Unveiling Scale-Dependent Elevational Patterns and Drivers of Tree β Diversity on a Subtropical Mountain Using Sentinel-2 Remote Sensing Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Field Survey
2.2. Sentinel-2 Spectral Reflectance Data
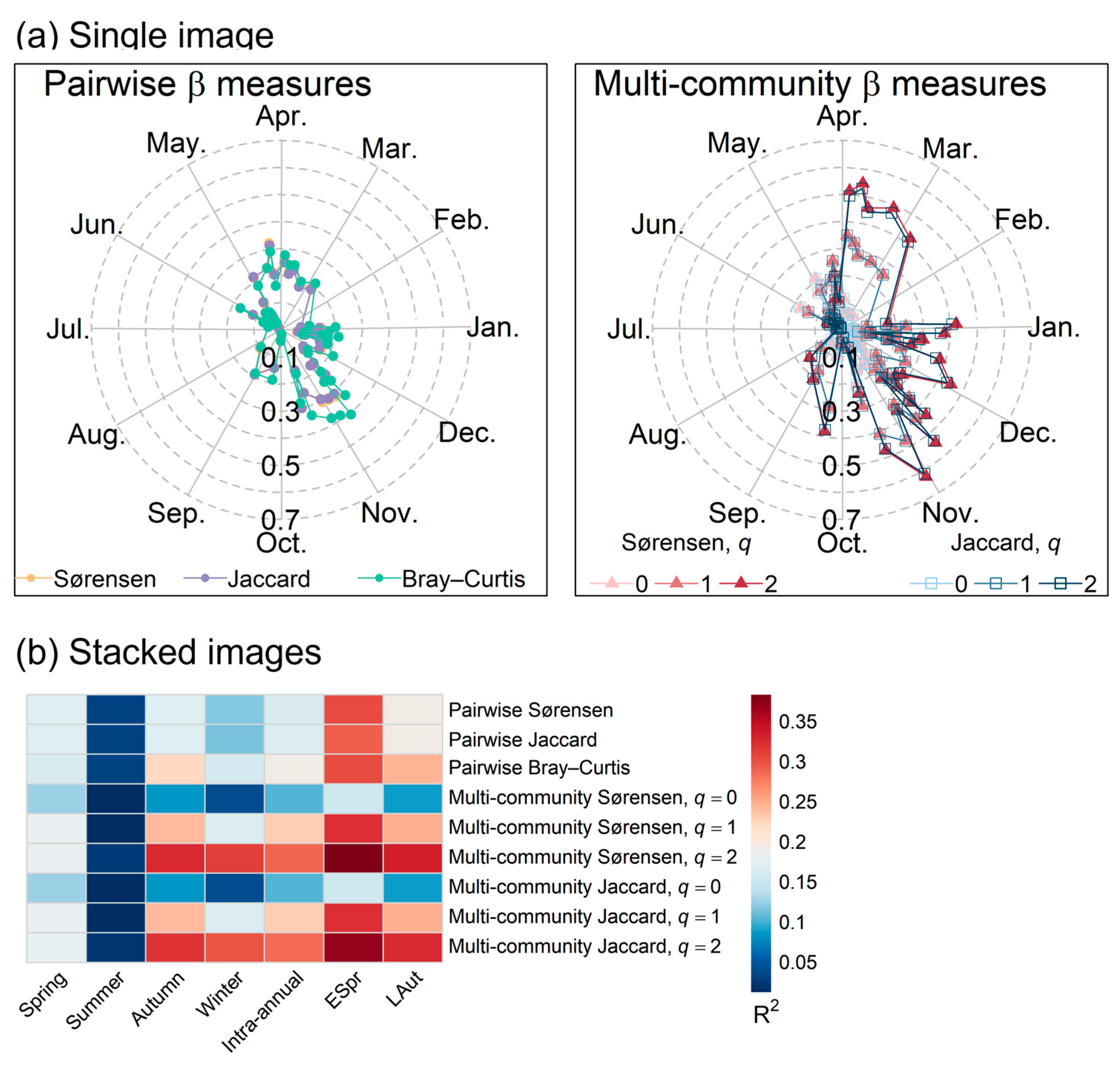
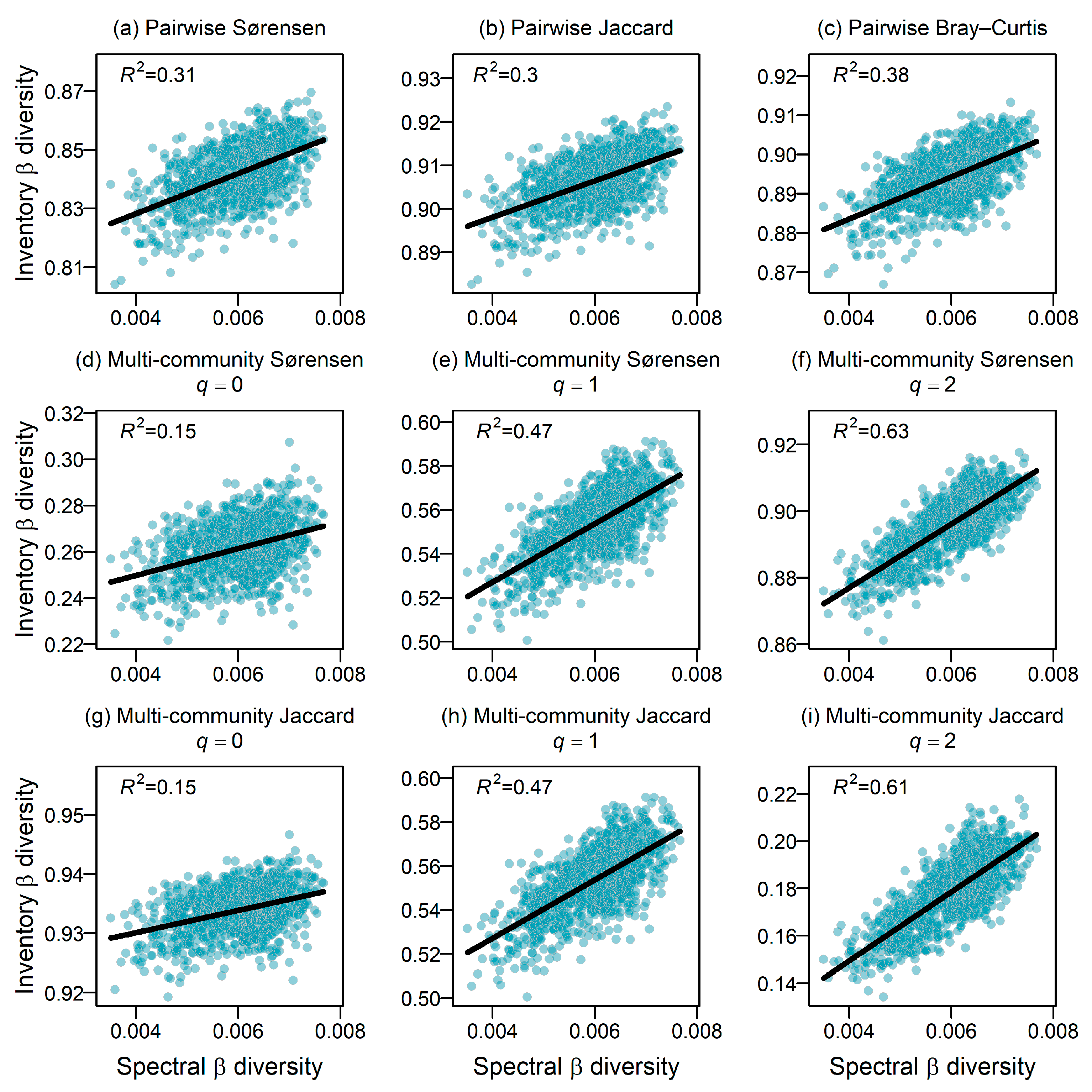
2.3. Strength of Association Between Spectral and Inventory β Diversities
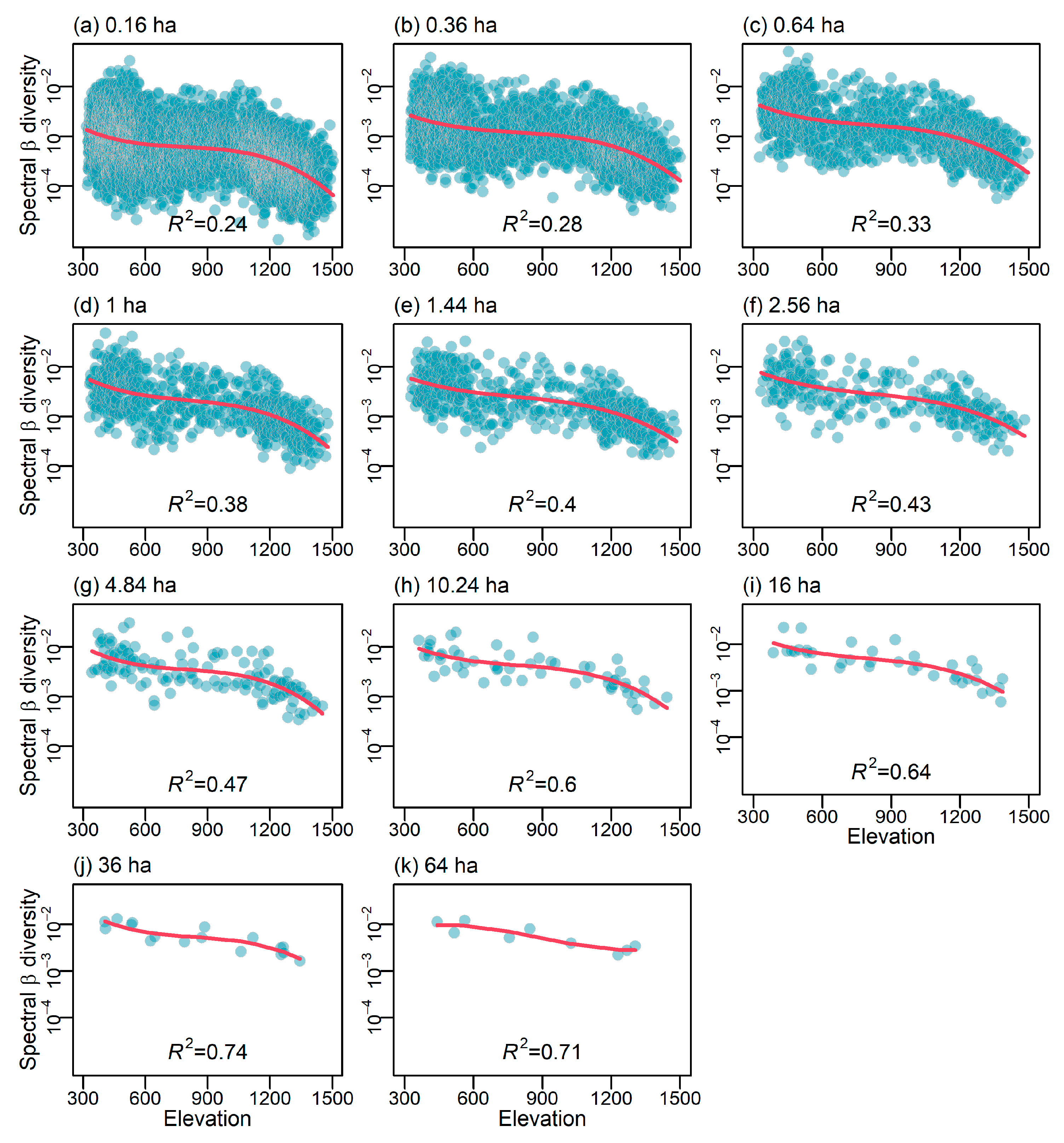
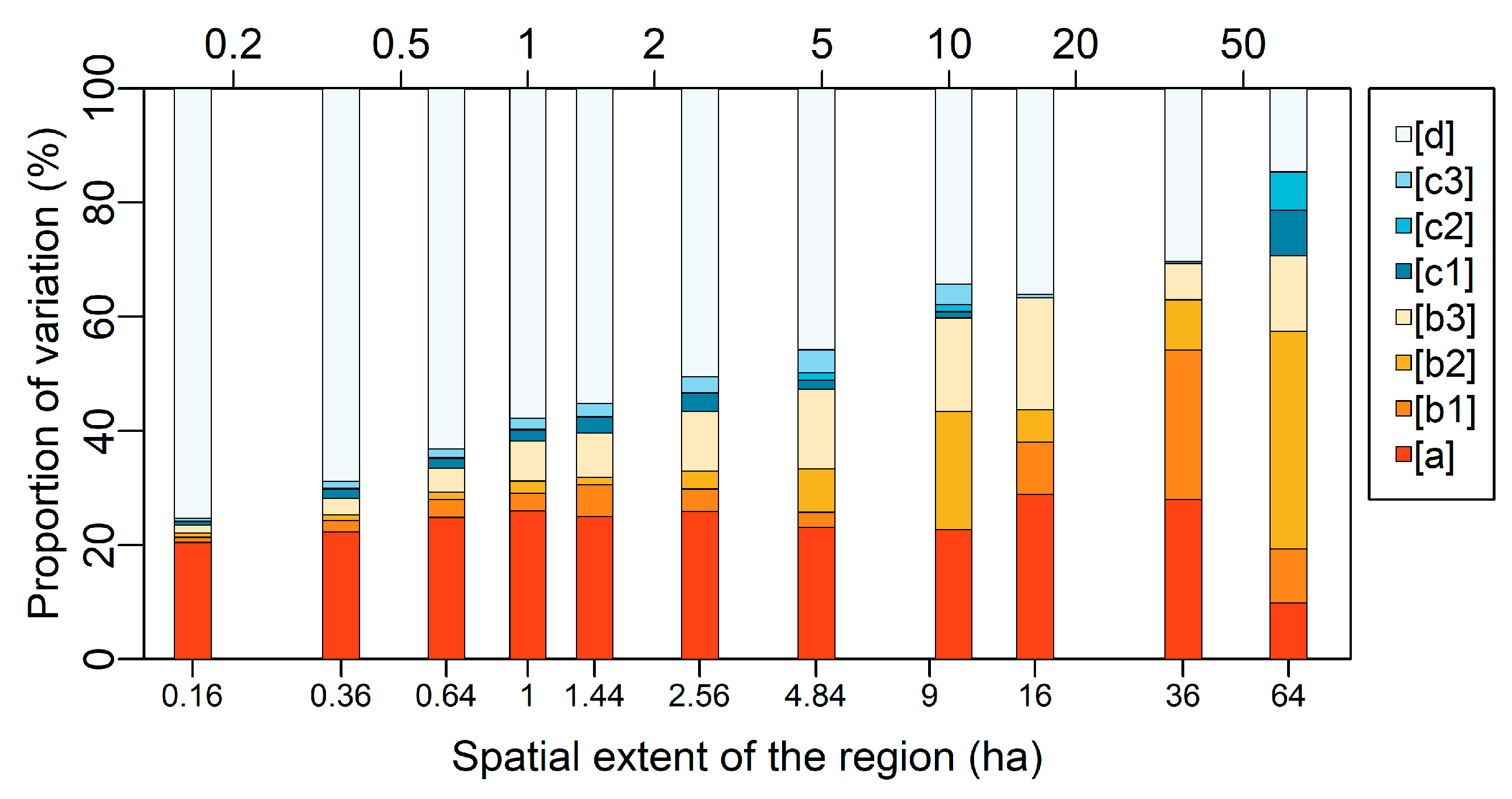
2.4. Scale-Dependent Elevational Gradient of Spectral β Diversity
3. Results
3.1. Strength of Association Between Spectral and Inventory β Diversity
3.2. Scale-Dependent Elevational Patterns and Drivers of Spectral β Diversity
4. Discussion
4.1. Strength of Association Between Spectral and Inventory β Diversity
4.2. Scale-Dependent Spatial Patterns and Drivers of Spectral β Diversity Along Elevation Gradient
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Whittaker, R.H. Vegetation of the Siskiyou Mountains, Oregon and California. Ecol. Monogr. 1960, 30, 279–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dornelas, M.; Gotelli, N.J.; McGill, B.; Shimadzu, H.; Moyes, F.; Sievers, C.; Magurran, A.E. Assemblage time series reveal biodiversity change but not systematic loss. Science 2014, 344, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, A.S.; Isbell, F.; Seidl, R. β-diversity, community assembly, and ecosystem functioning. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2018, 33, 549–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blowes, S.A.; McGill, B.; Brambilla, V.; Chow, C.F.Y.; Engel, T.; Fontrodona-Eslava, A.; Martins, I.S.; McGlinn, D.; Moyes, F.; Sagouis, A.; et al. Synthesis reveals approximately balanced biotic differentiation and homogenization. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadj9395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.; Ricklefs, R.E. A latitudinal gradient in large-scale beta diversity for vascular plants in North America. Ecol. Lett. 2007, 10, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraft, N.J.; Comita, L.S.; Chase, J.M.; Sanders, N.J.; Swenson, N.G.; Crist, T.O.; Stegen, J.C.; Vellend, M.; Boyle, B.; Anderson, M.J.; et al. Disentangling the drivers of beta diversity along latitudinal and elevational gradients. Science 2011, 333, 1755–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, D.; He, F. Environmental filtering explains a U-shape latitudinal pattern in regional beta-deviation for eastern North American trees. Ecol. Lett. 2019, 22, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Condit, R.; Mi, X.; Chen, L.; Ren, H.; Xu, W.; Burslem, D.; Cai, C.; Cao, M.; Chang, L.; et al. Species packing and the latitudinal gradient in beta-diversity. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2021, 288, 20203045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishizawa, K.; Shinohara, N.; Cadotte, M.W.; Mori, A.S. The latitudinal gradient in plant community assembly processes: A meta-analysis. Ecol. Lett. 2022, 25, 1711–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinohara, N.; Kobayashi, Y.; Nishizawa, K.; Kadowaki, K.; Yamawo, A. Plant–mycorrhizal associations may explain the latitudinal gradient of plant community assembly. Oikos 2024, 2024, e10367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tello, J.S.; Myers, J.A.; Macia, M.J.; Fuentes, A.F.; Cayola, L.; Arellano, G.; Loza, M.I.; Torrez, V.; Cornejo, M.; Miranda, T.B.; et al. Elevational gradients in β-diversity reflect variation in the strength of local community assembly mechanisms across spatial scales. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; He, F.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, X.; von Gadow, K. Latitudinal gradients and ecological drivers of β-diversity vary across spatial scales in a temperate forest region. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2020, 29, 1257–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wu, W.; Wang, K.; Ren, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Geng, J.; Yang, B. Latitudinal patterns of tree β-diversity and relevant ecological processes vary across spatial extents in forests of southeastern China. Plant Divers. 2025, 47, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cáceres, M.; Legendre, P.; Valencia, R.; Cao, M.; Chang, L.W.; Chuyong, G.; Condit, R.; Hao, Z.; Hsieh, C.F.; Hubbell, S.; et al. The variation of tree beta diversity across a global network of forest plots. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2012, 21, 1191–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, A.S.; Shiono, T.; Koide, D.; Kitagawa, R.; Ota, A.T.; Mizumachi, E. Community assembly processes shape an altitudinal gradient of forest biodiversity. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2013, 22, 878–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.; Chen, S.; Mao, L.; Ouyang, Z. Drivers of β-diversity along latitudinal gradients revisited. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2013, 22, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Chen, G.; Liu, C.; Ma, K. Latitudinal differences in species abundance distributions, rather than spatial aggregation, explain beta-diversity along latitudinal gradients. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2015, 24, 1170–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Villa, J.A.; González-Caro, S.; Duque, Á. The importance of grain and cut-off size in shaping tree beta diversity along an elevational gradient in the northwest of Colombia. For. Ecosyst. 2020, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinck, K.; Fischer, R.; Groeneveld, J.; Lehmann, S.; Dantas De Paula, M.; Pütz, S.; Sexton, J.O.; Song, D.; Huth, A. High resolution analysis of tropical forest fragmentation and its impact on the global carbon cycle. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavender-Bares, J.; Gamon, J.A.; Townsend, P.A. Remote Sensing of Plant Biodiversity; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Gamon, J.A. Remote sensing of terrestrial plant biodiversity. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavender-Bares, J.; Schneider, F.D.; Santos, M.J.; Armstrong, A.; Carnaval, A.; Dahlin, K.M.; Fatoyinbo, L.; Hurtt, G.C.; Schimel, D.; Townsend, P.A.; et al. Integrating remote sensing with ecology and evolution to advance biodiversity conservation. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 6, 506–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Gamon, J.A.; Schweiger, A.K.; Cavender-Bares, J.; Townsend, P.A.; Zygielbaum, A.I.; Kothari, S. Influence of species richness, evenness, and composition on optical diversity: A simulation study. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 211, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweiger, A.K.; Laliberté, E. Plant beta-diversity across biomes captured by imaging spectroscopy. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Lin, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Shang, K.; Zhao, M.; Huang, J.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; et al. Remote sensing of subtropical tree diversity: The underappreciated roles of the practical definition of forest canopy and phenological variation. For. Ecosyst. 2023, 10, 100122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Frey, J.; Munteanu, C.; Still, N.; Koch, B. Mapping tree species diversity in temperate montane forests using Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 imagery and topography data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 292, 113576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.J.; Teng, S.N.; Zheng, G.; Cui, L.; Li, S.; Staal, A.; Eitel, J.U.; Crowther, T.W.; Berdugo, M.; Mo, L.; et al. Inferring plant–plant interactions using remote sensing. J. Ecol. 2022, 110, 2268–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q. Linking variability in species composition and MODIS NDVI based on beta diversity measurements. Acta Oecol. 2009, 35, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmayne, J.; Möckel, T.; Prentice, H.C.; Schmid, B.C.; Hall, K. Assessment of fine-scale plant species beta diversity using WorldView-2 satellite spectral dissimilarity. Ecol. Inform. 2013, 18, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Meer, F.; Bakker, W.; Scholte, K.; Skidmore, A.; De Jong, S.; Clevers, J.; Addink, E.; Epema, G. Spatial scale variations in vegetation indices and above-ground biomass estimates: Implications for MERIS. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 3381–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Mahecha, M.D.; Migliavacca, M.; van der Plas, F.; Benavides, R.; Ratcliffe, S.; Kattge, J.; Richter, R.; Musavi, T.; Baeten, L.; et al. Inferring plant functional diversity from space: The potential of Sentinel-2. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 233, 111368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Féret, J.B.; Asner, G.P. Mapping tropical forest canopy diversity using high-fidelity imaging spectroscopy. Ecol. Appl. 2014, 24, 1289–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laliberté, E.; Schweiger, A.K.; Legendre, P. Partitioning plant spectral diversity into alpha and beta components. Ecol. Lett. 2020, 23, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draper, F.C.; Baraloto, C.; Brodrick, P.G.; Phillips, O.L.; Martinez, R.V.; Honorio Coronado, E.N.; Baker, T.R.; Zárate Gómez, R.; Amasifuen Guerra, C.A.; Flores, M.; et al. Imaging spectroscopy predicts variable distance decay across contrasting Amazonian tree communities. J. Ecol. 2019, 107, 696–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opedal, Ø.H.; Armbruster, W.S.; Graae, B.J. Linking small-scale topography with microclimate, plant species diversity and intra-specific trait variation in an alpine landscape. Plant Ecol. Divers. 2015, 8, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, R.; Dalling, J.W.; Harms, K.E.; Yavitt, J.B.; Stallard, R.F.; Mirabello, M.; Hubbell, S.P.; Valencia, R.; Navarrete, H.; Vallejo, M.; et al. Soil nutrients influence spatial distributions of tropical tree species. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 864–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zhang, X. Comprehensive Investigation Report on Natural Resource of Tianmu Mountain Nature Reserve; Zhejiang Science and Technology Press: Hangzhou, China, 1992. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Da, L.; Kang, M.; Song, K.; Shang, K.; Yang, Y.; Xia, A.; Qi, Y. Altitudinal zonation of human-disturbed vegetation on Mt. Tianmu, eastern China. Ecol. Res. 2009, 24, 1287–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Shang, K.; Zhao, M.; Kong, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Song, H.; Zhang, O.; Lv, X.; et al. A taxonomic and phylogenetic perspective on plant community assembly along an elevational gradient in subtropical forests. J. Plant Ecol. 2021, 14, 702–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drusch, M.; Del Bello, U.; Carlier, S.; Colin, O.; Fernandez, V.; Gascon, F.; Hoersch, B.; Isola, C.; Laberinti, P.; Martimort, P.; et al. Sentinel-2: ESA’s optical high-resolution mission for GMES operational services. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enache, S. Data Quality Report-Sentinel-2 L1C MSI; No. OMPC. CS. DQR. 01.01-2022; ESA: Paris, France, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, D.; He, F. Analytical models for β-diversity and the power-law scaling of β-deviation. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2021, 12, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendre, P.; De Cáceres, M. Beta diversity as the variance of community data: Dissimilarity coefficients and partitioning. Ecol. Lett. 2013, 16, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, A.; Chiu, C.H. Bridging the variance and diversity decomposition approaches to beta diversity via similarity and differentiation measures. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2016, 7, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuomisto, H. A diversity of beta diversities: Straightening up a concept gone awry. Part 1. Defining beta diversity as a function of alpha and gamma diversity. Ecography 2010, 33, 2–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; Version 4.0.5; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Australia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kollert, A.; Bremer, M.; Löw, M.; Rutzinger, M. Exploring the potential of land surface phenology and seasonal cloud free composites of one year of Sentinel-2 imagery for tree species mapping in a mountainous region. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 94, 102208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dronova, I.; Taddeo, S. Remote sensing of phenology: Towards the comprehensive indicators of plant community dynamics from species to regional scales. J. Ecol. 2022, 110, 1460–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Gamon, J.A.; Cavender-Bares, J. Seasonal patterns of spectral diversity at leaf and canopy scales in the Cedar Creek prairie biodiversity experiment. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 280, 113169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Kong, J.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, J.; Qin, Y.; Shang, K.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, J. Seeing Trees from Drones: The Role of Leaf Phenology Transition in Mapping Species Distribution in Species-Rich Montane Forests. Forests 2023, 14, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madonsela, S.; Cho, M.A.; Ramoelo, A.; Mutanga, O. Investigating the relationship between tree species diversity and landsat-8 spectral heterogeneity across multiple phenological stages. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornley, R.; Gerard, F.F.; White, K.; Verhoef, A. Intra-annual taxonomic and phenological drivers of spectral variance in grasslands. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 271, 112908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zutta, B. Assessing Vegetation Functional Type and Biodiversity in Southern California Using Spectral Reflectance. Ph.D. Thesis, California State University, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Schriever, J.R.; Congalton, R.G. Evaluating seasonal variability as an aid to cover-type mapping from Landsat Thematic Mapper data in the Northeast. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1995, 61, 321–327. [Google Scholar]
- Maeda, E.E.; Heiskanen, J.; Thijs, K.W.; Pellikka, P.K. Season-dependence of remote sensing indicators of tree species diversity. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 5, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, H.M.; Dogan, M. A new approach to diversity indices–modeling and mapping plant biodiversity of Nallihan (A3-Ankara/Turkey) forest ecosystem in frame of geographic information systems. Biodivers. Conserv. 2006, 15, 855–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldeland, J.; Wesuls, D.; Rocchini, D.; Schmidt, M.; Jürgens, N. Does using species abundance data improve estimates of species diversity from remotely sensed spectral heterogeity? Ecol. Indic. 2010, 10, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condit, R.; Ashton, P.S.; Baker, P.; Bunyavejchewin, S.; Gunatilleke, S.; Gunatilleke, N.; Hubbell, S.P.; Foster, R.B.; Itoh, A.; LaFrankie, J.V.; et al. Spatial patterns in the distribution of tropical tree species. Science 2000, 288, 1414–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatini, F.M.; Jiménez-Alfaro, B.; Burrascano, S.; Lora, A.; Chytrý, M. Beta-diversity of central European forests decreases along an elevational gradient due to the variation in local community assembly processes. Ecography 2018, 41, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantlon, J.E. Vegetation and microclimates on north and south slopes of Cushetunk Mountain, New Jersey. Ecol. Monogr. 1953, 23, 241–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, M.; Manabe, T.; Nishimura, N.; Yamamoto, S.I. Forest canopy and community dynamics in a temperate old-growth evergreen broad-leaved forest, south-western Japan: A 7-year study of a 4-ha plot. J. Ecol. 2001, 89, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comita, L.S.; Condit, R.; Hubbell, S.P. Developmental changes in habitat associations of tropical trees. J. Ecol. 2007, 95, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, B.; Li, D.; Mallik, A.U.; Xiang, W.; Ding, T.; Wen, S.; Lu, S.; Huang, F.; He, Y.; et al. Effects of topography and spatial processes on structuring tree species composition in a diverse heterogeneous tropical karst seasonal rainforest. Flora 2017, 231, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, W.; Baselga, A.; Kusumoto, B.; Shiono, T.; Tuomisto, H.; Kubota, Y. The tangley5asd link between β-and γ-diversity: A Narcissus effect weakens statistical inferences in null model analyses of diversity patterns. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2017, 26, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Season | Vegetation Phenology |
|---|---|
| Early spring (March–April) | Bud breaking and initial leaf sprouting |
| Late spring (May) | Leaf expansion and flowering |
| Summer (June–August) | Growing season/peak greenness |
| Early autumn (September) | Initial defoliation |
| Late autumn (October–November) | Leaf senescence and defoliation |
| Winter (December–February) | Dormant phase/evergreen persistence |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, R.; Huang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, P.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; et al. Unveiling Scale-Dependent Elevational Patterns and Drivers of Tree β Diversity on a Subtropical Mountain Using Sentinel-2 Remote Sensing Data. Forests 2025, 16, 917. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16060917
Zhang R, Huang J, Liu Y, Wang X, Li Y, Zeng Y, Liu P, Wang X, Zhang Z, Zhang J, et al. Unveiling Scale-Dependent Elevational Patterns and Drivers of Tree β Diversity on a Subtropical Mountain Using Sentinel-2 Remote Sensing Data. Forests. 2025; 16(6):917. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16060917
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ruyun, Jingyue Huang, Yongchao Liu, Xiaoning Wang, You Li, Yulin Zeng, Pengcheng Liu, Xiaoran Wang, Zhaochen Zhang, Jian Zhang, and et al. 2025. "Unveiling Scale-Dependent Elevational Patterns and Drivers of Tree β Diversity on a Subtropical Mountain Using Sentinel-2 Remote Sensing Data" Forests 16, no. 6: 917. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16060917
APA StyleZhang, R., Huang, J., Liu, Y., Wang, X., Li, Y., Zeng, Y., Liu, P., Wang, X., Zhang, Z., Zhang, J., & Xing, D. (2025). Unveiling Scale-Dependent Elevational Patterns and Drivers of Tree β Diversity on a Subtropical Mountain Using Sentinel-2 Remote Sensing Data. Forests, 16(6), 917. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16060917






