Eradication of Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci by Combining Phage and Vancomycin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial and Phage Strains
2.2. Materials
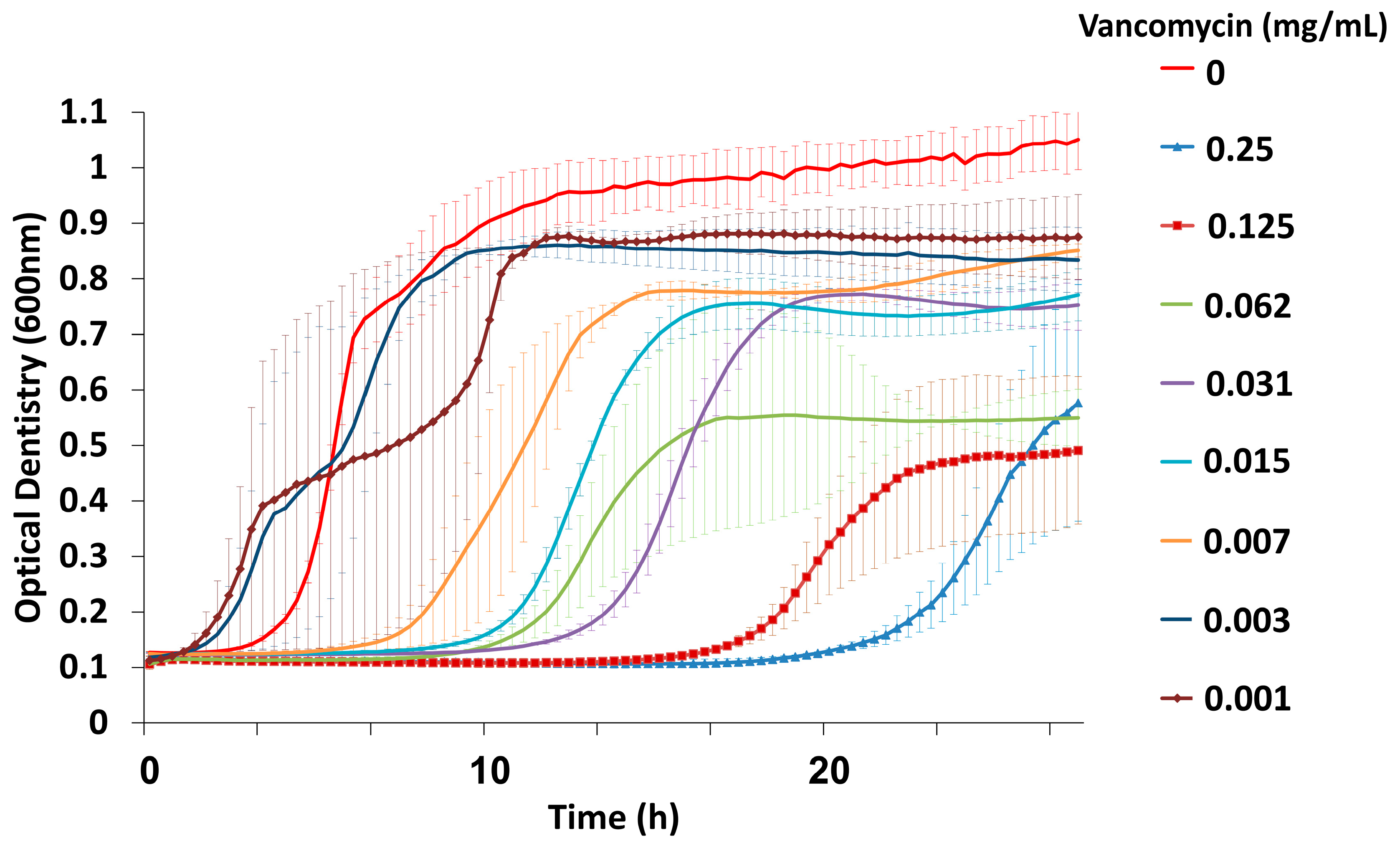
2.3. Determination of Vancomycin Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
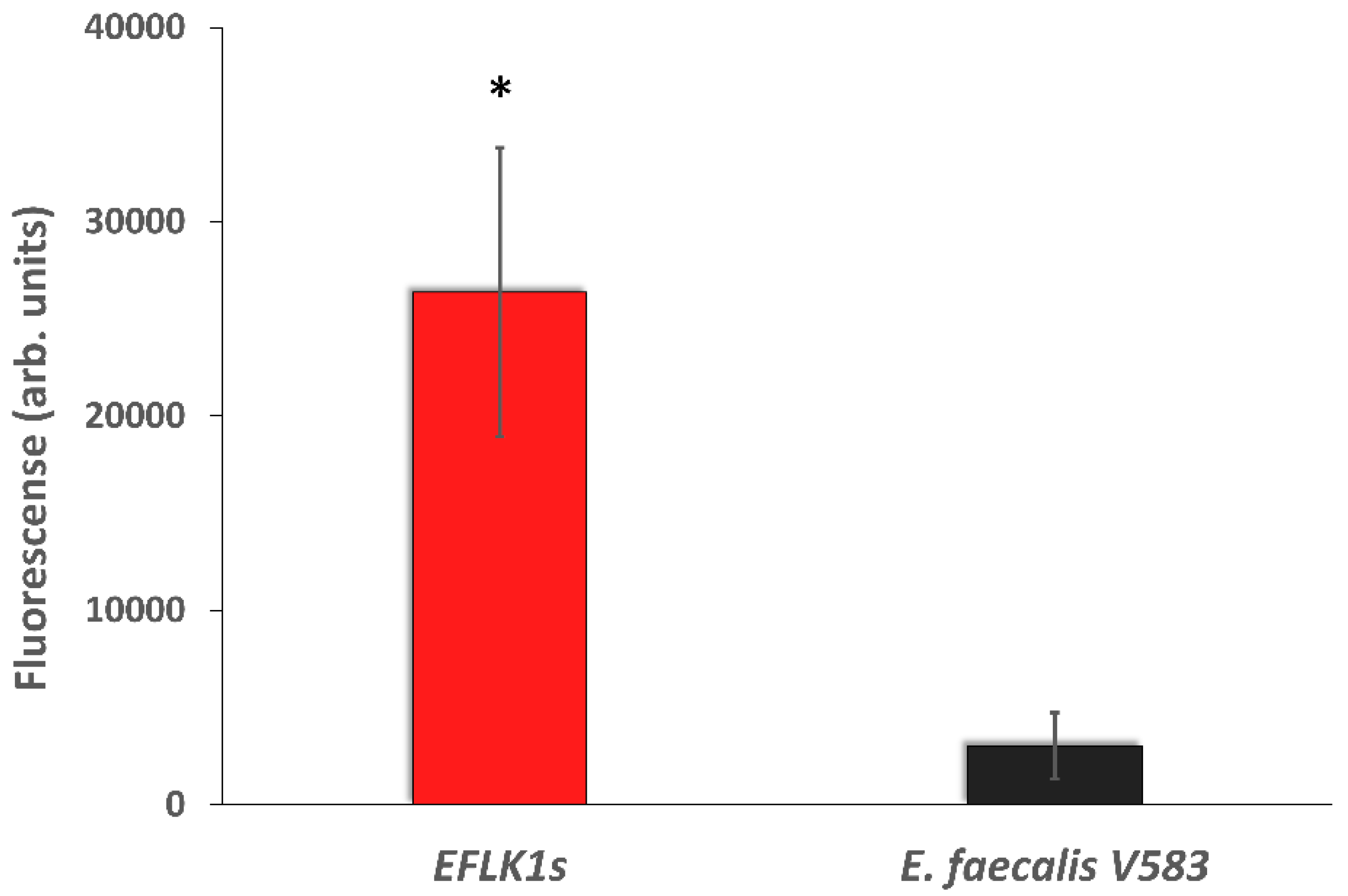
2.4. Host-Range Specificity Tests
2.5. Assessment of Phage and Antibiotic Lytic Activity in Planktonic Cultures
2.6. Assessment of Phage Lytic Activity in a Biofilm
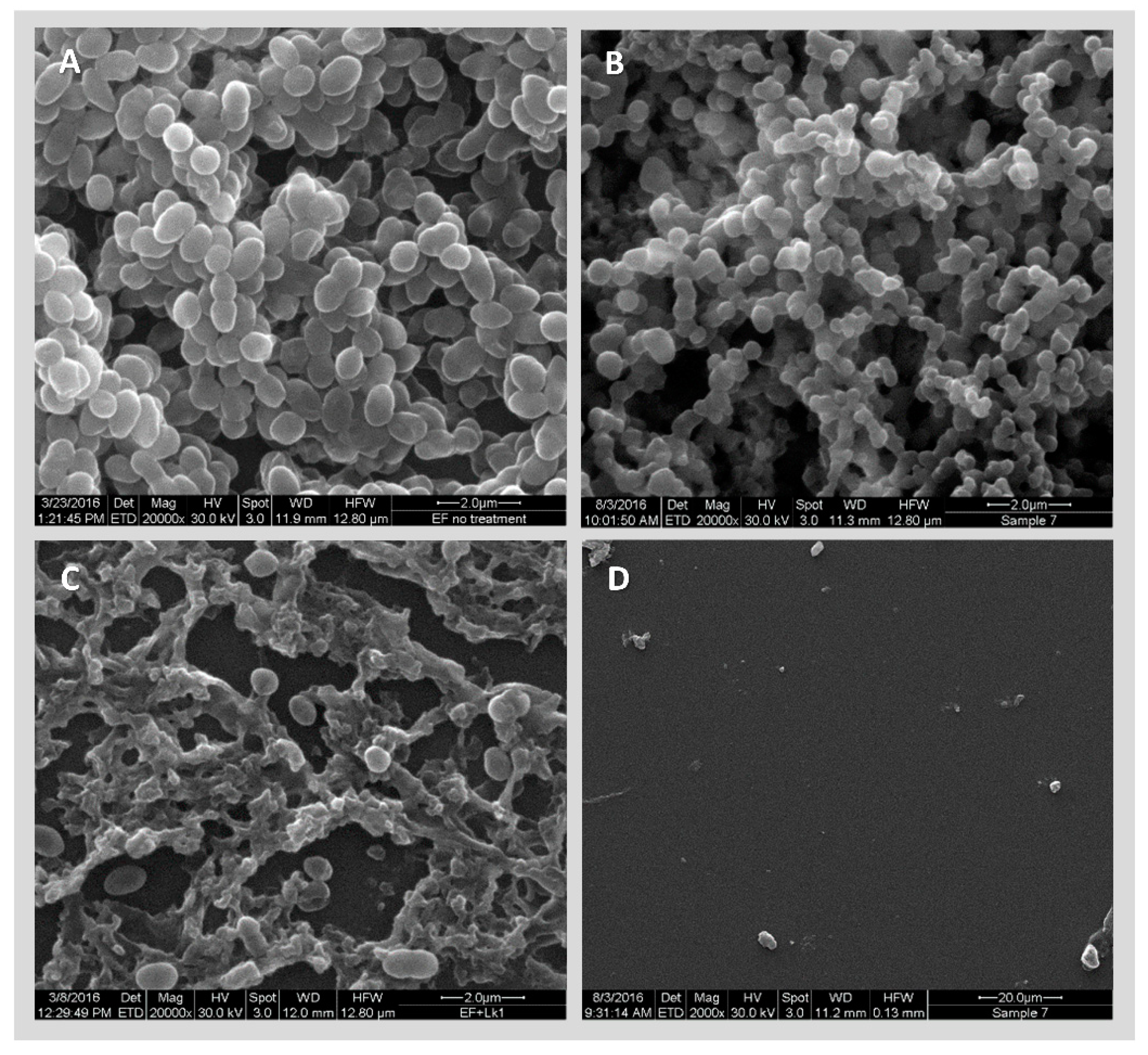
2.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
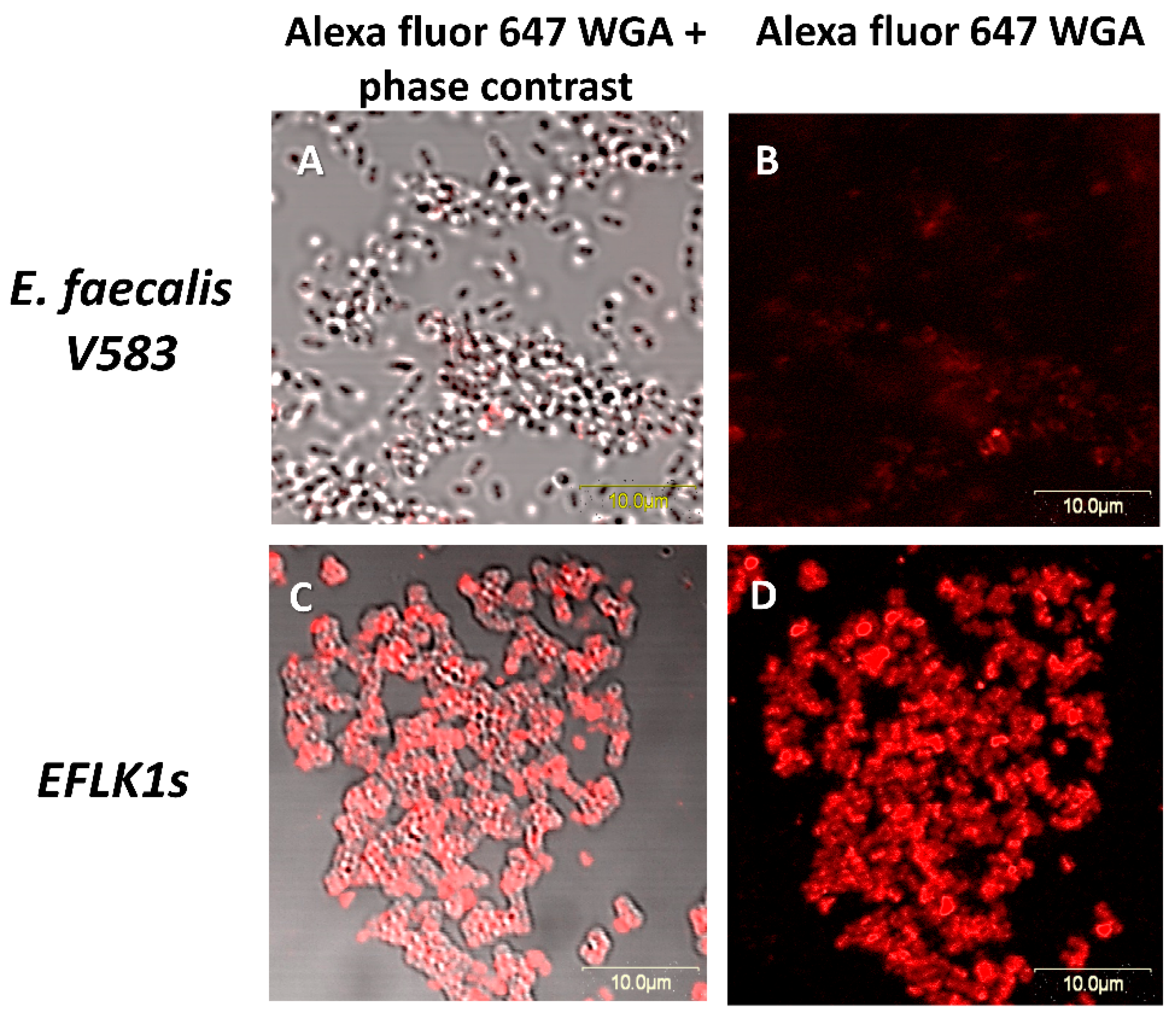
2.8. Detection of N-Acetylglucosamine in Cell-Wall
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
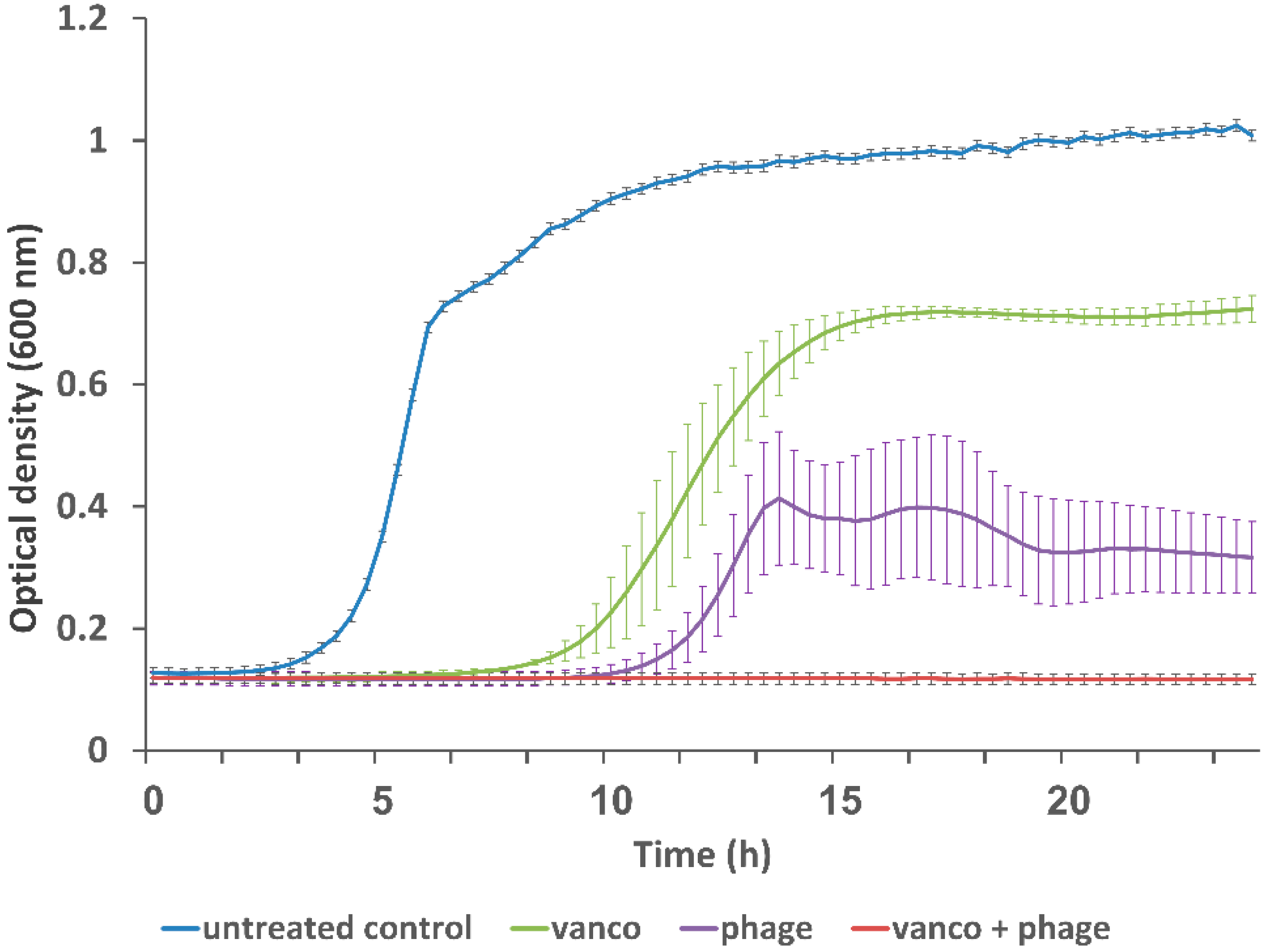
3.1. Combined Treatment with Vancomycin and Phage EFLK1 Reduced VRE Planktonic Growth
3.2. Combined Treatment of Vancomycin and Phage EFLK1 Reduced 72 h Biofilms
3.3. Identifying Cell Wall Changes Followed Phage Treatment
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bereket, W.; Hemalatha, K.; Getenet, B.; Wondwossen, T.; Solomon, A.; Zeynudin, A.; Kannan, S. Update on bacterial nosocomial infections. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 16, 1039–1044. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cabiltes, I.; Coghill, S.; Bowe, S.J.; Athan, E. Enterococcal bacteraemia “Silent but deadly”: A population-based cohort study. Intern. Med. J. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristich, C.J.; Rice, L.B.; Arias, C.A. Enterococcal Infection-Treatment and Antibiotic Resistance. In Enterococci: From Commensals to Leading Causes of Drug Resistant Infection; Gilmore, M.S., Clewell, D.B., Ike, Y., Shankar, N., Eds.; Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary: Boston, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Perl, T.M. The threat of vancomycin resistance. Am. J. Med. 1999, 106, 26S–37S, discussion 48S–52S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceci, M.; Delpech, G.; Sparo, M.; Mezzina, V.; Sanchez Bruni, S.; Baldaccini, B. Clinical and microbiological features of bacteremia caused by Enterococcus faecalis. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2015, 9, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brussow, H.; Canchaya, C.; Hardt, W.D. Phages and the evolution of bacterial pathogens: From genomic rearrangements to lysogenic conversion. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2004, 68, 560–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cisek, A.A.; Dabrowska, I.; Gregorczyk, K.P.; Wyzewski, Z. Phage Therapy in Bacterial Infections Treatment: One Hundred Years After the Discovery of Bacteriophages. Curr. Microbiol. 2017, 74, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedon, S.T. Ecology of anti-biofilm agents II: Bacteriophage exploitation and biocontrol of biofilm bacteria. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2015, 8, 559–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.M.; Koskella, B.; Lin, H.C. Phage therapy: An alternative to antibiotics in the age of multi-drug resistance. World J. Gastrointest. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 8, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, L.; Gelman, D.; Shlezinger, M.; Dessal, A.L.; Coppenhagen-Glazer, S.; Beyth, N.; Hazan, R. Defeating antibiotic-and phage-resistant Enterococcus faecalis using a phage cocktail in Vitro and in a clot model. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paisano, A.F.; Spira, B.; Cai, S.; Bombana, A.C. In vitro antimicrobial effect of bacteriophages on human dentin infected with Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 29212. Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 2004, 19, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shlezinger, M.; Friedman, M.; Houri-Haddad, Y.; Hazan, R.; Beyth, N. Phages in a thermoreversible sustained-release formulation targeting E. Faecalis in vitro and in vivo. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szafranski, S.P.; Winkel, A.; Stiesch, M. The use of bacteriophages to biocontrol oral biofilms. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 250, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loc-Carrillo, C.; Abedon, S.T. Pros and cons of phage therapy. Bacteriophage 2011, 1, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorski, A.; Miedzybrodzki, R.; Jonczyk-Matysiak, E.; Borysowski, J.; Letkiewicz, S.; Weber-Dabrowska, B. The fall and rise of phage therapy in modern medicine. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2019, 19, 1115–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalifa, L.; Coppenhagen-Glazer, S.; Shlezinger, M.; Kott-Gutkowski, M.; Adini, O.; Beyth, N.; Hazan, R. Complete Genome Sequence of Enterococcus Bacteriophage EFLK1. Genome Announc. 2015, 3, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard-Varona, C.; Hargreaves, K.R.; Abedon, S.T.; Sullivan, M.B. Lysogeny in nature: Mechanisms, impact and ecology of temperate phages. ISME J. 2017, 11, 1511–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accetto, T.; Janez, N. The lytic Myoviridae of Enterobacteriaceae form tight recombining assemblages separated by discontinuities in genome average nucleotide identity and lateral gene flow. Microb. Genom. 2018, 4, e000169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nir-Paz, R.; Gelman, D.; Khouri, A.; Sisson, B.M.; Fackler, J.; Alkalay-Oren, S.; Khalifa, L.; Rimon, A.; Yerushalmy, O.; Bader, R.; et al. Successful treatment of antibiotic resistant poly-microbial bone infection with bacteriophages and antibiotics combination. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, J.J.; Hyman, P. Phage choice, isolation, and preparation for phage therapy. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2010, 11, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Barcelo, C.; Hochberg, M.E. Evolutionary Rationale for Phages as Complements of Antibiotics. Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crain, C.M.; Kroeker, K.; Halpern, B.S. Interactive and cumulative effects of multiple human stressors in marine systems. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 1304–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelman, D.; Beyth, S.; Lerer, V.; Adler, K.; Poradosu-Cohen, R.; Coppenhagen-Glazer, S.; Hazan, R. Combined bacteriophages and antibiotics as an efficient therapy against VRE Enterococcus faecalis in a mouse model. Res. Microbiol. 2018, 169, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comeau, A.M.; Tetart, F.; Trojet, S.N.; Prere, M.F.; Krisch, H.M. Phage-Antibiotic Synergy (PAS): Beta-lactam and quinolone antibiotics stimulate virulent phage growth. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, E.M.; Alkawareek, M.Y.; Donnelly, R.F.; Gilmore, B.F. Synergistic phage-antibiotic combinations for the control of Escherichia coli biofilms in vitro. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 65, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedi, M.S.; Verma, V.; Chhibber, S. Amoxicillin and specific bacteriophage can be used together for eradication of biofilm of Klebsiella pneumoniae B5055. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 25, 1145–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, F.; Dennis, J.J. Burkholderia cepacia complex Phage-Antibiotic Synergy (PAS): Antibiotics stimulate lytic phage activity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 1132–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himmelweit, F. Combined action of penicillin and bacteriophage on staphylococci. Lancet 1945, 246, 104–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knezevic, P.; Curcin, S.; Aleksic, V.; Petrusic, M.; Vlaski, L. Phage-antibiotic synergism: A possible approach to combatting pseudomonas aeruginosa. Res. Microbiol. 2013, 164, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akturk, E.; Oliveira, H.; Santos, S.B.; Costa, S.; Kuyumcu, S.; Melo, L.D.R.; Azeredo, J. Synergistic action of phage and antibiotics: Parameters to enhance the killing efficacy against mono and dual-species biofilms. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oechslin, F.; Piccardi, P.; Mancini, S.; Gabard, J.; Moreillon, P.; Entenza, J.M.; Resch, G.; Que, Y.A. Synergistic interaction between phage therapy and antibiotics clears pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in endocarditis and reduces virulence. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 215, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Chang, R.Y.K.; Britton, W.J.; Morales, S.; Kutter, E.; Li, J.; Chan, H.K. Inhalable combination powder formulations of phage and ciprofloxacin for P. aeruginosa respiratory infections. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 142, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahm, D.F.; Kissinger, J.; Gilmore, M.S.; Murray, P.R.; Mulder, R.; Solliday, J.; Clarke, B. In vitro susceptibility studies of vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1989, 33, 1588–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulsen, I.T.; Banerjei, L.; Myers, G.S.; Nelson, K.E.; Seshadri, R.; Read, T.D.; Fouts, D.E.; Eisen, J.A.; Gill, S.R.; Heidelberg, J.F.; et al. Role of mobile DNA in the evolution of vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis. Science 2003, 299, 2071–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalifa, L.; Brosh, Y.; Gelman, D.; Coppenhagen-Glazer, S.; Beyth, S.; Poradosu-Cohen, R.; Que, Y.A.; Beyth, N.; Hazan, R. Targeting Enterococcus faecalis biofilms with phage therapy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 2696–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stepanovic, S.; Vukovic, D.; Dakic, I.; Savic, B.; Svabic-Vlahovic, M. A modified microtiter-plate test for quantification of staphylococcal biofilm formation. J. Microbiol. Methods 2000, 40, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nir-Paz, R.; Eugster, M.R.; Zeiman, E.; Loessner, M.J.; Calendar, R. Listeria monocytogenes tyrosine phosphatases affect wall teichoic acid composition and phage resistance. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2012, 326, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shlezinger, M.; Khalifa, L.; Houri-Haddad, Y.; Coppenhagen-Glazer, S.; Resch, G.; Que, Y.A.; Beyth, S.; Dorfman, E.; Hazan, R.; Beyth, N. Phage Therapy: A new horizon in the antibacterial treatment of oral pathogens. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 1199–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheviakova, O.I.; Sherman, R.Z.; Tatarinova, S.D. Treatment of dysentery in children with polymyxin and bacteriophage. Antibiotiki 1964, 9, 269–272. [Google Scholar]
- Sheviakova, O.I. Effect of bacteriophage on resistance of flexner’s bacillus to antibiotics. Antibiotiki (Mosc) 1956, 1, 40–42. [Google Scholar]
- Sheviakova, O.I.; IuS, K. Effect of combined antibiotics of the tetracycline series with bacteriophage on Shigella dysenteriae. Antibiotiki (Mosc) 1958, 3, 96–98. [Google Scholar]
- Chanishvili, N.; Chanishvili, T.; Tediashvili, M.; Barrow, P.A. Phages and their application against drug-resistant bacteria. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2001, 76, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegrzyn, G.; Licznerska, K.; Wegrzyn, A. Phage lambda—New insights into regulatory circuits. Adv. Virus Res. 2012, 82, 155–178. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huff, W.E.; Huff, G.R.; Rath, N.C.; Balog, J.M.; Donoghue, A.M. Therapeutic efficacy of bacteriophage and Baytril (enrofloxacin) individually and in combination to treat colibacillosis in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2004, 83, 1944–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagens, S.; Habel, A.; Blasi, U. Augmentation of the antimicrobial efficacy of antibiotics by filamentous phage. Microb. Drug Resist. 2006, 12, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Liang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, L.; Gong, P.; Cai, R.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Ge, J.; Ji, Y.; et al. The bacteriophage ef-p29 efficiently protects against lethal vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis and alleviates gut microbiota imbalance in a murine bacteremia model. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duerkop, B.A.; Huo, W.; Bhardwaj, P.; Palmer, K.L.; Hooper, L.V. Molecular basis for lytic bacteriophage resistance in enterococci. MBio 2016, 7, 4–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henein, A. What are the limitations on the wider therapeutic use of phage? Bacteriophage 2013, 3, e24872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busque, L.; Porwit, A.; Day, R.; Olney, H.J.; Leber, B.; Ethier, V.; Sirhan, S.; Foltz, L.; Prchal, J.; Kamel-Reid, S.; et al. Laboratory investigation of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms (MPNs): Recommendations of the Canadian Mpn Group. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2016, 146, 408–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, P.E. Structure, biochemistry and mechanism of action of glycopeptide antibiotics. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1989, 8, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, H.S. Vancomycin-resistant enterococci: Mechanisms and clinical observations. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 33, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, I.; Wang, I.; Roof, W.D. Phages will out: Strategies of host cell lysis. Trends Microbiol. 2000, 8, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latka, A.; Maciejewska, B.; Majkowska-Skrobek, G.; Briers, Y.; Drulis-Kawa, Z. Bacteriophage-encoded virion-associated enzymes to overcome the carbohydrate barriers during the infection process. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 3103–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Bacterial Strain | Origin a | Antibiotic Resistance b | Phage EFLK1 c | Vancomycin MIC (mg/mL) d | Phage EFLK1 + Vancomycin MIC (mg/mL) e |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enterococcus faecalis V583 | ATCC 700802 | Vancomycin Gentamicin | S | >0.25 | 0.015 |
| Enterococcus faecalis Aef01 | Clinically isolated from urine | - | S | 0.003 | <0.001 |
| Enterococcus faecalis Aef03 | Clinically isolated from urine | - | S | 0.007 | <0.001 |
| Enterococcus faecalis Aef05 | Clinically isolated from venal blood flow | Erythromycin Gentamicin | S | 0.003 | <0.001 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shlezinger, M.; Coppenhagen-Glazer, S.; Gelman, D.; Beyth, N.; Hazan, R. Eradication of Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci by Combining Phage and Vancomycin. Viruses 2019, 11, 954. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11100954
Shlezinger M, Coppenhagen-Glazer S, Gelman D, Beyth N, Hazan R. Eradication of Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci by Combining Phage and Vancomycin. Viruses. 2019; 11(10):954. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11100954
Chicago/Turabian StyleShlezinger, Mor, Shunit Coppenhagen-Glazer, Daniel Gelman, Nurit Beyth, and Ronen Hazan. 2019. "Eradication of Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci by Combining Phage and Vancomycin" Viruses 11, no. 10: 954. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11100954
APA StyleShlezinger, M., Coppenhagen-Glazer, S., Gelman, D., Beyth, N., & Hazan, R. (2019). Eradication of Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci by Combining Phage and Vancomycin. Viruses, 11(10), 954. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11100954





