Rainfall Partitioning by Two Alpine Shrubs in the Qilian Mountains, Northwest China: Implications for Hydrological Modeling in Cold Regions
Abstract
1. Introduction
| Shrubs | Study Area | Period | R/mm | TF% | SF% | IC% | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Birch | Trail Valley Creek, Western Canadian Arctic | 22 June to 28 August 2018 | 90 | 76 | 8 | 16 | Zwieback et al. (2019) [12] |
| Alder | 72 | 17 | 11 | ||||
| Potentilla fruticosa | Qinghai Lake, Qilian Mountains, China | June to October 2012 | 531.0 | 29.3 | 49.3 | 21.4 | Zhang et al. (2018) [26] |
| Potentilla fruticose | Shaliu River, Qilian Mountains, China | June to September 2012 | 231.6 | 44.5 | 18.6 | 36.5 | Zhang et al. (2023) [16] |
| Potentilla fruticose | Hulu catchment, Qilian Mountains, China | June to October 2010 | 298.6 | 62.0 | 3.4 | 34.6 | Liu et al. (2012) [24] |
| Caragana jubata | 60.2 | 4.2 | 35.6 | ||||
| Hippophae rhamnoides | 52.3 | 8.0 | 39.7 | ||||
| Salix cupularis | 63.5 | 3.2 | 33.3 | ||||
| Potentilla fruticose | Xishui, Qilian Mountains, China | May to September 2014 | 483.3 | 64.76 | 2.85 | 32.39 | Liu et al. (2016) [15] |
| Salix cupularis | 540.7 | 58.70 | 4.05 | 37.25 | |||
| Caragana stenphylla | 388.1 | 66.38 | 4.28 | 29.34 | |||
| Berberis diaphana | 399.0 | 53.34 | 3.84 | 42.82 | |||
| Caragana jubata | 567.3 | 66.24 | 3.26 | 30.50 | |||
| Quercus aquifolioides | Wolong nature reserve, Southwest China | July to September 2011; June to August 2002 | 545.4 | 75.05 | NA | 24.9 | Li et al. (2006) [17] |
| Quercus aquifolioides | June to September 2007 | 486.7 | 82.6 | 0.9 | 16.5 | He et al. (2010) [27] | |
| Coyrlus heterpolal | Maoer Mountains, Northeast China | May to September 2004 | 352.6 | 75.2 | NA | 24.8 | Kong (2005) [28] |
| Sambucus mandehuriea | 78.7 | NA | 21.3 | ||||
| Sorbaira sorbfolia | 80.9 | NA | 19.1 | ||||
| Lespedeza bicolor | 88.1 | NA | 11.9 | ||||
| Spiraea ussrtiensis | 92.3 | NA | 7.7 | ||||
| Caragana jubata | Pailugou, Qilian Mountains, China | May 2007 to May 2008 | 410.6 | 83.3 | NA | 16.7 | Nie (2009) [25] |
| Salix gilashanica | 79.5 | NA | 20.5 | ||||
| Potentilla fruticosa | 89.5 | NA | 10.4 | ||||
| Berberis diaphana | 326.5 | 77.5 | NA | 22.4 | |||
| Caragana tangutica | 308.2 | 93.0 | NA | 7.0 | |||
| Caragana jubata | Tianlaochi, Qilian Mountains, China | July to September 2011; June to September 2012 | 674.7 | 58.9 | 0.9 | 40.2 | Liu (2013) [29] |
| Potentilla fruticosa | 697.6 | 69.8 | 1.3 | 28.9 | |||
| Myricaria squamosa | Qinghai Lake, Qilian Mountains, China | 6 July to 30 September 2010 | 156.6 | 48.40 | 4.04 | 47.5 | Ma et al. (2012) [30] |
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Shrubs Selection and Measurements
2.3. Throughfall and Stemflow Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Rainfall Characteristics During Growing Season
3.2. Rainfall Partitioning Percentage of Alpine Shrub
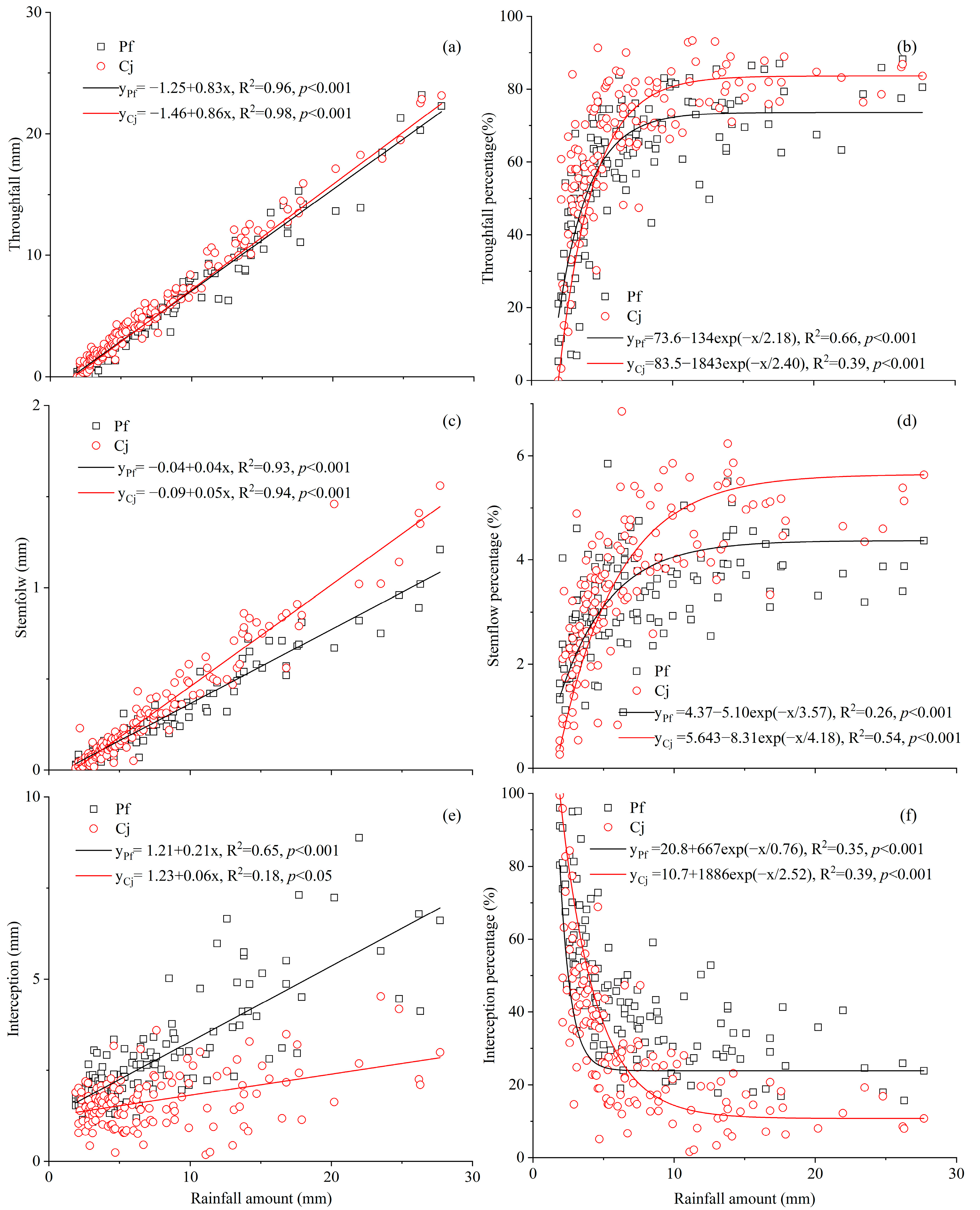
3.3. Rainfall Partitioning in Relation to Rainfall Amount
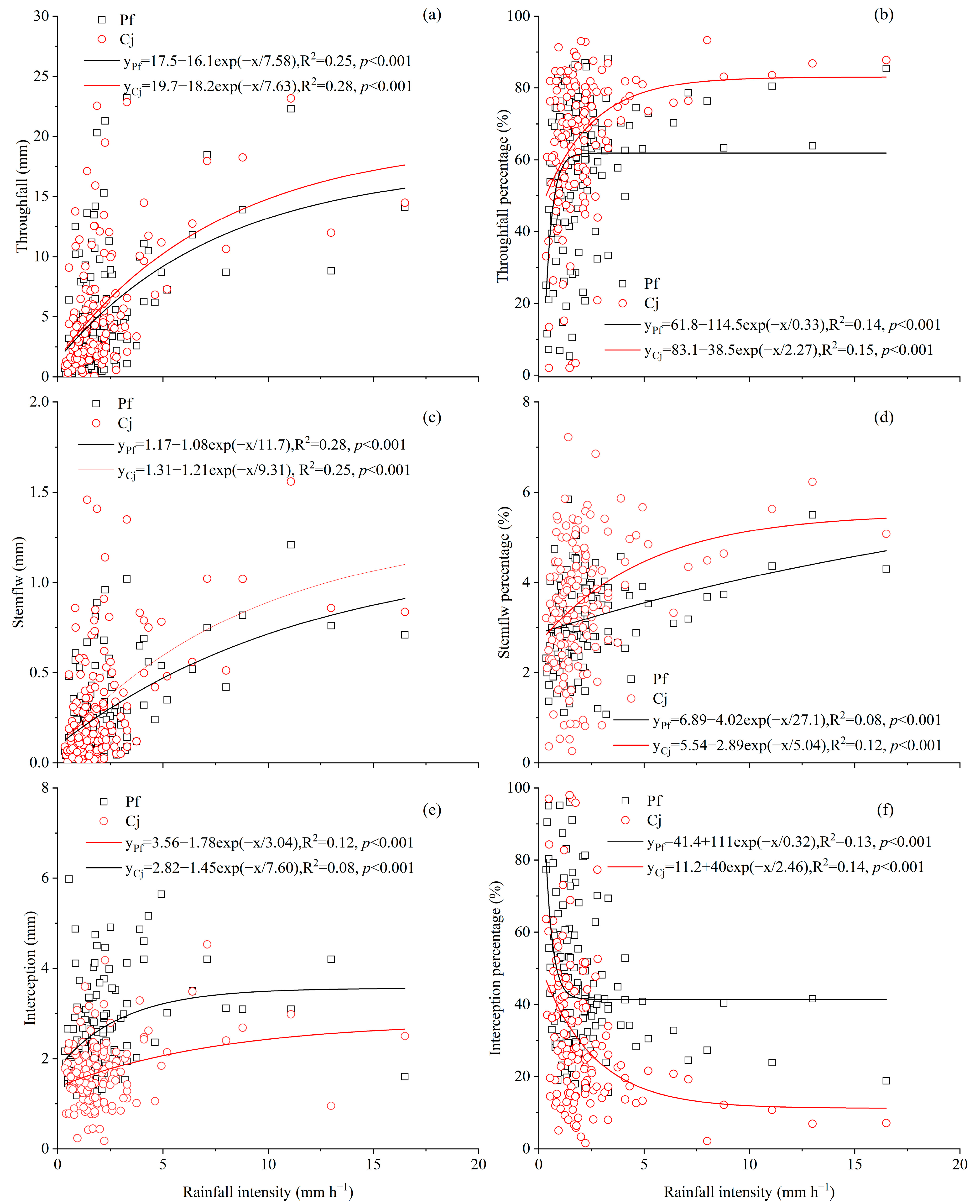
3.4. Rainfall Partitioning in Relation to Rainfall Intensity
3.5. Correlations and Regression Analysis Between Rainfall Partitioning and Meteorological and Canopy Variables
4. Discussions
4.1. Rainfall Partitioning by Shrubs in Cold Regions
4.2. Drivers of Rainfall Partitioning in Cold Environments
4.3. Structural and Ecological Implications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muzylo, A.; Llorens, P.; Valente, F.; Keizer, J.J.; Domingo, F.; Gash, J.H.C. A review of rainfall interception modelling. J. Hydrol. 2009, 370, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yuan, C.; Chen, N.; Levia, D.F. Rainfall partitioning by vegetation in China: A quantitative synthesis. J. Hydrol. 2023, 617, 128946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-F.; Pan, Y.-X.; Hu, R.; Wang, X.-P. Differential intra-specific stemflow funnelling efficiencies of Caragana korshinskii within arid desert ecosystems. Hydrol. Res. 2017, 48, 1611–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shachnovich, Y.; Berliner, P.R.; Bar, P. Rainfall interception and spatial distribution of throughfall in a pine forest planted in an arid zone. J. Hydrol. 2008, 349, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-Y.; Liu, L.; Gao, S.; Ma, Y.; Yang, Z. Stemflow in three shrubs and its effect on soil water enhancement in semiarid loess region of China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2008, 148, 1501–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, A.; Shen, L.; Dai, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fei, W.; Wu, J. The Impact of Canopy on Nutrient Fluxes through Rainfall Partitioning in a Mixed Broadleaf and Coniferous Forest. Forests 2024, 15, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, K.; De Frenne, P.; Fornara, D.A.; Van Meerbeek, K.; Li, W.; Peng, X.; Ni, X.; Peng, Y.; Wu, F.; Yang, Y.; et al. Global patterns and drivers of rainfall partitioning by trees and shrubs. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 3350–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Shi, C.; Zhao, T.; Lu, J.; Bi, B.; Luo, G. Canopy Interception of Different Rainfall Patterns in the Rocky Mountain Areas of Northern China: An Application of the Revised Gash Model. Forests 2022, 13, 1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlyle-Moses, D.E. Throughfall, stemflow, and canopy interception loss fluxes in a semi-arid Sierra Madre Oriental matorral community. J. Arid Environ. 2004, 58, 181–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levia, D.F.; Germer, S. A review of stemflow generation dynamics and stemflow-environment interactions in forests and shrublands. Rev. Geophys. 2015, 53, 673–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magliano, P.N.; Whitworth-Hulse, J.I.; Baldi, G. Interception, throughfall and stemflow partition in drylands: Global synthesis and meta-analysis. J. Hydrol. 2019, 568, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwieback, S.; Chang, Q.; Marsh, P.; Berg, A. Shrub tundra ecohydrology: Rainfall interception is a major component of the water balance. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo Neto, J.O.; Rodrigues, A.F.; Mello, C.R. On Canopy Rainfall Interception Modeling in a Eucalyptus Plantation. Forests 2024, 15, 1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Stan, J.T.; Gordon, D.A. Mini-Review: Stemflow as a Resource Limitation to Near-Stem Soils. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, W.; Chen, Z.; Yang, X.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, K. Comprehensive assessment of hydrological impacts of sub-alpine shrubs in Xishui Forest Area of Qilian Mountains. Arid. Land Geogr. 2016, 39, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, S.; Wu, H.; Shi, F.; Li, W.; Yuan, C. Estimating rainfall interception of xerophytic deciduous shrubs by static- and variable-parameter Gash models with stem- and leaf-dominated canopy water storage. J. Hydrol. 2023, 625, 130031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ouyang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Liu, X.; Su, Y. Comparison of rainfall redistribution in two ecosystems in Minjiang upper catchments, China. J. Plant Ecol. 2006, 30, 723–731. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Estringana, P.; Alonso-Blázquez, N.; Alegre, J. Water storage capacity, stemflow and water funneling in Mediterranean shrubs. J. Hydrol. 2010, 389, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klamerus-Iwan, A.; Błońska, E. Canopy storage capacity and wettability of leaves and needles: The effect of water temperature changes. J. Hydrol. 2018, 559, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, F.; Jiang, S.; Koppa, A.; Ren, L.; Liu, Y.Y.; Wang, M.; Miralles, D.G. Multi-Decadal Dynamics of Global Rainfall Interception and Their Drivers. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2024, 19, e2024GL109295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers-Smith, I.H.; Forbes, B.C.; Wilmking, M.; Hallinger, M.; Lantz, T.; Blok, D.; Tape, K.D.; Macias-Fauria, M.; Sass-Klaassen, U.; Lévesque, E.; et al. Shrub expansion in tundra ecosystems: Dynamics, impacts and research priorities. Environ. Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 045509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, S.M.M.; Gordon, A.G.; Van Stan, J.T. A Global Synthesis of Throughfall and Stemflow Hydrometeorology. In Precipitation Partitioning by Vegetation: A Global Synthesis; Van Stan, I.J.T., Gutmann, E.D., Friesen, J., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 49–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Chen, R.; Liu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Liu, J.; Song, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, G.; Guo, S.; Wang, X. Cryospheric Hydrometeorology Observation in the Hulu Catchment (CHOICE), Qilian Mountains, China. Vadose Zone J. 2018, 17, 180058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, R.; Song, Y.; Han, C. Characteristics of rainfall interception for four typical shrubs in Qilian Mountain. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2012, 32, 1337–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X. Study on Water Conservation Function of Shrub in Qilian Mountains. Master’s Thesis, Gansu Agriculture University, Lanzhou, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Li, X.Y.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Li, D.Q.; Lin, H. Modelling of rainfall partitioning by a deciduous shrub using a variable parameters Gash model. Ecohydrology 2018, 11, e2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.-Q.; Xue, J.-H.; Wu, Y.-B.; Zhang, L.-Y. Application of a revised Gash analytical model to simulate subalpine Quercus aquifolioides forest canopy interception in the upper reaches of Minjiang River. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2010, 30, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, L. Assessment and Mechanism of the Shrub Water Conservation Function in East Mountainous Region of Heilongjiang Province. Master’s Thesis, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y. Study on Rainfall Interception Characteristic of Vegetation in a Typical Small Watershed, Upper Reach of Heihe River Basin. Master’s Thesis, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.-J.; Gao, S.-Y.; Li, X.-Y.; Lu, R.-J.; Zhang, S.Y.; Li, G.-Y. Rainfall canopy partitioning and its influencing factors of Riparian shrub in the Alpine region. J. Desert Res. 2012, 32, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.S.; Song, Y.X.; Kang, E.S.; Han, C.T.; Liu, J.F.; Yang, Y.; Qing, W.W.; Liu, Z.W. A Cryosphere-Hydrology Observation System in a Small Alpine Watershed in the Qilian Mountains of China and Its Meteorological Gradient. Arct. Antarct. Alp. Res. 2014, 46, 505–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, R.; Qi, J.; Dang, Z.; Han, C.; Yang, Y. Control of Mosses on Water Flux in an Alpine Shrub Site on the Qilian Mountains, Northwest China. Plants 2022, 11, 3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Liu, Z.; Fan, Y.; Li, Y.; Tao, H.; Han, C.; Ao, X.; Chen, R. Patterns and Drivers of Surface Energy Flux in the Alpine Meadow Ecosystem in the Qilian Mountains, Northwest China. Plants 2025, 14, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaokui, C.; Li, J.; Guangcheng, H.; Jie, Z. Mapping of Interception Loss of Vegetation in the Heihe River Basin of China Using Remote Sensing Observations. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, C.; Liu, Y.; Chang, Y.; Huang, G.; Zang, F. Exploring the spatiotemporal distribution and driving factors of vegetation canopy rainfall interception in the Qilian Mountains, Northwest China. CATENA 2024, 237, 107829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, L.; Yang, X.-g.; Li, M.; Yu, D.; Song, N. Rainfall partitioning characteristics by two sand-binding shrubs and their impact on shallow soil moisture replenishment in the Northwestern desert steppe of China. Ecohydrology 2024, 17, e2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Yang, L.; Tang, W.; Tian, S.; Ma, R.; Sang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Shi, Y. Effects of plantations on rainfall redistribution in a rocky mountain area of North China. Hydrol. Process. 2024, 37, e14999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, R.; Song, Y.; Han, C. Water holding capacity of mosses under alpine shrubs in Qilian Mountains. Arid Land Geogr. 2011, 37, 696–703. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, C.; Gao, G.; Fu, B. Stemflow of a xerophytic shrub (Salix psammophila) in northern China: Implication for beneficial branch architecture to produce stemflow. J. Hydrol. 2016, 539, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.-G.; Chen, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Gu, J.-L.; Qu, W.-J.; Song, N.-P. Dynamic rainfall-partitioning relationships among throughfall, stemflow, and interception loss by Caragana intermedia. J. Hydrol. 2019, 574, 980–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Shao, M.a.; Jia, X.; Zhao, C. Rainfall partitioning characteristics and simulation of typical shelter forest in Chinese Mu Us Sandy Land. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 945, 174091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jiao, L.; Bai, Y.; Li, Z.; Yuan, C.; Li, Z.; Gao, G. Rainfall partitioning in the Robinia pseudodcacia plantations with different thinning intensities in the semiarid Loess Plateau of China. Ecol. Front. 2025, 45, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Wang, D.; Zha, T.; Wang, L.; Fu, B. A global synthesis of transpiration rate and evapotranspiration partitioning in the shrub ecosystems. J. Hydrol. 2022, 606, 127417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
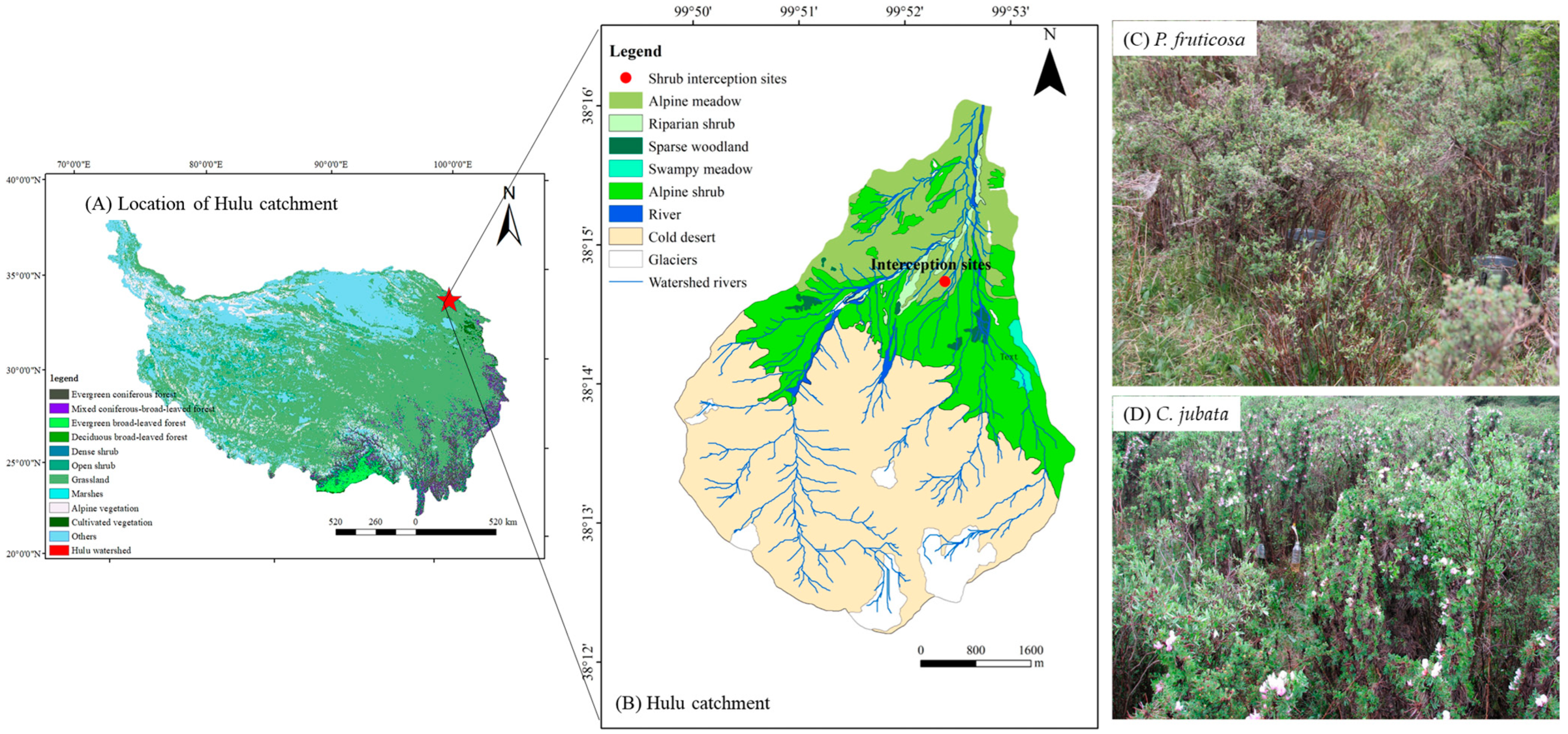
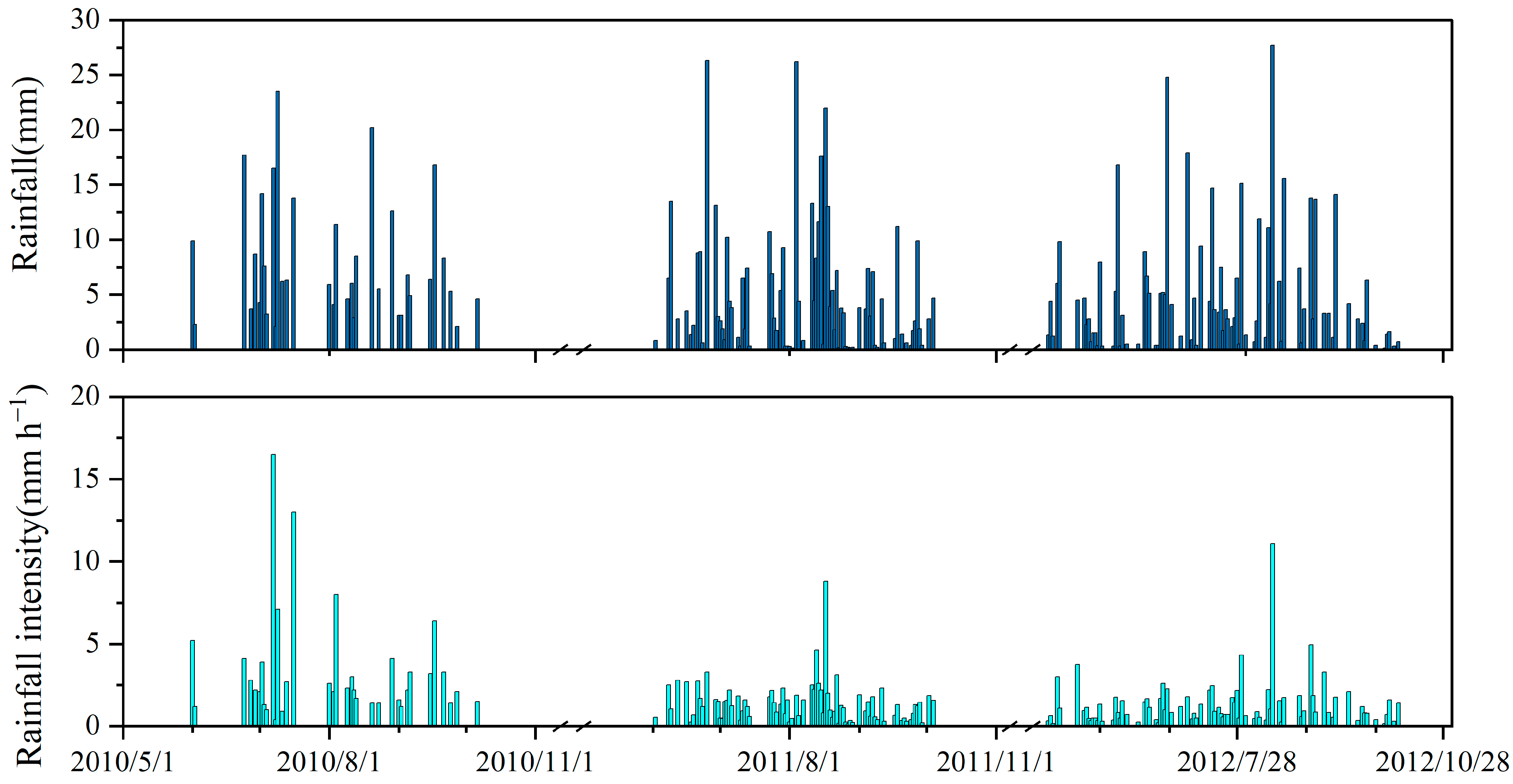


| Shrubs | Coverage (%) | Height (cm) | Area (cm2) | Diameter (cm) | Length (cm) | LAI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P. fruticose | 60 ± 6 | 65 ± 7 | 32 ± 6 | 0.7 ± 0.4 | 16 ± 6 | 1.57 ± 0.45 |
| C. jubata | 65 ± 8 | 58 ± 10 | 18 ± 8 | 1.8 ± 0.7 | 8 ± 3 | 2.56 ± 0.69 |
| Shrubs | Equation | R2 | p | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P. fruticose | TF = −0.98 − 0.25CA + 0.75RA − 0.06RI | 0.95 | <0.001 | 2.13 |
| SF = −0.047 + 0.19CA + 0.05RA + 0.02RI | 0.94 | <0.001 | 0.84 | |
| IC = 1.17 + 0.27CA + 0.04RI | 0.65 | <0.001 | 1.62 | |
| C. jubata | TF = −0.86 − 0.06CA + 0.75RA − 0.06RI | 0.96 | <0.01 | 1.76 |
| SF = −0.047 + 0.15CA + 0.04RA + 0.01RI | 0.92 | <0.001 | 0.73 | |
| IC = 1.12 + 0.22CA + 0.08RA − 0.04RI | 0.71 | <0.01 | 2.41 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.; Tian, Y.; Qi, J.; Dang, Z.; Chen, R.; Han, C.; Yang, Y. Rainfall Partitioning by Two Alpine Shrubs in the Qilian Mountains, Northwest China: Implications for Hydrological Modeling in Cold Regions. Forests 2025, 16, 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040658
Liu Z, Tian Y, Qi J, Dang Z, Chen R, Han C, Yang Y. Rainfall Partitioning by Two Alpine Shrubs in the Qilian Mountains, Northwest China: Implications for Hydrological Modeling in Cold Regions. Forests. 2025; 16(4):658. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040658
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Zhangwen, Yongxin Tian, Jinxian Qi, Zhiying Dang, Rensheng Chen, Chuntan Han, and Yong Yang. 2025. "Rainfall Partitioning by Two Alpine Shrubs in the Qilian Mountains, Northwest China: Implications for Hydrological Modeling in Cold Regions" Forests 16, no. 4: 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040658
APA StyleLiu, Z., Tian, Y., Qi, J., Dang, Z., Chen, R., Han, C., & Yang, Y. (2025). Rainfall Partitioning by Two Alpine Shrubs in the Qilian Mountains, Northwest China: Implications for Hydrological Modeling in Cold Regions. Forests, 16(4), 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040658







