS4 | NC_016766 | 67.83 | 75 |
| BVP1_2_NODE_3812 | 5557 | 8 | Prochlorococcus phage P-SSM2 | NC_006883 | 73.86 | 83 |
| BVP1_2_NODE_212 | 29427 | 32 | Prochlorococcus phage P-TIM68 | NC_028955 | 68.58 | 64 |
| BVP1_2_NODE_496 | 18281 | 20 | Synechococcus phage S-SKS1 | NC_020851 | 65.93 | 27 |
| BVP1_2_NODE_721 | 14952 | 5 | Synechococcus phage S-SM2 | NC_015279 | 72.46 | 58 |
| BVP1_2_NODE_856 | 13532 | 12 | Synechococcus phage S-SKS1 | NC_020851 | 70.82 | 81 |
| BVP1_2_NODE_996 | 12347 | 17 | Pelagibacter phage HTVC010P | NC_020481 | 82.53 | 77 |
| Name | Trophic Level | Average Depth (m) | Area (km2) | Country | Sampling Data |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lake Michigan | oligotrophic | 279 281 (max) | 58,030 | USA | 06.13 07.13 |
| Lake Baikal | oligotrophic with mesotrophic characteristics | 744.7 1681 (max) | 31,722 | Russia | This study |
| Lake Erie | mesotrophic | 19 64 (max) | 25,700 | USA, Canada | 07.13 |
| Lake Ontario | oligo-mesotrophic | 86 244 (max) | 19,500 | USA, Canada | 06.13 |
| Lough Neagh | eutrophic | 9 31 (max) | 392 | Northern Ireland | 04.14 |
| Lake Matoaka | eutrophic | 2.5 4.75 (max) | 0.16 | USA | 03.13 |
| Lake Limnopolar | ultra-oligotrophic | 5.5 (max) | 0.02 | Antarctica | 11.06 01.07 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Potapov, S.A.; Tikhonova, I.V.; Krasnopeev, A.Y.; Kabilov, M.R.; Tupikin, A.E.; Chebunina, N.S.; Zhuchenko, N.A.; Belykh, O.I. Metagenomic Analysis of Virioplankton from the Pelagic Zone of Lake Baikal. Viruses 2019, 11, 991. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11110991
Potapov SA, Tikhonova IV, Krasnopeev AY, Kabilov MR, Tupikin AE, Chebunina NS, Zhuchenko NA, Belykh OI. Metagenomic Analysis of Virioplankton from the Pelagic Zone of Lake Baikal. Viruses. 2019; 11(11):991. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11110991
Chicago/Turabian StylePotapov, Sergey A., Irina V. Tikhonova, Andrey Yu. Krasnopeev, Marsel R. Kabilov, Aleksey E. Tupikin, Nadezhda S. Chebunina, Natalia A. Zhuchenko, and Olga I. Belykh. 2019. "Metagenomic Analysis of Virioplankton from the Pelagic Zone of Lake Baikal" Viruses 11, no. 11: 991. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11110991
APA StylePotapov, S. A., Tikhonova, I. V., Krasnopeev, A. Y., Kabilov, M. R., Tupikin, A. E., Chebunina, N. S., Zhuchenko, N. A., & Belykh, O. I. (2019). Metagenomic Analysis of Virioplankton from the Pelagic Zone of Lake Baikal. Viruses, 11(11), 991. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11110991






