Genome-Wide Profiling of the Genes Resistant to Bursaphelenchus xylophilus in Pinus tabuliformis Carriere
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and B. xylophilus Inoculation
2.2. Physiological Index Assay
2.3. Transcriptome Analysis
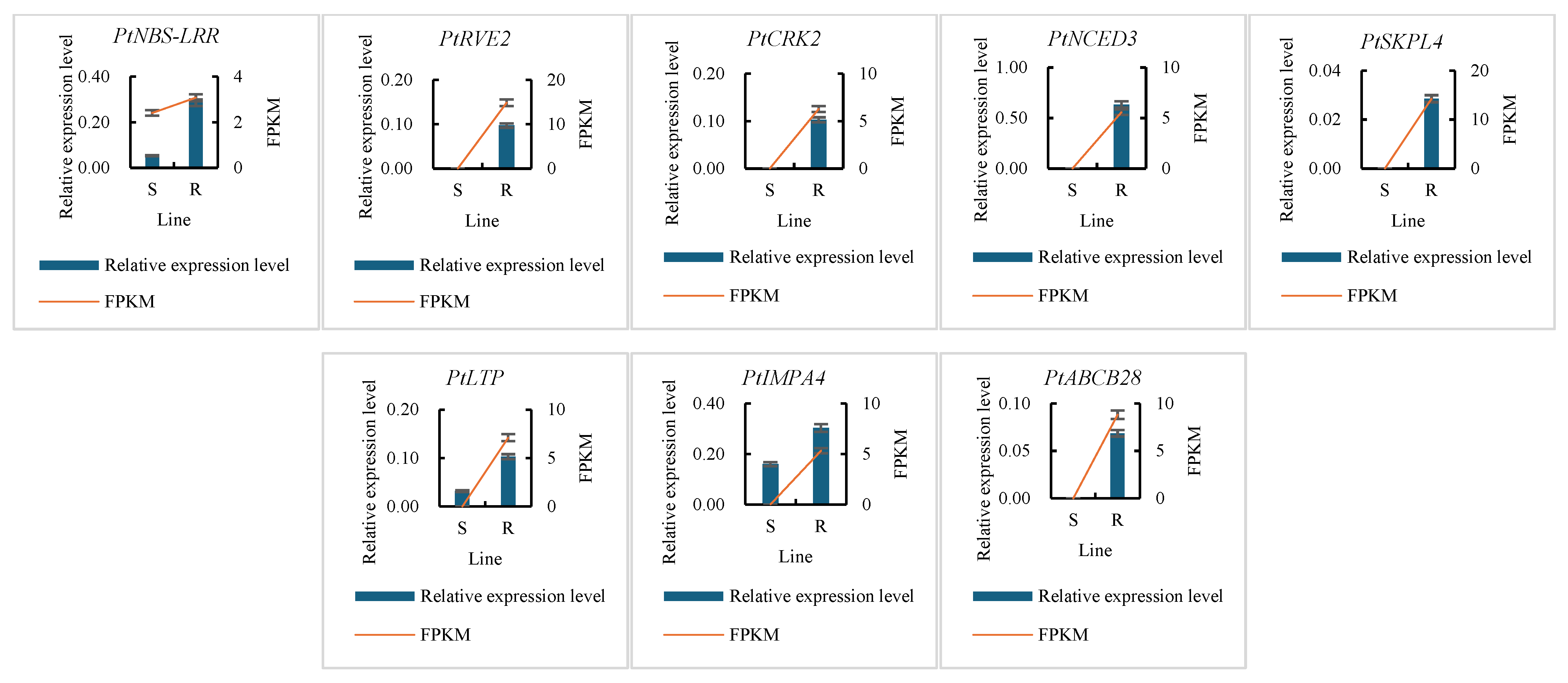
2.4. Gene Expression Assay
3. Results and Discussion
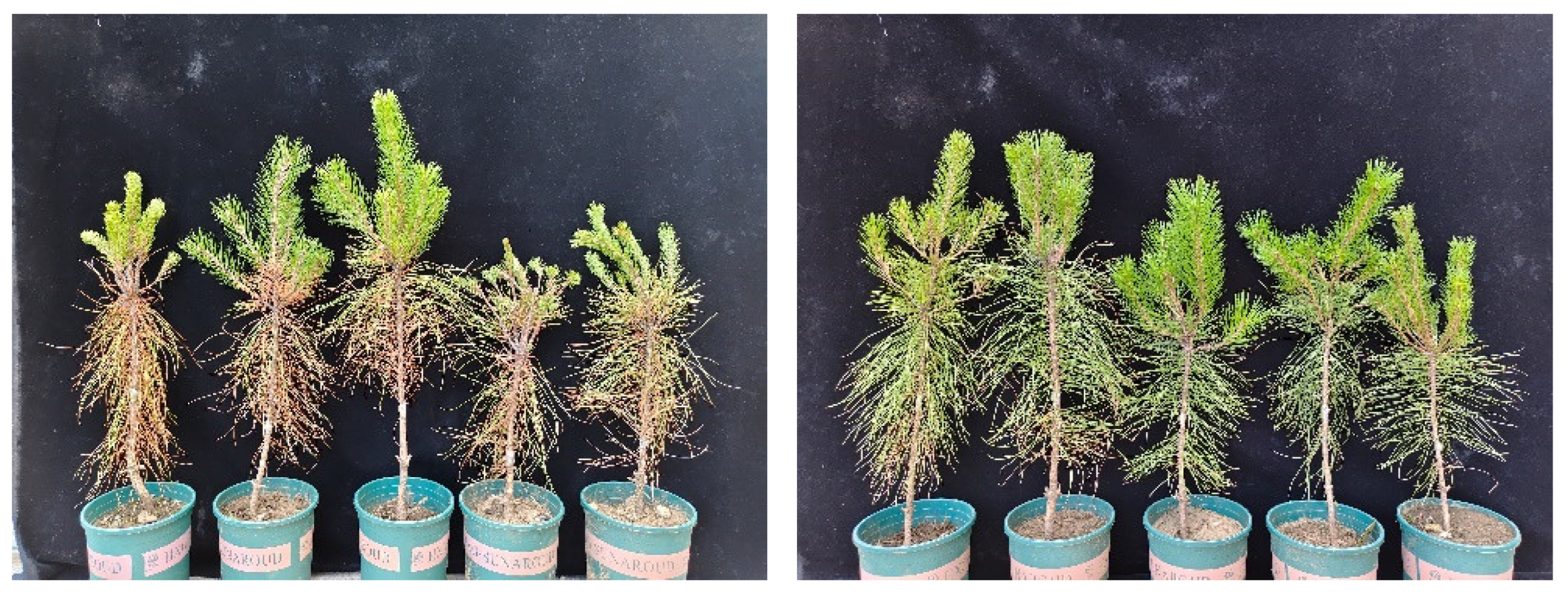
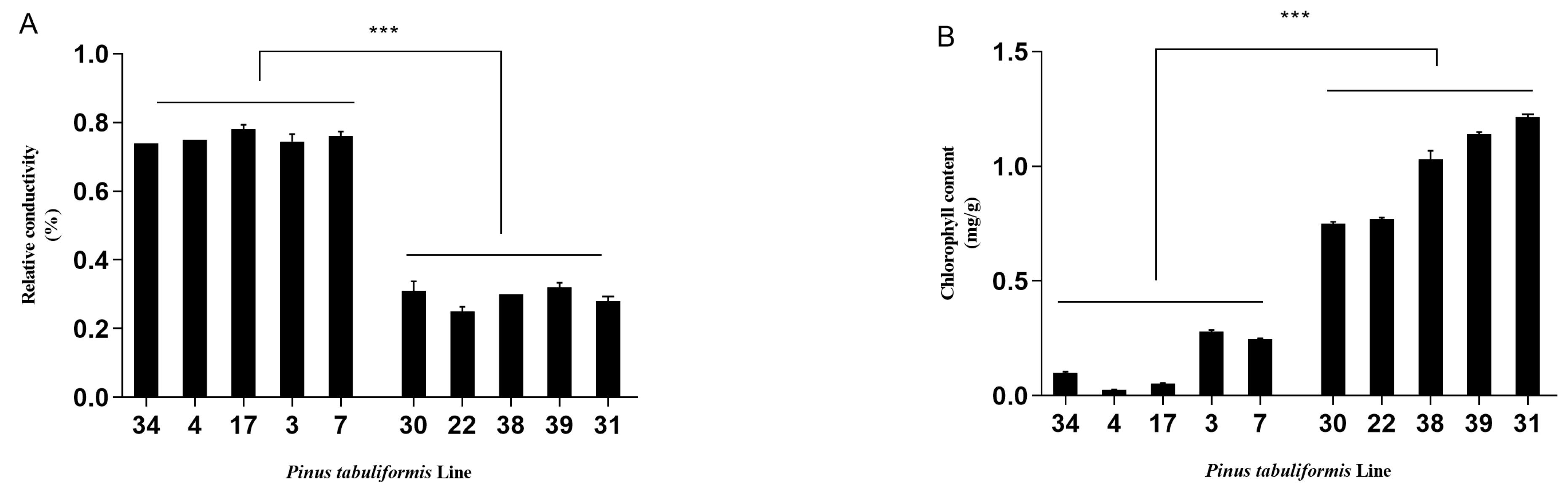
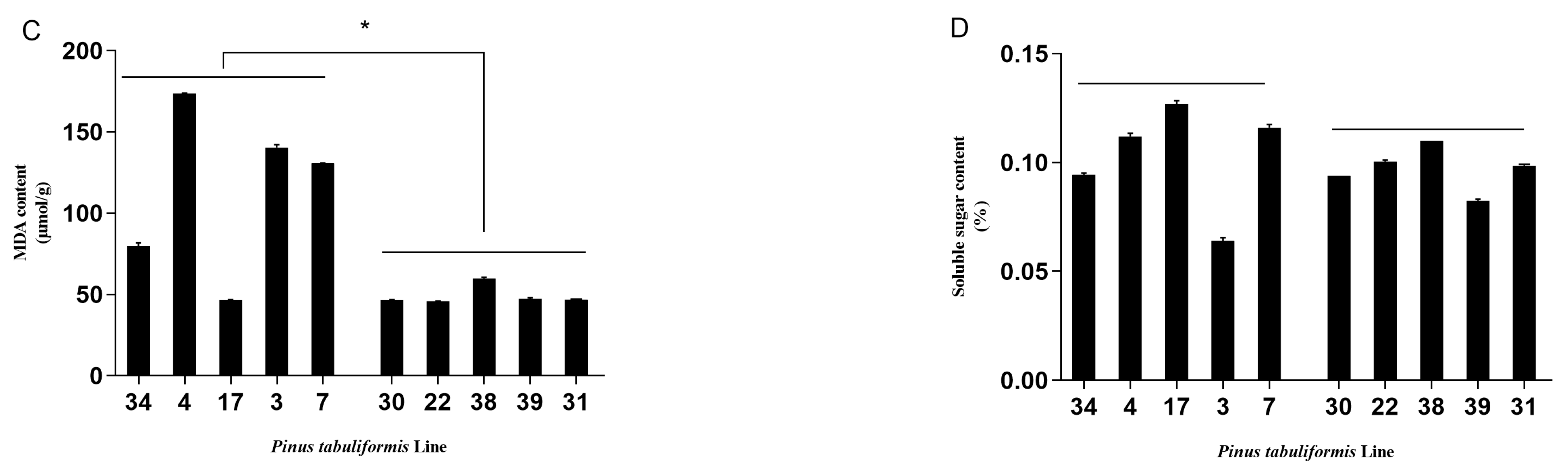
3.1. Evaluation of the Resistance of P. tabuliformis’ Germplasms to B. xylophilus
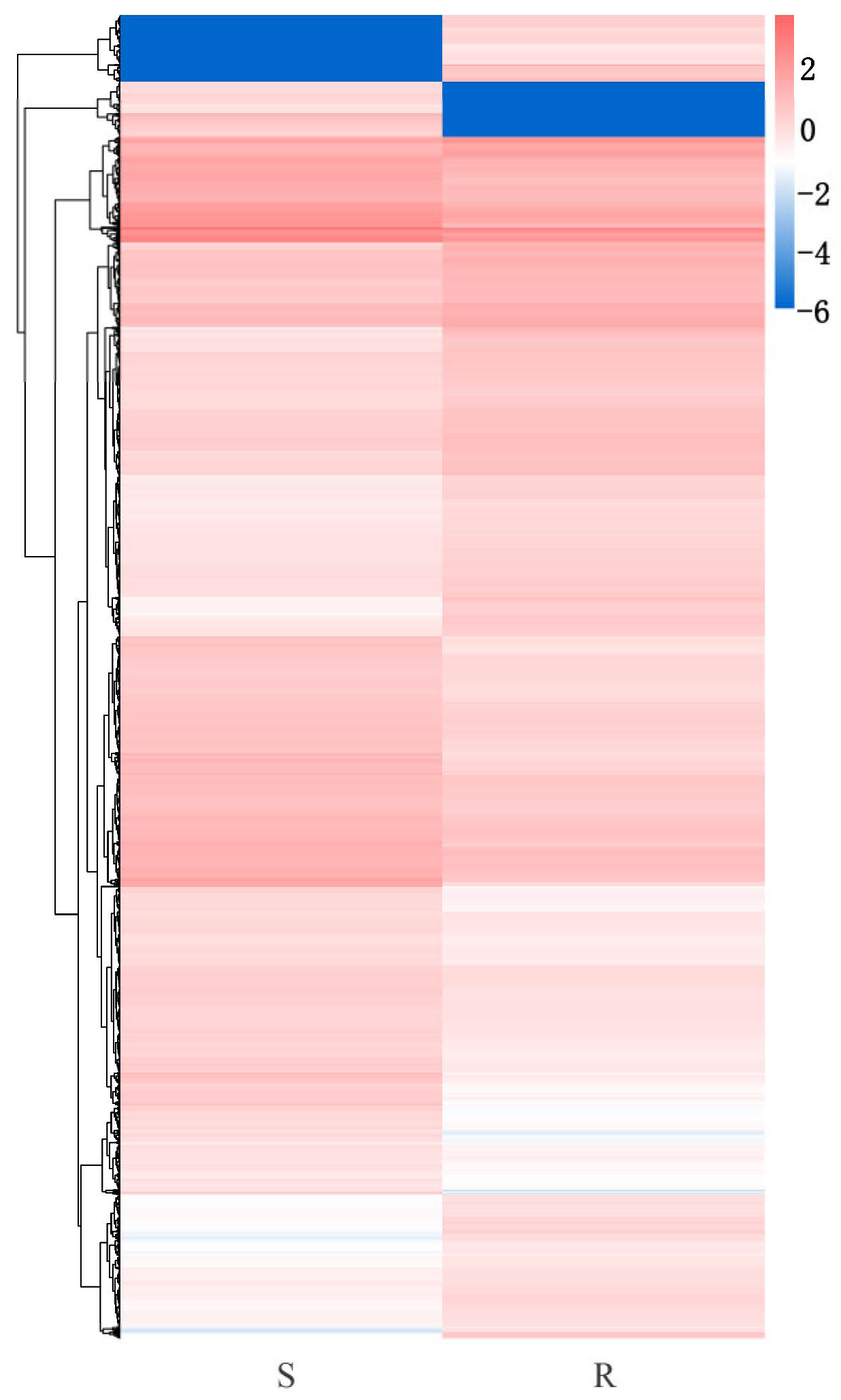
3.2. Transcriptome Analysis of P. tabuliformis Infected by B. xylophilus
3.3. Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs) Between the Resistant and Susceptible P. tabuliformis Lines to B. xylophilus
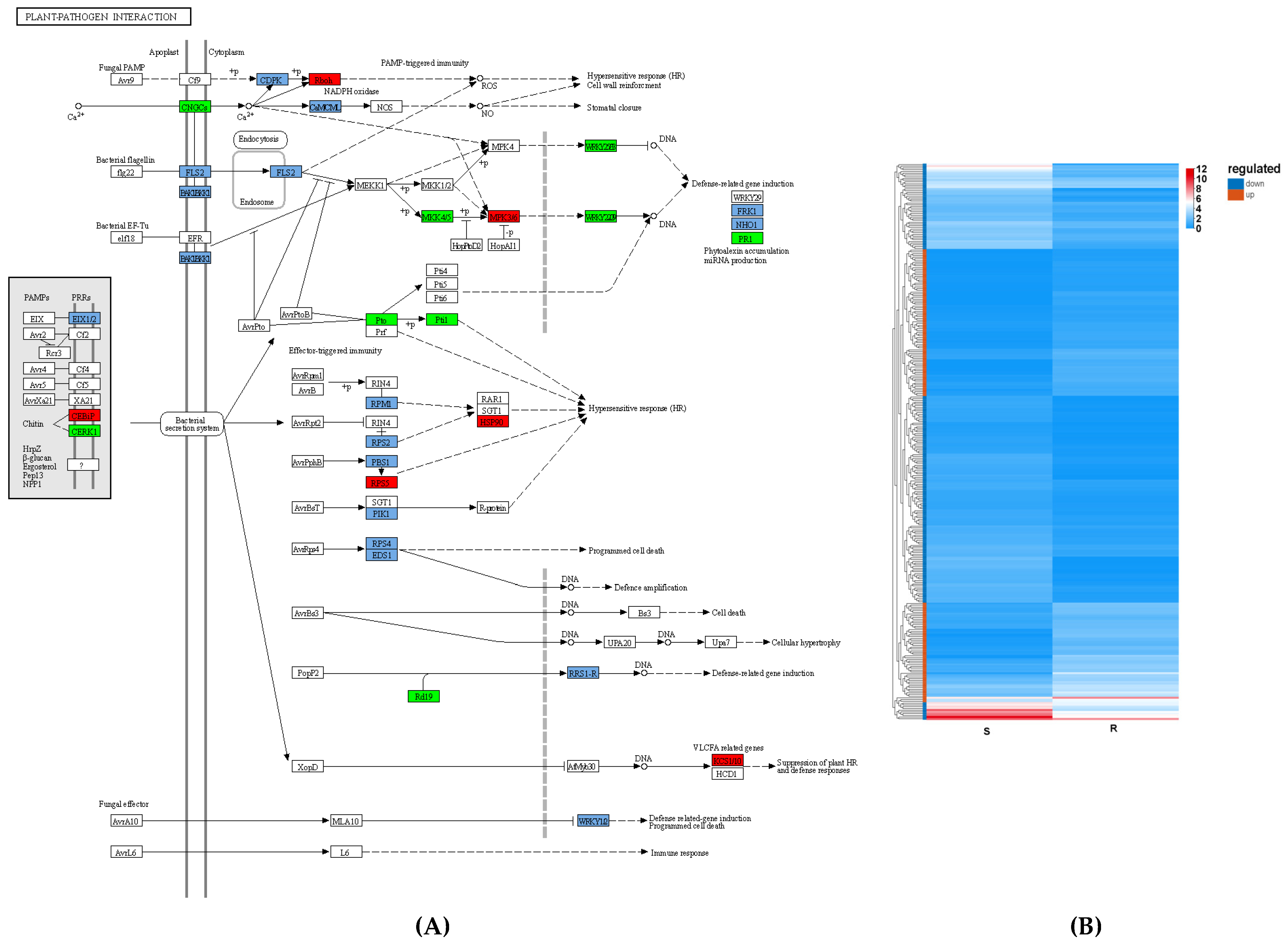
3.4. Immune System in PWN Resistance
3.5. Influence of Terpenoids on the Resistance of B. xylophilus
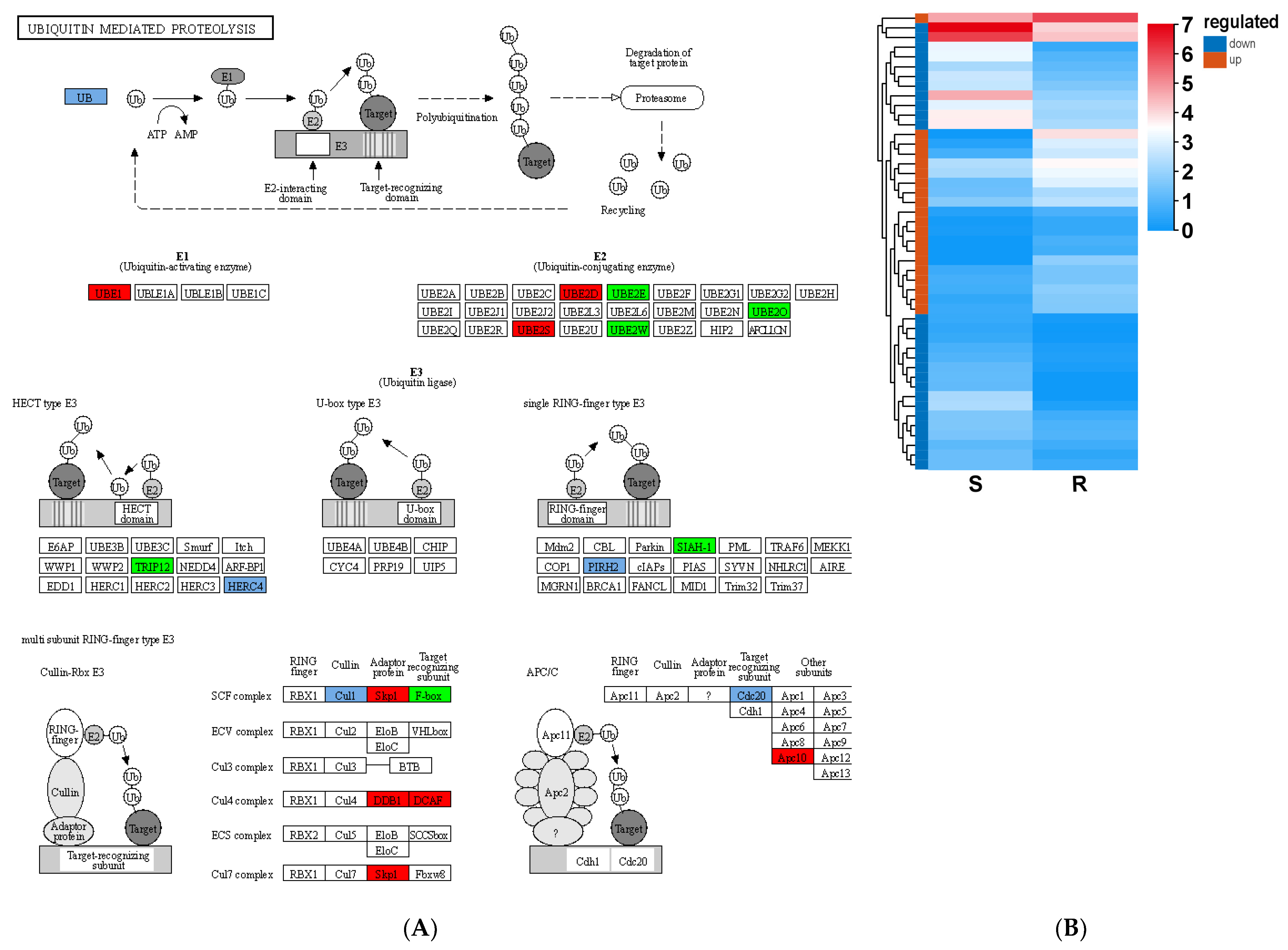
3.6. Resistance to B. xylophilus Stress Through Ubiquitination in Pine Plants
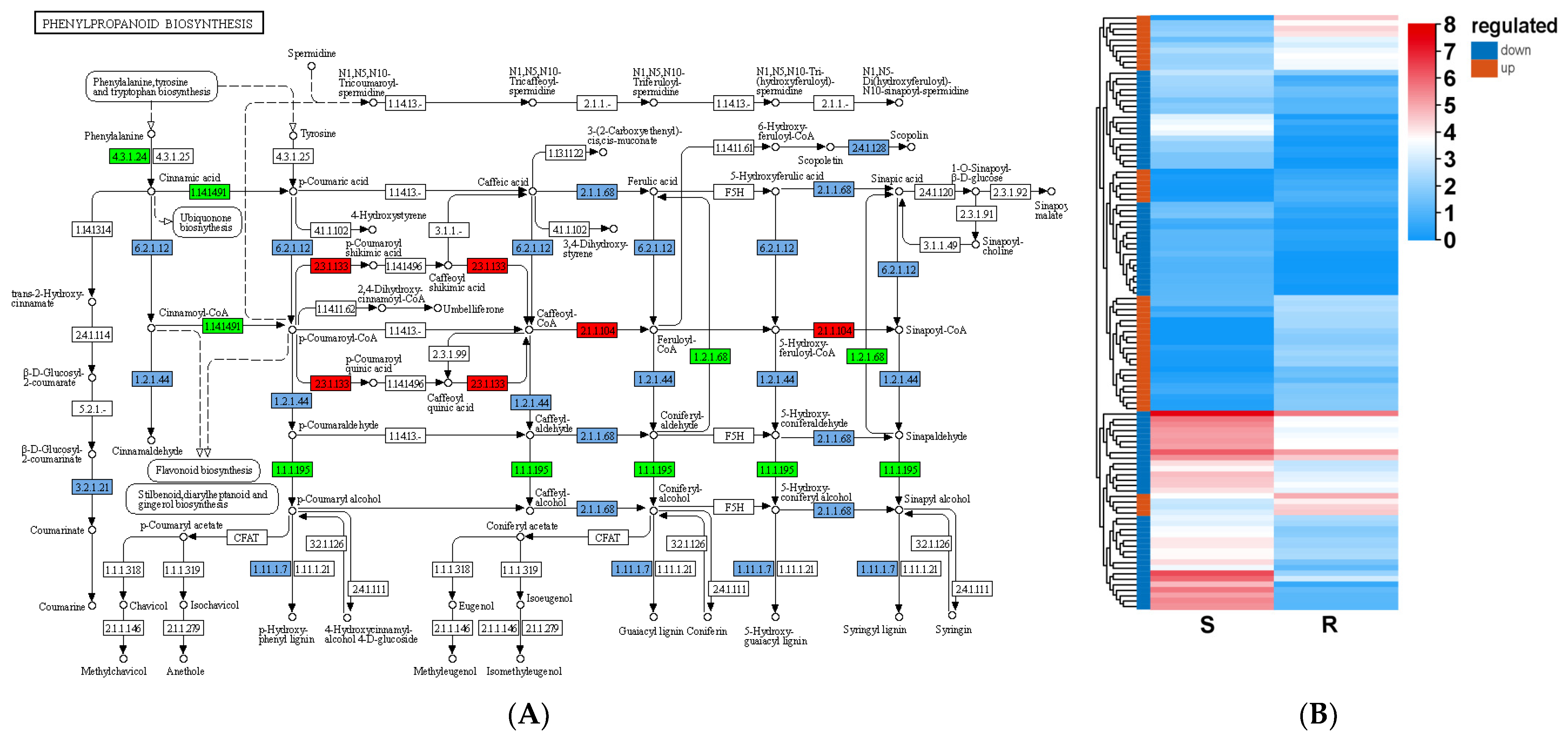
3.7. Elevating the Lignin Content Is an Effective Way to Defend Stress Conditions in Woody Plants
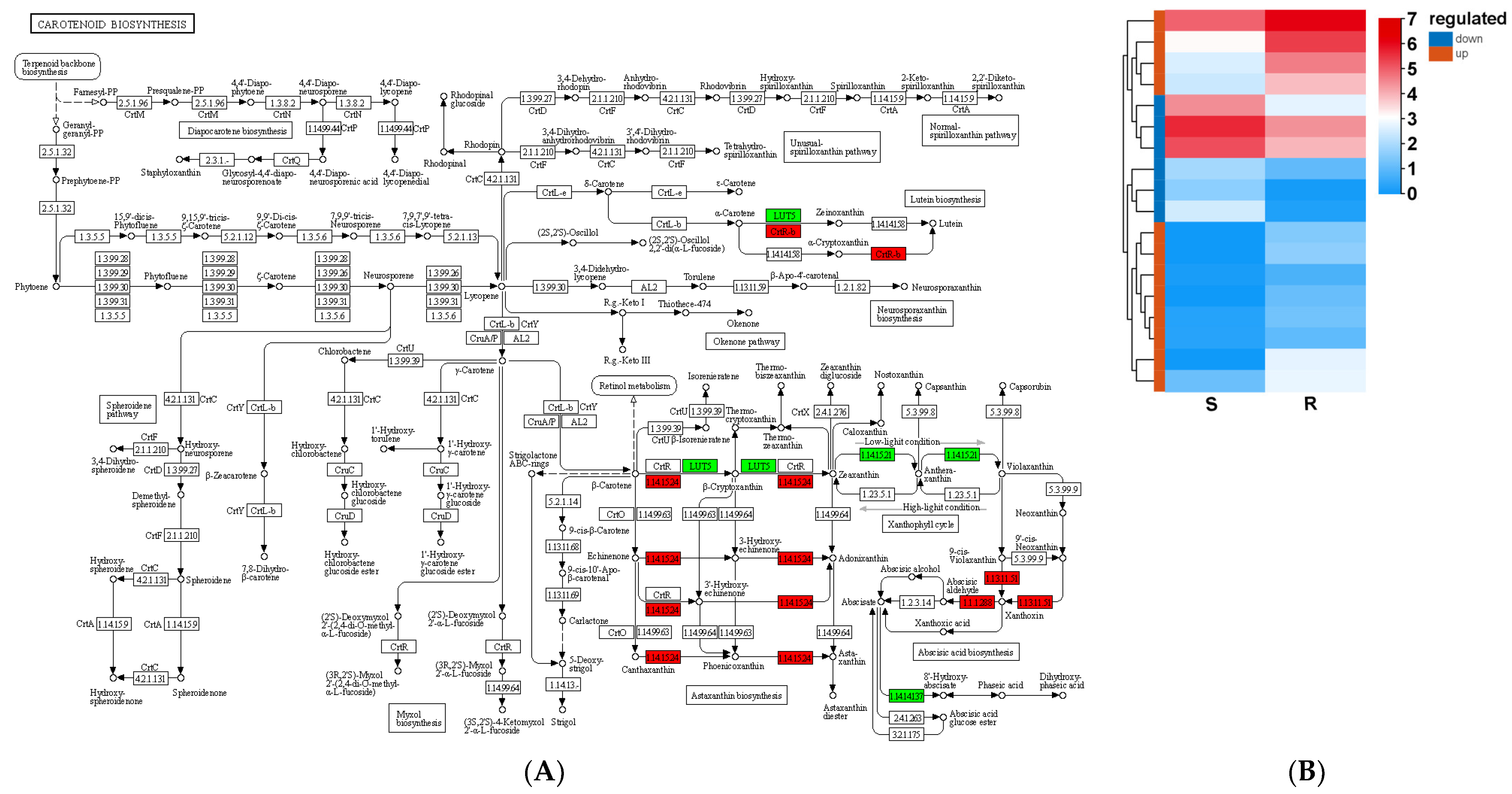
3.8. Carotenoid Biosynthesis in Relation to Resistance of Pine Plants to B. xylophilus
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vicente, C.; Espada, M.; Vieira, P.; Mota, M. Pine Wilt Disease: A threat to European forestry. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2012, 133, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inacio, M.; Nobrega, F.; Vieira, P.; Bonifacio, L.; Naves, P.; Sousa, E.; Mota, M. First detection of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus associated with Pinus nigra in Portugal and in Europe. For. Pathol. 2015, 45, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Li, D.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Y.; Fei, X.; Sun, L.; Li, F. Research progress on the resistance mechanism of host pine to pine wilt disease. Plant Pathol. 2024, 73, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Rahman, M.; Wu, X.; Ye, J. Resistant and susceptible Pinus thunbergii ParL. show highly divergent patterns of differentially expressed genes during the process of infection by Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Liang, G.; Huang, A.; Zhang, F.; Guo, W. Comparative study on the mRNA expression of Pinus massoniana infected by Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. J. For. Res. 2020, 31, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Choi, Y.; Kim, S.; Han, H.; Kim, H.; Shim, D. Temporal transcriptome profiling of Pinus densiflora infected with pine wood nematode reveals genetically programmed changes upon pine wilt disease. Phytopathology 2024, 114, 982–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.G.; Wang, J.J.; Ma, J.Y.; Jiang, X.; Zhou, Z.Q.; Shi, F. Effects of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus infestation on physiological and biochemical responses of Pinus tabuliformis. For. Pest Dis. 2024, 43, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J. Analysis of the current epidemiological status, control technology and countermeasures of pine wood nematode disease in China. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2019, 55, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Xu, J. The expansin gene SmEXPA13 in Salix matsudana in association with plant salt tolerance. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2023, 154, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Wu, D.; Zhao, H.; Gong, L.; Xu, J. Regulation of SmEXPA13 expression by SmMYB1R1-L enhances salt tolerance in Salix matsudana Koidz. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 270, 132292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.; Deng, Y.; Qi, J.; Chen, F.; Hao, D.; Tan, J.; Sun, S. Effects of inoculation with pine wood nematode on physiological indexes of Pinus sylvestris var. mongholica. J. Shenyang Agric. Univ. 2020, 51, 649–655. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, J.D.G.; Dang, J.L. The plant immune system. Nature 2006, 444, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, Z.; Li, W.; Deng, L.; Gao, K.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, Z. Comprehensive analysis of LRR-RLKs and key gene identification in Pinus massoniana resistant to pine wood nematode. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1043261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Liu, B.; Gao, K.; Zhao, Y.; Li, W.; Deng, L.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Q. Comprehensive analysis and functional verification of the Pinus massoniana NBS-LRR gene family involved in the resistance to Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazo-Molina, C.; Mainiero, S.; Hind, S.; Kraus, C.; Vachev, M.V.; Maviane-Macia, F.; Lindeberg, M.; Saha, S.; Strickler, S.; Feder, A. The Ptr1 locus of Solanum lycopersicoides confers resistance to race 1 strains of Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato and to Ralstonia pseudosolanacearum by recognizing the type III effectors AvrRpt2 and RipBN. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2019, 32, 949–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.; Tahir, J.; Siddiqui, A.; Magzoub, M.; Shahzad-Ul-Hussan, S.; Mackey, D. RIN4 homologs from important crop species differentially regulate the Arabidopsis NB-LRR immune receptor, RPS2. Plant Cell Rep. 2021, 40, 2341–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruitt, R.N.; Locci, F.; Wanke, F.; Zhang, L.; Saile, S.C.; Joe, A.; Karelina, D.; Hua, C.; Frhlich, K.; Wan, W.L. The EDS1–PAD4–ADR1 node mediates Arabidopsis pattern-triggered immunity. Nature 2021, 598, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, B.; Dahlbeck, D.; Huang, J.; Chisholm, S.T.; Staskawicz, B.J. Molecular basis for the rin4 negative regulation of rps2 disease resistance. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 1292–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B. Functional Characterization of Key Genes for Terpene Biosynthesis Involved in Defense to Pine Wood Nematode in Pinus massoiana. Ph.D. Thesis, Chinese Academy of Forestry, Beijing, China.
- Liu, B.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Luo, N.; Xie, Y.; Chen, X. Cloning of β-pinene synthase gene from Pinus massoniana and its response to pine wood nematode infestation. For. Res. 2020, 33, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Dong, X.; An, M.; Xia, Z.; Wu, Y. Progress in the functional study of ubiquitination-modified key enzymes in plant stress response. aBIOTECH 2024, 40, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Takizawa, M.; Goto, A.; Watanabe, Y. The tobacco ubiquitin-activating enzymes NtE1A and NtE1B are induced by tobacco mosaic virus, wounding and stress hormones. Mol. Cells 2005, 19, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, E.H.; Pak, J.H.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, H.J.; Shin, S.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, D.H.; Oh, J.S.; Oh, B.J.; Jung, H.W.; et al. Ectopic expression of ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme gene from wild rice, OgUBC1, confers resistance against UV-B radiation and Botrytis infection in Arabidopsis thaliana. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 427, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Song, L.; Choudhary, K.; Zhou, B.; Sun, G.; Broderick, K.; Giesler, L.; Zeng, L. Genome-wide analysis of genes encoding core components of the ubiquitin system in soybean (Glycine max) reveals a potential role for ubiquitination in host immunity against soybean cyst nematode. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Li, W.; Zhang, T.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L. Botrytis cinerea-induced F-box protein 1 enhances disease resistance by inhibiting JAO/JOX-mediated jasmonic acid catabolism in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 2023, 17, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.; Saeed, S.; Fan, X.; Salam, A.; Munir, R.; Yasin, U.; Khan, R.; Muhammad, S.; Ali, B.; Ali, I.; et al. The multifaceted role of jasmonic acid in plant stress mitigation: An overview. Plants 2023, 12, 3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtaza, K.; Sajid, A.; Ibrahim, A.; Saddam, S.; Fazal, U.; Asma, A.; Wajid, Z. The key roles of ROS and RNS as a signaling molecule in plant–microbe interactions. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesarino, I. Structural features and regulation of lignin deposited upon biotic and abiotic stresses. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2019, 56, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Sun, S.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, F.; Xue, F.; Sun, J. The cotton lignin biosynthetic gene Gh4CL30 regulates lignification and phenolic content and contributes to verticillium wilt resistance. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2021, 34, 240–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Qin, L.; Karunakaran, C.; Wei, Y.; Peng, G. Lignin accumulation in cell wall plays a role in clubroot resistance. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1401265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, X.; Wen, T.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, Y. Transcriptomic analysis reveals differentially expressed genes associated with pine wood nematode resistance in resistant Pinus thunbergii. Tree Physiol. 2023, 43, 995–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ines, M.; Lieven, S.; Vicent, A.; Aurelio, G.; Isabel, C.; Yves, V.; Celia, M. Insights into the mechanisms implicated in Pinus pinaster resistance to pine wood nematode. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 690857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hu, L.; Zhang, L.; Pan, X.; Hu, X. Exogenous spermidine is enhancing tomato tolerance to salinity–alkalinity stress by regulating chloroplast antioxidant system and chlorophyll metabolism. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomas, Z.; Hajnalka, L.D.; Tunde, N.T.; Zoltan, G. Carotenoids assist in cyanobacterial photosystem ii assembly and function. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demmig-Adams, B. Carotenoids and photoprotection in plants: A role for the xanthophyll zeaxanthin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1990, 1020, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.A.; Lim, W.H.; Le, V.V.; Ko, S.R.; Kim, B.; Oh, H.M. Lifespan extension and anti-oxidant effects of carotenoid pigments in Caenorhabditis elegans. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2022, 17, 100962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Jiang, X.; Gai, Y. Cloning of the LkF3H2 gene in Larix kaempferi and its function in regulating flavonoid metabolism. Biotechnol. Bull. 2024, 40, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Nie, T. Cloning and expression analysis of F3H gene in Caragana korshinskii. Guihaia 2017, 37, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X. Studies on the Mechanism of PmACRE Gene in Regulation of Plant Resistance to Pine Wood Nematode in Pinus massoniana. Master’s Thesis, Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, Fuzhou, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]





| Sample * | S | R |
|---|---|---|
| Total reads | 39,165,636 | 38,983,354 |
| Mapped reads | 33,334,699 (85.11%) | 35,505,333 (91.08%) |
| Uniq rapped reads | 29,390,667 (75.04%) | 32,114,829 (82.38%) |
| Multiple map reads | 3,944,032 (10.07%) | 3,390,504 (8.70%) |
| Reads map to ‘+’ | 19,721,921 (50.36%) | 20,203,642 (51.83%) |
| Reads map to ‘−’ | 19,750,035 (50.43%) | 20,172,513 (51.75%) |
| Clean reads | 19,582,818 | 19,491,677 |
| Clean bases | 5,865,086,862 | 5,838,137,580 |
| GC content | 45.55% | 44.69% |
| % ≥ Q30 | 94.33% | 94.04% |
| Database | S_vs_R |
|---|---|
| Total | 5869 |
| COG | 2213 |
| GO | 4780 |
| KEGG | 4095 |
| KOG | 2834 |
| NR | 5810 |
| Pfam | 4733 |
| Swiss-Prot | 4268 |
| eggNOG | 4815 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, M.; Yang, M.; Wang, L.; Gong, L.; Chen, Y.; Xu, J. Genome-Wide Profiling of the Genes Resistant to Bursaphelenchus xylophilus in Pinus tabuliformis Carriere. Forests 2025, 16, 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040677
Li M, Yang M, Wang L, Gong L, Chen Y, Xu J. Genome-Wide Profiling of the Genes Resistant to Bursaphelenchus xylophilus in Pinus tabuliformis Carriere. Forests. 2025; 16(4):677. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040677
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Mengtian, Mengjia Yang, Lei Wang, Longfeng Gong, Yuxi Chen, and Jichen Xu. 2025. "Genome-Wide Profiling of the Genes Resistant to Bursaphelenchus xylophilus in Pinus tabuliformis Carriere" Forests 16, no. 4: 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040677
APA StyleLi, M., Yang, M., Wang, L., Gong, L., Chen, Y., & Xu, J. (2025). Genome-Wide Profiling of the Genes Resistant to Bursaphelenchus xylophilus in Pinus tabuliformis Carriere. Forests, 16(4), 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040677




