Evolution of Tembusu Virus in Ducks, Chickens, Geese, Sparrows, and Mosquitoes in Northern China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Epidemiological Survey
2.3. Virus Isolate Descriptions
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. Viral Protein Structure Modeling and Glycosylation Site Prediction
3. Results
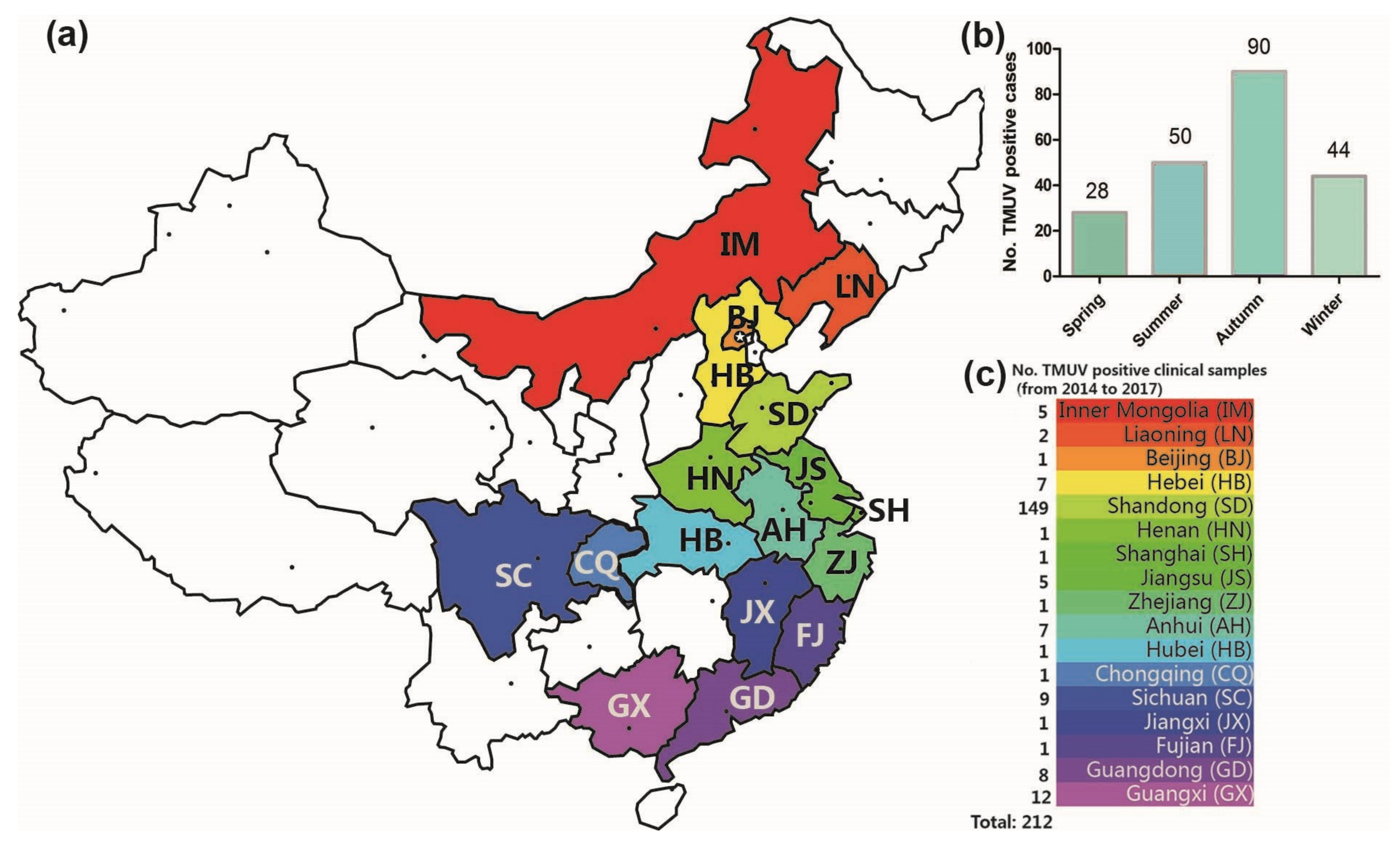
3.1. Epidemiological Survey
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
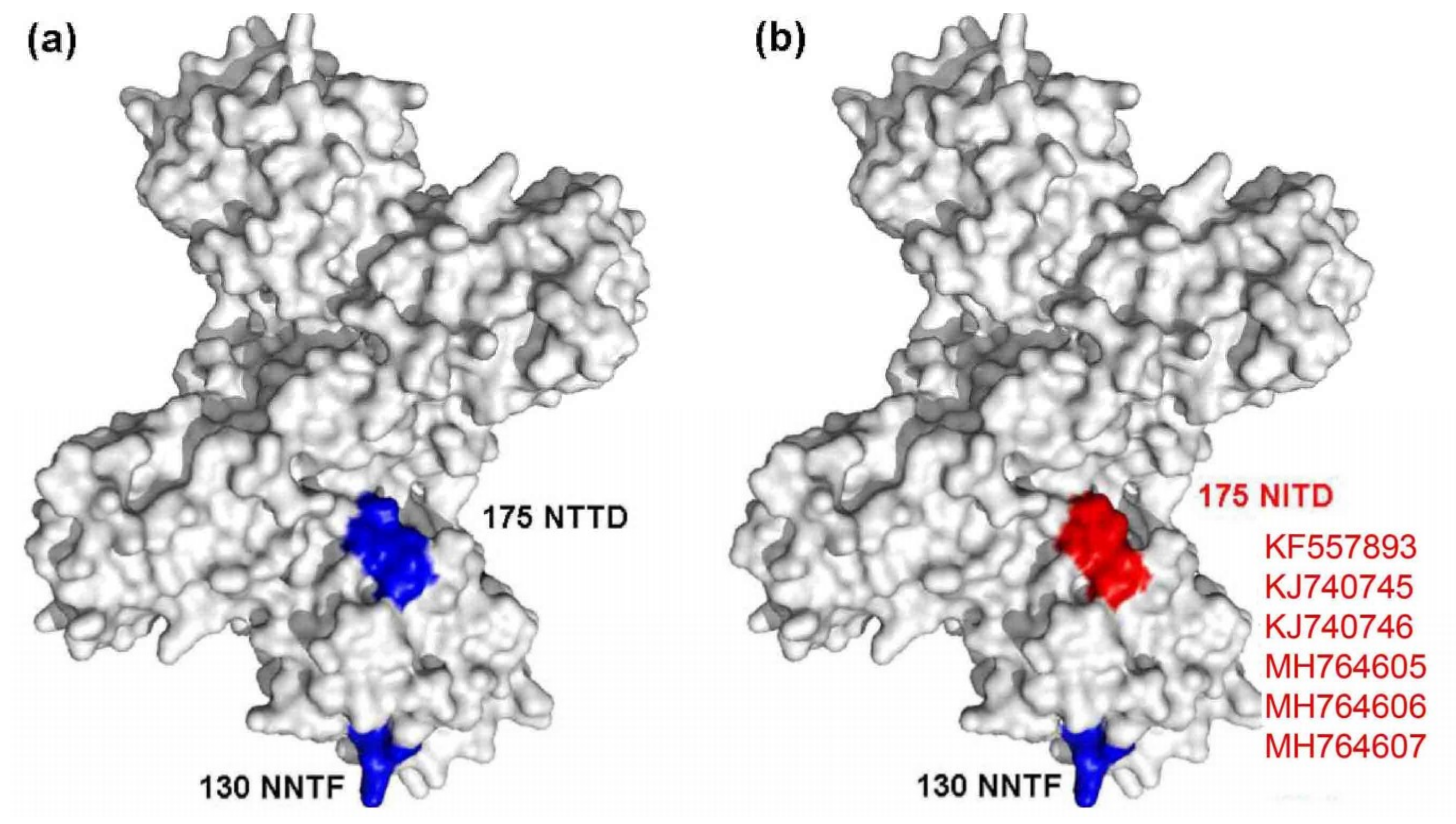
3.3. Viral Protein Structure and Glycosylation Site
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, G.; Lin, Y.; Tang, Y.; Diao, Y. Comparative Transcriptomic Analysis of Immune-Related Gene Expression in Duck Embryo Fibroblasts Following Duck Tembusu Virus Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, W.; Guo, X.; Fu, S.; Feng, Y.; Tao, X.; Gao, X.; Song, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, H.; Liang, G. The genetic characteristics and evolution of Tembusu virus. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 201, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homonnay, Z.G.; Kovacs, E.W.; Banyai, K.; Albert, M.; Feher, E.; Mato, T.; Tatar-Kis, T.; Palya, V. Tembusu-like flavivirus (Perak virus) as the cause of neurological disease outbreaks in young Pekin ducks. Avian Pathol. 2014, 43, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kono, Y.; Tsukamoto, K.; Hamid, M.; Darus, A.; Lian, T.; Sam, L.; Yok, C.; Di, K.; Lim, K.; Yamaguchi, S.; et al. Encephalitis and retarded growth of chicks caused by Sitiawan virus, a new isolate belonging to the genus Flavivirus.pdf. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2000, 63, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, K.; Sheng, Z.Z.; Huang, B.; Ma, X.; Li, Y.; Yuan, X.; Qin, Z.; Wang, D.; Chakravarty, S.; Li, F.; et al. Structural, antigenic, and evolutionary characterizations of the envelope protein of newly emerging Duck Tembusu Virus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Han, K.; Zhao, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Niu, H.; Zhang, K.; Zhu, J.; Wu, D.; Gao, L.; et al. Identification and molecular characterization of a novel flavivirus isolated from geese in China. Res. Vet. Sci. 2013, 94, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ti, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, F.; Diao, Y. Effect of age and inoculation route on the infection of duck Tembusu virus in Goslings. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 181, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Wang, A.; Chen, S.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Jia, R.; Zhu, D.; Liu, M.; Yang, Q.; et al. Differential immune-related gene expression in the spleens of duck Tembusu virus-infected goslings. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 212, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, G.; Chen, C.; Huang, Y.; Cheng, L.; Fu, Q.; Wan, C.; Shi, S.; Chen, H.; Liu, W. Comparative analysis of transcriptional profiles of retinoic-acid-induced gene I-like receptors and interferons in seven tissues from ducks infected with avian Tembusu virus. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Diao, Y.; Chen, H.; Ou, Q.; Liu, X.; Gao, X.; Yu, C.; Wang, L. Isolation and genetic characterization of a tembusu virus strain isolated from mosquitoes in Shandong, China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2015, 62, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Diao, Y.; Yu, C.; Gao, X.; Ju, X.; Xue, C.; Liu, X.; Ge, P.; Qu, J.; Zhang, D. Characterization of a Tembusu virus isolated from naturally infected house sparrows (Passer domesticus) in Northern China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2013, 60, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Lu, H.; Li, S.; Moureau, G.; Deng, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, T.; de Lamballerie, X.; Qin, C.F.; et al. Genomic and antigenic characterization of the newly emerging Chinese duck egg-drop syndrome flavivirus: Genomic comparison with Tembusu and Sitiawan viruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 2158–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Yu, X.; Tian, K.; Su, W.; Han, B.; Su, J. Duck Tembusu virus exhibits neurovirulence in BALB_c mice. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ti, J.; Zhang, M.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Diao, Y. Duck Tembusu Virus Exhibits Pathogenicity to Kunming Mice by Intracerebral Inoculation. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Gao, X.; Diao, Y.; Feng, Q.; Chen, H.; Liu, X.; Ge, P.; Yu, C. Tembusu virus in human, China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2013, 60, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Yu, X.; Yang, G.; Tang, Y.; Diao, Y. A novel diagnostic method to detect Duck Tembusu Virus: A colloidal gold-based immunochromatographic assay. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Z. Multiplicity of viral quasispecies and its evolution under selective pressure of antibody immunity. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 25, 843–852. [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger, J.J. Flavivirus nonstructural protein NS1: complementary surprises. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 18879–18880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tafuku, S.; Miyata, T.; Tadano, M.; Mitsumata, R.; Kawakami, H.; Harakuni, T.; Sewaki, T.; Arakawa, T. Japanese encephalitis virus structural and nonstructural proteins expressed in Escherichia coli induce protective immunity in mice. Microbes Infect. 2012, 14, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bralut, A.; Domi, A.; McDonald, E.M.; Talmi-Frank, D.; McCurley, N.; Basu, R.; Robinson, H.L.; Hellerstein, M.; Duggal, N.K.; Bowen, R.A.; et al. A Zika vaccine targeting NS1 protein protects immunocompetent adult mice in a lethal challenge model. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, D.A.; Young, P.R. The flavivirus NS1 protein: Molecular and structural biology, immunology, role in pathogenesis and application as a diagnostic biomarker. Antivir. Res. 2013, 98, 192–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akey, D.L.; Brown, W.C.; Dutta, S.; Konwerski, J.; Jose, J.; Jurkiw, T.J.; DelProposto, J.; Ogata, C.M.; Skiniotis, G.; Kuhn, R.J.; et al. Flavivirus NS1 structures reveal surfaces for associations with membranes and the immune system. Science 2014, 343, 881–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Lei, C.Q.; Ji, Y.; Zhou, H.; Ren, Y.; Peng, Q.; Zeng, Y.; Jia, Y.; Ge, J.; Zhong, B.; et al. Duck Tembusu Virus nonstructural protein 1 antagonizes IFN-β signaling pathways by targeting VISA. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 4704–4713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.; Li, S.; Hu, X.; Yu, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, P.; Lu, X.; Zhang, G.; Hu, X.; Liu, D.; et al. Duck egg-drop syndrome caused by BYD virus, a new Tembusu-related flavivirus. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Strains | Host | Age | Tissue | Co-Infection | Location | Date | Accession |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TC2B | Layer duck | 16 d | Liver | - | SD | 2011.09.25 | MH764605 |
| SDSG | Layer duck | 30 d | Liver | H9 | SD | 2011.11.01 | KJ740746 |
| lq-1 | Goose | 58 d | Brain | GoCV, GPV | SD | 2012.10.26 | KF557893 |
| SDMS | Culex mosquito | - | Body | - | SD | 2012.06.01 | KC333867 [10] |
| SDHS | House sparrow | - | Liver | - | SD | 2012.12.15 | KF826767 [11] |
| SX1 | Layer chicken | 45 d | Liver | H9 | SD | 2013.11.22 | KM066945 |
| SDXT | Layer duck | 210 d | Liver | DHAV-1 | SD | 2013.10.01 | KJ740745 |
| SDLC | Layer duck | 103 d | Liver | H7, H9 | SD | 2013.11.01 | KJ740747 |
| AHQY | Layer duck | 160 d | Liver | - | AH | 2013.11.06 | KJ740748 |
| SDDZ | Meat duck | 36 d | Liver | FAdV-4 | SD | 2016.10.17 | MH764606 |
| NMCF | Meat duck | 22 d | Liver | DHAV-1 | IM | 2017.01.02 | MH764607 |
| Strains | Nucleotide Homology (nt, %) | Amino Acid Homology (aa, %) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E | NS1 | NS3 | NS5 | E | NS1 | NS3 | NS5 | |
| TC2B | 86.8–100.0 | 86.2–100.0 | 87.7–100.0 | 86.5–100.0 | 96.6–100.0 | 93.5–100.0 | 98.4–100.0 | 97.9–100.0 |
| SDSG | 86.8–99.9 | 86.1–99.7 | 87.6–99.9 | 86.5–100.0 | 96.6–100.0 | 93.5–99.7 | 98.2–99.8 | 97.9–100.0 |
| lq-1 | 86.4–99.6 | 84.5–99.1 | 87.5–100.0 | 86.3–99.5 | 95.6–99.4 | 88.4–98.3 | 98.1–100.0 | 97.1–99.4 |
| SDMS | 87.0–100.0 | 86.1–100.0 | 87.8–100.0 | 86.8–100.0 | 96.8–100.0 | 92.9–100.0 | 98.4–100.0 | 97.9–100.0 |
| SDHS | 87.0–100.0 | 86.1–100.0 | 87.8–100.0 | 86.8–100.0 | 96.8–100.0 | 92.9–100.0 | 98.4–100.0 | 97.9–100.0 |
| SX1 | 86.6–99.7 | 85.0–99.6 | 87.4–99.7 | 86.3–99.8 | 96.2–99.6 | 91.5–99.4 | 97.6–99.2 | 97.8–99.9 |
| SDXT | 86.6–99.9 | 86.4–99.7 | 87.8–99.9 | 86.5–99.9 | 96.4–99.8 | 93.8–99.7 | 98.4–100.0 | 97.9–100.0 |
| SDLC | 86.5–100.0 | 85.4–99.8 | 87.3–99.6 | 86.2–99.9 | 96.8–100.0 | 92.0–99.7 | 97.6–99.2 | 98.0–100.0 |
| AHQY | 86.5–100.0 | 85.2–99.8 | 87.5–99.6 | 86.2–99.9 | 96.8–100.0 | 91.8–99.7 | 98.2–99.5 | 97.9–99.9 |
| SDDZ | 86.8–100.0 | 86.2–100.0 | 87.7–100 | 86.5–100.0 | 96.6–100.0 | 93.5–100.0 | 98.4–100.0 | 97.9–100.0 |
| NMCF | 86.8–100.0 | 86.2–100.0 | 87.7–100 | 86.5–100.0 | 96.6–100.0 | 93.5–100.0 | 98.4–100.0 | 97.9–100.0 |
| Mean value | 86.7–99.9 | 85.8–99.8 | 87.6–99.9 | 86.5–99.9 | 96.5–99.9 | 92.5–99.68 | 98.2–99.8 | 97.8–99.9 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, G.; Lin, Y.; Tang, Y.; Diao, Y. Evolution of Tembusu Virus in Ducks, Chickens, Geese, Sparrows, and Mosquitoes in Northern China. Viruses 2018, 10, 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10090485
Yu G, Lin Y, Tang Y, Diao Y. Evolution of Tembusu Virus in Ducks, Chickens, Geese, Sparrows, and Mosquitoes in Northern China. Viruses. 2018; 10(9):485. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10090485
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Guanliu, Yun Lin, Yi Tang, and Youxiang Diao. 2018. "Evolution of Tembusu Virus in Ducks, Chickens, Geese, Sparrows, and Mosquitoes in Northern China" Viruses 10, no. 9: 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10090485
APA StyleYu, G., Lin, Y., Tang, Y., & Diao, Y. (2018). Evolution of Tembusu Virus in Ducks, Chickens, Geese, Sparrows, and Mosquitoes in Northern China. Viruses, 10(9), 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10090485





