Improved Baculovirus Vectors for Transduction and Gene Expression in Human Pancreatic Islet Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells, Plasmids and Viruses
2.1.1. Cells
2.1.2. Transfer Plasmid Construction
2.1.3. BacMam Production
2.1.4. Virus Amplification
2.1.5. Titration of Virus Infectivity
2.2. Gene Delivery in Mammalian Cells Using BacMam Virus Vectors
2.2.1. In Vitro Gene Delivery
2.2.2. Ex Vivo Donor Islet Cells
2.3. Fluorescence Microscopy
2.4. Fractionation of Budded Virus Envelope
2.5. SDS-PAGE and Immunoblot Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. Flow Cytometry
2.8. Confocal Microscopy
3. Results
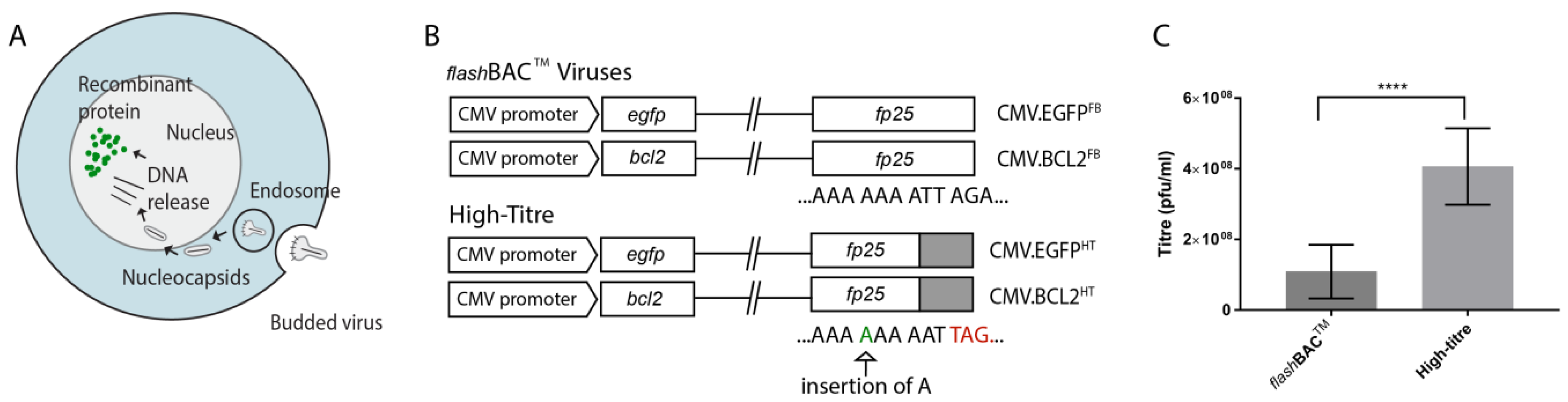
3.1. Enhancing Infectious Budded Virus Production Using BacMam with a Mutation in fp25
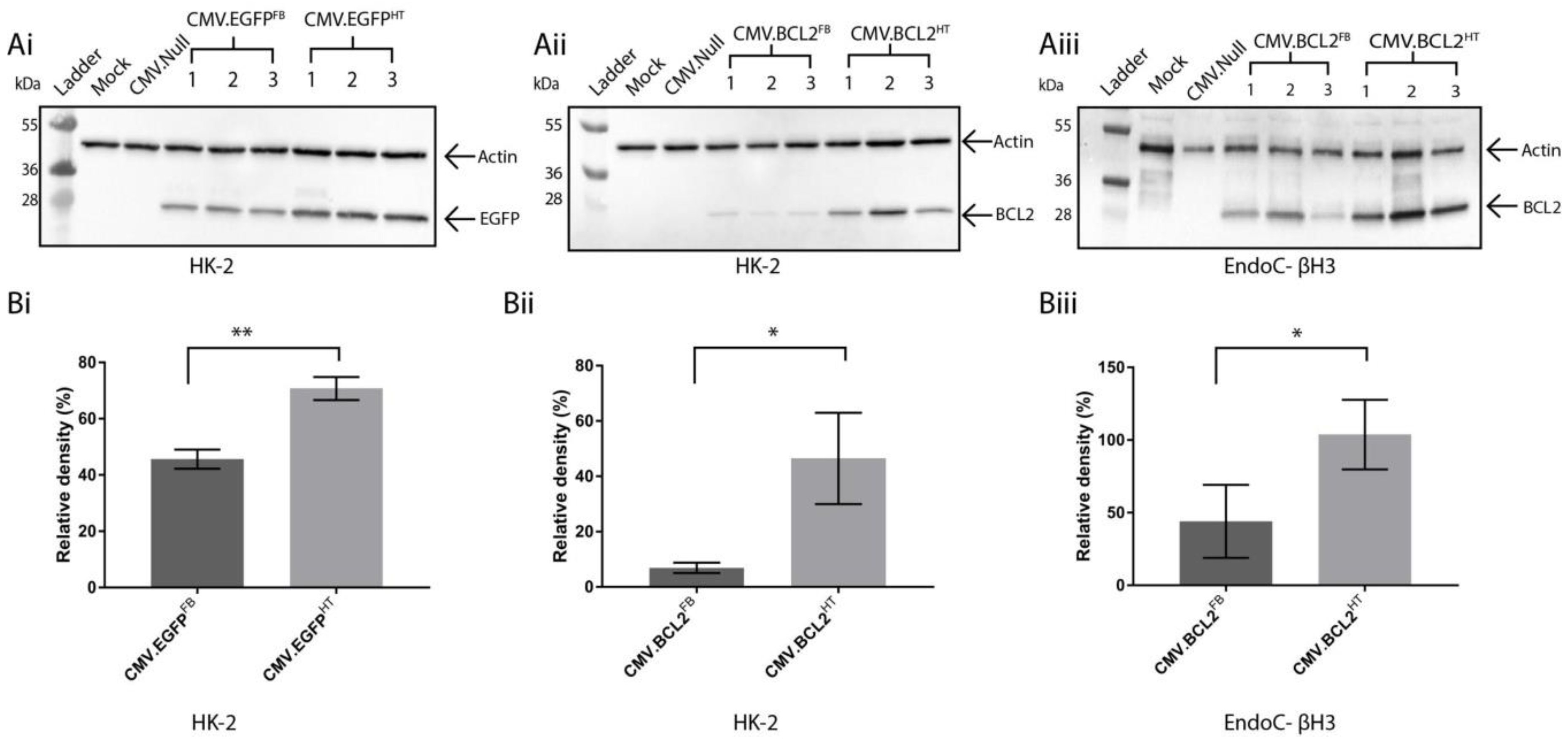
3.2. Improving BacMam-Mediated Gene Expression in Mammalian Cells
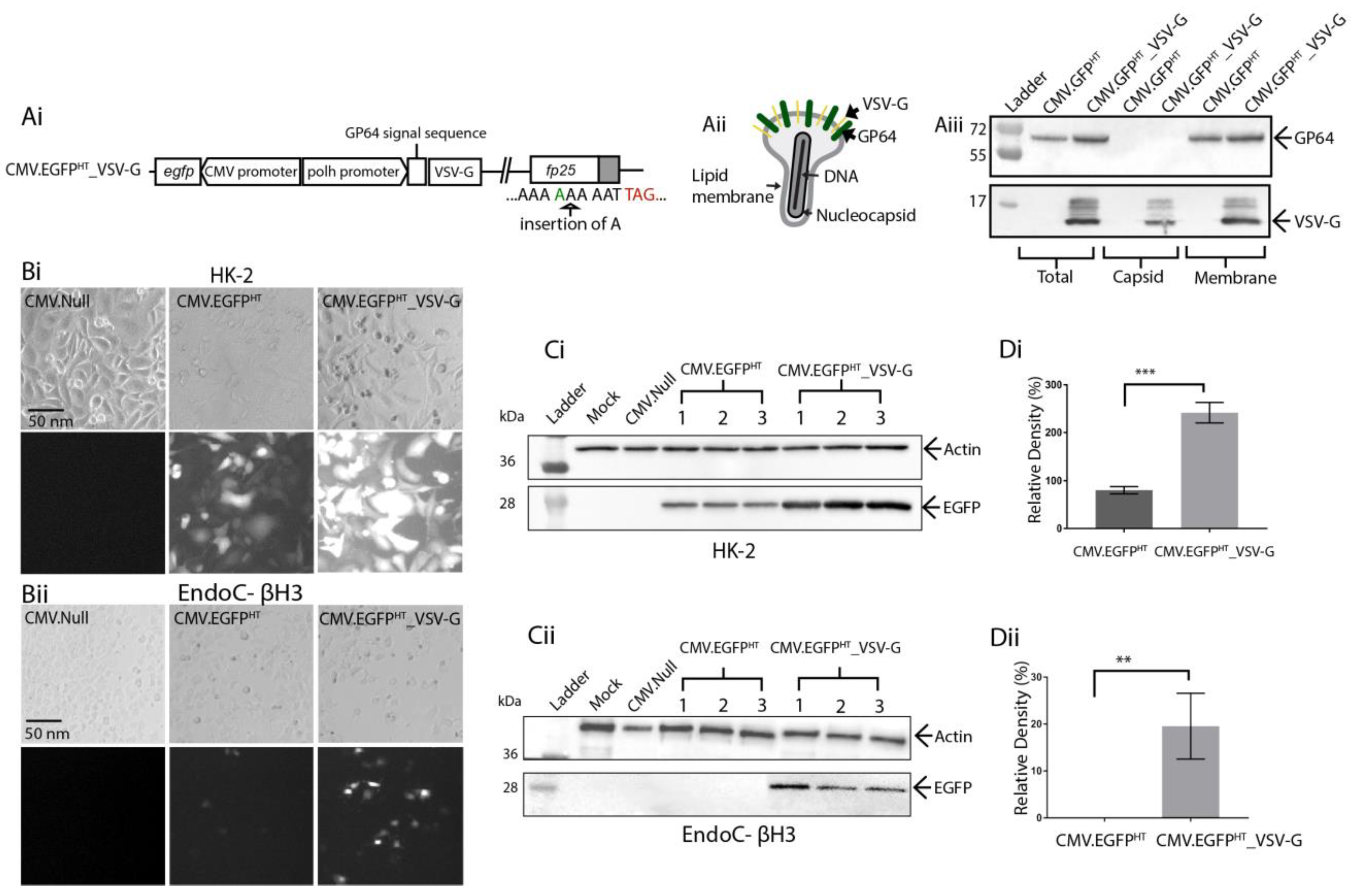
3.3. Pseudotyping Virus Particles with Truncated Vesicular Stomatitis Virus G-Protein to Enhance Transduction Efficacy
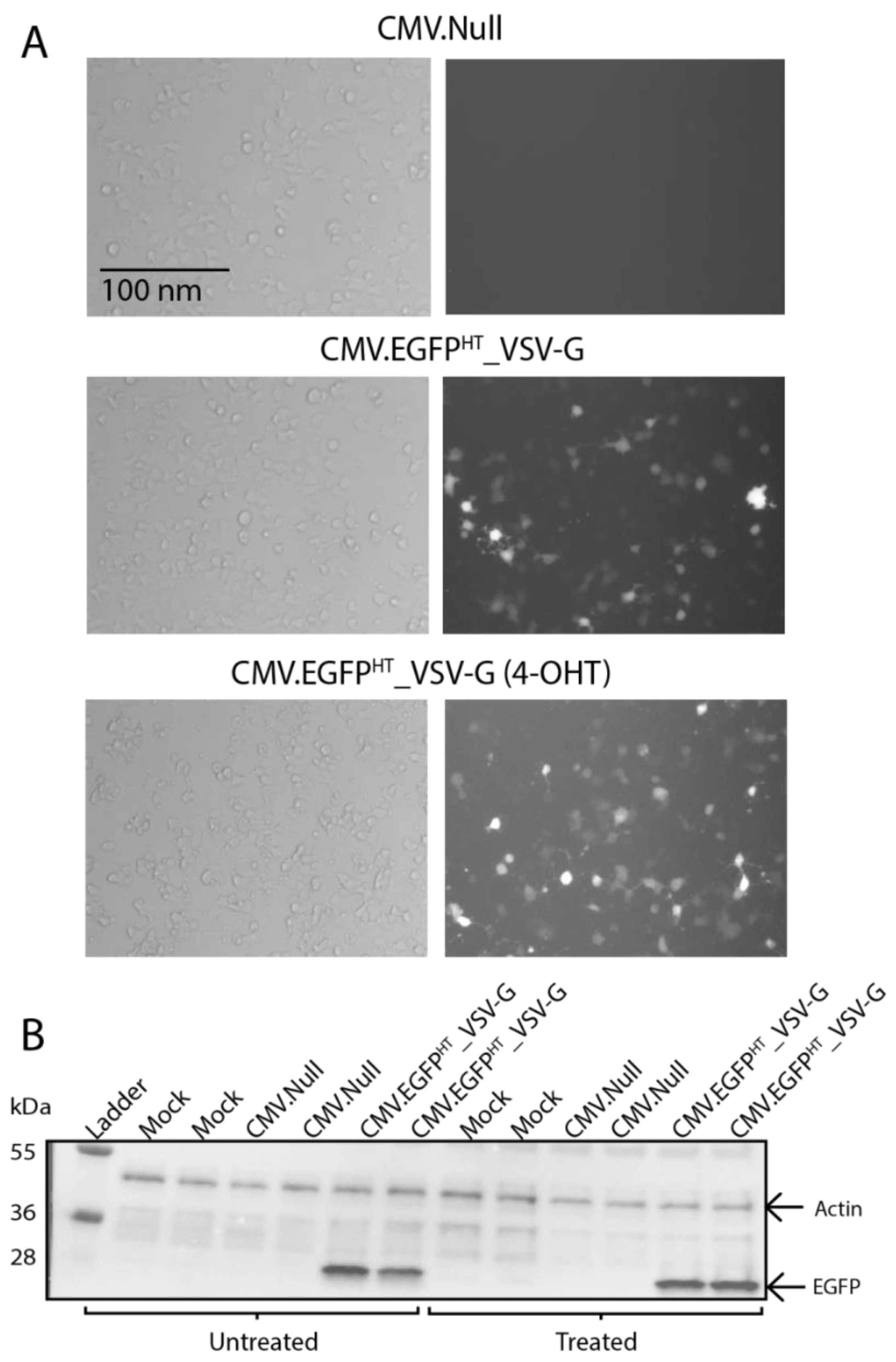
3.4. In Vitro Expression of egfp in a Non-Proliferative Human Beta Cell Line
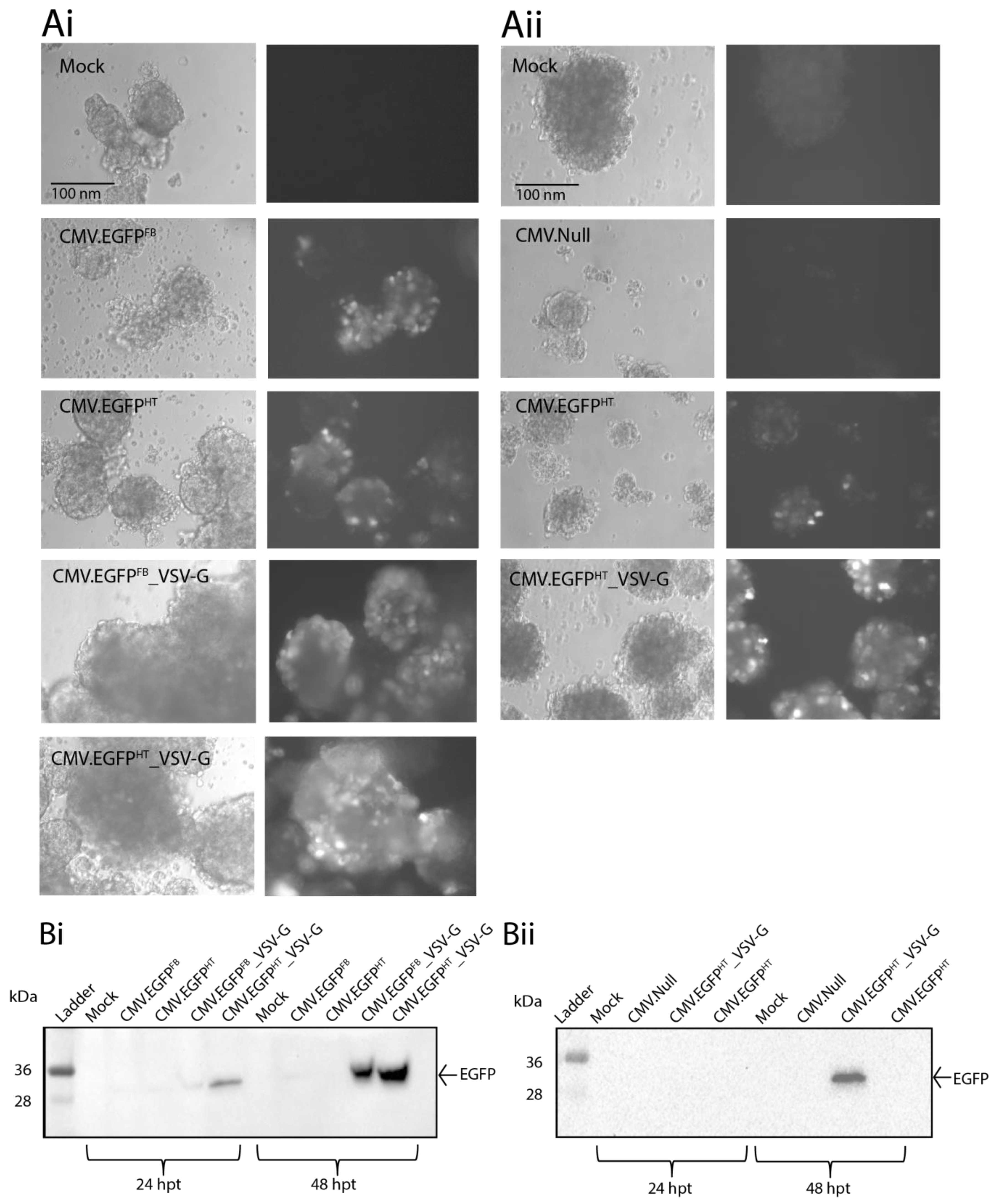
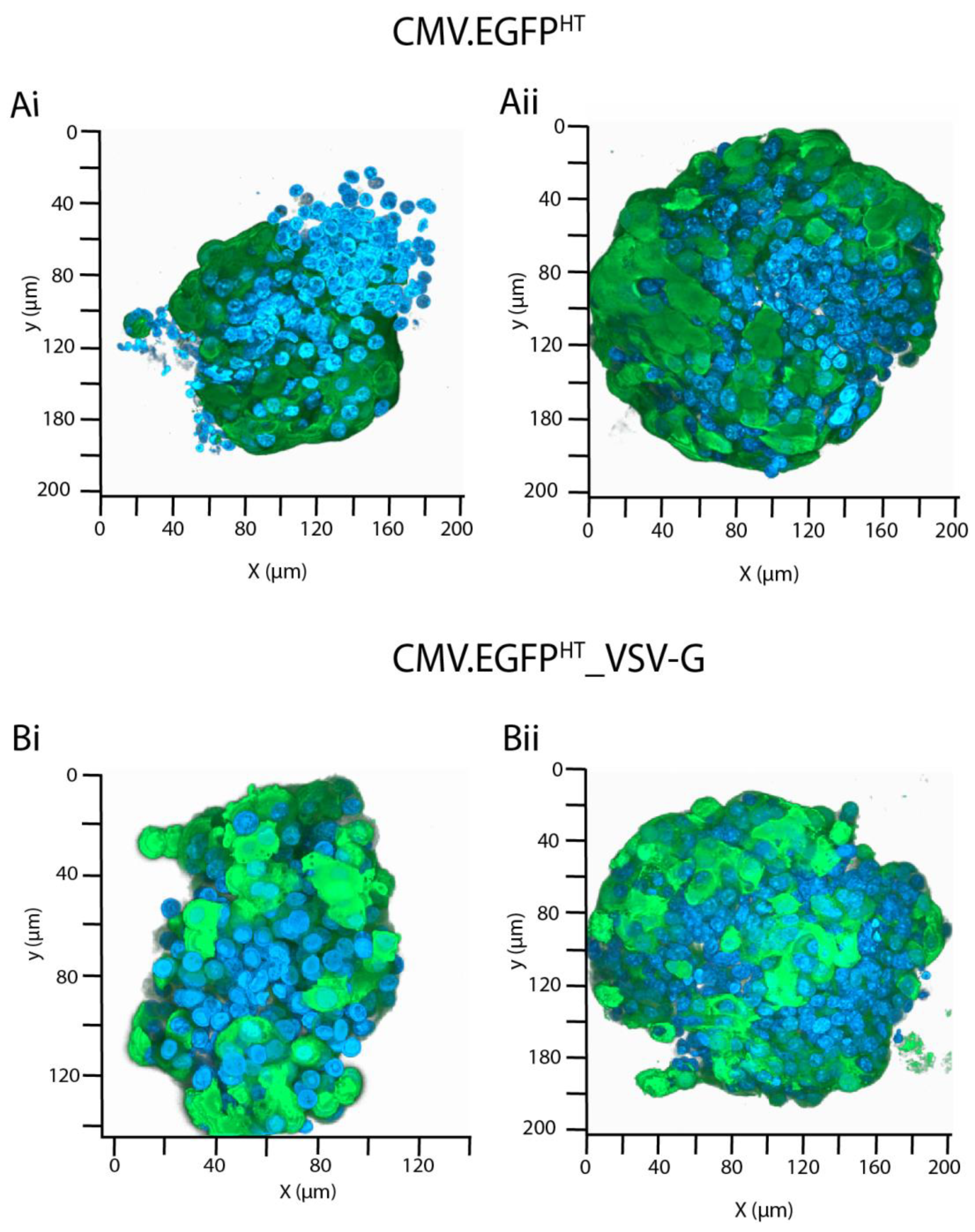
3.5. BacMam Mediated Gene Expression in Human Pancreatic Islet Cells from Cadaveric Donors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cabrera, O.; Berman, D.M.; Kenyon, N.S.; Ricordi, C.; Berggren, P.O.; Caicedo, A. The unique cytoarchitecture of human pancreatic islets has implications for islet cell function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 2334–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prado, C.L.; Pugh-Bernard, A.E.; Elghazi, L.; Sosa-Pineda, B.; Sussel, L. Ghrelin cells replace insulin-producing β cells in two mouse models of pancreas development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 2924–2929. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Michau, A.; Hodson, D.J.; Fontanaud, P.; Guillou, A.; Espinosa-Carrasco, G.; Molino, F.; Peters, C.J.; Robinson, I.C.; Le Tissier, P.; Mollard, P.; et al. Metabolism Regulates Exposure of Pancreatic Islets to Circulating Molecules in Vivo. Diabetes 2016, 65, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberti, K.G.; Zimmet, P.Z. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Provisional report of a WHO Consultation. Diabet. Med. 1998, 15, 539–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneman, D. Type 1 diabetes. Lancet 2006, 367, 847–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiel, S.A. “Brittle” diabetes. BMJ 1991, 303, 260–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quality, H. Pancreas Islet Transplantation for Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Clinical Evidence Review. Ont. Health Technol. Assess. Ser. 2015, 15, 1–84. [Google Scholar]
- Merani, S.; Shapiro, A.J. Current status of pancreatic islet transplantation. Clin. Sci. 2006, 110, 611–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barshes, N.R.; Lee, T.; Goodpasture, S.; Brunicardi, F.C.; Alejandro, R.; Ricordi, C.; Soltes, G.; Barth, M.; Hamilton, D.; Goss, J.A. Achievement of insulin independence via pancreatic islet transplantation using a remote isolation center: A first-year review. Transplant. Proc. 2004, 36, 1127–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenmochi, T.; Mullen, Y.; Miyamoto, M.; Stein, E. Protection of mouse islet isografts from early transplantation damage by nicotinamide treatment of recipients. Transplant. Proc. 1994, 26, 693. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bottino, R.; Fernandez, L.A.; Ricordi, C.; Lehmann, R.; Tsan, M.F.; Oliver, R.; Inverardi, L. Transplantation of allogeneic islets of Langerhans in the rat liver: Effects of macrophage depletion on graft survival and microenvironment activation. Diabetes 1998, 47, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, M.; Mullen, Y.; Matsuo, S.; Herrera, M.; Clare-Salzler, M. Destruction of islet isografts by severe nonspecific inflammation. Transplant. Proc. 1990, 22, 855–856. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alejandro, R.; Cutfield, R.G.; Shienvold, F.L.; Polonsky, K.S.; Noel, J.; Olson, L.; Dillberger, J.; Miller, J.; Mintz, D.H. Natural history of intrahepatic canine islet cell autografts. J. Clin. Investig. 1986, 78, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biarnés, M.; Montolio, M.; Nacher, V.; Raurell, M.; Soler, J.; Montanya, E. β-Cell Death and Mass in Syngeneically Transplanted Islets Exposed to Short- and Long-Term Hyperglycemia. Diabetes 2002, 51, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carden, D.L.; Granger, D.N. Pathophysiology of ischaemia–reperfusion injury. J. Pathol. 2000, 190, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korthuis, R.J.; Smith, J.K.; Carden, D.L. Hypoxic reperfusion attenuates postischemic microvascular injury. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 1989, 256, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hitchman, E.; Hitchman, R.B.; King, L.A. BacMam Delivery of a Protective Gene to Reduce Renal Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury. Hum. Gene Ther. 2017, 28, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daemen, M.; van’t Veer, C.; Denecker, G.; Heemskerk, V.H.; Wolfs, T.; Clauss, M.; Vandenabeele, P.; Buurman, W.A. Inhibition of apoptosis induced by ischemia-reperfusion prevents inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 104, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sakurai, H.; Kawabata, K.; Sakurai, F.; Nakagawa, S.; Mizuguchi, H. Innate immune response induced by gene delivery vectors. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 354, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falese, L.; Sandza, K.; Yates, B.; Triffault, S.; Gangar, S.; Long, B.; Tsuruda, L.; Carter, B.; Vettermann, C.; Zoog, S. Strategy to detect pre-existing immunity to AAV gene therapy. Gene Ther. 2017, 24, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Oers, M.M.; Pijlman, G.P.; Vlak, J.M. Thirty years of baculovirus–insect cell protein expression: From dark horse to mainstream technology. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 6–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kost, T.A.; Condreay, J.P.; Jarvis, D.L. Baculovirus as versatile vectors for protein expression in insect and mammalian cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, C.; Okamoto, T.; Abe, T.; Matsuura, Y. Baculovirus as a Tool for Gene Delivery and Gene Therapy. Viruses 2018, 10, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argilaguet, J.M.; Perez-Martin, E.; Lopez, S.; Goethe, M.; Escribano, J.M.; Giesow, K.; Keil, G.M.; Rodriguez, F. BacMam immunization partially protects pigs against sublethal challenge with African swine fever virus. Antiviral Res. 2013, 98, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansouri, M.; Berger, P. Baculovirus for gene delivery to mammalian cells: Past, present and future. Plasmid 2018, 98, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Airenne, K.; Hiltunen, M.; Turunen, M.; Turunen, A.; Laitinen, O.; Kulomaa, M.; Ylä-Herttuala, S. Baculovirus-mediated periadventitial gene transfer to rabbit carotid artery. Gene Ther. 2000, 7, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tani, H.; Limn, C.K.; Yap, C.C.; Onishi, M.; Nozaki, M.; Nishimune, Y.; Okahashi, N.; Kitagawa, Y.; Watanabe, R.; Mochizuki, R. In vitro and in vivo gene delivery by recombinant baculoviruses. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 9799–9808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condreay, J.P.; Witherspoon, S.M.; Clay, W.C.; Kost, T.A. Transient and stable gene expression in mammalian cells transduced with a recombinant baculovirus vector. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kelly, B.J.; King, L.A.; Possee, R.D.; Chapple, S.D.J. Dual mutations in the Autographa californica nucleopolyhedrovirus FP-25 and p35 genes result in plasma-membrane blebbing in Trichoplusia ni cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, R.L.; Jarvis, D.L.; Summers, M.D. The Role of the AcMNPV 25K Gene “FP25” in Baculovirus polh and p10 Expression. Virology 1996, 226, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, H.A. Isolation and replication of an occlusion body-deficient mutant of the Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. Virology 1980, 105, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaikkonen, M.U.; Raty, J.K.; Airenne, K.J.; Wirth, T.; Heikura, T.; Yla-Herttuala, S. Truncated vesicular stomatitis virus G protein improves baculovirus transduction efficiency in vitro and in vivo. Gene Ther. 2006, 13, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ernst, W.; Schinko, T.; Spenger, A.; Oker-Blom, C.; Grabherr, R. Improving baculovirus transduction of mammalian cells by surface display of a RGD-motif. J. Biotechnol. 2006, 126, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Reilly, D.R.; Miller, L.K.; Luckow, V.A. Baculovirus Expression Vectors: A Laboratory Manual; W. H. Freeman and Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. xiii + 347p. [Google Scholar]
- Vaughn, J.L.; Goodwin, R.H.; Tompkins, G.J.; McCawley, P. The establishment of two cell lines from the insect Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera; Noctuidae). In Vitro 1977, 13, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benazra, M.; Lecomte, M.J.; Colace, C.; Muller, A.; Machado, C.; Pechberty, S.; Bricout-Neveu, E.; Grenier-Godard, M.; Solimena, M.; Scharfmann, R.; et al. A human beta cell line with drug inducible excision of immortalizing transgenes. Mol. Metab. 2015, 4, 916–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weyer, U.; Knight, S.; Possee, R.D. Analysis of very late gene expression by Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus and the further development of multiple expression vectors. J. Gen. Virol. 1990, 71, 1525–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitts, P.A.; Possee, R.D. A method for producing recombinant baculovirus expression vectors at high frequency. Biotechniques 1993, 14, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- King, L.A.; Possee, R.D. The Baculovirus System, A Laboratory Guide; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Braunagel, S.C.; Summers, M.D. Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus, PDV, and ECV viral envelopes and nucleocapsids: Structural proteins, antigens, lipid and fatty acid profiles. Virology 1994, 202, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Wang, M.; Shen, S.; Hu, Z.; Wang, H.; Deng, F. The FP25K Acts as a Negative Factor for the Infectivity of AcMNPV Budded Virus. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, J.C.; Friedmann, T.; Driever, W.; Burrascano, M.; Yee, J.K. Vesicular stomatitis virus G glycoprotein pseudotyped retroviral vectors: Concentration to very high titer and efficient gene transfer into mammalian and nonmammalian cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 8033–8037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimm, D.; Zhou, S.; Nakai, H.; Thomas, C.E.; Storm, T.A.; Fuess, S.; Matsushita, T.; Allen, J.; Surosky, R.; Lochrie, M.; et al. Preclinical in vivo evaluation of pseudotyped adeno-associated virus vectors for liver gene therapy. Blood 2003, 102, 2412–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hughes, A.; Jessup, C.; Drogemuller, C.; Mohanasundaram, D.; Milner, C.; Rojas, D.; Russ, G.R.; Coates, P.T. Gene therapy to improve pancreatic islet transplantation for Type 1 diabetes mellitus. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2010, 6, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walther, W.; Stein, U. Viral vectors for gene transfer: A review of their use in the treatment of human diseases. Drugs 2000, 60, 249–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deters, N.; Stokes, R.; Gunton, J. Islet Transplantation: Factors in Short-Term Islet Survival. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2011, 59, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spirin, P.V.; Vilgelm, A.E.; Prassolov, V.S. Lentiviral vectors. Mol. Biol. 2008, 42, 814–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieger, J.C.; Samulski, R.J. Adeno-associated Virus as a Gene Therapy Vector: Vector Development, Production and Clinical Applications. In Gene Therapy and Gene Delivery Systems; Schaffer, D.V., Zhou, W., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 119–145. [Google Scholar]
- Panakanti, R. Diabetes Mellitus-Islet Transplantation & Gene Therapy. SM J. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 3, 1016. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, A.; Hasan, A.; Rodes, L.; Sangaralingam, M.; Prakash, S. Bioengineered baculoviruses as new class of therapeutics using micro and nanotechnologies: Principles, prospects and challenges. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 71, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hitchman, R.B.; Murguía-Meca, F.; Locanto, E.; Danquah, J.; King, L.A. Baculovirus as vectors for human cells and applications in organ transplantation. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2011, 107, S49–S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fornwald, J.A.; Lu, Q.; Wang, D.; Ames, R.S. Gene Expression in Mammalian Cells Using BacMam, a Modified Baculovirus System. In Baculovirus and Insect Cell Expression Protocols; Murhammer, D.W., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 95–114. [Google Scholar]
- Kay, M.A.; Glorioso, J.C.; Naldini, L. Viral vectors for gene therapy: The art of turning infectious agents into vehicles of therapeutics. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heikura, T.; Nieminen, T.; Roschier, M.M.; Karvinen, H.; Kaikkonen, M.U.; Mähönen, A.J.; Lesch, H.P.; Rissanen, T.T.; Laitinen, O.H.; Airenne, K.J.; et al. Baculovirus-mediated vascular endothelial growth factor-DΔNΔC gene transfer induces angiogenesis in rabbit skeletal muscle. J. Gene Med. 2012, 14, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Tamarina, N.; Wang, Y.; Kuznetsov, A.; Patel, N.; Kending, C.; Hering, B.J.; Philipson, L.H. Baculovirus-mediated gene transfer into pancreatic islet cells. Diabetes 2000, 49, 1986–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| 24 h Post-Transduction | 48 h Post-Transduction | 72 h Post-Transduction | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FB 1 | HT 2 | FB 1 | HT 2 | FB 1 | HT 2 | |
| % transduced HK-2 cells | 90 | 95 | 99 | 99 | 99 | 99 |
| % transduced HK-2 cells with FITC 3 reading above 107 | 21 | 42 | 21 | 47 | 10 | 27 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Graves, L.P.; Aksular, M.; Alakeely, R.A.; Ruiz Buck, D.; Chambers, A.C.; Murguia-Meca, F.; Plata-Muñoz, J.-J.; Hughes, S.; Johnson, P.R.V.; Possee, R.D.; et al. Improved Baculovirus Vectors for Transduction and Gene Expression in Human Pancreatic Islet Cells. Viruses 2018, 10, 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10100574
Graves LP, Aksular M, Alakeely RA, Ruiz Buck D, Chambers AC, Murguia-Meca F, Plata-Muñoz J-J, Hughes S, Johnson PRV, Possee RD, et al. Improved Baculovirus Vectors for Transduction and Gene Expression in Human Pancreatic Islet Cells. Viruses. 2018; 10(10):574. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10100574
Chicago/Turabian StyleGraves, Leo P., Mine Aksular, Riyadh A. Alakeely, Daniel Ruiz Buck, Adam C. Chambers, Fernanda Murguia-Meca, Juan-Jose Plata-Muñoz, Stephen Hughes, Paul R. V. Johnson, Robert D. Possee, and et al. 2018. "Improved Baculovirus Vectors for Transduction and Gene Expression in Human Pancreatic Islet Cells" Viruses 10, no. 10: 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10100574
APA StyleGraves, L. P., Aksular, M., Alakeely, R. A., Ruiz Buck, D., Chambers, A. C., Murguia-Meca, F., Plata-Muñoz, J.-J., Hughes, S., Johnson, P. R. V., Possee, R. D., & King, L. A. (2018). Improved Baculovirus Vectors for Transduction and Gene Expression in Human Pancreatic Islet Cells. Viruses, 10(10), 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10100574





