Review on Outbreak Dynamics, the Endemic Serotypes, and Diversified Topotypic Profiles of Foot and Mouth Disease Virus Isolates in Ethiopia from 2008 to 2018
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Global View on FMD Serotypes and Strains
2.1. FMDV Type O
2.2. FMDV Type A
2.3. FMDV Type SATs
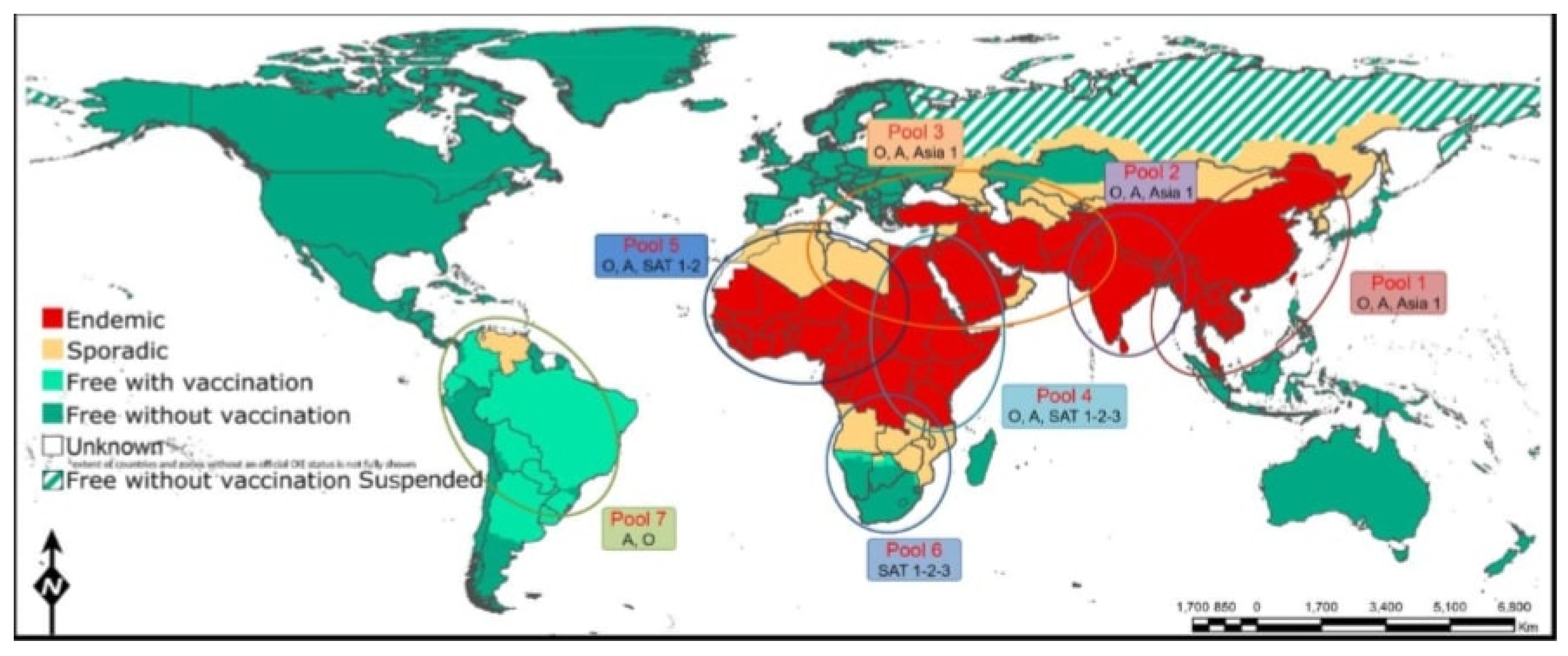
3. FMDV Serotypes Status on Sub-Sahara-African
4. Endemic Serotypes of FMDV in Ethiopia
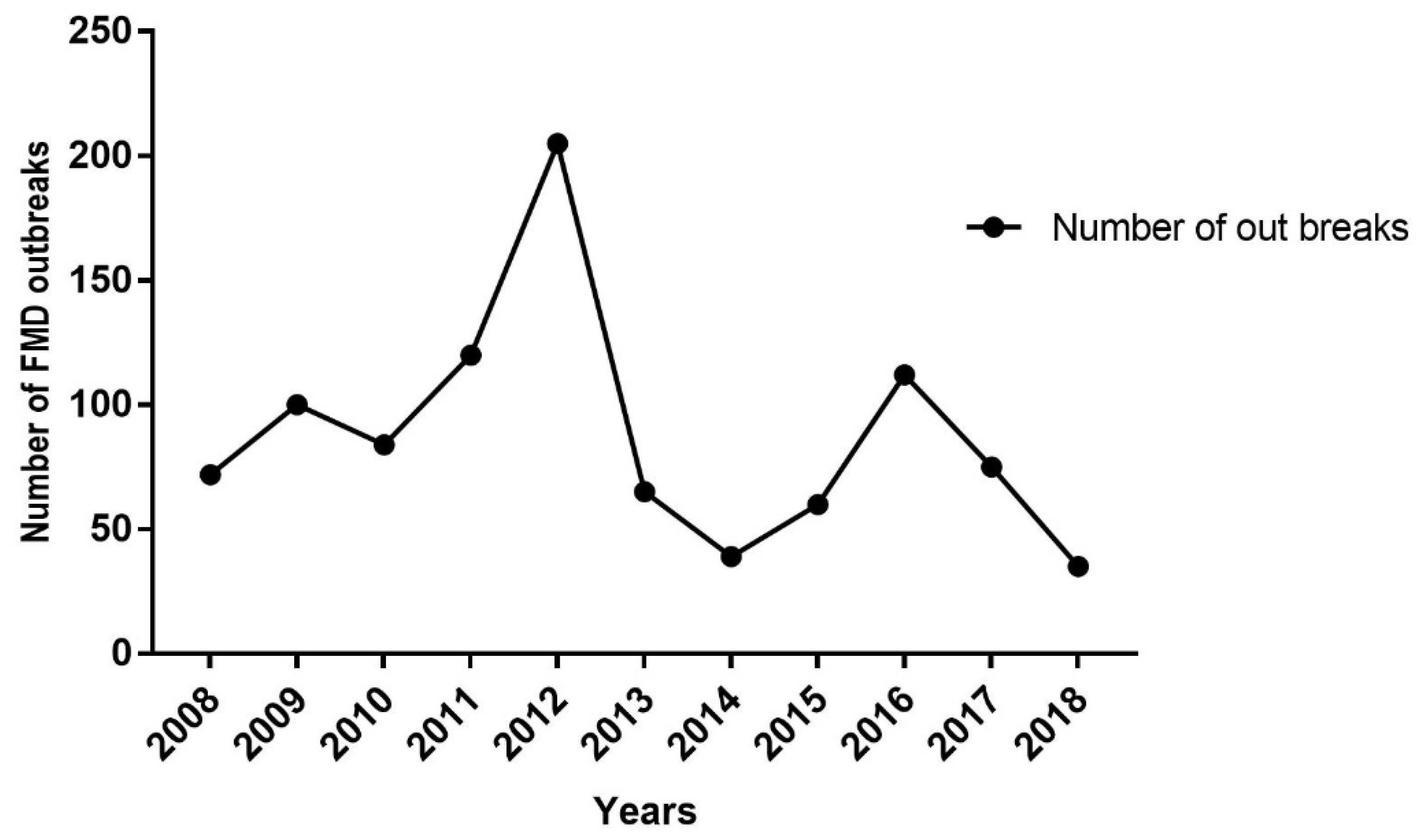
5. FMD Outbreak Dynamics in Ethiopia from 2008 to 2018
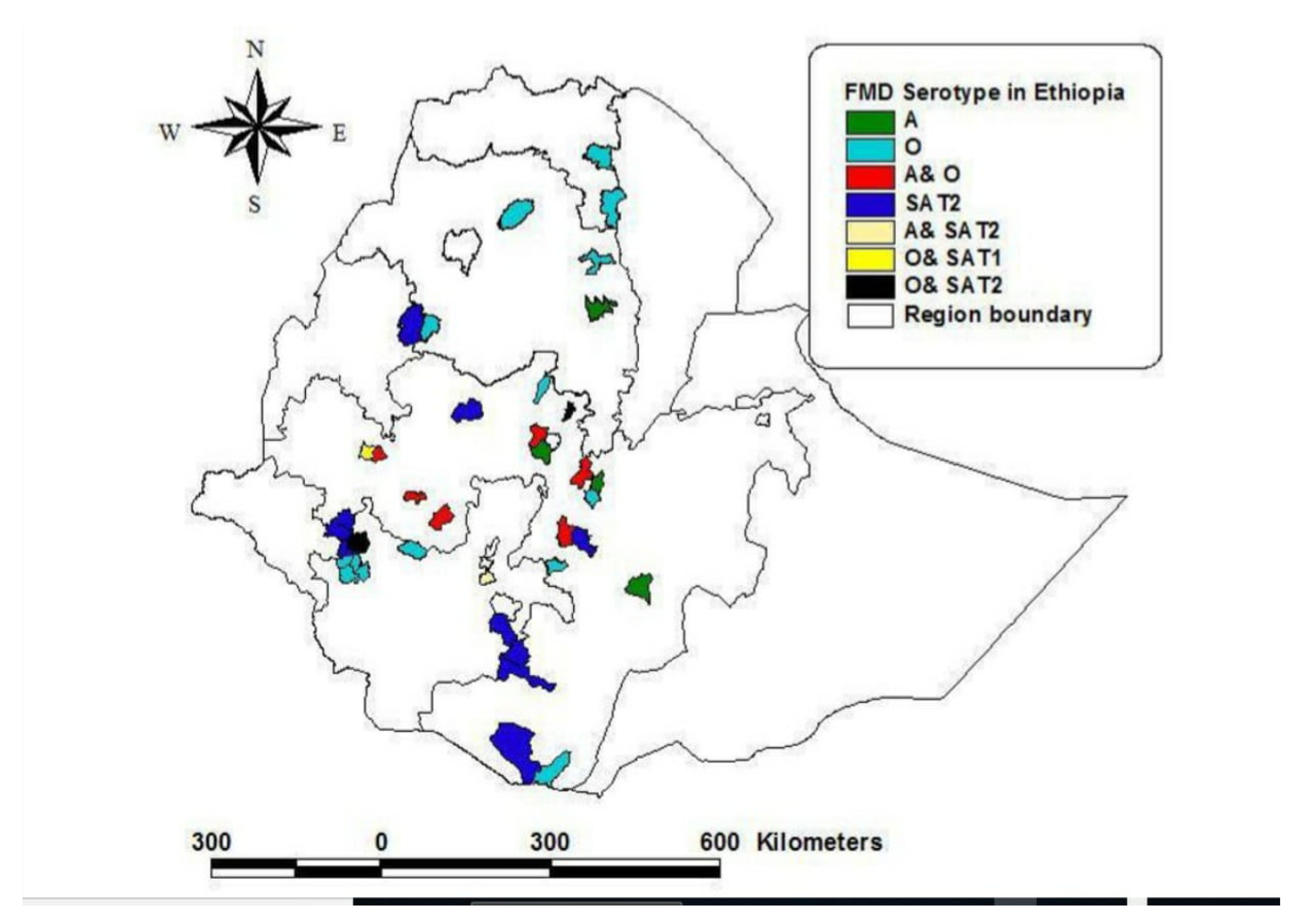
Topotypic Profiles of FMDV Serotypes in Ethiopia from 2008 to 2018
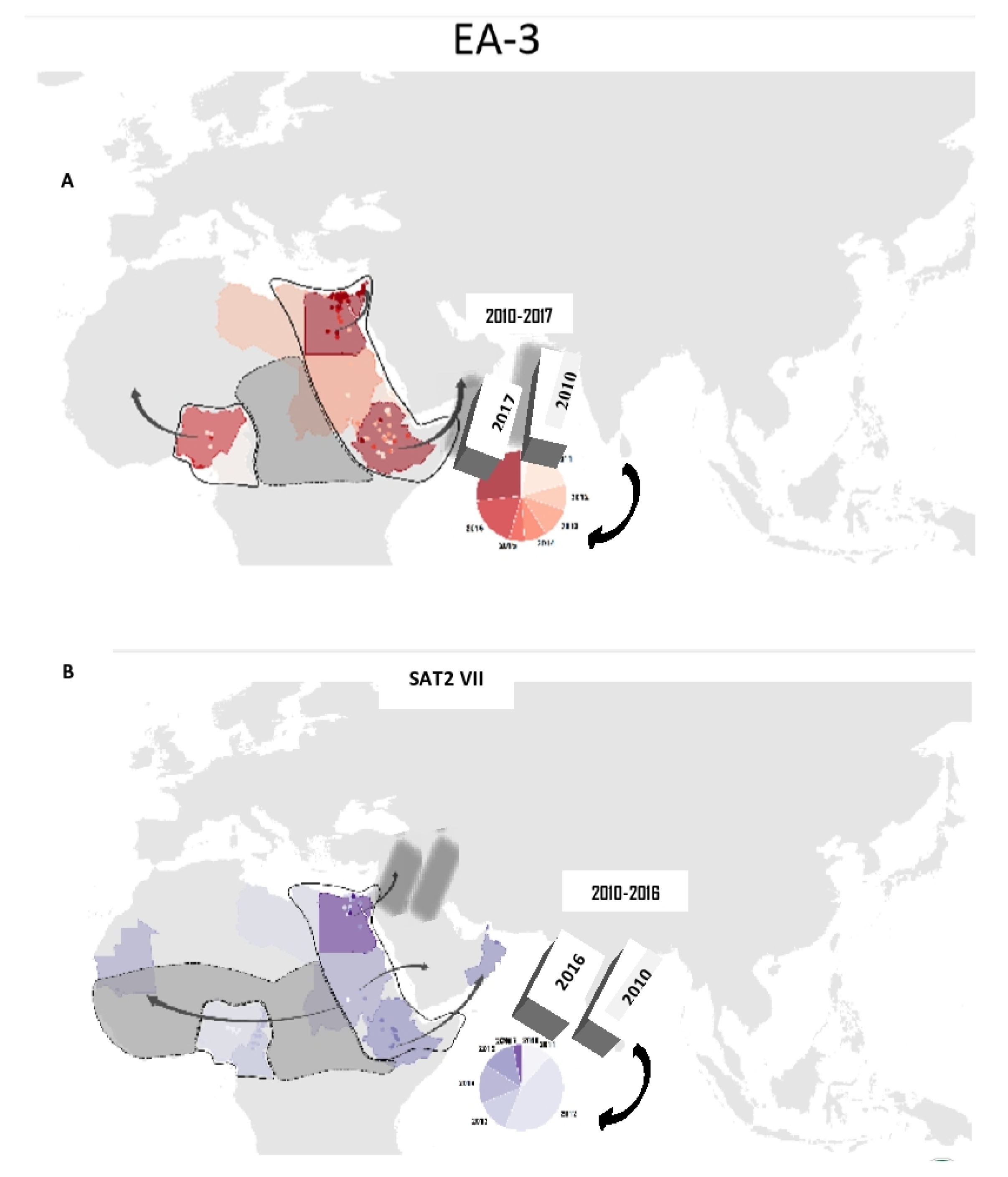
6. Estimates of EA3 and SAT2 Viral Movements
7. National Outbreak Investigation and Reporting System
8. National FMD Control Attempts, Approaches, and Perspectives
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FMD | Foot and Mouth Disease |
| NAHDIC | National Animal Health Diagnostic and Investigation Center |
| NVI | National Veterinary Institute |
| MoLF | Ministry Of Livestock and Fishery |
| MoARD | Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development |
| WRLFMD | World Reference Laboratory for Foot-and-Mouth Disease |
| OIE | Office International des Epizooties |
| PCP | Progressive Control Pathway |
References
- Maclachlan, N.J.; Dubovi, E.J. (Eds.) Fenner’s Veterinary Virology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Fracastorius, H. De Sympathia et Antipathia Rerum Liber Unus. De Contagione et Contagiosis Morbis et Eorum Curatione Liber I; Heirs of LA Junta: Venice, Italy, 1546. [Google Scholar]
- Cottam, E.M.; Wadsworth, J.; Shaw, A.E.; Rowlands, R.J.; Goatley, L.; Maan, S. Transmission pathways of foot-and-mouth disease virus in the United Kingdom in 2007. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musser, J.M. A practitioner’s primer on foot-and-mouth disease. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2004, 224, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schijven, J.; Rijs, G.B.; Roda Husman, A.M. Quantitative risk assessment of FMD virus transmission via water. Risk Anal. 2005, 25, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, M.; Sanson, R.L.; Stern, M.W.; O’Leary, B.D.; Moles Benfell, N.; Morris, R.S. Interpread Plus: A spatial and stochastic simulation model of disease in animal population. Prev. Vet. Med. 2013, 109, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandersen, S.; Zhang, Z.; Donaldson, A.I.; Garland, A.J.M. The pathogenesis and diagnosis of foot-and-mouth disease. J. Comp. Pathol. 2003, 129, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, M.; Firestone, Y.H.; Richard, B.; Takehisa, Y.; Toshiyuki, T.; Mark, A.S. Reconstructing foot-and-mouth disease outbreaks: A methods comparison of transmission network models. Sci. Rep. Nat. 2019, 9, 4809. [Google Scholar]
- Michael, P.; Benjamin, A.; Clark, J.D.; Smith, T.T.; Erica, M.; Lindsay, G.; Melia, P.; William, H.; Juan, M.; Pacheco, J.; et al. Foot-and-mouth disease virus 3C protease mutant L127P: Implications for FMD vaccine development. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00924-17. [Google Scholar]
- Pattnaik, B.; Subramanian, S.; Sanyal, A. Foot- and-Mouth disease: Global Status and Future Road Map for Control and Prevention in India. Agric. Res. 2012, 1, 32–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, K. History of Foot-and-mouth disease in North African countries. Vet. Italy 2018, 54, 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Amaral, D.C.M.; Gloster, J.; Valarcher, J.F. Airborne transmission of foot-and-mouth disease in pigs: Evaluation and optimization of instrumentation and techniques. Vet. J. 2009, 179, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konig, G.A.; Cottam, E.M.; Upadhyaya, S.; Gloster, J.; Mansley, L.M.; Haydon, D.T. Sequence data and evidence of possible airborne spread in the 2001 foot-and-mouth disease epidemic in the UK. Vet. Rec. 2009, 165, 410–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lycett, S.; Tanya, V.N.; Hall, M.; King, D.P.; Mazeri, S.; Mioulet, V.; Knowles, N.J.; Wadsworth, J.; Bachanek-Bankowska, K.; Ngwa, V.N.; et al. The evolution and phylodynamics of serotype A and SAT2 foot-and-mouth disease viruses in endemic regions of Africa. Sci. Rep. Nat. 2019, 9, 5614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anna, R.S.; James, A.R. NAHEMS Guidelines: Vaccination for Contagious Diseases, Appendix A. Foot and Mouth Disease. Veterinary Microbiology and Preventive Medicine Reports. 2. 2015. Available online: http://www.cfsph.iastate.edu/DiseaseInfo (accessed on 3 October 2019).
- Ma, J.; Xiao, J.; Gao, X.; Liu, B.; Chen, H.; Wang, H. Spatial pattern of foot-and-mouth disease in animals in China, 2010–2016. PeerJ 2017, 5, e4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooksby, J.B. Portraits of viruses: Foot-and-mouth disease virus. Intervirology 1982, 18, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight-Jones, T.J.D.; Rushton, J. The economic impacts of foot and mouth disease -what are they, how big are they and where do they occur? Prev. Vet. Med. 2013, 112, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, B.D.; Rich, K.M. Poverty impacts of foot-and-mouth disease and the poverty reduction implications of its control. Vet. Rec. 2007, 160, 238–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birhanu, T. Prevalence of the major infectious animal diseases affecting livestock trade industry in Ethiopia. J. Biol. Agric. Healthc. 2014, 4, 62–76. [Google Scholar]
- James, A.D.; Rushton, J. The economics of foot and mouth disease. Rev. Sci. Tech. Off. Int. Epiz. 2002, 21, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rufael, T.; Catley, A.; Bogale, A.; Sahle, M.; Shiferaw, Y. Foot and mouth disease in the Borana pastoral system, southern Ethiopia and implications for livelihoods and international trade. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2008, 40, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamond, J. FMD Vaccine: Practical Applications from an International Perspective-FMDV Vaccine to Live. Event Organ. NFUS Moredun Scottish Gov. 2011, 15, 1292–1298. [Google Scholar]
- Forman, S.; Le, G.F.; Belton, D.; Evans, B.; Franç, O.; Murray, J.L.; Sheesley, G.; Vandersmissen, D.; Yoshimura, A.S. Moving towardsthe global control of foot and mouth disease: An opportunity fordonors. Rev. Sci. Tech. Off. Int. Epiz. 2009, 28, 883–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miriam, C.B.; Richard, R.; Umesh, B.; Nick, J.K.; Harriet, A.; Katarzyna, B.B.; Veronica, L.F.; Robert, F.; Rudovick, K.; Tito, K.; et al. Waves of endemic foot-and-mouth disease in eastern Africa suggest feasibility of proactive vaccination approaches. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 1449–1457. [Google Scholar]
- Brito, B.; Rodriguez, L.; Hammond, J.; Pinto, J.; Perez, A. Review of the global distribution of foot-and-mouth disease virus from 2007 to 2014. Trans. Emerg. Dis. 2015, 1, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorraine, M.; Buried Alive; South Korea’s Animal Culls. Advocacy for Animals. 2011. Available online: advocacy.britannica.com/blog/advocacy/2011/05/buried-alive-south-koreas-animal-culls/ (accessed on 16 October 2019).
- Haydon, D.; Kao, R.R.; Haydon, D.T.; Kao, R.R.; Kitching, R.P. The UK foot-and-mouth disease outbreak the aftermath. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 675.
- Ding, Y.Z.; Chen, H.T.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, J.H.; Ma, L.N.; Zhang, L.; Gu, Y.; Liu, Y.S. An overview of control strategy and diagnostic technology for foot –and –mouth disease in China. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, L.; Knight-Jones, T.J.D.; Charleston, B.; Rodriguez, L.L.; Gay, C.G.; Sumption, K.J.; Vosloo, W. Global foot-and-mouth disease research update and gap analysis. Immunol. Trans. Emerg. Dis. 2016, 63, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemberu, W.T.; Mourists, M.C.M.; Sahle, M.; Siraw, B.; Vernooiji, J.C.M.; Hogeveen, H. Epidemiology of Foot and Mouth Disease in Ethiopia: Aretrospective anlaysis of Distric Level Outbreak, 2007–2012. Trans. Emerg. Dis. 2016, 63, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowles, N.J.; Samuel, A.R. Molecular epidemiology of foot-and-mouth disease virus. Virus Res. 2003, 91, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeder, P.L.; Knowles, N.J. Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus Type C Situation: The First Target for Eradication? In Report of the Session of the Research Group of the Standing Technical Committee of EUFMD, Erice, Italy, 14–17 October 2008. Available online: www.fao.org/ag/againfo/commissions/docs/research_group/erice/APPENDIX_07.pdf (accessed on 12 September 2019).
- Bastos, A.D.; Haydon, D.T.; Sangare, O.; Boshoff, C.I.; Edrich, J.L.; Thomson, G.R. The implications of virus diversity within the SAT 2 serotype for control of foot-and-mouth disease in sub-Saharan Africa. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 1595–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandeil, A.; Ghazi, R.E.; Yassmin, K. Characterization of the recent outbreak of foot-and-mouth disease virus serotype SAT2 in Egypt. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vosloo, W.; Boshoff, C.I.; Dwarka, R.; Bastos, A. The possible role that buffalo played in the recent outbreaks of foot-and-mouth disease in South Africa. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2002, 969, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tekleghiorghis, T.; Moormann, R.J.; Weerdmeester, K.; Dekker, A. Foot-and-mouth disease transmission in Africa: Implications for control, a review. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2016, 63, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahle, M.; Venter, E.H.; Dwarka, R.M.; Vosloo, W. Molecular epidemiology of serotype O foot-and-mouth disease virus isolated from cattle in Ethiopia between 1979–2001. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2004, 71, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayelet, G.; Mahapatra, M.; Gelaye, E.; Egziabher, B.G.; Rufeal, T.; Sahle, M.; Ferris, N.P.; Wadsworth, J.; Hutchings, G.H.; Knowles, N.J.K. Genetic characterization of foot-and-mouth disease viruses, Ethiopia 1981–2007. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1409–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, J. Understanding the molecular epidemiology of foot- and—Mouth disease virus. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2009, 9, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, A.R.; Knowles, N.J. Foot-and-mouth disease type O viruses exhibit genetically and geographically distinct evolutionary lineages (topotypes). J. Gen. Virol. 2001, 82, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktas, S.; Samuel, A.R. Identification of antigenic epitopes on the foot and mouth disease virus isolate O1/Manisa/Turkey/69 using monoclonal antibodies. Rev. Sci. Tech. Off. Int. Epiz. 2000, 19, 744–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WRLFMD. Available online: http://www.wrlfmd.org/east-africa/ethiopia (accessed on 5 September 2019).
- Jackson, A.L.; O’neill, H.; Maree, F.; Blignaut, B.; Carrillo, C.; Rodriguez, L.; Haydon, D.T. Mosaic structure of foot-and-mouth disease virus genomes. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmonds, P. Recombination and selection in the evolution of picornaviruses and other mammalian positive-stranded RNA viruses. Virol. J. 2006, 80, 11124–11140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kitching, R.P. Global epidemiology and prospects for control of foot-and-mouth disease. In Foot and Mouth Disease Virus; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 133–148. [Google Scholar]
- Vosloo, W.; Dwarka, R.M.; Bastos, A.D.S.; Esterhuysen, J.J.; Sahle, M.; Sangare, O. Molecular Epidemiological Studies of Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus in Sub-Saharan Africa Indicate the Presence of Large Numbers of Topotypes: Implications for Local and International Control; Report on the European Commission for the Control of Foot-and-Mouth Disease, Session of the Research Group of the Standing Technical Committee; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Chania, Greece, 2004; pp. 149–158. [Google Scholar]
- Miguel, E.; Grosbois, V.; Caron, A.; Boulinier, T.; Fritz, H.; Cornélis, D.; Foggin, C.; Makaya, P.V.; Tshabalala, P.T.; de Garine-Wichatitsky, M. Contacts and foot and mouth disease transmission from wild to domestic bovines in Africa. esajournals 2013, 4, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grazioli, S.; Fallacara, F.; Brocchi, E. Mapping of antigenic sites of foot-and-mouth disease virus serotype Asia 1 and relationships with sites described in other serotypes. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishamo, S.; Fufa, D.; Bedaso, M.; Daniel, G.; Dereje, S. Isolation, molecular characterization and sero-prevalence study of foot-and-mouth disease virus circulating in central Ethiopia. BMC Vet. Res. 2008, 14, 110. [Google Scholar]
- Grubman, M.J.; Baxt, B. Foot-and-mouth disease. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 17, 465–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rweyemamu, M.; Roeder, P.; Mackayl, D.; Sumption, K.; Brownlie, J.; Leforban, Y.; Valarcher, J.F.; Knowles, N.J.; Saraiva, V. Epidemiological patterns of foot-and-mouth disease worldwide. Transbound Emerg. Dis. 2008, 55, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maree, F.F.; Blignaut, B.; Esterhuysen, J.J.; de Beer, T.A.P.; Theron, J.; O’Neill, H.G.; Rieder, E. Predicting antigenic sites on the foot-and-mouth disease virus capsid of the South African Territories types using virus neutralization data. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 2297–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouton, L.; Dekker, A.; Bleijenberg, M.; Blanchet, M.; Coco-Martin, J.; Hudelet, P.; Goutebroze, S. A foot-and-mouth disease SAT2 vaccine protects swine against experimental challenge with a homologous virus strain, irrespective of mild pathogenicity in this species. Vaccine. 2018, 36, 2020–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, D.; Di-Nardo, A.; Henstock, M. OIE/FAO Foot-and-Mouth Disease Reference Laboratory Network Annual Report; The Pirbright Institute: Surrey, UK, 2017; pp. 12–23. [Google Scholar]
- Negussie, H.; Ayelet, G.; Jenberie, S.; Minda, S.; Tesfaw, L. Molecular epidemiology and vaccine matching study on foot-and-mouth disease virus circulating in Ethiopia. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 7, 5101–5106. [Google Scholar]
- Rweyemamu, M.M.; Garland, A.J.M. The design of vaccines and diagnostics for use in endemic FMD settings. In Proceedings of the Global Endemic FMD Roadmap Workshop, Agra, India, 29 November–1 December 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Paton, D.J.; Sumption, K.; Charleston, J. Options for control of foot-and-mouth disease: Knowledge, capability and policy. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. 2009, 364, 2657–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, N.A.; Knowles, N.J.; Paton, D.J. Combining livestock trade patterns with phylogenetics to help understand the spread of foot and mouth disease in sub-Saharan Africa, the Middle East and Southeast Asia. Rev. Sci. Tech. Off. Int. Epiz. 2011, 30, 63–85. [Google Scholar]
- Vosloo, W.; Bastos, A.; Boshoff, C. Retrospective genetic analysis of SAT1 type foot-and-mouth disease outbreaks in Southern Africa. Arch. Virol. 2006, 151, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vosloo, W.; Kirkbride, E.; Bengis, R.G.; Keet, D.F.; Thomson, G.R. Genome variation in the SAT types of foot-and-mouth disease viruses prevalent in buffalo (Syncerus caffer) in the Kruger National Park and other regions of southern Africa, 1986–1993. Epidemiol. Infect. 1995, 114, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Francois, F.M.; Christopher, J.K.; Katherin, A.S.; Pamela, A.O.; Melanie, C.; Abraham, K.S.; Raphael, S.; Yona, S.; Philemon, N.W.; Donald, P.K.; et al. Challenges and prospects for the control of foot-and-mouth disease: An African perspective. Vet. Med. Res. Rep. 2014, 5, 119–138. [Google Scholar]
- Seoke, L.A.T.O. Genetic and Antigenic Characterization of Foot and Mouth Disease Virus Strains Isolated in 2011 and 2015 in Ngamiland. Botswana. Master’s Thesis, Sokoine Univesity of Agriculture, Morogoro, Tanzania, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Martel, J.L. Comparative serological study of the principal strains of the foot and mouth disease virus isolated in Ethiopia 1969–1974. Rev. D’Elev. Med. Vet. Pays Trop. 1975, 28, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martel, J.L. Foot-and-mouth disease in Ethiopia. Distribution of serotypes of foot-and-mouth disease virus. Rev. D’Elev. Med. Vet. Pays Trop. 1974, 27, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roeder, P.L.; Abraham, G.; Mebratu, G.Y.; Kitching, R.P. Foot-and-mouth disease in Ethiopia from 1988 to 1991. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 1994, 26, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelaye, E.; Boyne, B.; Ayelet, G. Foot and mouth disease virus serotype identified in Ethiopia. Ethiopian. Vet. J. 2005, 9, 75–79. [Google Scholar]
- Legess, Y. Investigation of Foot and Mouth Disease Outbreaks and Assessment of Risk Factors in Oromia, Amhara, and Southern Nations, Nationalities and Peoples (SNNP) Regional States of Ethiopia. Master’s Thesis, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Addis Ababa University, Debrezeit, Ethiopia, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negussie, H.; Moses, K.; Yami, N.; Ayelet, G.; Jenberie, T. Outbreak investigations and genetic characterization of foot and mouth disease virus in Ethiopia. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2011, 43, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitching, R.P.; Hughes, G.J. Clinical variation in foot and mouth disease: Sheep and goats. Rev. Sci. Tech. Off. Int. Epiz. 2002, 21, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, G. FMD Status in Ethiopia from 2014–2017. In Proceedings of the 3rd East Africa FMD Roadmap Meeting, Entebbe, Uganda, 3–5 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development (MoARD). Agricultural Input and Products Marketing Strategy and Implementation Mechanism; MoARD, Agricultural Marketing and Inputs Sector State Ministry: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ayelet, G.; Gelaye, E.; Negussie, H.; Asmare, K. Study on the epidemiology of foot and mouth disease in Ethiopia. Rev. Sci. Tech. Off. Int. Epiz. 2012, 31, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development (MOARD) Ethiopia. Annual Report on Diseases of Livestock in Ethiopia; Veterinary Services Department: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2005; pp. 2–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Livestock and Fishery Ethiopia (MoLF). Foot and Mouth Disease Outbreaks Annual Report Recording Data Summary from the Years 2009–2017; Epidemiology Directorate: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gelagay, A. A Study on Serological and Molecular Epidemiology FMD Virus Circulating in Ethiopia and Selection of the Possible Vaccinal Strains (2008–2009); European Commission for Control of FMD(EUFMD): Kenya Nairobi, Kenya, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Rufael, T. Participatory Appraisal and Sero-Prevalence Study of Foot and Mouth Disease in Borana Pastoral System. South Ethiopia. Master’s Thesis, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Addis Ababa University, Bishoftu, Ethiopia, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Abunna, F.; Fikru, S.; Tesfaye, R. Seroprevalence of Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD) at Dire Dawa and Its Surroundings, Eastern Ethiopia. Glob. Vet. 2013, 11, 575–578. [Google Scholar]
- Zerabruk, G.; Romha, G.; Rufael, T. Sero-epidemiological investigation of foot and mouth disease in cattle managed under extensive husbandry system in Tigray, Northern Ethiopia. Glob. Vet. 2014, 13, 112–116. [Google Scholar]
- Molla, B.; Ayelet, G.; Asfaw, Y.; Jibril, Y.; Ganga, G.; Gelaye, E. Epidemiological study on foot-and-mouth disease in cattle: Seroprevalence and risk factor assessment in south omo zone, south-western Ethiopia. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2010, 57, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megersa, B.; Beyene, B.; Abunna, F.; Regassa, A.; Amenu, K.; Rufael, T. Risk factors for foot and mouth disease seroprevalence in indigenous cattle in southern Ethiopia: The effect of production system. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2009, 41, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamoud, A.; Tessema, E.; Degefu, H. Seroprevalence of bovine foot and mouth disease (FMD) in Awbere and Babille districts of Jijiga zone, Somalia Regional State, Eastern Ethiopia. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2011, 5, 3559–3563. [Google Scholar]
- Bayissa, B.; Ayelet, G.; Kyule, M.; Jibril, Y.; Gelaye, E. Study on seroprevalence, risk factors, and economic impact of foot-and-mouth disease in Borena pastoral and agro-pastoral system, southern Ethiopia. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2011, 43, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonen, H.; Beyene, D.; Rufael, T.; Feyisa, A. Study on the prevalence of Foot and Mouth Disease in Borana. Vet. World 2011, 4, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tefera, L. Sero-Prevalence, Involvement of Small Ruminants in the Epidemiology of FMD, and Characterization of FMD Virus Circulating in the Study Area and Assess Epidemiological Risk Factors Associated with FMD in Cattle in Selected Districts of Gambella Region, Ethiopia. Master’s Thesis, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Addis Ababa University, Debre Zeit, Ethiopia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sahle, M.; Rufael, T.; Gizaw, D. Status of Foot and Mouth Disease in Ethiopia from 2006–2016; National Animal Health Diagnostic and Investigation Center (NAHDIC): Sebeta, Ethiopia, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowles, N.; Wadsworth, J.; Bachanek-Bankowska, K.; King, D. VP1 sequencing protocol for foot-and-mouth disease virus molecular epidemiology. Revue Scientifique et Technique de l’OIE 2016, 35, 741–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valdazo-González, B.; Knowles, N.J.; Hammond, J.; King, D.P. Genome Sequences of SAT 2 Foot-and-Mouth Disease Viruses from Egypt and Palestinian Autonomous Territories (Gaza Strip). J. Virol. 2012, 86, 8901–8902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aidaros, H.A. Regional Status and Approaches to Control and Eradication of FMD in the Middle East and North Africa. Rev. Sci. Tech. Off. Int. Epiz. 2002, 21, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OIE/FAO FMD Reference Laboratory Network; Annual Reports; The Pirbright Institute: Surrey, UK, 2017; pp. 16–25. Available online: https://www.foot-and-mouth.org (accessed on 6 October 2019).
- WRLFMD. Molecular Epidemiology/Genotyping, OIE/FAO FMD Reference Laboratory Network. Annual Reports April to June. 2016, pp. 22–23. Available online: https://www.foot-and-mouth.org/science/wrlfmd-reports (accessed on 22 September 2019).
- Leforaban, Y. Report of a mission on Foot and Mouth disease in Ethiopia. Propos. Strateg. Plan Control Program Oriented Export 2005, 1022, 1242. [Google Scholar]
- Urge, B. Serotyping and Molecular Characterization of FMD Virus Isolated from Outbreak Cases in Selected Region and Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Master’s Thesis, College of Veterinary Medicine and Agriculture, Addis Ababa University, Bishoftu, Ethiopia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chaosuancharoen, T. Experience of FMD control in Thailand: The continual attempts and foresight. In Key Elements in the Prevention and Control of FMD and in Implementing the Strategy. In Proceedings of the FAO/OIE Global Conference on Foot and Mouth Disease Control Ensuring Excellence and Ethics of the Veterinary Profession, Bangkok, Thailand, 27–29 June 2012; pp. 121–124.
- Zewudie, S.; Asfaw, W.; Sahlie, M.; Gopilo, A.; G/Egziabher, B.; Bogale, A.; Demissie, A. Foot and Mouth Disease Control Plan; Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2006.
- Beyi, A. Costs and Benefits of Foot and Mouth Disease Vaccination Practice in Commercial Dairy Farms in Central Ethiopia. Master’s Thesis, Wageningen University, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Appliance of Science in the Progressive Control of FMD Open Sessions of the Standing Technical and Research Committees of the Eu FMD Commission; FAO: Jerez De La Frontera, Spain, 2012. [Google Scholar]

| Regional States | Outbreak Investigation Area | Tested Animal Populations | Prevalence % | Cited |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oromia | Borena | 134 | 55.6 | [77] |
| Moyale | 174 | 16.1 | [77] | |
| Adma-Mojo livestock export | 4321 | 12.5 | [20] | |
| Addis Ababa | Yeka | 40 | 30 | [73] |
| Bole | 40 | 12.5 | [78] | |
| Tigray | Central zone | 139 | 26.6 | [73] |
| Eastern zone | 41 | 41.5 | [73] | |
| Western zone | 195 | 16.9 | [79] | |
| Southern zone | 75 | 24 | [79] | |
| Amhara | South achefer | 101 | 52.5 | [69] |
| Habru | 218 | 38.7 | [69] | |
| Dangela | 104 | 43.3 | [69] | |
| SNPPR | Hammer | 104 | 13.5 | [80] |
| Arbaminch | 90 | 7.3 | [81] | |
| Jinka | 162 | 4.9 | [80] | |
| Semen bench | 153 | 5.8 | [39] | |
| Afar | Zone 4 | 299 | 4.5 | [73] |
| Somalia | Awabere | 225 | 14.2 | [82] |
| Babile | 159 | 15.1 | [82] |
| Serotypes | FMD Outbreak Reported Years |
|---|---|
| Untyped | 1998, 2000–2001, 2004–2006, 2008–2012 |
| O | 1957, 1961–1963, 1966, 1969, 1989, 1996, 2003–2018 |
| A | 1969, 1981, 2000–2002, 2008–2009, 2015, 2017–2018 |
| C | 1957, 1971, 1983 |
| SAT 1 | 2007 |
| SAT 2 | 1989–1991, 2007, 2009–2010, 2014–2015, 2018 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wubshet, A.K.; Dai, J.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J. Review on Outbreak Dynamics, the Endemic Serotypes, and Diversified Topotypic Profiles of Foot and Mouth Disease Virus Isolates in Ethiopia from 2008 to 2018. Viruses 2019, 11, 1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111076
Wubshet AK, Dai J, Li Q, Zhang J. Review on Outbreak Dynamics, the Endemic Serotypes, and Diversified Topotypic Profiles of Foot and Mouth Disease Virus Isolates in Ethiopia from 2008 to 2018. Viruses. 2019; 11(11):1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111076
Chicago/Turabian StyleWubshet, Ashenafi Kiros, Junfei Dai, Qian Li, and Jie Zhang. 2019. "Review on Outbreak Dynamics, the Endemic Serotypes, and Diversified Topotypic Profiles of Foot and Mouth Disease Virus Isolates in Ethiopia from 2008 to 2018" Viruses 11, no. 11: 1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111076
APA StyleWubshet, A. K., Dai, J., Li, Q., & Zhang, J. (2019). Review on Outbreak Dynamics, the Endemic Serotypes, and Diversified Topotypic Profiles of Foot and Mouth Disease Virus Isolates in Ethiopia from 2008 to 2018. Viruses, 11(11), 1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111076






