Estimating Forest Carbon Stock Using Enhanced ResNet and Sentinel-2 Imagery
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Enhanced deep regression model: We develop a modified ResNet incorporating multiscale residual blocks and channel attention mechanisms to strengthen spatial context learning and spectral feature extraction for carbon modeling.
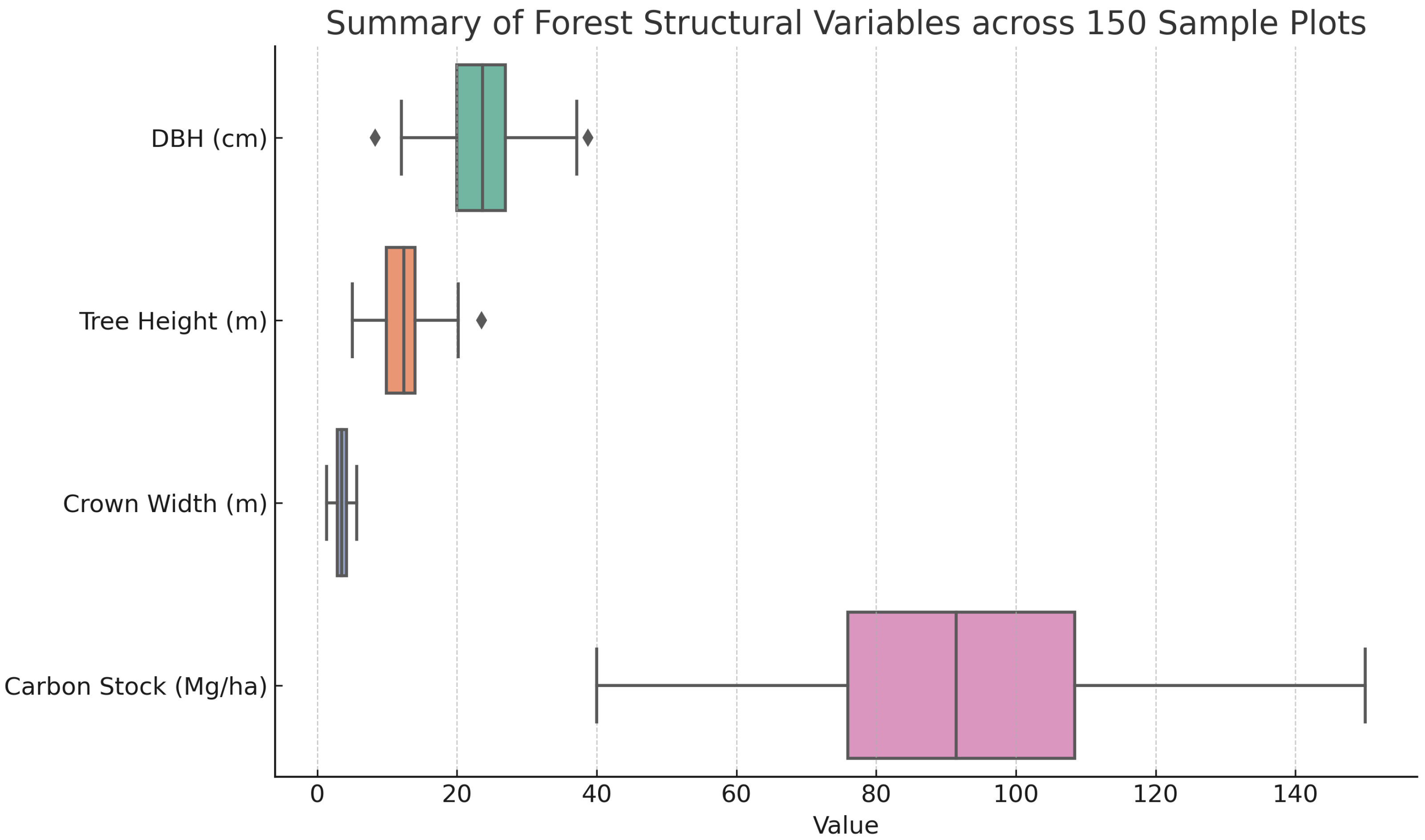
- Multisource dataset construction: We assemble a regional forest carbon stock dataset by integrating Sentinel-2 spectral variables with field-based carbon density measurements from 150 inventory plots in the Liuchong River Basin, Guizhou.
- Comprehensive performance evaluation: We benchmark the proposed model against a suite of classical and advanced models (RF, GBDT, ViT, Swin Transformer), demonstrating its superiority in accuracy and generalization across heterogeneous forest conditions.
- Can an enhanced ResNet architecture improve the accuracy of forest carbon stock estimation compared to conventional machine learning and deep learning models?
- How effectively can multispectral Sentinel-2 data represent structural and spectral heterogeneity of forest ecosystems in mountainous terrain?
- Is the proposed model generalizable across different forest types and elevation zones within the study area?
- What is the spatial mapping capability of the proposed framework in producing continuous, high-resolution carbon stock estimates?
2. Materials
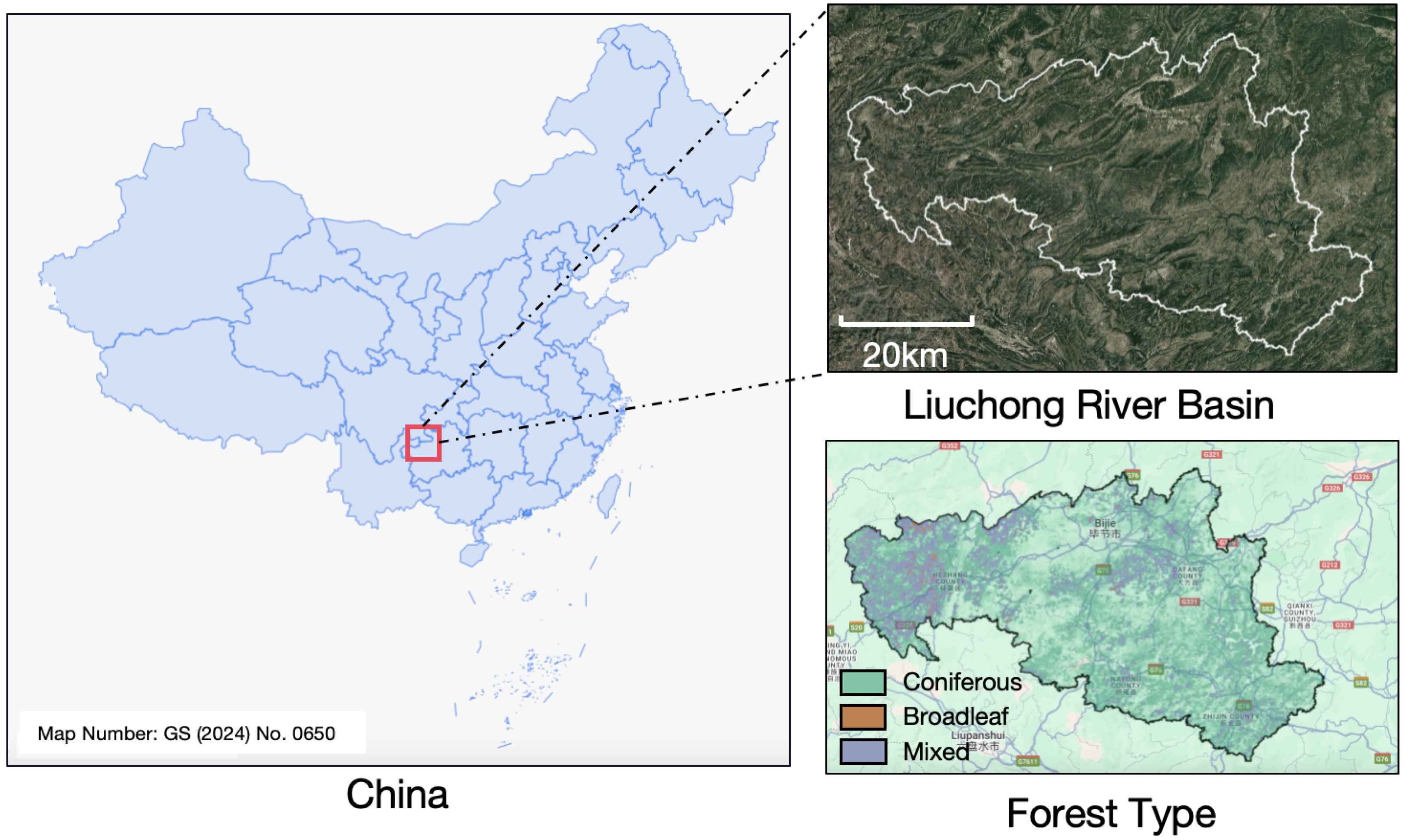
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Data Preprocessing
- Resampling: All 10 selected spectral bands were resampled to a uniform 20 m resolution via bilinear interpolation.
- Cloud and Shadow Masking: The Scene Classification Layer (SCL) was used to mask cloud and shadow pixels. Only classes corresponding to vegetation, bare soil, or water (SCL classes 4–7) were retained.
- Mosaicking: A median composite was generated from four cloud-free Sentinel-2 scenes to produce a radiometrically consistent mosaic.
- Normalization: Pixel values were normalized to the [0, 1] range using min-max normalization:
3. Methodology
3.1. Input Feature Construction
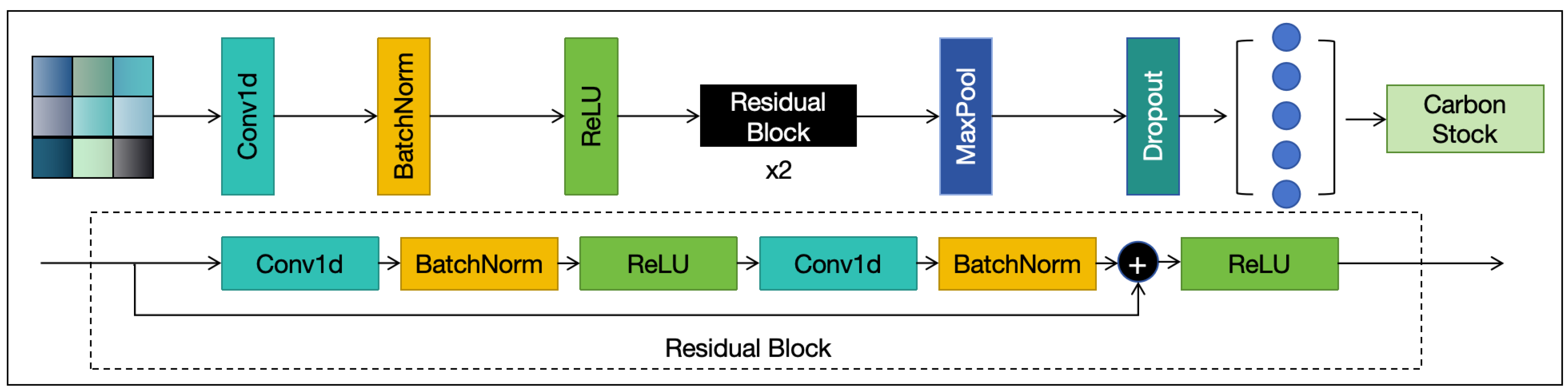
3.2. Enhanced ResNet Architecture
3.2.1. Multiscale Residual Block (MSRB)
- A standard convolution for fine-grained local details (e.g., leaf texture, small shadows);
- A convolution for medium-scale patterns such as tree crowns and canopy gaps;
- A dilated convolution (dilation rate = 2) for capturing broader contextual cues (e.g., tree clusters, terrain contours).
- It allows the network to capture both local and global spatial patterns, improving robustness to canopy size variation and forest fragmentation.
- It enhances the residual pathway with multi-receptive field aggregation, which improves spatial representation without a significant increase in parameters.
- It contributes to stable gradient propagation and faster convergence due to preserved residual connections.
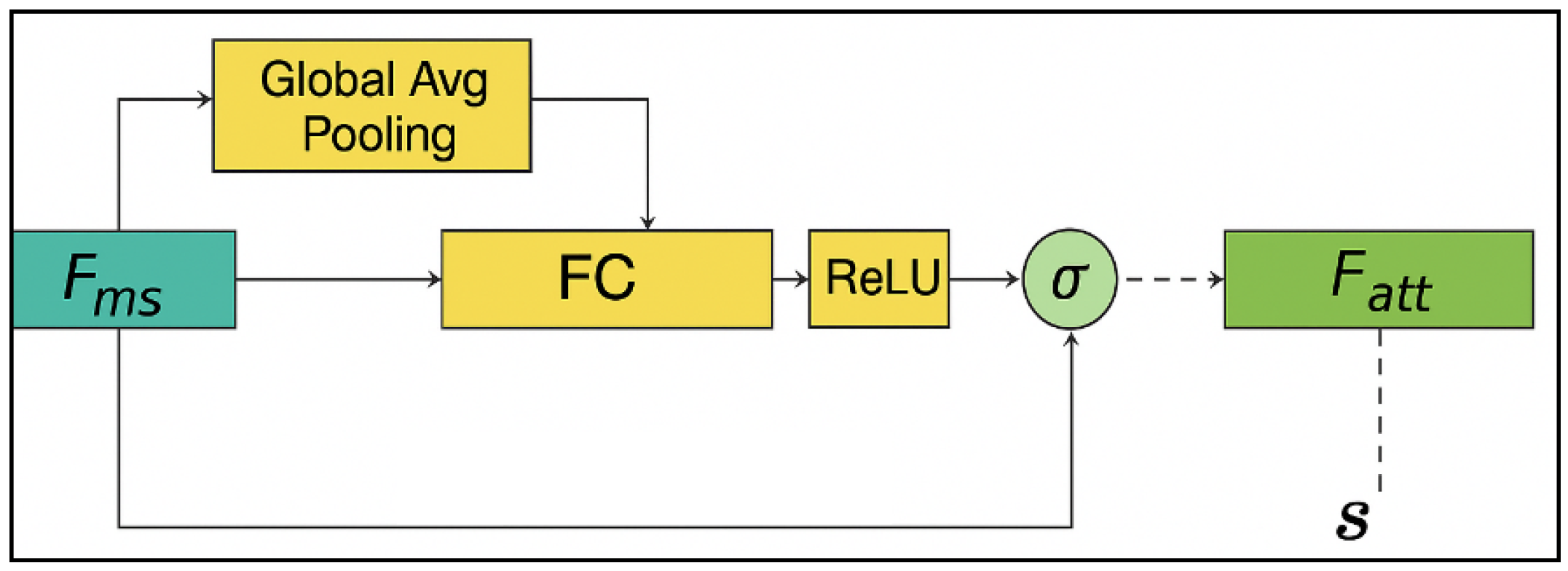
3.2.2. Channel Attention Mechanism
3.2.3. Regression Head
3.2.4. Model Efficiency
3.3. Regression Strategy and Optimization
3.3.1. Loss Function
3.3.2. Optimization
3.3.3. Dataset Split
3.3.4. Implementation
3.4. Evaluation Metrics
3.4.1. Coefficient of Determination ()
3.4.2. Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE)
3.4.3. Mean Absolute Error (MAE)
4. Results
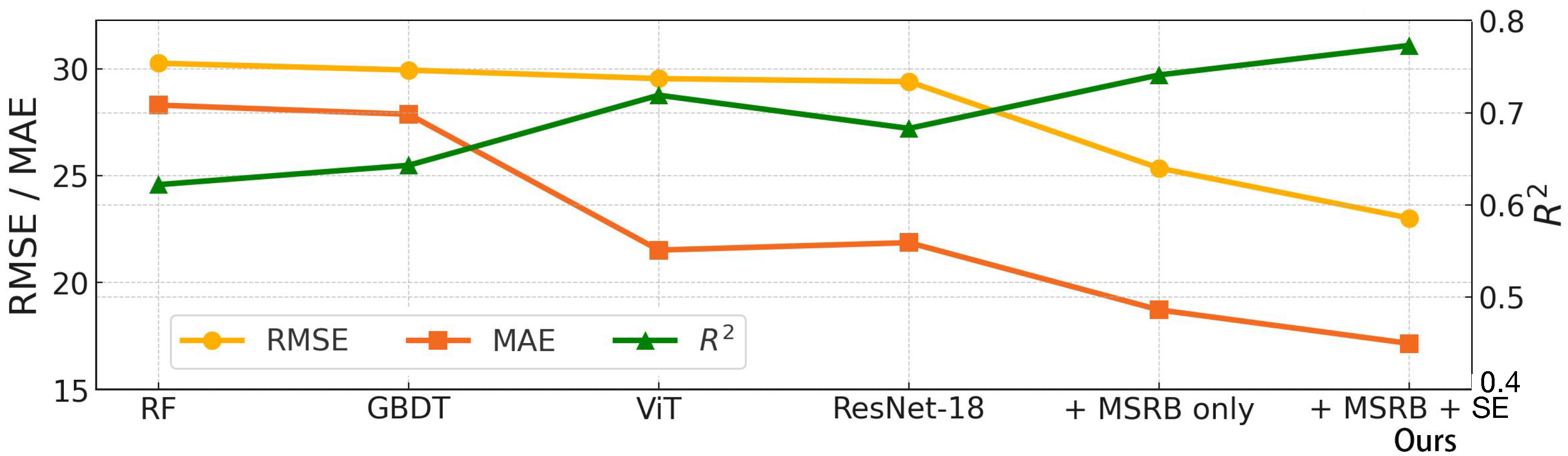
4.1. Performance Comparison
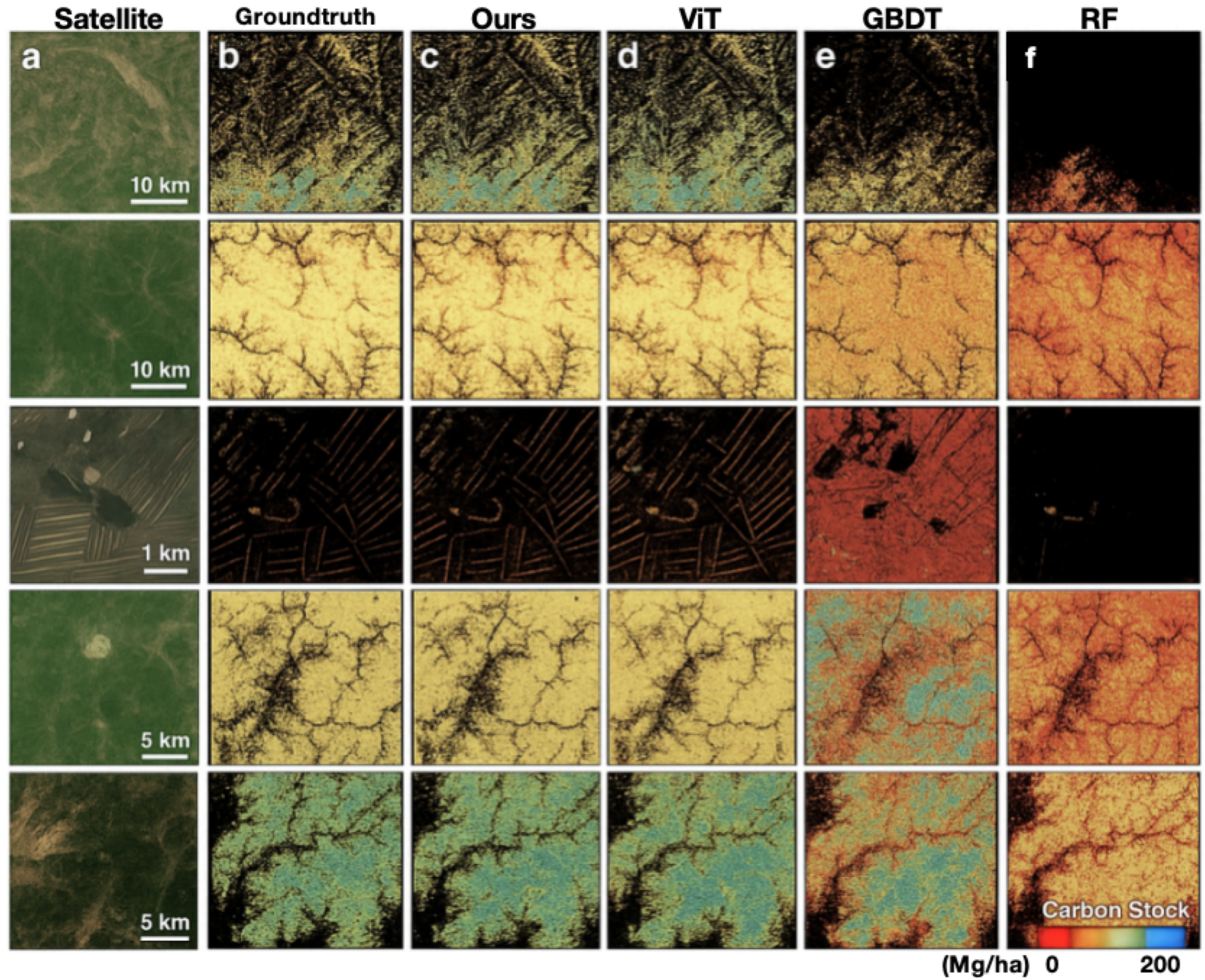
4.2. Spatial Distribution of Estimates
4.3. Error Analysis
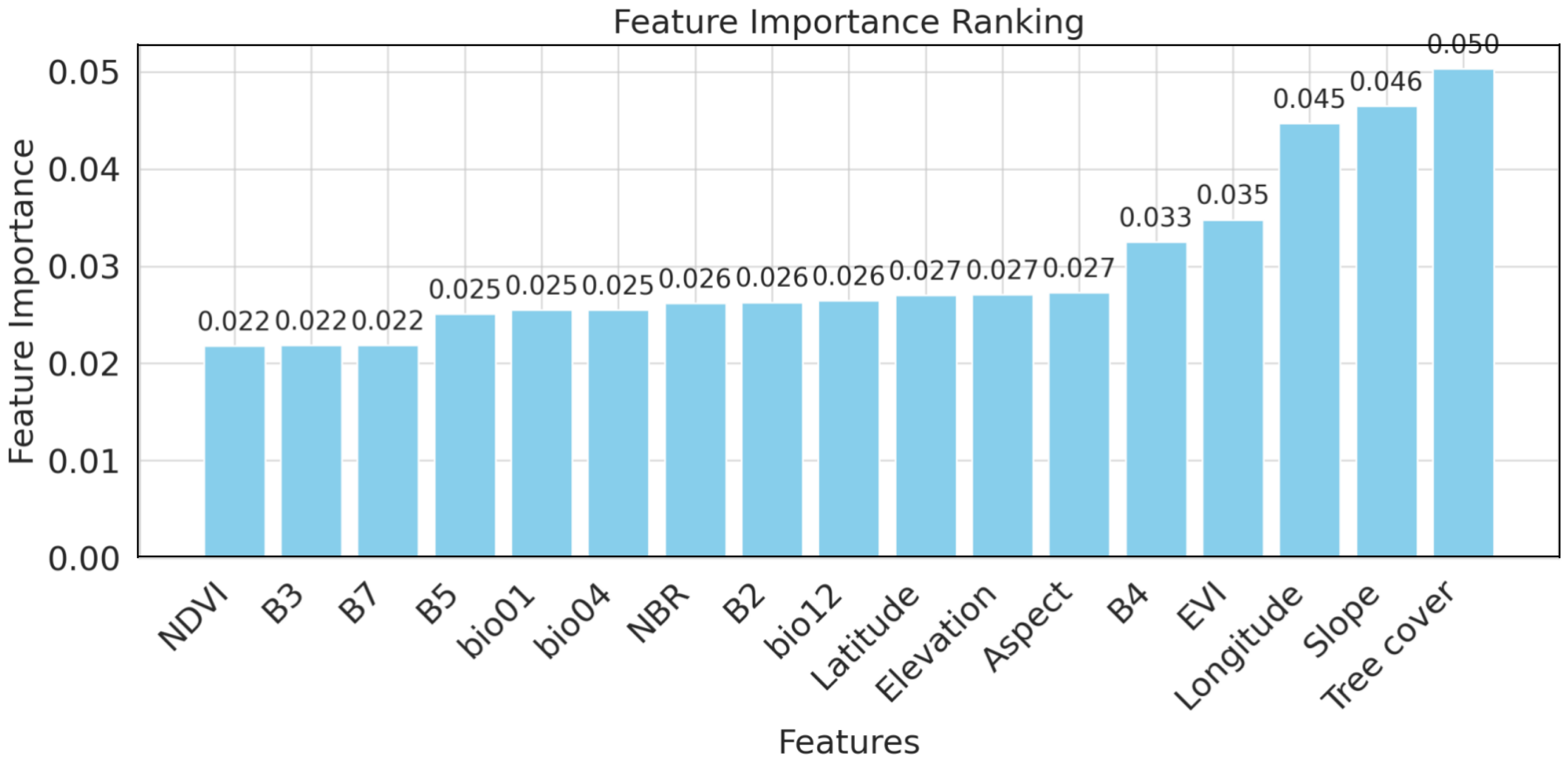
4.3.1. Feature Importance Ranking
4.3.2. RMSE, MAE, and Comparisons
4.3.3. Case Study of Extreme Prediction Error
4.4. Ablation Study
- Baseline ResNet: The original ResNet-18 architecture without any modifications.
- ResNet + MSRB: A variant in which the standard residual blocks are replaced with multiscale residual blocks (MSRBs) to capture spatial patterns across multiple receptive fields.
- Enhanced ResNet (MSRB + SE): The full version combining MSRB with Squeeze-and-Excitation (SE) modules to introduce channel-wise spectral attention.
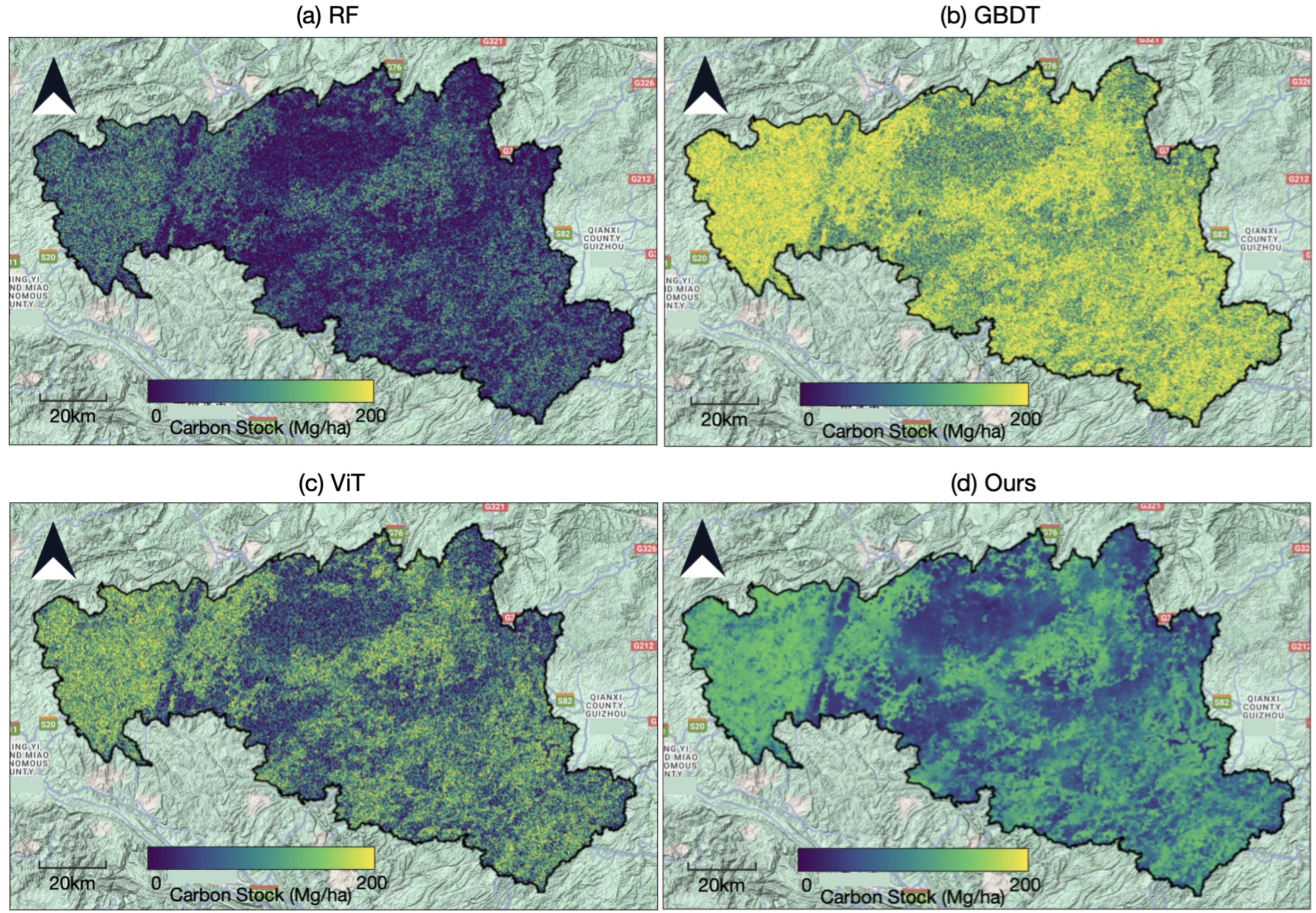
4.5. Regional Carbon Stock Mapping
5. Discussion
5.1. Effectiveness of the Enhanced ResNet Architecture
5.2. Comparison with Traditional Machine Learning Models
5.3. Limitations and Future Work
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Pan, Y.; Birdsey, R.A.; Phillips, O.L.; Houghton, R.A.; Fang, J.; Kauppi, P.E.; Keith, H.; Kurz, W.A.; Ito, A.; Lewis, S.L.; et al. The enduring world forest carbon sink. Nature 2024, 631, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Deng, J.; Ren, S.; Qu, G.; Wang, C.; Guo, R.; Zhao, X. Acoustic wave propagation characteristics and spontaneous combustion warning of coal during oxidative warming of loose coal. Fuel 2025, 398, 135528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Li, X.; Datta, R.; Chen, J.; Du, Y.; Du, D.L. Key factors shaping prokaryotic communities in subtropical forest soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 169, 104162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, M.J.; Li, G.; Nazir, M.M.; Zulfiqar, F.; Siddique, K.H.; Iqbal, B.; Du, D. Harnessing soil carbon sequestration to address climate change challenges in agriculture. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 237, 105959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Li, M.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, G.; Yu, J.; Ma, J.; Zhao, S. Comparison of evapotranspiration upscaling methods from instantaneous to daytime scale for tea and wheat in southeast China. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 264, 107464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Deng, Q.F.; Yang, K.; Yang, Y.; Shang, C.X.; Yu, Z.Y. Spatial-Temporal Change Evolution of PM 2.5 in Typical Regions of China in Recent 20 Years. Huan Jing Ke Xue = Huanjing Kexue 2018, 39, 3003–3013. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Gong, J.; Liu, J.; Ye, T. Effects of land use/cover changes on soil organic carbon stocks in Qinghai-Tibet plateau: A comparative analysis of different ecological functional areas based on machine learning methods and soil carbon pool data. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 139854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.H.; Kim, S.; Chang, H.; Li, G.; Son, Y. Increased soil temperature stimulates changes in carbon, nitrogen, and mass loss in the fine roots of Pinus koraiensis under experimental warming and drought. Turk. J. Agric. For. 2019, 43, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Xing, C.; Xue, M.; Fang, Y.; Li, P. Selective removal of Pb (II) from yellow rice wine using magnetic carbon-based adsorbent. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 6929–6939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, L.; Li, H.; Li, C.; Wang, A.; Yang, Y.; Wang, P. Hyperspectral sensing of plant diseases: Principle and methods. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Feng, Z.; Dai, S.; Zhang, P.; Wei, X. Using UAV multispectral remote sensing with appropriate spatial resolution and machine learning to monitor wheat scab. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, X.; Luo, Z.; Schillaci, C.; Arrouays, D.; Richer-de Forges, A.C.; Shi, Z. European topsoil bulk density and organic carbon stock database (0–20 cm) using machine-learning-based pedotransfer functions. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2024, 16, 2367–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakov, K.; Sajjad, R.; Annie, I.; Andrew, M.; Kazem, Z.; Nan, L.; Sami, U.; Khalid, M.; Muhammad, A.K.; Nadeem, S.; et al. Inorganic carbon is overlooked in global soil carbon research: A bibliometric analysis. Geoderma 2024, 443, 116831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Chen, T.; Meng, S.; Liu, D.; Dong, D.; You, T. Electric field-induced specific preconcentration to enhance DNA-based electrochemical sensing of Hg2+ via the synergy of enrichment and self-cleaning. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 7412–7419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, K.; Luo, Y.; Yu, Z. Spatial–temporal characteristics of surface thermal environment and its effect on Lake surface water temperature in Dianchi Lake basin. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 984692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Cheng, Y.; Luo, M.; Mai, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y. Progress and Limitations in Forest Carbon Stock Estimation Using Remote Sensing Technologies: A Comprehensive Review. Forests 2025, 16, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Manning, D.A.; Werner, D. The limited potential of soil and vegetation in urban greenspace for nature-based offsetting of institutional carbon emissions. Soil Use Manag. 2024, 40, e13081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, A.; Hu, Y.; Lu, Y. Improving carbon flux estimation in tea plantation ecosystems: A machine learning ensemble approach. Eur. J. Agron. 2024, 160, 127297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Meng, S.; Wang, M.; Li, W.; Dong, N.; Liu, D.; Li, Y.; You, T. In-depth interpretation of aptamer-based sensing on electrode: Dual-mode electrochemical-photoelectrochemical sensor for the ratiometric detection of patulin. Food Chem. 2023, 410, 135450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhan, Z.; Liang, X.; Xing, J. Estimation methods of wetland carbon sink and factors influencing wetland carbon cycle: A review. Carbon Res. 2024, 3, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, K.; Wei, W.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, F.; Du, D. Use of carbon nanotubes as a solid support to establish quantitative (centrifugation) and qualitative (filtration) immunoassays to detect gentamicin contamination in commercial milk. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 7874–7881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, C.; Guo, W.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Qiu, J.; Peng, J. A novel electrochemical sensor based on graphene oxide decorated with silver nanoparticles–molecular imprinted polymers for determination of sunset yellow in soft drinks. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 2293–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Xu, X.; Zhu, Q.; Meng, Y.; Yang, G.; Feng, H.; Yang, M.; Zhu, Q.; Xue, H.; Wang, B. Monitoring leaf nitrogen content in rice based on information fusion of multi-sensor imagery from UAV. Precis. Agric. 2023, 24, 2327–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Bai, X.; Zhao, C.; Luo, G.; Li, C.; Ran, C.; Zhang, S.; Xiong, L.; Liao, J.; Du, C.; et al. Unexpected response of terrestrial carbon sink to rural depopulation in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 948, 174595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, Y.; Li, W.; Ciais, P.; Sun, M.; Zhu, L.; Yue, C.; Chang, J.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; et al. Forest aging limits future carbon sink in China. One Earth 2024, 7, 822–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jing, Z.; Zhang, T.; Chen, Q.; Qiu, F.; Peng, Y.; Tang, S. Fabrication of functional biomass carbon aerogels derived from sisal fibers for application in selenium extraction. Food Bioprod. Process. 2018, 111, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yuan, D.; Guo, Q.; Qiu, F.; Yang, D.; Ou, Z. Preparation of a renewable biomass carbon aerogel reinforced with sisal for oil spillage clean-up: Inspired by green leaves to green Tofu. Food Bioprod. Process. 2019, 114, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, M.S.; Chen, S.; Niu, Y.; Zhou, W.; Elsherbiny, O.; Liang, R.; Du, Z.; Guo, X. Evaluating the efficacy of Sentinel-2B and Landsat-8 for estimating and mapping wheat straw cover in rice–wheat fields. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, H.; Shi, X.; Ren, X.; Yang, S.; Cai, M.; Pan, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Feng, D.; Zhou, B. Limited terrestrial carbon sinks and increasing carbon emissions from the Hu Line spatial pattern perspective in China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 162, 112035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Gong, H. The trajectory of carbon emissions and terrestrial carbon sinks at the provincial level in China. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Wang, M.; You, T.; Wang, K. Using magnetic multiwalled carbon nanotubes as modified QuEChERS adsorbent for simultaneous determination of multiple mycotoxins in grains by UPLC-MS/MS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 8035–8044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, Z.; Ding, J.; Zhang, T.; Yang, D.; Qiu, F.; Chen, Q.; Xu, J. Flexible, versatility and superhydrophobic biomass carbon aerogels derived from corn bracts for efficient oil/water separation. Food Bioprod. Process. 2019, 115, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Shen, C.; Liu, H.; Huang, J.; Tian, K.; Tang, Z. Review of the field environmental sensing methods based on multi-sensor information fusion technology. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2024, 17, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Zhou, H.; Cao, Y.; Liao, H.; Lu, X.; Yu, Z.; Yuan, W.; Liu, Z.; Lei, Y.; Sitch, S.; et al. Large potential of strengthening the land carbon sink in China through anthropogenic interventions. Sci. Bull. 2024, 69, 2622–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, C.; Guangqiao, C.; Yibai, L.; Dong, L.; Bin, M.; Jinlong, Z.; Liang, L.; Jianping, H. Research on monitoring methods for the appropriate rice harvest period based on multispectral remote sensing. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2022, 2022, 1519667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Cheng, K.W.; Xiao, J.; Wang, M. The multifunctional roles of flavonoids against the formation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) and AGEs-induced harmful effects. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 103, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yu, X.; Shi, X.; Han, Y.; Guo, Z.; Liu, Y. Development of carbon quantum dot–labeled antibody fluorescence immunoassays for the detection of morphine in hot pot soup base. Food Anal. Methods 2020, 13, 1042–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, K.; Qian, J.; Long, L. Construction of a colorimetric and near-infrared ratiometric fluorescent sensor and portable sensing system for on-site quantitative measurement of sulfite in food. Foods 2024, 13, 1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Yang, H.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, L.; Chai, X. Wheat biomass, yield, and straw-grain ratio estimation from multi-temporal UAV-based RGB and multispectral images. Biosyst. Eng. 2023, 234, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Han, I.; Wang, P.; Mei, Q.; Huang, Y. Effects of different straw biochars on soil organic carbon, nitrogen, available phosphorus, and enzyme activity in paddy soil. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, N.J.; Wang, Y.J.; Chu, J.; Kawasaki, S.; Tang, C.S.; Cheng, L.; Du, Y.J.; Shashank, B.S.; Singh, D.N.; Han, X.L.; et al. Bio-mediated soil improvement: An introspection into processes, materials, characterization and applications. Soil Use Manag. 2022, 38, 68–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Huang, A.; He, L.; Cai, C.; You, T. Recent advances in foodborne pathogen detection using photoelectrochemical biosensors: From photoactive material to sensing strategy. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2024, 8, 1432555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Zhang, Y.; Azi, F.; Zhou, J.; Liu, X.; Dai, Y.; Wang, Z.; Dong, M.; Xia, X. Inhibition of biofilm formation and quorum sensing by soy isoflavones in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Food Control 2022, 133, 108629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anees, S.A.; Mehmood, K.; Khan, W.R.; Sajjad, M.; Alahmadi, T.A.; Alharbi, S.A.; Luo, M. Integration of machine learning and remote sensing for above ground biomass estimation through Landsat-9 and field data in temperate forests of the Himalayan region. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 82, 102732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z. AI for Science: A Comprehensive Review on Innovations, Challenges, and Future Directions. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Sci. (IJAI4S) 2025, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, J.; Gan, L.; He, M.; Zhang, T.; Li, P.; Qiu, F. Preparation and application of Mg–Al composite oxide/coconut shell carbon fiber for effective removal of phosphorus from domestic sewage. Food Bioprod. Process. 2021, 126, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Gan, Z.; Zou, X.; Shi, J.; Huang, X.; Li, Z.; Li, Y. Green one-step synthesis of carbon quantum dots from orange peel for fluorescent detection of Escherichia coli in milk. Food Chem. 2021, 339, 127775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; He, Y.; Yuan, B.; Li, L.; Luo, L.; You, T. Simultaneous detection of multiple mycotoxins in agricultural products: Recent advances in optical and electrochemical sensing methods. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2024, 23, e70062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanase, M.A.; Mihai, M.; Miguel, S.; Cantero, A.; Tijerín, J.; Ruiz-Benito, P.; Domingo, D.; García-Martín, A.; Aponte, C.; Lamelas, M.T. Long-term annual estimation of forest above ground biomass, canopy cover, and height from airborne and spaceborne sensors synergies in the Iberian Peninsula. Environ. Res. 2024, 259, 119432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zou, X.; Shi, J.; Huang, X.; Liu, C.; et al. Rapid detection of cadmium ions in meat by a multi-walled carbon nanotubes enhanced metal-organic framework modified electrochemical sensor. Food Chem. 2021, 357, 129762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Wang, J.; Idris, M.Y.I. IIDM: Improved implicit diffusion model with knowledge distillation to estimate the spatial distribution density of carbon stock in remote sensing imagery. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2411.17973. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Zhang, C.; Ma, T.; Li, W. Estimation of summer maize biomass based on a crop growth model. Emir. J. Food Agric. (EJFA) 2021, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.M.; Zareef, M.; Jiao, T.; Liu, S.; Xu, Y.; Viswadevarayalu, A.; Li, H.; Chen, Q. Signal optimized rough silver nanoparticle for rapid SERS sensing of pesticide residues in tea. Food Chem. 2021, 338, 127796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awais, M.; Li, W.; Hussain, S.; Cheema, M.J.M.; Li, W.; Song, R.; Liu, C. Comparative evaluation of land surface temperature images from unmanned aerial vehicle and satellite observation for agricultural areas using in situ data. Agriculture 2022, 12, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; He, N.; Li, M.; Cai, W.; Yu, G. Spatiotemporal dynamics of carbon sinks in China’s terrestrial ecosystems from 2010 to 2060. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2024, 203, 107457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estévez, J.; Salinero-Delgado, M.; Berger, K.; Pipia, L.; Rivera-Caicedo, J.P.; Wocher, M.; Reyes-Muñoz, P.; Tagliabue, G.; Boschetti, M.; Verrelst, J. Gaussian processes retrieval of crop traits in Google Earth Engine based on Sentinel-2 top-of-atmosphere data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 273, 112958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Ali, S.; Haruna, S.A.; Ouyang, Q.; Li, H.; Chen, Q. Development of a fluorescence sensing platform for specific and sensitive detection of pathogenic bacteria in food samples. Food Control 2022, 131, 108419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusňák, T.; Kasanickỳ, T.; Malík, P.; Mojžiš, J.; Zelenka, J.; Sviček, M.; Abrahám, D.; Halabuk, A. Crop mapping without labels: Investigating temporal and spatial transferability of crop classification models using a 5-year sentinel-2 series and machine learning. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, G.; Zhong, Q.; Xing, L.; Du, H. Prediction of urban forest aboveground carbon using machine learning based on landsat 8 and Sentinel-2: A case study of Shanghai, China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.; Lin, H.; Jiang, H.; Yao-Say Solomon Adade, S.; Xue, Z.; Chen, Q. Advanced applications of chemo-responsive dyes based odor imaging technology for fast sensing food quality and safety: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 5145–5172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okeke, E.S.; Ezeorba, T.P.C.; Okoye, C.O.; Chen, Y.; Mao, G.; Feng, W.; Wu, X. Analytical detection methods for azo dyes: A focus on comparative limitations and prospects of bio-sensing and electrochemical nano-detection. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 114, 104778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Ou, G.; Wang, M.; Liu, C. Remote sensing estimation of forest carbon stock based on machine learning algorithms. Forests 2024, 15, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Wang, J.; Tan, Z.; Luo, Y. Impact of climate change on SARS-CoV-2 epidemic in China. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0285179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhihua, L.; Xue, Z.; Xiaowei, H.; Xiaobo, Z.; Jiyong, S.; Yiwei, X.; Xuetao, H.; Yue, S.; Xiaodong, Z. Hypha-templated synthesis of carbon/ZnO microfiber for dopamine sensing in pork. Food Chem. 2021, 335, 127646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Idris, M.Y.I.; Wang, H.; Wang, P.; Chen, J.; Wang, K. From Physics to Foundation Models: A Review of AI-Driven Quantitative Remote Sensing Inversion. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2507.09081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hong, D.; Gao, L.; Yao, J.; Zheng, K.; Zhang, B.; Chanussot, J. Deep learning in multimodal remote sensing data fusion: A comprehensive review. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 112, 102926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq, M.; Gu, Z. Deep residual learning for image recognition: A survey. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illarionova, S.; Tregubova, P.; Shukhratov, I.; Shadrin, D.; Efimov, A.; Burnaev, E. Advancing forest carbon stocks’ mapping using a hierarchical approach with machine learning and satellite imagery. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 21032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Zhou, P.; Wu, J.; Yao, Q.; Yang, Z.; Wang, X.; Wen, Y. Carbon stock inversion study of a carbon peaking pilot urban combining machine learning and Landsat images. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 159, 111657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Xie, Y.; Wei, X.S.; Zhao, B.R.; Chen, Z.M.; Tan, X. Delving deep into spatial pooling for squeeze-and-excitation networks. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 121, 108159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Wang, D.; Yao, X.; Wang, S.; Chi, T.; Meng, Y. Forest emissions reduction assessment using optical satellite imagery and space LiDAR fusion for carbon stock estimation. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Song, S.; Gui, S.; Chao, W.; Cheng, C.; Qin, R. Active and low-cost hyperspectral imaging for the spectral analysis of a low-light environment. Sensors 2023, 23, 1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fassnacht, F.E.; White, J.C.; Wulder, M.A.; Næsset, E. Remote sensing in forestry: Current challenges, considerations and directions. For. Int. J. For. Res. 2024, 97, 11–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, A.; Horanont, T.; Neupane, B.; Aryal, J. Deep learning for remote sensing image scene classification: A review and meta-analysis. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhu, X.X. Deep domain adaptation in remote sensing: A meta-review and future directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 171, 274–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, P.; Zuccarini, P.; Kennedy, R.E.; Gorelick, N.; Cohen, W.B.; Healey, S.P.; Yang, Z. LandTrendr: A decade of land cover change detection using Landsat time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 246, 111898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalponte, M.; Coomes, D.A. Tree-centric mapping of forest carbon density from airborne laser scanning and hyperspectral data. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2016, 7, 1236–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Description | Band | Wavelength (nm) | Resolution (m) | Resampled (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blue | B2 | 490 | 10 | 20 |
| Green | B3 | 560 | 10 | 20 |
| Red | B4 | 665 | 10 | 20 |
| Red-edge 1 | B5 | 705 | 20 | 20 |
| Red-edge 2 | B6 | 740 | 20 | 20 |
| Red-edge 3 | B7 | 783 | 20 | 20 |
| NIR | B8 | 842 | 10 | 20 |
| Narrow NIR | B8A | 865 | 20 | 20 |
| SWIR 1 | B11 | 1610 | 20 | 20 |
| SWIR 2 | B12 | 2190 | 20 | 20 |
| Model | RMSE (Mg/ha) | MAE (Mg/ha) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Random Forest (RF) | 30.27 | 28.31 | 0.622 |
| Gradient Boosting (GBDT) | 29.95 | 27.88 | 0.643 |
| Vision Transformer (ViT) | 29.55 | 21.52 | 0.719 |
| Enhanced ResNet (Ours) | 23.02 | 17.15 | 0.773 |
| Model Variant | RMSE (Mg/ha) | MAE (Mg/ha) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet-18 (Baseline) | 29.41 | 21.87 | 0.683 |
| +MSRB only | 25.36 | 18.72 | 0.741 |
| +MSRB + SE (Enhanced ResNet) | 23.02 | 17.15 | 0.773 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, J.; Liu, L.; Wu, Y.; Ouyang, L.; Yu, Z. Estimating Forest Carbon Stock Using Enhanced ResNet and Sentinel-2 Imagery. Forests 2025, 16, 1198. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16071198
Ren J, Liu L, Wu Y, Ouyang L, Yu Z. Estimating Forest Carbon Stock Using Enhanced ResNet and Sentinel-2 Imagery. Forests. 2025; 16(7):1198. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16071198
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Jintong, Lizhi Liu, You Wu, Lijian Ouyang, and Zhenyu Yu. 2025. "Estimating Forest Carbon Stock Using Enhanced ResNet and Sentinel-2 Imagery" Forests 16, no. 7: 1198. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16071198
APA StyleRen, J., Liu, L., Wu, Y., Ouyang, L., & Yu, Z. (2025). Estimating Forest Carbon Stock Using Enhanced ResNet and Sentinel-2 Imagery. Forests, 16(7), 1198. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16071198






