Rabies Surveillance Identifies Potential Risk Corridors and Enables Management Evaluation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
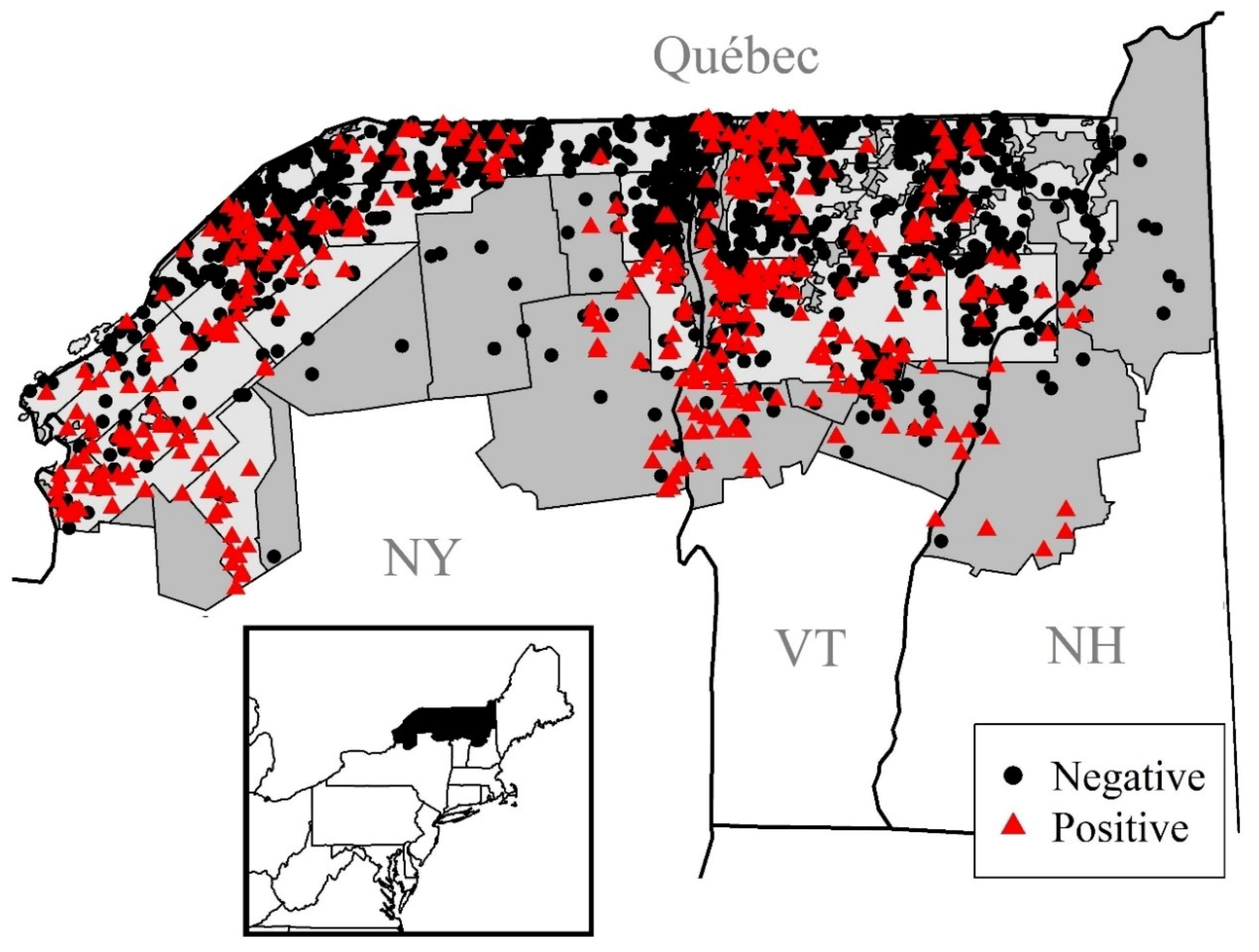
2.2. Data and Data Processing
2.3. Occupancy Analysis
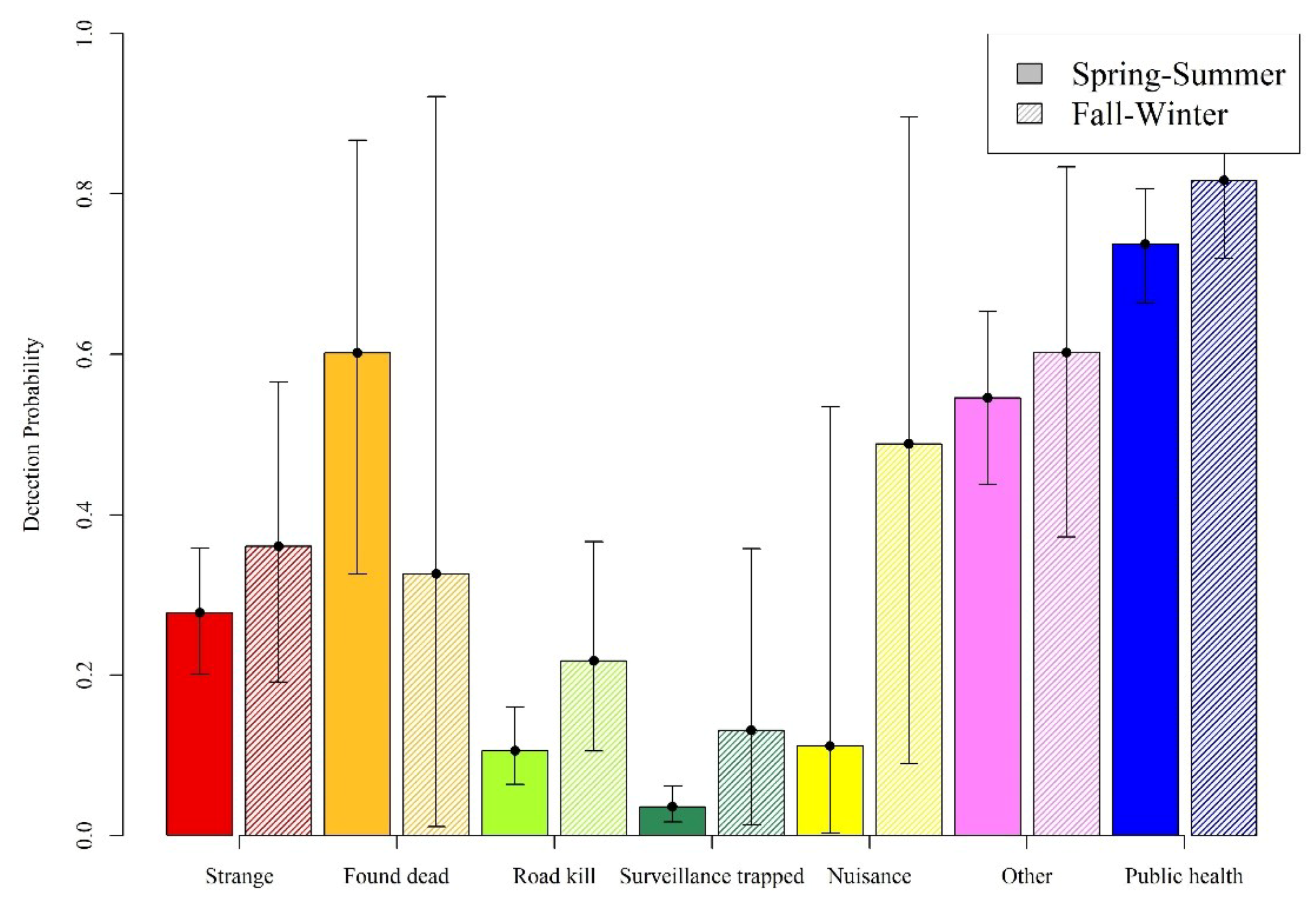
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reynolds, J.J.H.; Hirsch, B.T.; Gehrt, S.D.; Craft, M.E. Raccoon contact networks predict seasonal susceptibility to rabies outbreaks and limitations of vaccination. J. Anim. Ecol. 2015, 84, 1720–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coyne, M.; Smith, G.; McAllister, F. Mathematic model for the population biology of rabies in raccoons in the mid-atlantic states. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1989, 50, 2148–2154. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rees, E.E.; Pond, B.A.; Tinline, R.R.; Bélanger, D. Modelling the effect of landscape heterogeneity on the efficacy of vaccination for wildlife infectious disease control. J. Appl. Ecol. 2013, 50, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slate, D.; Algeo, T.P.; Nelson, K.M.; Chipman, R.B.; Donovan, D.; Blanton, J.D.; Niezgoda, M.; Rupprecht, C.E. Oral rabies vaccination in north america: Opportunities, complexities, and challenges. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2009, 3, e549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadidian, J.; Prange, S.; Rosatte, R.C.; Riley, S.P.; Gehrt, S.D. Raccoons (procyon lotor). In Urban Carnivores: Ecology, Conflict, and Conservation; Gehrt, S.D., Riley, S.P., Cypher, B.L., Eds.; The Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2010; pp. 35–47. [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell, B.F.; Seamans, T.W.; White, R.J.; Patton, Z.J.; Bush, R.M.; Cepek, J.D. Exposure time of oral rabies vaccine baits relative to baiting density and raccoon population density. J. Wildl. Dis. 2004, 40, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slate, D.; Saidy, B.D.; Simmons, A.; Nelson, K.M.; Davis, A.J.; Algeo, T.; Elmore, S.A.; Chipman, R.B. Raccoon population density indexes in the eastern united states: Implimcations for rabies management. J. Wildl. Manag. 2019. under review. [Google Scholar]
- Sattler, A.C.; Krogwold, R.A.; Wittum, T.E.; Rupprecht, C.E.; Algeo, T.P.; Slate, D.; Smith, K.A.; Hale, R.L.; Nohrenberg, G.A.; Lovell, C.D. Influence of oral rabies vaccine bait density on rabies seroprevalence in wild raccoons. Vaccine 2009, 27, 7187–7193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA. North American Rabies Management Plan; U.S. Departement of Agriculture: Concord, NH, USA, 2008.
- Slate, D.; Chipman, R.B.; Algeo, T.P.; Mills, S.A.; Nelson, K.M.; Croson, C.K.; Dubovi, E.J.; Vercauteren, K.; Renshaw, R.W.; Atwood, T. Safety and immunogenicity of ontario rabies vaccine bait (onrab) in the first us field trial in raccoons (procyon lotor). J. Wildl. Dis. 2014, 50, 582–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, A.T.; Johnson, S.R.; Nelson, K.M.; Chipman, R.B.; VerCauteren, K.C.; Algeo, T.P.; Rupprecht, C.E.; Slate, D. Field trials of ontario rabies vaccine bait in the northeastern usa, 2012–2014. J. Wildl. Dis. 2018, 54, 790–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, K.; Gilbert, A.T.; Nelson, K.M.; Morgan, D.P.; Davis, A.J.; VerCauteren, K.C.; Slate, D.; Chipman, R.B. Raccoon (procyon lotor) response to ontario rabies vaccine baits (onrab) in st. Lawrence county, new york, USA. J. Wildl. Dis. 2019, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Blanton, J.D.; Rathbun, S.R.; Rupprecht, C.E. Time series analysis of the impact of oral vaccination on raccoon rabies in west virginia, 1990–2007. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2010, 10, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recuenco, S.; Blanton, J.D.; Rupprecht, C.E. A spatial model to forecast raccoon rabies emergence. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2012, 12, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cullingham, C.I.; Kyle, C.J.; Pond, B.A.; Rees, E.E.; White, B.N. Differential permeability of rivers to raccoon gene flow corresponds to rabies incidence in ontario, canada. Mol. Ecol. 2009, 18, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homer, C.; Dewitz, J.; Yang, L.; Jin, S.; Danielson, P.; Xian, G.; Coulston, J.; Herold, N.; Wickham, J.; Megown, K. Completion of the 2011 national land cover database for the conterminous united states–representing a decade of land cover change information. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2015, 81, 345–354. [Google Scholar]
- Patrick, E.M.; Bjorklund, B.M.; Kirby, J.D.; Chipman, R.; Rupprecht, C. Enhanced rabies surveillance using a direct rapid immunohistochemical test. J. Vis. Exp. 2019, 146, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Protocol for Postmortem Diagnosis of Rabies in Animals by Direct Fluorescent Antibody Testing; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2018.
- Szanto, A.G.; Nadin-Davis, S.A.; Rosatte, R.C.; White, B.N. Re-assessment of direct fluorescent antibody negative brain tissues with a real-time pcr assay to detect the presence of raccoon rabies virus rna. J. Virol. Methods 2011, 174, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.M.; Slavinski, S.; Ettestad, P.; Sidwa, T.J.; Sorhage, F.E. Compendium of animal rabies prevention and control, 2016. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2016, 248, 505–517. [Google Scholar]
- Manning, S.E.; Rupprecht, C.E.; Fishbein, D.; Hanlon, C.A.; Lumlertdacha, B.; Guerra, M.; Meltzer, M.I.; Dhankhar, P.; Vaidya, S.A.; Jenkins, S.R. Human rabies prevention-united states, 2008. Mmwr. Recomm. Rep. 2008, 57, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Kirby, J.D.; Chipman, R.B.; Nelson, K.M.; Rupprecht, C.E.; Blanton, J.D.; Algeo, T.P.; Slate, D. Enhanced rabies surveillance to support effective oral rabies vaccination of raccoons in the eastern united states. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2017, 2, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKenzie, D.I.; Nichols, J.D.; Royle, J.A.; Pollock, K.H.; Bailey, L.L.; Hines, J.E. Occupancy Estimation and Modeling—Inferring Patterns and Dynamics of Species Occurrence; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bled, F.; Nichols, J.D.; Altwegg, R. Dynamic occupancy models for analyzing species’ range dynamics across large geographic scales. Ecol. Evol. 2013, 3, 4896–4909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R foundation for statistical computing: Vienna, Austria, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, A.J.; Kirby, J.D.; Chipman, R.B.; Nelson, K.M.; Xifara, T.; Webb, C.T.; Wallace, R.; Gilbert, A.T.; Pepin, K.M. Not all surveillance data are created equal—A multi-method dynamic occupancy approach to determine rabies elimination from wildlife. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, J.D.; Bailey, L.L.; Talancy, N.W.; Campbell Grant, E.H.; Gilbert, A.T.; Annand, E.M.; Husband, T.P.; Hines, J.E. Multi-scale occupancy estimation and modelling using multiple detection methods. J. Appl. Ecol. 2008, 45, 1321–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zipkin, E.F.; Grant, E.H.C.; Fagan, W.F. Evaluating the predictive abilities of community occupancy models using auc while accounting for imperfect detection. Ecol. Appl. 2012, 22, 1962–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hefley, T.J.; Broms, K.M.; Brost, B.M.; Buderman, F.E.; Kay, S.L.; Scharf, H.R.; Tipton, J.R.; Williams, P.J.; Hooten, M.B. The basis function approach for modeling autocorrelation in ecological data. Ecology 2017, 98, 632–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gruen, B.; Kosmidis, I.; Zeileis, A. Extended beta regression in r: Shaken, stirred, mixed, and partitioned. J. Stat. Softw. 2012, 48, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainguy, J.; Rees, E.E.; Canac-Marquis, P.; Bélanger, D.; Fehlner-Gardiner, C.; Séguin, G.; Larrat, S.; Lair, S.; Landry, F.; Côté, N. Oral rabies vaccination of raccoons and striped skunks with onrab® baits: Multiple factors influence field immunogenicity. J. Wildl. Dis. 2012, 48, 979–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainguy, J.; Fehlner-Gardiner, C.; Slate, D.; Rudd, R.J. Oral rabies vaccination in raccoons: Comparison of onrab® and raboral v-rg® vaccine-bait field performance in québec, canada and vermont, USA. J. Wildl. Dis. 2013, 49, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehlner-Gardiner, C.; Rudd, R.; Donovan, D.; Slate, D.; Kempf, L.; Badcock, J. Comparing onrab® and raboral v-rg® oral rabies vaccine field performance in raccoons and striped skunks, new brunswick, canada, and maine, USA. J. Wildl. Dis. 2012, 48, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, K.; Gilbert, A.T.; Wilhelm, E.S.; Nelson, K.M.; Davis, A.J.; Kirby, J.D.; VerCauteren, K.C.; Johnson, S.R.; Chipman, R.B. Effect of high-density oral rabies vaccine baiting on rabies virus neutralizing antibody response in raccoons (procyon lotor). J. Wildl. Dis. 2018, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandeler, A.; Capt, S.; Kappeler, A.; Hauser, R. Oral immunization of wildlife against rabies: Concept and first field experiments. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1988, 10, S649–S653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slate, D.; Rupprecht, C.E.; Rooney, J.A.; Donovan, D.; Lein, D.H.; Chipman, R.B. Status of oral rabies vaccination in wild carnivores in the united states. Virus Res. 2005, 111, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozek, C.K.; Prange, S.; Gehrt, S.D. The influence of anthropogenic resources on multi-scale habitat selection by raccoons. Urban Ecosyst. 2007, 10, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prange, S.; Gehrt, S.D.; Wiggers, E.P. Demographic factors contributing to high raccoon densities in urban landscapes. J. Wildl. Manag. 2003, 67, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosatte, R.; Donovan, D.; Allan, M.; Bruce, L.; Buchanan, T.; Sobey, K.; Stevenson, B.; Gibson, M.; MacDonald, T.; Whalen, M. The control of raccoon rabies in ontario canada: Proactive and reactive tactics, 1994–2007. J. Wildl. Dis. 2009, 45, 772–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosatte, R.C.; Power, M.J.; Machines, C.D.; Campbell, J.B. Trap-vaccinate-release and oral vaccination for rabies control in urban skunks, raccoons and foxes. J. Wildl. Dis. 1992, 28, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosatte, R.C. Evoluation of wildlife rabies control tactics. In Rabies, 3rd ed.; Jackson, A.C., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2011; pp. 617–670. [Google Scholar]
- Zeveloff, S.I.; Dewitte, E. Raccoons: A Natural History; UBC Press: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Elmore, S.A.; Chipman, R.B.; Slate, D.; Huyvaert, K.P.; VerCauteren, K.C.; Gilbert, A.T. Management and modeling approaches for controlling raccoon rabies: The road to elimination. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Factor | Estimate | Std. Error | z Value | Pr(>|z|) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 1.15 | 0.02 | 57.13 | 0.00 |
| Bait density by bait type interaction | 1.28 | 0.07 | 18.43 | 0.00 |
| Bait density | −1.18 | 0.06 | −20.46 | 0.00 |
| Year | −0.79 | 0.01 | −63.25 | 0.00 |
| Medium to high development | 0.62 | 0.25 | 2.52 | 0.01 |
| ONRAB duration BS-1 | −0.08 | 0.11 | −0.73 | 0.46 |
| ONRAB duration BS-2 | −0.13 | 0.04 | −3.36 | 0.00 |
| ONRAB duration BS-3 | −0.43 | 0.05 | −8.00 | 0.00 |
| Open to low development | −0.41 | 0.16 | −2.61 | 0.01 |
| Bait type | −0.41 | 0.05 | −8.32 | 0.00 |
| V-RG duration BS-1 | 0.20 | 0.05 | 3.86 | 0.00 |
| V-RG duration BS-2 | 0.32 | 0.05 | 5.93 | 0.00 |
| V-RG duration BS-3 | −0.40 | 0.06 | −6.37 | 0.00 |
| Deciduous forest | −0.36 | 0.02 | −17.05 | 0.02 |
| Spring | −0.34 | 0.01 | −45.09 | 0.00 |
| Summer | −0.29 | 0.01 | −37.89 | 0.00 |
| Hay/pasture | 0.26 | 0.04 | 6.61 | 0.00 |
| log(# raccoons vaccinated with trap–vaccinate–release management) | −0.25 | 0.00 | −69.24 | 0.00 |
| Cultivated crops | 0.15 | 0.07 | 2.33 | 0.02 |
| Wetlands | 0.14 | 0.04 | 3.39 | 0.00 |
| Winter | −0.13 | 0.01 | −16.53 | 0.00 |
| Years of total baiting | −0.08 | 0.02 | −3.98 | 0.00 |
| Mean elevation | −0.08 | 0.01 | −8.30 | 0.00 |
| Evergreen forest | 0.06 | 0.04 | 1.79 | 0.07 |
| Fall to Winter | Spring to Summer | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Negative | Positive | Total | Negative | Positive | Total |
| Strange acting | 99 | 12 | 111 | 388 | 50 | 438 |
| Found dead | 13 | 0 | 13 | 36 | 11 | 47 |
| Roadkill | 138 | 12 | 150 | 517 | 30 | 547 |
| Surveillance trapped | 70 | 1 | 71 | 608 | 9 | 617 |
| Nuisance | 25 | 2 | 27 | 251 | 2 | 253 |
| Other | 147 | 13 | 160 | 265 | 60 | 325 |
| Public health | 229 | 104 | 333 | 695 | 197 | 892 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Davis, A.J.; Nelson, K.M.; Kirby, J.D.; Wallace, R.; Ma, X.; Pepin, K.M.; Chipman, R.B.; Gilbert, A.T. Rabies Surveillance Identifies Potential Risk Corridors and Enables Management Evaluation. Viruses 2019, 11, 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111006
Davis AJ, Nelson KM, Kirby JD, Wallace R, Ma X, Pepin KM, Chipman RB, Gilbert AT. Rabies Surveillance Identifies Potential Risk Corridors and Enables Management Evaluation. Viruses. 2019; 11(11):1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111006
Chicago/Turabian StyleDavis, Amy J., Kathleen M. Nelson, Jordona D. Kirby, Ryan Wallace, Xiaoyue Ma, Kim M. Pepin, Richard B. Chipman, and Amy T. Gilbert. 2019. "Rabies Surveillance Identifies Potential Risk Corridors and Enables Management Evaluation" Viruses 11, no. 11: 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111006
APA StyleDavis, A. J., Nelson, K. M., Kirby, J. D., Wallace, R., Ma, X., Pepin, K. M., Chipman, R. B., & Gilbert, A. T. (2019). Rabies Surveillance Identifies Potential Risk Corridors and Enables Management Evaluation. Viruses, 11(11), 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111006





