Induction of Somatic Embryogenesis in Araucaria araucana (Molina) K. Koch: Considerations for Ex Situ Conservation of Ancient Tree in Chile
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
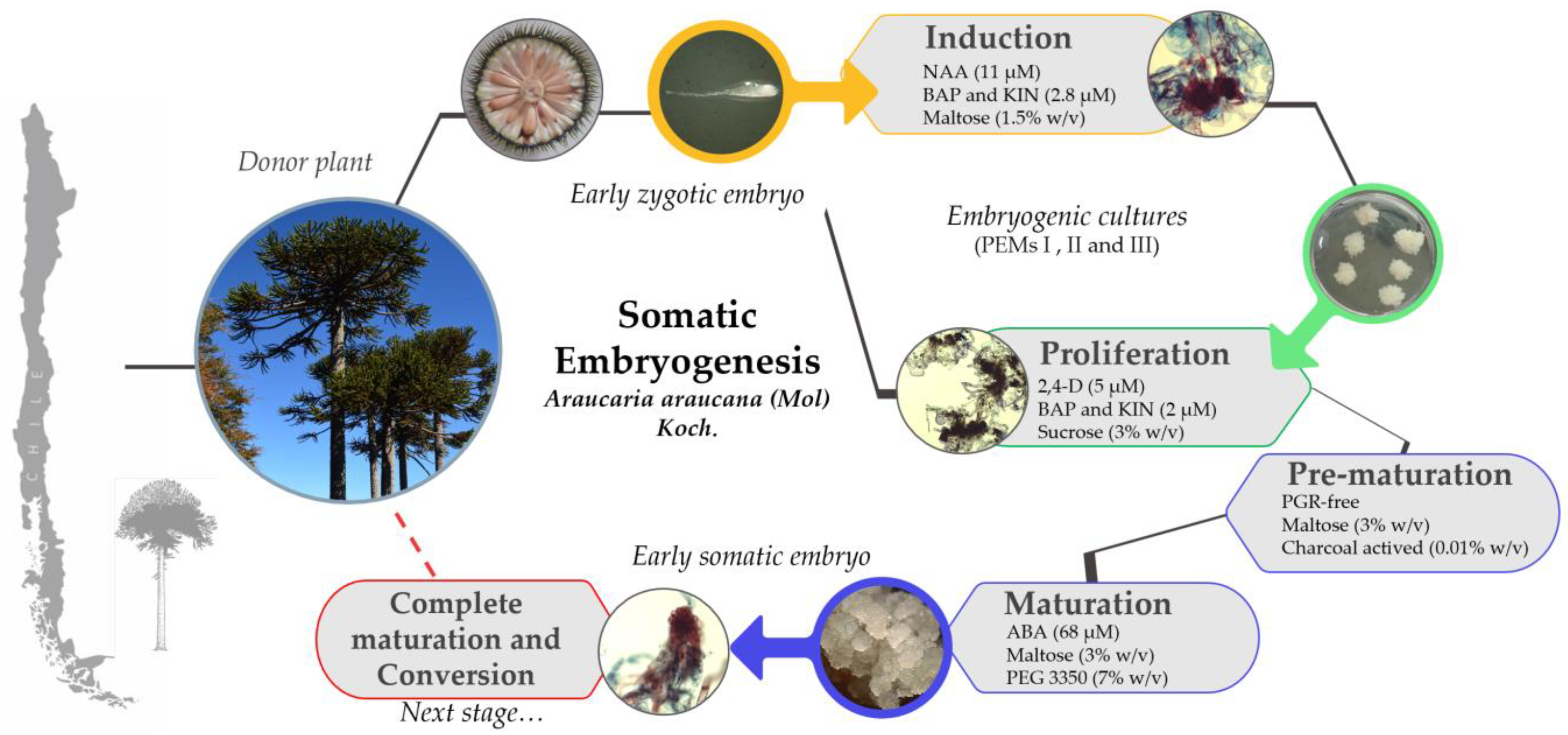
2.2. Induction of Embryogenic Culture
2.3. Embryogenic Culture Proliferation
2.4. Somatic Embryo Development in Pre-Maturation and Maturation
2.5. Morpho-Cytochemical Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
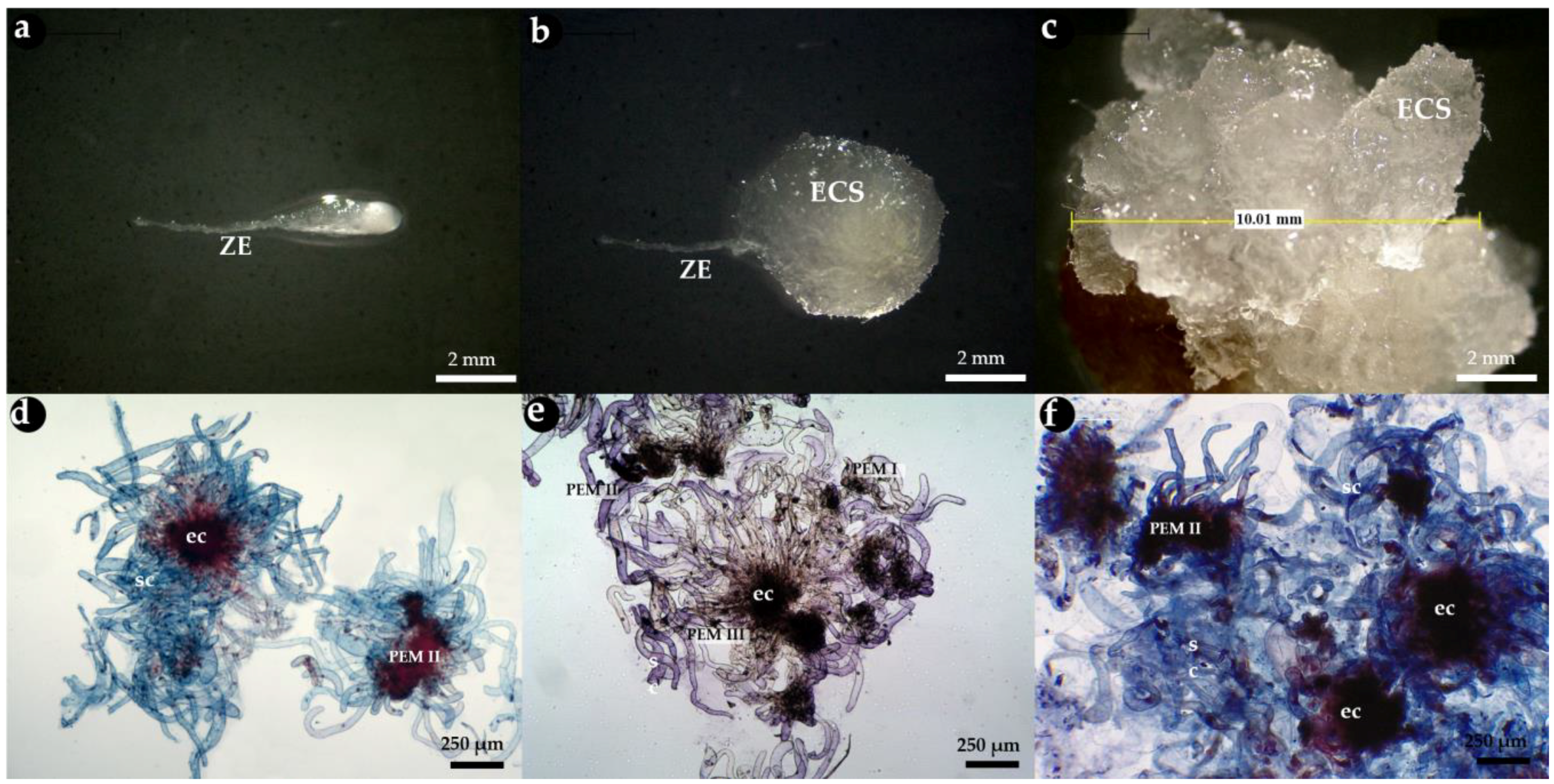
3.1. Zygotic Embryo Development Stage Is Affected by Provenance and Embryogenic Culture Induction
3.2. Embryogenic Culture Proliferation and Characterization of Pro-Embryogenic Masses
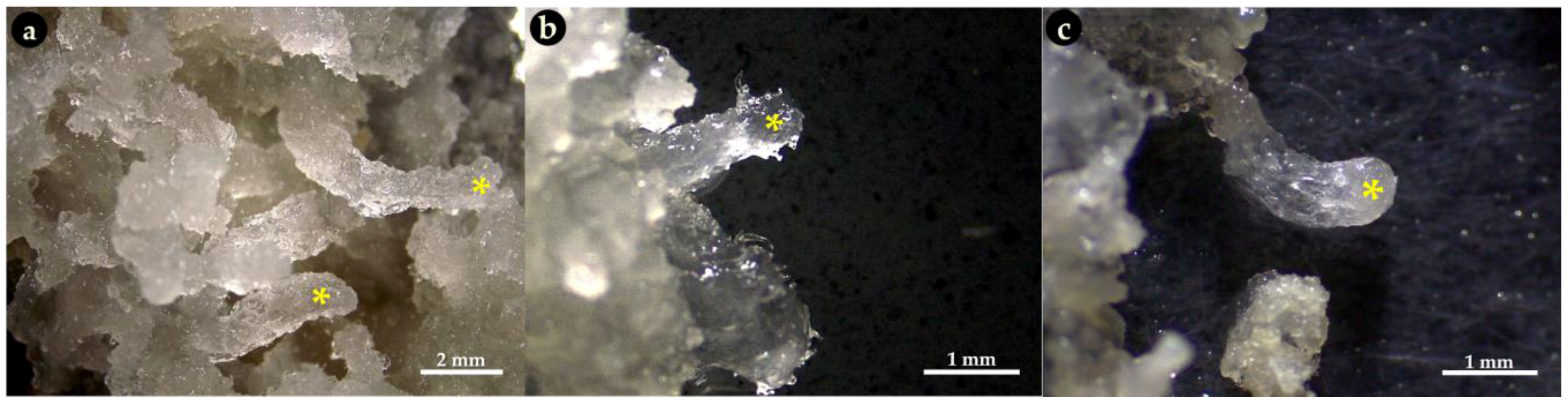
3.3. Pre-Maturation and Maturation of Embryogenic Culture
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABA | Abscisic acid |
| BM | Basal medium [7] |
| Ec | Embryogenic cell |
| Sc | Suspensor cell |
| ECLs | Embryogenic cell lines |
| FM | Fresh mass |
| IC | Induction medium control (PGR-free BM) |
| Kin | Kinetin |
| MA | Malalcahuello |
| MIP | Induction medium (BM with 11 μM NAA and others) |
| MIN | Induction medium (BM with 23 μM 2,4-D and others) |
| MP1 | Proliferation medium 1 (BM with 5 μM 2,4-D and others) |
| MP2 | Proliferation medium 2 (BM with 23 μM 2,4-D and others) |
| NAA | 1-naftalenacetic acid |
| NaClO | Sodium hypochlorite |
| PEG | Polyethyleneglycol 3350 |
| PEMs | Pro-embryogenic masses |
| PGR | Plant growth regulator |
| sc | Suspensor-like cell |
| SE | Somatic embryogenesis |
| TR | Trongol |
| VA | Villa las Araucarias |
| ZE | Zygotic embryo |
| 2,4-D | 2,4-diclorofenoxiacetic acid |
| 6-BA | 6-benzylaminopurine |
Appendix A
References
- González, M.; Cortés, M.; Izquierdo, F.; Gallo, L.; Echeverría, C.; Bekessy, S.; Montaldo, P. Araucaria araucana (Molina) K. Koch. Araucaria (o), Pehuén, Pino piñonero, Pino de Neuquén, Monkey Puzzle Tree. In Las especies arbóreas de los bosques templados de Chile y Argentina; Donoso, C., Ed.; Autoecología, Marisa Cuneo Ediciones: Valdivia, Chile, 2006; pp. 36–53. [Google Scholar]
- Zamorano, C.; Cortés, M.; Echeverría, C.; Hechenleitner, P.; Lara, A. Experiencias de Restauración con Especies Forestales Amenazadas En Chile. In Restauración de Bosques en América Latina; FIRE/Mundi-Prensa: Ciudad de México, México, 2008; pp. 18–36. [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann, T. Knowledge, values, uses and management of the Araucaria Araucana forest by the indigenous Mapuche Pewenche people: A basis for collaborative natural resource management in southern Chile. Nat. Resour. Forum 2005, 29, 120–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veblen, T.; Burns, R.; Kitzberger, T.; Lara, A.; Villalba, R. The ecology of the conifers of southern South America. In Ecology of the Southern Conifers; Enright, N., Hill, R., Eds.; Melbourne University Press: Parkville, Australia, 1995; pp. 120–155. [Google Scholar]
- IUCN. The IUCN Red list of threatened species. In Red List of Threatened Species; 2023. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/32975/2829141 (accessed on 13 March 2024).
- Balocchi, F.; Wingfield, M.; Ahumada, R.; Barnes, I. Pewenomyces kutranfy gen. nov. et sp. nov. causal agent of an important canker disease on Araucaria araucana in Chile. Plant Pathol. 2021, 70, 1243–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto Forestal (INFOR). INFOR and CMPC Sign Agreement for the Genetic Protection of the Araucaria. 21 June 2018. Available online: https://www.infor.cl/index.php/noticias/425-infor-y-cmpc-firman-convenio-para-el-resguardo-genetico-de-la-araucaria (accessed on 22 June 2018).
- Ministerio del Medio Ambiente. Araucaria araucana (Mol.) Koch, M.K. Species Classification: Species Background Sheet 2002, pp. 1–7. Available online: https://clasificacionespecies.mma.gob.cl/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/Araucaria_araucana_FINAL.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Convention on Biological Diversity. 1992. Available online: https://www.cbd.int/ (accessed on 12 November 2023).
- Ruiz, E.; González, F.; Torres-Díaz, C.; Fuentes, G.; Mardones, M.; Stuessy, T.; Samuel, R.; Becerra, J.; Silva, M. Genetic diversity and differentiation within and among Chilean populations of Araucaria araucana (Araucariaceae) based on allozyme variability. Taxon 2007, 56, 1221–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goeten, D.; Farias-Soares, F.; Rogge-Renner, G.D.; Pereira, M.L.T.; Walters, C.; Silveira, V.; Catarina, C.S.; Guerra, M.P.; Steiner, N. Carbohydrate and dehydrin-like protein profiles during Araucaria angustifolia seed development provides insights toward ex situ conservation. Trees 2023, 37, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lineros, Y.; Balocchi, C.; Muñoz, X.; Sánchez, M.; Ríos, D. Cryopreservation of Pinus radiata embryogenic tissue: Effects of cryoprotective pretreatments on maturation ability. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2018, 135, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefenon, V.M.; Marques-Pinheiro, V.; Goeten, D.; Ree, J.F.; Steiner, N.; Guerra, M.P. Advances and constraints in somatic embryogenesis of Araucaria angustifolia, Acca sellowiana and Bactris gasipaes. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2020, 143, 241–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, N.; Farias-Soares, F.; Schmidt, É.; Pereira, M.; Scheid, B.; Rogge-Renner, G.; Bouzon, Z.; Schmidt, D.; Maldonado, S.; Guerra, M.P. Toward establishing a morphological and ultrastructural characterization of proembryogenic masses and early somatic embryos of Araucaria angustifolia (Bert.) O. Kuntze. Protoplasma. 2016, 253, 487–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corredoira, E.; Merkle, S.; Martínez, M.; Toribio, M.; Canhoto, J.; Correia, S.; Ballester, A.; Vieitez, A. Non-zygotic embryogenesis in hardwood species. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2019, 38, 29–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaj, M. Factors influencing somatic embryogenesis induction and plant regeneration with particular reference to Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh. Plant Growth Regul. 2004, 43, 27–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehér, A. Somatic embryogenesis: Stress-induced plant cell fate remodeling. biochemistry Biography. Bioenergy Act 2015, 1849, 385–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehér, A. The initiation phase of somatic embryogenesis: What we know and what we don’t. Act Biol. 2008, 52, 53–56. Available online: https://abs.bibl.u-szeged.hu/index.php/abs/article/view/2579 (accessed on 13 April 2025).
- Su, Y.H.; Tang, L.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, X. Plant cell totipotency: Insights into cellular reprogramming. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2021, 63, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, E.F.; Hall, M.; Klerk, G. Plant Growth Regulators I: Introduction; Auxins, their analogues and Inhibitors. In Plant Propagation by Tissue Culture; George, E.F., Hall, M., Klerk, G., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 175–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wójcik, A.M.; Wójcikowska, B.; Gaj, M. Current Perspectives on the Auxin-Mediated Genetic Network that Controls the Induction of Somatic Embryogenesis in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkle, S.A. Strategies to address the limitations of somatic embryogenesis in hardwood trees. Plant Tissue Cult. Biotechnol. 1995, 31, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Ballester, A.; Corredoira, E.; Vieitez, A. Limitations of somatic embryogenesis in hardwood trees. In Vegetative Propagation of Forest Trees; Park, Y., Bonga, J., Moon, H., Eds.; National Institute of Forest Sciences: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2016; pp. 56–74. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10261/218291 (accessed on 13 April 2025).
- Goeten, D.; Rogge-Renner, G.; Schmidt, E.; Bouzon, Z.; Farias-Soares, F.; Guerra, M.P.; Steiner, N. Updating embryonic ontogenesis in Araucaria angustifolia: From Burlingame (1915) to the present. Protoplasma. 2020, 257, 931–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefenon, V.; Steiner, N.; Guerra, M.P.; Nodari, R. Integrating approaches towards the conservation of forest genetic resources: A case study of Araucaria angustifolia. Biodivers. Conserv. 2009, 18, 2433–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astarita, L.; Guerra, M.P.; Silveira, V.; Santos, A.W.; Nodari, R. Somatic embryogenesis in Araucaria angustifolia (Bert) O. Kuntze. In Somatic Embryogenesis in Woody Plants; Jain, S., Gupta, P., Newton, R., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2000; Volume 6, pp. 457–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, V.; Steiner, N.; dos Santos, A.; Nodari, R.; Guerra, M.P. Biotechnology tolls in Araucaria angustifolia conservation and improvement: Inductive factors affecting Somatic embryogenesis. Crop Breed. Appl. Biotechnol. 2002, 2, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Bucalo, K.; Determann, R.O.; Cruse-Sanders, J.; Pullman, G. Somatic embryogenesis, plant regeneration, and cryopreservation for Torreya taxifolia, a highly endangered coniferous species. Vitr. Cell Dev. Biol. Plant 2012, 48, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuri, S.; Shmoury, M.; Baalbaki, R.; Maunder, M.; Talhouk, S. Conservation of the Cedrus libani populations in Lebanon: History, current status and experimental application of somatic embryogenesis. Biodivers. Conserv. 2000, 9, 1261–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Arnold, S.; Egertsdotter, U.; Ekberg, I.; Gupta, P.; Mo, H.; Nörgaard, J. Somatic embryogenesis in Norway spruce (Picea abies). In Somatic Embryogenesis in Woody Plants; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1995; Volume 3, pp. 17–36. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, P.K.; Pullman, G. Method for Reproducing Coniferous Plants by Somatic Embryogenesis Using Adsorbent Materials in the Development Stage Media. U.S. Patent No. 5034326, 23 July 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, P.K.; Pullman, G.; Timmis, R.; Kreitinger, M.; Carlson, W.; Grob, J.; Welty, E. Forestry in the 21st century. The biotechnology of somatic embryogenesis. Biotechnology 1993, 11, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullman, G.; Webb, D. An embryo staging system for comparison of zygotic and somatic embryo development. In TAPPI R&D Division Biological Sciences Symposium; Springer: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 1994; pp. 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Pullman, G. Embryogenic tissue initiation in loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.). Step Wise Protoc. Somat. Embryog. Important Woody Plants 2018, 1, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.K.; Durzan, D. Shoot multiplication from mature trees of Douglas-fir (Pseudotsuga menziesii) and sugar pine (Pinus-lambertiana). Plant Cell Rep. 1985, 4, 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becwar, M.; Blush, T.; Brown, D.; Chesick, E. Multiple paternal genotypes in embryogenic tissue derived from individual immature loblolly pine seeds. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 1991, 26, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelu, M.; Bastien, C.; Drugeault, A.; Gouez, M.; Klimaszewska, K. Somatic embryogenesis and plantlet development in Pinus sylvestris and Pinus pinaster on medium with and without growth regulators. Physiol. Plant. 1999, 105, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimaszewska, K.; Smith, D. Maturation of somatic embryos of Pinus strobus is promoted by a high concentration of gellan gum. Physiol. Plant. 1997, 100, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astarita, L.; Guerra, M.P. Early somatic embryogenesis in Araucaria angustifolia: Induction and maintenance of embryonal-suspensor mass cultures. Braz. J. Plant Physiol. 1998, 10, 113–118. [Google Scholar]
- Haberlandt, G. Culturversuche mit isolierten Pflanzenzellen. In Plant Tissue Culture; Laimer, M., Rücker, W., Eds.; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2003; Volume 111, pp. 69–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huihui, G.; Li, Z.; Haixia, G.; Xiwang, C.; Yupeng, F.; Tongtong, L.; Xiushan, Q.; Tongdi, Y.; Aiyun, C.; Fengjuan, S.; et al. Single-cell transcriptome atlas reveals somatic cell embryogenic differentiation features during regeneration. Plant Physiol. 2024, 195, 1414–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Pond, S.; Bonga, J. Initiation of somatic embryogenesis in white spruce (Picea glauca): Genetic control, culture treatment effects, and implications for tree breeding. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1993, 86, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Dunstan, D. Growth parameters, protein and DNA synthesis of an embryogenic suspension culture of white spruce (Picea glauca). J. Plant Physiol. 1994, 144, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Dunstan, D. Cloning and characterization of six embryogenesis-associated cDNAs from somatic embryos of Picea glauca and their comparative expression during zygotic embryogenesis. Plant Mol. Biol. 1999, 39, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, A.; Silveira, V.; Steiner, N.; Vidor, M.; Guerra, M.P. Somatic embryogenesis in Parana pine (Araucaria angustifolia (Bert.) O. Kuntze). Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2002, 45, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filonova, L.; Bozkov, P.; von Arnold, S. Developmental pathway of somatic embryogenesis in Picea abies as revealed by time-lapse tracking. J. Exp. Bot. 2000, 51, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farias-Soares, F.; Steiner, N.; Schmidt, E.; Pereira, M.; Rogge-Renner, G.; Bouzon, Z.; Floh, E.; Guerra, M.P. The transition of proembryogenic masses to somatic embryos in Araucaria angustifolia (Bertol.) Kuntze is related to the endogenous contents of IAA, ABA and polyamines. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2014, 36, 1853–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H. Embryology of Gimnosperms. Encyclopedia of Plant Anatomy; Gebrüder Borntraeger: Berlin, Germany, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Attree, S.; Fowke, L. Embryogeny of gymnosperms: Advances in synthetic seed technology of conifers. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 1993, 35, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozhkov, P.V.; Von Arnold, S. Polyethylene glycol promotes maturation but inhibits further development of Picea abies somatic embryos. Physiol. Plant. 1998, 104, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hristoforoglu, K.; Schmidt, J.; Bolhar-Nordenkampf, H. Development and germination of Abies alba somatic embryos. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 1995, 40, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, F.; Murphy, J.; Gbur, E. Polyethylene glycol and maltose enhance somatic embryo maturation in loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.). In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol.-Plant 1998, 34, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salajova, T.; Salaj, J.; Kormutak, A. Initiation of embryogenic tissues and plantlet regeneration from somatic embryos of Pinus nigra Arn. Plant Sci. 1999, 145, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, F.; Gbur, E. Polyethylene glycol promoted development of somatic embryos in loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.). In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. -Plant 1997, 33, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Arnold, S.; Bozhkov, P.; Clapham, D.; Dyachok, J.; Filonova, L.; Högberg, K.; Ingouff, M.; Wiweger, M. Propagation of Norway spruce via somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2005, 81, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| S. America and Chile Geographical Location | Plant Population Provenance | Zygotic Embryo Development Stage (Months) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pro-Embryo (November) | Early (December) | Late (January) | ||
 | Malalcahuello 38°26’ S –  71 °31’ W 71 °31’ W |  |  |  |
Trongol 37°37’ S – 37°37’ S – 73°07’ W | 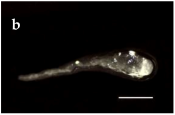 |  | 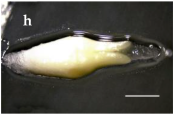 | |
Villa Las  Araucarias Araucarias38°29’ S – 73°14’ W | 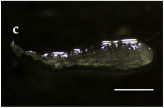 |  | 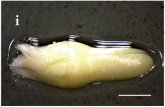 Scale: 1.0 mm | |
| Plant Population Provenance | Pro- Embryo (%) | Early (%) | Late (%) | Pro- Embryo (%) | Early (%) | Late (%) | Pro- Embryo (%) | Early (%) | Late (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC | MIP | MIN | |||||||
| Malalca huello | 6 Bb * | 3 Cb | 0 Cc | 0 Cc | 39 Aa | 0 Cc | 0 Cc | 3 Cb | 0 Cc |
| Trongol | 0 Cc | 17 Bb | 0 Cc | 0 Cc | 22 Ba | 0 Cc | 0 Cc | 19 Ba | 0 Cc |
| Villa Las Araucarias | 0 Cc | 11 Bb | 0 Cc | 0 Cc | 75 Aa | 0 Cc | 0 Cc | 17 Bb | 0 Cc |
| Morpho-Cytological Response of PEMs in Pre-Maturation and Maturation | ||
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 (PGR-free-42 days) | Step 2 (ABA-21 days) | PEMs Cytology (ABA-21 days) |
 | 34 μM ABA | |
 | 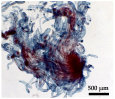 | |
 | 68 μM ABA | |
 | 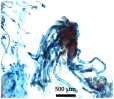 | |
 | 95 μM ABA | |
 | 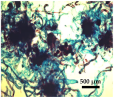 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Riffo-Agurto, D.; Steiner, N.; Cartes, P.; Quiroga, P.; Espejo, J.; San Martin, E.; Lasserre, J.-P.; Martínez-Montero, M.E.; Hernández de la Torre, M.; Ríos-Leal, D.; et al. Induction of Somatic Embryogenesis in Araucaria araucana (Molina) K. Koch: Considerations for Ex Situ Conservation of Ancient Tree in Chile. Forests 2025, 16, 732. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16050732
Riffo-Agurto D, Steiner N, Cartes P, Quiroga P, Espejo J, San Martin E, Lasserre J-P, Martínez-Montero ME, Hernández de la Torre M, Ríos-Leal D, et al. Induction of Somatic Embryogenesis in Araucaria araucana (Molina) K. Koch: Considerations for Ex Situ Conservation of Ancient Tree in Chile. Forests. 2025; 16(5):732. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16050732
Chicago/Turabian StyleRiffo-Agurto, Daniela, Neusa Steiner, Priscila Cartes, Pamela Quiroga, Jaime Espejo, Ester San Martin, Jean-Pierre Lasserre, Marcos Edel Martínez-Montero, Martha Hernández de la Torre, Darcy Ríos-Leal, and et al. 2025. "Induction of Somatic Embryogenesis in Araucaria araucana (Molina) K. Koch: Considerations for Ex Situ Conservation of Ancient Tree in Chile" Forests 16, no. 5: 732. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16050732
APA StyleRiffo-Agurto, D., Steiner, N., Cartes, P., Quiroga, P., Espejo, J., San Martin, E., Lasserre, J.-P., Martínez-Montero, M. E., Hernández de la Torre, M., Ríos-Leal, D., Ipinza, R., Sandoval, S., & Sánchez-Olate, M. (2025). Induction of Somatic Embryogenesis in Araucaria araucana (Molina) K. Koch: Considerations for Ex Situ Conservation of Ancient Tree in Chile. Forests, 16(5), 732. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16050732








